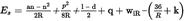2.Reduction formulae (in metres)U.K.
2.1Sections between bogie pivots or between end axlesU.K.
2.2Sections beyond bogie pivots or beyond end axles (vehicles with a overhang)U.K.
Notations:
reduction of the gauge half-width for cross sections between bogie pivots or between end axles. Es and Es∞ should not be taken into account unless their values are positive;
reduction of the gauge half-width for cross sections beyond bogie pivots or beyond end axles. Eu and Eu∞ should not be taken into account unless their values are positive;
distance between bogie pivots or between end axles(1);
distance between the cross section considered and the nearest bogie pivot, or the nearest end axle or the fictional pivot if the vehicle has no fixed pivot;
bogie wheelbase;
is the sum of the play between the axle box and the axle itself and of the possible play between the axle box and the bogie frame measured from the middle position with ultimately worn components;
possible transverse displacement of the bogie pivot, and the cradle in relation to the bogie frame or, for vehicles without bogie pivot, possible displacement of the bogie frame in relation to the vehicle frame measured from the middle position towards the internal side of the curve (varies according to the curve radius);
comme wiR, but towards the outside of the curve;
as wiR, but on a straight track, from the middle position and towards both side;
maximum track gauge in straight and in considered curved track = 1,544 m;
distance between ultimately worn wheel flanges, measured 10 mm outwards the running circle = 1,492 m;
curve radius;
If w is constant or varies linearly according to 1/R, the radius to be considered is 150 m.
In exceptional cases, the actual value of R ≥ 150 m should be used.
allowable gauge protrusion (to be increased by the 36/R widening of obstacle gauge) without the inclination due to the suspension flexibility;
= 0 for h < 330 mm for vehicles able to run over rail brakes (see Appendix B1),
= 0,06 m for h < 600 mm,
= 0,075 m for h ≥ 600 mm.
height above the running surface at the considered location, the vehicle being in its lowest position.
If the vehicle has no actual bogie pivot, a and n should be determined on the base of a fictional pivot located at the intersection of the longitudinal centrelines of the bogie and of the frame, the vehicle being in middle position (0,026 + q + w = 0) on a curved track of radius 150 m. If the distance between the pivot calculated by this manner and the bogie centre point is denoted y, the term p2 should be replaced by p2 - y2 in reduction formulae.