- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser (31/12/2020)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Council Directive 98/57/ECDangos y teitl llawn
Council Directive 98/57/EC of 20 July 1998 on the control of Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith) Yabuuchi et al.
You are here:
- Dangos Graddfa Ddaearyddol(e.e. Lloegr, Cymru, Yr Alban aca Gogledd Iwerddon)
- Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Rhagor o Adnoddau
PDF o Fersiynau Diwygiedig
- ddiwygiedig 30/07/20060.77 MB
- ddiwygiedig 21/08/19980.39 MB
Pan adawodd y DU yr UE, cyhoeddodd legislation.gov.uk ddeddfwriaeth yr UE a gyhoeddwyd gan yr UE hyd at ddiwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.). Ar legislation.gov.uk, mae'r eitemau hyn o ddeddfwriaeth yn cael eu diweddaru'n gyson ag unrhyw ddiwygiadau a wnaed gan y DU ers hynny.
Mae'r eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth yn tarddu o'r UE
Mae legislation.gov.uk yn cyhoeddi fersiwn y DU. Mae EUR-Lex yn cyhoeddi fersiwn yr UE. Mae Archif Gwe Ymadael â’r UE yn rhoi cipolwg ar fersiwn EUR-Lex o ddiwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: ANNEX II
Alternative versions:
Status:
Cyhoeddir Cyfarwyddebau’r UE ar y wefan hon i gynorthwyo croesgyfeirio o ddeddfwriaeth y DU. Ers diwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.) nid oes unrhyw ddiwygiadau wedi'u cymhwyso i'r fersiwn hon.
[F1ANNEX II U.K. TEST SCHEME FOR DIAGNOSIS, DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION OF RALSTONIA SOLANACEARUM (SMITH) YABUUCHI ET AL.
Textual Amendments
SCOPE OF THE TEST SCHEME U.K.
The presented scheme describes the various procedures involved in:
Diagnosis of brown rot in potato tubers and of bacterial wilt in potato, tomato and some other host plants;
Detection of Ralstonia solanacearum in samples of potato tubers, potato-, tomato- and other host plants, water and soil;
Identification of Ralstonia solanacearum (R. solanacearum) .
CONTENTS U.K.
| General principles | |||||
| SECTION I: | Application of the test scheme | ||||
| 1. | Detection scheme for the diagnosis of brown rot and bacterial wilt ( R. solanacearum ) in potato tubers and potato, tomato or other host plants with symptoms of brown rot or bacterial wilt | ||||
| 2. | Scheme for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in samples of asymptomatic potato tubers | ||||
| 3. | Scheme for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in samples of asymptomatic, potato, tomato or other host plants | ||||
| SECTION II: | Detailed methods for detection of R. solanacearum in potato tubers and potato, tomato or other host plants with symptoms of brown rot or bacterial wilt | ||||
| 1. | Symptoms | ||||
| 2. | Rapid screening tests | ||||
| 3. | Isolation procedure | ||||
| 4. | Identification tests for R. solanacearum | ||||
| SECTION III: | 1. | Detailed methods for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in samples of asymptomatic potato tubers | |||
| 1.1. | Sample preparation | ||||
| 1.2. | Testing | ||||
| 2. | Detailed methods for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in samples of asymptomatic potato, tomato or other plants | ||||
| 2.1. | Sample preparation | ||||
| 2.2. | Testing | ||||
| SECTION IV: | 1. | Scheme for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in water | |||
| 2. | Methods for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in water | ||||
| 2.1. | Sample preparation | ||||
| 2.2. | Testing | ||||
| SECTION V: | 1. | Scheme for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in soil | |||
| 2. | Methods for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in soil | ||||
| 2.1. | Samples preparation | ||||
| 2.2. | Testing | ||||
| SECTION VI: | Optimised protocols for detection and identification of R. solanacearum | ||||
| A | Diagnostic and detection tests | ||||
| 1. | Stem streaming test | ||||
| 2. | Detection of poly-ß-hydroxybutyrate granules | ||||
| 3. | Serological agglutination tests | ||||
| 4. | Selective isolation | ||||
| 4.1. | Selective plating | ||||
| 4.2. | Enrichment procedure | ||||
| 5. | Immunofluorescence test (IF test) | ||||
| 6. | Polymerase chain reaction test (PCR test) | ||||
| 6.1. | DNA purification methods | ||||
| (a) | Method according to Pastrik (2000) | ||||
| (b) | Other methods | ||||
| 6.2. | PCR | ||||
| 6.3. | Analysis of the PCR product | ||||
| 7. | Fluorescent in-situ hybridization test (FISH test) | ||||
| 8. | Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (ELISA) tests | ||||
| (a) | Indirect ELISA | ||||
| (b) | DASI (Double-Antibody Sandwich Indirect) ELISA | ||||
| 9. | Bioassay test | ||||
| B | Identification tests | ||||
| 1. | Nutritional and enzymatic identification tests | ||||
| 2. | IF test | ||||
| 3. | ELISA test | ||||
| 4. | PCR test | ||||
| 5. | FISH test | ||||
| 6. | Fatty acid profiling (FAP) | ||||
| 7. | Strain characterisation methods | ||||
| 7.1. | Biovar determination | ||||
| 7.2. | Genomic fingerprinting | ||||
| 7.3. | PCR methods | ||||
| C | Confirmation test | ||||
| Appendix 1 | Laboratories involved in optimisation and validation of protocols | ||||
| Appendix 2 | Media for isolation and culture of R. solanacearum | ||||
| Appendix 3 | (A) | Commercially available standardised control material | |||
| (B) | Preparation of controls | ||||
| Appendix 4 | Buffers for test procedures | ||||
| Appendix 5 | Determination of contamination level in IF and FISH tests | ||||
| Appendix 6 | Validated PCR protocols and reagents | ||||
| Appendix 7 | Validated reagents for FISH test | ||||
| Appendix 8 | Culture conditions for tomato and eggplant | ||||
| References | |||||
GENERAL PRINCIPLES U.K.
OptimiseOptimised protocols for the various methods, validated reagents and details for the preparation of test and control materials are provided in the Appendices. A list of the laboratories that were included in optimization and validation of protocols is provided in Appendix 1.
Since the protocols involve detection of a quarantine organism and will include the use of viable cultures of R. solanacearum as control materials, it will be necessary to perform the procedures under suitable quarantined conditions with adequate waste disposal facilities and under the conditions of appropriate licences as issued by the official plant quarantine authorities.
Testing parameters must assure consistent and reproducible detection of levels of R. solanacearum at the set thresholds of the selected methods.
Precise preparation of positive controls is imperative.
Testing according to the required thresholds also implies correct settings, maintenance and calibration of equipment, careful handling and preservation of reagents and all measures to prevent contamination between samples, e.g. separation of positive controls from test samples. Quality control standards must be applied to avoid administrative and other errors, especially concerning labelling and documentation.
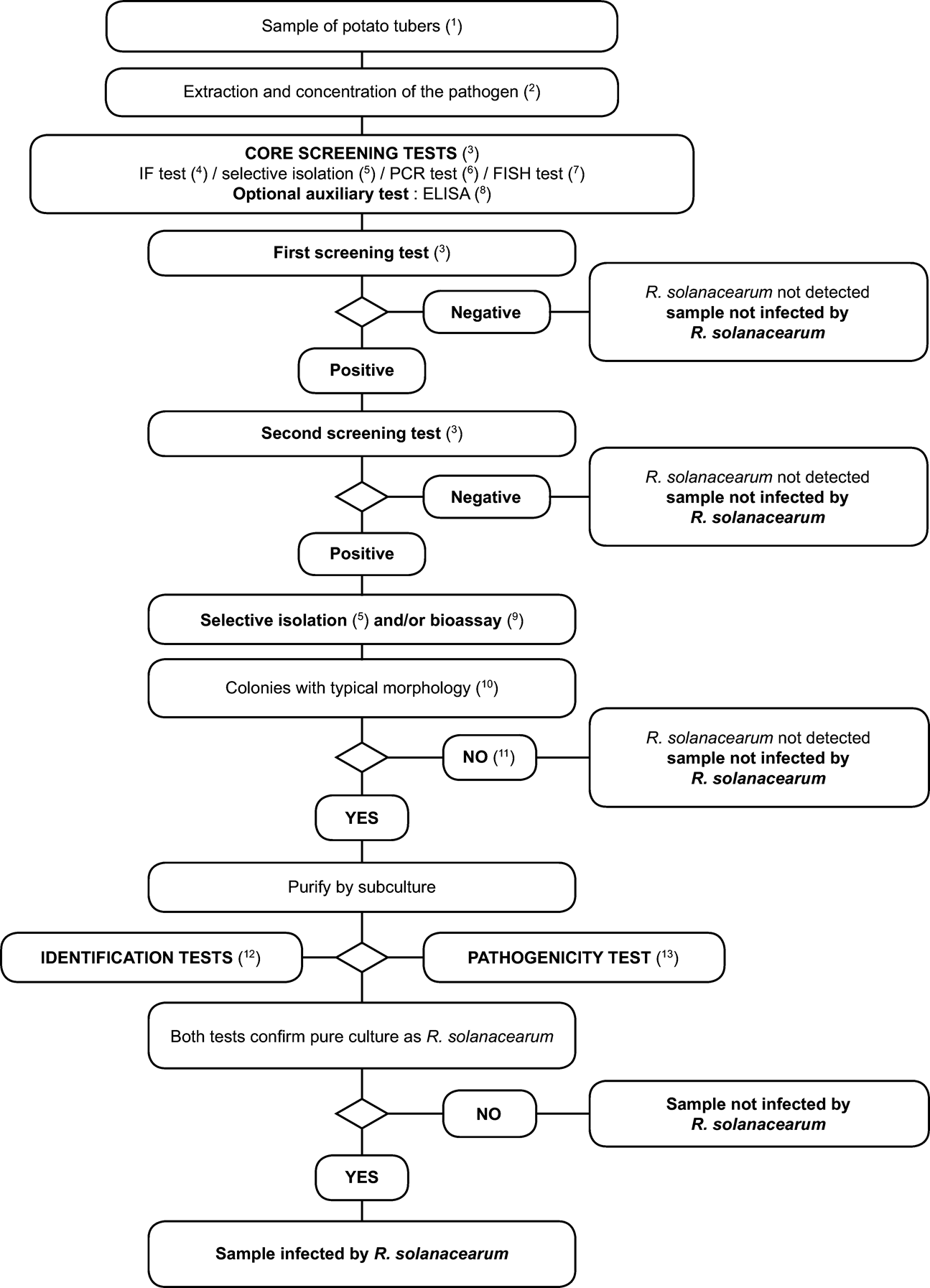
A suspected occurrence, as referred to in Article 4(2) of Directive 98/57/EC implies a positive result in diagnostic or screening tests performed on a sample as specified in flow charts below. A positive first screening test (IF test, PCR/FISH, selective isolation) must be confirmed by a second screening test based on a different biological principle.
If the first screening test is positive, then contamination with R. solanacearum is suspected and a second screening test must be done. If the second screening test is positive, than the suspicion is confirmed (suspected occurrence) and the testing according to the scheme must be continued. If the second screening test is negative, then the sample is considered not contaminated with R. solanacearum .
Confirmed presence as referred to in Article 5(1) in Directive 98/57/EC implies the isolation and identification of a pure culture of R. solanacearum with confirmation of pathogenicity.
SECTION I U.K. APPLICATION OF THE TEST SCHEME
1. Detection scheme for the diagnosis of brown rot and bacterial wilt ( Ralstonia solanacearum ) in potato tubers and potato, tomato or other host plants with symptoms of brown rot or bacterial wilt. U.K.
The testing procedure is intended for potato tubers and plants with symptoms typical or suspect of brown rot or vascular wilt. It involves a rapid screening test, isolation of the pathogen from infected vascular tissue on (selective) medium and, in case of a positive result, identification of the culture as Ralstonia solanacearum .
2. Scheme for detection and identification of Ralstonia solanacearum in samples of asymptomatic potato tubers U.K.
Principle: U.K.
The testing procedure is intended for detection of latent infections in potato tubers. A positive result from at least two screening tests ( 3 ), based on different biological principles, must be complemented by the isolation of the pathogen; followed by, in case of isolation of typical colonies, confirmation of a pure culture as R. solanacearum A positive result from only one of the screening tests is not sufficient to consider the sample suspect.
Screening tests and isolation tests must permit detection of 10 3 to 10 4 cells/ml of resuspended pellet, included as positive controls in each series of tests.
3. Scheme for detection and identification of Ralstonia solanacearum in samples of asymptomatic potato, tomato or other host plants U.K.
SECTION II U.K. DETAILED METHODS FOR DETECTION OF RALSTONIA SOLANACEARUM IN POTATO TUBERS AND POTATO, TOMATO OR OTHER HOST PLANTS WITH SYMPTOMS OF BROWN ROT OR BACTERIAL WILT
1. Symptoms (see website http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main) U.K.
1.1. Symptoms on potato U.K.
The potato plant . The early stage of infection in the field is recognised by wilting of the leaves towards the top of the plant at high temperatures during the day with recovery at night. In early stages of wilting leaves remain green, but later yellowing and brown necrosis develops. Epinasty also occurs. Wilting of one shoot or whole plants becomes rapidly irreversible and results in the collapse and death of the plant. The vascular tissue of transversely cut stems from wilted plants usually appears brown and a milky bacterial ooze exudes from the cut surface or can be expressed by squeezing. When a cut stem is placed vertically in water, threads of slime will stream from the vascular bundles.
The potato tuber . Potato tubers must be cut transversely close to the heel (stolon end) or longitudinally over the stolon end. The early stage of infection is recognised by a glassy yellow to light brown discolouration of the vascular ring from which a pale cream bacterial ooze emerges spontaneously after some minutes. Later, the vascular discolouration becomes a more distinct brown and necrosis can extend into the parenchymatous tissue. In advanced stages, infection breaks outwards from the heel end and the eyes from which bacterial slime may ooze causing soil particles to adhere. Reddish-brown slightly sunken lesions may appear on the skin due to collapse of vascular tissues internally. Secondary development of fungal and bacterial soft rots is common in the advanced stages of the disease.
1.2. Symptoms on tomato U.K.
The tomato plant . The first visible symptom is the flaccid appearance of the youngest leaves. Under favourable environmental conditions for the pathogen (soil temperatures of approximately 25 °C; saturated humidity), epinasty and wilting of one side or of the whole plant follows within a few days leading to total plant collapse. Under less favourable conditions (soil temperature below 21 °C), less wilting occurs, but large numbers of adventitious roots may develop on the stem. It is possible to observe watersoaked streaks from the base of the stem which is evidence of necrosis in the vascular system. When the stem is cut crosswise, discoloured brown vascular tissues exude white or yellowish bacterial ooze.
1.3. Symptoms on other hosts U.K.
Solanum dulcamara and S. nigrum plants . Under natural conditions, wilting symptoms are rarely observed in these weed hosts unless soil temperatures exceed 25 °C or inoculum levels are extremely high (e.g. as for S. nigrum growing adjacent to diseased potato or tomato plants). When wilting does occur, the symptoms are as described for tomato. Non-wilting S. dulcamara plants growing with stems and roots in water may show internal light brown discolouration of vascular tissues on transverse section of the stem base or underwater stem parts. Bacteria may ooze from cut vascular tissues or form threads of slime if the cut stem is placed vertically in water, even in the absence of wilting symptoms.
2. Rapid screening tests U.K.
Rapid screening tests may facilitate presumptive diagnosis but are not essential. Use one or more of the following validated tests: U.K.
2.1. Stem streaming test U.K.
(See Section VI.A.1.)
2.2. Detection of poly-ß-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) granules U.K.
Characteristic PHB granules in the cells of R. solanacearum are visualised by staining heat-fixed smears of bacterial ooze from infected tissue on a microscope slide with Nile Blue A or Sudan Black (See Section VI.A.2.).
2.3. Serological agglutination tests U.K.
(See Section VI.A.3.)
2.4. Other tests U.K.
Further appropriate rapid screening tests include the IF test (see Section VI.A.5.), FISH test (see Section VI.A.7.), ELISA tests (see Section VI.A.8.) and PCR tests (see Section VI.A.6).
3. Isolation procedure U.K.
Remove ooze or sections of discoloured tissue from the vascular ring in the potato tuber or from the vascular strands in stems of potato, tomato or other wilting host plants. Suspend in a small volume of sterile distilled water or 50mM phosphate buffer (Appendix 4) and leave for 5 to 10 minutes.
Prepare a series of decimal dilutions of the suspension.
Transfer 50-100 µl of the suspension and dilutions to a general nutrient medium (NA, YPGA or SPA; see Appendix 2) and/or to Kelman’s tetrazolium medium (Appendix 2) and/or a validated selective medium (e.g. SMSA; see Appendix 2). Spread or streak with an appropriate dilution plating technique. If useful, prepare separate plates with a diluted cell suspension of R. solanacearum biovar 2 as a positive control.
Incubate the plates for two to six days at 28 °C.
On the general nutrient media, virulent isolates of R. solanacearum develop pearly cream-white, flat, irregular and fluidal colonies often with characteristic whorls in the centre. Avirulent forms of R. solanacearum form small round non-fluidal, butyrous colonies which are entirely cream-white.
On Kelman’s tetrazolium and SMSA media, the whorls are blood red in colour. Avirulent forms of Ralstonia solanacearum form small round non-fluidal, butyrous colonies which are entirely deep red.
4. Identification tests for R. solanacearum U.K.
Tests to confirm identity of presumptive isolates of R. solanacearum are shown in Section VI.B.
SECTION III U.K.
1. Detailed methods for detection and identification of Ralstonia solanacearum in samples of asymptomatic potato tubers U.K.
1.1. Sample preparation U.K.
Note: U.K.
The standard sample size is 200 tubers per test. More intensive sampling requires more tests on samples of this size. Larger numbers of tubers in the sample will lead to inhibition or difficult interpretation of the results. However, the procedure can be conveniently applied for samples with less than 200 tubers where fewer tubers are available.
Validation of all detection methods described below is based on testing of samples of 200 tubers.
The potato extract described below can also be used for detection of the potato ring rot bacterium, Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus .
Optional pre-treatment in advance to sample preparation:
Incubation of samples at 25 to 30 °C, for up to two weeks before testing, to encourage multiplication of any R. solanacearum populations.
Wash the tubers. Use appropriate disinfectants (chlorine compounds when PCR-test is to be used in order to remove pathogen DNA) and detergents between each sample. Air dry the tubers. This washing procedure is particularly useful (but not required) for samples with excess soil and if a PCR-test or direct isolation procedure is to be performed.
1.1.1. Remove with a clean and disinfected scalpel or vegetable knife the skin at the heel (stolon) end of each tuber so that the vascular tissues become visible. Carefully cut out a small core of vascular tissue at the heel end and keep the amount of non-vascular tissue to a minimum. (see web site http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main). U.K.
Note: Set aside any (rotting) tubers with suspected brown rot symptoms and test separately. U.K.
If during removal of the heel end core suspect symptoms of brown rot are observed, a visual inspection of this tuber should be done and the tuber cut near the heel end. Any cut tuber with suspected symptoms should be kept for at least two days at room temperature in order to allow suberisation and stored refrigerated (at 4 to 10 °C) under proper quarantine conditions. All tubers including those with suspicioussymptoms should be kept according to Annex III.
1.1.2. Collect the heel end cores in unused disposable containers which can be closed and/or sealed (in case containers are reused they should be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected using chlorine compounds). Preferably, the heel end cores should be processed immediately. If this is not possible, store them in the container, without addition of buffer, refrigerated for not longer than 72 hours or for not longer than 24 hours at room temperature. U.K.
Process the heel end cores by one of the following procedures: either,
Cover the cores with sufficient volume (approximately 40 ml) of extraction buffer (Appendix 4) and agitate on a rotary shaker (50-100 rpm) for 4 hours below 24 °C or for 16 to 24 hours refrigerated,
or
Homogenise the cores with sufficient volume (approximately 40 ml) of extraction buffer (Appendix 4), either in a blender (e.g. Waring or Ultra Thurax) or by crushing in a sealed disposable maceration bag (e.g. Stomacher or Bioreba strong guage polythene, 150 mm × 250 mm; radiation sterilised) using a rubber mallet or suitable grinding apparatus (e.g. Homex).
Note: The risk of cross-contamination of samples is high when samples are homogenized using a blender. Take precautions to avoid aerosol generation or spillage during the extraction process. Ensure that freshly sterilised blender blades and vessels are used for each sample. If the PCR test is to be used, avoid carry-over of DNA on containers or grinding apparatus. Crushing in disposable bags and use of disposable tubes is recommended where PCR is to be used. U.K.
1.1.3. Decant the supernatant. If excessively cloudy, clarify either by slow speed centrifugation (at not more than 180 g for 10 minutes at a temperature between 4 to 10 °C) or by vacuum filtration (40 to 100 µm), washing the filter with additional (approximately 10 ml) extraction buffer. U.K.
1.1.4. Concentrate the bacterial fraction by centrifugation at 7 000 g for 15 minutes (or 10 000 g for 10 minutes) at a temperature between 4 to 10 °C and discard the supernatant without disturbing the pellet. U.K.
1.1.5. Resuspend the pellet in 1.5 ml pellet buffer (Appendix 4). Use 500 µl to test for R. solanacearum , 500 µl for Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus and 500 µl for reference purposes. Add sterile glycerol to final concentration of 10 to 25 % (v/v) to the 500 µl of the reference aliquot and to the remaining test aliquot, vortex and store at -16 to -24 °C (weeks) or at -68 to -86 °C (months). Preserve the test aliquots at 4 to 10 °C during testing. U.K.
Repeated freezing and thawing is not advisable.
If transport of the extract is required, ensure delivery in a cool box within 24 to 48 hours.
1.1.6. It is imperative that all R. solanacearum positive controls and samples are treated separately to avoid contamination. This applies to IF slides and to all tests. U.K.
1.2. Testing U.K.
See Flow chart and description of the tests and optimised protocols in the relevant appendices:
Selective isolation (see Section VI.A.4.)
IF test (see Section VI.A.5.)
PCR tests (see Section VI.A.6.)
FISH test (see Section VI.A.7.)
ELISA tests (see Section VI.A.8.)
Bioassay (see Section VI.A.9.)
2. Detailed methods for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in samples of asymptomatic potato, tomato or other host plants U.K.
2.1. Sample preparation U.K.
Note: For detection of latent R. solanacearum populations it is advised to test composite samples. The procedure can be conveniently applied for composite samples of up to 200 stem parts. Where surveys are performed they should be based on a statistically representative sample of the plant population under investigation. U.K.
2.1.1. Collect 1 to 2 cm stem segments in a closed sterile container according to the following sampling procedures: U.K.
Nursery tomato seedlings : With a clean disinfected knife, remove a 1 cm segment from the base of each stem, just above the soil level.
Field or glasshouse grown tomato plants : With a clean disinfected knife, remove the lowermost side shoot from each plant by cutting just above the joint with the main stem. Remove the lowermost 1cm segment from each side shoot.
Other hosts : With a clean disinfected knife or pruning shears, remove a 1 cm segment from the base of each stem, just above the soil level. In the case of S. dulcamara or other host plants growing in water, remove 1-2 cm sections from underwater stems or stolons with aquatic roots.
When sampling a particular location it is recommended to test a statistically representative sample of at least 10 plants per sampling point of each potential weed host. Pathogen detection will be most reliable during late spring, summer and autumn seasons, although natural infections can be detected all year round in the perennial Solanum dulcamara growing in watercourses. Known hosts include volunteer potato plants (groundkeepers), Solanum dulcamara, S. nigrum, Datura stramonium and other members of the family Solanaceae. Further hosts are Pelargonium spp. and Portulaca oleracea . Some European weed spp. which may potentially harbour R. solanacearum biovar 2/Race 3 populations in roots and/or rhizospheres under specific environmental conditions include Atriplex hastata, Bidens pilosa, Cerastium glomeratum, Chenopodium album, Eupatorium cannabinum, Galinsoga parviflora, Ranunculus scleratus, Rorippa spp, Rumex spp., Silene alba, S. nutans., Tussilago farfarra and Urtica dioica .
Note: Visual examination for internal symptoms (vascular staining or bacterial ooze) can be done at this stage. Set aside any stem segments with symptoms and test separately (See Section II). U.K.
2.1.2. Disinfect stem segments briefly with ethanol 70 % and immediately blot dry on tissue paper. Then process the stem segments by one of the following procedures: either, U.K.
Cover the segments with sufficient volume (approximately 40 ml) of extraction buffer (Appendix 4) and agitate on a rotary shaker (50 to 100 rpm) for four hours below 24 °C or for 16 to 24 hours refrigerated, or
Process immediately by crushing the segments in a strong maceration bag (e.g. Stomacher or Bioreba) with an appropriate volume of extraction buffer (Appendix 4) using a rubber mallet or appropriate grinding apparatus (e.g. Homex). If this is not possible, store the stem segments refrigerated for not longer than 72 hours or for not longer than 24 hours at room temperature.
2.1.3. Decant the supernatant after settling for 15 minutes. U.K.
2.1.4. Further clarification of the extract or concentration of the bacterial fraction are not usually required but may be achieved by filtration and/or centrifugation as described in Section III.1.1.3 – 1.1.5. U.K.
2.1.5. Divide the neat or concentrated sample extract into two equal parts. Maintain one half at 4 to 10 °C during testing and store the other half with 10 to 25 % (v/v) sterile glycerol at -16 to -24 °C (weeks) or at -68 to -86 °C (month) in case further testing is required. U.K.
2.2. Testing U.K.
See Flow chart and description of the tests and optimised protocols in the relevant appendices:
Selective isolation (see Section VI.A.4.)
IF test (see Section VI.A.5.)
PCR tests (see Section VI.A.6.)
FISH test (see Section VI.A.7.)
ELISA tests (see Section VI.A.8.)
Bioassay (see Section VI.A.9.)
SECTION IV U.K.
1. Scheme for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in water U.K.
2. Methods for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in water U.K.
Principle U.K.
The validated detection scheme, described in this section, is applicable for pathogen detection in samples of surface water and can also be applied for testing samples of potato processing or sewage effluents. However, it is important to note that the expected sensitivity of detection will vary with the substrate. Sensitivity of the isolation test is affected by populations of competing saprophytic bacteria which are generally much higher in potato processing and sewage effluents than in surface water. Whereas the scheme below is expected to detect as few as 10 3 cells per litre in surface water the sensitivity of detection in potato processing or sewage effluents is likely to be significantly lower. For this reason, it is recommended to test effluents after any purification treatments (e.g. sedimentation or filtration) during which saprophytic bacterial populations are reduced. The limitations in sensitivity of the test scheme should be considered when assessing the reliability of any negative results obtained. Whereas this scheme has been successfully used in survey work to determine presence or absence of the pathogen in surface water, its limitations should be realised when used in similar surveys of potato processing or sewage effluents.
2.1. Sample preparation U.K.
Note: U.K.
Detection of R. solanacearum in surface water is most reliable during late spring, summer and autumn seasons when water temperatures exceed 15 °C.
Repeated sampling at different times in the above mentioned period at designated sampling points will increase the reliability of detection by reducing the effects of climatic variation.
Take into account the effects of heavy rainfall and the geography of the watercourse to avoid extensive dilution effects that may obscure presence of the pathogen.
Take surface water samples in the vicinity of host plants if these hosts are present.
2.1.1. At selected sampling points, collect water samples by filling disposable sterile tubes or bottles at a depth if possible below 30 cm and within 2 m from the bank. For processing and sewage effluents, collect samples from the point of effluent discharge. Sample sizes up to 500 ml per sampling point are recommended. If smaller samples are preferred, it is advisable to take samples on at least three occasions per sampling point, each sample consisting of two replicated sub-samples of at least 30 ml. For intensive survey work, select at least three sampling points per 3 km of watercourse and ensure that tributaries entering the watercourse are also sampled. U.K.
2.1.2. Transport samples in cool dark conditions (4 to 10 °C) and test within 24 hours. U.K.
2.1.3. If required, the bacterial fraction may be concentrated using one of the following methods: U.K.
Centrifuge 30 to 50 ml sub-samples at 10 000 g for 10 minutes (or 7 000 g for 15 minutes) preferably at 4 to 10 °C, discard the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 1 ml pellet buffer (Appendix 4).
Membrane filtration (minimum pore size 0,45 µm) followed by washing the filter in 5 to 10 ml pellet buffer and retention of the washings. This method is suitable for larger volumes of water containing low numbers of saprophytes.
Concentration is usually not advisable for samples of potato processing or sewage effluent since increased populations of competing saprophytic bacteria will inhibit detection of Ralstonia solanacearum .
2.2. Testing U.K.
See flow chart and description of the tests in the relevant appendices.
SECTION V U.K.
1. Scheme for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in soil U.K.
2. Methods for detection and identification of R. solanacearum in soil U.K.
Principles U.K.
The validated detection scheme, described in this section, is applicable for pathogen detection in soil samples but can also be used to test samples of solid potato processing waste or sewage sludge. However, it should be noted that these methods are insufficiently sensitive to guarantee detection of low and/or irregularly dispersed populations of Ralstonia solanacearum that may occur in naturally infested samples of these substrates.
The limitations in sensitivity of this test scheme should be considered when assessing the reliability of any negative results obtained and also when used in surveys to determine presence or absence of the pathogen in soils or sludges. The most reliable test for presence of the pathogen in a field soil is to plant a susceptible host and monitor it for infection, but even with this method low levels of contamination will escape detection.
2.1. Sample preparation U.K.
2.1.1. Sampling of field soil should follow standard principals used for nematode sampling. Collect 0,5 to 1 kg of soil per sample from 60 sites per 0,3 ha from a depth of 10 to 20 cm (or in a grid of 7 x 7 metres) If the pathogen is suspected to be present, increase the number of collection points to 120 per 0,3 ha. Maintain samples at 12 to 15 °C prior to testing. Sample potato processing and sewage sludges by collecting a total of 1 kg from sites representing the total volume of sludge to be tested. Mix each sample well before testing. U.K.
2.1.2. Disperse sub-samples of 10 to 25 g of soil or sludge by rotary shaking (250 rpm) in 60 to 150 ml extraction buffer (Appendix 4) for up to two hours. If required, addition of 0,02 % sterile Tween-20 and 10 to 20 g sterile gravel may assist dispersion. U.K.
2.1.3. Maintain the suspension at 4 °C during testing. U.K.
2.2. Testing U.K.
See flow chart and description of the tests in the relevant appendices.
SECTION VI U.K. OPTIMISED PROTOCOLS FOR DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION OF R. SOLANACEARUM
A. DIAGNOSTIC AND DETECTION TESTS U.K.
1. Stem streaming test U.K.
The presence of R. solanacearum in stems of wilting potato, tomato or other host plants can be indicated by the following simple presumptive test: Cut the stem just above the soil level. Suspend the cut surface in a tube of clean water. Observe for characteristic spontaneous streaming of threads of bacterial slime from the cut vascular bundles after a few minutes.
2. Detection of poly-ß-hydroxybutyrate granules U.K.
Prepare a smear of bacterial ooze from infected tissue or from a 48-hour culture on YPGA or SPA medium (Appendix 2) on a microscope slide.
Prepare positive control smears of a biovar 2 strain of R. solanacearum and, if considered useful, a negative control smear of a known PHB negative sp.
Allow to air dry and pass the lower surface of each slide rapidly above a flame to fix the smears.
Stain preparation with either Nile Blue or Sudan Black and observe microscopically as described below:
Nile blue test: U.K.
Flood each slide with 1 % aquous solution of Nile Blue A and incubate for 10 minutes at 55 °C.
Drain off the staining solution. Wash briefly in gently running tap water. Remove excess water with tissue paper.
Flood the smear with 8 % aqueous acetic acid and incubate for one minute at ambient temperature.
Wash briefly in gently running tap water. Remove excess water with tissue paper.
Re-moisten with a drop of water and apply a coverslip.
Examine the stained smear with an epifluorescence microscope at 450 nm under oil immersion at a magnification of 600 to 1 000 using an oil- or water-immersion objective.
Observe for bright orange fluorescence of PHB granules. Also observe under transmitted normal light to ensure that the granules are intracellular and that cell morphology is typical of R. solanacearum .
Sudan Black test: U.K.
Flood each slide with 0,3 % Sudan Black B solution in 70 % ethanol and incubate for 10 minutes at ambient temperature.
Drain off the staining solution and wash briefly in tap water, removing excess water with tissue paper.
Dip the slides briefly in xylol and blot dry on tissue paper. Caution: Xylol is harmful, take necessary safety precautions and work in a fume cupboard .
Flood the slides with 0,5 % (w/v) aqueous safranin and leave for 10 seconds at ambient temperature. Caution: Safranin is harmful, take necessary safety precautions and work in a fume cupboard .
Wash in gently running tap water, blot dry on tissue paper and apply a coverslip.
Examine stained smears with a light microscope using transmitted light under oil immersion at a magnification of 1 000 using an oil-immersion objective.
Observe for blue-black staining of PHB granules in cells of R. solanacearum with pink-stained cell walls.
3. Serological agglutination tests U.K.
Agglutination of R. solanacearum cells in bacterial ooze or symptomatic tissue extracts is best observed using validated antibodies (see Appendix 3) labelled with appropriate coloured markers such as red Staphylococcus aureus cells or coloured latex particles. If using a commercially available kit (see Appendix 3), follow the manufacturers instructions. Otherwise perform the following procedure:
Mix drops of a suspension of labelled antibody and bacterial ooze (approximately 5 µl each) on windows of multiwell test slides.
Prepare positive and negative controls using suspensions of R. solanacearum biovar 2 and a heterologous strain.
Observe for agglutination in positive samples after gentle mixing for 15 seconds.
4. Selective isolation U.K.
4.1. Selective plating U.K.
Note: Before using this method for the first time, perform preliminary tests to ensure reproducible detection of 10 3 to 10 4 colony-forming units of R. solanacearum per ml added to extracts from samples which previously tested negative. U.K.
Use an appropriately validated selective medium such as SMSA (as modified by Elphinstone et al. , 1996; see Appendix 2).
Care is required to differentiate R. solanacearum from other bacteria able to develop colonies on the medium. Furthermore, colonies of R. solanacearum may show atypical morphology if plates are overcrowded or antagonistic bacteria are also present. Where effects of competition or antagonism are suspected, the sample should be re-tested using a different test.
Highest sensitivity of detection by this method can be expected when using freshly prepared sample extracts. However, the method is also applicable for use with extracts which have been stored under glycerol at -68 to -86 °C.
As positive controls, prepare decimal dilutions from a suspension of 10 6 cfu per ml of a virulent biovar 2 strain of R. solanacearum (e.g. NCPPB 4156 = PD 2762 = CFBP 3857). To avoid any possibility of contamination, prepare positive controls totally separately from samples to be tested.
For each newly prepared batch of a selective medium its suitability for growth of the pathogen should be tested before it is used to test routine samples.
Test control material in an identical manner as the sample(s).
4.1.1. Perform an appropriate dilution plating technique aiming to ensure that any background saprophytic colony-forming populations are diluted out. Spread 50 - 100 µl per plate of sample extract and each dilution. U.K.
4.1.2. Incubate plates at 28 °C. Read plates after 48 hours and daily thereafter up to six days. Typical R. solanacearum colonies on SMSA medium are milky white, flat, irregular and fluidal and after three days incubation develop pink to blood-red coloration in the centre with internal streaking or whorling. (see website http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main). U.K.
Note: Atypical colonies of R. solanacearum sometimes form on this medium. These may be small, round, entirely red in colour and non-fluidal or only partially fluidal and therefore difficult to distinguish from saprophytic colony-forming bacteria. U.K.
4.1.3. Purify presumptive R. solanacearum colonies after streaking or dilution plating onto a general nutrient medium to obtain isolated colonies (see Appendix 2). U.K.
4.1.4. Store cultures short-term in sterile water (pH 6 to 8, chlorine free) at room temperature in the dark, or long term in a suitable cryoprotectant medium at -68 to -86 °C or lyophilised. U.K.
4.1.5. Identify presumptive cultures (see Section VI.B.) and perform a pathogenicity test (see Section VI. C). U.K.
Interpretation of selective plating test results U.K.
The selective plating test is negative if no bacterial colonies are observed after six days or if no presumptive colonies typical of R. solanacearum are found, provided that no inhibition is suspected due to competition or antagonism by other bacteria and that typical R. solanacearum colonies are found in the positive controls.
The selective plating test is positive if presumptive R. solanacearum colonies are isolated.
4.2. Enrichment procedure U.K.
Use a validated enrichment medium such as modified Wilbrink broth (see Appendix 2). U.K.
This procedure can be used to selectively increase R. solanacearum populations in sample extracts and increase sensitivity of detection. The procedure also effectively dilutes inhibitors of the PCR reaction (1:100). It should be noted, however, that enrichment of R. solanacearum can fail due to competition or antagonism by saprophytic organisms which are often simultaneously enriched. For this reason, isolation of R.solanacearum from enriched broth cultures may be difficult. In addition, since populations of serologically related saprophytes can be increased, the use of specific monoclonal antibodies rather than polyclonal antibodies is recommended where the ELISA test is to be used.
4.2.1. For enrichment-PCR, transfer 100 µl of sample extract into 10 ml of enrichment broth (Appendix 2) previously aliquoted into DNA-free tubes or flasks. For enrichment-ELISA, higher proportions of sample extract to broth can be used (e.g. 100 µl in 1,0 ml of enrichment broth). U.K.
4.2.2. Incubate for 72 hours at 27 to 30 °C in shaking culture or static culture with caps loosely- fitted to permit aeration. U.K.
4.2.3. Mix well before using in ELISA or PCR tests. U.K.
4.2.4. Treat enriched broth in an identical manner as the sample(s) in the above tests. U.K.
Note: If inhibition of enrichment of R. solanacearum is anticipated, due to high populations of certain competing saprophytic bacteria, enrichment of sample extracts before any centrifugation or other concentration steps may give better results. U.K.
5. IF Test U.K.
Principle U.K.
The use of the IF test as the principal screening test is recommended because of its proven robustness to achieve the required thresholds.
When the IF test is used as the principal screening test and the IF reading is positive, the Isolation, PCR or FISH test must be performed as a second screening test. When the IF test is used as the second screening test and the IF reading is positive, further testing according to the flow scheme is required to complete the analysis.
Note: Use a validated source of antibodies to R. solanacearum (see web site http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main). It is recommended that the titre is determined for each new batch of antibodies. The titre is defined as the highest dilution at which optimum reaction occurs when testing a suspension containing 10 5 to 10 6 cells per ml of the homologous strain of R. solanacearum and using an appropriate fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) conjugate according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Validated polyclonal antisera all had an IF titre of at least 1: 2 000 . During testing, the antibodies should be used at a working dilution(s) close to or at the titre. U.K.
The test should be performed on freshly-prepared sample extracts. If necessary, it can be successfully performed on extracts stored at -68 to -86 °C under glycerol. Glycerol can be removed from the sample by addition of 1 ml pellet buffer (Appendix 4), re-centrifugation for 15 minutes at 7 000 g and re-suspension in an equal volume of pellet buffer. This is often not necessary, especially if samples are fixed to the slides by flaming.
Prepare separate positive control slides of the homologous strain or any other reference strain of R. solanacearum , suspended in potato extract, as specified in Appendix 3 B, and optionally in buffer.
Naturally infected tissue (maintained by lyophilisation or freezing at -16 to -24 °C) should be used where possible as a similar control on the same slide.
As negative controls, aliquots of sample extract which previously tested negative for R. solanacearum can be used.
Standardised positive and negative control materials available for use with this test are listed in Appendix 3.
Use multiwell microscope slides with preferably 10 windows of at least 6 mm diameter.
Test control material in an identical manner as the sample(s).
5.1. Prepare the test slides by one of the following procedures: U.K.
For pellets with relatively little starch sediment:
Pipette a measured standard volume (15 µl is appropriate for 6 mm window diameter – scale up volume for larger windows) of a 1/100 dilution of the resuspended potato pellet onto the first window. Subsequently pipette a similar volume of undiluted pellet (1/1) onto the remaining windows on the row. The second row can be used as duplicate or for a second sample as presented in Figure 1.
For other pellets:
Prepare decimal dilutions (1/10, 1/100) of the resuspended pellet in pellet buffer. Pipette a measured standard volume (15 µl is appropriate for 6 mm window diameter – scale up volume for larger windows) of the resuspended pellet and each dilution on a row of windows. The second row can be used as duplicate or for a second sample as presented in Figure 2.
5.2. Dry the droplets at ambient temperature or by warming to temperatures of 40 to 45 °C. Fix the bacterial cells to the slide either by heating (15 minutes at 60 °C), flaming, with 95 % ethanol or according to specific instructions from the suppliers of the antibodies. U.K.
If necessary, fixed slides may then be stored frozen in a desiccated box for as little time as necessary (up to a maximum of three months) prior to further testing.
5.3. IF procedure U.K.
According to test slide preparation in 5.1(i):
Prepare a set of twofold dilutions The first well should have 1/2 of the titre (T/2), the others 1/4 of the titre (T/4), 1/2 of the titre (T/2), the titre (T) and twice the titre (2T).
According to test slide preparation in 5.1(ii):
Prepare the working dilution (WD) of the antibody in IF buffer. The working dilution affects the specificity.
Figure 1.
Preparation of the test slide according to 5.1(i) and 5.3(i)
Figure 2.
Preparation of the test slide according to 5.1(ii) and 5.3(ii).
5.3.1. Arrange the slides on moist tissue paper. Cover each test window completely with the antibody dilution(s). The volume of antibody applied on each window must be at least the volume of extract applied. U.K.
The following procedure should be carried out in the absence of specific instructions from the suppliers of the antibodies:
5.3.2. Incubate the slides on moist paper under a cover for 30 minutes at ambient temperature (18 to 25 °C). U.K.
5.3.3. Shake the droplets off each slide and rinse carefully with IF buffer. Wash by submerging for five minutes in IF buffer-Tween (Appendix 4) and subsequently in IF buffer. Avoid causing aerosols or droplet transfer that could result in cross-contamination. Carefully remove excess moisture by blotting gently. U.K.
5.3.4. Arrange the slides on moist paper. Cover the test windows with the dilution of FITC conjugate used to determine the titre. The volume of conjugate applied on the windows must be identical to the volume of antibody applied. U.K.
5.3.5. Incubate the slides on moist paper under a cover for 30 minutes at ambient temperature (18 to 25 °C). U.K.
5.3.6. Shake the droplets of conjugate off the slide. Rinse and wash as before (5.3.3). U.K.
Carefully remove excess moisture.
5.3.7. Pipette 5 - 10 µl of 0,1M phosphate-buffered glycerol (Appendix 4) or a commercially antifading mountant on each window and apply a coverslip. U.K.
5.4. Reading the IF test: U.K.
5.4.1 Examine test slides on an epifluorescence microscope with filters suitable for excitation of FITC, under oil or water immersion at a magnification of 500- 1 000 . Scan windows across two diameters at right angles and around the perimeter. For samples showing no or low number of cells observe at least 40 microscope fields. U.K.
Check the positive control slide first. Cells must be bright fluorescent and completely stained at the determined antibody titre or working dilution. The IF test (Section VI.A.5.) must be repeated if the staining is aberrant.
5.4.2. Observe for bright fluorescing cells with characteristic morphology of R. solanacearum in the test windows of the test slides (see website http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main). The fluorescence intensity must be equivalent to the positive control strain at the same antibody dilution. Cells with incomplete staining or with weak fluorescence must be disregarded. U.K.
If any contamination is suspected the test must be repeated. This may be the case when all slides in a batch show positive cells due to the contamination of buffer or if positive cells are found (outside of the slide windows) on the slide coating.
5.4.3. There are several problems inherent to the specificity of the immunofluorescence test. Background populations of fluorescing cells with atypical morphology and cross reacting saprophytic bacteria with size and morphology similar to R. solanacearum are likely to occur in potato heel end core and stem segment pellets. U.K.
5.4.4. Consider only fluorescing cells with typical size and morphology at the titre or working dilution of the antibodies as in 5.3. U.K.
5.4.5. Interpretation of the IF reading: U.K.
If bright fluorescing cells with characteristic morphology are found, estimate the average number of typical cells per microscope field and calculate the number of typical cells per ml of resuspended pellet (Appendix 5).
The IF reading is positive for samples with at least 5 × 10 3 typical cells per ml of resuspended pellet. The sample is considered potentially contaminated and further testing is required.
The IF reading is negative for samples with less than 5 × 10 3 cells per ml of resuspended pellet and the sample is considered negative. Further testing is not required.
6. PCR tests U.K.
Principles U.K.
When the PCR test is used as the principal screening test and found to be positive, isolation or IF must be performed as a second compulsory screening test. When PCR is used as the second screening test and found to be positive, further testing according to the flow scheme is required to complete the diagnosis.
Full exploitation of this method as principal screening test is only recommended when specialised expertise has been acquired.
Note: Preliminary testing with this method should permit reproducible detection of 10 3 to 10 4 cells of R. solanacearum per ml added to sample extracts which previously tested negative. Optimisation experiments may be required to achieve maximum levels of sensitivity and specificity in all laboratories. U.K.
Use validated PCR reagents and protocols (see Appendix 6). Preferably select a method with an internal control.
Use appropriate precautions to avoid contamination of sample with target DNA. The PCR test should be performed by experienced technicians, in dedicated molecular biology laboratories, in order to minimise the possibility of contamination with target DNA.
Negative controls (for DNA extraction and PCR procedures) should always be handled as final samples in the procedure, to make evident whether any carry over of DNA has occurred.
The following negative controls should be included in the PCR test:
Sample extract that previously tested negative for R. solanacearum ,
Buffer controls used for extracting the bacterium and the DNA from the sample,
PCR-reaction mix.
The following positive controls should be included:
Aliquots of resuspended pellets to which R. solanacearum has been added (preparation see Appendix 3 B).
A suspension of 10 6 cells per ml of R. solanacearum in water from a virulent isolate (e.g. NCPPB 4156 = PD 2762 = CFBP 3857; see Appendix 3 B).
If possible use also DNA extracted from positive control samples in the PCR test.
To avoid potential contamination prepare positive controls in a separate environment from samples to be tested.
Sample extracts should be as free as possible from soil. It could therefore, in certain cases, be advisible to prepare extracts from washed potatoes if PCR protocols are to be used.
Standardized positive and negative control material available for use with this test are listed in Appendix 3).
6.1. DNA purification methods U.K.
Use positive and negative control samples as described above (see Appendix 3). U.K.
Test control material in an identical manner as the sample(s).
A variety of methods are available for purification of target DNA from complex sample substrates, thus removing inhibitors of PCR and other enzymatic reactions and concentrating target DNA in the sample extract. The following method has been optimised for use with the validated PCR methods shown in Appendix 6.
(a) Method according to Pastrik (2000) U.K.
Pipette 220 µl of lysis buffer (100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8,0], 1 mM EDTA [pH 8,0]) into a 1,5 ml Eppendorf tube.
Add 100 µl sample extract and place in a heating block or water bath at 95 °C for 10 min.
Put tube on ice for 5 min.
Add 80 µl Lysozyme stock solution (50 mg Lysozyme per ml in 10 mM Tris HCl, pH 8,0) and incubate at 37 °C for 30 min.
Add 220 µl of Easy DNA ® solution A (Invitrogen), mix well by vortexing and incubate at 65 °C for 30 min.
Add 100 µl of Easy DNA ® solution B (Invitrogen), vortex vigorously until the precipitate runs freely in the tube and the sample is uniformly viscous.
Add 500 µl of chloroform and vortex until the viscosity decreases and the mixture is homogeneous.
Centrifuge at 15 000 g for 20 min at 4 °C to separate phases and form the interphase.
Transfer the upper phase into a fresh Eppendorf tube.
Add 1 ml of 100 % ethanol ( -20 °C) vortex briefly and incubate on ice for 10 min.
Centrifuge at 15 000 g for 20 min at 4 °C and remove ethanol from pellet.
Add 500 µl 80 % ethanol ( -20 °C) and mix by inverting the tube.
Centrifuge at 15 000 g for 10 min at 4 °C, save the pellet and remove ethanol.
Allow the pellet to dry in air or in a DNA speed vac.
Resuspend the pellet in 100 µl sterile UPW and leave at room temperature for at least 20 minutes.
Store at -20 °C until required for PCR.
Spin down any white precipitate by centrifugation and use 5 µl of the supernatant containing DNA for the PCR.
(b) Other methods U.K.
Other DNA extraction methods, e.g. Qiagen DNeasy Plant Kit, could be applied providing that they are proven to be equally as effective in purifying DNA from control samples containing 10 3 to 10 4 pathogen cells per ml.
6.2. PCR U.K.
6.2.1. Prepare test and control templates for PCR according to the validated protocols (Section VI.A.6.). Prepare one decimal dilution of sample DNA extract (1:10 in UPW). U.K.
6.2.2. Prepare the appropriate PCR reaction mix in a contamination-free environment according to the published protocols (Appendix 6). Where possible, it is recommended to use a multiplex PCR protocol that also incorporates an internal PCR control. U.K.
6.2.3. Add 2-5 µl of DNA extract per 25 µl PCR reaction in sterile PCR tubes according to the PCR protocols, (see Appendix 6). U.K.
6.2.4. Incorporate a negative control sample containing only PCR reaction mix and add the same source of UPW as used in the PCR mix in place of sample. U.K.
6.2.5. Place tubes in the same thermal cycler which was used in preliminary testing and run the appropriately optimised PCR programme (Appendix 6). U.K.
6.3. Analysis of the PCR product U.K.
6.3.1. Resolve PCR amplicons by agarose gel electrophoresis. Run at least 12 µl of amplified DNA reaction mixture from each sample mixed with 3 µl loading buffer (Appendix 6) in 2,0 % (w/v) agarose gels in tris-acetate-EDTA (TAE) buffer (Appendix 6) at 5 to 8 V per cm. Use an appropriate DNA marker, e.g. 100 bp ladder. U.K.
6.3.2. Reveal DNA bands by staining in ethidium bromide (0,5 mg per L) for 30 to 60 minutes taking appropriate precautions for handling this mutagen. U.K.
6.3.3. Observe stained gel under short wave UV transillumination (λ = 302 nm) for amplified PCR products of the expected size (Appendix 6) and document. U.K.
6.3.4. For all new findings/cases verify authenticity of the PCR amplicon by performing restriction enzyme analysis on a sample of the remaining amplified DNA by incubating at the optimum temperature and time with an appropriate enzyme and buffer (see Appendix 6). Resolve the digested fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis as before and observe characteristic restriction fragment pattern under UV transillumination after ethidium bromide staining and compare with the undigested and digested positive control. U.K.
Interpretation of the PCR test result: U.K.
The PCR test is negative if the R. solanacearum -specific PCR amplicon of expected size is not detected for the sample in question but is detected for all positive control samples (in case of multiplex PCR with plant specific internal control primers: a second PCR-product of expected size must be amplified with the sample in question).
The PCR test is positive if the R. solanacearum -specific PCR amplicon of expected size and restriction pattern (when required) is detected, providing that it is not amplified from any of the negative control samples. Reliable confirmation of a positive result can also be obtained by repeating the test with a second set of PCR primers (Appendix 6).
Note: Inhibition of the PCR may be suspected if the expected amplicon is obtained from the positive control sample containing R. solanacearum in water but negative results are obtained from positive controls with R. solanacearum in potato extract. In multiplex PCR protocols with internal PCR controls, inhibition of the reaction is indicated when neither of the two amplicons are obtained. U.K.
Contamination may be suspected if the expected amplicon is obtained from one or more of the negative controls.
7. FISH test U.K.
Principle U.K.
When the FISH test is used as the first screening test and found to be positive, Isolation or the IF test must be performed as a second compulsory screening test. When the FISH test is used as the second screening test and found to be positive, further testing according to the flow scheme is required to complete the diagnosis.
Note: Use validated R. solanacearum -specific oligo-probes (see Appendix 7). Preliminary testing with this method should permit reproducible detection of at least 10 3 to 10 4 cells of R. solanacearum per ml added to sample extracts which previously tested negative. U.K.
The following procedure should preferably be performed on freshly prepared sample extract but can also be successfully performed on sample extract that has been stored under glycerol at -16 to -24 or -68 to -86 °C.
As negative controls, use aliquots of sample extract that previously tested negative for R. solanacearum .
As positive controls prepare suspensions containing 10 5 to 10 6 cells per ml of R. solanacearum biovar 2 (e.g. strain NCPPB 4156 = PD 2762 = CFBP 3857, see Appendix 3) in 0,01M phosphate buffer (PB) from a 3 to 5 day culture). Prepare separate positive control slides of the homologous strain or any other reference strain of R. solanacearum , suspended in potato extract, as specified in Appendix 3 B.
The use of the FITC-labelled eubacterial oligo-probe offers a control for the hybridisation process, since it will stain all eubacteria that are present in the sample.
Standardized positive and negative control material available for use with this test are listed in Appendix 3A).
Test control material in an identical manner as the sample(s).
7.1. Potato extract fixation U.K.
The following protocol is based upon Wullings et al. (1998): U.K.
7.1.1. Prepare fixative solution (see Appendix 7). U.K.
7.1.2. Pipette 100 µl of each sample extract into an Eppendorf tube and centrifuge for 7 minutes at 7 000 g. U.K.
7.1.3. Remove the supernatant and dissolve the pellet in 200 µl of fixative prepared < 24 hours previously. Vortex and incubate for one hour in the refrigerator. U.K.
7.1.4. Centrifuge for 7 minutes at 7 000 g, remove the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 75 µl 0,01M PB (see Appendix 7). U.K.
7.1.5. Spot 16 µl of the fixed suspensions onto a clean multitest slide as shown in Fig. 7.1. Applying two different samples per slide, undiluted and use 10 µl to make a 1:100 dilution (in 0,01 M PB). The remaining sample solution (49 µl) can be stored at -20 °C after addition of one volume of 96 % ethanol. In case the FISH assay requires repeating, remove the ethanol by centrifugation and add an equal volume of 0,01 PB (mix by vortexing). U.K.
Fig. 7.1
Layout for FISH slide
7.1.6. Air-dry the slides (or on slide dryer at 37 °C) and fix them by flaming. U.K.
At this stage the procedure may be interrupted and the hybridisation continued the following day. Slides should be stored dust-free and dry at room temperature.
7.2. Hybridisation U.K.
7.2.1. Dehydrate the cells in a graded ethanol series of 50 %, 80 % and 96 % for one minute each. Air dry the slides in a slide-holder. U.K.
7.2.2. Prepare a moist incubation chamber by covering the bottom of an air-tight box with tissue or filter paper soaked in 1x hybmix (Appendix 7). Pre-incubate the box in the hybridisation oven at 45 °C for at least 10 minutes. U.K.
7.2.3. Apply 10 μl of hybridisation solution (Appendix 7) to eight windows (windows 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9 and 10; see Fig 7.1) of each slide leaving the two centre windows (3 and 8) empty. U.K.
7.2.4. Apply coverslips (24 × 24 mm) to the first and last four windows without trapping air. Place the slides in the pre-warmed moist chamber and hybridise for five hours in the oven at 45 °C in the dark. U.K.
7.2.5. Prepare three beakers containing 1 l of Milli Q (molecular grade) water, 1 l of 1x hybmix (334 ml 3x hybmix and 666 ml Milli Q water) and 1 l of 1/8x hybmix (42 ml 3x hybmix and 958 ml Milli Q water). Pre-incubate each in a waterbath at 45 °C. U.K.
7.2.6. Remove the coverslips from the slides and place the slides in a slide holder. U.K.
7.2.7. Wash away excess probe by incubation for 15 minutes in the beaker with 1x hybmix at 45 °C. U.K.
7.2.8. Transfer the slide holder to 1/8 hybmix washing solution and incubate for a further 15 minutes. U.K.
7.2.9. Dip the slides briefly in Milli Q water and place them on filter paper. Remove excess moisture by covering the surface gently with filter paper. Pipette 5 to 10 μl of anti-fading mountant solution (e.g. Vectashield, Vecta Laboratories, CA, USA or equivalent) on each window and apply a large coverslip (24 × 60 mm) over the whole slide. U.K.
7.3. Reading the FISH test U.K.
7.3.1. Observe the slides immediately with a microscope fitted for epifluorescence microscopy at 630 or 1 000 × magnification under immersion oil. With a filter suitable for fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) eubacterial cells (including most gram negative cells) in the sample are stained fluorescent green. Using a filter for tetramethylrhodamine-5-isothiocyanate, Cy3-stained cells of R. solanacearum appear fluorescent red. Compare cell morphology with that of the positive controls. Cells must be bright fluorescent and completely stained The FISH test (Section VI.A.7.) must be repeated if the staining is aberrant. Scan windows across two diameters at right angles and around the perimeter. For samples showing no or low number of cells observe at least 40 microscope fields. U.K.
7.3.2. Observe for bright fluorescing cells with characteristic morphology of R. solanacearum in the test windows of the test slides (see web site http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main). The fluorescence intensity must be equivalent or better than that of the positive control strain. Cells with incomplete staining or with weak fluorescence must be disregarded. U.K.
7.3.3. If any contamination is suspected the test must be repeated. This may be the case when all slides in a batch show positive cells due to the contamination of buffer or if positive cells are found (outside of the slide windows) on the the slide coating. U.K.
7.3.4. There are several problems inherent to the specificity of the FISH test. Background populations of fluorescing cells with atypical morphology and cross reacting saprophytic bacteria with size and morphology similar to R. solanacearum may occur, although much less frequent as in the IF test, in potato heel end core and stem segment pellets. U.K.
7.3.5. Consider only fluorescing cells with typical size and morphology. U.K.
7.3.6. Interpretation of the FISH test result: U.K.
Valid FISH test results are obtained if bright green fluorescent cells of size and morphology typical of R. solanacearum are observed using the FITC filter and bright red fluorescent cells using the rhodamine filter in all positive controls and not in any of the negative controls. If bright fluorescing cells with characteristic morphology are found, estimate the average number of typical cells per microscope field and calculate the number of typical cells per ml of resuspended pellet (Appendix 4). Samples with at least 5 × 10 3 typical cells per ml of resuspended pellet are considered potentially contaminated. Further testing is required. Samples with less than 5 × 10 3 typical cells per ml of resuspended pellet are considered negative.
The FISH test is negative if bright red fluorescent cells with size and morphology typical of R. solanacearum are not observed using the rhodamine filter, provided that typical bright red fluorescent cells are observed in the positive control preparations when using the rhodamine filter.
8. ELISA tests U.K.
Principle U.K.
ELISA can only be used as an optional test in addition to IF, PCR or FISH due to a relatively low sensitivity of this test. When DAS ELISA is used enrichment and the use of monoclonal antibodies are compulsory (see web site http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main). Enrichment of the samples before using ELISA may be useful in order to increase the sensitivity of the test, but it can fail due to competition by other organisms in the sample.
Note: Use an validated source of antibodies to R. solanacearum (see web site http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main) It is recommended that the titre is determined for each new batch of antibodies. The titre is defined as the highest dilution at which optimum reaction occurs when testing a suspension containing 10 5 to 10 6 cells per ml of the homologous strain of R. solanacearum and using appropriate secondary antibody conjugates according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. During testing, the antibodies should be used at a working dilution close to or at the titre of the commercial formulation. U.K.
Determine the titre of the antibodies on a suspension of 10 5 to 10 6 cells per ml of the homologous strain of R. solanacearum .
Include a sample extract that previously tested negative for R. solanacearum and a suspension of a non-cross reacting bacterium in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) as negative controls.
As positive control use aliquots of sample extract, that previously tested negative, mixed with 10 3 to 10 4 cells per ml of R. solanacearum biovar 2 (e.g. strain NCPPB 4156 = PD 2762 = CFBP 3857, see Appendix 2 A and B). For comparison of results on each plate use a standard suspension of 10 5 to 10 6 cells per ml in PBS of R. solanacearum . Ensure positive controls are well separated on the microtitre plate from the sample(s) under test.
Standardised positive and negative control materials available for use with this test are listed in Appendix 3 A.
Test control material in an identical manner as the sample(s).
Two ELISA protocols have been validated. U.K.
(a) Indirect ELISA (Robinson Smith et al. , 1995) U.K.
Use 100 to 200 µl aliquots of sample extract. (Heating at 100 °C for four minutes in a waterbath or heating block may reduce non-specific results in some cases).
Add an equal volume of double strength coating buffer (Appendix 4) and vortex.
Apply 100 µl aliquots to each of at least two wells of a microtitre plate (e.g. Nunc-Polysorp or equivalent) and incubate for one hour at 37 °C or overnight at 4 °C.
Flick out the extracts from the wells. Wash the wells three times with PBS-Tween (Appendix 4), leaving the last washing solution in the wells for at least five minutes.
Prepare the appropriate dilution of antibodies against- R. solanacearum in blocking buffer (Appendix 4). For validated commercial antibodies, use the recommended dilutions (usually twice as concentrated as the titre).
Add 100 µl to each well and incubate for one hour at 37 °C.
Flick out the antibody solution from the wells and wash as before (4).
Prepare the appropriate dilution of secondary antibody-alkaline phosphatase conjugate in blocking buffer. Add 100 µl to each well and incubate for one hour at 37 °C.
Flick out conjugated antibody from wells and wash as before (4).
Add 100 µl alkaline phosphatase substrate solution (Appendix 4) to each well. Incubate in the dark at ambient temperature and read absorbance at 405 nm at regular intervals within 90 minutes.
(b) DASI ELISA U.K.
Prepare the appropriate dilution of anti- R. solanacearum polyclonal immunoglobulins in coating buffer pH 9.6 (Appendix 4). Add 200 µl to each well. Incubate at 37 °C for four to five hours or at 4 °C for 16 hours.
Wash the wells three times with PBS-Tween (Appendix 4).
Add 190 µl of sample extract to at least two wells. Also add positive and negative controls in two wells each per plate. Incubate for 16 hr at 4 °C.
Wash the wells three times with PBS-Tween (Appendix 4).
Prepare an appropriate dilution of R. solanacearum -specific monoclonal antibodies in PBS (Appendix 4) also containing 0,5 % bovine serum albumin (BSA) and add 190 µl to each well. Incubate at 37 °C for two hours.
Wash the wells three times with PBS-Tween (Appendix 4).
Prepare an appropriate dilution of anti-mouse immunoglobulins conjugated with alkaline phosphatase in PBS. Add 190 µl to each well. Incubate at 37 °C for two hours.
Wash the wells three times with PBS-Tween (Appendix 4).
Prepare an alkaline phosphatase substrate solution containing 1 mg p-nitrophenyl phosphate per ml of substrate buffer (Appendix 4). Add 200 µl to each well. Incubate in the dark at ambient temperature and read absorbance at 40 nm at regular intervals within 90 minutes.
Interpretation of ELISA test results: U.K.
The ELISA test is negative if the average optical density (OD) reading from duplicate sample wells is < 2x OD of that in the negative sample extract control well, providing the OD for the positive controls are all above 1,0 (after 90 minutes incubation with the substrate) and are greater than twice the OD obtained for negative sample extracts.
The ELISA test is positive if the average OD readings from duplicate sample wells is > 2x OD in the negative sample extract well provided that OD readings in all negative control wells are < 2x those in the positive control wells.
Negative ELISA readings in positive control wells indicate that the test has not been performed correctly or that it has been inhibited. Positive ELISA readings in negative control wells indicate that cross-contamination or non-specific antibody binding has occurred.
9. Bioassay test U.K.
Note: Preliminary testing with this method should permit reproducible detection of 10 3 to 10 4 colony-forming units of R. solanacearum per ml added to sample extracts that previously tested negative (preparation see Appendix 3). U.K.
Highest sensitivity of detection can be expected when using freshly prepared sample extract and optimal growth conditions. However, the method can be successfully applied to extracts that have been stored under glycerol at -68 to -86 °C.
The following protocol is based upon Janse (1988):
9.1. Use 10 test plants of a susceptible tomato cultivar (e.g. Moneymaker or cultivar with equivalent susceptibility as determined by the testing laboratory) at the third true leaf stage for each sample. For cultural details, see Appendix 8. Alternatively, use eggplants (e.g. cultivar Black Beauty or cultivars with equivalent susceptibility), use only plants at leaf stage two to three up to full expansion of the third true leaf. Symptoms have been show to be less severe and to develop more slowly in eggplant. Where possible, it is therefore recommended to use tomato seedlings. U.K.
9.2.
Distribute 100 µl of sample extract between the test plants. U.K.
9.2.1. Syringe inoculation U.K.
Inoculate the plant stems just above the cotyledons using a syringe fitted with a hypodermic needle (not less than 23G). Distribute the sample between the test plants.
9.2.2. Slit inoculation U.K.
Holding the plant between two fingers, pipette a drop (approximately 5 - 10 µl) of the suspended pellet on the stem between the cotyledons and the first leaf.
Using a sterile scalpel, make a diagonal slit, about 1.0 cm long and approximately 2/3 of the stem thickness deep, starting the cut from the pellet drop.
Seal the cut with sterile vaseline from a syringe.
9.3. Inoculate by the same technique, five seedlings with an aqueous suspension of 10 5 to 10 6 cells per ml prepared from a 48 hr culture of a virulent biovar 2 strain of R. solanacearum as a positive control and with pellet buffer (Appendix 4) as negative control. Separate positive and negative control plants from the other plants to avoid cross-contamination. U.K.
9.4. Grow the test plants in quarantine facilities for up to four weeks at 25 to 30 °C and high relative humidity with appropriate watering to prevent waterlogging or wilting through water deficiency. To avoid contamination incubate positive control and negative control plants on clearly separated benches in a glasshouse or growth chamber or, in case space is limited, ensure strict separation between treatments. If plants for different samples must be incubated close together, separate them with appropriate screens. When fertilising, watering, inspecting and any other manipulations take great care to avoid cross-contamination. It is essential to keep glasshouses and growth chambers free of all insect pests since they may transmit the bacterium from sample to sample. U.K.
Observe for symptoms of wilting, epinasty, chlorosis and/or stunting.
9.5. Isolate from infected plants (Section II.3.) and identify purified cultures of presumptive R. solanacearum (Section VI.B.). U.K.
9.6. If no symptoms are observed after three weeks perform IF/PCR/Isolation on a composite sample of 1 cm stem sections of each test plant taken above the inoculation site. If the test is positive perform dilution plating (section 4.1). U.K.
9.7. Identify any purified cultures of presumptive R. solanacearum (Section VI.B.). U.K.
Interpretation of the bioassay test results U.K.
Valid Bioassay test results are obtained when plants of the positive control show typical symptoms, the bacteria can be reisolated from these plants and no symptoms are found on the negative controls.
The bioassay test is negative if test plants are not infected by R. solanacearum , and provided that R. solanacearum is detected in positive controls.
The bioassay test is positive if the test plants are infected by R. solanacearum .
B. IDENTIFICATION TESTS U.K.
Identify pure cultures of presumptive R. solanacearum isolates using at least two of the following tests based on different biological principles. U.K.
Include known reference strains where appropriate for each test performed (see Appendix 3).
1. Nutritional and enzymatic identification tests U.K.
Determine the following phenotypic properties, which are universally present or absent in R. solanacearum , according to the methods of Lelliott and Stead (1987), Klement et al. (1990), Schaad (2001).
| Test | Expected result |
|---|---|
| Fluorescent pigment production | – |
| Poly-ß-hydroxybutyrate inclusions | + |
| Oxidation/fermentation (O/F) test | O+/F– |
| Catalase activity | + |
| Kovac’s oxidase test | + |
| Reduction of nitrate | + |
| Utilisation of citrate | + |
| Growth at 40 °C | – |
| Growth in 1 % NaCl | + |
| Growth in 2 % NaCl | – |
| Arginine dihydrolase activity | – |
| Gelatine liquefaction | – |
| Starch hydrolysis | – |
| Aesculin hydrolysis | – |
| Levan production | – |
2. IF test U.K.
2.1. Prepare a suspension of approximately 10 6 cells per ml in IF buffer (Appendix 4). U.K.
2.2. Prepare a twofold dilution series of an appropriate antiserum (see website http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main). U.K.
2.3. Apply the IF procedure (Section VI.A.5.). U.K.
2.4. A positive IF test is achieved if the IF titre of the culture is equivalent to that of the positive control. U.K.
3. ELISA test U.K.
Note: If performing only 2 identification tests, do not use another serological test in addition to this method. U.K.
3.1. Prepare a suspension of approximately 10 8 cells per ml in 1X PBS (Appendix 4). U.K.
3.2. Perform an appropriate ELISA procedure with a specific monoclonal antibody to R. solanacearum . U.K.
3.3. A positive ELISA test is achieved if the ELISA reading obtained from the culture is at least half that obtained for the positive control. U.K.
4. PCR tests U.K.
4.1. Prepare a suspension of approximately 10 6 cells per ml in molecular grade sterile water. U.K.
4.2. Heat 100 µl of the cell suspension in closed tubes in a heating block or boiling waterbath at 100 °C for four minutes. The samples may then be stored at -16 to -24 °C until required. U.K.
4.3. Apply appropriate PCR procedures to amplify R. solanacearum -specific amplicons (e.g. Seal et al. (1993); Pastrik and Maiss (2000); Pastrik et al. (2002); Boudazin et al. (1999); Opina et al. (1997), Weller et al. (1999). U.K.
4.4. A positive identification of R. solanacearum is achieved if the PCR amplicons are the same size and have the same restriction fragment length polymorphisms as for the positive control strain. U.K.
5. FISH test U.K.
5.1. Prepare a suspension of approximately 10 6 cells per ml in UPW. U.K.
5.2. Apply the FISH procedure (Section VI.A.7.) with at least 2 R. solanacearum -specific oligo-probes (Appendix 7). U.K.
5.3. A positive FISH test is achieved if the same reactions are achieved from the culture and the positive control. U.K.
6. Fatty acid profiling (FAP) U.K.
6.1. Grow the culture on trypticase soy agar (Oxoid) for 48 hours at 28 °C. U.K.
6.2. Apply an appropriate FAP procedure (Janse, 1991; Stead, 1992). U.K.
6.3. A positive FAP test is achieved if the profile of the presumptive culture is identical to that of the positive control. The presence of characteristic fatty acids are 14:0 3OH, 16:0 2OH, 16:1 2OH and 18:1 2OH and absence of 16:0 3OH is highly indicative of a Ralstonia sp. U.K.
7. Strain characterisation methods U.K.
Strain characterisation using one of the following methods is recommended for each new case of isolation of R. solanacearum . U.K.
Include known reference strains where appropriate for each test performed (see Appendix 3).
7.1. Biovar determination U.K.
R. solanacearum is separated into biovars on the basis of the ability to utilise and/or oxidise three disaccharides and three hexose alcohols (Hayward, 1964 and Hayward et al. , 1990). Growth media for the biovar test is described in Appendix 2. The test can be successfully performed by stab inoculating the media with pure cultures of R. solanacearum isolates and incubating at 28 °C. If the media are dispensed into sterile 96 well cell culture plates (200 µl per well) colour change from olive green to yellow can be observed within 72 hours, indicating a positive test result.
| Biovar | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Utilisation of: | |||||
| Maltose | – | + | + | – | + |
| Lactose | – | + | + | – | + |
| D (+) Cellobiose | – | + | + | – | + |
| Mannitol | – | – | + | + | + |
| Sorbitol | – | – | + | + | – |
| Dulcitol | – | – | + | + | – |
Additional tests differentiate biovar 2 sub-phenotypes
| a See Lelliott and Stead (1987) | |||
| Biovar 2A (Worldwide distribution) | Biovar 2A (Found in Chile and Colombia) | Biovar 2T (Found in tropical areas) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utilisation of trehalose | – | + | + |
| Utilisation of meso -inositol | + | – | + |
| Utilisation of D ribose | – | – | + |
| Pectolytic activity a | low | low | high |
7.2. Genomic fingerprinting U.K.
Molecular differentiation of strains in the R. solanacearum complex can be achieved using several techniques, including: U.K.
7.2.1. Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis (Cook et al. , 1989). U.K.
7.2.2. Repetitive sequence PCR using REP, BOX and ERIC primers (Louws et al. , 1995; Smith et al. , 1995). U.K.
7.2.3. Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) analysis (Van der Wolf et al. , 1998). U.K.
7.3. PCR methods U.K.
Specific PCR primers (Pastrik et al , 2002; see Appendix 6) can be used to differentiate strains belonging to division 1 (biovars 3, 4 and 5) and division 2 (biovars 1, 2A and 2T) of R. solanacearum , as originally defined by RFLP analysis (Cook et al. , 1989) and 16S rDNA sequencing (Taghavi et al. , 1996).
C. CONFIRMATION TEST U.K.
The pathogenicity test must be performed as final confirmation of a diagnosis of R. solanacearum and for assessment of virulence of cultures identified as R. solanacearum .
Prepare an inoculum of approximately 10 6 cells per ml from a 24 to 48 hour culture of the isolate to be tested and an appropriate positive control strain of R. solanacearum (e.g. NCPPB 4156 = PD 2762 = CFBP 3857; see Appendix 3).
Inoculate 5 to 10 susceptible tomato or eggplant seedlings at the third true leaf stage (see Section VI.A.9).
Incubate for up to two weeks at 25 to 28 °C and high relative humidity with appropriate watering to avoid waterlogging or drought stress. With pure cultures typical wilting should be obtained within 14 days. If after this period symptoms are not present, the culture cannot be confirmed as being a pathogenic form of R. solanacearum .
Observe for symptoms of wilting and/or epinasty, chlorosis and stunting.
Isolate from symptomatic plants by removing a section of stem about 2 cm above the inoculation point. Comminute and suspend in a small volume of sterile distilled water or 50 mM phosphate buffer (Appendix 4). Isolate from the suspension by dilution spreading or streaking on a suitable medium, preferably onto a selective medium (Appendix 2), incubate for 48 to 72 hours at 28 °C and observe the formation of colonies typical of R. solanacearum .
Appendix 1 Laboratories involved in optimisation and validation of protocols
| a Contact scientists: see web site http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main . | ||
| Laboratory a | Location | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Agentur für Gesundheit und Ernährungssicherheit | Vienna and Linz | Austria |
| Departement Gewasbescherming | Merelbeke | Belgium |
| Plantedirektoratet | Lyngby | Denmark |
| Central Science Laboratory | York | England |
| Scottish Agricultural Science Agency | Edinburgh | Scotland |
| Laboratoire National de la Protection des Végétaux, Unité de Bactériologie | Angers | France |
| Laboratoire National de la Protection des Végétaux, Station de Quarantaine de la Pomme de Terre | Le Rheu | France |
| Biologische Bundesanstalt | Kleinmachnow | Germany |
| Pflanzenschutzamt Hannover | Hannover | Germany |
| State Laboratory | Dublin | Ireland |
| Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Agroambientali | Bologna | Italy |
| Regione Veneto Unità Periferica per i Servizi Fitosanitari | Verona | Italy |
| Nederlandse Algemene Keuringsdienst | Emmeloord | Netherlands |
| Plantenziektenkundige Dienst | Wageningen | Netherlands |
| Direcção-Geral de Protecção das Culturas | Lisbon | Portugal |
| Centro Diagnostico de Aldearrubia | Salamanca | Spain |
| Instituto Valenciano de Investigaciones Agrarias | Valencia | Spain |
| Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences | Uppsala | Sweden |
Appendix 2 Media for isolation and culture of R. solanacearum
(a) General growth media U.K.
Nutrient Agar (NA) U.K.
| Nutrient Agar (Difco) | 23,0 g |
| Distilled water | 1,0 L |
Dissolve ingredients and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 min.
Yeast Peptone Glucose Agar (YPGA) U.K.
| Yeast extract (Difco) | 5,0 g |
| Bacto-Peptone (Difco) | 5,0 g |
| D(+) Glucose (monohydrate) | 10,0 g |
| Bacto-Agar (Difco) | 15,0 g |
| Distilled water | 1,0 L |
Dissolve ingredients and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes.
Sucrose Peptone Agar (SPA) U.K.
| Sucrose | 20,0 g |
| Bacto-Peptone (Difco) | 5,0 g |
| K 2 HPO 4 | 0,5 g |
| MgSO 4 .7H 2 O | 0,25 g |
| Bacto-Agar (Difco) | 15,0 g |
| Distilled water | 1,0 l |
| pH 7,2 – 7,4 |
Dissolve ingredients and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes.
Kelman’s Tetrazolium Medium U.K.
| Casamino acids (Difco) | 1,0 g |
| Bacto-Peptone (Difco) | 10,0 g |
| Dextrose | 5,0 g |
| Bacto-Agar (Difco) | 15,0 g |
| Distilled water | 1,0 l |
Dissolve ingredients and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes.
Cool to 50 °C and add a filter-sterilised solution of 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (Sigma) to obtain a final concentration of 50 mg per l.
(b) Validated selective growth media U.K.
SMSA medium (Englebrecht, 1994 as modified by Elphinstone et al. , 1996) U.K.
| Basal medium | |
| Casamino acids (Difco) | 1,0 g |
| Bacto-Peptone (Difco) | 10,0 g |
| Glycerol | 5,0 ml |
| Bacto-Agar (Difco); see Note 2 . | 15,0 g |
| Distilled water | 1,0 L |
Dissolve ingredients and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes.
Cool to 50 °C and add filter-sterilised aqueous stock solutions of the following ingredients to obtain the specified final concentrations:
| Crystal Violet (Sigma) | 5 mg per l |
| Polymixin-B-Sulphate (Sigma P-1004) | 600 000 U (approximately 100 mg) per l |
| Bacitracin (Sigma B-0125) | 1 250 U (approximately 25 mg) per l |
| Chloramphenicol (Sigma C-3175) | 5 mg per l |
| Penicillin-G (Sigma P-3032) | 825 U (approximately 0,5 mg) per l |
| 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (Sigma) | 50 mg per l |
Note: U.K.
1. Use of reagents other than those specified above may affect growth of R. solanacearum . U.K.
2. Oxoid Agar #1 can be used in place of Bacto-Agar (Difco). In this case growth of R. solanacearum will be slower, although growth of competing saprophytes may also be reduced. Typical colonies of R. solanacearum may take 1 to 2 days longer to form and the red colouration may be lighter and more diffuse than on Bacto-Agar. U.K.
3. Increasing bacitracin concentration to 2 500 U per l may reduce populations of competing bacteria without affecting growth of Ralstonia solanacearum . U.K.
Store media and stock solutions of antibiotics at 4 °C in the dark and use within one month.
Plates should be free from surface condensation before use.
Avoid excess drying of plates.
Quality control should be performed after preparation of each new batch of medium by plating a suspension of a reference culture of R. solanacearum (see Appendix 3) and observing formation of typical colonies after incubation at 28 °C for two to five days.
(c) Validated enrichment media U.K.
SMSA Broth (Elphinstone et al. , 1996) U.K.
Prepare as for SMSA selective agar medium but omit Bacto-Agar and 2,3,5-tetrazolium chloride.
Modified Wilbrink broth (Caruso et al. , 2002) U.K.
| Sucrose | 10 g |
| Proteose peptone | 5 g |
| K 2 HPO 4 | 0,5 g |
| MgSO 4 | 0,25 g |
| NaNO 3 | 0,25 g |
| Distilled water | 1 l |
Sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes and cool to 50 °C
Add antibiotic stock solutions as for SMSA broth.
Appendix 3
A. Commercially available standardised control material U.K.
(a) Bacterial isolates U.K.
The following bacterial isolates are recommended for use as standard reference material either as positive controls (Table 1) or during optimisation of tests to avoid cross-reactions (Table 2). All strains are commercially available from:
National Collection of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria (NCPPB), Central Science Laboratory, York, UK
Culture Collection of the Plant Protection Service (PD), Wageningen, the Netherlands.
Collection Française de Bactéries Phytopathogènes (CFBP), INRA Station Phytobactériologie, Angers, France.
Table 1
SMT reference panel of isolates of R. solanacearum
| a Use as standard reference strain of R. solanacearum biovar 2 (race 3). | ||||
| NCPPB code | SMT # | Other codes | Country of origin | Biovar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCPPB 4153 | 6 | CFBP 4582, Pr 3020, EURS11 | Egypt | 2 |
| NCPPB 4154 | 10 | CFBP 4585, 550, EURS21 | Turkey | 2 |
| NCPPB 3857 | 12 | CFBP 4587, Pr 1140, EURS26 | England | 2 |
| NCPPB 1584 | 23 | CFBP 4598, EURS49 | Cyprus | 2 |
| NCPPB 2505 | 24 | CFBP 4599, EURS50 | Sweden | 2 |
| NCPPB 4155 | 26 | CFBP 4601, 502, EURS55 | Belgium | 2 |
| NCPPB 4156 a | 71 a | PD 2762, CFBP 3857 | Netherlands | 2 |
| NCPPB 4157 | 66 | LNPV 15.59 | France | 2 |
| NCPPB 4158 | 39 | CFBP 4608, Port 448, EURS80 | Portugal | 2 |
| NCPPB 4160 | 69 | IVIA-1632-2 | Spain | 2 |
| NCPPB 4161 | 76 | B3B | Germany | 2 |
| NCPPB 325 | 41 | CFBP 2047, KEL60-1, R842 | USA | 1 |
| NCPPB 3967 | 42 | CFBP 4610, R285, GONg7 | Costa Rica | 1 |
| NCPPB 4028 | 43 | CFBP 4611, R303/571, CIP310, SEQ205 | Colombia | 2 |
| NCPPB 3985 | 44 | CFBP 4612, R578, CIP312 | Peru | 2T |
| NCPPB 3989 | 45 | CFBP 4613, R568, CIP226 | Brazil | 2T |
| NCPPB 3996 | 46 | CFBP 3928, R276/355, CIP72, SEQ225 | Peru | 3 |
| NCPPB 3997 | 47 | CFBP 4614, R280/363, CIP49, HAY0131a | Australia | 3 |
| NCPPB 4029 | 48 | CFBP 4615, R297/349, CIP121, CMIb2861 | Sri Lanka | 4 |
| NCPPB 4005 | 49 | CFBP 4616, R470 | Philippines | 4 |
| NCPPB 4011 | 50 | CFBP 4617, R288, HEmps2 | China | 5 |
Note: Authenticity of the above strains can be guaranteed only if obtained from an authentic culture collection. U.K.
Table 2:
SMT reference panel of serologically- or genetically-related bacteria for use in optimisation of detection tests
| a Potential cross-reacting strain in serological tests (IF and/or ELISA) with polyclonal antisera. | |||
| b Strain from which PCR product can be amplified in some laboratories of a similar size to that expected using specific primers OLI-1 and Y-2 (see Appendix 6). | |||
| c Likely to cross-react in most tests but known to occur only on banana in Indonesia. | |||
| NCPPB code | SMT # | Other code | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCPPB 4162 | 51 | CFBP 1954 | Bacillus polymyxa a |
| NCPPB 4163 | 52 | CFBP 1538 | Pseudomonas marginalis pv. marginalis a |
| NCPPB 4164 | — | CFBP 2227 | Burkholderia cepacia b |
| NCPPB 4165 | — | CFBP 2459 | Ralstonia pickettii b |
| NCPPB 4166 | 58 | CFBP 3567 CSL Pr1150 | Ralstonia pickettii a |
| NCPPB 4167 | 60 | CFBP 4618 PD 2778 | Ralstonia sp. a |
| NCPPB 1127 | 53 | CFBP 3575 | Burkholderia andropogonis a |
| NCPPB 353 | 54 | CFBP 3572 | Burkholderia caryophylli a |
| NCPPB 945 | 55 | CFBP 3569 | Burkholderia cepacia a |
| NCPPB 3708 | 56 | CFBP 3574 | Burkholderia glumae a |
| NCPPB 3590 | 57 | CFBP 3573 | Burkholderia plantarii a |
| NCPPB 3726 | 59 | CFBP 3568 | Banana Blood Disease Bacterium a b c |
| NCPPB 4168 | 61 | CFBP 4619 IPO S339 | Enterobacter sp. a |
| NCPPB 4169 | 62 | IPO 1695 | Enterobacter sp. a |
| NCPPB 4170 | 63 | CFBP 4621 IPO S306 | Ochrobactrum anthropi a b |
| NCPPB 4171 | 64 | CFBP 4622 IPO 1693 | Curtobacterium sp. a b |
| NCPPB 4172 | 65 | IPO 1696a | Pseudomonas sp. a |
| NCPPB 4173 | — | PD 2318 | Aureobacterium sp. b |
| NCPPB 4174 | 81 | IVIA 1844.06 | Flavobacterium sp. a b |
(b) Commercially available standardised control material U.K.
The following standard control material is available from the NCPPB culture collection.
Freeze dried pellet of potato extract from 200 healthy potato tubers as negative control for all tests.
Freeze dried pellet of potato extract from 200 healthy potato tubers containing 10 3 to 10 4 and 10 4 to 10 6 cells R. solanacearum biovar 2 (strain NCPPB 4156 = PD 2762 = CFBP 3857) as positive controls for serological and PCR tests. Since cell viability is affected during freeze-drying, these are not suitable as standard controls for isolation or bioassay tests.
Formalin-fixed suspensions of R. solanacearum biovar 2 (strain NCPPB 4156 = PD 2762 = CFBP 3857) at 10 6 cells per ml as positive controls for serological tests.
B. Preparation of positive and negative controls for the core screening tests PCR/IF and FISH U.K.
Produce a 48 hour culture of a virulent strain of R. solanacearum race3/biovar2 (e.g. strain NCPPB 4156 = PD 2762 = CFBP 3857) on basal SMSA medium and suspend in 10 mM phosphate buffer to obtain a cell density of approximately 2 × 10 8 cfu per ml. This is usually obtained by a faintly turbid suspension equivalent to an optical density of 0,15 at 600 nm.
Remove the heel end cores of 200 tubers taken from a white skin variety production known to be free from R. solanacearum .
Process the heel ends as usual and resuspend the pellet in 10 ml.
Prepare 10 sterile 1,5 ml microvials with 900 µl of the resuspended pellet.
Transfer 100 µl of the suspension of R. solanacearum to the first microvial. Vortex.
Establish decimal levels of contamination by further diluting in the next five microvials.
The six contaminated microvials will be used as positive controls. The four non-contaminated microvials will be used as negative controls. Label the microvials accordingly.
Prepare aliquots of 100 µl in sterile 1,5 ml microvials thus obtaining nine replicas of each control sample. Store at -16 to -24 °C until use.
The presence and quantification of R. solanacearum in the control samples should be first confirmed by IF.
For the PCR test perform DNA extraction from positive and negative control samples with each series of test samples.
For IF and FISH tests perform assays on positive and negative control samples with each series of test samples.
For IF, FISH and PCR assays R. solanacearum must be detected in at least the 10 6 and 10 4 cells/ml of the positive controls and not in any of the negative controls.
Appendix 4 Buffers for test procedures
General: Unopened sterilised buffers can be stored for up to one year U.K.
1. Buffers for extraction procedure U.K.
1.1. Extraction buffer (50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7,0) U.K.
This buffer is used for extraction of the bacterium from plant tissues by homogenisation or shaking.
| Na 2 HPO 4 (anhydrous) | 4,26 g |
| KH 2 PO 4 | 2,72 g |
| Distilled water | 1.00 l |
Dissolve ingredients, check pH and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 min.
Additional components may be useful as follows:
1.2. Pellet buffer (10 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7,2) U.K.
This buffer is used for resuspension and dilution of potato tuber heel-end core extracts following concentration to a pellet by centrifugation.
| Na 2 HPO 4 .12H 2 O | 2,7 g |
| NaH 2 PO 4 .2H 2 O | 0,4 g |
| Distilled water | 1,0 l |
Dissolve ingredients, check pH and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes.
2. Buffers for the IF test U.K.
2.1. IF-Buffer (10 mM phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.2) U.K.
This buffer is used for dilution of antibodies
| Na 2 HPO 4 .12H 2 O | 2,7 g |
| NaH 2 PO 4 .2H 2 O | 0,4 g |
| NaCL | 8,0 g |
| Distilled water | 1,0 l |
Dissolve ingredients, check pH and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes.
2.2. IF-buffer-Tween U.K.
This buffer is used to wash slides.
Add 0,1 % Tween 20 to the IF buffer.
2.3. Phosphate buffered glycerol, pH 7,6 U.K.
This buffer is used as a mountant fluid on the windows of IF slides to enhance fluorescence.
| Na 2 HPO 4 .12H 2 O | 3,2 g |
| NaH 2 PO 4 .2H 2 O | 0,15 g |
| Glycerol | 50 ml |
| Distilled water | 100 ml |
Anti-fading mountant solutions are commercially available e.g. Vectashield ® (Vector Laboratories) or Citifluor ® (Leica).
3. Buffers for the Indirect ELISA test U.K.
3.1. Double strength coating buffer, pH 9,6. U.K.
| Na 2 CO 3 | 6,36 g |
| NaHCO 3 | 11,72 g |
| Distilled water | 1,00 l |
Dissolve ingredients, check pH and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes.
Sodium sulphite (0.2 %) may be added as antioxidant if required to prevent build up of oxidised aromatic compounds.
3.2. 10X Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7,4 U.K.
| NaCL | 80,0 g |
| KH 2 PO 4 | 2,0 g |
| Na 2 HPO 4 .12H 2 O | 29,0 g |
| KCl | 2,0 g |
| Distilled water | 1,0 L |
3.3. PBS-Tween U.K.
| 10X PBS | 100 ml |
| 10 % Tween 20 | 5 ml |
| Distilled water | 895 ml |
3.4. Blocking (antibody) buffer (must be freshly prepared). U.K.
| 10X PBS | 10,0 ml |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone-44000 (PVP-44) | 2,0 g |
| 10 % Tween 20 | 0,5 ml |
| Milk powder | 0,5 g |
| Distilled water | make up to 100 ml |
3.5. Alkaline phosphatase substrate solution, pH 9,8 U.K.
| Diethanolamine | 97 ml |
| Distilled water | 800 ml |
Mix and adjust to pH 9,8 with concentrated HCl.
Make up to 1 L with distilled water.
Add 0,2 g MgCl 2 .
Dissolve 2 phosphatase substrate 5 mg tablets (Sigma) per 15 ml of solution.
4. Buffers for DASI ELISA test U.K.
4.1. Coating buffer, pH 9,6 U.K.
| Na 2 CO 3 | 1,59 g |
| NaHCO 3 | 2,93 g |
| Distilled water | 1 000 ml |
Dissolve ingredients and check pH 9,6
4.2. 10X Phosphate saline buffer(PBS) pH 7,2 to 7,4 U.K.
| NaCl | 80,0 g |
| NaH 2 PO 4 .2 H 2 O | 4,0 g |
| Na 2 HPO 4 .12H 2 O | 27,0 g |
| Distilled water | 1 000 ml |
4.3. PBS-Tween U.K.
| 10X PBS | 50 ml |
| 10 % Tween 20 | 5 ml |
| Distilled water | 950 ml |
4.4. Substrate buffer, pH 9,8 U.K.
| Diethanolamine | 100 ml |
| Distilled water | 900 ml |
Mix and adjust to pH 9,8 with concentrated HCl.
Appendix 5 Determination of contamination level in IF and FISH tests
Count the mean number of typical fluorescent cells per field of view (c).
Calculate the number of typical fluorescent cells per microscope slide window (C).
C = c × S/s
| where | S | = | surface area of window of multispot slide |
| and | s | = | surface area of objective field |
| s = πi 2 /4G 2 K 2 | where | i | = | field coefficient (varies from 8 to 24 depending upon ocular type) |
| K | = | tube coefficient (1 or 1,25) | ||
| G | = | magnification of objective (100 ×, 40 × etc.). |
Calculate the number of typical fluorescent cells per ml of re-suspended pellet (N).
N = C × 1 000 /y × F
| where | y | = | volume of re-suspended pellet on each window |
| and | F | = | dilution factor of re-suspended pellet. |
Appendix 6 Validated PCR protocols and reagents
NB: Preliminary testing should permit reproducible detection of 10 3 to 10 4 cells of R. solanacearum per ml of sample extract. U.K.
Preliminary testing should also show no false positive results with a panel of selected bacterial strains (see Appendix 3).
1. PCR protocol of Seal et al. (1993) U.K.
1.1. Oligonucleotide primers U.K.
| Forward primer OLI-1 | 5′-GGG GGT AGC TTG CTA CCT GCC-3′ |
| Reverse primer Y-2 | 5′-CCC ACT GCT GCC TCC CGT AGG AGT-3′ |
Expected amplicon size from R. solanacearum template DNA = 288 bp
1.2. PCR reaction mix U.K.
| a Method was validated using Taq polymerase from Perkin Elmer (AmpliTaq) and Gibco BRL. | ||
| Reagent | Quantity per reaction | Final concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Sterile UPW | 17,65 µl | |
| 10X PCR buffer a (15 mM MgCl 2 ) | 2,5 µl | 1X (1,5 mM MgCl 2 ) |
| dNTP mix (20 mM) | 0,25 µl | 0,2 mM |
| Primer OLI-1 (20 µM) | 1,25 µl | 1µM |
| Primer Y-2 (20 µM) | 1,25 µl | 1µM |
| Taq polymerase (5U/µl) a | 0,1 µl | 0,5 U |
| Sample volume | 2,0 µl | |
| Total volume | 25 µl | |
1.3. PCR reaction conditions U.K.
Run the following programme:
| 1 cycle of: | (i) | 2 minutes at 96 °C (denaturation of template DNA) |
| 35 cycles of: | (ii) | 20 seconds at 94 °C (denaturation of template DNA) |
| (iii) | 20 seconds at 68 °C (annealing of primers) | |
| (iv) | 30 seconds at 72 °C (extension of copy) | |
| 1 cycle of: | (v) | 10 minutes at 72 °C (final extension) |
| (vi) | hold at 4 °C. |
NB: This programme was optimised for use with a Perkin Elmer 9600 thermal cycler. Modification of the duration steps of cycles (ii), (iii) and (iv) may be required for use with other models. U.K.
1.4. Restriction enzyme analysis of amplicon. U.K.
PCR products amplified from R. solanacearum DNA produce a distinctive restriction fragment length polymorphism with enzyme Ava II after incubation at 37 °C.
2. PCR protocol of Pastrik and Maiss (2000) U.K.
2.1. Oligonucleotide primers U.K.
| Forward primer Ps-1 | 5′- agt cga acg gca gcg ggg g -3′ |
| Reverse primer Ps-2 | 5′- ggg gat ttc aca tcg gtc ttg ca -3′ |
Expected amplicon size from R. solanacearum template DNA = 553 bp.
2.2. PCR reaction mix U.K.
| a Methods were validated using Taq polymerase from Perkin Elmer (AmpliTaq) and Gibco BRL. | ||
| N.B. Originally optimised for MJ Research PTC 200 thermocycler with Gibco Taq Polymerase. Perkin Elmer AmpliTaq and buffer can also be used at the same concentrations. | ||
| Reagent | Quantity per reaction | Final concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Sterile UPW | 16,025 µl | |
| 10X PCR buffer a | 2,5 µl | 1X (1,5 mM MgCl 2 ) |
| BSA (fraction V) (10 %) | 0,25 µl | 0,1 % |
| d-nTP mix (20 mM) | 0,125 µl | 0,1 mM |
| Primer Ps-1 (10 µM) | 0,5 µl | 0,2 µM |
| Primer Ps-2 (10 µM) | 0,5 µl | 0,2 µM |
| Taq polymerase (5U/µl) a | 0,1 µl | 0,5 U |
| Sample volume | 5,0 µl | |
| Total volume: | 25,0 µl | |
2.3. PCR reaction conditions U.K.
Run the following programme:
| 1 cycle of: | (i) | 5 minutes at 95 °C (denaturation of template DNA) |
| 35 cycles of: | (ii) | 30 seconds at 95 °C (denaturation of template DNA) |
| (iii) | 30 seconds at 68 °C (annealing of primers) | |
| (iv) | 45 seconds at 72 °C (extension of copy) | |
| 1 cycle of: | (v) | 5 minutes at 72 °C (final extension) |
| (vi) | hold at 4 °C. |
NB: This programme is optimised for use with an MJ Research PTC 200 thermal cycler. Modification of the duration steps of cycles (ii), (iii) and (iv) may be required for use with other models. U.K.
2.4. Restriction enzyme analysis of amplicon. U.K.
PCR products amplified from R. solanacearum DNA produce a distinctive restriction fragment length polymorphism with enzyme Taq I after incubation at 65 °C for 30 minutes. The restriction fragments obtained from R. solanacearum -specific fragment are 457 bp and 96 bp in size.
3. Multiplex PCR protocol with internal PCR control (Pastrik et al. , 2002) U.K.
3.1. Oligonucleotide primers U.K.
| Forward primer RS-1-F | 5′- ACT AAC GAA GCA GAG ATG CAT TA -3′ |
| Reverse primer RS-1-R | 5′- CCC AGT CAC GGC AGA GAC T -3′ |
| Forward primer NS-5-F | 5′- AAC TTA AAG GAA TTG ACG GAA G -3′ |
| Reverse primer NS-6-R | 5′- GCA TCA CAG ACC TGT TAT TGC CTC -3′ |
Expected amplicon size from R. solanacearum template DNA = 718 bp (RS-primer set)
Expected amplicon size from the 18S rRNA internal PCR control = 310 bp (NS-primer set).
3.2. PCR reaction mix U.K.
| a Methods were validated using Taq polymerase from Perkin Elmer (AmpliTaq) and Gibco BRL. | ||
| b Concentration of primers NS-5-F and NS-6-R were optimised for potato heel end core extraction using the homogenisation method and DNA purification according to Pastrik (2000) (see Section VI.A.6.1.a.). Re-optimisation of reagent concentrations will be required if extraction by shaking or other DNA isolation methods are used. | ||
| Reagent | Quantity per reaction | Final concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Sterile UPW | 12,625 µl | |
| 10X PCR buffer a (15 mM MgCl 2 ) | 2,5 µl | 1X (1,5 mM MgCl 2 ) |
| BSA (fraction V) (10 %) | 0,25 µl | 0,1 % |
| d-nTP mix (20 mM) | 0,125 µl | 0,1 mM |
| Primer RS-1-F (10 µM) | 2,0 µl | 0,8 µM |
| Primer RS-1-R (10 µM) | 2,0 µl | 0,8 µM |
| Primer NS-5-F (10 µM) b | 0,15 µl | 0,06 µM |
| Primer NS-6-R (10 µM) b | 0,15 µl | 0,06 µM |
| Taq polymerase (5 U/µl) a | 0,2 µl | 1,0 U |
| Sample volume | 5,0 µl | |
| Total volume: | 25,0 µl | |
3.3. PCR reaction conditions U.K.
Run the following programme:
| 1 cycle of: | (i) | 5 minutes at 95 °C (denaturation of template DNA) |
| 35 cycles of: | (ii) | 30 seconds at 95 °C (denaturation of template DNA) |
| (iii) | 30 seconds at 58 °C (annealing of primers) | |
| (iv) | 45 seconds at 72 °C (extension of copy) | |
| 1 cycle of: | (v) | 5 minutes at 72 °C (final extension) |
| (vi) | hold at 4 °C. |
NB: This programme is optimised for use with an MJ Research PTC 200 thermal cycler. Modification of the duration steps of cycles (ii), (iii) and (iv) may be required for use with other models. U.K.
3.4. Restriction enzyme analysis of amplicon. U.K.
PCR products amplified from R. solanacearum DNA produce a distinctive restriction fragment length polymorphism with enzyme Bsm I or an Isoschizomere (e.g. Mva 1269 I) after incubation at 65 °C for 30 minutes.
4. R. solanacearum biovar-specific PCR protocol (Pastrik et al. , 2001) U.K.
4.1. Oligonucleotide primers U.K.
| Forward primer Rs-1-F | 5′- ACT AAC GAA GCA GAG ATG CAT TA -3′ |
| Reverse primer Rs-1-R | 5′- CCC AGT CAC GGC AGA GAC T -3′ |
| Reverse primer Rs-3-R | 5′- TTC ACG GCA AGA TCG CTC -3′ |
Expected amplicon size from R. solanacearum template DNA:
with Rs-1-F/Rs-1-R = 718 bp
with Rs-1-F/Rs-3-R = 716 bp.
4.2. PCR reaction mix U.K.
Biovar 1/2-specific PCR
| a Methods have been validated using Taq polymerase from Perkin Elmer (AmpliTaq) and Gibco BRL. | ||
| Reagent | Quantity per reaction | Final concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Sterile UPW | 12,925 µl | |
| 10X PCR Buffer a | 2,5 µl | 1X (1,5 mM MgCl 2 ) |
| BSA (fraction V) (10 %) | 0,25 µl | 0,1 % |
| d-NTP mix (20mM) | 0,125 µl | 0,1 mM |
| Primer Rs-1-F (10 µM) | 2 µl | 0,8 µM |
| Primer Rs-1-R (10 µM) | 2 µl | 0,8 µM |
| Taq polymerase (5U/µl) a | 0,2 µl | 1 U |
| Sample volume | 5,0 µl | |
| Total volume | 25,0 µl | |
Biovar 3/4/5-specific PCR
| a Methods have been validated using Taq polymerase from Perkin Elmer (AmpliTaq) and Gibco BRL. | ||
| Reagent | Quantity per reaction | Final concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Sterile UPW | 14,925 µl | |
| 10X PCR Buffer a | 2,5 µl | 1X (1,5 mM MgCl 2 ) |
| BSA (fraction V) (10 %) | 0,25 µl | 0,1 % |
| dNTP mix (20 mM) | 0,125 µl | 0,1 mM |
| Primer Rs-1-F (10 µM) | 1 µl | 0,4 µM |
| Primer Rs-3-R (10 µM) | 1 µl | 0,4 µM |
| Taq polymerase (5 U/µl) a | 0,2 µl | 1 U |
| Sample volume | 5,0 µl | |
| Total volume | 25,0 µl | |
4.3. PCR reaction conditions U.K.
Run the following programme for both biovar 1/2- and biovar 3/4/5-specific reactions:
| 1 cycle of: | (i) | 5 minutes at 95 °C (denaturation of template DNA) |
| 35 cycles of: | (ii) | 30 seconds at 95 °C (denaturation of template DNA) |
| (iii) | 30 seconds at 58 °C (annealing of primers) | |
| (iv) | 45 seconds at 72 °C (extension of copy) | |
| 1 cycle of: | (v) | 5 minutes at 72 °C (final extension) |
| (vi) | hold at 4 °C. |
NB: This programme was optimised for use with an MJ Research PTC 200 thermal cycler. Modification of the duration steps of cycles (ii), (iii) and (iv) may be required for use with other models. U.K.
4.4. Restriction enzyme analysis of amplicon. U.K.
PCR products amplified from R. solanacearum DNA using primers Rs-1-F and Rs-1-R produce a distinctive restriction fragment length polymorphism with enzyme Bsm I or an Isoschizomere (e.g. Mva 1269 I) after incubation at 65 °C for 30 minutes. PCR products amplified from R. solanacearum DNA using primers Rs-1-F and Rs-3-R have no restriction sites.
5. Preparation of the loading buffer U.K.
5.1. Bromphenol blue (10 %- stock solution ) U.K.
| Bromphenol blue | 5 g |
| Distilled water (bidest) | 50 ml |
5.2. Loading buffer U.K.
| Glycerol (86 %) | 3,5 ml |
| Bromphenol blue (5,1) | 300 µl |
| Distilled Water (bidest) | 6,2 ml |
6. 10X Tris Acetate EDTA (TAE) buffer, pH 8.0 U.K.
| Tris buffer | 48,40 g |
| Glacial acetic acid | 11,42 ml |
| EDTA (disodium salt) | 3,72 g |
| Distilled water | 1,00 L |
Dilute to 1X before use.
Also commercially available (e.g. Invitrogen or equivalent).
Appendix 7 Validated reagents for FISH test
1. Oligo-probes U.K.
R. solanacearum -specific probe OLI-1-CY3: 5′-ggc agg tag caa gct acc ccc-3′
Non-specific eubacterial probe EUB-338-FITC: 5′-gct gcc tcc cgt agg agt-3′
2. Fixative solution U.K.
(WARNING! THE FIXATIVE CONTAINS PARAFORMALDEHYDE WHICH IS TOXIC. WEAR GLOVES AND DO NOT INHALE. IT IS ADVISABLE TO WORK IN A FUME CUPBOARD.)
Heat 9 ml molecular grade water (e.g. Ultra pure water (UPW)) to about 60 °C and add 0,4 g paraformaldehyde. Paraformaldehyde dissolves after adding 5 drops of 1N NaOH and stirring with a magnetic stirrer.
Adjust pH to 7.0 by addition of 1ml of 0,1M phosphate buffer (PB; pH 7,0) and 5 drops of 1N HCl. Check pH with indicator strips and adjust if necessary with HCl or NaOH. (WARNING! DO NOT USE A PH METER IN SOLUTIONS WITH PARAFORMALEDHYDE.)
Filter the solution through a 0,22 µm membrane filter and keep dust-free at 4 °C until further use.
3. 3X Hybmix U.K.
| NaCl | 2,7 M |
| Tris-HCl | 60 mM (pH 7,4) |
| EDTA (filter sterilised and autoclaved) | 15 mM |
Dilute to 1X as required.
4. Hybridisation solution U.K.
| 1X Hybmix | |
| Sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) | 0,01 % |
| Formamide | 30 %, |
| probe EUB 338 | 5 ng/μl |
| probe OLI-1 or OLI-2 | 5 ng/μl |
Prepare quantities of hybridisation solution according to the calculations in Table 1. For each slide (containing 2 different samples in duplicate) 90 μl hybridisation solution is required. IMPORTANT: FORMAMIDE IS VERY TOXIC SO WEAR GLOVES AND TAKE NECESSARY SAFETY PRECAUTIONS!
Table 1
Suggested quantities for preparation of hybridisation mix
| NB: Store all solutions containing light sensitive oligo-probes in the dark at -20 °C. Protect from direct sunlight or electric light during use. | |||||
| Number of slides: | 1 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sterile UPW | 23,1 | 92,4 | 138,6 | 184,8 | 231,0 |
| 3x hybmix | 30,0 | 120,0 | 180,0 | 240,0 | 300,0 |
| 1 % SDS | 0,9 | 3,6 | 5,4 | 7,2 | 9,0 |
| Formamide | 27,0 | 108,0 | 162,0 | 216,0 | 270,0 |
| Probe EUB 338 (100 ng/μl) | 4,5 | 18,0 | 27,0 | 36,0 | 45,0 |
| Probe OLI-1 or OLI-2 (100 ng/μl) | 4,5 | 18,0 | 27,0 | 36,0 | 45,0 |
| Total volume (μl) | 90,0 | 360,0 | 540,0 | 720,0 | 900,0 |
5. 0,1M Phosphate buffer, pH 7,0 U.K.
| Na 2 HPO 4 | 8,52 g |
| KH 2 PO 4 | 5,44 g |
| Distilled water | 1,00 L |
Dissolve ingredients, check pH and sterilise by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 minutes.
Appendix 8 Eggplant and tomato culture
Sow seeds of tomato ( Lycopersicon esculentum ) or eggplant ( Solanum melongena ) in pasteurised seed compost. Transplant seedlings with fully expanded cotyledons (10 to 14 days) into pasteurised potting compost.
Eggplants or tomatoes should be grown in a glasshouse with the following environmental conditions prior to inoculation:
| Day length | 14 hours or natural day length if greater; |
| Temperature | day 21 to 24 °C, night14 to 18 °C. |
| Susceptible variety of tomato | ‘ “ Moneymaker ” ’ |
| Susceptible variety of eggplant | ‘ “ Black Beauty ” ’ |
| Suppliers | see website http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/sanco/Home/main |
REFERENCES U.K.
1. Amann, R.I., L. Krumholz and D.A. Stahl. 1990. Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic and environmental studies in microbiology. J. Bacteriol. 172: 762-770. U.K.
2. Anon. 1998. Council Directive 98/57/EC of 20 July 1998 on the control of Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith) Yabuuchi et al. Official Journal of the European Communities L235, 1-39. U.K.
3. Boudazin, G., A.C. Le Roux, K. Josi, P. Labarre and B. Jouan. 1999. Design of division specific primers of Ralstonia solanacearum and application to the identification of European isolates. European Journal of Plant Pathology 105; 373-380. U.K.
4. Caruso, P., Gorris, M.T., Cambra, M., Palomo, J.L., Collar, J and Lopez, M.M. 2002. Enrichment Double-Antibody Sandwich Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay That Uses a Specific Monoclonal Antibody for sensitive Detection of Ralstonia solanacearum in Asymptomatic Potato Tubers. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 3634-3638. U.K.
5. Cook, D., Barlow, E. and Sequeira, L. 1989. Genetic diversity of Pseudomonas solanacearum : detection of restriction fragment length polymorphisms with DNA probes that specify virulence and the hypersensitive response. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 1:113-121. U.K.
6. Elphinstone, J.G., Hennessy, J., Wilson, J.K. and Stead, D.E. 1996. Sensitivity of detection of Ralstonia solanacearum in potato tuber extracts. EPPO Bulletin 26; 663-678. U.K.
7. Englebrecht, M.C. (1994) Modification of a semi-selective medium for the isolation and quantification of Pseudomonas solanacearum . In: A.C. Hayward (ed.) Bacterial Wilt Newsletter 10, 3-5. Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research, Canberra, Australia. U.K.
8. Hayward, A.C. 1964. Characteristics of Pseudomonas solanacearum . Journal of Applied Bacteriology 27; 265-277. U.K.
9. Hayward, A.C., El-Nashaar, H.M., Nydegger, U. and De Lindo, L. 1990. Variation in nitrate metabolism in biovars of Pseudomonas solanacearum . Journal of Applied Bacteriology 69; 269-280. U.K.
10. Ito, S., Y. Ushijima, T. Fujii, S. Tanaka, M. Kameya-Iwaki, S. Yoshiwara and F. Kishi. 1998. Detection of viable cells of Ralstonia solanacearum in soil using a semi-selective medium and a PCR technique. J. Phytopathology 146; 379-384. U.K.
11. Janse, J.D. (1988) A detection method for Pseudomonas solanacearum in symptomless potato tubers and some data on its sensitivity and specificity. Bulletin OEPP/EPPO Bulletin 18, 343-351. U.K.
12. Janse, J.D. 1991. Infra- and intra-specific classification of Pseudomonas solanacaerum strains using whole cell fatty-acid analysis. Systematic and Applied Microbiology 14; 335-345. U.K.
13. Kelman, A. 1954. The relationship of pathogenicity of Pseudomonas solanacearum to colony appearance on a tetrazolium medium. Phytopathology 44; 693-695. U.K.
14. Klement Z.; Rudolph, K and D.C. Sands, 1990. Methods in Phytobacteriology. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, 568 pp. U.K.
15. Lelliott, R.A. and Stead, D.E. 1987. Methods for the diagnosis of bacterial diseases of plants. Blackwell scientific Publications Ltd., Oxford. 216 pp. U.K.
16. Lopez, M.M., Gorris, M.T., Llop, P., Cubero, J., Vicedo, B., Cambra, M., 1997. Selective enrichment improves selective isolation, serological and molecular detection of plant pathogenic bacteria. In: H.W. Dehne et al. , (eds). Klewer Academic Publishers. pp. 117-121. U.K.
17. Louws, F.J., Fulbright, D.W., Stephens, C.T. and De Bruijn, F.J., 1994. Specific genomic fingerprints of phytopathogenic Xanthomonas and Pseudomonas pathovars and strains generated with repetitive sequences and PCR. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 2286-2295. U.K.
18. Louws, F.J., Fulbright, D.W., Stephens, C.T. and De Bruijn, F.J. 1995. Differentiation of genomic structure by rep-PCR fingerprinting to rapidly classify Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria . Phytopathology 85; 528-536. U.K.
19. Opina, N., F. Tavner, G. Holloway, J.-F Wang, T.-H Li, R. Maghirang, M. Fegan, A.C. Hayward, V. Krishnapillai, W.F. Hong, B.W. Holloway, J.N. Timmis. 1997. A novel method for development of species and strain-specific DNA probes and PCR primers for identifying Burkholderia solanacearum (formerly Pseudomonas solanacearum ). As Pac. J. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 5; 19-33. U.K.
20. Pastrik, K.H. and Maiss, E. 2000. Detection of R. solanacearum in potato tubers by polymerase chain reaction. J. Phytopathology 148; 619-626. U.K.
21. Pastrik, K.H., Elphinstone, J.G. and Pukall, R. 2002. Sequence analysis and detection of Ralstonia solanacearum by multiplex PCR amplification of 16S-23S ribosomal intergenic spacer region with internal positive control. European Journal of Plant Pathology 108, 831-842. U.K.
22. Robinson-Smith, A., Jones, P., Elphinstone, J.G. and Forde, S.M.D. (1995) Production of antibodies to Pseudomonas solanacearum , the causative agent of bacterial wilt. Food and Agricultural Immunology 7, 67-79. U.K.
23. Schaad, W. 2001. Laboratory guide for identification of plant pathogenic bacteria. Schaad [Hrsg.]. - 3. ed.; St. Paul, Minnesota: 373 pp. U.K.
24. Seal, S.E., L.A. Jackson, J.P.W. Young, and M.J. Daniels. 1993. Detection of Pseudomonas solanacearum, Pseudomonas syzygii, Pseudomonas pickettii and Blood Disease Bacterium by partial 16S rRNA sequencing: construction of oligonucleotide primers for sensitive detection by polymerase chain reaction. J. Gen. Microbiol. 139: 1587-1594. U.K.
25. Smith, J.J., Offord, L.C., Holderness, M. and Saddler, G.S. 1995. Genetic diversity of Burkholderia solanacearum (synonym Pseudomonas solanacearum ) race 3 in Kenya. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61; 4262-4268. U.K.
26. Stead, D.E. 1992. Grouping of plant pathogenic and some other Pseudomonas spp. using cellular fatty-acid profiles. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 42; 281-295. U.K.
27. Taghavi, M., Hayward, A.C., Sly, L.I., Fegan, M. 1996. Analysiss of the phylogenetic relationships of strains of Burkholderia solanacearum, Pseudomonas syzygii , and the blood disease bacterium of banana based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 46; 10-15. U.K.
28. Van Der Wolf, J.M., Bonants, P.J.M., Smith, J.J., Hagenaar, M., Nijhuis, E., Van Beckhoven, J.R.C., Saddler, G.S., Trigalet, A., Feuillade, R. 1998. Genetic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum Race 3 in Western Europe as determined by AFLP, RC-PFGE and rep-PCR. In: Prior, P., Allen, C. and Elphinstone, J. (eds.) Bacterial wilt disease: Molecular and Ecological Aspects. Springer (Berlin) pp. 44-49. U.K.
29. Weller, S.A., Elphinstone, J.G., Smith, N., Stead, D.E. and Boonham, N. 1999. Detection of Ralstonia solanacearum strains using an automated and quantitative flourogenic 5’ nuclease TaqMan assay. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 66; 2853-2858. U.K.
30. Wullings, B.A., A.R. van Beuningen, J.D. Janse and A.D.L. Akkermans. 1998. Detection of R. solanacearum , which causes brown rot of potato, by fluorescent in situ hybridization with 23s rRNA-targeted probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 4546-4554.] U.K.
Options/Cymorth
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThis Annex only
You have chosen to open the Whole Directive
The Whole Directive you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
Y Rhestrau you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
Gweler y wybodaeth ychwanegol ochr yn ochr â’r cynnwys
Rhychwant ddaearyddol: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Mae’r llinell amser yma yn dangos y fersiynau gwahanol a gymerwyd o EUR-Lex yn ogystal ag unrhyw fersiynau dilynol a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig.
Cymerir dyddiadau fersiynau’r UE o ddyddiadau’r dogfennau ar EUR-Lex ac efallai na fyddant yn cyfateb â’r adeg pan ddaeth y newidiadau i rym ar gyfer y ddogfen.
Ar gyfer unrhyw fersiynau a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig, bydd y dyddiad yn cyd-fynd â’r dyddiad cynharaf y daeth y newid (e.e. ychwanegiad, diddymiad neu gyfnewidiad) a weithredwyd i rym. Am ragor o wybodaeth gweler ein canllaw i ddeddfwriaeth ddiwygiedig ar Ddeall Deddfwriaeth.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill