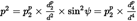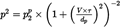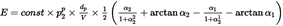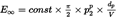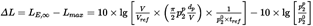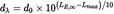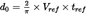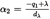- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser (31/12/2020)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Commission Directive (EU) 2015/996Dangos y teitl llawn
Commission Directive (EU) 2015/996 of 19 May 2015 establishing common noise assessment methods according to Directive 2002/49/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Dangos Graddfa Ddaearyddol(e.e. Lloegr, Cymru, Yr Alban aca Gogledd Iwerddon)
- Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Rhagor o Adnoddau
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
Mae hon yn eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n deillio o’r UE
Mae unrhyw newidiadau sydd wedi cael eu gwneud yn barod gan y tîm yn ymddangos yn y cynnwys a chyfeirir atynt gydag anodiadau.Ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael bydd tair fersiwn o’r ddeddfwriaeth yma i’w gwirio at ddibenion gwahanol. Y fersiwn legislation.gov.uk yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn y Deyrnas Unedig. Y Fersiwn UE sydd ar EUR-lex ar hyn o bryd yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn yr UE h.y. efallai y bydd arnoch angen y fersiwn hon os byddwch yn gweithredu busnes yn yr UE. EUR-Lex Y fersiwn yn yr archif ar y we yw’r fersiwn swyddogol o’r ddeddfwriaeth fel yr oedd ar y diwrnod ymadael cyn cael ei chyhoeddi ar legislation.gov.uk ac unrhyw newidiadau ac effeithiau a weithredwyd yn y Deyrnas Unedig wedyn. Mae’r archif ar y we hefyd yn cynnwys cyfraith achos a ffurfiau mewn ieithoedd eraill o EUR-Lex. The EU Exit Web Archive legislation_originated_from_EU_p3
Changes over time for: Appendix E
Alternative versions:
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
Appendix E The finite segment correction
This appendix outlines the derivation of the finite segment correction and the associated energy fraction algorithm described in Section 2.7.19.
E1GEOMETRYU.K.
The energy fraction algorithm is based on the sound radiation of a ‘fourth-power’ 90-degree dipole sound source. This has directional characteristics which approximate those of jet aircraft sound, at least in the angular region that most influences sound event levels beneath and to the side of the aircraft flight path.
Figure E-1 illustrates the geometry of sound propagation between the flight path and the observer location O. The aircraft at P is flying in still uniform air with a constant speed on a straight, level flight path. Its closest point of approach to the observer is Pp . The parameters are:
distance from the observer to the aircraft
perpendicular distance from the observer to the flight path (slant distance)
distance from P to Pp = – V · τ
speed of the aircraft
time at which the aircraft is at point P
time at which the aircraft is located at the point of closest approach Pp
flight time = time relative to time at Pp = t – tp
angle between flight path and aircraft-observer vector
It should be noted that, since the flight time τ relative to the point of closest approach is negative when the aircraft is before the observer position (as shown in Figure E-1), the relative distance q to the point of closest approach becomes positive in that case. If the aircraft is ahead of the observer, q becomes negative.
E2ESTIMATION OF THE ENERGY FRACTIONU.K.
The basic concept of the energy fraction is to express the noise exposure E produced at the observer position from a flight path segment P1P2 (with a start-point P1 and an end-point P2 ) by multiplying the exposure E∞ from the whole infinite path flyby by a simple factor — the energy fraction factor F:
| E = F · E∞ | (E-1) |
Since the exposure can be expressed in terms of the time-integral of the mean-square (weighted) sound pressure level, i.e.
to calculate E, the mean-square pressure has to be expressed as a function of the known geometric and operational parameters. For a 90° dipole source,
where p 2 and pp 2 are the observed mean-square sound pressures produced by the aircraft as it passes points P and Pp .
This relatively simple relationship has been found to provide a good simulation of jet aircraft noise, even though the real mechanisms involved are extremely complex. The term dp 2/d2 in equation E-3 describes just the mechanism of spherical spreading appropriate to a point source, an infinite sound speed and a uniform, non-dissipative atmosphere. All other physical effects — source directivity, finite sound speed, atmospheric absorption, Doppler-shift etc. — are implicitly covered by the sin2ψ term. This factor causes the mean square pressure to decrease inversely as d4 ; whence the expression ‘fourth power’ source.
Introducing the substitutions
the mean-square pressure can be expressed as a function of time (again disregarding sound propagation time):
Putting this into equation (E-2) and performing the substitution
the sound exposure at the observer from the flypast between the time interval [τ1 ,τ2 ] can be expressed as
The solution of this integral is:
Integration over the interval [–∞,+∞] (i.e. over the whole infinite flight path) yields the following expression for the total exposure E∞ :
and hence the energy fraction according to equation E-1 is
E3CONSISTENCY OF MAXIMUM AND TIME INTEGRATED METRICS — THE SCALED DISTANCEU.K.
A consequence of using the simple dipole model to define the energy fraction is that it implies a specific theoretical difference ΔL between the event noise levels Lmax and LE . If the contour model is to be internally consistent, this needs to equal the difference of the values determined from the NPD curves. A problem is that the NPD data are derived from actual aircraft noise measurements — which do not necessarily accord with the simple theory. The theory therefore needs an added element of flexibility. But in principal the variables α1 and α2 are determined by geometry and aircraft speed — thus leaving no further degrees of freedom. A solution is provided by the concept of a scaled distance dλ as follows.
The exposure level LE,∞ as tabulated as a function of dp in the ANP database for a reference speed Vref, can be expressed as
where p 0 is a standard reference pressure and tref is a reference time (= 1 s for SEL). For the actual speed V it becomes
Similarly the maximum event level Lmax can be written
For the dipole source, using equations E-8, E-11 and E-12, noting that (from equations E-2 and E-8) 
This can only be equated to the value of ΔL determined from the NPD data if the slant distance dp used to calculate the energy fraction is substituted by a scaled distance dλ given by
or
Replacing dp by dλ in equation E-5 and using the definition q = Vτ from Figure E-1 the parameters α1 and α2 in equation E-9 can be written (putting q = q1 at the start-point and q – λ = q2 at the endpoint of a flight path segment of length λ) as
Having to replace the slant actual distance by scaled distance diminishes the simplicity of the fourth-power 90 degree dipole model. But as it is effectively calibrated in situ using data derived from measurements, the energy fraction algorithm can be regarded as semi-empirical rather than a pure theoretical.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThe Whole Annex
You have chosen to open the Whole Directive
The Whole Directive you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
Y Rhestrau you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
Gweler y wybodaeth ychwanegol ochr yn ochr â’r cynnwys
Rhychwant ddaearyddol: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Mae’r llinell amser yma yn dangos y fersiynau gwahanol a gymerwyd o EUR-Lex yn ogystal ag unrhyw fersiynau dilynol a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig.
Cymerir dyddiadau fersiynau’r UE o ddyddiadau’r dogfennau ar EUR-Lex ac efallai na fyddant yn cyfateb â’r adeg pan ddaeth y newidiadau i rym ar gyfer y ddogfen.
Ar gyfer unrhyw fersiynau a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig, bydd y dyddiad yn cyd-fynd â’r dyddiad cynharaf y daeth y newid (e.e. ychwanegiad, diddymiad neu gyfnewidiad) a weithredwyd i rym. Am ragor o wybodaeth gweler ein canllaw i ddeddfwriaeth ddiwygiedig ar Ddeall Deddfwriaeth.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill