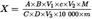- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser (24/05/2017)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Commission Regulation (EC) No 152/2009Dangos y teitl llawn
Commission Regulation (EC) No 152/2009 of 27 January 2009 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of feed (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Dangos Graddfa Ddaearyddol(e.e. Lloegr, Cymru, Yr Alban aca Gogledd Iwerddon)
- Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Rhagor o Adnoddau
PDF o Fersiynau Diwygiedig
- ddiwygiedig 16/11/20202.10 MB
- ddiwygiedig 24/05/20171.85 MB
- ddiwygiedig 26/04/20171.62 MB
- ddiwygiedig 17/07/20142.16 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/01/20142.40 MB
- ddiwygiedig 12/02/20132.46 MB
- ddiwygiedig 18/04/20122.15 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
Mae hon yn eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n deillio o’r UE
Mae unrhyw newidiadau sydd wedi cael eu gwneud yn barod gan y tîm yn ymddangos yn y cynnwys a chyfeirir atynt gydag anodiadau.Ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael bydd tair fersiwn o’r ddeddfwriaeth yma i’w gwirio at ddibenion gwahanol. Y fersiwn legislation.gov.uk yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn y Deyrnas Unedig. Y Fersiwn UE sydd ar EUR-lex ar hyn o bryd yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn yr UE h.y. efallai y bydd arnoch angen y fersiwn hon os byddwch yn gweithredu busnes yn yr UE. EUR-Lex Y fersiwn yn yr archif ar y we yw’r fersiwn swyddogol o’r ddeddfwriaeth fel yr oedd ar y diwrnod ymadael cyn cael ei chyhoeddi ar legislation.gov.uk ac unrhyw newidiadau ac effeithiau a weithredwyd yn y Deyrnas Unedig wedyn. Mae’r archif ar y we hefyd yn cynnwys cyfraith achos a ffurfiau mewn ieithoedd eraill o EUR-Lex. The EU Exit Web Archive legislation_originated_from_EU_p3
Changes over time for: Division G.
Alternative versions:
Status:
Point in time view as at 24/05/2017.
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects for the Commission Regulation (EC) No 152/2009, Division G..![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
G.DETERMINATION OF TRYPTOPHANU.K.
1.Purpose and scopeU.K.
The method makes the determination possible of the total and free tryptophan in feed. It does not distinguish between D- and L- forms.
2.PrincipleU.K.
For the determination of the total tryptophan, the sample is hydrolysed under alkaline conditions with saturated barium hydroxide solution and heated to 110 oC for 20 hours. After hydrolysis internal standard is added.
For the determination of free tryptophan, the sample is extracted under mild acidic conditions in the presence of internal standard.
The tryptophan and the internal standard in the hydrolysate or in the extract are determined by HPLC with fluorescence detection.
3.ReagentsU.K.
3.1.Double distilled water or water of equivalent quality must be used (conductivity < 10 μS/cm).U.K.
3.2.Standard substance: tryptophan (purity/content ≥ 99 %) dried under vacuum over phosphorous pentoxide.U.K.
3.3.Internal standard substance: α-methyl-tryptophan (purity/content ≥ 99 %), dried under vacuum over phosphorous pentoxide.U.K.
3.4.Barium hydroxide octa-hydrate (care shall be taken not to expose the Ba(OH)2 .8 H2O excessively to air in order to avoid formation of BaCO3, which could disturb the determination) (see observation 9.3).U.K.
3.5.Sodium hydroxide.U.K.
3.6.Ortho-phosphoric acid, w (w/w) = 85 %.U.K.
3.7.Hydrochloric acid, ρ201,19 g/ml.U.K.
3.8.Methanol, equivalent to HPLC grade.U.K.
3.9.Light petroleum, boiling range 40-60 oC.U.K.
3.10.Sodium hydroxide solution, c = 1 mol/l:U.K.
Dissolve 40,0 g NaOH (3.5) in water and make up to 1 litre with water (3.1).
3.11.Hydrochloric acid, c = 6 mol/l:U.K.
Take 492 ml HCl (3.7) and make up to 1 litre with water.
3.12.Hydrochloric acid, c = 1 mol/l:U.K.
Take 82 ml HCl (3.7) and make up to 1 litre with water.
3.13.Hydrochloric acid, c = 0,1 mol/l:U.K.
Take 8,2 ml HCl (3.7) and make up to 1 litre with water.
3.14.Ortho-phosphoric acid, c = 0,5 mol/l:U.K.
Take 34 ml ortho-phosphoric acid (3.6) and make up to 1 litre with water (3.1).
3.15.Concentrated solution of tryptophan (3.2), c = 2,5 μmol/ml:U.K.
In a 500 ml volumetric flask dissolve 0,2553 g tryptophan (3.2) in hydrochloric acid (3.13) and make up to the mark with hydrochloric acid (3.13). Store at - 18 oC for a maximum of 4 weeks.
3.16.Concentrated internal standard solution, c = 2,5 μmol/ml:U.K.
In a 500 ml volumetric flask dissolve 0,2728 g α-methyl-tryptophan (3.3) in hydrochloric acid (3.13) and make up to the mark with hydrochloric acid (3.13). Store at - 18 oC for a maximum of 4 weeks.
3.17.Calibration standard solution of tryptophan and internal standard:U.K.
Take 2,0 ml concentrated solution of tryptophan (3.15), and 2,0 ml of concentrated internal standard (α-methyl-tryptophan) solution (3.16). Dilute with water (3.1) and methanol (3.8) to approximately the same volume and to approximately the same concentration of methanol (10 %-30 %) as the finished hydrolysate.
This solution must be prepared freshly before use.
Protect from direct sunlight during preparation.
3.18.Acetic acidU.K.
3.19.1,1,1-trichloro-2-methyl-2-propanol.U.K.
3.20.Ethanolamine w (w/w) > 98 %.U.K.
3.21.Solution of 1 g 1,1,1-trichloro-2-methyl-2-propanol (3.19) in 100 ml methanol (3.8).U.K.
3.22.Mobile phase for HPLC: 3,0 g acetic acid (3.18) + 900 ml water (3.1) +50,0 ml solution (3.21) of 1,1,1-trichloro-2-methyl-2-propanol (3.19) in methanol (3.8) (1g/100ml). Adjust pH to 5,0 using ethanolamine (3.20). Make up to 1 000 ml with water (3.1).U.K.
4.ApparatusU.K.
4.1.HPLC equipment with a spectrofluorometric detector.U.K.
4.2.Liquid chromatographic column, 125 mm x 4 mm, C18, 3 μm packing, or equivalent.U.K.
4.3.pH-meter.U.K.
4.4.Polypropylene flask, capacity 125 ml, with wide neck and screw cap.U.K.
4.5.Membrane filter, 0,45 μm.U.K.
4.6.Autoclave, 110 (± 2) oC, 1,4 (±0,1) bar.U.K.
4.7.Mechanical shaker or magnetic stirrer.U.K.
4.8.Vortex mixer.U.K.
5.ProcedureU.K.
5.1.Preparation of samplesU.K.
The sample is ground to pass through a 0,5 mm sieve. Samples high in moisture must be either air-dried at a temperature not exceeding 50 oC or freeze dried prior to grinding. Samples with high fat content shall be extracted with light petroleum (3.9) prior to grinding.
5.2.Determination of free tryptophan (extract)U.K.
Weigh to the nearest 1 mg an appropriate amount (1-5 g) of the prepared sample (5.1), into a conical flask. Add 100,0 ml hydrochloric acid, (3.13) and 5,0 ml concentrated internal standard solution (3.16). Shake or mix for 60 min. using a mechanical shaker or a magnetic stirrer (4.7). Allow the sediment to settle and pipette 10,0 ml of the supernatant solution into a beaker. Add 5 ml ortho-phosphoric acid (3.14). Adjust the pH to 3 using sodium hydroxide (3.10). Add sufficient methanol (3.8) to give a concentration of between 10 % and 30 % of methanol in the final volume. Transfer to a volumetric flask of appropriate volume and dilute with water to a volume necessary for the chromatography (approx. the same volume as the calibration standard solution (3.17)).
Filter a few ml of the solution through a 0,45 μm membrane filter (4.5) before injection on the HPLC column. Proceed to the chromatography step according to paragraph 5.4.
Protect standard solution and extracts against direct sunlight. If it is not possible to analyse the extracts the same day, the extracts may be stored at 5 oC for a maximum of 3 days.
5.3.Determination of total tryptophan (hydrolysate)U.K.
Weigh to the nearest 0,2 mg from 0,1 to 1 g of the prepared sample (5.1) into the polypropylene flask (4.4). The weighed sample portion shall have a nitrogen content of about 10 mg. Add 8,4 g barium hydroxide octa-hydrate (3.4) and 10 ml water. Mix on a vortex mixer (4.8) or magnetic stirrer (4.7). Leave the teflon coated magnet in the mixture. Wash down the walls of the vessel with 4 ml water. Put on the screw cap and close the flask loosely. Transfer to an autoclave (4.6) with boiling water and steam for 30-60 minutes. Close the autoclave and autoclave at 110 (± 2) oC for 20 hours.
Before opening the autoclave reduce the temperature to just under 100 oC. In order to avoid crystallisation of Ba(OH)2 · 8 H2O, add to the warm mixture 30 ml water which is at room temperature. Shake or stir gently. Add 2,0 ml concentrated internal standard (α-methyl-tryptophan) solution (3.16). Cool the vessels on water/ice bath for 15 minutes.
Then, add 5 ml ortho-phosphoric acid (3.14). Keep the vessel in the cooling bath and neutralise with HCl (3.11) whilst stirring and adjust the pH to 3,0 using HCl (3.12). Add sufficient methanol to give a concentration of between 10 % and 30 % of methanol in the final volume. Transfer to a volumetric flask of appropriate volume and dilute with water to the defined volume necessary for the chromatography (for example 100 ml). The addition of methanol shall not cause precipitation.
Filter a few ml of the solution through a 0,45 μm membrane filter (4.5) before injection on the HPLC column. Proceed to the chromatography step according to paragraph 5.4.
Protect standard solution and hydrolysates against direct sunlight. If it is not possible to analyse the hydrolysates the same day, they may be stored at 5 oC for a maximum of 3 days.
5.4.HPLC determinationU.K.
The following conditions for isocratic elution are offered for guidance; other conditions may be used, provided they yield equivalent results (see also observations 9.1 and 9.2):
| Liquid chromatographic column (4.2): | 125 mm x 4 mm, C18, 3 μm packing or equivalent |
| Column temperature: | Room temperature |
| Mobile phase (3.22): | 3,0 g acetic acid (3.18) + 900 ml water (3.1) +50,0 ml solution (3.21) of 1,1,1-trichloro-2- methyl-2-propanol (3.19) in methanol (3.8) (1 g/100 ml). Adjust pH to 5,0 using ethanolamine (3.20). Make up to 1 000 ml with water (3.1) |
| Flow rate: | 1 ml/min. |
| Total run time: | approx. 34 min. |
| Detection wavelength: | excitation: 280 nm, emission: 356 nm. |
| Injection volume | 20 μl |
6.Calculation of resultsU.K.
The amount of tryptophane (X), in g per 100g sample, is calculated as follows:
=
peak area of internal standard, calibration standard solution (3.17)
=
peak area of tryptophan, extract (5.2) or hydrolysate (5.3)
=
volume in ml (2 ml) of concentrated tryptophan solution (3.15) added to the calibration solution (3.17)
=
concentration in μmol/ml (= 2,5) of concentrated tryptophan solution (3.15) added to calibration solution (3.17)
=
volume in ml of concentrated internal standard solution (3.16) added at the extraction (5.2) (= 5,0 ml) or to the hydrolysate (5.3) (= 2,0 ml)
=
peak area of internal standard, extract (5.2) or hydrolysate (5.3)
=
peak area of tryptophan, calibration standard solution (3.17)
=
volume in ml (= 2,0 ml) of concentrated internal standard solution (3.16) added to calibration standard solution (3.17)
=
sample weight in g (corrected to original weight if dried and/or defatted)
=
molar weight of tryptophan (= 204,23 g/mol)
7.RepeatabilityU.K.
The difference between the results of two parallel determinations carried out on the same sample must not exceed 10 % relative to the highest result.
8.Results of a collaborative studyU.K.
An EC collaborative study (4th intercomparison) was arranged in which three samples were analysed by up to 12 laboratories to certify the method for hydrolysis. Replicate (5) analyses were performed on each sample. The results are given in the following table:
| Sample 1Pig feed | Sample 2Pig feed supplemented with L-tryptophan | Sample 3Feed concentrate for pigs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| n | 50 | 55 | 50 |
| Mean [g/kg] | 2,42 | 3,4 | 4,22 |
| sr [g/kg] | 0,05 | 0,05 | 0,08 |
| r [g/kg] | 0,14 | 0,14 | 0,22 |
| CVr [%] | 1,9 | 1,6 | 1,9 |
| SR [g/kg] | 0,15 | 0,2 | 0,09 |
| R [g/kg] | 0,42 | 0,56 | 0,25 |
| CVR [%] | 6,3 | 6,0 | 2,2 |
=
number of laboratories submitting results
=
number of single results retained eliminating outliers (identified by Cochran, Dixon outlier test)
=
standard deviation of repeatability
=
standard deviation of reproducibility
=
repeatability
=
reproducibility
=
coefficient of variation of repeatability, %
=
coefficient of variation of reproducibility, %
Another EC collaborative study (3rd intercomparison) was arranged in which two samples were analysed by up to 13 laboratories to certify the method for extraction of free tryptophan. Replicate (5) analyses were performed on each sample. The results are given in the following table:
| Sample 4Wheat and soya mixture | Sample 5Wheat and soya mixture (= sample 4) with added tryptophan (0,457g/kg1) | |
|---|---|---|
| L | 12 | 12 |
| n | 55 | 60 |
| Mean [g/kg] | 0,391 | 0,931 |
| sr [g/kg] | 0,005 | 0,012 |
| r [g/kg] | 0,014 | 0,034 |
| CVr [%] | 1,34 | 1,34 |
| SR [g/kg] | 0,018 | 0,048 |
| R [g/kg] | 0,05 | 0,134 |
| CVR [%] | 4,71 | 5,11 |
=
number of laboratories submitting results
=
number of single results retained after eliminating outliers (identified by Cochran, Dixon outlier test)
=
standard deviation of repeatability
=
standard deviation of reproducibility
=
repeatability
=
reproducibility
=
coefficient of variation of repeatability, %
=
coefficient of variation of reproducibility, %
Another EC intercomparison study was arranged in which four samples were analysed by up to 7 laboratories with the aim of a tryptophan certification for hydrolysis. The results are given below. Replicate (5) analyses were performed on each sample.
| Sample 1Mixed pig feed(CRM 117) | Sample 2Low fat fish meal(CRM 118) | Sample 3Soybean meal(CRM 119) | Sample 4Skimmed milk powder(CRM 120) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| n | 25 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Mean [g/kg] | 2,064 | 8,801 | 6,882 | 5,236 |
| sr [g/kg] | 0,021 | 0,101 | 0,089 | 0,04 |
| r [g/kg] | 0,059 | 0,283 | 0,249 | 0,112 |
| CVr [%] | 1,04 | 1,15 | 1,3 | 0,76 |
| SR [g/kg] | 0,031 | 0,413 | 0,283 | 0,221 |
| R [g/kg] | 0,087 | 1,156 | 0,792 | 0,619 |
| CVR [%] | 1,48 | 4,69 | 4,11 | 4,22 |
=
number of laboratories submitting results
=
number of single results retained after eliminating outliers (identified by Cochran, Dixon outlier test)
=
standard deviation of repeatability
=
standard deviation of reproducibility
=
repeatability
=
reproducibility
=
coefficient of variation of repeatability, %
=
coefficient of variation of reproducibility, %
9.ObservationsU.K.
9.1.Following special chromatographic conditions may give better separation between tryptophan and α-methyl-tryptophan.U.K.
Isocratic elution followed by gradient column cleaning:
| Liquid chromatographic column: | 125 mm x 4 mm, C18, 5 μm packing or equivalent | ||
| Column temperature: | 32 oC | ||
| Mobile phase: | A: 0,01 mol/l KH2PO4/méthanol, 95+5 (V+V). B: methanol | ||
| Gradient program: | 0 min. | 100 % A | 0 % B |
| 15 min. | 100 % A | 0 % B | |
| 17 min. | 60 % A | 40 % B | |
| 19 min. | 60 % A | 40 % B | |
| 21 min. | 100 % A | 0 % B | |
| 33 min. | 100 % A | 0 % B | |
| Flow rate: | 1,2 ml/min. | ||
| Total run time: | approx. 33 min. | ||
9.2.The chromatography will vary according to the type of HPLC and column packing material used. The chosen system must be capable of giving baseline separation between the tryptophan and the internal standard. Moreover it is important that degradation products are well separated from the tryptophan and the internal standard. Hydrolysates without internal standard shall be run in order to check the base line under the internal standard for impurities. It is important that the run time is sufficiently long for the elution of all the degradation products, otherwise late eluting peaks may interfere with subsequent chromatographic runs.U.K.
In the range of operation, the chromatographic system shall give linear response. The linear response shall be measured with a constant (the normal) concentration of the internal standard and varying concentrations of tryptophan. It is of importance that the size of both the tryptophan and internal standard peaks are within the linear range of the HPLC/fluorescence system. If either the tryptophan and/or the internal standard peak(s) is (are) too small or too high the analysis shall be repeated with another sample size and/or a changed final volume.
9.3. Barium hydroxide U.K.
With age barium hydroxide becomes more difficult to dissolve. This results in an unclear solution for the HPLC determination, which may produce low results for tryptophan.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThe Whole Annex
PrintThis Division only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
Y Rhestrau you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
Gweler y wybodaeth ychwanegol ochr yn ochr â’r cynnwys
Rhychwant ddaearyddol: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Mae’r llinell amser yma yn dangos y fersiynau gwahanol a gymerwyd o EUR-Lex yn ogystal ag unrhyw fersiynau dilynol a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig.
Cymerir dyddiadau fersiynau’r UE o ddyddiadau’r dogfennau ar EUR-Lex ac efallai na fyddant yn cyfateb â’r adeg pan ddaeth y newidiadau i rym ar gyfer y ddogfen.
Ar gyfer unrhyw fersiynau a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig, bydd y dyddiad yn cyd-fynd â’r dyddiad cynharaf y daeth y newid (e.e. ychwanegiad, diddymiad neu gyfnewidiad) a weithredwyd i rym. Am ragor o wybodaeth gweler ein canllaw i ddeddfwriaeth ddiwygiedig ar Ddeall Deddfwriaeth.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill