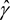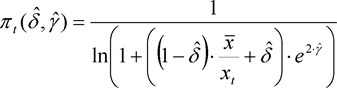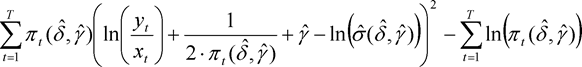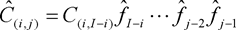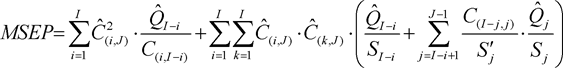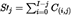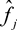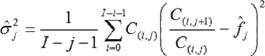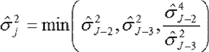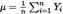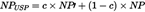- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/35Dangos y teitl llawn
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/35 of 10 October 2014 supplementing Directive 2009/138/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the taking-up and pursuit of the business of Insurance and Reinsurance (Solvency II) (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Rheoliadau yn deillio o’r UE
- 2015 No. 35
- ANNEX XVII
Rhagor o Adnoddau
PDF o Fersiynau Diwygiedig
- ddiwygiedig 30/07/202048.27 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/01/202048.00 MB
- ddiwygiedig 08/07/201944.91 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/01/201946.16 MB
- ddiwygiedig 15/09/201740.90 MB
- ddiwygiedig 09/04/201746.19 MB
- ddiwygiedig 02/04/201646.19 MB
- ddiwygiedig 17/01/201539.54 MB
Pan adawodd y DU yr UE, cyhoeddodd legislation.gov.uk ddeddfwriaeth yr UE a gyhoeddwyd gan yr UE hyd at ddiwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.). Ar legislation.gov.uk, mae'r eitemau hyn o ddeddfwriaeth yn cael eu diweddaru'n gyson ag unrhyw ddiwygiadau a wnaed gan y DU ers hynny.
Mae'r eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth yn tarddu o'r UE
Mae legislation.gov.uk yn cyhoeddi fersiwn y DU. Mae EUR-Lex yn cyhoeddi fersiwn yr UE. Mae Archif Gwe Ymadael â’r UE yn rhoi cipolwg ar fersiwn EUR-Lex o ddiwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Status:
EU_status_warning_original_version
This legislation may since have been updated - see the latest available (revised) version
ANNEX XVII METHOD-SPECIFIC DATA REQUIREMENTS AND METHOD SPECIFICATIONS FOR UNDERTAKING-SPECIFIC PARAMETERS OF THE STANDARD FORMULA
A. Definitions and notations
(1)For the purpose of this Annex, the following definitions shall apply:
‘accident year’ means, with respect to a payment for an insurance or reinsurance claim, the year in which the insured event that gave rise to that claim took place;
‘development year’ means, with respect to a payment for an insurance or reinsurance claim, the difference between the year of that payment and the accident year of that payment.
‘reporting year’ means, with respect to a payment for an insurance or reinsurance claim, the year in which the insured event that gave rise to that claim was notified to the insurance or reinsurance undertaking;
‘financial year’ means, with respect to a payment for an insurance or reinsurance claim, the year in which this payment took place.
(2)For the purpose of this annex, ‘segment s’ denotes the segment for which the undertaking-specific parameter is determined, being one of the segments set out in Annex II or one of the segments set out in Annex XIV.
B. Premium risk method
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific standard deviation of segment s shall consist of the following:
the payments made and the best estimates of the provision for claims outstanding in segment s after the first development year of the accident year of those claims (aggregated losses);
the premiums earned in segment s;
Those aggregated losses and earned premiums shall be available separately for each accident year of the insurance and reinsurance claims in segment s.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the premium risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months;
data are available for at least five consecutive accident years;
where the premium risk method is applied to replace the standard parameters referred to in Article 218(1)(a)(i) and (c)(i), the aggregated losses and earned premiums are not adjusted for recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles or reinsurance premiums;
where the premium risk method is applied to replace the standard parameters referred to in Article 218(1)(a)(ii) and (c)(ii):
the aggregated losses are adjusted for amounts recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles which are consistent with the reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles that are in place to provide cover for the following twelve months;
the earned premiums are adjusted for reinsurance premiums which are consistent with the reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles that are in place to provide cover for the following twelve months;
the aggregated losses are adjusted for catastrophe claims to the extent that the risk of those claims is reflected in the non-life or health catastrophe risk sub-modules;
the aggregated losses include the expenses incurred in servicing the insurance and reinsurance obligations;
the data fit the following assumptions:
expected aggregated losses in a particular segment and accident year are linear proportional in premiums earned in a particular accident year;
the variance of aggregated losses in a particular segment and accident year is quadratic in premiums earned in a particular accident year;
aggregated losses follow a lognormal distribution;
maximum likelihood estimation is appropriate.
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4-6, the following notation shall apply:
accident years are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 1 for the first accident year for which data are available;
T denotes the latest accident year for which data are available;
for all accident years, the aggregated losses in segment s in a particular accident year t are denoted by yt ;
for all accident years, the premiums earned in segment s in a particular accident year t are denoted by xt .
(4)The undertaking-specific standard deviation of segment s shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
σ(prem,s) denotes the standard parameter that should be replaced by the undertaking-specific parameter.
(5)The standard deviation function shall be equal to the following function of two variables:
where:
(6)The mixing parameter and the logarithmic variation coefficient shall be the values  and
and  respectively for which the following amount becomes minimal:
respectively for which the following amount becomes minimal:
where:
For the determination of the minimal amount, no values for the mixing parameter less than zero or exceeding 1 shall be considered.
C. Reserve risk method 1
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific standard deviation for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s shall consist of the following:
the sum of the best estimate provision at the end of the financial year for claims that were outstanding in segment s at the beginning of the financial year and the payments made during the financial year for claims that were outstanding in segment s at the beginning of the financial year;
the best estimate of the provision for claims outstanding in segment s at the beginning of the financial year.
The amounts referred to in points (a) and (b) shall be available separately for different financial years.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the reserve risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months
data are available for at least five consecutive financial years;
the data are adjusted for amounts recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles which are consistent with the reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles that are in place to provide cover for the following twelve months;
the data include the expenses incurred in servicing the insurance and reinsurance obligations.
the data fit the following assumptions:
the amount referred to paragraph 1(a) in that particular segment and financial year is linear proportional in the best estimate of the provision for claims outstanding in that particular segment and financial year;
the variance of the amount referred to paragraph 1(a) in a particular segment and financial year is quadratic in the provision for claims outstanding in a particular segment and financial year;
the amount referred to paragraph 1(a) follows a lognormal distribution;
maximum likelihood estimation is appropriate.
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4-6, the following notation shall apply:
the financial years are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 1 for the first financial year for which data are available;
T denotes the latest financial year for which data are available;
for all financial years, the amount referred to paragraph 1(a) in segment s in a particular financial year t is denoted by yt ;
for all financial years, the best estimate of the provision for claims outstanding in segment s in a particular financial year t are denoted by xt .
(4)The undertaking-specific standard deviation for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
σ(prem,s) denotes the standard parameter that should be replaced by the undertaking-specific parameter.
(5)The standard deviation function shall be equal to the following function of two variables:
where:
(6)The mixing parameter and the logarithmic variation coefficient shall be the values 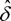 and
and  respectively for which the following amount becomes minimal:
respectively for which the following amount becomes minimal:
where:
For the determination of the minimal amount, no values for the mixing parameter less than zero or exceeding 1 shall be considered.
D. Reserve risk method 2
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific standard deviation for deviation for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s shall consist of cumulative payment amounts for insurance or reinsurance claims in segment s (cumulative claims amounts), separately for each accident year and development year of the payments.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the reserve risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months;
data are available for at least five consecutive accident years;
in the first accident year, data are available for at least five consecutive development years;
in the first accident year the cumulative payment amount of the last development year for which data are available includes all the payments of the accident year except an immaterial amount;
the number of consecutive accident years for which data are available is not less than the number of consecutive development years in the first accident year for which data are available;
the cumulative claims amounts are adjusted for amounts recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles which are consistent with the reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles that are in place to provide cover for the following twelve months;
the cumulative claims amounts shall include the expenses incurred in servicing the insurance or reinsurance obligations;
the data are consistent with the following assumptions about the stochastic nature of cumulative claims amounts:
cumulative claims amounts for different accident years are mutually stochastically independent;
for all accident years the implied incremental claim amounts are stochastically independent;
for all accident years the expected value of the cumulative claims amount for a development year is proportional to the cumulative claims amount for the preceding development year;
for all accident years the variance of the cumulative claims amount for a development year is proportional to the cumulative claims amount for the preceding development year.
For the purposes of point (d), a payment amount shall be considered to be material where ignoring it in the calculation of the undertaking-specific parameter could influence the decision-making or the judgement of the users of that information, including the supervisory authorities
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4 and 5, the following notation shall apply:
the accident years are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 0 for the first accident year for which data are available;
I denotes the latest accident year for which data are available;
J denotes the latest development year in the first accident year for which data are available;
C(i,j) denotes the cumulative claims for accident year i and development year j.
(4)The undertaking-specific standard deviation for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
MSEP denotes the mean squared error of prediction as specified in paragraph 5;
for all accident years and development years, 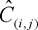
where for all development years 
σ(res,s) denotes the standard parameter for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s.
(5)The mean squared error of prediction shall be equal to the following:
where:
E. Revision risk method
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific increase in the amount of annuity benefits shall consist of annual amounts of annuity benefits of annuity insurance obligations where the benefits payable could increase as a result of changes in the legal environment or in the state of health of the person insured (annuity benefits), separately for consecutive financial years and each beneficiary.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the revision risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months;
data are available for at least five consecutive financial years;
the annuity benefits are gross, without deduction of the amounts recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles;
the annuity benefits shall include the expenses incurred in servicing the annuity obligations;
the data are consistent with the following assumptions about the stochastic nature of increases in the amount of annuity benefits:
the annual number of annuity increases follows a negative binomial distribution, including in the tail of the distribution;
the amount of an annuity increase follows a lognormal distribution, including in the tail of the distribution;
the annual number of annuity increases and the amounts of the annuity increase are mutually stochastically independent.
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4-8, the following notation shall apply:
the financial years are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 1 for the first financial year for which data are available;
T denotes the latest financial year for which data are available;
A(i,t) denotes the annuity benefits of beneficiary i in financial year t;
(4)The undertaking-specific increase in the amount of annuity benefits shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
VaR 0,995(R) denotes the 99,5 % quantile of the distribution of annuity increases set out in paragraph 6;
S is equal to 3 % where the calculation is done for the purpose of the revision risk sub-module set out in Article 141 and equal to 4 % where the calculation is done for the purpose of the health revision risk sub-module set out in Article 158.
(5)The expected value of annuity increases shall be equal to the following:
where:
(6)The annuity increases shall be equal to the following:
where:
N denotes the annual number of annuity increases and follows a negative binominal distribution with an expected value that is equal to the estimated number of changes in annuity benefits set out in point (b) of paragraph 5 and with a standard deviation that is equal to the estimated standard deviation of the number of changes in annuity benefits set out in paragraph 7;
Xk denotes the amount of an annuity increase and follows a lognormal distribution with an expected value that is equal to the estimated average change in annuity benefits set out in point (a) of paragraph 5 and with a standard deviation that is equal to the estimated standard deviation of changes in annuity benefits set out in paragraph 8;
the annual number of annuity increases and the amounts of the annuity increase are mutually stochastically independent.
(7)The estimated standard deviation of the number of changes in annuity benefits shall be equal to the following:
where:
(8)The estimated standard deviation of changes in annuity benefits shall be equal to the following:
where:
F. Non-proportional reinsurance method
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance shall consist of the ultimate claim amounts of insurance and reinsurance claims that were reported to the insurance or reinsurance undertaking in segment s during the last financial years, separately for each insurance and reinsurance claim.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the premium risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months;
the data do not indicate a higher premium risk than reflected in the standard deviation for premium risk used to calculate the Solvency Capital Requirement;
the ultimate claim amounts are estimated in the year the insurance and reinsurance claims were reported;
data are available for at least five reporting years;
where the recognisable excess of loss reinsurance contract applies to gross claims, the ultimate claim amounts are gross;
where the recognisable excess of loss reinsurance contract applies to claims after deduction of the recoverables from certain other reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles, the amounts receivable from those certain other reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles are deducted from the ultimate claim amounts;
the ultimate claim amounts shall not include expenses incurred in servicing the insurance and reinsurance obligations;
the data are consistent with the assumption that ultimate claim amounts follow a lognormal distribution, including in the tail of the distribution.
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4-7, the following notation shall apply:
insurance and reinsurance claims for which data are available are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 1;
n denotes the number of insurance and reinsurance claim for which data are available;
Yi denotes the ultimate claim amount of insurance or reinsurance claim i;
μ and ω denote the first and second moment, respectively, of the claim amount distribution, being equal to the following amounts:
b 1 denotes the amount of the retention of the recognisable excess of loss reinsurance contract referred to in Article 218(2);
where the recognisable excess of loss reinsurance contract referred to in Article 196(1) provides compensation only up to a specified limit, b 2 denotes the amount of that limit.
(4)The undertaking-specific specific adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
NP′ denotes the estimated adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance set out in paragraph 5;
NP denotes the adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance set out in Article 117(2).
(5)The estimated adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance shall be equal to the following:
where the parameters μ 2, ω 1 and ω 2 are set out in paragraph 6.
(6)The parameters, μ 2, ω 1 and ω 2 shall be equal to the following:
where:
(7)Notwithstanding paragraph 5, where non-proportional reinsurance covers homogeneous risk-groups within a segment, the estimated adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance shall be equal to the following:
where:
V(prem,h) denotes the volume measure for premium risk of the homogeneous risk group h determined in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 116;
NP′(h) denotes the estimated adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance of homogeneous risk group h determined in accordance with paragraph 5.
G. Credibility factor
(1)The credibility factor for segments 1, 5 and 6 set out in Annex II shall be equal to the following:
| Time lengths in years | Credibility factor c |
|---|---|
| 5 | 34 % |
| 6 | 43 % |
| 7 | 51 % |
| 8 | 59 % |
| 9 | 67 % |
| 10 | 74 % |
| 11 | 81 % |
| 12 | 87 % |
| 13 | 92 % |
| 14 | 96 % |
| 15 and larger | 100 % |
(2)The credibility factor for segments 2 to 4 and 7 to 12 set out in Annex II, for the segments set out Annex XIV and for the revision risk method shall be equal to the following:
| Time lengths in years | Credibility factor c |
|---|---|
| 5 | 34 % |
| 6 | 51 % |
| 7 | 67 % |
| 8 | 81 % |
| 9 | 92 % |
| 10 and larger | 100 % |
(3)The time length shall be equal to the following:
for the premium risk method, the number of accident years for which data are available;
for reserve risk method 1, the number of financial years for which data are available;
for reserve risk method 2, the number of accident years for which data are available;
for the revision risk method, the number of financial years for which data are available;
for the non-proportional reinsurance method, the number of reporting years for which data are available.
Options/Cymorth
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThis Annex only
You have chosen to open The Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open The Whole Regulation as a PDF
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation without Annexes
The Whole Regulation without Annexes you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
Y Rhestrau you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill