- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser (31/12/2020)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2016/1240Dangos y teitl llawn
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2016/1240 of 18 May 2016 laying down rules for the application of Regulation (EU) No 1308/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to public intervention and aid for private storage (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Rheoliadau yn deillio o’r UE
- 2016 No. 1240
- attachment 1
- Dangos Graddfa Ddaearyddol(e.e. Lloegr, Cymru, Yr Alban aca Gogledd Iwerddon)
- Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Rhagor o Adnoddau
PDF o Fersiynau Diwygiedig
- ddiwygiedig 07/02/20181.05 MB
- ddiwygiedig 24/08/20170.52 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
Mae hon yn eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n deillio o’r UE
Mae unrhyw newidiadau sydd wedi cael eu gwneud yn barod gan y tîm yn ymddangos yn y cynnwys a chyfeirir atynt gydag anodiadau.Ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael bydd tair fersiwn o’r ddeddfwriaeth yma i’w gwirio at ddibenion gwahanol. Y fersiwn legislation.gov.uk yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn y Deyrnas Unedig. Y Fersiwn UE sydd ar EUR-lex ar hyn o bryd yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn yr UE h.y. efallai y bydd arnoch angen y fersiwn hon os byddwch yn gweithredu busnes yn yr UE. EUR-Lex Y fersiwn yn yr archif ar y we yw’r fersiwn swyddogol o’r ddeddfwriaeth fel yr oedd ar y diwrnod ymadael cyn cael ei chyhoeddi ar legislation.gov.uk ac unrhyw newidiadau ac effeithiau a weithredwyd yn y Deyrnas Unedig wedyn. Mae’r archif ar y we hefyd yn cynnwys cyfraith achos a ffurfiau mewn ieithoedd eraill o EUR-Lex. The EU Exit Web Archive legislation_originated_from_EU_p3
Status:
Point in time view as at 31/12/2020.
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects for the Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2016/1240.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
[F1Appendix
METHOD FOR THE DETECTION OF COW'S MILK AND CASEINATE IN CHEESES FROM EWE'S MILK, GOAT'S MILK OR BUFFALO MILK OR MIXTURES OF EWE'S MILK, GOAT'S MILK AND BUFFALO MILK U.K.
1. SCOPE U.K.
Detection of cow's milk and caseinate in cheeses made from ewe's milk, goat's milk, buffalo milk or mixtures of ewe's, goat's and buffalo milk by isoelectric focusing of γ-caseins after plasminolysis.
2. FIELD OF APPLICATION U.K.
The method is suitable for sensitive and specific detection of native and heat-treated cow's milk and caseinate in fresh and ripened cheeses made from ewe's milk, goat's milk, buffalo milk or mixtures of ewe's, goat's and buffalo milk. It is not suitable for the detection of milk and cheese adulteration by heat-treated bovine whey protein concentrates.
3. PRINCIPLE OF THE METHOD U.K.
3.1. Isolation of caseins from cheese and the reference standards U.K.
3.2. Dissolving of the isolated caseins and submitting to plasmin (EC.3.4.21.7) cleavage U.K.
3.3. Isoelectric focusing of plasmin-treated caseins in the presence of urea and staining of proteins U.K.
3.4. Evaluation of stained γ 3 and γ 2 -casein patterns (evidence of cow's milk) by comparison of the pattern obtained from the sample with those obtained in the same gel from the reference standards containing 0 % and 1 % cow's milk. U.K.
4. REAGENTS U.K.
Unless otherwise indicated, analytical grade chemicals shall be used. Water shall be double-distilled or of equivalent purity.
Note: The following details apply to laboratory prepared polyacrylamide gels containing urea, of dimensions 265 × 125 × 0,25 mm. Where other sizes and types of gel are used, the separation conditions may have to be adjusted. U.K.
Isoelectric focusing U.K.
4.1. Reagents for production of the urea containing polyacrylamide gels U.K.
4.1.1. Stock gel solution U.K.
Dissolve:
4,85 g acrylamide
0,15 g N, N′-methylene-bis-acrylamide (BIS)
48,05 g urea
15,00 g glycerol (87 % w/w),
in water and make up to 100 ml and store in a brown glass bottle in the refrigerator.
Note: A commercially available pre-blended acrylamide/BIS solution may be used in preference to the quoted fixed weights of the neurotoxic acrylamides. Where such a solution contains 30 % w/v acrylamide and 0,8 % w/v BIS, a volume of 16,2 ml shall be used for the formulation instead of the fixed weights. The shelf life of the stock solution is a maximum of 10 days; if its conductivity is more than 5 μS, de-ionize by stirring with 2 g Amberlite MB-3 for 30 minutes, then filter through a 0,45 μm membrane. U.K.
4.1.2. Gel solution U.K.
Prepare a gel solution by mixing additives and ampholytes (*) with the stock gel solution (see 4.1.1).
9,0 ml stock solution
24 mg β-alanine
500 μl ampholyte pH 3,5-9,5
250 μl ampholyte pH 5-7
250 μl ampholyte pH 6-8
Mix the gel solution and de-gas for two to three minutes in an ultrasonic bath or in vacuum.
Note: Prepare the gel solution immediately prior to pouring it (see 6.2). U.K.
4.1.3. Catalyst solutions U.K.
4.1.3.1. N, N, N′ N′ — tetramethylethylenediamine (Temed) U.K.
4.1.3.2. 40 % w/v ammonium persulphate (PER): U.K.
Dissolve 800 mg PER in water and make up to 2 ml.
Note: Always use freshly prepared PER solution. U.K.
4.2. Contact fluid U.K.
Kerosene or liquid paraffin
4.3. Anode solution U.K.
Dissolve 5,77 g phosphoric acid (85 % w/w) in water and dilute to 100 ml.
4.4. Cathode solution U.K.
Dissolve 2,00 g sodium hydroxide in water and dilute to 100 ml with water.
Sample preparation U.K.
4.5. Reagents for protein isolation U.K.
4.5.1. Dilute acetic acid (25,0 ml of glacial acetic acid made up to 100 ml with water) U.K.
4.5.2. Dichloromethane U.K.
4.5.3. Acetone U.K.
4.6. Protein dissolving buffer U.K.
Dissolve
5,75 g glycerol (87 % w/w)
24,03 g urea
250 mg dithiothreitol,
in water and make up to 50 ml
Note: Store in a refrigerator, maximum shelf-life one week. U.K.
4.7. Reagents for plasmin cleavage of caseins U.K.
4.7.1. Ammonium carbonate buffer U.K.
Titrate a 0,2 mol/l ammonium hydrogencarbonate solution (1,58 g/100 ml water) containing 0,05 mol/l ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA, 1,46 g/100 ml with a 0,2 mol/l ammonium carbonate solution (1,92 g/100 ml water) containing 0,05 mol/l EDTA to pH 8.
4.7.2. Bovine plasmin (EC. 3.4.21.7), activity at least 5 U/ml U.K.
4.7.3. ε-Aminocaproic acid solution for enzyme inhibition U.K.
Dissolve 2,624 g ε-aminocaproic acid (6 amino-n-hexanoic acid) in 100 ml of 40 % (v/v) ethanol.
4.8. Standards U.K.
4.8.1. Certified reference standards of a mixture of renneted ewe's and goat's skimmed milk containing 0 % and 1 % of cow's milk are available from the Commission's Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements, B-2440 Geel, Belgium U.K.
4.8.2. Preparation of laboratory interim-standards of buffalo's renneted milk containing 0 % and 1 % of cow's milk U.K.
Skimmed milk is prepared by centrifuging of either buffalo or bovine raw bulk milk at 37 °C at 2 500 g for 20 minutes. After cooling the tube and contents rapidly to 6 to 8 °C, the upper fat layer is removed completely. For the preparation of the 1 % standard add 5,00 ml of bovine skimmed milk to a 495 ml of buffalo's skimmed milk in a 1 l beaker, adjust the pH to 6,4 by the addition of dilute lactic acid (10 % w/v). Adjust the temperature to 35 °C and add 100 μl of calf rennet (rennet activity 1: 10 000 , c. 3 000 U/ml), stir for 1 minute and then leave the beaker covered with an aluminium foil at 35 °C for one hour to allow formation of the curd. After the curd has formed, the whole renneted milk is freeze-dried without prior homogenization or draining of the whey. After freeze-drying it is finely ground to produce a homogeneous powder. For the preparation of the 0 % standard, carry out the same procedure using genuine buffalo skimmed milk. The standards shall be stored at – 20 °C.
Note: It is advisable to check the purity of the buffalo milk by isoelectric focusing of the plasmin-treated caseins before preparation of the standards. U.K.
Reagents for protein staining U.K.
4.9. Fixative U.K.
Dissolve 150 g trichloroacetic acid in water and make up to 1 000 ml.
4.10. Destaining solution U.K.
Dilute 500 ml methanol and 200 ml glacial acetic acid to 2 000 ml with distilled water.
Note: Prepare the destaining solution fresh every day; it can be prepared by mixing equal volumes of stock solutions of 50 % (v/v) methanol and 20 % (v/v) glacial acetic acid. U.K.
4.11. Staining solutions U.K.
4.11.1. Staining solution (stock solution 1) U.K.
Dissolve 3,0 g Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 (C.I. 42655) in 1 000 ml 90 % (v/v) methanol using a magnetic stirrer (approximately 45 minutes), filter through two medium-speed folded filters.
4.11.2. Staining solution (stock solution 2) U.K.
Dissolve 5,0 g copper sulphate pentahydrate in 1 000 ml 20 % (v/v) acetic acid.
4.11.3. Staining solution (working solution) U.K.
Mix together 125 ml of each of the stock solutions (4.11.1, 4.11.2) immediately prior to staining.
Note: The staining solution should be prepared on the day that it is used. U.K.
5. EQUIPMENT U.K.
5.1. Glass plates (265 × 125 × 4 mm); rubber roller (width 15 cm); levelling table U.K.
5.2. Gel carrier sheet (265 × 125 mm) U.K.
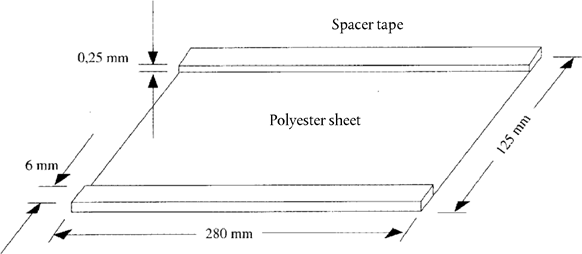
5.3. Covering sheet (280 × 125 mm). Stick on strip of adhesive tape (280 × 6 × 0,25 mm) to each long edge (see Figure 1) U.K.
5.4. Electrofocusing chamber with cooling plate (e.g. 265 × 125 mm) and suitable power supply (≥ 2,5 kV) or automatic electrophoresis device U.K.
5.5. Circulation cryostat, thermostatically controlled at 12 ± 0,5 °C U.K.
5.6. Centrifuge, adjustable to 3 000 g U.K.
5.7. Electrode strips (≥ 265 mm long) U.K.
5.8. Plastic dropping bottles for the anode and cathode solutions U.K.
5.9. Sample applicators (10 × 5 mm, viscose or low protein-adsorption filter paper) U.K.
5.10. Stainless steel or glass staining and destaining dishes (e.g. 280 × 150 mm instrument trays) U.K.
5.12. Adjustable rod homogenizer (10 mm shaft diameter), rpm range 8 000 to 20 000 U.K.
5.13. Magnetic stirrer U.K.
5.14. Ultrasonic bath U.K.
5.15. Film welder U.K.
5.16. 25 μl micropipettes U.K.
5.17. Vacuum concentrator or freeze-dryer U.K.
5.18. Thermostatically controlled water bath adjustable to 35 and 40 ± 1 °C with shaker U.K.
5.19. Densitometer equipment reading at λ = 634 nm U.K.
6. PROCEDURE U.K.
6.1. Sample preparation U.K.
6.1.1. Isolation of caseins U.K.
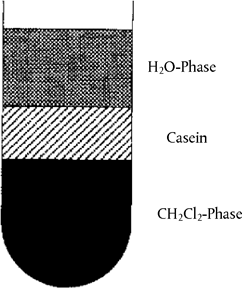
Weigh the amount equivalent to 5 g dry mass of cheese or the reference standards into a 100 ml centrifuge tube, add 60 ml distilled water and homogenize with a rod homogenizer ( 8 000 to 10 000 rpm). Adjust to pH 4,6 with dil. acetic acid (4.5.1) and centrifuge (5 minutes, 3 000 g). Decant the fat and whey, homogenize the residue at 20 000 rpm in 40 ml distilled water adjusted to pH 4,5 with dil. acetic acid (4.5.1), add 20 ml dichloromethane (4.5.2), homogenize again and centrifuge (5 minutes, 3 000 g). Remove the casein layer that lies between the aqueous and organic phases (see Figure 2) with a spatula and decant off both phases. Rehomogenise the casein in 40 ml distilled water (see above) and 20 ml dichloromethane (4.5.2) and centrifuge. Repeat this procedure until both extraction phases are colourless (two to three times). Homogenize the protein residue with 50 ml acetone (4.5.3) and filter through a medium-speed folded filter paper. Wash the residue on the filter with two separate 25 ml portions of acetone each time and allow to dry in the air or a stream of nitrogen, then pulverize finely in a mortar.
Note: Dry casein isolates should be kept at –20 °C. U.K.
6.1.2. Plasmin cleavage of β-caseins to intensify γ-caseins U.K.
Disperse 25 mg of isolated caseins (6.1.1) in 0,5 ml ammonium carbonate buffer (4.7.1) and homogenize for 20 minutes by e.g. using ultrasonic treatment. Heat to 40 °C and add 10 μl plasmin (4.7.2), mix and incubate for one hour at 40 °C with continuous shaking. To inhibit the enzyme add 20 μl ε-aminoproic acid solution (4.7.3), then add 200 mg of solid urea and 2 mg of dithiothreitol.
Note: To obtain more symmetry in the focused casein bands it is advisable to freeze-dry the solution after adding the ε-aminocaproic acid and then dissolving the residues in 0,5 ml protein dissolving buffer (4.6). U.K.
6.2. Preparation of the urea containing polyacrylamide gels U.K.
With the aid of a few drops of water roll the gel carrier sheet (5.2) onto a glass plate (5.1), removing any extraneous water with paper towel or tissue. Roll the cover sheet (5.3) with spacers (0,25 mm) onto another glass plate in the same way. Lay the plate horizontally on a levelling table.
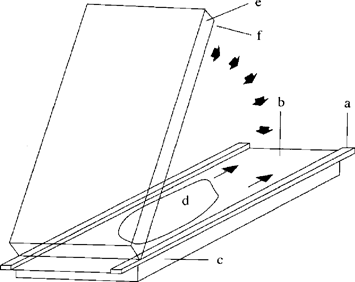
Add 10 μl Temed (4.1.3.1) to the prepared and de-aerated gel solution (4.1.2), stir and add 10 μl PER-solution (4.1.3.2), mix thoroughly and immediately pour out evenly onto the centre of the cover sheet. Place one edge of the gel carrier plate (sheet side down) on the cover sheet plate and lower it slowly so that a gel film forms between the sheets and spreads out regularly and free of bubbles (Figure 3). Carefully lower the gel carrier plate completely using a thin spatula and place three more glass plates on top of it to act as weights. After polymerization is complete (about 60 minutes) remove the gel polymerized onto the gel carrier sheet along with the cover sheet by tipping the glass plates. Clean the reverse of the carrier sheet carefully to remove gel residues and urea. Weld the gel sandwich into a film tube and store in a refrigerator (maximum six weeks).
Note: The cover sheet with the spacers can be re-used. The polyacrylamide gel can be cut to smaller sizes, recommended when there are few samples or if an automatic electrophoresis device is used (two gels, size 4,5 × 5 cm). U.K.
6.3. lsoelectric focusing U.K.
Set the cooling thermostat to 12 °C. Wipe off the reverse of the gel carrier sheet with kerosene, then drip a few drops of kerosene (4.2) onto the centre of the cooling block. Then roll the gel sandwich, carrier side down, onto it, taking care to avoid bubbles. Wipe off any excess kerosene and remove the cover sheet. Soak the electrode strips with the electrode solutions (4.3, 4.4), cut to gel length and place in the positions provided (distance of electrodes 9,5 cm).
Conditions for isoelectric focusing: U.K.
6.3.1. Gel size 265 × 125 × 0,25 mm U.K.
| a Sample application: After pre-focusing (step 1), pipette 18 μl of the sample and standard solutions onto the sample applicators (10 × 5 mm), place them on the gel at 1 mm intervals from each other and 5 mm longitudinally from the anode and press lightly. Carry out focusing using the above conditions, carefully removing the sample applicators after the 60 minutes of sample focusing. | |||||
| Step | Time (min.) | Voltage (V) | Current (mA) | Power (W) | Volt-hours (Vh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1. Pre-focusing | 30 | maximum 2 500 | maximum 15 | constant 4 | c. 300 |
2. Sample focusing a | 60 | maximum 2 500 | maximum 15 | constant 4 | c. 1 000 |
3. Final focusing | 60 | maximum 2 500 | maximum 5 | maximum 20 | c. 3 000 |
| 40 | maximum 2 500 | maximum 6 | maximum 20 | c. 3 000 | |
| 30 | maximum 2 500 | maximum 7 | maximum 25 | c. 3 000 | |
Note: If thickness or width of the gels are changed, the values for current and power have to be suitably adjusted (e.g. double the values for electric current and power if a 265 × 125 × 0,5 mm gel is used). U.K.
6.3.2. Example of a voltage programme for an automatic electrophoresis device (2 gels of 5,0 × 4,5 cm), electrodes without strips applied directly to the gel U.K.
Place sample applicator in step 2 at 0 Vh.
Remove sample applicator in step 2 at 30 Vh.
6.4. Protein staining U.K.
6.4.1. Protein fixation U.K.
Remove the electrode strips immediately after turning off the power and put the gel immediately into a staining/destaining dish filled with 200 ml fixative (4.9); leave for 15 minutes, shaking continuously.
6.4.2. Washing and staining the gel plate U.K.
Thoroughly drain off the fixative and wash the gel plate twice for 30 seconds each time with 100 ml destaining solution (4.10). Pour off the destaining solution and fill the dish with 250 ml staining solution (4.11.3); allow to stain for 45 minutes with gentle shaking.
6.4.3. Destaining the gel plate U.K.
Pour off the staining solution, wash the gel plate twice using a 100 ml destaining solution (4.10) each time, then shake with 200 ml destaining solution for 15 minutes and repeat the destaining step at least two or three times until the background is clear and uncoloured. Then rinse the gel plate with distilled water (2 × 2 minutes) and dry in the air (2 to 3 hours) or with a hairdryer (10 to 15 minutes).
Note 1: Carry out fixing, washing, staining and destaining at 20 °C. Do not use elevated temperatures. U.K.
Note 2: If more sensitive silver staining (e.g. Silver Staining Kit, Protein, Pharmacia Biotech, Code No 17-1150-01) is preferred, plasmin-treated casein samples have to be diluted to 5 mg/ml. U.K.
7. EVALUATION U.K.
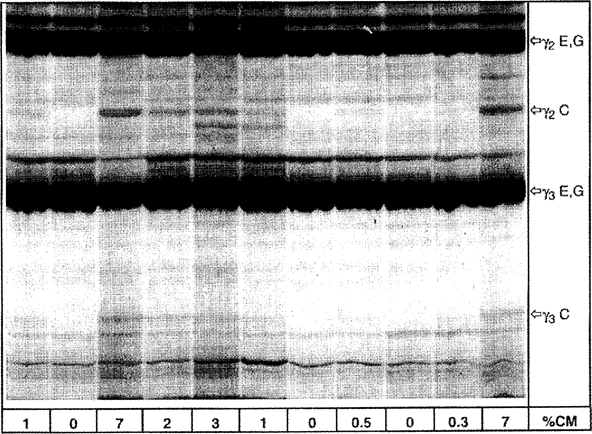
Evaluation is performed by comparing the protein patterns of the unknown sample with reference standards on the same gel. Detection of cow's milk in cheeses from ewe's milk, goat's milk and buffalo milk and mixtures of ewe's, goat's and buffalo milk is done via the γ 3 - and γ 2 -caseins, whose isoelectric points range between pH 6,5 and pH 7,5 (Figures 4 a, b, Figure 5). The detection limit is less than 0,5 %.
7.1. Visual estimation U.K.
For visual evaluation of the amount of bovine milk it is advisable to adjust the concentrations of samples and standards to obtain the same level of intensity of the ovine, caprine and/or buffalo γ 2 - and γ 3 -caseins (see ‘γ 2 E,G,B’ and ‘γ 3 E,G,B’ in Figures 4 a, b and Figure 5). After which the amount of bovine milk (less than, equal to or greater than 1 %) in the unknown sample can be judged directly by comparing the intensity of the bovine γ 3 - and γ 2 -caseins (see ‘γ 3 C’ and ‘γ 2 C’ in Figures 4 a, b and Figure 5) to those of the 0 % and 1 % reference standards (ewe, goat) or, laboratory interim-standards (buffalo).
7.2. Densitometric estimation U.K.
If available, apply densitometry (5.19) for the determination of the peak area ratio of bovine to ovine, caprine and/or buffalo γ 2 - and γ 3 -caseins (see Figure 5). Compare this value to γ 2 - and γ 3 -casein peak area ratio of the 1 % reference standard (ewe, goat) or laboratory interim-standard (buffalo) analysed on the same gel.
Note: The method is operating satisfactorily, if there is a clear positive signal for both bovine γ 2 - and γ 3 -caseins in the 1 % reference standard but not in the 0 % reference standard. If not, optimize the procedure following the details of the method precisely. U.K.
A sample is judged as being positive, if both bovine γ 2 - and γ 3 -caseins or the corresponding peak area ratios are equal to or greater than the level of the 1 % reference standard.
8. REFERENCES U.K.
Addeo F., Moio L., Chianese L., Stingo C., Resmini P., Berner I, Krause I., Di Luccia A., Bocca A.: Use of plasmin to increase the sensitivity of the detection of bovine milk in ovine and/or caprine cheese by gel isoelectric focusing of γ 2 -caseins. Milchwissenschaft 45, 708-711 (1990).
Addeo F., Nicolai M.A., Chianese L., Moio L., Spagna Musso S., Bocca A., Del Giovine L.: A control method to detect bovine milk in ewe and water buffalo cheese using immunoblotting. Milchwissenschaft 50, 83-85 (1995).
Krause I., Berner I, Klostermeyer H.: Sensitive detection of cow milk in ewe and goat milk and cheese by carrier ampholyte — and carrier ampholyte/immobilized pH gradient — isoelectric focusing of γ-caseins using plasmin as signal amplifier. in: Electrophoresis-Forum 89 (B. J. Radola, ed.) pp 389-393, Bode-Verlag, München (1989).
Krause Ι., Belitz H.-D., Kaiser K.-P.: Nachweis von Kuhmilch in Schaf and Ziegenmilch bzw. -käse durch isoelektrische Fokussierung in harnstoffhaltigen Polyacrylamidgelen. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 174, 195-199 (1982).
Radola B.J.: Ultrathin-layer isoelectric focusing in 50-100 μm polyacrylamide gels on silanised glass plates or polyester films. Electrophoresis 1, 43-56 (1980).
Figure 1 Schematic drawing of the covering sheet U.K.
Figure 2 Casein layer floating between aqueous and organic phases after centrifugation U.K.
Figure 3 Flapping technique for casting of ultrathin polyacrylamide gels U.K.
a = spacer tape (0,25 mm); b = covering sheet (5.3); c, e = glass plates (5.1); d = gel solution (4.1.2); f = gel carrier sheet (5.2)
Figure 4a Isoelectric focusing of plasmin-treated caseins from ewe's and goat's milk cheese containing different amounts of cow's milk. U.K.
% CM = percentage of cow's milk, C = cow, E = ewe, G = goat
Upper half of the IEF gel is shown.
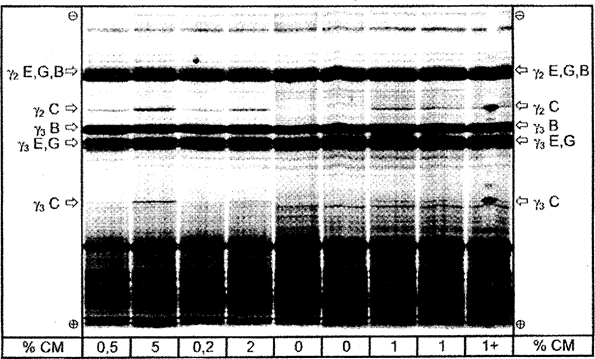
Figure 4b Isoelectric focusing of plasmin treated caseins from cheese made from mixtures of ewe's, goat's and buffalo milk containing different amounts of cow's milk. U.K.
% CM = percentage of cow's milk; 1 + = sample containing 1 % of cow's milk and spiked with pure bovine casein at the middle of the track. C = cow, E = ewe, G = goat, B = buffalo.
Total separation distance of the IEF gel is shown.
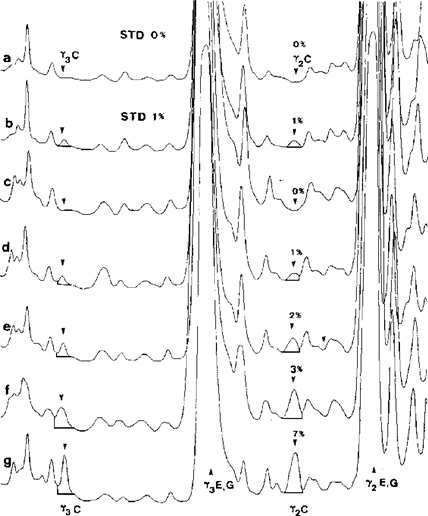
Figure 5 Superposition of densitograms of standards (STD) and cheese samples made from a mixture of ewe's and goat's milk after isoelectric focusing. U.K.
a,b = standards containing 0 and 1 % of cow's milk; c-g = cheese samples containing 0, 1, 2, 3 and 7 % of cow's milk. C = cow, E = ewe, G = goat.
Upper half of the IEF gel was scanned at λ = 634 nm.]
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThis Attachment only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
Y Rhestrau you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
Gweler y wybodaeth ychwanegol ochr yn ochr â’r cynnwys
Rhychwant ddaearyddol: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Mae’r llinell amser yma yn dangos y fersiynau gwahanol a gymerwyd o EUR-Lex yn ogystal ag unrhyw fersiynau dilynol a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig.
Cymerir dyddiadau fersiynau’r UE o ddyddiadau’r dogfennau ar EUR-Lex ac efallai na fyddant yn cyfateb â’r adeg pan ddaeth y newidiadau i rym ar gyfer y ddogfen.
Ar gyfer unrhyw fersiynau a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig, bydd y dyddiad yn cyd-fynd â’r dyddiad cynharaf y daeth y newid (e.e. ychwanegiad, diddymiad neu gyfnewidiad) a weithredwyd i rym. Am ragor o wybodaeth gweler ein canllaw i ddeddfwriaeth ddiwygiedig ar Ddeall Deddfwriaeth.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill