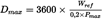- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/1718Dangos y teitl llawn
Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/1718 of 20 September 2016 amending Regulation (EU) No 582/2011 with respect to emissions from heavy-duty vehicles as regards the provisions on testing by means of portable emission measurement systems (PEMS) and the procedure for the testing of the durability of replacement pollution control devices (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
Rhagor o Adnoddau
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
Mae hon yn eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n deillio o’r UE
Mae unrhyw newidiadau sydd wedi cael eu gwneud yn barod gan y tîm yn ymddangos yn y cynnwys a chyfeirir atynt gydag anodiadau.Ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael bydd tair fersiwn o’r ddeddfwriaeth yma i’w gwirio at ddibenion gwahanol. Y fersiwn legislation.gov.uk yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn y Deyrnas Unedig. Y Fersiwn UE sydd ar EUR-lex ar hyn o bryd yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn yr UE h.y. efallai y bydd arnoch angen y fersiwn hon os byddwch yn gweithredu busnes yn yr UE. EUR-Lex Y fersiwn yn yr archif ar y we yw’r fersiwn swyddogol o’r ddeddfwriaeth fel yr oedd ar y diwrnod ymadael cyn cael ei chyhoeddi ar legislation.gov.uk ac unrhyw newidiadau ac effeithiau a weithredwyd yn y Deyrnas Unedig wedyn. Mae’r archif ar y we hefyd yn cynnwys cyfraith achos a ffurfiau mewn ieithoedd eraill o EUR-Lex. The EU Exit Web Archive legislation_originated_from_EU_p3
Status:
EU_status_warning_original_version
This legislation may since have been updated - see the latest available (revised) version
ANNEX II
Annex II to Regulation (EU) No 582/2011 is amended as follows:
point 2.1 is replaced by the following:
‘2.1.The conformity of in-service vehicles or engines of an engine family shall be demonstrated by testing vehicles on the road operated over their normal driving patterns, conditions and payloads. The in-service conformity test shall be representative for vehicles operated on their real driving routes, with their normal payload and with the usual professional driver of the vehicle. When the vehicle is operated by a driver other than the usual professional driver of the particular vehicle, the alternative driver shall be skilled and trained to operate vehicles of the category subject to be tested.’;
point 2.3 is replaced by the following:
‘2.3.The manufacturer shall demonstrate to the approval authority that the chosen vehicle, driving patterns and conditions are representative for the engine family. The requirements as specified in point 4.5 shall be used to determine whether the driving patterns are acceptable for in-service conformity testing.’;
point 4.1 is replaced by the following:
‘4.1. Vehicle payload
Normal payload is a payload between 10 and 100 % of the maximum payload.
The maximum payload is the difference between technically permissible maximum laden mass of the vehicle and the mass of the vehicle in running order as specified in accordance to Annex I to Directive 2007/46/EC.
For the purpose of in-service conformity testing, the payload may be reproduced and an artificial load may be used.
Approval authorities may request to test the vehicle with any payload between 10 and 100 % of the maximum vehicle payload. In case the mass of the PEMS equipment needed for operation exceeds 10 % of the maximum vehicle payload this mass may be considered as minimum payload.
Vehicles of category N3 shall be tested, when applicable, with a semi-trailer.’;
points 4.4.1 to 4.5.5 are replaced by the following:
‘4.4.1.The test lubricating oil shall be market oil and must comply with the specifications of the engine manufacturer.
Oil samples shall be taken.
4.4.2. Fuel
The test fuel shall be market fuel covered by Directive 98/70/EC and relevant CEN standards or reference fuel as specified in Annex IX to this Regulation. Fuel samples shall be taken.
A manufacturer may request not to sample the fuel from a gas engine.
4.4.2.1.If the manufacturer has, in accordance with Section 1 of Annex I to this Regulation, declared the capability to meet the requirements of this Regulation on market fuels declared in point 3.2.2.2.1 of the Information Document as set out in Appendix 4 to Annex I to this Regulation, at least one test shall be conducted on each of the declared market fuels.
4.4.3.For exhaust after-treatment systems that use a reagent to reduce emissions, the reagent shall be market reagent and must comply with the specifications of the engine manufacturer. A sample of the reagent shall be taken. The reagent shall not be frozen.
4.5. Trip requirements
The shares of operation shall be expressed as a percentage of the total trip duration.
The trip shall consist of urban driving followed by rural and motorway driving according to the shares specified in points 4.5.1 to 4.5.4. Where another testing order is justified for practical reasons and after the agreement of the approval authority another order may be used, however, the test shall always start with the urban driving.
For the purpose of this Section, ‘approximately’ shall mean the target value ± 5 %.
Urban, rural and motorway parts can be determined either on the basis of:
geographical coordinates (by means of a map), or
first acceleration method.
In case the trip composition is determined on the basis of geographical coordinates, the vehicle should not exceed, for a cumulative period longer than 5 % of the total duration of each part of the trip, the following speed:
50 km/h in the urban part,
75 km/h in the rural part (90 km/h in the case of vehicles of categories M1 and N1)
In case the trip composition is determined by means of the first acceleration method, the first acceleration above 55 km/h (70 km/h in the case of vehicles of categories M1 and N1) shall indicate the beginning of the rural part and the first acceleration above 75 km/h (90 km/h in the case of vehicles of categories M1 and N1) shall indicate the beginning of the motorway part.
The criteria for differentiation between urban, rural and motorway operation shall be agreed with the approval authority prior to the beginning of the test.
Average speed in urban operation shall be between 15 and 30 km/h.
Average speed in rural operation shall be between 45 and 70 km/h (60 and 90 km/h in the case of vehicles of categories M1 and N1).
Average speed in motorway operation shall be above 70 km/h (90 km/h in the case of vehicles of categories M1 and N1).
4.5.1.For M1 and N1 vehicles the trip shall consist of approximately 34 % urban, 33 % rural and 33 % motorway operation.
4.5.2.For N2, M2 and M3 vehicles the trip shall consist of approximately 45 % urban, 25 % rural and 30 % motorway operation. M2 and M3 vehicles of Class I, II or Class A as defined in UN/ECE Regulation 107 shall be tested in approximately 70 % urban and 30 % rural operation.
4.5.3.For N3 vehicles the trip shall consist of approximately 20 % urban, 25 % rural and 55 % motorway operation.
4.5.4.For the purpose of the assessment of the trip composition, the duration of the share shall be calculated from the moment when the coolant temperature has reached 343 K (70 °C) for the first time or after the coolant temperature is stabilised within +/– 2 K over a period of 5 minutes whichever comes first but no later than 15 minutes after engine start. In accordance with paragraph 4.5 the period elapsed to reach the coolant temperature of 343 K (70 °C) shall be operated under urban driving conditions.
Artificial warming-up of the emission control systems prior to the test is prohibited.
4.5.5.The following distribution of the characteristic trip values from the WHDC database may serve as additional guidance for the evaluation of the trip:
accelerating: 26,9 % of the time;
decelerating: 22,6 % of the time;
cruising: 38,1 % of the time;
stop (vehicle speed = 0): 12,4 % of the time.’;
point 4.6.5 is replaced by the following:
‘4.6.5.The test duration shall be long enough to complete between four and seven times the work performed during the WHTC or produce between four and seven times the CO2 reference mass in kg/cycle from the WHTC as applicable.’;
point 4.6.10 is replaced by the following:
‘4.6.10.If the particle exhaust after-treatment system undergoes a non-continuous regeneration event during the trip or an OBD class A or B malfunction occurs during the test, the manufacturer can request the trip to be voided.’;
point 5.1.2.2 is replaced by the following:
‘5.1.2.2.The conformity of the ECU torque signal is considered to be sufficient if the calculated torque remains within the full load torque tolerance specified in point 5.2.5 of Annex I.’;
Appendix 1 is amended as follows:
point 1 is replaced by the following:
‘1.INTRODUCTION
This Appendix describes the procedure to determine gaseous emissions from on-vehicle on-road measurements using portable emissions measurement systems (hereinafter ‘PEMS’). The pollutant emissions to be measured from the exhaust of the engine include the following components: carbon monoxide, total hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides for compression ignition engines and carbon monoxide, non-methane hydrocarbons, methane and nitrogen oxides for positive ignition engines. Additionally, carbon dioxide shall be measured to enable the calculation procedures described in Sections 4 and 5.
For engines fuelled with natural gas, the manufacturer, technical service or approval authority may choose to measure the total hydrocarbon (THC) emissions only instead of measuring the methane and non-methane hydrocarbon emissions. In that case, the emission limit for the total hydrocarbon emissions is the same as the one specified in Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 for methane emissions. For the purposes of the calculation of the conformity factors pursuant to points 4.2.3 and 4.3.2, the applicable limit shall in that case be the methane emission limit only.
For engines fuelled with gases other than natural gas, the manufacturer, technical service or approval authority may choose to measure the total hydrocarbon (THC) emissions instead of measuring the non-methane hydrocarbon emissions. In that case, the emission limit for the total hydrocarbon emissions is the same as the one specified in Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 for non-methane hydrocarbon emissions. For the purposes of the calculation of the conformity factors pursuant to points 4.2.3 and 4.3.2, the applicable limit shall in that case be the non-methane emission limit.’;
in point 2.2., the sentence ‘The parameters summarised in Table 1 shall be measured and recorded:’ is replaced by the following:
‘The parameters as specified in Table 1 shall be measured and recorded at a constant frequency of 1,0 Hz or higher. The original raw data shall be kept by the manufacturer and shall be made available, upon request, to the approval authority and the Commission.’;
the following point 2.2.1 is inserted:
‘2.2.1. Data reporting format
Emission values as well as any other relevant parameters shall be reported and exchanged as csv-formatted data file. Parameter values shall be separated by a comma, ASCII-Code #h2C. The decimal marker of numerical values shall be a point, ASCII-Code #h2E. Lines shall be terminated by carriage return, ASCII-Code #h0D. No thousands separators shall be used.’;
points 2.6.1 and 2.6.2 are replaced by the following:
‘2.6.1. Test start
Emissions sampling, measurement of the exhaust parameters and recording of the engine and ambient data shall commence prior to starting the engine. The coolant temperature shall not exceed 303 K (30 °C) at the beginning of the test. In case ambient temperature exceeds 303 K (30 °C) at the beginning of the test, the coolant temperature shall not exceed the ambient temperature by more than 2 °C. The data evaluation shall start after the coolant temperature has reached 343 K (70 °C) for the first time or after the coolant temperature is stabilised within +/– 2 K over a period of 5 minutes whichever comes first but no later than 15 minutes after engine start.
2.6.2. Test run
Emission sampling, measurement of the exhaust parameters and recording of the engine and ambient data shall continue throughout the normal in-use operation of the engine. The engine may be stopped and started, but emissions sampling shall continue throughout the entire test.
Periodic zero-checks of the PEMS gas analysers may be conducted every 2 hours and the results may be used to perform a zero drift correction. The data recorded during the checks shall be flagged and shall not be used for the emission calculations.
In case of interrupted GPS signal the GPS data may be calculated based on the ECU vehicle speed and a map, for a consecutive period of less than 60 s. If the cumulative loss of GPS signal exceeds 3 % of the total trip duration, the trip should be declared void.’;
point 3.2.1 is replaced by the following:
‘3.2.1. Analysers and EFM data
The consistency of the data (exhaust mass flow measured by the EFM and gas concentrations) shall be verified using a correlation between the measured fuel flow from the ECU and the fuel flow calculated using the formula in paragraph 8.4.1.7 of Annex 4 to UN/ECE Regulation No 49. A linear regression shall be performed for the measured and calculated fuel rate values. The method of least squares shall be used with the best fit equation having the form:
y = mx + b
where:
y is the calculated fuel flow [g/s]
m is the slope of the regression line
x is the measured fuel flow [g/s]
b is the y intercept of the regression line
The slope (m) and the coefficient of determination (r2) shall be calculated for each regression line. It is recommended to perform this analysis in the range from 15 % of the maximum value to the maximum value and at a frequency greater or equal to 1 Hz. For a test to be considered valid, the following two criteria shall be evaluated:
Table 2
Tolerances
| Slope of the regression line, m | 0,9 to 1,1 — Recommended |
| Coefficient of determination r2 | min. 0,90 — Mandatory’; |
point 4.1 is replaced by the following:
‘4.1. Averaging window principle
The emissions shall be integrated using a moving averaging window method, based on the reference CO2 mass or the reference work. The principle of the calculation is as follows: The mass emissions are not calculated for the complete data set, but for sub-sets of the complete data set, the length of these sub-sets being determined so as to match the engine CO2 mass or work measured over the reference laboratory transient cycle. The moving average calculations are conducted with a time increment Δt equal to the data sampling period. These sub-sets used to average the emissions data are referred to as “averaging windows” in the following points.
Any invalidated data shall not be considered for the calculation of the work or CO2 mass and the emissions of the averaging window.
The following data shall be considered as not valid data:
zero drift check of the instruments;
the data outside the conditions specified in points 4.2 and 4.3 of Annex II.
The mass emissions (mg/window) shall be determined as described in paragraph 8.4.2.3 of Annex 4 to UN/ECE Regulation No 49.
Figure 1 Vehicle speed versus time and vehicle averaged emissions, starting from the first averaging window, versus time
’;
point 4.2.2 is replaced by the following:
‘4.2.2. Selection of valid windows
4.2.2.1.Before the dates referred to in Article 17a, points 4.2.2.1.1 to 4.2.2.1.4 shall apply.
4.2.2.1.1.The valid windows are the windows whose average power exceeds the power threshold of 20 % of the maximum engine power. The percentage of valid windows shall be equal or greater than 50 %.
4.2.2.1.2.If the percentage of valid windows is less than 50 %, the data evaluation shall be repeated using lower power thresholds. The power threshold shall be reduced in steps of 1 % until the percentage of valid windows is equal to or greater than 50 %.
4.2.2.1.3.In any case, the lower threshold shall not be lower than 15 %.
4.2.2.1.4.The test shall be void if the percentage of valid windows is less than 50 % at a power threshold of 15 %.
4.2.2.2.From the dates referred to in Article 17a, points 4.2.2.2.1 and 4.2.2.2.2 shall apply.
4.2.2.2.1.The valid windows are the windows whose average power exceeds the power threshold of 10 % of the maximum engine power.
4.2.2.2.2.The test shall be void if the percentage of valid windows is less than 50 % or if there are no valid windows left in urban only operations after the 90 percentile rule has been applied.’;
point 4.3.1 is replaced by the following:
‘4.3.1. Selection of valid windows
4.3.1.1.Before the dates referred to in Article 17a, points 4.3.1.1.1 to 4.3.1.1.4 shall apply.
4.3.1.1.1.The valid windows shall be the windows whose duration does not exceed the maximum duration calculated from:
where:
D max is the maximum window duration, s,
P max is the maximum engine power, kW.
4.3.1.1.2.If the percentage of valid windows is less than 50 %, the data evaluation shall be repeated using longer window durations. This is achieved by decreasing the value of 0,2 in the formula given in point 4.3.1 by steps of 0,01 until the percentage of valid windows is equal to or greater than 50 %.
4.3.1.1.3.In any case, the lowered value in above formula shall not be lower than 0,15.
4.3.1.1.4.The test shall be void if the percentage of valid windows is less than 50 % at a maximum window duration calculated in accordance with points 4.3.1.1, 4.3.1.1.2 and 4.3.1.1.3.
4.3.1.2.From the dates referred to in Article 17a, points 4.3.1.2.1 and 4.3.1.2.2 shall apply.
4.3.1.2.1.The valid windows shall be the windows whose duration does not exceed the maximum duration calculated from:
where:
D max is the maximum window duration, s,
P max is the maximum engine power, kW.
4.3.1.2.2.The test shall be void if the percentage of valid windows is less than 50 %.’;
in Appendix 2, point 3.1 is replaced by the following:
‘3.1. Exhaust gas flow meter (EFM) tailpipe connection
The installation of the EFM shall not increase the backpressure by more than the value recommended by the engine manufacturer, nor increase the length of the tailpipe by more than 2 m. As for the all the components of the PEMS equipment, the installation of the EFM shall comply with the locally applicable road safety regulations and insurance requirements.’.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThis Annex only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
Y Rhestrau you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill