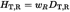- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Council Directive 2013/59/EuratomShow full title
Council Directive 2013/59/Euratom of 5 December 2013 laying down basic safety standards for protection against the dangers arising from exposure to ionising radiation, and repealing Directives 89/618/Euratom, 90/641/Euratom, 96/29/Euratom, 97/43/Euratom and 2003/122/Euratom
You are here:
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 17/01/20141.05 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: CHAPTER II
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
CHAPTER IIU.K. DEFINITIONS
Article 4U.K.Definitions
For the purpose of this Directive, the following definitions shall apply:
"Absorbed dose" (D) is the energy absorbed per unit mass
where
is the mass of the matter in this volume element.
In this Directive, absorbed dose denotes the dose averaged over a tissue or an organ. The unit for absorbed dose is the gray (Gy) where one gray is equal to one joule per kilogram: 
"accelerator" means equipment or installation in which particles are accelerated, emitting ionising radiation with energy higher than 1 mega-electron volt (MeV);
"accidental exposure" means an exposure of individuals, other than emergency workers, as a result of an accident;
"activation" means a process through which a stable nuclide is transformed into a radionuclide by irradiating with particles or high-energy photons the material in which it is contained;
"activity" (A) is the activity of an amount of a radionuclide in a particular energy state at a given time. It is the quotient of dN by dt, where dN is the expectation value of the number of nuclear transitions from that energy state in the time interval dt:
The unit of activity is the becquerel (Bq);
"apprentice" means a person receiving training or instruction within an undertaking with a view to exercising a specific skill;
"authorisation" means the registration or licensing of a practice;
"becquerel" (Bq) is the special name of the unit of activity. One becquerel is equivalent to one nuclear transition per second: 
"building material" means any construction product for incorporation in a permanent manner in a building or parts thereof and the performance of which has an effect on the performance of the building with regard to exposure of its occupants to ionising radiation;
"carers and comforters" means individuals knowingly and willingly incurring an exposure to ionising radiation by helping, other than as part of their occupation, in the support and comfort of individuals undergoing or having undergone medical exposure;
"clearance levels" means values established by the competent authority or in national legislation, and expressed in terms of activity concentrations, at or below which materials arising from any practice subject to notification or authorisation may be released from the requirements of this Directive;
"clinical audit" means a systematic examination or review of medical radiological procedures which seeks to improve the quality and outcome of patient care through structured review, whereby medical radiological practices, procedures and results are examined against agreed standards for good medical radiological procedures, with modification of practices, where appropriate, and the application of new standards if necessary;
"clinical responsibility" means responsibility of a practitioner for individual medical exposures, in particular, justification; optimisation; clinical evaluation of the outcome; cooperation with other specialists and staff, as appropriate, regarding practical aspects of medical radiological procedures; obtaining information, if appropriate, on previous examinations; providing existing medical radiological information and/or records to other practitioners and/or the referrer, as required; and giving information on the risk of ionising radiation to patients and other individuals involved, as appropriate;
"committed effective dose" (E(τ)) is the sum of the committed organ or tissue equivalent doses HT(τ) resulting from an intake, each multiplied by the appropriate tissue weighting factor wT. It is defined by:
In specifying E(τ), is given in the number of years over which the integration is made. For the purpose of complying with dose limits specified in this Directive, is a period of 50 years following intake for adults and up to the age of 70 for infants and children. The unit for committed effective dose is the sievert (Sv);
"committed equivalent dose" (HT(τ)) is the integral over time (t) of the equivalent dose rate in tissue or organ T that will be received by an individual as a result of an intake.
It is given by:
for an intake at time t0 where
is the time over which the integration is performed.
In specifying HT(τ), is given in number of years over which the integration is made. For the purpose of complying with dose limits specified in this Directive, τ is a period of 50 years for adults and up to the age of 70 for infants and children. The unit for committed equivalent dose is the sievert (Sv);
"competent authority" means an authority or system of authorities designated by Member States as having legal authority for the purposes of this Directive;
"consumer product" means a device or manufactured item into which one or more radionuclides have deliberately been incorporated or produced by activation, or which generates ionising radiation, and which can be sold or made available to members of the public without special surveillance or regulatory control after sale;
"contamination" means the unintended or undesirable presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids or gases or on the human body;
"controlled area" means an area subject to special rules for the purpose of protection against ionising radiation or preventing the spread of radioactive contamination and to which access is controlled;
"diagnostic reference levels" means dose levels in medical radiodiagnostic or interventional radiology practices, or, in the case of radio-pharmaceuticals, levels of activity, for typical examinations for groups of standard-sized patients or standard phantoms for broadly defined types of equipment;
"disused source" means a sealed source which is no longer used or intended to be used for the practice for which authorisation was granted but continues to require safe management;
"dose constraint" means a constraint set as a prospective upper bound of individual doses, used to define the range of options considered in the process of optimisation for a given radiation source in a planned exposure situation;
"dose limit" means the value of the effective dose (where applicable, committed effective dose) or the equivalent dose in a specified period which shall not be exceeded for an individual;
"dosimetry service" means a body or an individual competent to calibrate, read or interpret individual monitoring devices, or to measure radioactivity in the human body or in biological samples, or to assess doses, whose capacity to act in this respect is recognised by the competent authority;
"effective dose" (E) is the sum of the weighted equivalent doses in all the tissues and organs of the body from internal and external exposure. It is defined by the expression:
where
is the absorbed dose averaged over tissue or organ T, due to radiation R,
is the radiation weighting factor and
is the tissue weighting factor for tissue or organ T.
The values for wT and wR are specified in Annex II. The unit for effective dose is the sievert (Sv);
"emergency" means a non-routine situation or event involving a radiation source that necessitates prompt action to mitigate serious adverse consequences for human health and safety, quality of life, property or the environment, or a hazard that could give rise to such serious adverse consequences;
"emergency exposure situation" means a situation of exposure due to an emergency;
"emergency management system" means a legal or administrative framework establishing responsibilities for emergency preparedness and response, and arrangements for decision making in the event of an emergency exposure situation;
"emergency occupational exposure" means exposure received in an emergency exposure situation by an emergency worker;
"emergency response plan" means arrangements to plan for adequate response in the event of an emergency exposure situation on the basis of postulated events and related scenarios;
"emergency worker" means any person having a defined role in an emergency and who might be exposed to radiation while taking action in response to the emergency;
"environmental monitoring" means the measurement of external dose rates due to radioactive substances in the environment or of concentrations of radionuclides in environmental media;
"equivalent dose" (HT) is the absorbed dose, in tissue or organ T weighted for the type and quality of radiation R. It is given by:
where
is the absorbed dose averaged over tissue or organ T, due to radiation R,
is the radiation weighting factor.
When the radiation field is composed of types and energies with different values of wR, the total equivalent dose, HT, is given by:
The values for wR are specified in Annex II, Part A. The unit for equivalent dose is the sievert (Sv);
"exemption level" means a value established by a competent authority or in legislation and expressed in terms of activity concentration or total activity at or below which a radiation source is not subject to notification or authorisation;
"existing exposure situation" means an exposure situation that already exists when a decision on its control has to be taken and which does not call or no longer calls for urgent measures to be taken;
"exposed worker" means a person, either self-employed or working under an employer, who is subject to exposure at work carried out within a practice regulated by this Directive and who is liable to receive doses exceeding one or other of the dose limits for public exposure;
"exposure" means the act of exposing or condition of being exposed to ionising radiation emitted outside the body (external exposure) or within the body (internal exposure);
"extremities" means the hands, forearms, feet and ankles;
"health detriment" means reduction in length and quality of life occurring in a population following exposure, including those arising from tissue reactions, cancer and severe genetic disorder;
"health screening" means a procedure using medical radiological installations for early diagnosis in population groups at risk;
"high-activity sealed source" means a sealed source for which the activity of the contained radionuclide is equal to or exceeds the relevant activity value laid down in Annex III;
"individual detriment" means clinically observable deleterious effects in individuals or their descendants, the appearance of which is either immediate or delayed and, in the latter case, implies a probability rather than a certainty of appearance;
"inspection" means an investigation by or on behalf of any competent authority to verify compliance with national legal requirements;
"intake" means the total activity of a radionuclide entering the body from the external environment;
"interventional radiology" means the use of X-ray imaging techniques to facilitate the introduction and guidance of devices in the body for diagnostic or treatment purposes;
"ionising radiation" means energy transferred in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves of a wavelength of 100 nanometres or less (a frequency of 3 × 1015 hertz or more) capable of producing ions directly or indirectly;
"licence" means permission granted in a document by the competent authority to carry out a practice in accordance with specific conditions laid down in that document;
"medical exposure" means exposure incurred by patients or asymptomatic individuals as part of their own medical or dental diagnosis or treatment, and intended to benefit their health, as well as exposure incurred by carers and comforters and by volunteers in medical or biomedical research;
"medical physics expert" means an individual or, if provided for in national legislation, a group of individuals, having the knowledge, training and experience to act or give advice on matters relating to radiation physics applied to medical exposure, whose competence in this respect is recognised by the competent authority;
"medical radiological" means pertaining to radiodiagnostic and radiotherapeutic procedures, and interventional radiology or other medical uses of ionising radiation for planning, guiding and verification purposes;
"medical radiological installation" means a facility where medical radiological procedures are performed;
"medical radiological procedure" means any procedure giving rise to medical exposure;
"members of the public" means individuals who may be subject to public exposure;
"natural radiation source" means a source of ionising radiation of natural, terrestrial or cosmic origin;
"non-medical imaging exposure" means any deliberate exposure of humans for imaging purposes where the primary intention of the exposure is not to bring a health benefit to the individual being exposed;
"normal exposure" means exposure expected to occur under the normal operating conditions of a facility or activity (including maintenance, inspection, decommissioning), including minor incidents that can be kept under control, i.e. during normal operation and anticipated operational occurrences;
"notification" means submission of information to the competent authority to notify the intention to carry out a practice within the scope of this Directive;
"occupational exposure" means exposure of workers, apprentices and students, incurred in the course of their work;
"occupational health service" means a health professional or body competent to perform medical surveillance of exposed workers and whose capacity to act in that respect is recognised by the competent authority;
"orphan source" means a radioactive source which is neither exempted nor under regulatory control, e.g. because it has never been under regulatory control or because it has been abandoned, lost, misplaced, stolen or otherwise transferred without proper authorisation;
"outside worker" means any exposed worker who is not employed by the undertaking responsible for the supervised and controlled areas, but performs activities in those areas, including, apprentices and students;
"planned exposure situation" means an exposure situation that arises from the planned operation of a radiation source or from a human activity which alters exposure pathways, so as to cause the exposure or potential exposure of people or the environment. Planned exposure situations may include both normal exposures and potential exposures.
"potential exposure" means exposure that is not expected with certainty but may result from an event or sequence of events of a probabilistic nature, including equipment failures and operating errors;
"practical aspects of medical radiological procedures" means the physical conduct of a medical exposure and any supporting aspects, including handling and use of medical radiological equipment, the assessment of technical and physical parameters (including radiation doses), calibration and maintenance of equipment, preparation and administration of radio-pharmaceuticals, and image processing;
"practice" means a human activity that can increase the exposure of individuals to radiation from a radiation source and is managed as a planned exposure situation;
"practitioner" means a medical doctor, dentist or other health professional who is entitled to take clinical responsibility for an individual medical exposure in accordance with national requirements;
"processing" means chemical or physical operations on radioactive material including the mining, conversion, enrichment of fissile or fertile nuclear material and the reprocessing of spent fuel;
"protective measures" means measures, other than remedial measures, for the purpose of avoiding or reducing doses that might otherwise be received in an emergency exposure situation or an existing exposure situation;
"public exposure" means exposure of individuals, excluding any occupational or medical exposure;
"quality assurance" means all those planned and systematic actions necessary to provide adequate assurance that a structure, system, component or procedure will perform satisfactorily in compliance with agreed standards. Quality control is a part of quality assurance;
"quality control" means the set of operations (programming, coordinating, implementing) intended to maintain or to improve quality. It includes monitoring, evaluation and maintenance at required levels of all characteristics of performance of equipment that can be defined, measured, and controlled;
"radiation generator" means a device capable of generating ionising radiation, such as X-rays, neutrons, electrons or other charged particles;
"radiation protection expert" means an individual or, if provided for in the national legislation, a group of individuals having the knowledge, training and experience needed to give radiation protection advice in order to ensure the effective protection of individuals, and whose competence in this respect is recognised by the competent authority;
"radiation protection officer" means an individual who is technically competent in radiation protection matters relevant for a given type of practice to supervise or perform the implementation of the radiation protection arrangements;
"radiation source" means an entity that may cause exposure, such as by emitting ionising radiation or by releasing radioactive material;
"radioactive material" means material incorporating radioactive substances;
"radioactive source" means a radiation source incorporating radioactive material for the purpose of utilising its radioactivity;
"radioactive substance" means any substance that contains one or more radionuclides the activity or activity concentration of which cannot be disregarded from a radiation protection point of view;
"radioactive waste" means radioactive material in gaseous, liquid or solid form for which no further use is foreseen or considered by the Member State or by a legal or natural person whose decision is accepted by the Member State, and which is regulated as radioactive waste by a competent regulatory authority under the legislative and regulatory framework of the Member State;
"radiodiagnostic" means pertaining to in-vivo diagnostic nuclear medicine, medical diagnostic radiology using ionising radiation, and dental radiology;
"radiotherapeutic" means pertaining to radiotherapy, including nuclear medicine for therapeutic purposes;
"radon" means the radionuclide Rn-222 and its progeny, as appropriate;
"exposure to radon" means exposure to radon progeny;
"reference level" means in an emergency exposure situation or in an existing exposure situation, the level of effective dose or equivalent dose or activity concentration above which it is judged inappropriate to allow exposures to occur as a result of that exposure situation, even though it is not a limit that may not be exceeded;
"referrer" means a medical doctor, dentist or other health professional who is entitled to refer individuals for medical radiological procedures to a practitioner, in accordance with national requirements;
"registration" means permission granted in a document by the competent authority, or granted by national legislation, through a simplified procedure, to carry out a practice in accordance with conditions laid down in national legislation or specified by a competent authority for this type or class of practice;
"regulatory control" means any form of control or regulation applied to human activities for the enforcement of radiation protection requirements;
"remedial measures" means the removal of a radiation source or the reduction of its magnitude (in terms of activity or amount) or the interruption of exposure pathways or the reduction of their impact for the purposes of avoiding or reducing doses that might otherwise be received in an existing exposure situation;
"representative person" means an individual receiving a dose that is representative of the more highly exposed individuals in the population, excluding those individuals having extreme or rare habits;
"sealed source" means a radioactive source in which the radioactive material is permanently sealed in a capsule or incorporated in a solid form with the objective of preventing, under normal conditions of use, any dispersion of radioactive substances;
"sievert" (Sv) is the special name of the unit of equivalent or effective dose. One sievert is equivalent to one joule per kilogram: 
"storage" means the holding of radioactive material, including spent fuel, a radioactive source or radioactive waste, in a facility with the intention of retrieval;
"supervised area" means an area subject to supervision for the purpose of protection against ionising radiation;
"source container" means an assembly of components intended to guarantee the containment of a sealed source, where it is not an integral part of the source but is meant for shielding the source during its transport and handling;
"spacecraft" means a manned vehicle designed to operate at an altitude of more than 100 km above sea level;
"standard values and relationships" means values and relationships recommended in chapters 4 and 5 of ICRP Publication 116 for the estimation of doses from external exposure and chapter 1 of ICRP Publication 119 for the estimation of doses from internal exposure, including updates approved by Member States. Member State may approve the use of specific methods in specified cases relating to the physico-chemical properties of the radionuclide or other features of the exposure situation or of the exposed individual;
"thoron" means the radionuclide Rn-220 and its progeny, as appropriate;
"undertaking" means a natural or legal person who has legal responsibility under national law for carrying out a practice, or for a radiation source (including cases where the owner or holder of a radiation source does not conduct related human activities);
"unintended exposure" means medical exposure that is significantly different from the medical exposure intended for a given purpose.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThis Chapter only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources