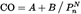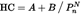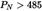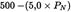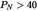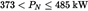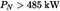- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As made)
The Recreational Craft Regulations 2017
You are here:
- UK Statutory Instruments
- 2017 No. 737
- SCHEDULE 1
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects for the The Recreational Craft Regulations 2017, SCHEDULE 1.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
Regulation 2(1)
SCHEDULE 1U.K.(Annex I of the Directive)
Commencement Information
I1Sch. 1 in force at 3.8.2017, see reg. 1
A.Essential requirements for the design and construction of products referred to in Article 2(1)
1.WATERCRAFT DESIGN CATEGORIES
| Design category | Wind force(Beaufort scale) | Significant wave height(H ⅓, metres) |
|---|---|---|
| A | exceeding 8 | exceeding 4 |
| B | up to, and including, 8 | up to, and including, 4 |
| C | up to, and including, 6 | up to, and including, 2 |
| D | up to, and including, 4 | up to, and including, 0,3 |
Explanatory notes:
A recreational craft given design category A is considered to be designed for winds that may exceed wind force 8 (Beaufort scale) and significant wave height of 4 m and above but excluding abnormal conditions, such as storm, violent storm, hurricane, tornado and extreme sea conditions or rogue waves.
A recreational craft given design category B is considered to be designed for a wind force up to, and including, 8 and significant wave height up to, and including, 4 m.
A watercraft given design category C is considered to be designed for a wind force up to, and including, 6 and significant wave height up to, and including, 2 m.
A watercraft given design category D is considered to be designed for a wind force up to, and including, 4 and significant wave height up to, and including, 0,3 m, with occasional waves of 0,5 m maximum height.
Watercraft in each design category must be designed and constructed to withstand the parameters in respect of stability, buoyancy, and other relevant essential requirements listed in this [F1Annex] [F1Schedule], and to have good handling characteristics.
Textual Amendments
F1Word in Sch. 1 Pt. A substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(2)(a) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
2.GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1.Watercraft identification
Each watercraft shall be marked with an identification number including the following information:
Textual Amendments
F2Words in Sch. 1 Pt. A para. 2.1 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(2)(b)(i) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
F3Words in Sch. 1 Pt. A para. 2.1 substituted (N.I.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment) (Northern Ireland) (EU Exit) Regulations 2020 (S.I. 2020/1112), reg. 1(b), Sch. 15 para. 7(a)(i)
Detailed requirements for the identification number referred to in the first paragraph are set out in the relevant [F4harmonised][F4designated] standard.
Textual Amendments
F4Word in Sch. 1 Pt. A para. 2.1 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(2)(b)(ii) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
2.2.Watercraft builder’s plate
Each watercraft shall carry a permanently affixed plate mounted separately from the watercraft identification number, containing at least the following information:
manufacturer’s name, registered trade name or registered trade mark, as well as contact address;
watercraft design category in accordance with Section 1;
manufacturer’s maximum recommended load derived from point 3.6 excluding the weight of the contents of the fixed tanks when full;
number of persons recommended by the manufacturer for which the watercraft was designed.
Textual Amendments
F5Words in Sch. 1 Pt. A para. 2.2 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(2)(c)(i) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
In the case of post-construction assessment, the contact details and the requirements referred to in point (a) shall include those of the [F6notified] [F6approved] body which has carried out the conformity assessment.
Textual Amendments
F6Word in Sch. 1 Pt. A para. 2.2 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(2)(c)(ii) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
2.3.Protection from falling overboard and means of reboarding
Watercraft shall be designed to minimise the risks of falling overboard and to facilitate reboarding. Means of reboarding shall be accessible to or deployable by a person in the water unaided.
2.4.Visibility from the main steering position
For recreational craft, the main steering position shall give the operator, under normal conditions of use (speed and load), good all-round visibility.
2.5.Owner’s manual
Each product shall be provided with an owner’s manual [F7in accordance with Article 7(7) and Article 9(4)] [F7including the instructions and safety information referred to in regulations 15 and 22]. That manual shall provide all the information necessary for safe use of the product drawing particular attention to set up, maintenance, regular operation, prevention of risks and risk management.
Textual Amendments
F7Words in Sch. 1 Pt. A para. 2.5 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(2)(d) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
3.INTEGRITY AND STRUCTURAL REQUIREMENTS
3.1.Structure
The choice and combination of materials and its construction shall ensure that the watercraft is strong enough in all respects. Special attention shall be paid to the design category in accordance with Section 1, and the manufacturer’s maximum recommended load in accordance with point 3.6.
3.2.Stability and freeboard
The watercraft shall have sufficient stability and freeboard considering its design category in accordance with Section 1 and the manufacturer’s maximum recommended load in accordance with point 3.6.
3.3.Buoyancy and flotation
The watercraft shall be constructed as to ensure that it has buoyancy characteristics appropriate to its design category in accordance with Section 1 and the manufacturer’s maximum recommended load in accordance with point 3.6. All habitable multihull recreational craft susceptible of inversion shall have sufficient buoyancy to remain afloat in the inverted position.
Watercraft of less than 6 metres in length that are susceptible to swamping when used in their design category shall be provided with appropriate means of flotation in the swamped condition.
3.4.Openings in hull, deck and superstructure
Openings in hull, deck(s) and superstructure shall not impair the structural integrity of the watercraft or its weather tight integrity when closed.
Windows, port lights, doors and hatch covers shall withstand the water pressure likely to be encountered in their specific position, as well as point loads applied by the weight of persons moving on deck.
Through hull fittings designed to allow water passage into the hull or out of the hull, below the waterline corresponding to the manufacturer’s maximum recommended load in accordance with point 3.6, shall be fitted with a means of shutoff which shall be readily accessible.
3.5.Flooding
All watercraft shall be designed so as to minimise the risk of sinking.
Where appropriate, particular attention shall be paid to:
cockpits and wells, which should be self-draining or have other means of keeping water out of the watercraft interior;
ventilation fittings;
removal of water by pumps or other means.
3.6.Manufacturer’s maximum recommended load
The manufacturer’s maximum recommended load (fuel, water, provisions, miscellaneous equipment and people (in kilograms)) for which the watercraft was designed, shall be determined in accordance with the design category (Section 1), stability and freeboard (point 3.2) and buoyancy and flotation (point 3.3).
3.7.Life raft stowage
All recreational craft of design categories A and B, and recreational craft of design categories C and D longer than 6 metres shall be provided with one or more stowage points for a life raft (life rafts) large enough to hold the number of persons the recreational craft was designed to carry as recommended by the manufacturer. Life raft stowage point(s) shall be readily accessible at all times.
3.8.Escape
All habitable multihull recreational craft susceptible of inversion shall be provided with viable means of escape in the event of inversion. Where there is a means of escape provided for use in the inverted position, it shall not compromise the structure (point 3.1), the stability (point 3.2) or buoyancy (point 3.3) whether the recreational craft is upright or inverted.
Every habitable recreational craft shall be provided with viable means of escape in the event of fire.
3.9.Anchoring, mooring and towing
All watercraft, taking into account their design category and their characteristics, shall be fitted with one or more strong points or other means capable of safely accepting anchoring, mooring and towing loads.
4.HANDLING CHARACTERISTICS
The manufacturer shall ensure that the handling characteristics of the watercraft are satisfactory with the most powerful propulsion engine for which the watercraft is designed and constructed. For all propulsion engines, the maximum rated engine power shall be declared in the owner’s manual.
5.INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS
5.1.Engines and engine compartments
5.1.1.Inboard engine
All inboard mounted engines shall be placed within an enclosure separated from living quarters and installed so as to minimise the risk of fires or spread of fires as well as hazards from toxic fumes, heat, noise or vibrations in the living quarters.
Engine parts and accessories that require frequent inspection and/or servicing shall be readily accessible.
The insulating materials inside the engine compartment shall not sustain combustion.
5.1.2.Ventilation
The engine compartment shall be ventilated. The ingress of water into the engine compartment through openings must be minimised.
5.1.3.Exposed parts
Unless the engine is protected by a cover or its own enclosure, exposed moving or hot parts of the engine that could cause personal injury shall be effectively shielded.
5.1.4.Outboard propulsion engine starting
Every outboard propulsion engine fitted on any watercraft shall have a device to prevent the engine being started in gear, except:
when the engine produces less than 500 Newton’s (N) of static thrust;
when the engine has a throttle limiting device to limit thrust to 500 N at the time of starting the engine.
5.1.5.Personal watercraft running without driver
Personal watercraft shall be designed either with an automatic propulsion engine cut-off or with an automatic device to provide reduced speed, circular, forward movement when the driver dismounts deliberately or falls overboard.
5.1.6.Tiller-controlled outboard propulsion engines shall be equipped with an emergency stopping device which can be linked to the helmsman.
5.2.Fuel system
5.2.1.General
The filling, storage, venting and fuel-supply arrangements and installations shall be designed and installed so as to minimise the risk of fire and explosion.
5.2.2.Fuel tanks
Fuel tanks, lines and hoses shall be secured and separated or protected from any source of significant heat. The material the tanks are made of and their method of construction shall be in accordance with their capacity and the type of fuel.
Petrol fuel tank spaces shall be ventilated.
Petrol fuel tanks shall not form part of the hull and shall be:
protected against fire from any engine and from all other sources of ignition;
separated from living quarters.
Diesel fuel tanks may be integral with the hull.
5.3.Electrical system
Electrical systems shall be designed and installed so as to ensure proper operation of the watercraft under normal conditions of use and shall be such as to minimise risk of fire and electric shock.
All electrical circuits, except engine starting circuits supplied from batteries, shall remain safe when exposed to overload.
Electric propulsion circuits shall not interact with other circuits in such a way that either would fail to operate as intended.
Ventilation shall be provided to prevent the accumulation of explosive gases which might be emitted from batteries. Batteries shall be firmly secured and protected from ingress of water.
5.4.Steering system
5.4.1.General
Steering and propulsion control systems shall be designed, constructed and installed in order to allow the transmission of steering loads under foreseeable operating conditions.
5.4.2.Emergency arrangements
Every sailing recreational craft and single-propulsion engine non-sailing recreational craft with remote-controlled rudder steering systems shall be provided with emergency means of steering the recreational craft at reduced speed.
5.5.Gas system
Gas systems for domestic use shall be of the vapour-withdrawal type and shall be designed and installed so as to avoid leaks and the risk of explosion and be capable of being tested for leaks. Materials and components shall be suitable for the specific gas used to withstand the stresses and exposures found in the marine environment.
Each gas appliance intended by the manufacturer for the application for which it is used shall be so installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Each gas-consuming appliance must be supplied by a separate branch of the distribution system, and each appliance must be controlled by a separate closing device. Adequate ventilation must be provided to prevent hazards from leaks and products of combustion.
All watercraft with a permanently installed gas system shall be fitted with an enclosure to contain all gas cylinders. The enclosure shall be separated from the living quarters, accessible only from the outside and ventilated to the outside so that any escaping gas drains overboard.
In particular, any permanently installed gas system shall be tested after installation.
5.6.Fire protection
5.6.1.General
The type of equipment installed and the layout of the watercraft shall take account of the risk and spread of fire. Special attention shall be paid to the surroundings of open flame devices, hot areas or engines and auxiliary machines, oil and fuel overflows, uncovered oil and fuel pipes and routing of electrical wiring in particular away from heat sources and hot areas.
5.6.2.Fire-fighting equipment
Recreational craft shall be supplied with fire-fighting equipment appropriate to the fire hazard, or the position and capacity of fire-fighting equipment appropriate to the fire hazard shall be indicated. The craft shall not be put into service until the appropriate fire-fighting equipment is in place. Petrol engine compartments shall be protected by a fire extinguishing system that avoids the need to open the compartment in the event of fire. Where fitted, portable fire extinguishers shall be readily accessible and one shall be so positioned that it can easily be reached from the main steering position of the recreational craft.
5.7.Navigation lights, shapes and sound signals
Where navigation lights, shapes and sound signals are fitted, they shall comply with the 1972 COLREG (The International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea) or CEVNI (European Code for Interior Navigations for inland waterways) Regulations as appropriate.
5.8.Discharge prevention and installations facilitating the delivery ashore of waste
Watercraft shall be constructed so as to prevent the accidental discharge of pollutants (oil, fuel, etc.) overboard.
Any toilet fitted in a recreational craft shall be connected solely to a holding tank system or water treatment system.
Recreational craft with installed holding tanks shall be fitted with a standard discharge connection to enable pipes of reception facilities to be connected with the recreational craft discharge pipeline.
In addition, any through-the-hull pipes for human waste shall be fitted with valves which are capable of being secured in the closed position.
B.Essential requirements for exhaust emissions from propulsion engines
Propulsion engines shall comply with the essential requirements for exhaust emissions set out in this Part.
1.PROPULSION ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
1.1.Each engine shall be clearly marked with the following information:
engine manufacturer’s name, registered trade name or registered trade mark and contact address; and, if applicable, the name and contact address of the person adapting the engine;
engine type, engine family, if applicable;
a unique engine serial number;
Textual Amendments
F8Words in Sch. 1 Pt. B para. 1.1 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(3)(a) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
1.2.The marks referred to in point 1.1 must be durable for the normal life of the engine and must be clearly legible and indelible. If labels or plates are used, they must be attached in such a manner that the fixing is durable for the normal life of the engine, and the labels/plates cannot be removed without destroying or defacing them.
1.3.The marks must be secured to an engine part necessary for normal engine operation and not normally requiring replacement during the engine life.
1.4.The marks must be located so as to be readily visible after the engine has been assembled with all the components necessary for engine operation.
2.EXHAUST EMISSION REQUIREMENTS
Propulsion engines shall be designed, constructed and assembled so that when correctly installed and in normal use, emissions shall not exceed the limit values obtained from point 2.1, Table 1 and point 2.2, Tables 2 and 3:
2.1.Values applying for the purposes of Article 55(2) and Table 2 of point 2.2:
Table 1
Where A, B and n are constants in accordance with the table, PN is the rated engine power in kW.
2.2.Values applying from 18 January 2016:
Table 2
Exhaust emission limits for compression ignition (CI) engines(2)
b ++ Any compression-ignition engine shall not exceed a Carbon monoxide (CO) emission limit of 5,0 g/kWh. | |||
| Swept VolumeSV(L/cyl) | Rated Engine Power PN(kW) | ParticulatesPT(g/kWh) | Hydrocarbons + Nitrogen Oxides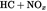 (g/kWh) (g/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  | The values referred to in table 1 | |
 (1) (1) | 0,3 | 4,7 | |
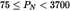 | 0,15 | 5,8 | |
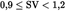 |  | 0,14 | 5,8 |
 | 0,12 | 5,8 | |
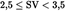 | 0,12 | 5,8 | |
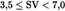 | 0,11 | 5,8 | |
Table 3
Exhaust emission limits for spark ignition (SI) engines
2.3.Test cycles:
Test cycles and weighting factors to be applied:
The following requirements of ISO standard 8178-4:2007 shall be used, taking into account the values set out in the table below.
For variable speed CI engines test cycle E1 or E5 shall be applied or alternatively, above 130 kW, test cycle E3 may be applied. For variable speed SI engines test cycle E4 shall be applied.
| Cycle E1, Mode number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Rated speed | Intermediate speed | Low-idle speed | |||
| Torque, % | 100 | 75 | 75 | 50 | 0 | |
| Weighting factor | 0,08 | 0,11 | 0,19 | 0,32 | 0,3 | |
| Speed | Rated speed | Intermediate speed | Low-idle speed | |||
| Cycle E3, Mode number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Speed, % | 100 | 91 | 80 | 63 | ||
| Power, % | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | ||
| Weighting factor | 0,2 | 0,5 | 0,15 | 0,15 | ||
| Cycle E4, Mode number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Speed, % | 100 | 80 | 60 | 40 | Idle | |
| Torque, % | 100 | 71,6 | 46,5 | 25,3 | 0 | |
| Weighting factor | 0,06 | 0,14 | 0,15 | 0,25 | 0,4 | |
| Cycle E5, Mode number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Speed, % | 100 | 91 | 80 | 63 | Idle | |
| Power, % | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 0 | |
| Weighting factor | 0,08 | 0,13 | 0,17 | 0,32 | 0,3 | |
[F9Notified] [F9Approved] bodies may accept tests carried out on the basis of other tests cycles as specified in a [F10harmonised] [F10designated] standard and as applicable for the engine duty cycle.
Textual Amendments
F9Word in Sch. 1 Pt. B para. 2.3 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(3)(b)(i) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
F10Word in Sch. 1 Pt. B para. 2.3 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(3)(b)(ii) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
2.4.Application of the propulsion engine family and choice of parent propulsion engine
The engine manufacturer shall be responsible for defining those engines from his range which are to be included in an engine family.
A parent engine shall be selected from an engine family in such a way that its emissions characteristics are representative for all engines in that engine family. The engine incorporating those features that are expected to result in the highest specific emissions (expressed in g/kWh), when measured on the applicable test cycle, should normally be selected as the parent engine of the family.
2.5.Test fuels
The test fuel used for exhaust emission testing shall meet the following characteristics:
| Petrol Fuels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Property | RF-02-99Unleaded | RF-02-03Unleaded | ||
| min | max | min | max | |
| Research Octane Number (RON) | 95 | — | 95 | — |
| Motor Octane Number (MON) | 85 | — | 85 | — |
| Density at 15 oC (kg/m3) | 748 | 762 | 740 | 754 |
| Initial boiling point (°C) | 24 | 40 | 24 | 40 |
| Mass fraction of sulphur (mg/kg) | — | 100 | — | 10 |
| Lead content (mg/l) | — | 5 | — | 5 |
| Reid vapour pressure (kPa) | 56 | 60 | — | — |
| Vapour pressure (DVPE) (kPa) | — | — | 56 | 60 |
| Diesel Fuels | ||||
| Property | RF-06-99 | RF-06-03 | ||
| min | max | min | max | |
| Cetane number | 52 | 54 | 52 | 54 |
| Density at 15 oC (kg/m3) | 833 | 837 | 833 | 837 |
| Final boiling point (°C) | — | 370 | — | 370 |
| Flash point (°C) | 55 | — | 55 | — |
| Mass fraction of sulphur (mg/kg) | To be reported | 300 (50) | — | 10 |
| Mass fraction of ash (%) | To be reported | 0,01 | — | 0,01 |
[F11Notified] [F11Approved] bodies may accept tests carried out on the basis of other tests fuel as specified in a [F12harmonised] [F12designated] standard.
Textual Amendments
F11Word in Sch. 1 Pt. B para. 2.5 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(3)(b)(i) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
F12Word in Sch. 1 Pt. B para. 2.5 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(3)(b)(ii) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
3.DURABILITY
The manufacturer of the engine shall supply engine installation and maintenance instructions, which if applied should mean that the engine in normal use will continue to comply with the limits set out in points 2.1 and 2.2 throughout the normal life of the engine and under normal conditions of use.
This information shall be obtained by the engine manufacturer by use of prior endurance testing, based on normal operating cycles, and by calculation of component fatigue so that the necessary maintenance instructions may be prepared by the manufacturer and issued with all new engines when first placed on the market.
The normal life of the engine is as follows:
For CI engines: 480 hours of operation or 10 years, whichever occurs first;
For SI inboard or stern drive engines with or without integral exhaust:
personal watercraft engines: 350 hours of operation or five years, whichever occurs first;
outboard engines: 350 hours of operation or 10 years, whichever occurs first
4.OWNER’S MANUAL
Each engine shall be provided with an owner’s manual in [F13a language or languages which can be easily understood by consumers and other end-users, as determined by the [F14relevant state] in which the engine is to be marketed] [F13English].
Textual Amendments
F13Word in Sch. 1 Pt. B para. 4 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(3)(c)(i) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
F14Words in Sch. 1 Pt. B para. 4 substituted (N.I.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment) (Northern Ireland) (EU Exit) Regulations 2020 (S.I. 2020/1112), reg. 1(b), Sch. 15 para. 7(a)(ii)
The owner’s manual shall:
Textual Amendments
F15Word in Sch. 1 Pt. B para. 4 substituted (E.W.S.) (31.12.2020) by The Product Safety and Metrology etc. (Amendment etc.) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/696), reg. 1, Sch. 28 para. 43(3)(c)(ii) (with Sch. 28 para. 41) (as amended by S.I. 2020/676, regs. 1(1), 2); 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
C.Essential requirements for noise emissions
Recreational craft with inboard or stern drive engines without integral exhaust, personal watercraft and outboard engines and stern drive engines with integral exhaust shall comply with the essential requirements for noise emissions set out in this Part.
1.NOISE EMISSION LEVELS
1.1.Recreational craft with inboard or stern drive engines without integral exhaust, personal watercraft and outboard engines and stern drive engines with integral exhaust shall be designed, constructed and assembled so that noise emissions shall not exceed the limit values in the following table:
where PN = rated engine power in kW of a single engine at rated speed and LpASmax = maximum sound pressure level in dB.
For twin-engine and multiple-engine units of all engine types an allowance of 3 dB may be applied.
1.2.As an alternative to sound measurement tests, recreational craft with inboard engine configuration or stern drive engine configuration, without integral exhaust, shall be deemed to comply with the noise requirements set out in point 1.1 if they have a Froude number of ≤ 1,1 and a Power to Displacement ratio of ≤ 40 and where the engine and exhaust system are installed in accordance with the engine manufacturer’s specifications.
1.3.‘Froude number’ Fn shall be calculated by dividing the maximum recreational craft speed V (m/s) by the square root of the waterline length lwl (m) multiplied by a given gravitational acceleration constant, g, of 9,8 m/s2.
‘Power to Displacement ratio’ shall be calculated by dividing the rated engine power PN (in kW) by the recreational craft’s displacement D (in tonnes)
2.OWNER’S MANUAL
For recreational craft with inboard engine or stern drive engines without integral exhaust and personal watercraft, the owner’s manual required under point 2.5 of Part A, shall include information necessary to maintain the recreational craft and exhaust system in a condition that, insofar as is practicable, will ensure compliance with the specified noise limit values when in normal use.
For outboard engines and stern drive engines with integral exhaust, the owner’s manual required under Section 4 of Part B shall provide the instructions necessary to maintain the engine in a condition, that insofar as is practicable, will ensure compliance with the specified noise limit values when in normal use.
3.DURABILITY
The provisions on the durability in Section 3 of Part B shall apply mutatis mutandis to the compliance with the requirements on noise emissions set out in Section 1 of this part.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Instrument
PrintThis Schedule only
You have chosen to open The Whole Instrument
The Whole Instrument you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open The Whole Instrument as a PDF
The Whole Instrument you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open the Whole Instrument
The Whole Instrument you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
The Schedules you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As Enacted or Made): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was enacted or made. No changes have been applied to the text.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Explanatory Memorandum
Explanatory Memorandum sets out a brief statement of the purpose of a Statutory Instrument and provides information about its policy objective and policy implications. They aim to make the Statutory Instrument accessible to readers who are not legally qualified and accompany any Statutory Instrument or Draft Statutory Instrument laid before Parliament from June 2004 onwards.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as enacted version that was used for the print copy
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Impact Assessments
Impact Assessments generally accompany all UK Government interventions of a regulatory nature that affect the private sector, civil society organisations and public services. They apply regardless of whether the regulation originates from a domestic or international source and can accompany primary (Acts etc) and secondary legislation (SIs). An Impact Assessment allows those with an interest in the policy area to understand:
- Why the government is proposing to intervene;
- The main options the government is considering, and which one is preferred;
- How and to what extent new policies may impact on them; and,
- The estimated costs and benefits of proposed measures.
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different points in time where a change occurred. The dates will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. The first date in the timeline will usually be the earliest date when the provision came into force. In some cases the first date is 01/02/1991 (or for Northern Ireland legislation 01/01/2006). This date is our basedate. No versions before this date are available. For further information see the Editorial Practice Guide and Glossary under Help.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as made version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources