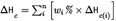- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Council Directive of 20 May 1975 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to aerosol dispensers (75/324/EEC)
You are here:
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 12/02/20180.46 MB
- Revised 09/04/20130.41 MB
- Revised 20/04/20090.26 MB
- Revised 29/04/20080.15 MB
- Revised 05/06/20030.05 MB
- Revised 17/02/19940.05 MB
- Revised 01/01/19860.05 MB
- Revised 01/01/19810.04 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Division 1.
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
1.DEFINITIONSU.K.
1.1.PressuresU.K.
‘Pressures’ means the internal pressures expressed in bars (relative pressures).
1.2.Test pressureU.K.
‘Test pressure’ means the pressure to which an unfilled aerosol dispenser container may be subjected for 25 seconds without any leakage being caused or, in the case of metal or plastic containers, any visible or permanent distortion except as allowed under 6.1.1.2.
1.3.Bursting pressureU.K.
‘Bursting pressure’ means the minimum pressure which causes the aerosol dispenser container to burst or rupture.
1.4.Total capacity of the containerU.K.
‘Total capacity of the container’ means the volume in millilitres of an open container up to the rim of the opening.
1.5.Net capacityU.K.
‘Net capacity’ means the volume in millilitres of a filled and closed aerosol dispenser.
1.6.Volume of liquid phaseU.K.
‘Volume of liquid phase’ means the volume of the non-gaseous phases in the filled and closed aerosol dispenser.
1.7.Test conditionsU.K.
‘Test conditions’ means the values of test and bursting pressures exerted hydraulically at 20° C (± 5° C).
[F11.7a. Substance U.K.
‘ Substance ’ means substance as defined in Article 2(7) of Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008.
Textual Amendments
F1 Inserted by Commission Directive 2013/10/EU of 19 March 2013 amending Council Directive 75/324/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to aerosol dispensers in order to adapt its labelling provisions to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures (Text with EEA relevance).
1.7b. Mixture U.K.
‘ Mixture ’ means mixture as defined in Article 2(8) of Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008.]
[F21.8. Flammable contents U.K.
Contents of aerosols shall be considered as flammable if they contain any component which is classified as flammable:
flammable liquid means a liquid having a flashpoint of not more than 93 °C.
flammable solid means a solid substance or mixture which is readily combustible, or may cause or contribute to fire as a result of friction. Readily combustible solids are powdered, granular, or pasty substances or mixtures which are dangerous if they can be easily ignited by brief contact with an ignition source, such as a burning match, and if the flame spreads rapidly.
flammable gas means a gas or gas mixture having a flammable range with air at 20 °C and a standard pressure of 1,013 bar.
This definition does not cover pyrophoric, self-heating or water-reactive substances and mixtures, which shall never be components of aerosol contents.]
Textual Amendments
[F31.9. Flammable aerosols U.K.
For the purpose of this Directive, an aerosol is considered as ‘ non-flammable ’ , ‘ flammable ’ or ‘ extremely flammable ’ according to its chemical heat of combustion and mass content of flammable components, as follows:
The aerosol is classified as ‘ extremely flammable ’ if it contains 85 % or more flammable components and the chemical heat of combustion exceeds or is equal to 30 kJ/g;
The aerosol is classified as ‘ non-flammable ’ if it contains 1 % or less flammable components and the chemical heat of combustion is less than 20 kJ/g;
All other aerosols will be submitted to the following flammability classification procedures or shall be classified as ‘ extremely flammable ’ . The ignition distance test, the enclosed space test and the foam flammability test shall comply with point 6.3.
1.9.1. Flammable spray aerosols U.K.
In the case of spray aerosols the classification shall be made taking into account the chemical heat of combustion and on the basis of the results of the ignition distance test, as follows:
If the chemical heat of combustion is less than 20 kJ/g:
The aerosol is classified as ‘ flammable ’ if ignition occurs at a distance equal or greater than 15 cm but less than 75 cm;
The aerosol is classified as ‘ extremely flammable ’ if ignition occurs at a distance of 75 cm or more;
If no ignition occurs in the ignition distance test, the enclosed space test shall be performed and in this case, the aerosol is classified as ‘flammable’ if the time equivalent is less than or equal to 300 s/m 3 or the deflagration density is less than or equal to 300 g/m 3 ; otherwise the aerosol is classified as ‘non-flammable’;
If the chemical heat of combustion is equal to or more than 20 kJ/g, the aerosol is classified as ‘ extremely flammable ’ if ignition occurs at a distance of 75 cm or more; otherwise the aerosol is classified as ‘ flammable ’ .
1.9.2. Flammable foam aerosols U.K.
In the case of foam aerosols, the classification shall be made on the basis of the results of the foam flammability test.
The aerosol product shall be classified as ‘ extremely flammable ’ if:
the flame height is 20 cm or more and the flame duration is two seconds or more;
or
the flame height is 4 cm or more and the flame duration is seven seconds or more.
The aerosol product which does not meet the criteria in (a) is classified as ‘ flammable ’ if the flame height is 4 cm or more and the flame duration is two seconds or more.]
Textual Amendments
[F31.10. Chemical Heat of Combustion U.K.
The chemical heat of combustion ΔH c shall be either determined by:
acknowledged rules of technology, described e.g. in standards such as ASTM D 240, ISO 13943 86.1 to 86.3 and NFPA 30B, or found in the scientifically established literature;
or
applying the following calculation method:
The chemical heat of combustion (ΔH c ), in kilojoules per gram (kJ/g), can be calculated as the product of the theoretical heat of combustion (ΔH comb ), and a combustion efficiency, usually less than 1,0 (a typical combustion efficiency is 0,95 or 95 %).
For a composite aerosol formulation, the chemical heat of combustion is the summation of the weighted heats of combustion for the individual components, as follows:
where:
=
chemical heat of combustion (kJ/g) of the product;
=
mass fraction of component i in the product;
=
specific heat of combustion (kJ/g) of component i in the product.
The person responsible for the marketing of the aerosol dispenser has to describe the method used for determining the chemical heat of combustion in a document to be made readily available in an official Community language at the address specified on the label in accordance with point (a) of Article 8(1), if the chemical heat of combustion is used as a parameter for assessing the flammability of aerosols according to the provisions of this Directive.]
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThe Whole Annex
PrintThis Division only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources