- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (31/01/2020)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Council Directive of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to units of measurement and on the repeal of Directive 71/354/EEC (80/181/EEC)
You are here:
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 13/06/20200.32 MB
- Revised 27/05/20090.08 MB
- Revised 09/02/20000.06 MB
- Revised 30/11/19890.15 MB
- Revised 20/12/19840.23 MB
- Revised 21/12/19790.22 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: ANNEX
Version Superseded: 13/06/2020
Alternative versions:
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
[X1ANNEX U.K.
Editorial Information
CHAPTER I U.K. LEGAL UNITS OF MEASUREMENT REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 1 (a)
1. SI UNITS AND THEIR DECIMAL MULTIPLES AND SUBMULTIPLES U.K.
1.1. SI base units U.K.
| Quantity | Unit | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | |
| Length | metre | m |
| Mass | kilogram | kg |
| Time | second | s |
| Electric current | ampere | A |
| Thermodynamic temperature | kelvin | K |
| Amount of substance | mole | mol |
| Luminous intensity | candela | cd |
Definitions of SI base units: U.K.
[F1Unit of length U.K.
A metre is the length of the path travelled in a vacuum by light during 1/ 299 792 458 seconds.
(Seventeenth CGPM (1983), Resolution 1).]
Textual Amendments
Unit of mass U.K.
The kilogram is the unit of mass; it is equal to the mass of the international prototype of the kilogram.
(Third CGPM (1901), page 70 of the conference report).
Unit of time U.K.
The second is the duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium-133 atom.
(Thirteenth CGPM (1967), resolution 1).
Unit of electric current U.K.
The ampere is that constant current, which if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed one metre apart in vacuum, would produce between those conductors a force equal to 2 × 10 -7 newton per metre of length.
(CIPM (1946), resolution 2, approved by the ninth CGPM (1948)).
[F2Unit of thermodynamic temperature U.K.
The kelvin, unit of thermodynamic temperature, is the fraction 1/273,16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.
This definition refers to water having the isotopic composition defined by the following amount-of-substance ratios: 0,00015576 mole of 2 H per mole of 1 H, 0,0003799 mole of 17 O per mole of 16 O and 0,0020052 mole of 18 O per mole of 16 O.
(Thirteenth CGPM (1967), resolution 4 and Twenty-third CGPM (2007), resolution 10)]
Textual Amendments
Unit of amount of substance U.K.
The mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0·012 kilogram of carbon 12.
When the mole is used, the elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles.
(Fourteenth CGPM (1971), resolution 3).
Unit of luminous intensity U.K.
The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency of 540 × 10 12 hertz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of (1/683) watt per steradian.
(Sixteenth CGPM (1979), resolution 3).
1.1.1. [F2Special name and symbol of the SI derived unit of temperature for expressing Celsius temperature] U.K.
| Quantity | Unit | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | |
| Celsius temperature | degree Celsius | °C |
[F3Celsius temperature [X2t] is defined as the difference [X2t = T - T 0] between the two thermodynamic temperatures [X2T] and [X2T 0 where T 0] = 273,15 K. An interval or difference of temperature may be expressed either in kelvins or in degrees Celsius. The unit ‘ degree Celsius ’ is equal to the unit ‘ kelvin ’ .]
Editorial Information
X2 Substituted by Corrigendum to Directive 1999/103/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 January 2000 amending Council Directive 80/181/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to units of measurement (Official Journal of the European Communities L 34 of 9 February 2000).
Textual Amendments
[F21.2. SI derived units] U.K.
F41.2.1.SI supplementary unitsU.K.
| [ F4 |
F4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .]
F4Definitions of SI supplementary units:U.K.
F4Unit of plane angleU.K.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
F4Unit of solid angleU.K.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Textual Amendments
[F21.2.2. General rule for SI derived units U.K.
Units derived coherently from SI base units are given as algebraic expressions in the form of products of powers of the SI base units with a numerical factor equal to 1.
1.2.3. SI derived units with special names and symbols U.K.
| a Special names for the unit of power: the name volt–ampere (symbol ‘ VA ’ ) when it is used to express the apparent power of alternating electric current, and var (symbol ‘ var ’ ) when it is used to express reactive electric power. The ‘ var ’ is not included in GCPM resolutions. | ||||
| Quantity | Unit | Expression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | In terms of other SI units | In terms of SI base units | |
| Plane angle | radian | rad | m · m –1 | |
| Solid angle | steradian | sr | m 2 · m –2 | |
| Frequency | hertz | Hz | s –1 | |
| Force | newton | N | m · kg · s –2 | |
| Pressure, stress | pascal | Pa | N · m –2 | m –1 · kg · s –2 |
| Energy, work; quantity of heat | joule | J | N · m | m 2 · kg · s –2 |
| Power a , radiant flux | watt | W | J · s –1 | m 2 · kg · s –3 |
| Quantity of electricity, electric charge | coulomb | C | s · A | |
| Electric potential, potential difference, electromotive force | volt | V | W · A –1 | m 2 · kg · s –3 · A –1 |
| Electric resistance | ohm | Ω | V · A –1 | m 2 · kg · s –3 · A –2 |
| Conductance | siemens | S | A · V –1 | m –2 · kg –1 · s 3 · A 2 |
| Capacitance | farad | F | C · V –1 | m –2 · kg –1 · s 4 · A 2 |
| Magnetic flux | weber | Wb | V · s | m 2 · kg · s –2 · A –1 |
| Magnetic flux density | tesla | T | Wb · m –2 | kg · s –2 · A –1 |
| Inductance | henry | H | Wb · A –1 | m 2 · kg · s –2 · A –2 |
| Luminous flux | lumen | lm | cd · sr | cd |
| Illuminance | lux | lx | lm · m –2 | m –2 · cd |
| Activity (of a radionuclide) | becquerel | Bq | s –1 | |
| Absorbed dose, specific energy imparted, kerma, absorbed dose index | gray | Gy | J · kg –1 | m 2 · s –2 |
| Dose equivalent | sievert | Sv | J · kg –1 | m 2 · s –2 |
| Catalytic activity | katal | kat | mol · s –1 | |
Units derived from SI base units may be expressed in terms of the units listed in Chapter I.
In particular, derived SI units may be expressed by the special names and symbols given in the above table; for example, the SI unit of dynamic viscosity may be expressed as m –1 · kg · s –1 or N · s · m –2 or Pa · s.]
1.3. Prefixes and their symbols used to designate certain decimal multiples and submultiples U.K.
| [F3Factor | Prefix | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 10 24 | yotta | Y |
| 10 21 | zetta | Z |
| 10 18 | exa | E |
| 10 15 | peta | P |
| 10 12 | tera | T |
| 10 9 | giga | G |
| 10 6 | mega | M |
| 10 3 | kilo | [X3k] |
| 10 2 | hecto | [X3h] |
| 10 1 | deca | da |
| 10 -1 | deci | d |
| 10 -2 | centi | c |
| 10 -3 | milli | m |
| 10 -6 | micro | μ |
| 10 -9 | nano | n |
| 10 -12 | pico | p |
| 10 -15 | femto | f |
| 10 -18 | atto | a |
| 10 -21 | zepto | z |
| 10 -24 | yocto | y] |
The names and symbols of the decimal multiples and submultiples of the unit of mass are formed by attaching prefixes to the word ‘ gram ’ and their symbols to the symbol ‘ g ’ .
Where a derived unit is expressed as a fraction, its decimal multiples and submultiples may be designated by attaching a prefix to units in the numerator or the denominator, or in both these parts.
Compound prefixes, that is to say prefixes formed by the juxtaposition of several of the above prefixes, may not be used.
1.4. Special authorized names and symbols of decimal multiples and submultiples of SI units U.K.
| a The two symbols ‘ I ’ and ‘ L ’ may be used for the litre unit. (Sixteenth CGPM (1979), resolution 6). | |||
| b Unit listed in the International Bureau of Weights and Measures booklet as among the units to be permitted temporarily. | |||
| Quantity | Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | Value | |
| Volume | litre | 1 or L a | 1 l = 1 dm 3 = 10 -3 m 3 |
| Mass | tonne | t | 1 t = 1 Mg = 10 3 kg |
| Pressure, stress | bar | bar b | 1 bar = 10 5 Pa |
Note: U.K.
The prefixes and their symbols listed in 1.3 may be used in conjunction with the units and symbols contained in Table 1.4. U.K.
2. UNITS WHICH ARE DEFINED ON THE BASIS OF SI UNITS BUT ARE NOT DECIMAL MULTIPLES OR SUBMULTIPLES THEREOF U.K.
| a The character (*) after a unit name or symbol indicates that it does not appear in the lists drawn up by the CGPM, CIPM o BIPM. This applies to the whole of this Annex. | |||
| b No international symbol exists. | |||
| Quantity | Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | Value | |
| Plane angle | revolution* a b | 1 revolution = 2 π rad | |
| grade* or gon* | gon* |  | |
| degree | ° | 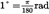 | |
| minute of angle | ′ | 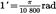 | |
| second of angle | ″ | 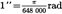 | |
| Time | minute | min | 1 min = 60 s |
| hour | h | 1 h = 3 600 s | |
| day | d | 1 d = 86 400 s | |
Note: U.K.
The prefixes listed in 1.3 may only be used in conjunction with the names ‘ grade ’ or ‘ gon ’ and the symbol ‘ gon ’ . U.K.
[F33. UNITS USED WITH THE SI, WHOSE VALUES IN SI ARE OBTAINED EXPERIMENTALLY U.K.
| Note: | |||
| The prefixes and their symbols listed in 1.3 may be used in conjunction with these two units and with their symbols.] | |||
| Quantity | Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | Definition | |
| Energy | Electronvolt | eV | The electron volt is the kinetic energy acquired by an electron in passing through a potential difference of 1 volt in vaccum |
| Mass | Unified atomic mass unit | u | The unified atomic mass units is equal to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of the nuclide 12 C. |
4. UNITS AND NAMES OF UNITS PERMITTED IN SPECIALIZED FIELDS ONLY U.K.
| Quantity | Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | Value | |
| Vergency of optical systems | dioptre* | 1 dioptre = 1 m -1 | |
| Mass of precious stones | metric carat | 1 metric carat = 2 × 10 -4 kg | |
| Area of farmland and building land | are | a | 1 a = 10 2 m 2 |
| Mass per unit length of textile yarns and threads | tex* | tex* | 1 tex = 10 -6 kg · m -1 |
| Blood pressure and pressure of other body fluids | Millimetre of mercury | mm Hg(*) | 1 mm Hg = 133,322 Pa |
| Effective cross-sectional area | Barn | b | 1 b = 10 -28 m 2 |
Note: U.K.
[F1The prefixes and their symbols listed in 1.3 may be used in conjunction with the above units and symbols, with the exception of the millimetre of mercury and its symbol. The multiple of 10 2 a is, however, called a ‘ hectare ’ .] U.K.
5. COMPOUND UNITS U.K.
Combinations of the units listed in Chapter I form compound units.
[F5CHAPTER II U.K. LEGAL UNITS OF MEASUREMENT REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 1 (b), PERMITTED FOR SPECIFIC USES ONLY
| Field of application | Unit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Approximate value | Symbol | ||
| Road traffic signs, distance and speed measurement | mile | 1 mile = | 1 609 m | mile |
| yard | 1 yd = | 0,9144 m | yd | |
| foot | 1 ft = | 0,3048 m | ft | |
| inch | 1 in = | 2,54 × 10 -2 m | in | |
| Dispense of draught beer and cider; milk in returnable containers | pint | 1 pt = | 0,5683 × 10 -3 m 3 | pt |
| [ F4 ] | ||||
| Transaction in precious metals | troy ounce | 1 oz tr = | 31,10 × 10 -3 kg | oz tr |
[F2The units listed in this Chapter may be combined with each other or with those in Chapter I to form compound units.] ]
Textual Amendments
CHAPTER III U.K. LEGAL UNITS OF MEASUREMENT REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 1 (c)
| QUANTITIES, NAMES OF UNITS, SYMBOLS AND APPROXIMATE VALUES | ||
| a [ F6 ] | ||
| Length | ||
|---|---|---|
| inch | 1 in | = 2·54 × 10 -2 m |
| foot | 1 ft | = 0·3048 m |
| [ F6 ] | ||
| mile | 1 mile | = 1 609 m |
| yard | 1 yard | = 0·9144 m |
| Area | ||
| square foot | 1 sq ft | = 0·929 × 10 -1 m 2 |
| acre | 1 ac | = 4 047 m 2 |
| square yard | 1 sq yd | = 0·8361 m 2 |
| Volume | ||
| fluid ounce | 1 fl oz | = 28·41 × 10 -6 m 3 |
| gill | 1 gill | = 0·1421 × 10 -3 m 3 |
| pint | 1 pt | = 0·5683 × 10 -3 m 3 |
| quart | 1 qt | = 1·137 × 10 -3 m 3 |
| gallon | 1 gal | = 4·546 × 10 -3 m 3 |
| Mass | ||
| ounce (avoirdupois) | 1 oz | = 28·35 × 10 -3 kg |
| troy ounce | 1 oz tr | = 31·10 × 10 -3 kg |
| pound | 1 lb | = 0·4536 kg |
| Energy | ||
| therm | 1 therm | = 105·506 × 10 6 J |
Textual Amendments
Until the date to be fixed under Article 1 (c), the units listed in Chapter III may be combined with each other or with those in Chapter I to form compound units.]
[F7CHAPTER IV U.K. LEGAL UNITS OF MEASUREMENT REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE I (d), PERMITTED IN SPECIALIZED FIELDS ONLY
| Field of application | Unit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Approximate value | Symbol | ||
| Marine navigation | fathom | 1 fm = | 1,829 m | fm |
| Beer, cider, waters, lemonades and fruit juices in returnable containers | pint | 1 pt = | 0,5683 × 10 -3 m 3 | pt |
| fluid ounce | 1 fl oz = | 28,41 × 10 -6 m 3 | fl. oz | |
| Spirit drinks | gill | 1 gill = | 0,142 × 10 -3 m 3 | gill |
| Goods sold loose in bulk | ounce (avoir dupois) | 1 oz = | 28,35 × 10 -3 kg | oz |
| pound | 1 lb = | 0,4536 kg | lb | |
| Gas supply | therm | 1 therm = | 105,506 × 10 6 J | therm |
Until the date to be fixed under Article 1 (d), the units listed in this Chapter may be combined with each other or with those in Chapter I to form compound units.]
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThis Annex only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources
