- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (17/05/2005)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Directive 97/24/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (repealed)Show full title
Directive 97/24/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 1997 on certain components and characteristics of two or three-wheel motor vehicles (repealed)
You are here:
- Directives originating from the EU
- 1997 No. 24
- attachment 2
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 01/01/20160.44 MB
- Revised 11/12/20137.75 MB
- Revised 07/09/20096.33 MB
- Revised 28/11/20063.25 MB
- Revised 08/09/20063.29 MB
- Revised 28/03/20065.31 MB
- Revised 17/05/20054.11 MB
- Revised 10/09/20034.13 MB
- Revised 20/09/20024.04 MB
- Revised 18/08/19974.02 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for:
Version Superseded: 28/03/2006
Alternative versions:
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
CHAPTER 2
LIGHTING AND LIGHT-SIGNALLING DEVICES OF TWO OR THREE-WHEEL MOTOR VEHICLES
[X1LIST OF ANNEXES
| ANNEX I | General requirements applying to the component type-approval of a type of lighting and light-signalling device for two or three-wheel motor vehicles … |
| Appendix 1 | Colours of light emitted — Trichromatic coordinates … |
| Appendix 2 | Examples of arrangements of approval marks … |
| ANNEX II | Requirements concerning the component type-approval of front position (side) lamps, rear lamps, stop lamps, direction indicator lamps, rear registration-plate illuminating device, front fog lamps, rear fog lamps, reversing lamps and retro-reflectors fitted to two or three-wheel motor vehicles … |
| Appendix 1 | Minimum horizontal (H) and vertical (V) angles of spatial light distribution … |
| Appendix 2 | Photometric measurements … |
| Appendix 3 | Photometric measurements of the rear registration-plate illuminating device … |
| Appendix 4 | Information document … |
| Appendix 5 | Component type-approval certificate … |
| ANNEX III | Requirements relating to the component type-approval of devices (headlamps) using incandescent or halogen filament lamps emitting a passing and/or driving beam fitted to two or three-wheel motor vehicles … |
| ANNEX III-A | Headlamps for mopeds … |
| Appendix 1 | Photometric tests on headlamps equipped with category S 3 and S 4 lamps … |
| Appendix 2 | Photometric tests on headlamps equipped with category HS 2 halogen lamps … |
| Appendix 3 | Information document in respect of a type of headlamp intended for mopeds … |
| Appendix 4 | Component type-approval certificate in respect of a type of headlamp intended for mopeds … |
| ANNEX III-B | Headlamps for motorcycles and tricycles emitting a symmetrical passing beam and a driving beam by means of filament lamps … |
| Appendix 1 | Photometric tests … |
| Appendix 2 | Test on the stability of the photometric behaviour of headlamps in operation … |
| Appendix 3 | Requirements for lamps incorporating lenses of plastic material and testing of lens or material samples and of complete lamps … |
| Appendix 4 | Information document in respect of a type of headlamp fitted with filament lamps, emitting a symmetrical passing beam and a driving beam and intended to be fitted to motorcycles and tricycles … |
| Appendix 5 | Component type-approval certificate in respect of a type of headlamp fitted with filament lamps, emitting a symmetrical passing beam and a driving beam and intended for motorcycles and tricycles … |
| ANNEX III-C | Headlamps for motorcycles and tricycles emitting an asymmetrical passing beam and a driving beam and fitted with halogen filament lamps (HS 1 lamps) or filament lamps of category R 2 … |
| Appendix 1 | Measuring screen … |
| Appendix 2 | Test on the stability of the photometric performance of headlamps in operation |
| Appendix 3 | Requirements for lamps incorporating lenses of plastic material and testing of lens or material samples and of complete lamps … |
| Appendix 4 | Information document in respect of a type of headlamp fitted with halogen filament lamps (HS 1 lamps) or filament lamps of category R 2 , emitting an asymmetrical passing beam and a driving beam and intended to be fitted to motorcycles and tricycles … |
| Appendix 5 | Component type-approval certificate in respect of a type of headlamp fitted with halogen filament lamps, (HS 1 lamps) or filament lamps of category R 2 , emitting an asymmetrical passing beam and a driving beam and intended to be fitted to motorcycles and tricycles … |
| ANNEX III-D | Headlamps for motorcycles and tricycles emitting an asymmetrical passing beam and a driving beam and fitted with halogen filament lamps other than HS 1 lamps … |
| Appendix 1 | Measuring screen … |
| Appendix 2 | Tests on the stability of the photometric performance of headlamps in operation |
| Appendix 3 | Requirements for lamps incorporating lenses of plastic material and testing of lens or material samples and of complete lamps … |
| Appendix 4 | Information document in respect of a type of headlamp fitted with halogen filament lamps, emitting an asymmetrical passing beam and a driving beam and intended to be fitted to motorcycles and tricycles … |
| Appendix 5 | Component type-approval certificate in respect of a type of headlamp fitted with halogen filament lamps, emitting an asymmetrical passing beam and a driving beam and intended to be fitted to motorcycles and tricycles … |
| ANNEX IV | Incandescent lamps intended for use in component type-approved lamps for mopeds, motorcycles and tricycles … |
| Appendices 1 to 22 | (See Annex IV) … |
| Appendix 23 | Example of the arrangement of the approval mark … |
| Appendix 24 | Luminous centre and shapes of lamp filaments …] |
ANNEX I
GENERAL REQUIREMENTS APPLYING TO THE COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVAL OF A TYPE OF LIGHTING AND LIGHT-SIGNALLING DEVICE FOR TWO OR THREE-WHEEL MOTOR VEHICLES
1.For the purposes of this Chapter:U.K.
‘type of device’
means devices which do not differ among themselves in such essential respects as the following:
1.1.make or trade name;U.K.
1.2.the characteristics of the optical system;U.K.
1.3.the addition or deletion of components likely to alter the optical results as a result of reflection, refraction or absorption and/or deformation during their operation;U.K.
1.4.their intended use in either right-hand or left-hand driving or both;U.K.
1.5.the materials constituting the lenses and coatings, if any.U.K.
2.APPLICATION FOR THE COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVAL OF A TYPE OF DEVICEU.K.
2.1.The application for the component type-approval of a type of device submitted in compliance with Article 3 of Council Directive 92/61/EEC of 30 June 1992 on the type-approval of two or three-wheel motor vehicles must, moreover, provide the following details:U.K.
2.1.1.the intended function(s) of the device;U.K.
2.1.2.in the case of a headlamp, if designed for running on either side of the road or for left-hand or right-hand running only;U.K.
2.1.3.in the case of a direction indicator: its category.U.K.
2.2.For each type of device for which component type-approval is requested the application must be accompanied by:U.K.
2.2.1.drawings, in triplicate, in sufficient detail to permit identification of the type and setting out the geometrical conditions under which it is fitted to the vehicle, together with the direction of observation which must be taken into account as the reference axis during the tests (horizontal angle H = 0, vertical angle V = 0)and the point which must be taken as the centre of reference during these tests; in the case of a headlamp the drawings must show a vertical (axial) section and a head-on view with, where appropriate, details of the lens fluting; the drawings must also illustrate the position intended for the mandatory component type-approval mark and, where appropriate, additional symbols in relation to the rectangle for that mark;U.K.
2.2.2.a brief technical description giving details, in particular, with the exception of lamps with non-replaceable light sources, of the intended category or categories of filament lamp.U.K.
2.3.Applicants must also submit two samples of the device for which component type-approval is requested.U.K.
2.4.For the test of the plastic material of which the lenses of headlamps(1) and front fog-lamps are made, the following must be supplied:U.K.
2.4.1.thirteen lenses:U.K.
2.4.1.1.six of these lenses may be replaced by six samples of material at least 60 mm × 80 mm in size, having a flat or convex outer surface and a substantially flat area (radius of curvature not less than 300 mm) in the middle measuring at least 15 mm × 15 mm;U.K.
2.4.1.2.every such lens or sample of material must be produced by the method to be used in series production;U.K.
2.4.2.a reflector to which the lens can be fitted in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.U.K.
2.5.The materials making up the lenses and coatings, if any, must be accompanied by the test report on the characteristics of these materials and coatings if they have already been tested.U.K.
2.6.The competent authority must verify the existence of satisfactory arrangements for ensuring effective control of the conformity of production before type-approval is granted.U.K.
3.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS CONCERNING THE MARKING OF AND MARKS ON DEVICESU.K.
3.1.Devices must bear the following in a clearly visible and indelible manner:U.K.
3.1.1.make or trade name;U.K.
3.1.2.a statement of the intended category or categories of filament lamp(s): this is not valid for lamps with non-replaceable light sources;U.K.
3.1.3.in the case of lamps with non-replaceable light sources the rated voltage and rated wattage should be stated;U.K.
3.1.4.the component type-approval mark in accordance with the provisions of Article 8 of Directive 92/61/EEC. In the case of headlamps the marks must be placed on the lens or main body of the lamp (the mirror being considered to be a main body). If the lens cannot be separated from the main body a position on the lens will suffice. That position must be shown on the designs referred to in 2.2.1. For examples, see Appendix 2 to this Annex.U.K.
4.COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVAL OF A DEVICEU.K.
4.1.When at least two devices form part of the same device component type-approval can be granted only if each of those devices meets the requirements of this Chapter.U.K.
5.MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR CONFORMITY OF PRODUCTION CONTROL PROCEDURESU.K.
5.1.GeneralU.K.
5.1.1.The conformity requirements are considered satisfied from a mechanical and geometric standpoint, if the differences do not exceed inevitable manufacturing deviations within the requirements of this Directive.U.K.
5.1.2.With respect to photometric performances, the conformity of series-produced devices must not be contested if, when testing photometric performances of any device chosen at random and in the case of signalling lamps, headlamps or front fog-lamps equipped with standard filament-lamps, no measured value deviates unfavourably by more than 20 % from the minimum values prescribed in this Directive.U.K.
5.1.3.If the results of the test described above do not meet the requirements, in the case of signalling lamps, headlamps or front fog-lamps, tests on devices must be repeated using another standard filament-lamp.U.K.
5.1.4.Devices with apparent defects are disregarded.U.K.
5.1.5.The trichromatic coordinates must be complied with in the case of signalling lamps, headlamps or front fog-lamps when these are equipped with filament lamps set to Standard A colour temperature.U.K.
5.2.Minimum requirements for verification of conformity by the manufacturerU.K.
For each type of device the holder of the approval mark must carry out at least the following tests at appropriate intervals. The tests must be carried out in accordance with the provisions of this Directive.
If any sampling shows non-conformity with regard to the type of test concerned, further samples are taken and tested. The manufacturer must take steps to ensure the conformity of the production concerned.
5.2.1.Nature of testsU.K.
Tests of conformity to this Directive must cover the photometric and colorimetric characteristics for headlamps of motorcycles and tricycles and the verification of the change in vertical position of the cut-off line unde the influence of heat.
5.2.2.Methods used in testsU.K.
5.2.2.1.Tests must generally be carried out in accordance with the methods set out in this Directive.U.K.
5.2.2.2.In any test of conformity carried out by the manufacturer, equivalent methods may be used with the consent of the competent authority responsible for approval tests. The manufacturer is responsible for proving that the methods applied are equivalent to those laid down in this Directive.U.K.
5.2.2.3.The application of 5.2.2.1 and 5.2.2.2 requires regular calibration of test apparatus and its correlation with measurements made by a competent authority.U.K.
5.2.2.4.In all cases, the reference methods must be those laid down in this Directive, particularly for the purpose of administrative verification and sampling.U.K.
5.2.3.Nature of samplingU.K.
Samples of devices are selected at random from the production of a uniform batch. A uniform batch means a set of devices of the same type, defined according to the production methods of the manufacturer.
The assessment must in general cover series production from individual factories. However, a manufacturer may group together records concerning the same type from several factories, provided these operate under the same quality system and quality management.
5.2.4.Measured and recorded photometric and colorimetric characteristicsU.K.
The sampled device is subjected to photometric measurements at the points provided for in the relevant Annexes unless otherwise prescribed. The trichromatic coordinates must be complied with.
5.2.5.Criteria governing acceptabilityU.K.
The manufacturer is responsible for carrying out a statistical study of the test results and for defining, in agreement with the competent authority, criteria governing the acceptability of his products, in order to meet the specifications laid down for the verification of conformity of products in Annex VI to Directive 92/61/EEC.
The criteria governing the acceptability must be such that, with a confidence level of 95 %, the minimum probability of passing a spot check in accordance with section 6 (first sampling) would be 0,95.
6.MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR SAMPLING BY AN INSPECTORU.K.
6.1.GeneralU.K.
6.1.1.The conformity requirements are considered satisfied from a mechanical and a geometric standpoint if the differences do not exceed inevitable manufacturing deviations within the requirements of this Directive.U.K.
6.1.2.With respect to photometric performance, the conformity of series-produced devices must not be contested if, when testing photometric performances of any device chosen at random and in the case of signalling lamps, headlamps or front fog-lamps equipped with standard filament lamps, no measured value deviates unfavourably by more than 20 % from the minimum values prescribed in this Directive.U.K.
6.1.3.The trichromatic coordinates must be complied with in the case of signalling lamps, headlamps or front fog-lamps when these are equipped with filament lamps set to Standard A colour temperature.U.K.
6.2.First samplingU.K.
In the first sampling four devices are selected at random. The first sample of two is marked A, the second sample of two is marked B.
6.2.1.Instances where conformity is not contested.U.K.
6.2.1.1.Following the sampling procedure shown in Figure 1 of this Annex the conformity of series-produced devices must not be contested if the deviation of the measured values of the device in the unfavourable directions are:U.K.
6.2.1.1.1.sample AU.K.
| A1: | one device | 0 %, |
| one device not more than | 20 %; | |
| A2: | both devices more than | 0 %, |
| but not more than | 20 %, |
go to sample B
6.2.1.1.2.sample BU.K.
| B1: | both devices | 0 %. |
6.2.2.The conformity is contested.U.K.
6.2.2.1.Following the sampling procedure shown in Figure 1 of this Annex the conformity of series-produced devices must be contested and the manufacturer requested to make his production meet the requirements (alignment) if the deviations of the measured values of the devices are:U.K.
6.2.2.1.1.sample AU.K.
| A3: | one device not more than | 20 %, |
| one device more than | 20 %, | |
| but not more than | 30 %. |
6.2.2.1.2.sample BU.K.
| B2: | in the case of A2 | |
| one device more than | 0 %, | |
| but not more than | 20 %, | |
| one device not more than | 20 %; | |
| B3: | in the case of A2 | |
| one device | 0 %, | |
| one device more than | 20 %, | |
| but not more than | 30 %. |
6.2.3.Approval withdrawnU.K.
Conformity must be contested and Article 10 of Directive 92/61/EEC applied if, following the sampling procedure in Figure 1 of this Annex, the deviations of the measured values of the devices are:
6.2.3.1.sample AU.K.
| A4: | one device not more than | 20 %, |
| one device more than | 30 %; | |
| A5: | both devices more than | 20 %. |
6.2.3.2.sample BU.K.
| B4: | in the case of A2 | |
| one device more than | 0 %, | |
| but not more than | 20 %, | |
| one device more than | 20 %; | |
| B5: | in the case of A2 | |
| both devices more than | 20 %; | |
| B6: | in the case of A2 | |
| one device | 0 %, | |
| one device more than | 30 %. |
6.3.Repeated samplingU.K.
In the cases of A3, B2, B3 a repeated sampling, third sample C of two devices and fourth sample D of two special warning lamps, selected from stock manufactured after alignment, is necessary within two months following the notification.
6.3.1.The conformity is not contested.U.K.
6.3.1.1.Following the sampling procedure shown in Figure 1 of this Annex the conformity of series-produced devices must not be contested if the deviations of the measured values of the devices are:U.K.
6.3.1.1.1.sample CU.K.
| C1: | one device | 0 %, |
| one device not more than | 20 %; | |
| C2: | both devices more than | 0 %, |
| but not more than | 20 %, |
go to sample D
6.3.1.1.2.sample DU.K.
| D1: | in the case of C2 | |
| both devices | 0 %. |
6.3.2.The conformity is contested.U.K.
6.3.2.1.Following the sampling procedure shown in Figure 1 of this Annex the conformity of series-produced devices must be contested and the manufacturer requested to make his production meet the requirements (alignment) if the deviations of the measured values of the devices are:U.K.
6.3.2.1.1.sample DU.K.
| D2: | in the case of C2 | |
| one device more than | 0 %, | |
| but not more than | 20 %, | |
| one device not more than | 20 %. |
6.3.3.Approval withdrawnU.K.
Conformity must be contested and Article 10 of Directive 92/61/EEC applied if, following the sampling procedure in Figure 1 of this Annex, the deviations of the measured values of the devices are:
6.3.3.1.sample CU.K.
| C3: | one device not more than | 20 %, |
| one device more than | 20 %; | |
| C4: | both devices more than | 20 %. |
6.3.3.2.sample DU.K.
| D3: | in the case of C2 | |
| one device egual to or more than | 0 %, | |
| one device more than | 20 %. |
Appendix 1
Colours of Light emitted
Trichomatic co-ordinates
| RED: | limit towards yellow: | y ≤ 0,335 |
| limit towards purple: | z ≤ 0,008 | |
| WHITE: | limit towards blue: | x ≥0,31 |
| limit towards yellow: | x ≤ 0,5 | |
| limit towards green: | y ≤ 0,15 + 0,64× | |
| limit towards green: | y ≤ 0,44 | |
| limit towards purple: | y ≥ 0,05 + 0,75 × | |
| limit towards red: | y ≥ 0,382 | |
| AMBER: | limit towards yellow: | y ≤ 0,429 |
| limit towards red: | y ≥ 0,398 | |
| limit towards white: | z ≤ 0,007 |
For verifying the limits above, a source of light at a colour temperature of 2 856 K (illuminant A of the International Commission on Illumination (CIE)), in combination with appropriate filters, may be used.
For retro-reflectors the device is illuminated by CIE standard illuminant A, with an angle of divergence of 1/3o and an illumination angle V = H = 0o, or, if this produces a colourless surface reflection, an angle V = ± 5o, H = 0o, the trichomatic co-ordinates of the reflected luminous flux must be within the limits above.
Appendix 2
Examples of arrangements of approval marksU.K.
A device bearing the EC component type-approval mark shown above is a direction indicator of category 11 approved in the Netherlands (e4) under the number 00243. The first two digits of the approval number indicate that the approval was granted in accordance with the requirements of Annex II to this Directive in its original version.
For a direction indicator, the arrow indicates that the luminous distribution is asymmetrical in a horizontal plane and that the photometric values required are satisfied up to an angle of 80o to the right, the device being seen in the opposite sense of the light emitted. The example shows a direction indicator mounted on the right-hand side of the vehicle.
Simplified marking of grouped, combined or reciprocally incorporated lamps when two or more lamps are part of the same assembly.
Note:U.K.
These three examples of approval marks (models A, B and C) represent three possible variables for the marking of a lighting device when two or more lamps are part of the same assembly of grouped, combined or reciprocally incorporated lamps.U.K.
They indicate that the device was approved in the Netherlands (e4) under approval number 3333 and comprises:U.K.
a retro-reflector of Class 1, approved in accordance with Directive 76/757/EEC in its original version;
a red rear-position (side) lamp (R) approved in accordance with Annex II to this Directive in its original version;
a rear fog-lamp (F) approved in accordance with Directive 77/538/EEC in its original version;
a reversing lamp (AR) approved in accordance with Directive 77/539/EEC in its original version;
a stop-lamp (S) approved in accordance with Annex II to this Directive in its original version.
Example of EC component type-approval markU.K.
The retro-reflector bearing the EC component type-approval mark shown above is a Class 1 reflector approved in the Netherlands (4) under the number 216 in accordance with Directive 76/757/EEC; the requirements for retro-reflectors in section 9.1 of Annex II to this Directive apply where a ≥ 4 mm.
The headlamp bearing the above EC component type-approval mark was approved in the Netherlands (e4) pursuant to Annex III-A to this Directive in its original version, under approval number 00243. The first two digits of the approval number indicate that the approval was granted in accordance with the requirements of this Directive in its original version.
The headlamp bearing the above EC component type-approval mark is a headlamp meeting the requirements of Annex III-B to this Directive in its original version and is designed for right-hand traffic only.
| The headlamp bearing the above EC component type-approval mark is a headlamp meeting the requirements of Annex III-B to this Directive in its original version and is designed: | |
| For left-hand traffic only. | For both traffic systems by means of an appropriate adjustment of the setting of the optical unit or the lamp on the vehicle. |
The headlamp bearing the above EC component type-approval mark is a headlamp incorporating a lens of plastic material and meeting the requirements of Annex III-C to this Directive in its original version.
It is so designed that the filament of the passing beam can be lit together simultaneously with the driving beam and/or another reciprocally incorporated lighting function.
| The headlamp bearing the EC component type-approval mark shown above is a headlamp incorporating the lens of plastic material meeting the requirements of Annex III-D to this Directive in its original version with respect to the passing beam only, and designed: | |
| For both traffic systems | For right-hand traffic only. |
Simplified marking for grouped, combined or reciprocally incorporated lamps
Note:U.K.
The four examples shown above correspond to a lighting device bearing an EC component type-approval mark relating to:U.K.
a front position (side) lamp (A) approved in accordance with Annex II to this Directive in its original version;
a headlamp (HCR) with a passing beam designed for right-hand and left-hand traffic and a driving beam with a maximum intensity comprised between 86.250 and 101.250 candelas (as indicated by the number 30), approved in accordance with Annex III-D to this Directive in its original version and incorporating a lens of plastic material;
a front fog-lamp B approved in accordance with Directive 76/762/EEC in its original version and incorporating a lens of plastic material;
a front direction-indicator lamp of category 11 approved in accordance with Annex II to this Directive in its original version.
| Identification of a headlamp incorporating the lens of plastic material meeting the requirements of Directive 76/761/EEC with respect to Appendix 3 of Annex III-D to this Directive. | |
| For both the passing beam and the driving beam and designed for right-hand traffic only. | For the passing beam only and designed for left-hand traffic only. |
| The passing lamp filament must not be lit simultaneously with the driving lamp filament and/or any other headlamp with which it is reciprocally incorporated. | |
ANNEX II
REQUIREMENTS CONCERNING THE COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVAL OF FRONT POSITION (SIDE) LAMPS, REAR LAMPS, STOP LAMPS, DIRECTION-INDICATOR LAMPS, REAR REGISTRATION-PLATE ILLUMINATING DEVICE, FRONT FOG-LAMPS, REAR FOG-LAMPS, REVERSING LAMPS AND RETRO-REFLECTORS FITTED TO TWO OR THREE-WHEEL MOTOR VEHICLES
1.DEFINITIONSU.K.
The relevant definitions set out in Annex I to Council Directive 93/92/EEC of 29 October 1993 on the fitting of lighting and light-signalling devices to two or three-wheel motor vehicles apply.
1.1.‘Lens’ means the outermost component of the lamp (device) which transmits light through the illuminating surface;U.K.
1.2.‘Coating’ means any product or products applied in one or more layers to the outer face of a lens;U.K.
1.3.‘Devices of different types’ are devices which differ in such essential respects as:U.K.
1.3.1.the make or trade name,U.K.
1.3.2.the characteristics of the optical system,U.K.
1.3.3.the inclusion or elimination of components capable of altering the optical effects by reflection, refraction, absorption and/or deformation during operation,U.K.
1.3.4.the type of filament lamp,U.K.
1.3.5.the materials constituting the lenses and coating, if any.U.K.
2.INFORMATION THAT IS ADDITIONAL TO THE COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVAL MARK FOR DIRECTION INDICATORS:U.K.
2.1.In the general case of a direction indicator a number stating that it is a front direction-indicator (category 11) or a rear direction-indicator (category 12) must be affixed close to the rectangle for the component type-approval mark and opposite the component type-approval number.U.K.
2.2.In the case of a direction indicator which does not, in accordance with 4.7.1. on one side achieve the minimum luminous intensity required up to an angle of H = 80o, a horizontal arrow, the tip of which is pointing in the direction where the minimum luminous intensity in accordance with 4.7.1 is achieved up to an angle of at least H = 80o, must be affixed below the rectangle for the component type-approval mark.U.K.
3.GENERAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
Devices must be designed and constructed in such a way that, under their normal conditions of use and despite any vibrations to which they may be submitted, their proper functioning remains unimpaired and they retain the characteristics required by this Annex.
4.INTENSITY OF THE LIGHT EMITTEDU.K.
Within the reference axis the intensity of the light emitted by each of the two devices must be at least equal to the two minimum values and at most equal to the maximum values set out in the table below. In no direction must the maximum values stated be exceeded.
| a Applies solely to the area between the two vertical lines passing through V = 0o/H = ± 5o and two horizontal lines passing through V = ± 10o/H = 0o. A maximum of 400 cd is applicable to all other directions. | |||
| min (cd) | max (cd) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.1. | Rear position (side) lamps | 4 | 12 |
| 4.2. | Front position (side) lamps | 4 | 60 |
| 4.3. | Stop lamps | 40 | 100 |
| 4.4. | Direction-indicator lamps | ||
| 4.4.1. | Front (category 11) (see Appendix 1) | 90 | 700a |
| 4.4.2. | Rear (category 12) (see Appendix 1) | 50 | 200 |
4.5.Outside the reference axis the intensity of the light emitted within the angular fields defined in the diagrams in Appendix 1 must, in each direction corresponding to the points in the light distribution table set out in Appendix 2, be at least equal to the product of the minima set out in 4.1 to 4.4 and to the percentage set out in that table for the direction at issue.U.K.
4.6.By way of derogation from 4.1 a maximum luminous intensity of 60 cd is permitted for rear position (side) lamps that are reciprocally incorporated with stop lamps below a plane forming an angle of 5o downwards from the horizontal plane.U.K.
4.7.Moreover:U.K.
4.7.1.Throughout the fields defined in Appendix 1 the intensity of the light emitted must be at least 0,05 cd for position (side) lamps and at least 0,3 cd for stop lamps and direction-indicator lamps.U.K.
4.7.2.When a position (side) lamp has been grouped together or reciprocally incorporated with a stop lamp the ratio of the actually measured light intensities from the two lamps when lit simultaneously to the intensity of the rear position (side) lamp when lit alone must be at least 5:1 at the eleven measuring points defined in Appendix 2 and located within the field bounded by the vertical straight lines passing through 0o V/± 10o H and the horizontal straight lines passing through ± 5o V/0o H shown in the light distribution table.U.K.
4.7.3.The requirements set out in section 2.2 of Appendix 2 concerning local variations in intensity must be met.U.K.
4.8.The light intensities must be measured with the lamp constantly lit. Where lamps operate intermittently it must be ensured that the device does not overheat.U.K.
4.9.Appendix 2 as referred to in 4.5 provides details on the methods of measurement to be used.U.K.
4.10.The rear registration-plate illuminating device must meet the conditions set out in Appendix 3.U.K.
4.11.The photometric performance of lamps equipped with several light sources must be checked in accordance with the provisions of Appendix 2.U.K.
5.CONDITIONS ATTACHED TO THE TESTSU.K.
5.1.All the measurements must be carried out with a standard colourless lamp falling within the category intended for the device and adjusted in order to emit the reference light flux required for the lamp at issue. However, for lamps equipped with non-replaceable light sources, all measurements must be made at 6,75 V and 13,5 V respectively.U.K.
5.2.The vertical and horizontal edges of the light-emitting surface of the device are determined and dimensioned in relation to its reference centre.U.K.
6.COLOUR OF LIGHT EMITTEDU.K.
Stop lamps and rear position (side) lamps must emit red light, front position (side) lamps must emit white light, and direction indicators amber light.
The colour of the light emitted, measured by using a filament lamp of the category specified by the manufacturer, must be within the limits of the trichromatic coordinates prescribed in Appendix 1 to Annex I when this filament lamp is operated at its test voltage as specified in Annex IV.
However, for lamps equipped with non-replaceable light sources, the colorimetric characteristics must be verified with the light sources present in the lamps at a voltage of 6,75 V, 13,5 V or 28,0 V.
7.FRONT AND REAR FOG-LAMPSU.K.
The requirements of Directive 76/762/EEC on front fog-lamps and of Directive 77/538/EEC on rear fog-lamps apply.
8.REVERSING LAMPSU.K.
The requirements of Directive 77/539/EEC on reversing lamps apply.
9.RETRO-REFLECTORSU.K.
9.1.Pedal retro-reflectorsU.K.
9.1.1.The shape of the retro-reflectors must be so that these are able to fit into a rectangle, the side dimensions of which are in a ratio of not more than 8.U.K.
9.1.2.The pedal retro-reflectors must meet the requirements set out in Annex VIII to Directive 76/757/EEC in amber colour.U.K.
9.1.3.The functioning reflecting surface of each of the four pedal retro-reflectors must not be less than 8 cm2.U.K.
9.2.Other retro-reflectorsU.K.
The requirements set out in Directive 76/757/EEC on retro-reflectors apply.
Appendix 2
Photometric measurements
1.METHODS OF MEASUREMEMTU.K.
1.1.Interference reflections during the photometric measurements must be avoided by means of appropriate masking.U.K.
1.2.Should the results of the measurements be contested, they must be carried out in such a way that:U.K.
1.2.1.the measuring distance is such that the inverse square law of the distance applies;U.K.
1.2.2.the measuring apparatus is such that the angular aperture of the receiver viewed from the centre of reference of the lamp lies between ten minutes of an angle and one degree;U.K.
1.2.3.the intensity requirement for a given direction of observation is satisfactory provided that requirement is met in a direction not diverging by more than a quarter of a degree from the direction of observation.U.K.
2.STANDARDIZED TABLE SHOWING SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF LIGHTU.K.
2.1.Direction H = 0o and V = 0o corresponds to the axis of reference (on the vehicle it is horizontal and parallel to the median longitudinal plane of the vehicle and pointing towards the required field of view). It passes through the centre of reference. The values set out in the table give the minimum intensities for the various directions of measurement as a percentage of the minimum required for each lamp within the axis (in direction H = 0o and V = 0o).U.K.
2.2.Within the field of light distribution represented in diagrammatic form in section 2 by a grid, the distribution of the light must essentially be uniform in such a way that the light intensity in each direction of a part of the field formed by the lines of the grid reaches at least the lowest minimum value specified as a percentage (or the lowest available value) on the lines of the grid which surround the direction at issue.U.K.
3.PHOTOMETRIC MEASUREMENT OF LAMPS EQUIPPED WITH SEVERAL LIGHT SOURCESU.K.
The photometric performance must be checked:
3.1.For non-replaceable (fixed) filament lamps or other light sources:U.K.
at the voltage prescribed by the manufacturer; the technical service may require from the manufacturer the special power supply needed to supply such lamps.
3.2.For replaceable filament lamps:U.K.
when equipped with mass-production filament lamps at 6,75 V, 13,5 V or 28,0 V the luminous intensity values produced must lie between the maximum limit and the minimum limit given in this Annex increased in accordance with the permissible deviation of the luminous flux permitted for the type of filament lamp chosen, as stated in Annex IV for production filament lamps; alternatively a standard filament lamp may be used in turn, in each of the inidvidual positions, operated at its reference flux, the individual measurements in each position being added.
Appendix 3
Photometric measurements of the rear registration-plate illuminating device
1.POSITION TO BE ILLUMINATEDU.K.
Devices may fall within category 1 or 2. The category 1 devices must be designed in such a way as to illuminate a position measuring at least 130 × 240 mm and the category 2 devices in such a way as to illuminate a position measuring at least 200 × 280 mm.
2.COLOUR OF LIGHT EMITTEDU.K.
The colour of the light emitted by the lamp used in the device must be white, but sufficiently neutral so as not to cause any appreciable change in the colour of the registration plate.
3.LIGHT INDICENCEU.K.
The manufacturer of the illuminating device must lay down the conditions for the fitting of the device in relation to the position intended for the registration plate. That device must occupy a position such that at none of the points on the surface to be illuminated with the angle of incidence of the light on the surface of the plate exceed 82o, that angle being measured in relation to the extremity of the light-emitting surface of the device that is furthest from the surface of the plate. Where there is more than one optical component this requirement applies only to the part of the plate intended to be illuminated by the relevant component.
The device must be designed in such a manner that no ray of light shines directly towards the rear with the exception of rays of red light where the device is combined or grouped with a rear lamp.
4.METHOD OF MEASUREMENTU.K.
The levels of luminance are measured on a sheet of clean white blotting paper having a minimum factor of diffuse reflection of 70 % and the same dimensions as the registration plate and placed at the position it would normally occupy but 2 mm in front of its support.
The level of luminance is measured at right angles to the surface of the paper at the points shown in the diagram in section 5 below, each point representing a circular area 25 mm in diameter.
5.PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICSU.K.
Luminance B must be at least 2 cd/m2 at each of the measuring points defined below.
The luminance gradient between values B
1
and B
2
, measured at any two points 1 and 2 selected from among the points referred to above must not exceed 2 × B
o
/cm, B
o
being the minimum luminance recorded at the various measuring points, or in other words
ANNEX III
REQUIREMENTS RELATING TO THE COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVAL OF DEVICES (HEADLAMPS) USING INCANDESCENT OR HALOGEN FILAMENT LAMPS EMITTING A PASSING AND/OR DRIVING BEAM FITTED TO TWO OR THREE-WHEEL MOTOR VEHICLES
1.DEFINITIONSU.K.
The relevant definitions set out in Annex I to Directive 93/92/EEC apply.
1.1.‘Lens’ means the outermost component of the headlamp (unit) which transmits light through the illuminating surface;U.K.
1.2.‘Coating’ means any product or products applied in one or more layers to the outer face of a lens;U.K.
1.3.‘Headlamps of different types’ are headlamps which differ in such essential respects as:U.K.
1.3.1.the make or trade name;U.K.
1.3.2.the characteristics of the optical system;U.K.
1.3.3.the inclusion or elimination of components capable of altering the optical effects by reflection, refraction, absorption and/or deformation during operation. However, the fitting or elimination of filters designed to change the colour of the beam and not its light distribution does not constitute a change in the type;U.K.
1.3.4.suitability for right-hand or left-hand traffic or for both traffic systems;U.K.
1.3.5.the kind of beam produced (passing beam, driving beam or both);U.K.
1.3.6.the holder intended to accommodate the filament lamp (or lamps) of one of the relevant categories;U.K.
1.3.7.the materials constituting the lenses and coating, if any.U.K.
2.HEADLAMPSU.K.
A distinction is drawn between:
2.1.Headlamps for mopedsU.K.
(see Annex III-A)U.K.
| 2.1.1 | with a single-filament lamp | 15 W (category S3) |
| 2.1.2. | with a two-filament lamp | 15/15 W (category S4) |
| 2.1.3. | with a single-filament halogen lamp | 15 W (category HS2) |
2.2.Headlamps for motorcycles and tricyclesU.K.
(see Annexes IIIB and IIIC)U.K.
| 2.2.1. | with a two-filament lamp | 25/25 W (category S1) |
| 2.2.2. | with a two-filament lamp | 35/35 W (category S2) |
| 2.2.3. | with a two-filament halogen lamp | 35/35 W (category HS1) |
| 2.2.4. | with a two-filament lamp | 40/45 W (category R2) |
2.3.Headlamps for motorcycles and tricyclesU.K.
(see Annex III-D — headlamps with halogen filament lamps other than HS1)U.K.
| 2.3.1. | with a single filament lamp | 55 W (category H1) |
| 2.3.2. | with a single filament lamp | 55 W (category H2) |
| 2.3.3. | with a single filament lamp | 55 W (category H3) |
| 2.3.4. | with a single filament lamp | 60 W (category HB3) |
| 2.3.5. | with a single filament lamp | 51 W (category HB4) |
| 2.3.6. | with a single filament lamp | 55 W (category H7) |
| 2.3.7. | with a two-filament lamp | 55/60 W (category H4) |
ANNEX III-A
HEADLAMPS FOR MOPEDS
1.GENERAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
1.1.Headlamps must be designed and manufactured in such a way that, under normal conditions of use and despite any vibrations to which they may be exposed, they continue to function correctly and retain the characteristics laid down in this Annex.U.K.
1.2.The parts intended to attach the lamp must be designed in such a way that, even in the dark, the lamp may be correctly fitted in its appropriate position.U.K.
2.SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTSU.K.
2.1.The correct position of the lens in relation to the optical system must be clearly marked and locked in position in order to prevent rotation during use.U.K.
2.2.A measuring screen as described in Appendix 1 or 2 and a standard lamp using a smooth colourless filament lamp falling within one of the categories provided for in section 2.1 and in Annex III must be used in order to check the illumination provided by the headlamp.U.K.
The standard lamps must be adjusted to the relevant reference light flux in accordance with the values laid down for those lamps in the relevant technical document (see Annex IV).
2.3.The passing beam must produce a cut-off of such sharpness that correct adjustment by means thereof is a practical possibility. The cut-off must be perceptibly horizontal and as straight as possible over a horizontal length of at least ± 900 mm, measured at a distance of 10 m (in the case of a halogen lamp): length of at least ± 2 250 mm measured at a distance of 25 m; see Appendix 2). When adjusted in accordance with Appendix 1 headlamps must meet the conditions set out therein.U.K.
2.4.The light distribution must not vary in lateral terms in a way that impairs good visibility.U.K.
2.5.The illumination on the screen referred to in 2.2 must be measured by means of a photo receiver for a usable area lying within a 65 mm square.U.K.
3.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS ATTACHED TO ANY INSPECTIONS WHICH MAY BE CARRIED OUT BY THE COMPETENT AUTHORITIES WHEN CHECKING CONFORMITY OF PRODUCTION IN ACCORDANCE WITH SECTION 5.2.4 OF ANNEX IU.K.
Any records of the photometric characteristics of headlamps taken in accordance with the general requirements concerning conformity testing must be restricted to points HV — LH — RH — L600 — R600 (see figure in Appendix 1).
Appendix 1
Photometric tests on headlamps equipped with category S3 and S4 lamps
1.For the measurements the measuring screen is placed at a distance of 10 m in front of the headlamp and at right angles to the line joining the driving beam filament of the lamp and point HV (see figure below); line H-H must be horizontal.U.K.
2.REQUIREMENTS ATTACHED TO PASSING BEAMU.K.
2.1.In lateral terms the headlamp must be aligned in such a way that its beam is as symmetrical as possible in relation to line V-V.U.K.
2.2.In vertical terms the headlamp must be adjusted in such a manner that its cut-off is 100 mm below line H-H.U.K.
2.3.When the headlamp has been adjusted in accordance with 2.1 and 2.2 the illumination values shall be as follows:U.K.
2.3.1.On line H-H and above: 2 lux at the most;U.K.
2.3.2.On a line situated 300 mm below line H-H and over a width of 900 mm either side of vertical line V-V: 8 lux at least;U.K.
2.3.3.On a line 600 mm below line H-H and over a width 900 mm either side of the vertical line V-V: at least 4 lux.U.K.
3.REQUIREMENTS CONCERNING THE DRIVING BEAM (if any)U.K.
3.1.When it has been adjusted in accordance with 2.1 and 2.2 the headlamps must meet the following requirements in respect of the driving beam:U.K.
3.1.1.The point of intersection (HV) of lines H-H and V-V must lie within the isolux denoting 80 % of maximum illumination.U.K.
3.1.2.Maximum illumination (Emax) of the driving beam must not be less than 50 lux.U.K.
3.1.3.Starting from point HV the illumination by the driving beam to the right and left must be at least Emax/4 up to a distance of 0,90 m.U.K.
MEASURING SCREENU.K.
Appendix 2
Photometric tests on headlamps equipped with category HS2 halogen lamps
1.For the measurements the measuring screen is placed 25 m in front of the headlamp in such a way that it is at right angles to the line joining the filament of the lamp and pont HV (see figure below); line H-H must be horizontal.U.K.
2.In lateral terms the headlamp must be aligned in such a way that the distribution of the beam is symmetrical in relation to line V-V.U.K.
3.In vertical terms the headlamp must be adjusted in such a way that its cut-off is 250 mm below line H-H. It must also be as horizontal as possible.U.K.
4.When the headlamp has been adjusted in accordance with sections 2 and 3 the following conditions must be met:U.K.
| Measuring point | Ilumination E/lux |
|---|---|
| Each point on and above line H-H | ≤ 0,7 |
| Each point on line 35L-35R with the exception of 35V | ≥ 1 |
| Point 35V | ≥ 2 |
| Each point on line 25L-25R | ≥ 2 |
| Each point on line 15L-15R | ≥ 0,5 |
5.Measuring screenU.K.
MEASURING SCREENU.K.
ANNEX III-B
HEADLAMPS FOR MOTORCYCLES AND TRICYCLES EMITTING A SYMMETRICAL PASSING BEAM AND A DRIVING BEAM BY MEANS OF FILAMENT LAMPS
1.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS CONCERNING MARKS AND THE MARKING OF SPECIFIC DEVICESU.K.
1.1.Headlamps must bear in a clearly legible and indelible manner the letters ‘MB’ (symbol for driving-beam headlamp) opposite the component type-approval number.U.K.
1.2.All headlamps designed in such a way as to preclude any simultaneous lighting-up of the passing-beam filament and that of any other light source with which they may be integrated may be marked with an oblique stroke (/) following the symbol (MB) for the passing beam in the component type-approval mark.U.K.
1.3.On headlamps incorporating a lens of plastic material, the letters ‘PL’ must be affixed near the symbol prescribed in 1.1.U.K.
2.GENERAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
2.1.Each of the samples must meet the specifications set out in section 3 below.U.K.
2.2.Headlamps must be designed and manufactured in such a way that, under normal conditions of use and despite any vibrations to which they may be exposed, they continue to function properly and retain the required characteristics.U.K.
2.2.1.Headlamps must be fitted with a device enabling them to be adjusted on the vehicle in accordance with the rules applying to them. A device of this type may be dispensed with where headlamp units consists of a reflector and lens which cannot be separated where the use of units of this type is restricted to vehicles on which the headlamps are adjusted by other means.U.K.
If headlamps specifically designed for driving-beam operation and headlamps specifically designed for passing-beam operation, each of which has an individual lamp, are grouped together or reciprocally incorporated in a single device, the setting device must enable each of the optical systems to be adjusted individually in order to achieve the offical settings.
2.2.2.However, these provisions do not apply to headlamp assemblies whose reflectors are indivisible. For this type of assembly the requirements set out in section 3.3 apply. Where more than one light source is used to provide the main beam, the combined functions must be used to determine the maximum value of the illumination (Emax).U.K.
2.3.The parts intended to attach the filament lamp must be made in such a way that, even in the dark, the filament lamp can be attached without uncertainty in its appropriate position.U.K.
2.4.Additional tests meeting the requirements of Appendix 2 must be carried out in order to ensure that there are no excessive variations in photometric performance during use.U.K.
2.5.If the lens of the headlamp is of plastic material, additional tests must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of Appendix 3.U.K.
3.SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTSU.K.
3.1.The correct position of the lens in relation to the optical system must be clearly marked and locked in position in order to prevent rotation during use.U.K.
3.2.In order to check the illumination produced by the headlamp a measuring screen as described in Appendix 1 is used, together with a standard lamp (S1 and/or S2, see Annex IV) having a smooth colourless filament lamp.U.K.
Standard lamps must be adjusted to the relevant reference light flux applying in accordance with the values required for such lamps.
3.3.The passing beam must produce a cut-off of such sharpness that correct adjustment by means thereof is a practical possibility. The cut-off must be as straight and as horizontal as possible over a horizontal length of at least ± 5o. When adjusted in accordance with Appendix 1 headlamps must meet the conditions set out therein.U.K.
3.4.The light distribution must not vary in lateral terms in a way that impairs good visibility.U.K.
3.5.The illumination on the screen referred to in 3.2 must be measured by means of a functioning-surface photocell lying within a 65 mm square.U.K.
4.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS APPLYING TO ANY INSPECTIONS WHICH MAY BE CARRIED OUT BY THE COMPETENT AUTHORITIES WHEN CHECKING CONFORMITY OF PRODUCTION IN ACCORDANCE WITH SECTION 5.1 OF ANNEX IU.K.
4.1.For value in zone III, the maximum unfavourable deviation may be respectively:U.K.
0,3 lux equivalent 20 %
0,45 lux equivalent 30 %.
4.2.if, for the driving beam, HV being situated within the isolux 0,75 Emax, a tolerance of + 20 % for maximum values and − 20 % for minimum values is observed for the photometric values at any measuring point specified in sections 4.3 and 4.4 of Appendix 1 to this Directive.U.K.
4.3.With respect to the verification of the change in the vertical position of the cut-off line under the influence of heat, the following procedure is applied:U.K.
One of the sampled headlamps is tested in accordance with the procedure described in section 2.1 of Appendix 2 after being subjected three consecutive times to the cycle described in section 2.2.2 of Appendix 2.
The headlamp is considered to be acceptable if Δr does not exceed 1,5 mrad.
If this value exceeds 1,5 mrad but is not more than 2,0 mrad, a second headlamp is subjected to the test, after which the mean of the absolute values recorded on both samples may not exceed 1,5 mrad.
Appendix 1
Photometric tests
1.For adjustment purposes the relevant screen must be placed at least 10 m before the headlamp, line h-h being horizontal. For the measurements the photocell must be 25 m in front of the headlamp and at right angles to the line joining the incandescent filament lamp and point HV.U.K.
2.In lateral terms the headlamp must be aligned in such a way that the distribution of the driving beam is symmetrical in relation to line v-v.U.K.
3.In vertical terms the headlamp must be adjusted in such way that the passing beam cut-off is 250 mm below line h-h (at a distance of 25 m).U.K.
4.When the headlamp has been adjusted in accordance with sections 2 and 3, conditions for which are similar to those relating to driving beams, the following conditions must be met:U.K.
4.1.the lighting centre of the driving beam must not be more than 0,6o above or below line h-h;U.K.
4.2.the illumination provided by the driving beam must reach its maximum value (Emax) at the centre of the entire light distribution and diminish laterally;U.K.
4.3.the maximum illumination (Emax) of the driving beam must be at least 32 lux;U.K.
4.4.the illumination produced by the driving beam must correspond to the following values:U.K.
4.4.1.the point of intersection between lines h-h and v-v HV must lie within the isolux for 90 % of maximum illumination.U.K.
4.4.2.starting from HV horizontally to the right and left the illumination provided by the driving beam must be at least 12 lux up to a distance of 1,125 m and not less than 3 lux up to a distance of 2,25 m.U.K.
4.5.The illumination provided by the passing beam must correspond to the following values:U.K.
| Each point on and above line h-h | ≤ 0,7 lux |
| Each point on the line 50L-50R with the exception of 50Va | ≥ 1,5 lux |
| Point 50V | ≥ 3,0 lux |
| Each point on the line 25L-25R | ≥ 3,0lux |
| All points within zone IV | ≥ 1,5 lux |
5.MEASURING AND ADJUSTING SCREENU.K.
Appendix 2
Test on the stability of the photometric behaviour of headlamps in operation
Compliance with the requirements of this Appendix is not an adequate criterion for the component type-approval of headlamps incorporating plastic lenses.
See Appendix 2 to Annex III-D.
Appendix 3
Requirements for lamps incorporating lenses of plastic material and testing of lens or material samples and of complete lamps
See Appendix 3 to Annex III-D.
ANNEX III-C
HEADLAMPS FOR MOTORCYCLES AND TRICYCLES EMITTING AN ASYMMETRICAL PASSING BEAM AND A DRIVING BEAM AND FITTED WITH HALOGEN FILAMENT LAMPS (HS1 LAMPS) OR FILAMENT LAMPS OF CATEGORY R2
1.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS CONCERNING MARKS AND THE MARKING OF DEVICESU.K.
1.1.Headlamps designed in such a way as to meet the requirement of a single rule of the road (driving on either the right or the left) must, on the lens, bear the limits of the area which may possibly be masked in order to avoid distracting road users in a country where the rule of the road is not that for which the headlamp has been designed. However, when that area is directly identifiable by design any such delimitation is not necessary.U.K.
1.2.Headlamps designed in such a way as to meet the requirements of driving on the right and those for driving on the left must bear markings in order to locate the two positions for the fixing in position of the light unit on the vehicle or the lamp on the reflector; these markings consist of the letters ‘R/D’ for the position corresponding to driving on the right and the letters ‘L/G’ for the position corresponding to driving on the left.U.K.
1.3.All headlamps designed in such a way as to preclude any simultaneous lighting-up of the dipped-beam filament and that of any other light source with which they may be associated must be marked with an oblique stroke (/) within the component type-approval mark, after the passing beam headlamp symbol.U.K.
1.4.Where headlamps meet only the requirements of driving on the left, a horizontal arrow pointing to the right of an observer looking at the headlamp head on, i.e. towards the side of the road driven upon, must be entered below the component type-approval mark.U.K.
1.5.Where, by means of a deliberate alteration in the adjustment of the light unit or lamp, headlamps meet the requirements of both rules of the road, a horizontal arrow having two tips pointing one to the left and the other to the right must be entered below the component type-approval mark.U.K.
1.6.The letters ‘MBH’ on headlamps with HS1 lamps are placed opposite the component type-approval mark.U.K.
1.7.The marks and symbols referred to above must be clearly visible and indelible.U.K.
1.8.On headlamps incorporating a lens of plastic material, the letters ‘PL’ must be affixed near the symbols prescribed in 1.2 to 1.7.U.K.
2.GENERAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
2.1.Each of the samples must meet the specifications set out in sections 3 to 5.U.K.
2.2.Headlamps must be designed and manufactured in such a way that under the normal conditions of use and despite any vibrations to which they may be exposed they continue to function properly and retain the characteristics required by this Annex.U.K.
2.2.1.Headlamps must be fitted with a device enabling them to be adjusted on the vehicle in such a way as to meet the rules applying to them. This said device does not need to be attached to the parts within which the reflector and diffuser lens cannot be separated, provided that the use of those parts is restricted to vehicles on which the headlamps may be adjusted by other means.U.K.
Where a headlamp emitting a driving beam and a headlamp emitting a passing beam, each being equipped with its own lamp, are grouped together to form a composite unit, the setting device must enable each individual optical system to be set in an appropriate manner.
2.2.2.However, these provisions do not apply to headlamp assemblies whose reflectors are indivisible. In this instance the requirements of section 2 of this Annex shall apply. When more than one light source provides the driving beam those sources must be combined in order to determine the maximum illumination value (Emax).U.K.
2.3.The parts intended to attach the filament lamp to the reflector must be made in such a way that, even in the dark, the filament lamp can be attached without uncertainty in its appropriate position.U.K.
2.4.The correct position of the lens in relation to the optical system must be clearly marked and locked in position in order to avoid any rotation.U.K.
2.5.Where headlamps have been designed in such a way as to meet the requirements of driving on both the right and the left, adaptation to a given rule of the road may be obtained by a suitable initial setting when the vehicle is equipped or via a deliberate action on the part of the user. That initial setting or that deliberate action must, for example, consist of a specific angular setting either of the sealed-beam assembly on the vehicle or of the lamp in relation to that assembly. In all cases only two different setting positions that have been clearly specified and correspond in each case to a rule of the road (driving on the right or left) must be possible and any shift into an intermediate position must be made impossible. When the lamp is able to occupy two different positions the parts intended to attach the lamp to the reflector must be designed and manufactured in such a way that, in each of those two positions, the lamp is attached with the same precision as required for headlamps designed for just one rule of the road. Conformity must be checked visually and, where appropriate, by means of a test assembly.U.K.
2.6.In order to ensure that operation does not involve any excessive variation in photometric performance, additional tests must be carried out as required by Appendix 2.U.K.
2.7.If the lens of the headlamps is of plastic material, additional tests must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of Appendix 3.U.K.
3.ILLUMINATION REQUIREMENTSU.K.
3.1.General requirementsU.K.
3.1.1.Headlamps must be designed in such a way that, with adequate HS1 or R2 lamps, they emit a light that is not dazzling but is nevertheless adequate on passing beam and provides good illumination on driving beam.U.K.
3.1.2.A screen placed vertically at a distance of 25 m in front of the headlamp, as shown in Appendix 1, must be used to check the illumination produced by the headlamp.U.K.
3.1.3.A colourless reference lamp designed for a nominal voltage of 12 V must be used in examining headlamps. The current at the terminals of the lamp during examination of the headlamp must be set to the following characteristics:U.K.
The headlamp must be considered acceptable if it meets the requirements set out in section 3 with at least one reference lamp which may be presented together with the headlamp.
3.1.4.The dimensions determining the position of the filaments within the HS1 or R2 filament reference lamp are set out in Annex IV.U.K.
3.1.5.The bulb for the filament reference lamp must be of such a shape and optical quality that it causes a minimum of reflection or refraction which may have an adverse effect on the light distribution.U.K.
3.2.Requirement relating to the passing beamU.K.
3.2.1.The passing beam must produce a cut-off of such distinctness that it is possible to carry out adjustments correctly using the said cut-off. The cut-off must be a straight horizontal line on the side opposite to the rule of the road for which the headlamp is intended. On the other side the cut-off must not go beyond either broken line HV-H1 and H4 formed by a straight line formed by HV-H1 lying at an angle of 45o with the horizontal and a straight line H1-H4 offset by 1 % in relation to straight line h-h, or straight line HV-H3 inclined by 15o to the horizontal (see Appendix 1). In no case is a cut-off going beyond both line HV-H2 and line H2-H4 and resulting from the combination of the two preceding possibilities acceptable.U.K.
3.2.2.The headlamp must be aligned in such a way that:U.K.
3.2.2.1.where headlamps are designed to meet the requirements of driving on the right the cut-off on the left-hand half of the screen must be horizontal and for headlamps designed to meet the requirements of driving on the left the cut-off in the right-hand half of the screen must be horizontal. The setting screen must be sufficiently wide to permit examination of the cut-off over at least 5o on each side of line v-v;U.K.
3.2.2.2.on the screen this horizontal part of the cut-off must be 25 cm below the horizontal plane passing through the focal centre of the headlamp (see Appendix 1);U.K.
3.2.2.3.the tip of the cut-off must be on straight line v-v. If the beam does not have a cut-off, a clear ‘elbow’ lateral setting must be presented in such a way as best to meet the illumination requirements applying to points 75 R and 50 R for driving on the right and point 75 L and 50 L for driving on the left.U.K.
3.2.3.When aligned in this manner the headlamp must meet the requirements referred to in 3.2.5 to 3.2.7 and 3.3.U.K.
3.2.4.Where a headlamp aligned as referred to above does not meet the requirements of 3.2.5 to 3.2.7 and 3.3 it is permissible to alter the setting provided that the axis of the beam is not moved sideways by more than 1o (= 44 cm) to the right or left. The incorrect setting limit of 1o to the right or left is not compatible with a vertical incorrect setting upwards or downwards which is restricted only by the requirements laid down in 3.3. However, the horizontal part of the cut-off must not go beyond line h-h. In order to make settings easier by means of the cut-off it is permissible partly to mask the headlamp in order to make the cut-off more distinct.U.K.
3.2.5.The illumination produced on the screen by the passing beam must meet the requirements set out in the following table:U.K.
| Point on measuring screen | Illumination required, in lux | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Headlamps for on-road use/Driving on the right | Headlamps for on-road use/Driving on the left | |||
| Point | B 50 L | Point | B 50 R | ≤ 0,3 |
| Point | B 75 R | Point | B 75 L | ≥ 6 |
| Point | B 50 R | Point | B 50 L | ≥ 6 |
| Point | B 25 L | Point | B 25 R | ≥ 1,5 |
| Point | B 25 R | Point | B 25 L | ≥ 1,5 |
| All points within zone III | ≤ 0,7 | |||
| All points within zone IV | ≥ 2 | |||
| All points within zone I | ≤ 20 | |||
3.2.6.In none of the zones I, II, III and IV must there be lateral variations that impair good visibility.U.K.
3.2.7.Headlamps designed to meet the requirements of driving on the right and those for driving on the left must, for each of the two locations of the sealed beam unit or lamp meet the requirements set out above for the rule of the road corresponding to the location under consideration.U.K.
3.3.Requirements concerning the driving beamU.K.
3.3.1.The illumination produced on the screen by the driving beam must be measured using the same headlamp setting as for the measurements defined in 3.2.5 to 3.2.7.U.K.
3.3.2.The illumination produced on the screen by the driving beam must meet the following requirements:U.K.
3.3.2.1.Point of intersection HV of lines h-h and v-v must be at the isolux representing 90 % of maximum illumination. Maximum value Em must be at least 32 lux. Its value must not exceed 240 lux.U.K.
3.3.2.2.Starting from the HV point horizontally to the right and to the left, the illumination must be at least 16 lux at a distance of 1,125 m and at least equal to 4 lux up to a distance of 2,25 m.U.K.
3.4.The illumination on the screen referred to in 3.2.5 to 3.2.7 and 3.3 must be measured by means of a useable-area photo receiver acting within a 65 mm square.U.K.
4.REFRENCE HEADLAMPU.K.
A headlamp which:
4.1.meets the component type-approval requirements set out below;U.K.
4.2.has an effective diameter of at least 160 mm;U.K.
4.3.provides illumination, with a reference lamp, at various points within the various areas provided for in 3.2.5;U.K.
4.3.1.which is at least 90 % of the maximum values, andU.K.
4.3.2.at least 120 % of the minimum limits as required by the table in 3.2.5, is considered to be a reference headlamp.U.K.
5.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS ATTACHED TO ANY INSPECTIONS WHICH MAY BE CARRIED OUT, BY THE COMPETENT AUTHORITIES WHEN CHECKING CONFORMITY OF PRODUCTION ACCORDING TO SECTION 5.1 OF ANNEX IU.K.
5.1.For values B 50 L (or R) and Zone III the maximum deviation may be respectivelyU.K.
5.2.For the passing beam, the prescribed values in this Directive are met at HV (with a tolerance of 0,2 lux) and related to that aiming at least one point of each area delimited on the measuring screen (at 25 m) by a circle 15 cm in radius around points B 50 L (or R) (with a tolerance of 0,1 lux), 75 R (or L), 50 R (or L), 25 R, 25 L and in the entire area of zone IV which is not more than 22,5 cm above line 25 R and 25 L.U.K.
5.2.1.If, for the driving beam, HV being situated within the isolux 0,75 Emax, a tolerance of + 20 % for maximum values and − 20 % for minimum values is observed for the photometric values at any measuring point specified in section 3.2.5 of this Annex, the reference mark is disregarded.U.K.
5.3.If the results of the tests described above do not meet the requirements, the alignment of the headlamp may be changed, provided that the axis of the beam is not displaced laterally by more than 1o to the right or left.U.K.
5.4.Headlamps with apparent defects are disregarded.U.K.
5.5.The reference mark is disregarded.U.K.
Appendix 2
Tests on the stability of the photometric performance of headlamps in operation
Compliance with the requirements is not a sufficient criterion for the component type-approval of headlamps fitted with plastic lenses.
See Appendix 2 to Annex III-D.
Appendix 3
Requirements for lamps incorporating lenses of plastic material and testing of lens or material samples and of complete lamps
See Appendix 3 to Annex III-D.
ANNEX III-D
HEADLAMPS FOR MOTORCYCLES AND TRICYCLES EMITTING AN ASYMMETRICAL PASSING BEAM, A DRIVING BEAM AND FITTED WITH HALOGEN FILAMENT LAMPS OTHER THAN HS1 LAMPS
1.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS CONCERNING MARKS AND THE MARKING OF DEVICESU.K.
1.1.Headlamps designed in such a way as to meet the requirement of a single rule of the road (driving on either the right or the left) must, on the lens, bear the limits of the area which may possibly be masked in order to avoid distracting road users in a country where the rule of the road is not that for which the headlamp has been designed. However, when that area is directly identifiable by design any such delimitation is not necessary.U.K.
1.2.Headlamps designed in such a way as to meet the requirements of driving on the right and those for driving on the left must bear markings in order to locate the two positions for the fixing in position of the light unit on the vehicle or the lamp on the reflector; these markings consist of the letters ‘R/D’ for the position corresponding to driving on the right and the letters ‘L/G’ for the position corresponding to driving on the left.U.K.
1.3.All headlamps designed in such a way as to preclude any simultaneous lighting-up of the dipped-beam filament and that of any other light source with which they may be associated must be marked with an oblique stroke (/) within the component type-approval mark, after the passing beam-headlamp symbol.U.K.
1.4.Where headlamps meet only the requirements of driving on the left, a horizontal arrow pointing to the right of an observer looking at the headlamp head-on, i.e. towards the side of the road driven upon, must be entered below the component type-approval mark.U.K.
1.5.Where by means of a deliberate alteration in the adjustment of the light unit or lamp, headlamps meet the requirements of both rules of the road, a horizontal arrow having two tips pointing one to the left and the other to the right must be entered below the component type approval mark.U.K.
1.6.The following additional symbol or symbols:U.K.
1.6.1.on headlamps meeting left-hand traffic requirements only, a horizontal arrow pointing to the right of an observer facing the headlamp, i.e. to the side of the road on which traffic moves;U.K.
1.6.2.on headlamps designed to meet the requirements of both traffic systems by means of an appropriate adjustment of the setting of the optical unit or the filament lamp, a horizontal arrow with a head at each end, the heads pointing respectively to the left and to the right;U.K.
1.6.3.on headlamps meeting the requirements of this Directive in respect of the passing beam only, the letters ‘HC’;U.K.
1.6.4.on headlamps meeting the requirements of this Directive in respect of the driving beam only, the letters ‘HR’;U.K.
1.6.5.on headlamps meeting the requirements of this Directive in respect of both the passing and the driving beam, the letters ‘HCR’;U.K.
1.6.6.on headlamps incorporating a lens of plastic material, the letters ‘PL’ to be affixed near the symbols prescribed in 1.6.3 to 1.6.5.U.K.
2.GENERAL SPECIFICATIONSU.K.
2.1.Each sample must conform to the specifications set out in sections 6 to 8.U.K.
2.2.Headlamps must be so made as to retain their prescribed photometric characteristics and to remain in good working order when in normal use, in spite of the vibrations to which they may be subjected.U.K.
2.2.1.Headlamps must be fitted with a device enabling them to be so adjusted on the vehicle in such a way as to comply with the rules applicable to them. Such a device need not be fitted on components in which the reflector and the lens cannot be separated provided the use of such components is confined to vehicles on which the headlamp setting can be adjusted by other means. Where a headlamp providing a driving beam and a headlamp providing a passing beam, each equipped with its own filament lamp, are assembled to form a composite unit, the adjusting device must enable each optical system individually to be duly adjusted. However, this does not apply to headlamp assemblies whose reflectors are indivisible. For this type of assembly, the requiremens of section 6 apply.U.K.
2.3.The components by which the filaments lamp(s) is/are fixed to the reflector must be made in such a way that, even in darkness, the filament lamp(s) can be fixed in no other position but the correct one(3) (4).U.K.
The filament lamp-holder must conform to the dimensional characteristics as given in the following data sheets of CIE Publication 61-2:
| Filament lamps | Holder | Data Sheets |
|---|---|---|
| H1 | P 14.5s | 7005.46.3 |
| H2 | X 5111 | 7005.99.2 |
| H3 | PK 22s | 7005.47.1 |
| HB3 | P 20d | 7005.31.1 |
| HB4 | P 22d | 7005.32.1 |
| H7 | PX 26d | 7005.5.1 |
| H4 | P43t-38 | 7005.39.2 |
2.4.Headlamps designed to satisfy the requirements of both right-hand and left-hand traffic may be adapted for traffic on a given side of the road either by an appropriate initial setting when fitted on the vehicle or by selective setting by the user. Such initial or selective setting may consist, for example, of fixing either the optical unit at a given angle on the vehicle or the filament lamp at a given angle in relation to the optical unit. In all cases, only two precise setting positions, one for right-hand and one for left-hand traffic, must be possible, and the design must preclude inadvertent shifting of the headlamp from one position to the other or its setting in an intermediate position. Where two different setting positions are provided for the filament lamp, the components attaching the filament lamp to the reflector must be designed and made so that, in each of its two settings, the filament lamp is held in position with the precision required for headlamps intended for traffic on only one side of the road. Conformity with the requirements of this section must be verified visually and, where necessary, by a test fitting.U.K.
2.5.Only for headlamps equipped with single-filament halogen lamps: On headlamps designed to provide alternately a driving beam and a passing beam, any mechanical, eletro-mechanical or other device incorporated in the headlamp for switching from one beam to the other(5) must be so constructed that:U.K.
2.5.1.the device is strong enough to be worked 50 000 times without suffering damage despite the vibration to which it may be subjected in normal use;U.K.
2.5.2.in the case of failure it is possible to obtain the passing beam automatically;U.K.
2.5.3.either the passing beam or the driving beam can always be obtained without any possibility of the mechanism stopping in between the two positions;U.K.
2.5.4.the user cannot, with ordinary tools, change the shape or position of the moving parts.U.K.
2.6.Complementary tests must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of Appendix 2 to ensure that in use there is no excessive change in photometric performance.U.K.
2.7.If the lens of the headlamp is of plastic material, tests must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of Appendix 3.U.K.
3.ILLUMINATIONU.K.
3.1.General provisionsU.K.
3.1.1.Headlamps must be made in such a way that, with suitable H1, H2, H3, HB3, HB4, H7 and/or H4 filament lamps, they provide adequate illumination without dazzle in the case of the passing beam and good illumination in the case of the driving beam.U.K.
3.1.2.The illumination produced by the headlamp must be checked on a vertical screen set at a distance of 25 m in front of the headlamp and at right angles to its axis (see Appendix 1).U.K.
3.1.3.The headlamps must be checked by means of (a) standard (reference) filament lamp(s) designed for a rated voltage of 12 V. During the checking of the headlamp, the voltage at the terminals of the filament lamp must be regulated so as to obtain the following characteristics:U.K.
| Filament lamps | Approximate supply voltage (in V) for measurement | Light flux in lumens |
|---|---|---|
| H1 | 12 | 1 150 |
| H2 | 12 | 1 300 |
| H3 | 12 | 1 100 |
| HB3 | 12 | 1 300 |
| HB4 | 12 | 825 |
| H7 | 12 | 1 100 |
| H4 passing driving | 12 12 | 750 1 250 |
The headlamp is deemed satisfactory if the photometric requirements are met with at least one standard (reference) 12-volt filament lamp which may be supplied with the headlamp.
3.1.4.The dimensions determining the position of the filament inside the standard (reference) 12-volt filament lamp are shown on the relevant data sheet of Annex 4.U.K.
3.1.5.The bulb of the standard (reference) filament lamp must be of such optical shape and quality that it does not cause any reflection or refraction adversely affecting the light distribution. Compliance with this requirement must be checked by measuring the light distribution obtained when a standard headlamp is fitted with the standard (reference) filament lamp.U.K.
3.2.Provisions regarding passing beamsU.K.
3.2.1.The passing beam must produce a sufficiently sharp cut-off to permit satisfactory adjustment with its aid. The cut-off must be horizontal straight line on the side opposite to the direction of traffic for which the headlamps is intended; on the other side it must extend neither beyond the broken line H-V, H1-H4 formed by a straight line HV-H1 standing at an angle of 45o to the horizontal and a straight line H1-H4 lying 25 cm above the straight line hh, nor beyond the straight line HV-H3, inclined at an angle of 15o above the horizontal (see Appendix 1). A cut-off extending beyond both line HV-H2 and H2-H4 and resulting from a combination of the above two possibilities shall in no circumstances be permitted.U.K.
3.2.2.The headlamp must aimed in such a way that:U.K.
3.2.2.1.in the case of headlamps designed to meet the requirements of right-hand traffic, the cut-off on the left half of the screen(6) is horizontal and in the case of headlamps designed to meet the requirements of left-hand traffic, the cut-off on the right half of the screen is horizontal.U.K.
3.2.2.2.this horizontal part of the cut-off is situated 25 cm below the line h-h (see Appendix 1);U.K.
3.2.2.3.the elbow of the cut-off is on line v-v(7).U.K.
3.2.3.when so aimed the headlamp need, if its approval is sought solely for a passing beam(8), comply only with the requirements referred to in 3.2.5 to 3.2.7 and 3.3.U.K.
3.2.4.Where a headlamp so aimed does not meet the requirements of 3.2.5 to 3.2.7 and 3.3, its alignment may be changed provided that the axis of the beam is not laterally displaced by more than 1o (= 44 cm) to the right or left(9). To faciltate adjustment by means of the cut-off, the headlamp may be partially occluded in order to sharpen the cut-off.U.K.
3.2.5.The illumination produced on the screen by the passing beam must meet the following requirements:U.K.
| a E50 R and E50 L are the illuminations actually measured. | ||||
| Point on measuring screen | Illumination required, in lux | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Headlamps for right-hand traffic | Headlamps for left-hand traffic | |||
| Point | B 50 L | Point | B 50 R | ≤ 0,4 |
| Point | B 75 R | Point | B 75 L | ≥ 12 |
| Point | B 75 L | Point | B 75 R | ≤ 12 |
| Point | B 50 L | Point | B 50 R | ≤ 15 |
| Point | B 50 R | Point | B 50 L | ≥ 12 |
| Point | B 50 V | Point | B 50 V | ≥ 6 |
| Point | B 25 L | Point | B 25 R | ≥ 2 |
| Point | B 25 R | Point | B 25 L | ≥ 2 |
| Any point in zone III | ≤ 0,7 | |||
| Any point in zone IV | ≥ 3 | |||
| Any point in zone I | ≤ 2 × (E50 R and E50 L)a | |||
3.2.6.There must be no lateral variations detrimental to good visibility in any of the zones I, II, III and IV.U.K.
3.2.7.The illumintation values in zones ‘A’ and ‘B’ as shown in figure C in Annex IV must be checked by the measurement of the photometric values of points 1 to 8 on this figure; these values must lie within the following limits:U.K.
0,7 lux ≥ 1, 2, 3, 7 ≥ 0,1 lux
0,7 lux ≥ 4, 5, 6, 8 ≥ 0,2 lux
3.2.8.Headlamps designed to meet the requirements of both right-hand and left-hand traffic must in each of the two setting positions of the optical unit or of the filament lamp, meet the requirements set out above for the corresponding direction of traffic.U.K.
3.3.Provisions regarding driving beamsU.K.
3.3.1.In the case of a headlamp designed to provide a driving beam and a passing beam, measurements of the illumination produced on the screen by the driving beam must be taken with the same headlamp alignment as for measurements under 3.2.5 to 3.2.7. In the case of a headlamp providing a driving beam only, it must be adjusted that the area of maximum illumination is centred on the point of intersection of the lines h-h and v-v. Such a headlamp need meet only the requirements referred to in 3.3.U.K.
3.3.2.The illumination produced on the screen by the driving beam must meet the following requirements:U.K.
3.3.2.1.the point of intersection (HV) of lines h-h and v-v must be situated within the isolux representing 90 % of maximum illumination. This maximum value (Emax) must be not less than 48 lux. The maximum value must in no case exceed 240 lux. Moreover, in the case of a combined passing and driving headlamp, this maximum value must not be more than 16 times the immumination measured for the passing beam at point 75 R (or 75 L).U.K.
3.3.2.1.1.the maximum luminous intensity (lmax) of the driving beam expressed in thousands of candelas must be calculated by means of the formula:U.K.
lmax = 0,625 Emax
3.3.2.1.2.the refrence mark (l′max) indicating this maximum intensity and referred to in 1.6 must be obtained by means of the formula:U.K.
this value being rounded to whichever is the nearest of the following: 7,5, 10, 12,5, 17,5, 20, 25, 27,5, 30, 37,5, 40, 45, 50.
3.3.2.2.Starting from the HV point horizontally to the right and left, the illumination must not be less than 24 lux up to a distance of 1,125 m and not less than 6 lux up to a distance of 2,25 m.U.K.
3.4.The screen illumination values referred to in 3.2.5 to 3.2.7 and 3.3 must be measured by means of a photoreceptor, the effective area of which must be contained within a square of 65 mm side.U.K.
4.GAUGING DISCOMFORTU.K.
The discomfort caused by the passing beam of headlamps must be gauged.
5.STANDARD HEADLAMPU.K.
5.1.A headlamp is deemed to be a standard (reference) headlamp if it:U.K.
5.1.1.satisfies the abovementioned requirements for approval;U.K.
5.1.2.has an effective diameter of not less than 160 mm;U.K.
5.1.3.provides with a standard filament lamp, at the various points and in the various zones referred to in 3.2.5, illumination equal to:U.K.
5.1.3.1.not more than 90 % of the maximum limits andU.K.
5.1.3.2.not less than 120 % of the minimum limits prescribed in the table in 3.2.5.U.K.
6.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS ATTACHED TO ANY INSPECTIONS WHICH MAY BE CARRIED OUT BY THE COMPETENT AUTHORITIES WHEN CHECKING CONFORMITY OF PRODUCTION IN ACCORDANCE WITH SECTION 5.1 OF ANNEX IU.K.
6.1.For values B 50 L (or R) and Zone III the maximum deviation may be respectivelyU.K.
6.2.For the passing beam, the prescribed values in this Directive are met at HV (with a tolerance of 0,2 lux) and related to that aiming at least one point of each area delimited on the measuring screen (at 25 m) by a circle 15 cm in radius around point B 50 L (or R) (with a tolerance of 0,1 lux), 75 R (or L), 50 R (or L), 25 R, 25 L and in the entire area of zone IV which is not more than 22,5 cm above line 25 R and 25 L.U.K.
6.2.1.If, for the driving beam, HV being situated within the isolux 0,75 Emax, a tolerance of + 20 % for maximum values and − 20 % for minimum values is observed for the photometric values at any measuring point specified in section 3.2.5 of this Annex, the reference mark is disregarded.U.K.
6.3.If the results of the tests described above do not meet the requirements, the alignment of the headlamp may be changed, provided that the axis of the beam is not displaced laterally by more than 1o to the right or left.U.K.
6.4.Headlamps with apparent defects are disregarded.U.K.
6.5.The reference mark is disregarded.U.K.
Appendix 1
Measuring screen
Standard European beam
A.Headlamp for right-hand trafficU.K.
B.Headlamp for left-hand trafficU.K.
C.Measuring points for illumination valuesU.K.
Note:U.K.
Figure C shows the measuring point for right-hand traffic. Points 7 and 8 move to their corresponding location at the right-hand side of the picture for left-hand traffic.U.K.
Appendix 2
Tests on the stability of the photometric performance of headlamps in operation
TESTS ON COMPLETE HEADLAMPSU.K.
Once the photometric values have been measured according to the requirements of this Directive, in points Emax for driving beam and HV, 50 R, B 50 L for passing beam (or HV, 50 L, B 50 R for headlamps designed for left-hand traffic) a complete headlamp sample is tested for stability of photometric performance in operation. ‘Complete headlamp’ is understood to mean the complete lamp itself including those surrounding body parts and lamps which could influence its thermal dissipation.
1.TEST OF STABILITY OF PHOTOMETRIC PERFORMANCEU.K.
The tests are carried out in a dry and still atmosphere at an ambient temperature of 23 oC ± 5 oC, the complete headlamp being mounted on a base representing the correct installation on the vehicle.
1.1.Clean headlampU.K.
The headlamp is operated for 12 hours as described in 1.1.1 and checked as prescribed in 1.1.2.
1.1.1.Test procedureU.K.
The headlamp is operated for a period according to the specified time, so that:
1.1.1.1.
in the case where only one lighting function (driving or passing beam) is to be approved, the corresponding filament is for the prescribed time(10),
in the case of a reciprocally incorporated passing lamp and driving lamp (dual-filament lamp or two filament lamps):
If the applicant declares that the headlamp is to be used with a single filament lit(11), the test is carried out in accordance with this condition activating(10) each specified function successfully for half the time specified in 1.1,
in all other cases(12) (13), the headlamp is subjected to the following cycle until the time specified is reached:
15 minutes, passing beam filament lit
5 minutes, all filaments lit,
in the case of grouped lighting functions all the individual functions must be lit simultaneously for the time specified for individual lighting functions (a) also taking into account the use of reciprocally incorporated lighting functions (b), according to the manufacturer's specifications.
1.1.1.2.Test voltageU.K.
The voltage must be adjusted so as to supply 90 % of the maximum wattage specified in Annex IV. The applied wattage must in all cases comply with the corresponding value of a filament lamp of 12 V rated voltage, except if the applicant for approval specifies that the headlamp may be used at a different voltage. In the latter case, the test is carried out with the filament lamp whose wattage is the highest that can be used.
1.1.2.Test resultsU.K.
1.1.2.1.Visual inspectionU.K.
Once the headlamp has been stabilized to the ambient temperature, the headlamp lens and the external lens, if any, must be cleaned with a clean, damp cloth. It must then be inspected visually; no distortion, deformation, cracking or change in colour of either the headlamps or the external lens, if any, must be noticeable.
1.1.2.2.Photometric testU.K.
To comply with the requirements of this directive, the photometric values must be verified in the following points:
Passing beam:
50 R — B 50 L — HV for headlamps designed for right-hand traffic,
50 L — B 50 R — HV for headlamps designed for left-hand traffic.
Driving beam:
Point of Emax.
Another adjustment may be carried out to allow for any deformation of the headlamp base due to heat (the change of the position of the cut-off line is covered in section 2 of this Appendix).
A 10 % discrepancy between the photometric characteristics and the values measured prior to the test is permissible, including the tolerances of the photometric procedure.
1.2.Dirty headlamp,U.K.
After being tested as specified in 1.1, the headlamp must be operated for one hour as described in 1.1.1, after being prepared as prescribed in 1.2.1, and checked as prescribed in 1.1.2.
1.2.1.Preparation of the headlampU.K.
1.2.1.1.Test mixtureU.K.
The mixture of water and polluting agent to be applied to the headlamp must be composed of nine parts (by mass) of silica sand with a grain size distributed between 0 and 100 µm, one part (by mass) of vegetal carbon dust of a grain size distributed between 0 and 100 µm, 0,2 (by mass) of NaCMC(14) and an appropriate quantity of distilled water, the conductivity of which is lower than 1 mS/m for the purpose of this test.
The mixture must not be more than 14 days old.
1.2.1.2.Application of the test mixture to the headlampU.K.
The test mixture must be uniformly applied to the entire light-emitting surface of the headlamp and then left to dry. This procedure is repeated until the illuminating value has dropped to 15 — 20 % of the values measured for each following point under the conditions described in paragraph 1 above:
Emax in driving beam for a driving/passing lamp,
Emax in driving beam for a driving lamp only.
50 R and 50 V(15) for a passing lamp only, designed for right-hand traffic.
50 L and 50 V for a passing lamp only, designed for left-hand traffic.
1.2.1.3.Measuring equipmentU.K.
The measuring equipment must be equivalent to that used during headlamp approval tests. A standard (reference) filament lamp is used for the photometric verification.
2.TEST FOR CHANGE IN VERTICAL POSITION OF THE CUT-OFF LINE UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF HEATU.K.
This test consists of verifying that the vertical drift of the cut-off line under the influence of heat does not exceed a specified value for an operating passing lamp.
The headlamp tested in accordance with section 1 must be subjected to the test described in 2.1 without being removed from or readjusted in relation to its test fixture.
2.1.TestU.K.
The test must be carried out in a dry and still atmosphere at an ambient temperature of 23 oC ± 5 oC.
Using a series-production filament lamp which has been aged for at least one hour the headlamp is operated on passing beam without being removed from or readjusted in relation to its test fixture. (For the purpose of this test, the voltage must be adjusted as specified in 1.1.1.2.) The position of the cut-off line in its horizontal part (between VV and the vertical line passing through point B 50 R for left-hand traffic or B 50 L for right-hand traffic) must be verified 3 minutes (r3) and 60 minutes (r60) after operation.
The measurement of the variation in the cut-off line position as described above is carried out by any method giving acceptable accuracy and reproducible results.
2.2.Test resultsU.K.
The result expressed in milliradians (mrad) is considered as acceptable when the absolute value 
2.2.1.However, if this value is more than 1,0 mrad but not more than 1,5 mrad (1,0 mrad < Δr1 ≤ 1,5 mrad) a second headlamp must be tested as described in 2.1 after being subjected three consecutive times to the cycle as described below, in order to stabilize the position of mechanical parts of the headlamp on a base representative of the correct installation on the vehicle:U.K.
Operation of the passing lamp for one hour (the voltage must be adjusted as specified in 1.1.1.2.)
Period of rest for one hour.
The headlamp type is considered as acceptable if the mean value of the absolute values Δr
1
measured on the first sample and Δr
11
measured on the second sample is not more than 1,0 mrad.
Appendix 3
Requirements for lamps incorporating lenses of plastic material and testing of lens or material samples and of complete lamps
1.GENERAL SPECIFICATIONSU.K.
1.1.The samples supplied pursuant to section 2.4 of Annex I must satisfy the specifications indicated in section 2.1 to 2.5 of this Appendix.U.K.
1.2.The two samples of complete lamps supplied in accordance with section 2.3 of Annex I incorporating lenses of plastic material must, with regard to the lens material, satisfy the specifications indicated in section 2.6 of this Appendix.U.K.
1.3.The samples of lenses of plastic material or samples of material are subjected, with the reflector to which they are intended to be fitted (where applicable), to approval tests in the chronological order indicated in table A reproduced in Appendix 3.1.U.K.
1.4.However, if the lamp manufacturer can prove that the product has already passed the tests prescribed in 2.1 to 2.5 below, or the equivalent tests pursuant to another Directive, those tests need not be repeated; only the tests prescribed in Appendix 3.1, table B, are mandatory.U.K.
2.TESTSU.K.
2.1.Resistance to temperature changesU.K.
2.1.1.TestsU.K.
Three new samples (lenses) are subjected to five live cycles of temperature and humidity (RH = relative humidity) change in accordance with the following programme:
3 hours at 40 oC ± 2 oC and 85 %—95 % RH;
1 hour at 23 oC ± 5 oC and 60 %—75 % RH;
15 hours at −30 oC ± 2 oC;
1 hour at 23 oC ± 5 oC and 60 %—75 % RH;
3 hours at 80 oC ± 2 oC;
1 hour at 23 oC ± 5 oC and 60 %—75 % RH.
Before this test, the samples must be kept at 23 oC ± 5 oC and 60 %—75 % RH for at least four hours.
Note:U.K.
The periods of one hour at 23 oC ± 5 oC must include the periods of transition from one temperature to another which are needed in order to avoid thermal shock effect.U.K.
2.1.2.Photometric measurementsU.K.
2.1.2.1.MethodU.K.
Photometric measurements must be carried out on the samples before and after the test.
These measurements must be made using a standard lamp, at the following points:
B 50 L and 50 R for the passing beam of a passing lamp or a passing/driving lamp (B 50 R and 50 L in the case of headlamps intended for left-hand traffic) or B 50 and 50 R/L in the case of symmetrical passing beam;
Emax route for the driving beam of a driving lamp or a passing/driving lamp;
HV and Emax zone D for a front fog-lamp.
2.1.2.2.ResultsU.K.
The variation between the photometric values measured on each sample before and after the test must not exceed 10 % including the tolerances of the photometric procedure.
2.2.Resistance to atmospheric and chemical agentsU.K.
2.2.1.Resistance to atmospheric agentsU.K.
Three new samples (lenses or samples of material) are exposed to radiation from a source having a spectral energy distribution similar to that of a black body at a temperature between 5 500 K and 6 000 K. Appropriate filters must be placed between the source and the samples so as to reduce as far as possible radiations with wave lengths smaller than 295 nm and greater than 2 500 nm. The samples are exposed to an energetic illumination of 1 200 W/m2 ± 200 W/m2 for a period such that the luminous energy that they receive is equal to 4 500 MJ/m2 ± 200 MJ/m2. Within the enclosure, the temperature measured on the black panel placed on a level with the samples must be 50 oC ± 5 oC. In order to ensure a regular exposure, the samples must revolve around the source of radiation at a speed of between 1 and 5 1/min.
The samples are sprayed with distilled water of conductivity lower than 1 mS/m at a temperature of 23 oC ± 5 oC, in accordance with the following cycle:
2.2.2.Resistance to chemical agentsU.K.
After the test described in 2.2.1 and the measurement described in 2.2.3.1 have been carried out, the outer face of the said three samples is treated as described in 2.2.2.2 with the mixture defined in 2.2.2.1.
2.2.2.1.Test mixtureU.K.
The test mixture is composed of 61,5 % n-heptane, 12,5 % toluene, 7,5 % ethyl tetrachloride, 12,5 % trichlorethylene and 6 % xylene (% volume).
2.2.2.2.Application of the test mixtureU.K.
A piece of cotton cloth is soaked (as per ISO 105) until the mixture is saturated as defined in 2.2.2.1 and, within 10 seconds, applied for 10 minutes to the outer face of the sample at a pressure of 50 N/cm2, corresponding to an effort of 100 N applied on a test surface fo 14 × 14 mm.
During this 10-minute period, the cloth pad must be soaked again with the mixture so that the composition of the liquid applied is continuously identical with that of the test mixture prescribed.
During the period of application, it is permissible to compensate the pressure applied to the sample in order to prevent it from causing cracks.
2.2.2.3.CleaningU.K.
At the end of the application of the test mixture, the samples must be dried in the open air and then washed with the solution described in 2.3 (Resistance to detergents) at 23 oC ± 5 oC.
Afterwards the samples must be carefully rinsed with distilled water containing not more than 0,2 % impurities at 23 oC ± 5 oC and then wiped off with a soft cloth.
2.2.3.ResultsU.K.
2.2.3.1.After the test for resistance to atmospheric agents, the outer face of the samples must be free from cracks, scratches, chipping and deformation, and the mean variation in transmissionU.K.
,
measured on the three samples according to the procedure described in Appendix 3.2 to this Annex must not exceed 0,020 ( Δtm ≤ 0,020).
2.2.3.2.After the test of resistance to chemical agents, the samples must not bear any traces of chemical staining likely to cause a variation of flux diffusion, whose mean variationU.K.
,
measured on the three samples according to the procedure described in Appendix 3.2 to this Annex must not exceed 0,020 ( Δdm ≤ 0,020).
2.3.Resistance to detergents and hydrocarbonsU.K.
2.3.1.Resistance to detergentsU.K.
The outer face of three samples (lenses or samples of material) is heated to 50 oC ± 5 oC and then immersed for five minutes in a mixture maintained at 23 oC ± 5 oC and composed of 99 parts distilled water containing not more than 0,02 % impurities and one part alkylaryl sulphonate.
At the end of the test, the samples are dried at 50 oC ± 5 oC. the surface of the samples is cleaned with a moist cloth.
2.3.2.Resistance to hydrocarbonsU.K.
The outer face of these three samples is then lightly rubbed for one minute with a cotton cloth soaked in a mixture composed of 70 % n-heptane and 30 % toluene (% volume), and then dried in the open air.
2.3.3.ResultsU.K.
After the above two tests have been performed successively, the mean value of the variation in transmission
,
measured on the three samples according to the procedure described in Appendix 3.2 to this Annex must not exceed 0,010 ( Δtm ≤ 0,010).
2.4.Resistance to mechanical deteriorationU.K.
2.4.1.Mechanical deterioration methodU.K.
The outer face of the three new samples (lenses) is subjected to the uniform mechanical deterioration test by the method described in Appendix 3.3 to this Annex.
2.4.2.ResultsU.K.
After this test, the variations:
in transmission:
and in diffusion:
are measured according to the procedure described in Appendix 3.2 to this Annex in the area specified in 2.2.4. The mean value of the three samples must be such that
Δtm ≤ 0,100
Δdm ≤ 0,050.
2.5.Test of adherence of coatings, if anyU.K.
2.5.1.Preparation of the sampleU.K.
A surface of 20 mm × 20 mm in area of the coating of a lens is cut with a razor blade or a needle into a grid of squares approximately 2 mm × 2 mm. The pressure on this blabe or needle must be sufficient to cut at least the coating.
2.5.2.Description of the testU.K.
An adhesive tape is used with a force of adhesion of 2 N/(cm of width) ± 20 % measured under the standardized conditions specified in Appendix 3.4 to this Annex. This adhesive tape, which must be at least 25 mm wide, is pressed for at least five minutes to the surface prepared as prescribed in 2.5.1.
The end of the adhesive tape is then loaded in such a way that the force of adhesion to the surface considered is balanced by a force perpendicular to that surface. At this stage, the tape is torn off at a constant speed of 1,5 m/s ± 0,2 m/s.
2.5.3.ResultsU.K.
There must be no appreciable impairment of the gridded area. Impairments at the intersections between squares or at the edges of the cuts are permitted, provided that the impaired area does not exceed 15 % of the gridded surface.
2.6.Tests of the complete headlamp incorporating a lens of plastic materialU.K.
2.6.1.Resistance to mechanical deterioration of the lens surfaceU.K.
2.6.1.1.TestsU.K.
The lens of lamp sample No 1 is subjected to the test described in 2.4.1 above.
2.6.1.2.ResultsU.K.
After the test, the results of photometric measurements carried out on the headlamp in accordance with this Directive must not exceed by more than 30 % the maximum values prescribed at point B 50 L and HV and not by more than 10 % below the minimum values prescribed at point 75 R (in the case of headlamps intended for left-hand traffic, the points to be considered are B 50 R, HV and 75 L). In the case of the symmetrical crossing beam the points to be considered are B 50 and H.
2.6.2.Test of adherence of coatings, if anyU.K.
The lens of lamp sample No 2 is subjected to the test described in 2.5.
3.VERIFICATION OF THE CONFORMITY OF PRODUCTIONU.K.
3.1.With regard to the materials used for the manufacture of lenses, the lamps of a series are recognized as complying with this Directive if:U.K.
3.1.1.After the test for resistance to chemical agents and the test for resistance to detergents and hydrocarbons, the outer face of the samples exhibits no cracks, chipping or deformation visible to the naked eye (see 2.2.2, 2.3.1 and 2.3.2);U.K.
3.1.2.After the test described in 2.6.1.1, the photometric values at the points of measurement considered in 2.6.1.2 are within the limits prescribed for conformity of production by this Directive.U.K.
3.2.If the test results fail to satisfy the requirements, the tests must be repeated on another sample of headlamps selected at random.U.K.
Appendix 3.1
Chronological order of approval tests
A.Tests on plastic materials (lenses or samples of material supplied pursuant to section 1.2.4 of Annex I)U.K.
B.Tests on complete headlamps (supplied pursuant to section 1.2.3 of Annex I)U.K.
Appendix 3.2
Method of measurement of the diffusion and transmission of light
1.EQUIPMENT (see figure)U.K.
The beam of a collimator K with a half divergence
is limited by a diaphragm DT with an opening of 6 mm against which the sample stand is placed.
A convergent achromatic lens L
2
corrected for spherical aberrations, links the diaphragm D
T
with the receiver R; the diameter of the lens L
2
must be such that it does not diaphragm the light diffused by the sample in a cone with a half top angle
An annular diaphragm DD with angles 
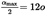
placed in an image focal plane of the lens L2.
The non-transparent central art of the diaphragm is necessary in order to eliminate the light arriving directly from the light source. It must be possible to remove the central part of the diaphragm from the light beam in such a manner that it returns exactly to its original position.
The distance L2 DT and the focal length F2 (16) of the lens L2 must be so chosen that the image of DT completely covers the receiver R.
When the initial incident flux is referred to 1 000 units, the absolute precision of each reading must be better than 1 unit.
2.MEASUREMENTU.K.
The following readings are taken:
| Reading | with sample | with central part of DD | Quantity represented |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | no | no | Incident flux in initial reading |
| T2 | yes (before test) | no | Flux transmitted by the new material in a field of 24 oC |
| T3 | yes (after test) | no | Flux transmitted by the tested material in a field of 24 oC |
| T4 | yes (before test) | yes | Flux diffused by the new material |
| T5 | yes (after test) | yes | Flux diffused by the tested material |
Appendix 3.3
Spray testing method
1.TEST EQUIPMENTU.K.
1.1.Spray gunU.K.
The spray gun used must be equipped with a nozzle 1,3 mm in diameter allowing a liquid flow-rate of 0,24 ± 0,02 1/minute at an operating pressure of 6,0 bars − 0, + 0,5 bar.
Under these operating conditions the fan pattern obtained must be 170 mm ± 50 mm in diameter on the surface exposed to deterioration, at a distance of 380 mm ± 10 mm from the nozzle.
1.2.Test mixtureU.K.
The test mixture is composed of:
Silica sand of hardness 7 on the Mohs scale, with a grain size between 0 and 0,2 mm and an almost normal distribution, with an angular factor of 1,8 to 2;
Water of hardness not exceeding 205 g/m3 for a mixture comprising 25 g of sand per litre of water
2.TESTU.K.
The outer surface of the lamp lenses is subjected once or more than once to the action of the sand jet produced as described above. the jet must be sprayed almost perpendicular to the surface to be tested.
The deterioration is checked by means of one or more samples of glass placed as a reference near the lenses to be tested. The mixture must be sprayed until the variation in the diffusion of light on the sample or samples measured by the method described in Appendix 2 is such that:
Several reference samples may be used to check that the whole surface to be tested has deteriorated homogeneously.
Appendix 3.4
Adhesive tape adherence test
1.PURPOSEU.K.
This method allows to determination under standard conditions of the linear force of adhesion of an adhesive tape to a glass plate.
2.PRINCIPLEU.K.
Measurement of the force necessary to unstick an adhesive tape from a glass plate at an angle of 90o.
3.SPECIFIED ATMOSPHERIC CONDITIONSU.K.
The ambient conditions must be at 23 oC ± 5 oC and 65 % ± 15 % relative humidity (RH).
4.TEST-PIECESU.K.
Before the test, the sample roll of adhesive tape must be conditioned for 24 hours in the specified atmosphere (see section 3 above).
Five test-pieces each 400 mm long are tested from each roll. These test-pieces are taken from the roll after the first three turns have been discarded.
5.PROCEDUREU.K.
The test must be carried out under the ambient conditions specified in section 3.
The five test pieces are taken while the tape is radially unrolled at a speed of approximately 300 mm/s, and the test-pieces are then applied within 15 seconds in the following manner:
The tape is applied to the glass plate progressively with a slight lengthwise rubbing movement of the finger, without excessive pressure, in such a manner as to leave no air bubble between the tape and the glass plate.
The assembly is left in the specified atmospheric conditions for 10 minutes.
About 25 mm of the test-piece is unstuck from the plate in a plane perpendicular to the axis of the test-piece.
The plate is fixed and the free end of the tape folded back at 90o. Force is applied in such a manner that the separation line between the tape and the plate is perpendicular to this force and perpendicular to the plate.
The tape is then pulled to unstick at a speed of 300 mm/s and the force required is recorded.
6.RESULTSU.K.
The five values obtained are arranged in order and the median value taken as the results of the measurement. This value is expressed in Newtons per centimetre of width of the tape.
ANNEX IV
INCANDESCENT LAMPS INTENDED FOR USE IN COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVED LAMPS FOR MOPEDS, MOTORCYCLES AND TRICYCLES
| Appendix 1 | Category R2 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 2 | Category H1 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 3 | Category H2 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 4 | Category H3 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 5 | Category H4 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 6 | Category HS1 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 7 | Category HB3 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 8 | Category HB4 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 9 | Category H7 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 10 | Category HS2 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 11 | Category S1 and S2 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 12 | Category S3 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 13 | Category S4 Filament lamps |
| Appendix 14 | Category P21W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 15 | Category P21/5W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 16 | Category R5W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 17 | Category R10W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 18 | Category T4W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 19 | Category C5W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 20 | Category C21W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 21 | Category W3W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 22 | Category W5W Filament lamps |
| Appendix 23 | Example of the arrangement of the approval mark of a filament lamp |
| Appendix 24 | Luminous centre and shapes of lamp filaments |
1.APPLICATION FOR THE COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVAL OF A FILAMENT LAMPU.K.
1.1.The application for the component type-approval of a filament lamp submitted in compliance with Article 3 of Directive 92/61/EEC must, moreover, provide the following details:U.K.
1.1.1.drawings in triplicate, sufficiently detailed to permit identification of the type;U.K.
1.1.2.a brief technical description;U.K.
1.1.3.five samples of each colour which has been applied for;U.K.
1.2.In the case of a type of filament lamp differing only by the make or trade name from a type that has already been approved it is sufficient to submit:U.K.
1.2.1.a declaration by the lamp manufacturer that the type submitted is identical (except in the make or trade name) with and has been produced by the same manufacturer as the type already approved, the latter being identified by its approval code;U.K.
1.2.2.two samples bearing the new make or trade name.U.K.
2.ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS CONCERNING THE MARKING OF AND MARKS ON FILAMENT LAMPSU.K.
2.1.Filament lamps submitted for type-approval must bear on the cap or bulb (in the latter case the luminous characteristics must not be adversely affected);U.K.
2.1.1.the make or trade name of the applicant;U.K.
2.1.2.the rated voltage;U.K.
2.1.3.the international designation of the relevant category;U.K.
2.1.4.the rated wattage (in the sequence, principal filament/secondary filament for dual filament lamps); this need not be indicated separately if it is part of the international designation of the relevant filament-lamp category;U.K.
2.1.5.a space of sufficient size to accommodate the approval mark.U.K.
2.2.The space mentioned in 2.1.5 must be indicated in the drawings accompanying the application for type-approval.U.K.
2.3.Other inscriptions than those covered by 2.1 may be affixed, providing they do not adversely affect the luminous characteristics.U.K.
3.COMPONENT TYPE-APPROVAL OF A FILAMENT LAMPU.K.
3.1.If all the samples of a type of filament lamp which are submitted in pursuance of 1.1.3 or 1.2.2 meet the requirements of this Annex, type-approval is granted.U.K.
3.2.A component type-approval mark in accordance with the provisions of Article 8 of Directive 92/61/EEC must be placed in the space referred to in 2.1.5.U.K.
3.3.Appendix 23 to this Annex gives an example of the arrangement of the approval mark.U.K.
4.TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
4.1.The technical requirements are those set out in sections 2.1 and 3 of United Nations ECE Regulation 37 which has been consolidated by the following document:U.K.
Revision 2 incorporating the 02 and 03 series of amendments, Corrigendum 2 and supplements 1 to 9 to the 03 series of amendments.
5.CONFORMITY OF PRODUCTIONU.K.
5.1.Filament lamps approved pursuant to this Annex must be manufactured so as to conform to the type approved by meeting the marking and technical requirements set forth in 2.1, 3.2 and 4 and in the relevant Appendices to this Annex.U.K.
5.2.In order to verify that the requirements of 5.1 are met, checks on production must be carried out as defined in paragraph 4 and Annexes 6, 7, 8 and 9 of United Nations ECE Regulation 37 as referred to in 4.1.U.K.
5.3.The type-approval granted in respect of a type of filament lamp pursuant to this Annex may be withdrawn if the requirements of 5.1 and 5.2 are not met or if a filament lamp bearing an approval mark does not conform to the type approved.U.K.
Appendix 1
Category R2 lamps
SHEET R2/1U.K.
The drawings are intended only to illustrate the essential dimensions of the filament lamp
| a The values indicated on the left and on the right refer to the driving-beam filament and the passing-beam filament respectively. | |||||||||
| Electrical and photometric characteristics | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||||||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6a | 12a | 24a | 12a | ||||
| Watts | 45 | 40 | 45 | 40 | 55 | 50 | 45 | 40 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,3 | 13,2 | 28 | 13,2 | ||||
| Objective values | Watts | 53 max. | 47 max. | 57 max. | 51 max. | 76 max. | 69 max. | 52 + 0 % − 10 % | 46 ± 5 % |
| Luminous flux lm | 720 min. | 570 ± 15 % | 860 min. | 675 ± 15 % | 1 000 min. | 860 ± 15 % | |||
| Reference luminous flux at approximately 12 V | 700 | 450 | |||||||
SHEET R2/2Position and dimensions of shield and filamentsU.K.
The drawings are not mandatory with respect to the design of the shield and filaments.
SHEET R2/3U.K.
| a The position and dimensions of the shield and filaments must be checked by means of the method of measurement as described in IEC Publication 809. | ||||||
| b To be measured at the distance from the reference plane indicated in millimetres behind the stroke. | ||||||
| c mv = measured value. | ||||||
| d The angle γ is only for shield design and need not be checked on finished filament lamps. | ||||||
| Filaments and shield position and dimensionsa | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions in mm | Tolerance | |||||
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||||
| 6 V | 12 V | 24 V | 12 V | |||
| a | 0,6 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | |||
| b1/30,0b b1/33,0 | 0,2 b1/30,0 mvc | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | |||
| b2/30,0b b2/33,0 | 0,2 b2/30,0 mvc | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | |||
| c/30,0b c/33,0 | 0,5 c/30,0 mvc | ± 0,3 | ± 0,15 | |||
| e | 6 V, 12 V 24 V | 28,5 28,8 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | ||
| f | 6 V, 12 V 24 V | 1,8 2,2 | ± 0,4 | ± 0,2 | ||
| g | 0 | ± 0,5 | ± 0,3 | |||
| h/30,0b h/33,0 | 0 h/30,0 mvc | ± 0,5 | ± 0,3 | |||
| 1/2 (p—q) | 0 | ± 0,6 | ± 0,3 | |||
| lc | 5,5 | ± 1,5 | ± 0,5 | |||
| γd | 15o nom. | |||||
| Cap P45t-41 in accordance with IEC Publ. 61 (sheet 7004-95-4) | ||||||
Appendix 2
Category H1 lamps
SHEET H1/1U.K.
The drawings are intended only to illustrate the essential dimensions of the filament lamp.
SHEET H1/2U.K.
| Dimensions in mm | Tolerances | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||||
| 6 V | 12 V | 24 V | ||||
| b | 0,7 f | |||||
| e (5) (9) | 25,0 | (8) | ± 0,15 | |||
| f (5) (9) | 6 V | 4,5 | ± 1,0 | |||
| 12 V | 5,0 | ± 0,5 | + 0,5 0 | |||
| 24 V | 5,5 | ± 1,0 | ||||
| g (6) | 0,5 d (7) | ± 0,5 d | ± 0,25 d | |||
| h1 | 0 | (8) | ± 0,2 (4) | |||
| h2 | (8) | ± 0,25(4) | ||||
| ε | 45o | ± 12o | ± 3o | |||
| Cap P 14,5s in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-46-1) | ||||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 | |
| Watts | 55 | 70 | 55 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,3 | 13,2 | 28,0 | ||
| Objective values | Watts | max. 63 | max. 68 | max. 84 | max. 68 at 13,2 V | |
| Luminous flux lm | 1 350 | 1 550 | 1 900 | |||
| ± % | 15 | |||||
| Reference luminous flux for headlamp testing: 1 150 lm at approx. 12 V. | ||||||
SHEET H1/3U.K.
(1)The reference axis is the perpendicular to the reference plane and passing through the point defined by the dimensions marked with (1).U.K.
(2)Both current lead-in electrodes must be positioned in the bulb, the longer electrode above the filament (the lamp being viewed as shown in the figure). The internal design of the lamp must then be such that stray light images and reflections are reduced to the minimum, e.g. by fitting cooling jackets over the non-coiled parts of the filament.U.K.
(3)The cylindrical portion of the bulb over length ‘f’ must be such as not to deform the projected image of the filament to such an extent as appreciably to affect the optical results.U.K.
(4)The eccentricity is measured only in the horizontal and vertical directions of the filament lamp as shown in the figure. The points to be measured are those where the projection of the outside of the end turns nearest to or furthest from the reference plane crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(5)The viewing direction is the perpendicular to the reference axis contained in the plane defined by the reference axis and the centre of the second pin of the cap.U.K.
(6)Offset of filament in relation to bulb axis measured at 27,5 mm from the reference plane.U.K.
(7)d: diameter of filament.U.K.
(8)To be checked by means of a ‘box-system’, sheet H1/4.U.K.
(9)The ends of the filament are defined as the points where, when the viewing direction is as defined in footnote 5 above, the projection of the outside of the end turns nearest to or furthest from where the reference plane crosses the reference axis (special instructions for coiled-coil filaments are under consideration).U.K.
SHEET H1/4Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine, by checking whether the filament is correctly positioned relatively to the reference axis and the reference plane, whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements.
| a1 | a2 | b1 | b2 | c1 | c2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 1,4 d | 1,9 d | 0,25 | 6 | 3,5 | |
| 12 V | 6 | 4,5 | ||||
| 24 V | 7 | 4,5 | ||||
d = diameter of filament
The beginning of the filament as defined on sheet H1/1, footnote 2, must lie between lines Z1 and Z2.
The filament position is checked solely in directions FH and FV as shown on sheet H1/1.
The filament must lie entirely within the limits shown.
Appendix 3
Category H2 lamps
SHEET H2/1U.K.
The drawings are intended only to illustrate the essential dimensions of the filament lamp.
SHEET H2/2U.K.
| Dimensions in mm | Tolerances | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filament lamp of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||||
| 6 V | 12 V | 24 V | ||||
| e (6) | 12,25 | (5) | ± 0,15 | |||
| f (6) | 6 V | 4,5 | ± 1,0 | |||
| 12 V | 5,5 | ± 0,5 | ||||
| 24 V | ||||||
| g (1) (2) | 0,5 d | ± 0,5 d | ± 0,25 d | |||
| h1 (2) | 7,1 | (5) | ± 0,2 | |||
| h2 (4) | (5) | ± 0,25 | ||||
| h3 (1) (2) | 0,5 d | (5) | ± 0,2 | |||
| h4 (1) (4) | (5) | ± 0,25 | ||||
| Cap X 511 in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-99-2) | ||||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 | |
| Watts | 55 | 70 | 55 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,3 | 13,2 | 28,0 | ||
| Objective values | Watts | max. 63 | max. 68 | max. 84 | max. 68 at 13,2 V | |
| Luminous flux lm | 1 300 | 1 800 | 2 150 | |||
| ± % | 15 | |||||
| Reference luminous flux for headlamp testing: 1 300 lm at approx. 12 V. | ||||||
SHEET H2/3U.K.
(1)d: diameter of filament.U.K.
(2)These offsets must be measured in a cross-section perpendicular to the axis of the bulb and passing through that end of the filament(17) which is nearer to the cap.U.K.
(3)The three crosses on the supporting plane show the positions of the three bosses defining this plane on the holder. Within a circle 3 mm in diameter centred on these points there must be no apparent deformation and no notches affecting the positioning of the filament lamp.U.K.
(4)These offsets must be measured in a cross-section perpendicular to the axis of the bulb and passing through that end of the filament(17) which is further from the cap.U.K.
(5)To be checked by means of a ‘box-system’, sheet H2/4.U.K.
(6)The ends of the filament are defined as the points where, when the viewing direction is as defined by ‘D’ (sheet H2/1), the projection of the outside of the end turns nearest to or furthest from the cap crosses a line parallel to and at a distance of 7,1 mm from line ZZ (special instructions for coiled-coil filaments are under consideration).U.K.
SHEET H2/4Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine, by checking whether a filament is correctly positioned relatively to the references axes x-x, y-y and z-z(18), whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements.
The end of the filament(19) which is nearer to the cap must lie between b1 and b2. The filament must lie entirely within the limits shown.
| 6 V | 12 V | 24 V | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | d + 0,5 | d + 1,0 | |
| a2 | d + 1,0 | ||
| b1, b2 | 0,25 | ||
| d1 | 7,1 | ||
| d2 | 0,5 d − 0,35 | ||
| h | 6 | 7 | |
d = diameter of filament
Appendix 4
Category H3 lamps
SHEET H3/1U.K.
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
SHEET H3/2U.K.Definition: Ring centre and reference axis (2)U.K.Filament dimensions and tolerances for standard filament lamps, see sheet H3/3U.K.
SHEET H3/3U.K.
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 12 V | 24 V | |||
| e | 18,0(5) | 18,0 | |||
| f (7) | 3,0 min | 4,0 min | 5,0 ± 0,5 | ||
| k | (5) | 0 ± 0,2 | |||
| h1 | 0 ± 0,15 (6) | ||||
| h3 | |||||
| h2 | 0 ± 0,25 (6) | ||||
| h4 | |||||
| Cap PK 22s in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-47-2) | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 |
| Watts | 55 | 70 | 55 | ||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,3 | 13,2 | 28,0 | |
| Objective values | Watts | max 63 | max 68 | max 84 | max 68 at 13,2 V |
| luminous flux lm | 1 050 | 1 450 | 1 750 | ||
| ± % | 15 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux for headlamp testing: 1 100 lm at approx. 12 V. | |||||
SHEET H3/4U.K.
(1)The distortion of the base-end portion of the bulb must not be visible from any direction outside the obscuration angle of 80o max. The shields must produce no inconvenient reflections. The angle between the reference axis and the plane of each shield, measured on the bulb side, must not exceed 90o.U.K.
(2)The permissible deviation of the ring centre from the reference axis is 0,5 mm in the direction perpendicular to the Z-Z line and 0,05 mm in the direction parallel to the Z-Z line.U.K.
(3)Minimum length above the height of the light-emitting centre (‘e’) over which the bulb must be cylindrical.U.K.
(4)No part of the spring and no component of the lamp-holder may bear on the prefocus ring elsewhere than outside the rectangle shown in discontinuous outline.U.K.
(5)These dimensions of lamps of normal production must be checked by means of a ‘box-system’ (sheet H3/5).U.K.
(6)For standard filament lamps the points to be measured are those where the projection of the outside of the end turns crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(7)the positions of the first and the last turn of the filament are defined by the intersections of the outside of the first and the outside of the last light-emitting turn, respectively, with the plane parallel to and 13 mm distant from the reference plane (additional instructions for coiled-coil filaments are under consideration).U.K.
SHEET H3/5Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine, by checking whether the filament is correctly positioned relatively to the reference axis and the reference plane, whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements.
| a | c | k | g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 1,8 d | 1,6 d | 1,0 | 2,0 |
| 12 V | 2,8 | |||
| 24 V | 2,9 |
d = diameter of the filament
The filament must lie entirely within the limits shown.
The centre of the filament must lie within the limits of dimension k.
Appendix 5
Category H4 lamps
SHEET H4/1U.K.
The drawings are not mandatory; their sole purpose is to show which dimensions must be verified.
| Reference | Dimension | Tolerance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 V | 24 V | 12 V | 24 V | |
| + 0,45 | ||||
| e | 28,5 | 29,0 | − 0,25 | ± 0,35 |
| p | 28,95 | 29,25 | — | — |
| m (1) | max. 60,0 | — | ||
| n (1) | max. 34,5 | — | ||
| s (2) | 45,0 | — | ||
| α (3) | max. 40o | — | ||
SHEET H4/2CharacteristicsU.K.
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamps | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rated values | Volts | 12 (4) | 24 (4) | 12 (4) | |||
| Watts | 60 | 55 | 75 | 70 | 60 | 55 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 13,2 | 28 | ||||
| Objective values | Watts | max. 75 | max. 68 | max. 85 | max. 80 | max. 75 at 13,2 V | max. 68 at 13,2 V |
| Luminous flux lm | 1 650 | 1 000 | 1 900 | 1 200 | |||
| ± % | 15 | ||||||
| Reference luminous flux at approximately 12 V lm | 1 250 | 750 | |||||
| Cap P43t-38 in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-39-2) | |||||||
SHEET H4/3U.K.
SHEET H4/4U.K.
SHEET H4/5ADDITIONAL EXPLANATIONS TO SHEETS H4/3 AND H4/4U.K.
The dimensions below are measured in three directions:
for dimensions a, b1, c, d, e, f, lR and lC;
for dimensions g, h, p and q;
for dimensions b2.
Dimensions p and q are measured in a plane parallel to and 33 mm away from the reference plane.
Dimensions b1, b2, c and h are measured in planes parallel to and 29,5 mm (30,0 mm for 24-V lamps) and 33 mm away from the reference plane.
Dimensions a and g are measured in planes parallel to and 26,0 mm and 23,5 mm away from the reference plane.
Note: For the method of measurement, see Appendix E of IEC Publication 809.U.K.
SHEET H4/6Table of the dimensions referred to in the diagrams on sheets H4/3 and H4/4 (in mm)U.K.
| a Dimension to be measured at the distance from the reference plane indicated in mm after the stroke. | ||||||
| b ‘29,5 mv’ or ‘30,0 mv’ means the value measured at a distance of 29,5 mm or 30,0 mm from the reference plane. | ||||||
| Reference | Dimension | Tolerances | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||||
| 12 V | 24 V | 12 V | 24 V | 12 V | 24 V | 12 V |
| a/26a | 0,8 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | |||
| a/23,5a | 0,8 | ± 0,6 | ± 0,2 | |||
| b1/29,5a | 30,0a | 0 | ± 0,3 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | |
| b1/33a | b1/29,5 mvb | 30,0 mvb | ± 0,3 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | |
| b2/29,5a | 30,0a | 0 | ± 0,3 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | |
| b2/33a | b2/29,5 mvb | 30,0 mvb | ± 0,3 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | |
| c/29,5a | 30,0a | 0,6 | 0,75 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | |
| c/33a | c/29,5 mvb | 30,0 mvb | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | ||
| d | min. 0,1 | — | — | |||
| e (7) | 28,5 | 29,0 | + 0,35 − 0,25 | ± 0,35 | + 0,2 − 0,0 | |
| f (5) (6) (8) | 1,7 | 2,0 | + 0,5 − 0,3 | ± 0,4 | + 0,3 − 0,1 | |
| g/26a | 0 | ± 0,5 | ± 0,3 | |||
| g/23,5a | 0 | ± 0,7 | ± 0,3 | |||
| h/29,5a | 30,0a | 0 | ± 0,5 | ± 0,3 | ||
| h/33a | h/29,5 mvb | 30,0 mvb | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | ||
| lR (5) (8) | 4,5 | 5,25 | ± 0,8 | ± 0,4 | ||
| lC (5) (6) | 5,5 | 5,25 | ± 0,5 | ± 0,8 | ± 0,35 | |
| p/33a | Depends on the shape of the shield | — | — | |||
| q/33a |  | ± 0,6 | ± 0,3 | |||
SHEET H4/7U.K.
(1)‘m’ and ‘n’ denote the maximum dimensions of the lampU.K.
(2)It must be possible to insert the lamp into a cylinder of diameterr ‘s’ concentric with the reference axis and limited at one end by a plane parallel to and 20 mm distant from the reference plane and at the other end by a hemisphere of radiusU.K.
(3)The obscuration must extend at least as far as the cylindrical part of the bulb. It must also overlap the internal shield when the latter is viewed in a direction perpendicular to the reference axis. The effect sought by obscuration may also be achieved by other means.U.K.
(4)The values indicated in the left-hand column relate to the driving beam. Those indicated in the right-hand column relate to the passing beam.U.K.
(5)The end turns of the filaments are defined as being the first luminous turn and the last luminous turn that are at substantially the correct helix angle. For coiled-coil filaments, the turns are defined by the envelope of the primary coil.U.K.
(6)For the passing-beam filament the points to be measured are the intersections, seen in direction  , of the lateral edge of the shield with the outside of the end turns defined under footnote 5.U.K.
, of the lateral edge of the shield with the outside of the end turns defined under footnote 5.U.K.
(7)‘e’ denotes the distance from the reference plane to the beginning of the passing-beam filament as defined above.U.K.
(8)For the driving beam filament the points to be measured are the intersections, seen in direction  , of a plane, parallel to plane HH and situated at a distance of 0,8 mm below it, with the end turns defined under footnote 5.U.K.
, of a plane, parallel to plane HH and situated at a distance of 0,8 mm below it, with the end turns defined under footnote 5.U.K.
(9)The reference axis is the line perpendicular to the reference plane and passing through the centre of the circle of diameter ‘M’ (see sheet H4/1).U.K.
(10)Plane VV is the plane perpendicular to the reference plane and passing through the reference axis and through the intersection of the circle of diameter ‘M’ with the axis of the reference pin.U.K.
(11)Plane HH is the plane perpendicular to both the reference plane and plane VV and passing through the reference axis.U.K.
Appendix 6
Category HS1
SHEET HS1/1U.K.
The drawings are not mandatory; their sole purpose is to show which dimensions must be verified.
| Reference | Dimension | Tolerance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 12 V | 6 V | 12 V | |
| o | 28,5 | + 0,45 − 0,25 | ||
| p | 28,95 | — | ||
| m (1) | max. 60,0 | — | ||
| n (1) | max. 34,5 | — | ||
| s (2) | 45,0 | — | ||
| α (3) | max. 40o | — | ||
SHEET HS1/2CharacteristicsU.K.
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamps | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rated values | Volts | 6 (4) | 12 (4) | 12 (4) | |||
| Watts | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,3 | 13,2 | ||||
| Objective values | Watts | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 at 13,2 V | 35 at 13,2 V |
| ± % | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Luminous flux lm | 700 | 440 | 825 | 525 | |||
| ± % | 15 | ||||||
| Reference luminous flux at approximately 12 V lm | 700 | 450 | |||||
| Cap PX43t-38 in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-34-1). | |||||||
SHEET HS1/3Table of the dimensions referred to in the diagrams on sheets HS1/4 and HS1/5 (in mm)U.K.
| a Dimension to be measured at the distance from the reference plane indicated in mm after the stroke. | ||||||
| Reference | Dimension | Tolerances | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||||
| 6 V | 12 V | 6 V | 12 V | 6 V | 12 V | 12 V |
| a/26a | 0,8 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | |||
| a/25a | 0,8 | ± 0,55 | ± 0,2 | |||
| b1/29,5a | 0 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | |||
| b1/33a | b1/29,5 mv | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | |||
| b2/29,5a | 0 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | |||
| b2/33a | b2/29,5 mv | ± 0,35 | ± 0,15 | |||
| c/29,5a | 0,5 | ± 0,35 | ± 0,2 | |||
| c/31a | c/29,5 mv | ± 0,3 | ± 0,15 | |||
| d | min. 0,1 max. 1,5 | — | — | |||
| e (7) | 28,5 | + 0,45 − 0,25 | + 0,2 − 0,0 | |||
| f (5) (6) (8) | 1,7 | + 0,5 − 0,3 | + 0,3 − 0,1 | |||
| g/25a | 0 | ± 0,5 | ± 0,3 | |||
| g/25a | 0 | ± 0,7 | ± 0,3 | |||
| h/29,5a | 0 | ± 0,5 | ± 0,3 | |||
| h/31a | h/29,5 | ± 0,3 | ± 0,2 | |||
| lR (5) (8) | 3,5 | 4,0 | ± 0,8 | ± 0,4 | ||
| lC (5) (6) | 3,3 | 4,5 | ± 0,8 | ± 0,35 | ||
| p/33a | Depends on the shape of the shield | — | — | |||
| q/33a |  | ± 0,6 | ± 0,3 | |||
SHEET HS1/4Position of filaments(20) U.K.
SHEET HS1/5Position of shield(21) U.K.
SHEET HS1/6ADDITIONAL EXPLANATION TO SHEETS HS1/4 AND HS1/5U.K.
The dimensions below are measured in three directions:
for dimensions a, b1, c, d, e, f, lR and lC;
for dimensions g, h, p and q;
for dimension b2.
Dimension p and q are measured in a plane parallel to 33 mm away from the reference plane.
Dimensions b1 and b2 are measured in planes parallel to and 29,5 mm and 33 mm away from the reference plane.
Dimensions a and g are measured in planes parallel to and 25 mm and 36 mm away from the reference plane.
Dimensions c and h are measured in planes parallel to and 29,5 mm and 31 mm away from the reference plane.
SHEET HS1/7U.K.
(1)‘m’ and ‘n’ denote the maximum dimensions of the lamp.U.K.
(2)it must be possible to insert the lamp into a cylinder of diameter ‘s’ concentric with the reference axis and limited at one end by a plane parallel to and 20 mm distant from the reference plane and at the other end by a hemisphere of radiusU.K.
.
(3)The obscuration must extend at least as far as the cylindrical part of the bulb. It must also overlap the internal shield when the latter is viewed in a direction perpendicular to the reference axis. The effect sought by obscuration may also be achieved by other means.U.K.
(4)The values indicated in the left-hand column relate to the driving beam. Those indicated in the right-hand column relate to the passing beam.U.K.
(5)The end turns of the filaments are defined as being the first luminous turn and the last luminous turn that are at substantially the correct helix angle. For coiled-coil filaments, the turns are defined by the envelope of the primary coil.U.K.
(6)For the passing-beam filament the points to be measured are the intersections, seen in direction  , of the lateral edge of the shield with the outside of the end turns defined under footnote 5.U.K.
, of the lateral edge of the shield with the outside of the end turns defined under footnote 5.U.K.
(7)‘e’ denotes the distance from the reference plane to the beginning of the passing-beam filament as defined above.U.K.
(8)For the driving beam filament the points to be measured are the intersections, seen in direction  , of a plane, parallel to plane HH and situated at a distance of 0,8 mm below it, with the end turns defined under footnote 5.U.K.
, of a plane, parallel to plane HH and situated at a distance of 0,8 mm below it, with the end turns defined under footnote 5.U.K.
(9)The reference axis is the line perpendicular to the reference plane and passing through the centre of the circle of diameter ‘M’ (see sheet HS1/1).U.K.
(10)Plane VV is the plane perpendicular to the reference plane and passing through the reference axis and through the intersection of the circle of diameter ‘M’ with the axis of the reference pin.U.K.
(11)Plane HH is the plane perpendicular to both the reference plane and plane VV and passing through the reference axis.U.K.
Appendix 7
Category HB3
SHEET HB3/1U.K.
The drawings are intended only to illustrate essential dimensions of the filament lamp
SHEET HB3/2U.K.
| Dimensions in mm (11) | Tolerances | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||
| e (8) (4) | 31,5 | (7) | ± 0,16 |
| f (8) (4) | 5,1 | (7) | ± 0,16 |
| h1, h2 | 0 | (7) | ± 0,15 (3) |
| h3 | 0 | (7) | ± 0,08 (3) |
| γ1 (5) | 45o min. | — | — |
| γ2 (5) | 52o min. | — | — |
| Cap P 20d in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-31-1) | |||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||
| Rated values | Volts | 12 | 12 |
| Watts | 60 | 60 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 13,2 | 13,2 |
| Objective values | Watts | 73 max. | 73 max. |
| Luminous flux lm | 1 860 | ||
| ± % | 12 | ||
| Reference luminous flux for headlamp testing: 1 300 lm at approx. 12 V | |||
SHEET HB3/3U.K.
(1)The reference plane is the plane formed by the meeting points of the cap-holder fit.U.K.
(2)The reference axis is the axis perpendicular to the reference plane and concentric with the 17,46 mm diameter of the cap.U.K.
(3)The eccentricity is measured only in viewing directions(22) A and B as shown in the figure on Sheet HB3/1. The points to be measured are those where the projection of the outside of the end turns nearest to or furthest from the reference plane crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(4)The viewing direction is direction(23) B as shown in the figure on Sheet HB3/1.U.K.
(5)Glass bulb periphery must be optically distortion-free axially within the angles γ1 and γ2. This requirement applies to the whole bulb circumference within the angles γ1 and γ2. The colour of the light emitted must be white.U.K.
(6)Glass bulb and supports must not exceed the envelope and not interfere with insertion past the lamp key. The envelope is concentric to the reference axis.U.K.
(7)To be checked by means of a ‘box-system’, Sheet HB3/4(24).U.K.
(8)The ends of the filament are defined as the points where, when the viewing direction(25) as defined in footnote 4 above, the projection of the outside of the end turns crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(9)The keyway is mandatory.U.K.
(10)The filament lamp must be rotated in the measuring holder until the reference lug contacts plane C of the holder.U.K.
(11)Dimensions must be checked with O-ring removed.U.K.
SHEET HB3/4Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine, by checking whether the filament is correctly positioned relatively to the reference axis and the reference plane, whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements.
| p | q | r | s | t | u | v | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 V | 1,3 d | 1,6 d | 3,0 | 2,9 | 0,9 | 0,4 | 0,7 |
d is the diameter of the filament
The filament position is checked solely in directions A and B als shown on sheet HB3/1.
The beginning of the filament as defined on sheet HB3/3, note 8, must be in volume ‘B’ and the end of the filament in volume ‘C’.
The filament must lie entirely within the limits shown. Volume ‘A’ does not involve any filament centre requirement.
Appendix 8
Category HB4
SHEET HB4/1U.K.
The drawings are intended only to illustrate the essential dimensions of the filament lamp
SHEET HB4/2U.K.
| Dimensions in mm (12) | Tolerances | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||
| e (4) (9) | 31,5 | (8) | ± 0,16 |
| f (4) (9) | 5,1 | (8) | ± 0,16 |
| h1, h2 | 0 | (8) | ± 0,15 (3) |
| h3 | 0 | (8) | ± 0,08 (3) |
| g (4) | 0,75 | ± 0,5 | ± 0,3 |
| γ1 (5) | 50o min. | — | — |
| γ2 (5) | 52o min. | — | — |
| γ3 (7) | 45o | ± 5o | ± 5o |
| Cap P 22d in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-32-1) | |||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||
| Rated Values | Volts | 12 | 12 |
| Watts | 51 | 51 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 13,2 | 13,2 |
| Objective values | Watts | 62 max. | 62 max. |
| luminous flux lm | 1 095 | ||
| ± % | 15 | ||
| Reference luminous flux for headlamp testing: 825 lm at approx. 12 V. | |||
SHEET HB4/3U.K.
(1)The reference plane is the plane formed by the meeting points of the cap-holder fit.U.K.
(2)The reference axis is the axis perpendicular to the reference plane and concentric with the 19,46 mm diameter of the cap.U.K.
(3)The eccentricity is measured only in viewing directions(26) A and B as shown in the figure on Sheet HB4/1. The points to be measured are those where the projection of the outside of the end turns nearest to or furthest from the reference plane crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(4)The viewing direction is direction(26) B as shown in the figure on Sheet HB4/1.U.K.
(5)Glass bulb periphery must be optically distortion-free axially within the angles γ1 and γ2. This requirement applies to the whole bulb circumference within the angles γ1 und γ2. The colour of the light emitted must be white.U.K.
(6)Glass bulb and supports must not exceed the envelope and not interfere with insertion past the lamp key. The envelope is concentric to the reference axis.U.K.
(7)The obscuration must extend at least to angle γ3 and be at least as far as the undistorted part of the bulb defined by angle γ1.U.K.
(8)To be checked by means of a ‘box-system’, Sheet HB4/4(26).U.K.
(9)The ends of the filament are defined on the points where, when the viewing direction(26) as defined in footnote 4 above, the projection of the outside of the end turns crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(10)The keyway is mandatory.U.K.
(11)The filament lamp must be rotated in the measuring holder until the reference lug contacts plane C of the holder.U.K.
(12)Dimensions must be checked with O-ring removed.U.K.
SHEET HB4/4Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine, by checking whether the filament is correctly positioned relative to the reference axis and the reference plane, whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements.
| p | q | r | s | t | u | v | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 V | 1,3 d | 1,6 d | 3,0 | 2,9 | 0,9 | 0,4 | 0,7 |
d is the diameter of the filament
The filament position is checked solely in directions A and B as shown on sheet HB4/1.
The beginning of the filament as defined on sheet HB4/3, note 9, must be in volume ‘B’ and the end of the filament in volume ‘C’.
The filament must lie entirely within the limits shown. Volume ‘A’ does not involve any filament centre requirement.
Appendix 9
Category H7
SHEET H7/1U.K.
The drawings are intended only to illustrate the essential dimensions of the filament lamp
SHEET H7/2U.K.
| Rated voltage 12 V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions in mm | Tolerances | ||
| Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||
| e (7) | 25,0 | (8) | ± 0,1 |
| f (7) | 4,1 | (8) | ± 0,1 |
| g (10) | 0,5 | min. | u.c. |
| h1 (9) | 0 | (8) | ± 0,1 |
| h2 (9) | 0 | (8) | ± 0,15 |
| γ1 (4) | 40o min. | — | — |
| γ2 (4) | 50o min. | — | — |
| γ3 (5) | 30o min. | — | — |
| Cap PX 26d in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-5-1) | |||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||
| Rated values | Volts | 12 | 12 |
| Watts | 55 | 55 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 13,2 | 13,2 |
| Objective values | Watts | max. 58 | max. 58 |
| luminous flux lm | 1 500 | ||
| ± % | 10 | ||
| Reference luminous flux for headlamp testing: 1 100 lm at approx. 12 V. | |||
SHEET H7/3U.K.
(1)The reference plane is defined by the points on the surface of the holder on which the three supporting bosses of the cap ring will rest.U.K.
(2)The reference axis is perpendicular to the reference plane and crosses the intersection of the two perpendiculars as indicated in figure 3 on Sheet H7/1.U.K.
(3)Glass bulb and supports must not exceed the envelope as indicated in figure 2 on Sheet H7/1. The envelope is concentric to the reference axis.U.K.
(4)(Glass bulb must be optically distortion free within the angles γ1 and γ2. This requirement applies to the whole bulb circumference within the angles γ1 and γ2.U.K.
(5)The obscuration must extend at least to angle γ3 and extend at least to the cylindrical part of the bulb on the whole bulb top circumference.U.K.
(6)The internal design of the lamp must be such that stray light images and reflections are only located above the filament itself seen from the horizontal direction. (View as indicated in figure 1 on Sheet H7/1). No metal parts other than filament turns may be located in the shaded areas as seen in figure 5 on Sheet H7/1.U.K.
as indicated in figure 1 on Sheet H7/1). No metal parts other than filament turns may be located in the shaded areas as seen in figure 5 on Sheet H7/1.U.K.
(7)The ends of the filament are defined as the points where, when the viewing direction as shown in figure 1 on Sheet H7/1, the projection of the outside of the end turns crosses the filament axis.U.K.
as shown in figure 1 on Sheet H7/1, the projection of the outside of the end turns crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(8)To be checked my means of a ‘box-system’, Sheet H7/4.U.K.
(9)The offset of the filament with respect to the reference axis is measured only in viewing directions and
and , as shown in figure 1 on Sheet H7/1. The points to be measured are those where the projection of the outside of the end turns nearest to or furthest from where the reference plane crosses the filament axis.U.K.
, as shown in figure 1 on Sheet H7/1. The points to be measured are those where the projection of the outside of the end turns nearest to or furthest from where the reference plane crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(10)Offset of filament in relation to bulb axis measured in two planes parallel to the reference plane where the projection of the outside of the end turns nearest to or furthest from the reference plane crosses the filament axis.U.K.
(11)The colour of the light emitted must be white.U.K.
(12)Notes concerning the filament diameterU.K.
No actual diameter restrictions apply but the objective for future developments is to have d max. = 1,3 mm
For the same manufacturer the design diameter of standard (étalon) filament lamp and filament lamp of normal production must be the same.
SHEET H7/4Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine, by checking whether the filament is correctly positioned relative to the reference axis and the reference plane, whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements.
| a1 | a2 | b1 | b2 | c1 | c2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 V | d + 0,3 | d + 0,5 | 0,2 | 4,6 | 4,0 | |
d is the diameter of the filament
The ends of the filament as defined on sheet H7/3, footnote (7), must lie between lines Z1 and Z2 and between lines Z3 and Z4.
The filament position is checked solely in directions

The filament must lie entirely within the limits shown.
Appendix 10
Category HS2
SHEET HS2/1U.K.
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Nominal | Maximum | ||
| e | 11,0 (3) | 11,0 ± 0,15 | ||
| f (6 V) (6) | 1,5 | 2,5 | 3,5 | 2,5 ± 0,15 |
| f (12 V) (6) | 2,0 | 3,0 | 4,0 | |
| h1, h2 | (3) | 0 ± 0,15 | ||
| α (4) | 40 | |||
| β (5) | − 15o | 90o | + 15o | 90o ± 5o |
| γ1 (7) | 15o | 15o min. | ||
| γ2 (7) | 40o | 40o min. | ||
| Cap P × 13,5s in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-35-1) | ||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | ||||
| Values | Volts (6) | 6 | 12 | 6 |
| Watts | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | |
| Objective value | Watts | 15 | 15 | 15,0 at 6,75 V |
| ± % | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Luminous flux lm | 320 | 320 | ||
| ± % | 15 | 15 | ||
| Reference luminous flux: 320 lm at approximately 6,75 volts. | ||||
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
SHEET HS2/2U.K.
(1)The reference axis is perpendicular to the reference plane and passes through the intersection of this plane with the axis of the cap ring.U.K.
(2)To be reserved.U.K.
(3)To be checked by means of the ‘box-system’, sheet HS2/3.U.K.
(4)All parts which may obscure the light or may influence the light beam shall lie within angle α.U.K.
(5)Angle β denotes the position of the plane through the inner leads with reference to the reference notch.U.K.
(6)In order to avoid rapid lamp failure the supply voltage must not exceed 8,5 V for 6 V lamps and 15 V for 12 V filament lamps.U.K.
(7)In the area between the other legs of the angles γ1 and γ2 the bulb must have no optically distorting areas and the curvature of the bulb must have a radius not less than 50 % of the actual bulb diameter.U.K.
SHEET HS2/3Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements, by checking whether the filament is correctly positioned in relation to the reference axis and the reference plane.
View A + B
| a1 | a2 | b1 | b2 | c1 (6 V) | c1 (12 V) | c2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 V | d + 1,0 | d + 1,4 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 4,0 | 4,5 | 1,75 |
d = actual filament diameter
The filament must lie entirely within the limits shown.
The beginning of the filament must lie between lines Z1 and Z2.
Appendix 11
Category S1 and S2
SHEET S1/S2/1U.K.
NoteU.K.
Plane V-V contains the reference axis and the centre line of the lugs.U.K.
Plane H-H (the normal positions of the shield) is perpendicular to plane V-V and contains the reference axis.U.K.
SHEET S1/S2/2Category S1 and S2 filament lamps — DimensionsU.K.
| Dimensions (mm) | Filament lamps of normal production (5) | Standard filament lamp | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | ||
| e | 32,35 | 32,70 | 33,05 | 32,7 ± 0,15 |
| f | 1,4 | 1,8 | 2,2 | 1,8 ± 0,2 |
| l | 4 | 5,5 | 7 | 5,5 ± 0,5 |
| c (3) | 0,2 | 0,5 | 0,8 | 0,5 ± 0,15 |
| b (3) | − 0,15 | 0,2 | 0,55 | 0,2 ± 0,15 |
| a (3) | 0,25 | 0,6 | 0,95 | 0,6 ± 0,15 |
| h | − 0,5 | 0 | 0,5 | 0 ± 0,2 |
| g | − 0,5 | 0 | 0,5 | 0 ± 0,2 |
| β (3) (4) | − 2o 30′ | 0o | 2o 30′ | 0o ± 1o |
| Cap BA 20d in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-12-5) | ||||
SHEET S1/S2/3ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICSU.K.
Category S1 filament lampU.K.
| Filament lamps of (5) normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 6 | |||
| Watts | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | — | |||
| Objective values | Watts | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| at 6,75 V | |||||||
| ± % | 5 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| Lumens | 435 | 315 | 435 | 315 | — | ||
| ± % | 20 | 20 | — | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 398 lm and 284 lm respectively at approx. 6 V | |||||||
Category S2 filament lampU.K.
| Filament lamps of (5) normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 12 | |||
| Watts | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,3 | 13,5 | — | |||
| Objective values | Watts | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| at 13,5 V | |||||||
| ± % | 5 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| Lumens | 650 | 465 | 650 | 465 | — | ||
| ± % | 20 | 20 | — | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 568 lm and 426 lm respectively at approx. 12 V | |||||||
NotesU.K.
(1)The colour of the light emitted must be white.U.K.
(2)The reference plane is perpendicular to the reference axis and touches the upper surface of the lug having a width of 4,5 mm.U.K.
(3)Dimensions a, b, c and β refer to a plane parallel to the reference plane and cutting the two edges of the shield at a distance of e + 1,5 mm.U.K.
(4)Admissible angular deviation of the shield plane position from the normal position.U.K.
(5)Type approval requirements. Requirements for the conformity of production are under consideration.U.K.
Appendix 12
Category S3
SHEET S3/1U.K.
| Dimensions (mm) | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | ||
| e (2) | 19,0 | 19,5 | 20,0 | 19,5 ± 0,25 |
| f (6 V) | 3,0 | 2,5 ± 0,5 | ||
| f (12 V) | 4,0 | |||
| d1, d2 (3) | − 0,5 | 0 | + 0,5 | ± 0,3 |
| Cap P26s in accordance with Publication IEC 61 (sheet 7004-36-1) | ||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | ||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 6 |
| Watts | 15 | 15 | ||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | — |
| Objective values | Watts | 15 | 15 at 6,75 V | |
| ± % | 6 | 6 | ||
| Lumen | 240 | — | ||
| ± % | 15 | — | ||
| Reference luminous flux: 240 lm at approx. 6,75 V | ||||
NotesU.K.
(1)The colour of the light emitted must be white.U.K.
(2)Distance related to the luminous centre of gravity.U.K.
(3)Lateral deviation of filament axis with respect to the reference axis. It is sufficient to check this deviation in two reciprocally perpendicular planes.U.K.
Appendix 13
Category S4
SHEET S4/1U.K.
NotesU.K.
Plane VV contains the reference axis and the centre line of the reference pin.U.K.
Plane HH contains the reference axis and is perpendicular to plane VV.U.K.
Objective position of plane SS through the shield edges parallel to plane HH.U.K.
SHEET S4/2S4 filament lamp for moped headlampU.K.
| Dimensions (mm) | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||||||
| e | 33,25 | 33,6 | 33,95 | 33,6 ± 0,15 | |||||
| f | 1,45 | 1,8 | 2,15 | 1,8 ± 0,2 | |||||
| lC, lR | 2,5 | 3,5 | 4,5 | 3,5 ± 0,5 | |||||
| c (2) | 0,05 | 0,4 | 0,75 | 0,4 ± 0,15 | |||||
| b (2) | − 0,15 | 0,2 | 0,55 | 0,2 ± 0,15 | |||||
| a (2) | 0,25 | 0,6 | 0,95 | 0,6 ± 0,15 | |||||
| h | − 0,5 | 0 | 0,5 | 0 ± 0,2 | |||||
| g | − 0,5 | 0 | 0,5 | 0 ± 0,2 | |||||
| β (2) (5) | − 2o 30′ | 0 | 2o 30′ | 0 ± 1o | |||||
| BAX 15d (1) | |||||||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||||
| Rated voltage | Volts | 6 | 12 | 6 | |||||
| Rated wattage (6) | Watts | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | ||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | ||||||
| Objective wattage (6) | Watts | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | ||
| (at 6,75 V) | |||||||||
| Tolerance | ± % | 6 | 6 | 6 | |||||
| Objective values | lum. flux lm (4) (6) | 180 | 125 | 190 | 180 | 125 | 190 | ||
| min. | min. | max. | min. | min. | max. | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 240 lm (driving beam), 160 lm (passing beam) at approx. 6 V (4) | |||||||||
SHEET S4/3U.K.
NotesU.K.
(1)Cap in accordance with IEC Publication 61 in preparation.U.K.
(2)Dimensions a, b, c and β refer to a plane parallel to the reference plane and cutting the two edges of the shield at a distance of e + 1,5 mm.U.K.
(3)The reference plane is perpendicular to the reference axis and touches the upper surface of the pin having a length of 2 mm.U.K.
(4)The colour of the light emitted must be white.U.K.
(5)Admissible deviation of the plane through the shield edges from the objective position.U.K.
(6)Values in the left-hand column refer to the driving beam filament, values in the right-hand column refer to the passing beam filament.U.K.
Appendix 14
Category P21W
SHEET P21W/1U.K.
| a Maximum lateral deviation of filament centre from two reciprocally perpendicular planes both containing the reference axis of cap and one containing axis of pins. | |||||
| b Lamps with cap BA 15d may be used for special purposes: they have the same dimensions. | |||||
| c To be checked by means of a ‘box-system’, sheet P21W/2. | |||||
| d For 24 volt heavy-duty lamps having a different filament shape, additional specifications are under consideration. | |||||
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||
| e | 31,8a | 31,8± 0,3 | |||
| f | 12 V | 5,5 | 6,0 | 7,0 | 6,0 ± 0,5 |
| 6,24 Vd | 7,0 | ||||
| β | 75o | 90o | 105o | 90o ± 5o | |
| Lateral deviationa | c | 0,3 max. | |||
| Cap BA 15s in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-11A-7)b | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 |
| Watts | 21 | 21 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | 28,0 | |
| Objective values | Watts | 26 | 25 | 28 | 25 at 13,5 V |
| ± % | 6 | 6 | |||
| Luminous flux lm | 460 | ||||
| ± % | 15 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 460 lm at approximately 13,5 V | |||||
The colour of the light must be white.
SHEET P21W/2Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine, by checking whether the filament is correctly positioned relative to the reference axis and the reference plane and has an axis perpendicular, within ± 15o, to the plane through the centres of the pins and the reference axis, whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements.
| reference | a | b | h | k |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dimension | 3,5 | 3,0 | 9,0 | 1,0 |
Test procedure and requirementsU.K.
1.The lamp is placed in a holder (socket) capable of being rotated about its axis and having either a calibrated scale or fixed stops corresponding to the angular-displacement tolerance limits, i.e. ± 15o. The holder is then so rotated that an end view of the filament is seen on the screen on to which the image of the filament is projected. The end view of the filament is obtained within the angular-displacement tolerance limits (± 15o).U.K.
2.Side elevationU.K.
The lamp being placed with the cap down, the reference axis vertical, and the filament seen end-on, the projection of the filament must lie entirely within a rectangle of height ‘a’ and width ‘b’ having its centre at the theoretical position of the centre of the filament.
3.Front elevationU.K.
The lamp being placed with the cap down and the reference axis vertical, the lamp being viewed in a direction at right-angles to the filament axis:
3.1.the projection of the filament must lie entirely within a rectangle of height ‘a’ and width ‘b’ centred on the theoretical position of the centre of the filament; andU.K.
3.2.the centre of the filament must not be offset by more than the distance ‘k’ from the reference axis.U.K.
Appendix 15
Category P21/5W
SHEET P21/5W/1U.K.
| a These dimensions should be checked by means of a ‘box-system’ (P21/5W/2, P21/5W/3) based on the dimensions and tolerances shown above. ‘x’ and ‘y’ refer to the main (high-wattage) filament, not to the lamp axis (P21/5W/2). Means of increasing the positioning accuracy of the filament and of the cap-holder assembly are under consideration. | ||||||||
| b Maximum lateral deviation of main (high-wattage) filament centre from two mutually perpendicular planes both containing reference axis and one containing axis of pins. | ||||||||
| c The 24 volt filament lamp is not recommended for future embodiments. | ||||||||
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | ||||||
| e | 31,8a | 31,8 ± 0,3 | ||||||
| f | 7,0a | 7,0 − 0 − 2 | ||||||
| Lateral deviation | a | 0,3 max.b | ||||||
| x, y | a | 2,8 ± 0,3 | ||||||
| β | 75o a | 90o | 105o a | 90o ± 5o | ||||
| Cap BAY 15d in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-11B-5) | ||||||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24c | 12 | |||
| Watts | 21 | 5 | 21 | 5 | 21 | 5 | 21/5 | |
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | 28,0 | ||||
| Objective values | Watts | 26 | 6 | 25 | 6 | 28 | 10 | 25 and 6 at 13,5 V |
| ± % | 6 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 6 and 10 | |
| Luminous flux lm | 440 | 35 | 440 | 35 | 440 | 40 | ||
| ± % | 15 | 20 | 15 | 20 | 15 | 20 | ||
| Reference luminous flux: 440 lm and 35 lm at approx. 13,5 V | ||||||||
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
SHEET P21/5W/2Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine, by checking
whether the main (high-wattage) filament is correctly positioned relative to the reference axis and the reference plane and has an axis perpendicular, within ± 15o, to the plane through the centres of the pins and the reference axis; and
whether the auxiliary (low-wattage) filament is correctly positioned relative to the main (high-wattage) filament
whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements.
Test procedure and requirementsU.K.
1.The lamp is placed in a holder (socket) capable of being rotated about its axis and having either a calibrated scale or fixed stops corresponding to the angular-displacement tolerance limits, i.e. ± 15o. The holder is then so rotated that an end view of the main (high-wattage) filament is seen on the screen onto which the image of the filament is projected. The end view of the main (high-wattage) filament is obtained within the angular-displacement tolerance limits (± 15o).U.K.
2.Side elevationU.K.
The lamp being placed with the cap down, the reference axis vertical, and the main (high-wattage) filament seen end-on:
2.1.the projection of the main (high-wattage) filament lies entirely within a rectangle of height ‘a’ and width ‘b’ having its centre at the theoretical position of the centre of the filament.U.K.
2.2.the projection of the auxiliary (low-wattage) filament lies entirely:U.K.
2.2.1.within a rectangle of width ‘c’ and height ‘d’ having its centre at a distance ‘v’ to the right of and at a distance ‘u’ above the theoretical position of the centre of the main (high-wattage) filament;U.K.
2.2.2.above a straight line tangential to the upper edge of the projection of the main (high-wattage) filament and rising from left to right at an angle of 25o;U.K.
2.2.3.to the right of the projection of the main (high-wattage) filament.U.K.
3.Front elevationU.K.
The lamp being placed with the cap down and the reference axis vertical, the lamp being viewed in a direction at right-angles to the axis of the main (high-wattage) filament:
3.1.the projection of the main (high-wattage) filament lies entirely within a rectangle of height ‘a’ and width ‘h’ centred on the theoretical position of the centre of the filament; andU.K.
3.2.the centre of the main (high-wattage) filament must not be offset by more than the distance ‘k’ from the reference axis;U.K.
3.3.the centre of the auxiliary (low-wattage) filament must not be offset from the reference axis by more than ± 2 mm (± 0,4 mm for standard filament lamps).U.K.
SHEET P21/5W/3U.K.
Side elevation
| Reference | a | b | c | d | u | v |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | 3,5 | 3,0 | 4,8 | 2,8 | ||
Front elevation
| Reference | a | h | k |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | 3,5 | 9,0 | 1,0 |
Appendix 16
Category R5W
SHEET R5W/1U.K.
| Reference plane | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||
| e | 17,5 | 19,0 | 20,5 | 19,0 ± 0,3 | |
| Lateral deviation (2) | 1,5 | 0,3 max. | |||
| β | 60o | 90o | 120o | 90o ± 5o | |
| Cap BA 15s in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-11A-6) (1) | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 (3) | 12 |
| Watts | 5 | 5 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | 28,0 | |
| Objective values | Watts | 5 | 7 | 5 at 13,5 V | |
| ± % | 10 | 10 | |||
| Luminous flux lm | 50 | ||||
| ± % | 20 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 50 lm at approx. 13,5 V | |||||
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
(1)Filament lamps with cap BA 15d may be used for special purposes: they have the same dimensions.U.K.
(2)Maximum lateral deviation of filament centre from two reciprocally perpendicular planes both containing reference axis and one containing axis of pins.U.K.
(3)For 24 volt heavy-duty lamps having a different filament shape, additional specifications are under consideration.U.K.
(4)See Appendix 24.U.K.
Appendix 17
Category R10W
SHEET R10W/1U.K.
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamp of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||
| e | 17,5 | 19,0 | 20,5 | 19,0 ± 0,3 | |
| Lateral deviation (2) | 1,5 | 0,3 max. | |||
| β | 60o | 90o | 120o | 90o ± 5o | |
| Cap BA 15s in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-11A-6) (1) | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 (3) | 12 |
| Watts | 10 | 10 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | 28,0 | |
| Objective values | Watts | 10 | 12,5 | 10 at 13,5 V | |
| ± % | 10 | 10 | |||
| Luminous flux lm | 125 | ||||
| ± % | 20 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 125 lm at approx. 13,5 V | |||||
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
(1)Filament lamps with cap BA 15d may be used for special purposes: they have the same dimensions.U.K.
(2)Maximum lateral deviation of filament centre from two reciprocally perpendicular planes both containing reference axis and one containing axis of pins.U.K.
(3)For 24 volt heavy-duty filament lamps having a different filament shape, additional specifications are under consideration.U.K.
(4)See Appendix 24.U.K.
Appendix 18
Category T4W
SHEET T4W/1U.K.
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||
| e | 13,5 | 15,0 | 16,5 | 15,0 ± 0,3 | |
| lateral deviation (1) | 1,5 | 0,5 max. | |||
| β | 90o | 90o ± 5o | |||
| Cap BA 9s in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-14-6) (3) | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 |
| Watts | 4 | 4 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | 28,0 | |
| Objective values | Watts | 4 | 5 | 4 at 13,5 V | |
| ± % | 10 | 10 | |||
| Luminous flux lm | 35 | ||||
| ± % | 20 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 35 lm at approx. 13,5 V | |||||
(1)Maximum lateral deviation of filament centre from two reciprocally perpendicular planes both containing reference axis and one containing axis of pins.U.K.
(2)See Appendix 24.U.K.
(3)Over the entire length of the cap there must be no projections or soldering extending beyond the permissible maximum diameter of the cap.U.K.
Appendix 19
Category C5W
SHEET C5W/1U.K.
| a This dimension corresponds to the distance between two apertures of 3,5 mm diameter each bearing against one of the caps. | |||||
| b The filament must be housed in a cylinder 19 mm long co-axial with the filament lamp axis and placed symmetrically about the lamp centre. The diameter of this cylinder is for 6 volt and 12 volt filament lamps: d + 4 mm (for standard filament lamps: d + 2 mm) and for 24 volt filament lamps: d + 5 mm, ‘d’ being the nominal diameter of the filament as stated by the manufacturer. | |||||
| c The deviation of the filament centre from the centre of the lamp's length should not be more than ± 2 mm (for standard filament lamps: ± 0,5 mm) measured in the direction of the reference axis. | |||||
| d 4,5 mm for 6 volt filament lamps. | |||||
| e 16,5 mm for 24 volt filament lamps. | |||||
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||
| ba | 34,0 | 35,0 | 36,0 | 35 ± 0,5 | |
| fb c | 7,5d | 15e | 9 ± 1,5 | ||
| Cap SV 8,5 in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-81-3) | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 |
| Watts | 5 | 5 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | 28,0 | |
| Objective values | Watts | 5 | 7 | 5 at 13,5 V | |
| ± % | 10 | 10 | |||
| Luminous flux lm | 45 | ||||
| ± % | 20 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 45 lm at approx. 13,5 V | |||||
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
Appendix 20
Category C21W
SHEET C21W/1U.K.
| a This dimension corresponds to the distance between two apertures of 3,5 mm diameter. | |||||
| b The position of the filament is checked by means of a ‘box-system’, sheet C21W/2. | |||||
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||
| ba | 40,0 | 41,0 | 42,0 | 41 ± 0,5 | |
| fb | 7,5 | 10,5 | 8 ± 1 | ||
| Cap SV 8,5 in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-81-3) | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 12 | 12 | ||
| Watts | 21 | 21 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 13,5 | |||
| Objective values | Watts | 25 | 25 at 13,5 V | ||
| ± % | 6 | 6 | |||
| Luminous flux lm | 460 | ||||
| ± % | 15 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 460 lm at approx. 13,5 V | |||||
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
SHEET C21W/2Screen projection requirementsU.K.
This test is used to determine whether a filament lamp complies with the requirements, by checking whether the filament is correctly positioned relative to the reference axis and to the centre of the lamp's lenght.
| a | h | k | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 V | 4,0 + d | 14,5 | 2,0 |
d = nominal diameter of filament as stated by the manufacturer.
For standard filament lamp: a = 2,0 + d k = 0,5
Test procedure and requirementsU.K.
1.The lamp is placed in a holder (socket) capable of being so rotated through 360o about the reference axis that the front elevation is seen on the screen on to which the image of the filament is projected. The reference plane on the screen must coincide with the centre of the lamp. The central axis sought on the screen must coincide with the centre of the lamp's length.U.K.
2.Front elevationU.K.
2.1.The projection of the filament must lie entirely within the rectangle when the lamp is rotated through 360o.U.K.
2.2.The centre of the filament must not be offset by more than the distance ‘k’ from the central axis sought.U.K.
Appendix 21
Category W3W
SHEET W3W/1U.K.
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||
| e | 11,2 | 12,7 | 14,2 | 12,7 ± 0,3 | |
| Lateral deviation (2) | 1,5 | 0,5 max. | |||
| β | − 15o | 0o | + 15o | 0o ± 5o | |
| Cap W 2,1 × 9,5d in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-91-2) (1) | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 |
| Watts | 3 | 3 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | 28,0 | |
| Objective values | Watts | 3 | 4 | 3 at 13,5 V | |
| ± % | 15 | 15 | |||
| Luminous flux lm | 22 | ||||
| ± % | 30 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 22 lm at approx. 13,5 V | |||||
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
(1)This type is protected by patents; ISO/IEC conditions apply.U.K.
(2)Maximum lateral deviation of filament centre from two reciprocally perpendicular planes both containing reference axis and one containing axis X-X.U.K.
(3)See Appendix 24.U.K.
Appendix 22
Category W5W
SHEET W5W/1U.K.
| Dimensions in mm | Filament lamps of normal production | Standard filament lamp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min. | nom. | max. | |||
| e | 11,2 | 12,7 | 14,2 | 12,7± 0,3 | |
| Lateral deviation (2) | 1,5 | 0,5 max. | |||
| β | − 15o | 0o | + 15o | 0o ± 5o | |
| Cap W 2,1 × 9,5d in accordance with IEC Publication 61 (sheet 7004-91-2) (1) | |||||
| ELECTRICAL AND PHOTOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||
| Rated values | Volts | 6 | 12 | 24 | 12 |
| Watts | 5 | 5 | |||
| Test voltage | Volts | 6,75 | 13,5 | 28,0 | |
| Objective values | Watts | 5 | 7 | 5 at 13,5 V | |
| ± % | 10 | 10 | |||
| Luminous flux lm | 50 | ||||
| ± % | 20 | ||||
| Reference luminous flux: 50 lm at approx. 13,5 V | |||||
The colour of the light emitted must be white.
(1)This type is protected by patents; ISO/IEC conditions apply.U.K.
(2)Maximum lateral deviation of filament centre from two reciprocally perpendicular planes both containing reference axis and one containing axis XX.U.K.
(3)(See Appendix 24.U.K.
Appendix 23
Example of the arrangement of the approval mark
The above EC component type-approval mark affixed to a filament lamp indicates that the lamp has been approved in Germany (e1) under the approval number A3. The first character of the approval code (0) indicates that the approval was granted in accordance with the requirements of Annex IV to this Directive in its original form.
Appendix 24
Luminous centre and shapes of lamp filaments
Save as possibly otherwise indicated on the lamp data sheets, this standard is applicable to the determination of the luminous centre of different filament shapes if the filament is shown as a point in at least one view in the lamp data sheets.
The position of the luminous centre depends upon the filament shape.
| No | Filament shapes | Observations |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | With b > 1,5 h, the deviation of the filament axis with respect to a plane normal to the reference axis must not exceed 15o. | |
| 2 | Only applicable to filaments which can be inscribed in a rectangle of b > 3 h. | |
| 3 | Applicable to filaments which can be inscribed in a rectangle of b < 3 h, where however k < 2 h. |
The side lines of the circumscribed rectangle in Nos 2 and 3 are parallel and perpendicular, respectively, to the reference axis.
The luminous centre is the point of intersection of the dash-dot lines.
Headlamps of Annex III-B, III-C and III-D.
The measuring screen for driving on the left must be symmetrical to line v-v shown in the diagram in this Annex.
Technical requirements for filament lamps: see Annex IV.
A headlamp is regarded as satisfying the requirements of this paragraph if the filament lamp can easily be fitted into the headlamp and the positioning lugs can be correctly fitted into their slots even in darkness.
These provisions do not apply to the control switch.
The test screen must be sufficiently wide to allow examination of the cut-off over a range of at least 5o each side of the line v-v.
If, in the case of headlamp designed to satisfy the requirements of this Directive with respect to the passing beam only, the focal axis diverges appreciably from the general direction of the beam, or if, whatever the type of headlamp (passing only or combined passing and driving), the beam does not have a cut-off with a clear elbow, the lateral adjustment must be affected in the manner which best satisfies the requirements for illumunation at points 75 R and 50 R for right-hand traffic and at points 75 L and 50 L for left-hand traffic.
A headlamp designed to emit a passing beam may incorporate a driving beam not complying with this specification.
The limit of re-alignment of 1o towards the right or left is not incompatible with upward or downward vertical re-alignment. The latter is limited only by the requirements laid down in section 3.3; however, the horizontal part of the cut-off should not extend beyond the line h-h (the provisions of section 3.3 are not applicable to headlamps intended to meet the requirements of this Annex for passing beam only).
When the tested headlamp is grouped and/or reciprocally incorporated with signalling lamps, the latter must be lit for the duration of the test. In the case of a direction indicator lamp, it must be lit in flashing operation mode with an on/off time ratio of approximately one to one.
If two or more lamp filaments are simultaneously lit when headlamp flashing is used, this is not considered as being normal use of the filament simultaneously.
When the tested headlamp is grouped and/or reciprocally incorporated with signalling lamps, the latter must be lit for the duration of the test. In the case of a direction indicator lamp, it must be lit in flashing operation mode with an on/off time ratio of approximately one to one.
If two or more lamp filaments are simultaneously lit when headlamp flashing is used, this is not considered as being normal use of the filament simultaneously.
NaCMC represents the sodium salt of carboxymethylcellulose, customarily referred to as CMC. The NaCMC used in the dirt mixture must have a degree of substitution (DS) of 0,6-0,7 and a viscosity of 200-300 cP for a 2 % solution 20 oC.
50 V is situated 375 mm below HV on the vertical line v-v on the screen at 25 m distance.
For L2 the use of a focal distance of about 80 mm is recommended.
The points to be measured are those where the outside of the end turn that is nearest to or furthest from the cap crosses the filament axis.
The cap must be pressed in these directions.
The end of the filament is defined at sheet H2/3.
The drawing is not mandatory with respect to the design of the shield.
The drawing is not mandatory with respect to the design of the shield.
Manufacturers may choose another set of perpendicular viewing directions. The viewing directions specified by the manufacturer are to be used by the testing laboratory when checking filament dimensions and position.
Manufacturers may choose another set of perpendicular viewing directions. The viewing directions specified by the manufacturer are to be used by the testing laboratory when checking filament dimensions and position.
Manufacturers may choose another set of perpendicular viewing directions. The viewing directions specified by the manufacturer are to be used by the testing laboratory when checking filament dimensions and position.
Manufacturers may choose another set of perpendicular viewing directions. The viewing directions specified by the manufacturer are to be used by the testing laboratory when checking filament dimensions and position.
Manufacturers may choose another set of perpendicular viewing directions. The viewing directions specified by the manufacturer are to be used by the testing laboratory when cheching filament dimensions and position.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThis Attachment only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources








































































































