- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (11/12/2013)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Directive 97/24/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (repealed)Show full title
Directive 97/24/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 1997 on certain components and characteristics of two or three-wheel motor vehicles (repealed)
You are here:
- Directives originating from the EU
- 1997 No. 24
- attachment 3
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 01/01/20160.44 MB
- Revised 11/12/20137.75 MB
- Revised 07/09/20096.33 MB
- Revised 28/11/20063.25 MB
- Revised 08/09/20063.29 MB
- Revised 28/03/20065.31 MB
- Revised 17/05/20054.11 MB
- Revised 10/09/20034.13 MB
- Revised 20/09/20024.04 MB
- Revised 18/08/19974.02 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for:
Version Superseded: 01/01/2016
Alternative versions:
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
CHAPTER 3
EXTERNAL PROJECTIONS FROM TWO OR THREE-WHEEL MOTOR VEHICLES
[X1LIST OF ANNEXES
| ANNEX I | [F1Requirements applying to external projections from two-wheel motor vehicles] |
| Appendix | Testing device and text conditions |
| ANNEX II | [F1Requirements applying to external projections from two-wheel motor vehicles] |
| Appendix | Measurement of projections and gaps |
| ANNEX III | |
| Appendix 1 | Information document in respect of external projections from a type of two or three-wheel motor vehicle |
| Appendix 2 | Certificate of component type approval in respect of external projections from a type of two or three-wheel vehicle] |
ANNEX I
[F1REQUIREMENTS APPLYING TO EXTERNAL PROJECTIONS FROM TWO-WHEEL MOTOR VEHICLES]
1.DEFINITIONSU.K.
For the purposes of this Annex:
1.1.‘outer parts of the vehicle’: means the parts of the vehicle likely to be involved with external obstacles in the event of a collision;U.K.
1.2.‘grazing’: means any contact which, under certain conditions, could cause injury by laceration;U.K.
1.3.‘collision’: means any contact which, under certain conditions could cause penetration injuries;U.K.
1.4.‘type of vehicle in respect of external projections’: means vehicles not differing essentially from one another with regard, in particular, to the shape, dimensions, direction of travel and hardness of the outer parts of the vehicle;U.K.
1.5.‘radius of curvature’: means radius ‘r’ of the arc of the circle most closely approaching the rounded shape of the part under consideration.U.K.
2.CRITERIA FOR DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ‘GRAZING’ AND ‘COLLISION’U.K.
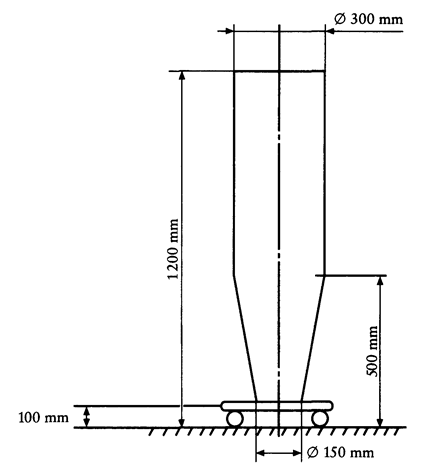
2.1.When the testing device (shown in Figure A in the Appendix) is moved along the vehicle as described in item 4.2 below, the parts of the vehicle touched by that device must be considered to fall within:U.K.
2.1.1.group 1: if the parts of the vehicle graze the testing device; orU.K.
2.1.2.group 2: if the parts of the vehicle collide with the testing device.U.K.
2.1.3.In order to differentiate unequivocally between group 1 parts or components and those falling within group 2, the testing device must be applied in accordance with the method shown in the following diagram:U.K.
3.GENERAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
3.1.Notwithstanding the requirements of item 3.2, the outside of all types of vehicle shall incorporate no pointed, sharp or protruding parts, pointing outwards, of such a shape, dimension, angle of direction or hardness that it increases the risk or seriousness of body lesions suffered by any person struck or grazed by the vehicle in the event of an accident.U.K.
3.2.Vehicles shall be designed in such a way that the parts with which other road users are likely to come into contact comply with items 5 and 6, as appropriate.U.K.
3.3.All external projections covered by this Annex which are made of or covered with soft rubber or plastic having a hardness of less than 60 Shore A are considered to meet the requirements set out in items 5 and 6.U.K.
3.4.However, the following specifications shall not apply to the space between the side-car and motorcycle in motorcycle combinations.U.K.
3.5.Where mopeds are fitted with pedals, compliance with all of the requirements or parts of these laid down by this Directive in respect of the pedals is optional. Where the requirements are not met, manufacturers' shall inform the authorities receiving the request for the component type-approval of external projections from a type of vehicle and shall at the same time describe the measures taken in order to ensure safety.U.K.
[F23.6. In the case of two-wheel vehicles that are fitted with a form of structure or panels intended to enclose, or partially enclose, the driver or passengers or to cover components of the vehicle, the type-approval authority or technical service may, at its discretion and in discussion with the vehicle manufacturer, apply the requirements of this Annex, or of Annex II, to all or part of the vehicle based on an assessment of the worst case condition.] U.K.
Textual Amendments
F2 Inserted by Commission Directive 2006/27/EC of 3 March 2006 amending for the purposes of adapting to technical progress Council Directives 93/14/EEC on the braking of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 93/34/EEC on statutory markings for two- or three-wheel motor vehicles, Directives of the European Parliament and of the Council 95/1/EC on the maximum design speed, maximum torque and maximum net engine power of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 97/24/EC on certain components and characteristics of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles (Text with EEA relevance).
4.TEST METHODSU.K.
4.1.Testing device and test conditionsU.K.
4.1.1.The testing device shall be as described in the Appendix, Fig. A.U.K.
4.1.2.The test vehicle shall be held in a straight line and a vertical position with both wheels touching the ground. The steering device shall be free to move within its normal range.U.K.
An AM 50 percentile anthropomorphic dummy or a person of similar physical characteristics shall be placed on the test vehicle in the normal driving position in such a way that it does not hamper the free movement of the steering device.
4.2.Test procedureU.K.
The test device shall be moved from the front towards the rear of the test vehicle and (if it is able to strike the testing device) the steering control shall be rotated into its fully locked position. The test device must remain in contact with the vehicle (see Figure B in the Appendix). The test shall be carried out on both sides of the vehicle.
5.CRITERIAU.K.
5.1.The criteria set out in this item shall not apply to the parts covered by the requirements of item 6 below.U.K.
5.2.Apart from the exemption set out in item 3.3 above, the following minimum criteria shall apply:U.K.
5.2.1.Requirements applying to the group 1 parts:U.K.
5.2.1.1.PlatesU.K.
the corners of a single plate shall have a radius of curvature of at least 3 mm,
the edges of a single plate shall have a radius of curvature of at least 0,5 mm.
5.2.1.2.Stems:U.K.
stems shall have a diameter at least 10 mm
the edges on the end of a stem shall have a radius of curvature of at least 2 mm.
5.2.2.Requirements applying to group 2 parts:U.K.
5.2.2.1.Plates:U.K.
the edges and corners shall have a radius of curvature of at least 2 mm;
5.2.2.2.Stems:U.K.
shall not be longer than half of the diameter of the stem if that diameter is less than 20 mm.
the radius of curvature of the edges at the end of a stem shall be at least 2 mm if the diameter of the stem is at least 20 mm;
6.SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTSU.K.
6.1.The upper edge of the windscreen of fairing shall have a radius of curvature of at least 2 mm or else be covered with an edge-protection material in accordance with item 3.3.U.K.
[F16.2. The end of the clutch and brake levers shall be perceptibly spherical and have a radius of curvature of at least 7 mm. The outer edges of these levers shall have a radius of curvature of not less than 2 mm. The verification is done with the levers in non-applied position.] U.K.
6.3.The leading edge of the front mudguard shall have a radius of curvature of at least 2 mm.U.K.
6.4.The rear edge of any filler cap located on the upper surface of the fuel tank and thus likely to be struck by the rider in a collision shall not extend more than 15 mm above the underlying surface; any connection with the underlying surface shall be smooth or perceptibly spherical. If the 15 mm requirement cannot be met other measures — such as a protective device located behind the filler neck — must be provided (see, for example, the following sketch).U.K.
6.5.The ignition keys shall have protective cap. This requirement does not apply to folding keys or keys which are flush with the surface.U.K.
Textual Amendments
F2 Inserted by Commission Directive 2006/27/EC of 3 March 2006 amending for the purposes of adapting to technical progress Council Directives 93/14/EEC on the braking of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 93/34/EEC on statutory markings for two- or three-wheel motor vehicles, Directives of the European Parliament and of the Council 95/1/EC on the maximum design speed, maximum torque and maximum net engine power of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 97/24/EC on certain components and characteristics of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles (Text with EEA relevance).
ANNEX II
[F1REQUIREMENTS APPLYING TO EXTERNAL PROJECTIONS FROM THREE-WHEEL MOTOR VEHICLES, LIGHT QUADRICYCLES AND QUADRICYCLES
GENERAL U.K.
The requirements set out in Directive 74/483/EEC (1) relating to the external projections of (category M1) motor vehicles shall apply to three-wheel motor vehicles intended for the carriage of passengers.
However, bearing in mind the variety of forms of construction of these vehicles, the type approval authority or technical service may, at its discretion and in discussion with the vehicle manufacturer, apply the requirements of this Annex, or of Annex I to all or part of the vehicle, based on an assessment of the worst case condition.
This shall also apply to the requirements given below with regard to the requirements for three-wheel vehicles, light quadricycles and quadricycles.
The following requirements shall apply to three-wheel motor vehicles, light quadricycles and quadricycles intended for the carriage of goods.]
1.SCOPEU.K.
1.1.This Annex shall apply to external projections ahead of the rear bulkhead of the cab on vehicles intended for the carriage of goods, those external projections being restricted to the outer surface as defined below. It does not apply to outside rear view mirrors, including their stem, or to accessories such as radio aerials and luggage carriers.U.K.
1.2.The aim is to reduce the risk or seriousness of injuries sustained by any person coming into contact with the outer surface of the vehicle in the event of a collision.U.K.
2.DEFINITIONSU.K.
For the purpose of this Annex:
2.1.‘outer surface’ means the part of the vehicle ahead of the rear bulkhead of the cab as defined in 2.4 below, with the exception of the rear bulkhead itself, but including components such as any front wing(s) and front bumper and the front wheel(s) (if fitted);U.K.
2.2.‘type of vehicle in respect of external projections’ means vehicles not differing essentially from one another with regard, in particular, to the shape, dimensions, direction of travel and hardness of the outer parts of the vehicle;U.K.
2.3.‘cab’ means that part of the bodywork constituting the compartment reserved for the driver and passenger, including its doors;U.K.
2.4.‘rear cab bulkhead’ means the part situated furthermost to the rear of the outer surface of the compartment reserved for the driver and passenger;U.K.
2.5.‘reference plane’ a horizontal plane passing through the centre of the front wheel(s), or a horizontal plane located 50 cm above the ground, the lower of the two being selected. This plane is defined for a laden vehicle;U.K.
2.6.‘floor line’ means a line determined as follows: a vertical-axis cone of an indeterminate height having a half-angle of 15 % is moved all around the outside structure of the vehicle in such a way that it remains tangent, as low as possible, to the outer surface of the bodywork. The floor line is the geometrical trace of the tangency points.U.K.
When the floor line is determined, account shall not be taken of the exhaust pipes, wheels or localized operational mechanical components attached to the floor pan, such as jacking points, suspension mountings, attachment points for towing or transport purposes. It is assumed that any gaps directly above the wheel arches are filled by an imaginary surface directly prolonging the adjacent outside surface. In order to determine the floor line, depending upon the type of vehicle under consideration, account shall be taken of the extremity of the profile of the body panel, of any wing or wings (if fitted) and of any outside angle of the bumper section (if fitted). If there are simultaneously two or several tangency points, it is the lower or the lowest tangency point which determines the floor line;
2.7.‘radius of curvature’ means the radius of the arc of a circle closest to the rounded shape of the part under consideration;U.K.
2.8.‘laden vehicle’ means the vehicle bearing its maximum technically permissible load, that load being distributed among the axles in accordance with the manufactuer's instructions.U.K.
3.GENERAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
3.1.The provisions of this Annex shall not apply to the parts of the ‘outer surface’ of the vehicle which, when the vehicle is unladen and the doors, windows and hatches providing access to the cab etc. are in their closed position, are located:U.K.
3.1.1.outside an area the upper limit of which is a horizontal plane located 2 m above the ground and, according to the manufacturer's choice, the lower limit of which is either the reference plane defined in item 2.5 above or the floor line defined in item 2.6,U.K.
or
3.1.2.in such a way that they cannot be touched, under static conditions, by a sphere 100 mm in diameter.U.K.
3.1.3.Where the reference plane is the lower limit of the zone, account is also taken of the parts of the vehicle below the reference plane falling between two vertical planes, one touching the external surface of the vehicle and the other parallel to it and set at 80 mm, towards the interior of the vehicle from the point at which the reference plane touches the bodywork of the vehicle.U.K.
3.2.The ‘external surface’ of the vehicle shall not include any part, pointing towards the outside, which could catch against pedestrians, cyclists or motor cyclists.U.K.
3.3.None of the components defined in item 4 below may incorporate any pointed or sharp component facing towards the outside, or any projection, shape, dimensions, direction or hardness of which would be likely to increase the risk or seriousness of corporal lesions to a person hit or grazed by the external surface in the event of a collision.U.K.
3.4.Projections from the external surface having a hardness of not more than 60 Shore (A) may have a radius of curvature less than the values laid down in item 4 below.U.K.
3.5.If, by way of a departure from the requirements of item 4, the radius of curvature of any outer projection is less than 2,5 mm, it shall be covered by a form of protection having the characteristics stated in 3.4.U.K.
4.SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTSU.K.
4.1.Ornamental motifs, trade symbols, commercial-logo letters and digitsU.K.
4.1.1.Ornamental motifs, trade symbols, trade-logo letters and digits shall not include any radius of curvature of less than 2,5 mm. This requirement shall not apply to components projecting by less than 5 mm from the adjacent surface, provided that they do not have any cutting edges pointing to the outside.U.K.
4.1.2.Ornamental motifs, trade symbols, trade-logo letters and digits projecting by more than 10 mm from the surrounding surface shall retract, detach or fold back under a force of 10 daN exerted on their most projecting point in any direction within a plane roughly parallel to the surface to which they relate.U.K.
The force of 10 daN shall be exerted by means of a flat-tipped punch having a maximum diameter of 50 mm. Failing this, an equivalent method shall be used. Once any ornamental motifs have been retracted, detached or folded back the remaining parts shall not project by more than 10 mm or incorporate any pointed, sharp or cutting edges.
4.2.Headlamp peaks and surroundsU.K.
4.2.1.Projecting peaks and surrounds shall be permitted on headlamps provided that they do not project by more than 30 mm from the outer transparent surface of the headlamp and that their radius of curvature is at no point less than 2,5 mm.U.K.
4.2.2.Pop-up headlamps shall meet the requirements set out in item 4.2.1 above in both their operating and concealed position.U.K.
4.2.3.The provisions of item 4.2.1 above shall not apply to headlamps which are embedded or recessed in the bodywork if this complies with item 3.2 above.U.K.
4.3.GrillsU.K.
Grill components shall have radii of curvature of
at least 2,5 mm if the distance between consecutive components exceeds 40 mm
at least 1 mm if that distance lies between 25 mm and 40 mm
at least 0,5 mm if that distance is less than 25 mm.
4.4.Windscreen and headlamp wash/wipe systemU.K.
4.4.1.The abovementioned devices shall be mounted in such a way that the wiper-blade spindle is covered with a protector having a radius of curvature of at least 2,5 mm and a minimum area of 150 mm2 measured in the form of a projection over a section which is at the most 6,5 mm from the most projecting point.U.K.
4.4.2.The windscreen and headlamp-washer nozzles shall have a radius of curvature of at least 2,5 mm. If they project by less than 5 mm their sharp edges pointing to the outside shall be smooth polished.U.K.
4.5.Wing (if fitted)U.K.
If the wing is the part of the vehicle located furthest ahead of the cab, its constituent parts shall be designed in such a way that all of the rigid parts facing the outside have a radius of curvature of at least 5 mm.
4.6.Protective devices (bumpers) (if fitted)U.K.
4.6.1.The extremities of the front protective devices shall be turned down towards the external surface of the bodyworkU.K.
4.6.2.The components of the front protective devices shall be designed in such a way that all of the rigid surfaces pointing to the outside cover a radius of curvature of at least 5 mm.U.K.
4.6.3.Accessories such as tow hooks and winches shall not project beyond the foremost surface of the bumpers. However, winches may project beyond the foremost surface of the bumpers provided that they are covered, when not in use, by an appropriate protective device having a radius of curvature of at least 2,5 mm.U.K.
4.6.4.The requirements set out in item 4.6.2 shall not apply to components relating to the bumpers or forming part thereof or to components integral with the bumpers and not projecting by more than 5 mm. The edges of devices protruding by less than 5 mm shall be smooth polished. The specific requirements relating to devices attached to the bumpers and referred to in other items in this Annex shall remain applicable.U.K.
4.7.Handles, hinges and push buttons for doors, bootlids and bonnets, access shutters and flaps and grab handlesU.K.
4.7.1.Push buttons shall not protrude by more than 30 mm, grab handles and bonnet-locking grips by more than 70 mm or any other cases by more than 50 mm. Their radius of curvature shall be at least 2,5 mm.U.K.
4.7.2.If the handles for the side doors are of the rotary type, they shall meet one of the following two conditions:U.K.
4.7.2.1.where the handles pivot in parallel to the door plane, the open extremity of the handle shall point towards the rear. That extremity shall be folded towards the door plane and be located within a protective housing or be recessed;U.K.
4.7.2.2.handles pivoting towards the outside in a direction which is not parallel to the door plane shall, in the closed position, be located within a protective housing or in a recess. The open extremity shall point either rearward or downward. However, handles which do not meet this latter requirement may be accepted if:U.K.
they have an independent return mechanism;
where the return mechanisms do not operate, they do not protrude more than 15 mm;
in that open position they have a radius of curvature of at least 2,5 mmm (that condition does not apply if, in the fully-open position, the projection is less than 5 mm, in which case the angles of the parts pointing outwards must be smooth polished);
the area of their free extremity is not less than 150 mm2 when measured less than 6,5 mm from the point protruding furthest forward.
4.8.Side air and rain deflectors and window dirt deflectorsU.K.
Edges which may point outwards shall have a radius of curvature of at least 1 mm.
4.9.Sheet metal edgesU.K.
Sheet metal edges shall be permitted provided that they are covered with a protector having a radius of curvature of at least 2,5 mm or with a material meeting the requirements stated in item 3.4.
4.10.Wheel nuts, hubcaps and protective devicesU.K.
4.10.1.Wheel nuts, hubcaps and protective devices shall not incorporate any projections in the form of fins.U.K.
4.10.2.When the vehicle is travelling in a straight line no part of the wheels other than the tyres located above the horizontal plane passing through their axis of rotation shall extend beyond the vertical projection, in a horizontal plane, of the edge of the body panel above the wheel. However, where so justified by operating requirements, the protectors covering the wheel nuts and hubs may extend beyond the vertical projection of that edge provided that the radius of curvature of the surface of the projecting part is at least 5 mm and that, in relation to the vertical projection of the body-panel edge, the projection in no case exceeds 30 mm.U.K.
4.10.3.Where the nuts and bolts extend outside the plane projection from the outer surface of the tyres (part of the tyres located above the horizontal plane passing through the axis of rotation of the wheel), a protector or protectors complying with item 4.10.2 above shall be fitted.U.K.
4.11.Jacking points and exhaust pipe(s)U.K.
4.11.1.Jacking points and exhaust pipe(s), if any, shall not extend more than 10 mm beyond either the vertical projection of the floor line or the vertical projection of the intersection of the reference plane with the outer surface of the vehicle.U.K.
4.11.2.By way of departure from this requirement, an exhaust pipe may form a projection of more than 10 mm provided that its extreme sharp ends are rounded off to a minimum radius of curvature of 2,5 mm.U.K.
4.12.The projections and distances shall be measured in accordance with the requirements referred to in the Appendix.U.K.
Appendix
Measurement of projections and gaps
1.METHOD OF DETERMINING THE EXTENT OF PROJECTION OF A COMPONENT MOUNTED ON THE OUTER SURFACEU.K.
1.1.The extent of projection of a component mounted on a convex panel may be determined either directly or by reference to a sketch of an appropriate section of that component in its fitted position.U.K.
1.2.If the extent of the projection of a component mounted on a panel other than convex cannot be determined by means of a simple measurement, it must be determined via the maximum variation in the distance between the centre of a 100 mm diameter sphere and the nominal line of the panel when the sphere is moved, while remaining constantly in contact with that component. An example of the use of this method is given in Figure 1.U.K.
1.3.The extent of projection of, in particular, grab handles shall be measured in relation to a plane passing through the attachment points for those handles. Figure 2 shows an example.U.K.
2.METHOD OF DETERMINING THE EXTENT OF PROJECTION OF HEADLAMP PEAKS AND SURROUNDSU.K.
2.1.The projection beyond the outer surface of the headlamp shall be measured horizontally from the point of tangency of a 100 mm-diameter sphere as shown in Figure 3.U.K.
3.METHOD OF DETERMINING THE SIZE OF A GAP BETWEEN GRILL COMPONENTSU.K.
3.1.The size of any gap between grill components shall be determined via the distance between two planes passing through the points of tangency of the sphere and at right angles to the line joining those same points of tangency. Figures 4 and 5 give examples of the use of that method.U.K.
Editorial Information
X1 Substituted by Corrigendum to Directive 97/24/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 1997 on certain components and characteristics of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles (Official Journal of the European Communities L 226 of 18 August 1997).
Textual Amendments
F1 Substituted by Commission Directive 2006/27/EC of 3 March 2006 amending for the purposes of adapting to technical progress Council Directives 93/14/EEC on the braking of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 93/34/EEC on statutory markings for two- or three-wheel motor vehicles, Directives of the European Parliament and of the Council 95/1/EC on the maximum design speed, maximum torque and maximum net engine power of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 97/24/EC on certain components and characteristics of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles (Text with EEA relevance).
F2 Inserted by Commission Directive 2006/27/EC of 3 March 2006 amending for the purposes of adapting to technical progress Council Directives 93/14/EEC on the braking of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 93/34/EEC on statutory markings for two- or three-wheel motor vehicles, Directives of the European Parliament and of the Council 95/1/EC on the maximum design speed, maximum torque and maximum net engine power of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 97/24/EC on certain components and characteristics of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles (Text with EEA relevance).
Textual Amendments
F1 Substituted by Commission Directive 2006/27/EC of 3 March 2006 amending for the purposes of adapting to technical progress Council Directives 93/14/EEC on the braking of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 93/34/EEC on statutory markings for two- or three-wheel motor vehicles, Directives of the European Parliament and of the Council 95/1/EC on the maximum design speed, maximum torque and maximum net engine power of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles and 97/24/EC on certain components and characteristics of two- or three-wheel motor vehicles (Text with EEA relevance).
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThis Attachment only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources