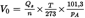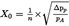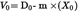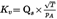- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (28/09/2005)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Directive 2005/55/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (repealed)Show full title
Directive 2005/55/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 28 September 2005 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to the measures to be taken against the emission of gaseous and particulate pollutants from compression-ignition engines for use in vehicles, and the emission of gaseous pollutants from positive-ignition engines fuelled with natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas for use in vehicles (Text with EEA relevance) (repealed)
You are here:
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 31/12/20130.45 MB
- Revised 08/08/20082.04 MB
- Revised 10/06/20064.30 MB
- Revised 19/12/20052.67 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
2.CALIBRATION OF THE CVS-SYSTEMU.K.
2.1.GeneralU.K.
The CVS system shall be calibrated by using an accurate flowmeter traceable to national or international standards and a restricting device. The flow through the system shall be measured at different restriction settings, and the control parameters of the system shall be measured and related to the flow.
Various types of flowmeters may be used, e.g. calibrated venturi, calibrated laminar flowmeter, calibrated turbinemeter.
2.2.Calibration of the Positive Displacement Pump (PDP)U.K.
All parameters related to the pump shall be simultaneously measured with the parameters related to the flowmeter which is connected in series with the pump. The calculated flow rate (in m3/min at pump inlet, absolute pressure and temperature) shall be plotted versus a correlation function which is the value of a specific combination of pump parameters. The linear equation which relates the pump flow and the correlation function shall then be determined. If a CVS has a multiple speed drive, the calibration shall be performed for each range used. Temperature stability shall be maintained during calibration.
2.2.1.Data analysisU.K.
The air flowrate (Qs) at each restriction setting (minimum six settings) shall be calculated in standard m3/min from the flowmeter data using the manufacturer's prescribed method. The air flow rate shall then be converted to pump flow (V0) in m3/rev at absolute pump inlet temperature and pressure as follows:
where,
=
air flow rate at standard conditions (101,3 kPa, 273 K), m3/s
=
temperature at pump inlet, K
=
absolute pressure at pump inlet (pB-p1), kPa
=
pump speed, rev/s
To account for the interaction of pressure variations at the pump and the pump slip rate, the correlation function (X0) between pump speed, pressure differential from pump inlet to pump outlet and absolute pump outlet pressure shall be calculated as follows:
where,
=
pressure differential from pump inlet to pump outlet, kPa
=
absolute outlet pressure at pump outlet, kPa
A linear least-square fit shall be performed to generate the calibration equation as follows:
D0 and m are the intercept and slope constants, respectively, describing the regression lines.
For a CVS system with multiple speeds, the calibration curves generated for the different pump flow ranges shall be approximately parallel, and the intercept values (D0) shall increase as the pump flow range decreases.
The calculated values from the equation shall be within ± 0,5 % of the measured value of V0. Values of m will vary from one pump to another. Particulate influx over time will cause the pump slip to decrease, as reflected by lower values for m. Therefore, calibration shall be performed at pump start-up, after major maintenance, and if the total system verification (Section 2.4) indicates a change of the slip rate.
2.3.Calibration of the Critical Flow Venturi (CFV)U.K.
Calibration of the CFV is based upon the flow equation for a critical venturi. Gas flow is a function of inlet pressure and temperature, as shown below:
where,
=
calibration coefficient
=
absolute pressure at venturi inlet, kPa
=
temperature at venturi inlet, K
2.3.1.Data analysisU.K.
The air flowrate (Qs) at each restriction setting (minimum eight settings) shall be calculated in standard m3/min from the flowmeter data using the manufacturer's prescribed method. The calibration coefficient shall be calculated from the calibration data for each setting as follows:
where,
=
air flow rate at standard conditions (101,3 kPa, 273 K), m3/s
=
temperature at the venturi inlet, K
=
absolute pressure at venturi inlet, kPa
To determine the range of critical flow, Kv shall be plotted as a function of venturi inlet pressure. For critical (choked) flow, Kv will have a relatively constant value. As pressure decreases (vacuum increases), the venturi becomes unchoked and Kv decreases, which indicates that the CFV is operated outside the permissible range.
For a minimum of eight points in the region of critical flow, the average Kv and the standard deviation shall be calculated. The standard deviation shall not exceed ± 0,3 % of the average KV.
2.4.Total system verificationU.K.
The total accuracy of the CVS sampling system and analytical system shall be determined by introducing a known mass of a pollutant gas into the system while it is being operated in the normal manner. The pollutant is analysed, and the mass calculated according to Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.3 except in the case of propane where a factor of 0,000472 is used in place of 0,000479 for HC. Either of the following two techniques shall be used.
2.4.1.Metering with a critical flow orificeU.K.
A known quantity of pure gas (carbon monoxide or propane) shall be fed into the CVS system through a calibrated critical orifice. If the inlet pressure is high enough, the flow rate, which is adjusted by means of the critical flow orifice, is independent of the orifice outlet pressure (≡ critical flow). The CVS system shall be operated as in a normal exhaust emission test for about 5 to 10 minutes. A gas sample shall be analysed with the usual equipment (sampling bag or integrating method), and the mass of the gas calculated. The mass so determined shall be within ± 3 % of the known mass of the gas injected.
2.4.2.Metering by means of a gravimetric techniqueU.K.
The weight of a small cylinder filled with carbon monoxide or propane shall be determined with a precision of ± 0,01 gram. For about 5 to 10 minutes, the CVS system shall be operated as in a normal exhaust emission test, while carbon monoxide or propane is injected into the system. The quantity of pure gas discharged shall be determined by means of differential weighing. A gas sample shall be analysed with the usual equipment (sampling bag or integrating method), and the mass of the gas calculated. The mass so determined shall be within ± 3 % of the known mass of the gas injected.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThe Whole Annex
PrintThis Division only
You have chosen to open the Whole Directive
The Whole Directive you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
The Schedules you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources