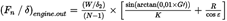B7POWER CUTBACK (TRANSITION SEGMENT)U.K.
Power is reduced, or cut back, from take-off setting at some point after takeoff in order to extend engine life and often to reduce noise in certain areas. Thrust is normally cut back during either a constant speed climb segment (Section B6) or an acceleration segment (Section B8). As it is a relatively brief process, typically of only 3-5 seconds′ duration, is it modelled by adding a ‘transition segment’ to the primary segment. This is usually taken to cover a horizontal ground distance of 1 000 ft (305 m).
Amount of thrust reduction U.K.
In normal operation the engine thrust is reduced to the maximum climb thrust setting. Unlike the take-off thrust, climb thrust can be sustained indefinitely, usually in practice until the aeroplane has reached its initial cruise altitude. The maximum climb thrust level is determined with equation B-1 using the manufacturer supplied maximum thrust coefficients. However, noise abatement requirements may call for additional thrust reduction, sometimes referred to as a deep cutback. For safety purposes the maximum thrust reduction is limited(1) to an amount determined by the performance of the aeroplane and the number of engines.
The minimum ‘reduced-thrust’ level is sometimes referred to as the engine-out ‘reduced thrust’:
where
is the pressure ratio at altitude h2
is the engine-out percentage climb gradient:
= 0 % for aeroplanes with automatic thrust restoration systems; otherwise,
= 1,2 % for 2-engine aeroplane
= 1,5 % for 3-engine aeroplane
= 1,7 % for 4-engine aeroplane
Constant speed climb segment with cutback U.K.
The climb segment gradient is calculated using equation B-12, with thrust calculated using either B-1 with maximum climb coefficients, or B-16 for reduced thrust. The climb segment is then broken into two sub-segments, both having the same climb angle. This is illustrated in Figure B-2.
The first sub-segment is assigned a 1 000 ft (304 m) ground distance, and the corrected net thrust per engine at the end of 1 000 ft is set equal to the cutback value. (If the original horizontal distance is less than 2 000 ft, one half of the segment is used to cutback thrust.) The final thrust on the second sub-segment is also set equal to the cutback thrust. Thus, the second sub-segment is flown at constant thrust.
‘Noise Abatement Procedures’, ICAO Document 8168 ‘PANS-OPS’ Vol.1 Part V, Chapter 3, ICAO 2004.