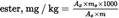- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91Show full title
Commission Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91 of 11 July 1991 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis
You are here:
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 20/10/20193.52 MB
- Revised 04/12/20163.60 MB
- Revised 11/10/20163.55 MB
- Revised 04/08/20163.60 MB
- Revised 16/10/20153.42 MB
- Revised 01/01/20153.68 MB
- Revised 01/03/20143.69 MB
- Revised 01/01/20142.84 MB
- Revised 09/08/20122.49 MB
- Revised 01/04/20112.46 MB
- Revised 01/10/20081.42 MB
- Revised 01/01/20081.42 MB
- Revised 01/11/20035.95 MB
- Revised 22/05/20020.48 MB
- Revised 01/11/20010.66 MB
- Revised 01/07/20010.66 MB
- Revised 01/06/19990.65 MB
- Revised 01/11/19980.65 MB
- Revised 10/02/19980.65 MB
- Revised 31/10/19950.59 MB
- Revised 28/05/19950.59 MB
- Revised 01/11/19940.55 MB
- Revised 19/02/19940.55 MB
- Revised 05/02/19940.55 MB
- Revised 01/05/19930.55 MB
- Revised 21/03/19930.56 MB
- Revised 20/02/19930.56 MB
- Revised 01/11/19920.55 MB
- Revised 21/07/19920.55 MB
- Revised 03/07/19920.54 MB
- Revised 05/06/19920.54 MB
- Revised 21/12/19910.52 MB
- Revised 06/09/19910.52 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Division 5.
Changes to legislation:
There are outstanding changes not yet made to Commission Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91. Any changes that have already been made to the legislation appear in the content and are referenced with annotations.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. Changes and effects are recorded by our editorial team in lists which can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area. Where those effects have yet to be applied to the text of the legislation by the editorial team they are also listed alongside the legislation in the affected provisions. Use the ‘more’ link to open the changes and effects relevant to the provision you are viewing.
Changes and effects yet to be applied to the whole legislation item and associated provisions
- Signature words omitted by S.I. 2019/1422 reg. 6(10)
- Art. 1(8) inserted by S.I. 2019/1422 reg. 6(2)(b)
- Art. 1(8)(a)(ii)(bb) omitted in earlier amending provision S.I. 2019/1422, reg. 6(2)(b) by S.I. 2020/1453 reg. 14(16)(a)(i)
- Art. 1(8)(b) words substituted in earlier amending provision S.I. 2019/1422, reg. 6(2)(b) by S.I. 2020/1453 reg. 14(16)(a)(ii)
- Art. 1(8)(c)(ii) omitted in earlier amending provision S.I. 2019/1422, reg. 6(2)(b) by S.I. 2020/1453 reg. 14(16)(a)(iii)
- Annex 1a para. 1.1 words substituted by S.I. 2019/1422 reg. 6(11)(a)
- Annex 1a para. 1.2 words substituted by S.I. 2019/1422 reg. 6(11)(b)
- Art. 2a(3)(e) words substituted by S.I. 2019/1422 reg. 6(4)(c) (This amendment not applied to legislation.gov.uk. Reg. 6(4)(c) substituted immediately before IP completion day by S.I. 2020/1453, regs. 1(2)(b), 14(16)(c)(ii))
- Art. 2a(3)(e) words substituted by S.I. 2019/1422, reg. 6(4)(c) (as substituted) by S.I. 2020/1453 reg. 14(16)(c)(ii)
- Art. 3 words substituted by S.I. 2019/1422 reg. 6(5)(a)
- Art. 3 words substituted by S.I. 2019/1422 reg. 6(5)(b)
[F15. PROCEDURE U.K.
5.1. Preparation of the chromatographic column. U.K.
Suspend 15 g of silica gel (4.1) in the n-hexane (4.2) and introduce it into the column (3.2). Allow to settle spontaneously. Complete settling with the aid of an electrovibrator (3.5) to make the chromatographic layer more homogeneous. Percolate 30 ml of n-hexane to remove any impurities. Using the balance (3.8) weigh exactly 500 mg of the sample into the 25 ml Erlenmeyer flask (3.1), add the appropriate quantity of the internal standard (4.5) according to the presumed wax content. For example, add 0,1 mg of lauryl arachidate for olive oil, and 0,25 to 0,5 mg for olive-residue oil. Transfer the prepared sample to the chromotography column using two 2 ml portions of n-hexane (4.2).
Allow the solvent to flow away until it reaches 1 mm above the upper level of the absorbant then percolate a further 70 ml of n-hexane in order to eliminate the n-alkanes naturally present. Then start the chromatographic elution by collecting 180 ml of the mixture of n-hexane/ethyl ether (ratio 99:1), keeping a rate of flow of approximately 15 drops every 10 seconds. Elution of the sample must be carried out at a room temperature of 22 ± 4 °C.
NB: U.K.
The n-hexane/ethyl ether mixture (99:1) must be prepared every day.
For a visual check on the correct elution of the waxes 100 μl of 1 % Sudan in the elution mixture can be added to the sample in solution. Since the colourant has an intermediate retention, between waxes and triglycerides, when the coloration has reached the bottom of the column the elution should be suspended because all the waxes will have been eluted.
Dry the fraction thus obtained in a rotary evaporator (3.6.) until virtually all the solvent has been eliminated. Eliminate the final 2 ml of solvent with the aid of a weak current of nitrogen; then add 2-4 ml n-heptane.
5.2. Analysis by gas chromatography U.K.
5.2.1. Preparatory work U.K.
Fit the column to the gas chromatograph (3.3) by connecting the inlet port to the on-column system and the outlet port to the detector. Perform a general check on the GC apparatus (operation of gas circuits, detector and recorder efficiency, etc.).
If the column is being used for the first time it should be conditioned first. Pass a little gas through the column, then turn on the GC apparatus. Heat gradually until 350 °C is reached after about four hours. Maintain that temperature for at least two hours then regulate the apparatus to operating conditions (set gas flow, light flame, connect to the electronic recorder (3.3.4), set temperature of column chamber, detector, etc.) and record the signal at a sensitivity at least twice as high as that required for the analysis. The baseline must be linear, with no peaks of any kind, and must not show any deviation.
A negative straight-line drift indicates that the column connections are not tight; a positive drift that the column has not been sufficiently conditioned.
5.2.2. Choice of operating conditions U.K.
The operating conditions are generally as follows:
column temperature:
20 °C/minute 5 °C/minute 20 °C/minute Initially 80 °C
(1′)
→ 240 °C → 325 °C
(6′)
→ 340 °C
(10′)
detector temperature: 350 °C;
quantity of substance injected: 1 μl of the n-heptane solution (2-4 ml);
carrier gas: helium or hydrogen at the correct linear velocity for the gas selected (see Appendix);
instrument sensitivity: suitable for the following conditions:
The conditions may be modified according to the characteristics of the column and the GC apparatus to obtain separation of all the waxes and a satisfactory peak resolution (see figure); the internal standard C 32 retention time must be 18 ± 3 minutes. The most representative wax peak must be at least 60 % of the full scale.
The peak integration parameters must be established so as to obtain a correct evaluation of the areas of the peaks in question.
NB : Given the high final temperature, a positive drift of no more than 10 % of the full scale is permitted. U.K.
5.3. Performance of the analysis U.K.
Sample 1 μl of the solution using the 10 μl microsyringe; withdraw the syringe plunger so that the needle is empty. Place the needle in the injector and after 1-2 seconds inject quickly; remove the needle slowly after about five seconds.
Record until the waxes are completely eluted.
The base line must always satisfy the required conditions.
5.4. Identification of peaks U.K.
Identification of the different peaks should be based on retention time by comparison with wax mixtures of known retention times analysed under the same conditions.
The figure is a chromatogram of the waxes of a virgin olive oil.
5.5. Evaluation of quantity U.K.
Calculate the areas of the peaks of the internal standard and the aliphatic esters of C 40 to C 46 using the integrator.
Calculate the wax content of each of the esters in mg/kg fat using the formula:
where:
=
area of each ester’s peak, in square millimetres;
=
area of the internal standard’s peak, in square millimetres;
=
mass of added internal standard, in milligrams;
=
mass of sample for analysis, in grams.]
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThe Whole Annex
PrintThis Division only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
The Schedules you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources