- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (31/12/2020)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Regulation (EU) No 965/2012Show full title
Commission Regulation (EU) No 965/2012 of 5 October 2012 laying down technical requirements and administrative procedures related to air operations pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 216/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council
You are here:
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 31/12/20203.47 MB
- Revised 14/08/20203.42 MB
- Revised 25/09/20193.18 MB
- Revised 09/07/20195.04 MB
- Revised 08/04/20195.08 MB
- Revised 01/01/20194.89 MB
- Revised 14/08/20184.84 MB
- Revised 01/07/20184.87 MB
- Revised 22/03/20174.82 MB
- Revised 25/08/20164.79 MB
- Revised 18/02/20164.47 MB
- Revised 01/10/20154.33 MB
- Revised 14/05/20154.33 MB
- Revised 19/02/20154.32 MB
- Revised 01/07/20144.99 MB
- Revised 17/02/20145.41 MB
- Revised 25/08/20133.65 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Division SECTION 2
Status:
Point in time view as at 31/12/2020.
Changes to legislation:
Commission Regulation (EU) No 965/2012, Division
SECTION 2
is up to date with all changes known to be in force on or before 21 February 2025. There are changes that may be brought into force at a future date. Changes that have been made appear in the content and are referenced with annotations.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Changes and effects yet to be applied by the editorial team are only applicable when viewing the latest version or prospective version of legislation. They are therefore not accessible when viewing legislation as at a specific point in time. To view the ‘Changes to Legislation’ information for this provision return to the latest version view using the options provided in the ‘What Version’ box above.
[F1 SECTION 2 U.K. Helicopters
NCO.IDE.H.100 Instruments and equipment — general U.K.
(a) Instruments and equipment required by this Subpart shall be approved in accordance with the applicable airworthiness requirements if they are: U.K.
used by the flight crew to control the flight path;
used to comply with NCO.IDE.H.190;
used to comply with NCO.IDE.H.195; or
installed in the helicopter.
[F2(b) The following items, when required under this Subpart, do not need an equipment approval: U.K.
independent portable lights;
an accurate time piece;
first-aid kit;
survival and signalling equipment;
sea anchor and equipment for mooring;
child restraint device;
a simple PCDS used by a task specialist as a restraint device.
Textual Amendments
F2Substituted by Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/1384 of 24 July 2019 amending Regulations (EU) No 965/2012 and (EU) No 1321/2014 as regards the use of aircraft listed on an air operator certificate for non-commercial operations and specialised operations, the establishment of operational requirements for the conduct of maintenance check flights, the establishment of rules on non-commercial operations with reduced cabin crew on board and introducing editorial updates concerning air operations requirements (Text with EEA relevance).
(c) Instruments and equipment or accessories not required under Annex VII (Part-NCO), as well as any other equipment that is not required under this Regulation, but carried on a flight, shall comply with the following requirements: U.K.
the information provided by those instruments, equipment or accessories shall not be used by the flight crew members to comply with Annex II to Regulation (EU) 2018/1139 or points NCO.IDE.H.190 and NCO.IDE.H.195 of Annex VII;
the instruments and equipment or accessories shall not affect the airworthiness of the helicopter, even in the case of failures or malfunction.]
(d) Instruments and equipment shall be readily operable or accessible from the station where the flight crew member that needs to use it is seated. U.K.
(e) All required emergency equipment shall be easily accessible for immediate use. U.K.
NCO.IDE.H.105 Minimum equipment for flight U.K.
A flight shall not be commenced when any of the helicopter’s instruments, items of equipment or functions required for the intended flight are inoperative or missing, unless:
the helicopter is operated in accordance with the MEL, if established; or
the helicopter is subject to a permit to fly issued in accordance with the applicable airworthiness requirements.
NCO.IDE.H.115 Operating lights U.K.
Helicopters operated at night shall be equipped with:
an anti-collision light system;
navigation/position lights;
a landing light;
lighting supplied from the helicopter’s electrical system to provide adequate illumination for all instruments and equipment essential to the safe operation of the helicopter;
lighting supplied from the helicopter’s electrical system to provide illumination in all passenger compartments;
an independent portable light for each crew member station; and
lights to conform with the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea if the helicopter is amphibious.
NCO.IDE.H.120 Operations under VFR — flight and navigational instruments and associated equipment U.K.
(a) Helicopters operated under VFR by day shall be equipped with a means of measuring and displaying the following: U.K.
magnetic heading;
time in hours, minutes and seconds;
[F2barometric altitude;]
indicated airspeed; and
slip.
(b) Helicopters operated under VMC at night, or when the visibility is less than 1 500 m, or in conditions where the helicopter cannot be maintained in a desired flight path without reference to one or more additional instruments, shall be, in addition to (a), equipped with: U.K.
a means of measuring and displaying the following:
attitude;
vertical speed; and
stabilised heading; and
a means of indicating when the supply of power to the gyroscopic instruments is not adequate.
(c) Helicopters operated when the visibility is less than 1 500 m, or in conditions where the helicopter cannot be maintained in a desired flight path without reference to one or more additional instruments, shall be, in addition to (a) and (b), equipped with a means of preventing malfunction of the airspeed indicating system required in (a)(4) due to condensation or icing. U.K.
NCO.IDE.H.125 Operations under IFR — flight and navigational instruments and associated equipment U.K.
Helicopters operated under IFR shall be equipped with:
a means of measuring and displaying the following:
magnetic heading;
time in hours, minutes and seconds;
[F2barometric altitude;]
indicated airspeed;
vertical speed;
slip;
attitude;
stabilised heading; and
outside air temperature;
a means of indicating when the supply of power to the gyroscopic instruments is not adequate;
a means of preventing malfunction of the airspeed indicating system required by (a)(4) due to condensation or icing; and
an additional means of measuring and displaying attitude as a standby instrument.
NCO.IDE.H.126 Additional equipment for single pilot operations under IFR U.K.
Helicopters operated under IFR with a single pilot shall be equipped with an autopilot with at least altitude hold and heading mode.
NCO.IDE.H.135 Flight crew interphone system U.K.
Helicopters operated by more than one flight crew member shall be equipped with a flight crew interphone system, including headsets and microphones for use by all flight crew members.
NCO.IDE.H.140 Seats, seat safety belts, restraint systems and child restraint devices U.K.
(a) Helicopters shall be equipped with: U.K.
[F2a seat or berth for each person on board who is aged 24 months or more, or a station for each crew member or task specialist on board;
a seat belt on each passenger seat and restraining belts for each berth, and restraint devices for each station;]
for helicopters first issued with an individual CofA after 31 December 2012 , a seat belt with an upper torso restraint system for each passenger who is aged 24 months or more;
a child restraint device for each person on board younger than 24 months; and
a seat belt with upper torso restraint system incorporating a device that will automatically restrain the occupant’s torso in the event of rapid deceleration on each flight crew seat.
(b) A seat belt with upper torso restraint system shall have a single point release. U.K.
NCO.IDE.H.145 First-aid kit U.K.
(a) Helicopters shall be equipped with a first-aid kit. U.K.
(b) The first-aid kit shall be: U.K.
readily accessible for use; and
kept up-to-date.
[F3NCO.IDE.H.155 Supplemental oxygen — non-pressurised helicopters U.K.
Non-pressurised helicopters operated when an oxygen supply is required in accordance with NCO.OP.190 shall be equipped with oxygen storage and dispensing apparatus capable of storing and dispensing the required oxygen supplies.]
Textual Amendments
NCO.IDE.H.160 Hand fire extinguishers U.K.
(a) Helicopters, except ELA2 helicopters, shall be equipped with at least one hand fire extinguisher: U.K.
in the flight crew compartment; and
in each passenger compartment that is separate from the flight crew compartment, except if the compartment is readily accessible to the flight crew.
(b) The type and quantity of extinguishing agent for the required fire extinguishers shall be suitable for the type of fire likely to occur in the compartment where the extinguisher is intended to be used and to minimise the hazard of toxic gas concentration in compartments occupied by persons. U.K.
NCO.IDE.H.165 Marking of break-in points U.K.
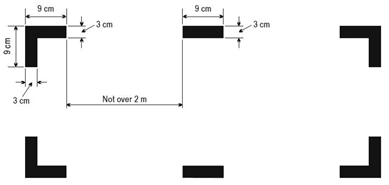
If areas of the helicopter’s fuselage suitable for break-in by rescue crews in an emergency are marked, such areas shall be marked as shown in Figure 1.
NCO.IDE.H.170 Emergency locator transmitter (ELT) U.K.
(a) Helicopters certified for a maximum passenger seating configuration above six shall be equipped with: U.K.
an automatic ELT; and
one survival ELT (ELT(S)) in a life-raft or life-jacket when the helicopter is operated at a distance from land corresponding to more than 3 minutes flying time at normal cruising speed.
(b) Helicopters certified for a maximum passenger seating configuration of six or less shall be equipped with an ELT(S) or a personal locator beacon (PLB), carried by a crew member or a passenger. U.K.
(c) ELTs of any type and PLBs shall be capable of transmitting simultaneously on 121,5 MHz and 406 MHz. U.K.
NCO.IDE.H.175 Flight over water U.K.
(a) Helicopters shall be equipped with a life-jacket for each person on board or equivalent individual flotation device for each person on board younger than 24 months, which shall be worn or stowed in a position that is readily accessible from the seat or berth of the person for whose use it is provided, when: U.K.
flying over water beyond autorotational distance from land where in case of the critical engine failure, the helicopter is not able to sustain level flight; or
flying over water at a distance of land corresponding to more than 10 minutes flying at normal cruising speed, where in case of the critical engine failure, the helicopter is able to sustain level flight; or
taking off or landing at an aerodrome/operating site where the take-off or approach path is over water.
(b) Each life-jacket or equivalent individual flotation device shall be equipped with a means of electric illumination for the purpose of facilitating the location of persons. U.K.
(c) The pilot-in-command of a helicopter operated on a flight over water at a distance from land corresponding to more than 30 minutes flying time at normal cruising speed or 50 NM, whichever is less, shall determine the risks to survival of the occupants of the helicopter in the event of a ditching, based on which he/she shall determine the carriage of: U.K.
equipment for making the distress signals;
life-rafts in sufficient numbers to carry all persons on board, stowed so as to facilitate their ready use in emergency; and
life-saving equipment, to provide the means of sustaining life, as appropriate to the flight to be undertaken.
(d) The pilot-in-command shall determine the risks to survival of the occupants of the helicopter in the event of a ditching, when deciding if the life-jackets required in (a) shall be worn by all occupants. U.K.
NCO.IDE.H.180 Survival equipment U.K.
Helicopters, operated over areas in which search and rescue would be especially difficult, shall be equipped with such signalling devices and life-saving equipment, including means of sustaining life, as may be appropriate to the area overflown.
[F2NCO.IDE.H.185 All helicopters on flights over water — ditching U.K.
Helicopters flying over water in a hostile environment beyond a distance of 50 NM from land shall be either of the following:
designed for landing on water in accordance with the relevant certification specifications;
certified for ditching in accordance with the relevant certification specifications;
fitted with emergency flotation equipment.]
NCO.IDE.H.190 Radio communication equipment U.K.
(a) Where required by the airspace being flown helicopters shall be equipped with radio communication equipment capable of conducting two-way communication with those aeronautical stations and on those frequencies to meet airspace requirements. U.K.
(b) Radio communication equipment, if required by (a), shall provide for communication on the aeronautical emergency frequency 121,5 MHz. U.K.
(c) When more than one communications equipment unit is required, each shall be independent of the other or others to the extent that a failure in any one will not result in failure of any other. U.K.
(d) When a radio communication system is required, and in addition to the flight crew interphone system required in NCO.IDE.H.135, helicopters shall be equipped with a transmit button on the flight controls for each required pilot and/or crew member at his/her working station. U.K.
NCO.IDE.H.195 Navigation equipment U.K.
(a) Helicopters operated over routes that cannot be navigated by reference to visual landmarks shall be equipped with navigation equipment that will enable them to proceed in accordance with: U.K.
the ATS flight plan, if applicable; and
the applicable airspace requirements.
(b) Helicopters shall have sufficient navigation equipment to ensure that, in the event of the failure of one item of equipment at any stage of the flight, the remaining equipment shall allow safe navigation in accordance with (a), or an appropriate contingency action, to be completed safely. U.K.
(c) Helicopters operated on flights in which it is intended to land in IMC shall be equipped with navigation equipment capable of providing guidance to a point from which a visual landing can be performed. This equipment shall be capable of providing such guidance for each aerodrome at which is intended to land in IMC and for any designated alternate aerodromes. U.K.
[F4(d) For PBN operations the aircraft shall meet the airworthiness certification requirements for the appropriate navigation specification.] U.K.
Textual Amendments
[F5(e) Helicopters shall be equipped with surveillance equipment in accordance with the applicable airspace requirements.] U.K.
Textual Amendments
F5Inserted by Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/1384 of 24 July 2019 amending Regulations (EU) No 965/2012 and (EU) No 1321/2014 as regards the use of aircraft listed on an air operator certificate for non-commercial operations and specialised operations, the establishment of operational requirements for the conduct of maintenance check flights, the establishment of rules on non-commercial operations with reduced cabin crew on board and introducing editorial updates concerning air operations requirements (Text with EEA relevance).
NCO.IDE.H.200 Transponder U.K.
Where required by the airspace being flown, helicopters shall be equipped with a secondary surveillance radar (SSR) transponder with all the required capabilities.
[F4NCO.IDE.H.205 Management of aeronautical databases U.K.
Aeronautical databases used on certified aircraft system applications shall meet data quality requirements that are adequate for the intended use of the data.
The operator shall ensure the timely distribution and insertion of current and unaltered aeronautical databases to the aircraft that require them.
Notwithstanding any other occurrence reporting requirements as defined in Regulation (EU) No 376/2014, the operator shall report to the database provider instances of erroneous, inconsistent or missing data that might be reasonably expected to constitute a hazard to flight.
In such cases, the pilot-in-command shall not use the affected data.]]
Textual Amendments
F1Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) No 800/2013 of 14 August 2013 amending Regulation (EU) No 965/2012 laying down technical requirements and administrative procedures related to air operations pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 216/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance).
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThe Whole Annex
PrintThe Whole Division
PrintThis Section only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
The Schedules you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources