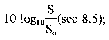- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As made)
The Lawnmowers (Harmonization of Noise Emission Standards) Regulations 1992
You are here:
- UK Statutory Instruments
- 1992 No. 168
- SCHEDULE 3
More Resources
Status:
This is the original version (as it was originally made). This item of legislation is currently only available in its original format.
Regulation 3(1)
SCHEDULE 3
PART 1METHOD OF DETERMINING AIRBORNE NOISE EMITTED BY LAWNMOWERS (ALSO REFERRED TO AS MOWERS IN THIS SCHEDULE)
1 OBJECT
The purpose of this method is to determine the noise emitted by all categories of lawnmowers. For the purposes of this method, lawnmowers are called sound sources.
This method defines the various acoustic criteria which may be adopted to characterize a sound source, and the means of determining these criteria.
The values obtained by this method constitute the basic data for checking that the noise emission of lawnmowers complies with requirements for noise limitation. Unless otherwise indicated, these values are inclusive of tolerances.
2 SCOPE
2.1 Type of noise
This method is applicable to any type of noise emitted by a sound source normally used in the open air.
2.2 Size of sound source
This method is applicable to sound sources of all sizes.
3 DEFINITIONS
3.1 Sound pressure level LpA
The sound pressure level LpA is obtained by applying the weighting A to the sound pressure level Lp.
The sound pressure level Lp, expressed in dB, of a noise is defined by:
where:
p is the effective sound pressure value measured at a particular point, expressed in Pa;
p0 is the effective reference sound pressure, equal to 20 μPa.
The value LpA of the A-weighted sound pressure level, expressed in dB, is obtained by applying the weighting A to the measuring system.
3.2 Measuring surface
The measuring surface of area S is a hypothetical surface surrounding the sound source and on which the measuring points are arranged (see 6.4).
3.3 Surface sound pressure level LpAM
The surface sound pressure level LpAM is the root mean square of the sound pressures recorded on the measuring surface, calculated in accordance with the method set out in 8.4.
3.4 Sound power level LWA is obtained by applying the weighting A to the sound power level LW.
The sound power level LW expressed in dB, of a sound source is defined by:
where:
W is the total sound power generated by the sound source, expressed in watts;
W0 is the reference sound power, equal to 10−12 W.
The value LWA of the A-weighted sound power level, expressed in dB, is obtained by applying the weighting A to the measuring system.
3.5 Limit value of the sound power level LWA1
The limit value of the sound power level LWA, expressed in A-weighted dB, shall be termed LWA1.
3.6 Directivity index (DI)
The directivity index (DI), expressed in dB, to be adopted in applying this method is defined by the formula:
DI = LpAmax - LpAm + 3
where:
LpAmax is the highest of the sound pressure levels recorded at the measuring points (see 6.4.2), calculated in accordance with 8.1.1 and corrected in accordance with the general principles laid down in 8.6.1, 8.6.3 and 8.6.4,
LpAm is the surface sound pressure level determined in accordance with 8.4,
3 is a conventional additive term.
In determining the values LpAmax and LpAm only the measuring points prescribed need to be taken into account.
3.7 Extraneous noise
Extraneous noise means the noise resulting from background noise and parasitic noise.
3.7.1 Background noise
Background noise means any noise recorded at the measuring points which is not generated by the sound source.
3.7.2 Parasitic noise
Parasitic noise means any noise at the measuring points which is generated by the sound source but not directly radiated by it.
4 CRITERIA TO BE USED FOR EXPRESSING RESULTS
4.1 Acoustic criteria for the environment
The acoustic criterion for the environment of a lawnmower shall be expressed by the sound power level.
5 MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
5.1 General
The instruments shall be designed to measure the A-weighted level of the root mean square of the sound pressure. The level of the root mean square value in time for a measurement point is obtained either by direct reading of the instrument, or by calculation in accordance with section 11.
5.2 Measuring instruments
The following instruments may be used to satisfy the preceding requirement:
(a)a sound level meter which at least meets the requirements of IEC Publication 651, first edition, 1979 for the type of meters in Class 1. The meter must be used in the S response mode;
(b)an integrator effecting analog or digital integration of the squared signal over a given time interval.
Note:
If, for any measurement, instruments other than a precision sound level meter or combinations of instruments, such as integrators are used, all the specifications of such instruments shall comply with the relevant requirements of IEC publication 651, first edition, 1979.
5.3 Microphone with cable
Use shall be made of a microphone with cable complying with IEC publication 651, first edition, 1979 and calibrated for free-field measurement.
5.4 Weighting network
Use shall be made of an A-weighting network meeting the requirements of IEC publication 651, first edition, 1979.
5.5 Inspection of the measuring apparatus
Before the tests, the acoustic properties of the entire apparatus (measuring instruments including microphone and cable) shall be checked by means of a calibrated sound source with an accuracy of at least 0.5 dB (e.g. a pistonphone); the apparatus shall be checked again immediately after each series of measurements.
These on-the-spot checks shall be supplemented by more thorough calibrations to be carried out at least once a year in a specially equipped laboratory.
6 MEASURING CONDITIONS
6.1 Purpose of the measurement
Lawnmowers designed to be equipped with a device for collecting the grass shall be tested under normal conditions of use with that device fitted.
The cutting device shall be adjusted to a height of 3 cm. If for technical reasons this is not possible, the cutting device shall be adjusted as close as possible to a height of 3 cm. The grass in the test area shall be mown with this cutting device setting before any sound measurement is taken where tests are made under 6.3.3. below.
For the sound measurement, all grass shall be removed from the lawnmower and the grass collector shall be empty.
The cutting devices of cylinder lawnmowers shall be adjusted with a cylinder/cutting edge gap specified by the manufacturer such that:
a standardized shell of paper of 80 g/m2 weight (kraft paper ISO/R4046) is cut over at least 50% of the cutting width, or
the distance between the cylinder blades and the cutting edge is not more than 0.15 mm over the whole length of the cutting-width, or
the cutting mechanism shall be adjusted until the blades touch and then backed off until contact just ceases when the cylinder is rotating at maximum speed.
The option of making use of the test method laid down in the third indent is limited to electrically powered cylinder mowers with a cutting width of less than 50 cm.
Before and during the operation, the cutting device shall be lubricated with SAE 20/50 oil.
6.2 Operation of the sound source during measurement
Before each sound measurement is taken, the lawnmower shall be warmed up in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
The sound power level of lawnmowers shall, in principle, be measured when the lawnmower is stationary without its operator being present and the cutting device and the motor are operating at maximum speed.
If the cutting device cannot be separated from the driving wheels of the lawnmower, the mower shall be tested either with the mower on supports or while moving and driven by an operator under the following conditions:
direct drive lawnmower:
in this case, it shall be moving at a speed such that the cutting device is operating at the maximum speed laid down by the manufacturer,
variable-drive lawnmower:
in this case, the highest gear shall be selected. The lawnmower shall be moving at a speed such that the cutting device is operating at the maximum speed laid down by the manufacturer.
(a)Lawnmowers with combustion engines:
The engine oil used for operating the mower during measurement shall be as specified by the manufacturer. The fuel tank shall not be more than half full.
(b)Lawnmowers with electric motors:
If the lawnmower is powered by battery, the battery shall be fully charged. If the lawnmower is powered by a generator or from the mains, the frequency of the supply current, specified for the motor by the manufacturer, shall be stable during the test at ±1 Hz if the lawnmower is equipped with an induction motor, and the supply voltage at ±1.0% of the rated voltage if the lawnmower is equipped with a commutator motor. The voltage is measured at the plug of a non-detachable cable or cord, or at the inlet of the lawnmower if a detachable cable is provided. The waveform of the current supplied from the generator shall be similar to that obtained from the mains.
(c)Lawnmowers which hover or are hand held:
These mowers shall be restrained or supported to achieve their normal working position. The supports shall be made in such a way that they do not influence the measurement results.
6.3 Measuring site
6.3.1 General
The measuring site must comply with the specifications of points 6.3.2, 6.3.3 or 6.3.4.
In case of dispute, measurements shall be carried out on a measuring site according to point 6.3.2.
6.3.2 Measurements in the open air on artificial flooring
The test area must be flat and horizontal. The test area, including the vertical projection of the microphone positions, shall be of concrete or non-porous asphalt covered by an artificial flooring in accordance with Annex A of this Schedule, the centre of which coincides with the geometric centre of the hemisphere mentioned in point 6.4 and the corners of which are aimed at the vertical axes of the microphone positions 2, 4, 6 and 8.
If the wheels of the lawnmower could cause a compression of the artificial flooring of more than 1 cm the wheels shall be placed on supports so that they are level with the artificial flooring before compression. The supports shall be made in such a way that they do not influence the measurement results.
6.3.3 Measurements in the open air on grass
The test area must be flat and horizontal. The test area including the vertical projection of the microphone positions shall be covered in grass turf which is not wet.
6.3.4 Measurements indoors
The sound field inside the measurement room shall be similar to that of an acoustical free field, and the value of the constant C shall be determined in accordance with point 8.6.2.
The floor must be flat and horizontal. The test area, including the vertical projection of the microphone positions shall have the acoustical properties of concrete or non-porous asphalt and be covered by an artificial flooring in accordan ce with Annex A of this Schedule, the centre of which coincides with the geometric centre of the hemisphere mentioned in point 6.4 and the corners of which are aimed at the vertical axes of the microphone positions 2, 4, 6 and 8.
If the wheels of the lawnmower could cause a compression of the artificial flooring of more than 1 cm the wheels shall be placed on supports so that they are level with the artificial flooring before compression. The supports shall be made in such a way that they do not influence the measurement results.
6.4 Measuring surface, measuring distance, location and number of measuring points
6.4.1 Measuring surface
The measuring surface to be used for the test shall be a hemisphere. The radius of the hemisphere shall be determined by the width of cut of the lawnmower.
The radius shall be:
4m, where the width of cut of the lawnmower to be tested is no more than 1.2m
10m, where the width of cut of the lawnmower to be tested exceeds 1.2m.
6.4.2 Location and number of measuring points
6.4.2.1 General
For the purpose of measuring the noise emitted by lawnmowers when stationary and in motion, six measuring points shall be used, i.e. points 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12. When measurements are taken for stationary mowers, the centre of the hemisphere shall coincide with the projection of the geometric centre of the lawnmower to the ground, pointing from measuring point 1 towards point 5. For moving measurements, the displacement axis shall pass through the positions of measuring points 1 and 5 (See Figures 1 and 2).
6.4.2.2 Position of the measuring points on a hemisphere of radius r
In the case of a hemisphere there shall, in principle, be 12 measuring points with the following coordinates (see Figure 2) although, for the measurements on lawnmowers, not all are used:
=
(x/r) r
=
(y/r) r
=
(z/r) r
The values x/r, y/r, z/r and z are given in Table 1:
Table I
| x/r | y/r | z/r | z | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | — | 1.5 m |
| 2 | 0.7 | 0.7 | — | 1.5 m |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | — | 1.5 m |
| 4 | −0.7 | 0.7 | — | 1.5 m |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | — | 1.5 m |
| 6 | −0.7 | −0.7 | — | 1.5 m |
| 7 | 0 | −1 | — | 1.5 m |
| 8 | 0.7 | −0.7 | — | 1.5 m |
| 9 | 0.65 | 0.27 | 0.71 | — |
| 10 | −0.27 | 0.65 | 0.71 | — |
| 11 | −0.65 | −0.27 | 0.71 | — |
| 12 | 0.27 | −0.65 | 0.71 | — |
7 MEASUREMENTS
7.1 Measurement of the acoustic properties of the measuring site
The environmental conditions at the measuring site shall be checked before measurements are carried out. The following factors shall be checked:
(a)extraneous noise;
(b)wind interference;
(c)operating conditions such as vibrations, temperature, humidity, barometric pressure;
(d)acoustic properties of the test area;
(e)acoustic reflections from obstacles in the measuring site which might affect the results of the measurements.
7.1.1 Extraneous noise
The measurement of the level of parasitic noise shall not be taken into consideration.
Measurement of background noise
Background noise shall be recorded at the measuring points (see 6.4.2) with the sound source switched off (no sound emission) (see method given in 7.2).
7.1.2 Wind speed and direction
The wind speed and direction are established at a point above the test area. Account shall be taken of the provisions laid down in 8.6.4.
7.1.3 Measurement of temperature, humidity, barometric pressure and other disturbances
Only disturbances likely to have a bearing on the acoustic measurements need be measured (see 8.6.3).
7.1.4 Acoustic quality of the test area
The acoustic quality of the test area may be characterised by the environmental constant C as defined in 8.6.2.
The procedure to be followed for determining the value of C is defined in 8.6.2.
This constant C also allows an assessment to be made as to whether partially reflecting ground can be validly used as a test area.
7.1.5 Presence of obstacles
A visual check in a circular area of a radius equal to three times that of the measurement hemisphere, the centre of which coincides with that of the hemisphere, shall be adequate to ensure that the environment of the measuring site shall be free from reflecting objects which might influence measurement results.
7.2 Measurement of the sound pressure level LpA
To measure the sound pressure level LpA, use shall be made of an instrument as defined in 5.2. The sound pressure level LpA at a given measuring point is the root mean square value in time of the sound pressures. If a sound level meter is used, a number of readings shall be taken at this point and their mean value in time calculated in accordance with section 11.
When the mower is stationary the measuring time at each point shall be 15 seconds. If an integrator is used, the integrating times shall be equal to that measuring time.
When the mower is in motion, the measuring time shall be the time which it takes to cover the 2 metre distance AB (as shown in Figure 1) at constant speed.
The sound pressure levels LpA of a lawnmower shall be measured at least three times. If the sound power levels obtained from these measurements differ by more than 1 dB, further measurements shall be taken until two power levels are obtained which do not differ by more than 1 dB and the higher of which shall be the sound power level of the lawnmower.
Note:
Where a sound level meter is used for measurements with the mower in motion, in most cases LpA shall be equal to the level measured when the mower passes the centre of the hemisphere.
7.3 Determination of the nature of the noise generated by the sound source
For reasons of environmental protection the nature of the noise emitted should be identified so that an assessment may be made of the annoyance caused. Consequently it is appropriate to define a method of characterising noise of an impulsive character and noise with discrete tones.
7.3.1 Detection of noise of an impulsive character
Comparison of the readings on a precision sound level meter set at ‘slow’ response with those of a precision impulse sound level meter set at ‘impulsive’ response (IEC Publication 651, first edition, 1979) allows an assessment to be made of whether or not a noise is of an impulsive character. According to this measurement procedure, the difference between the root mean square values in time of the sound pressure levels measured with the sound level meter at slow and impulsive response respectively is taken as an indication of the impulsive character of a noise. The sound pressure level obtained with the ‘impulsive’ response is referred to as the ‘impulsive sound pressure level’.
This shall be determined at one of the measuring points laid down.
A noise is considered to be impulsive in character if the difference between the two above-mentioned levels is greater than or equal to 4 dB.
7.3.2 Detection of a noise with discrete tones
A method to detect a noise with discrete tones has not yet been agreed for lawnmowers.
8 USE OF RESULTS
8.1 Calculation of root mean square values
8.1.1 Root mean square value at a measuring point
The values obtained from the measurements referred to in 7.2 are root mean square values in time.
8.1.2 Root mean square value on the measuring surface
The level corresponding to the root mean square value in space of the sound pressure levels for all the measuring points shall be calculated on the basis of the values established in accordance with the method described in 8.1.1.
8.2 Calculation of average extraneous noise level
The average extraneous noise level over the measuring surface is obtained by applying the method described in 8.1.2 to the extraneous noise levels established at the different measuring points.
8.3 Calculation of the area S of the measuring surface
In the case of a hemisphere, the area S, expressed in m2, of the measuring surface is determined as follows:
S = 2πr2
where
r = the radius of the measuring hemisphere in m.
8.4 Calculation of the surface sound pressure level LpAm
The surface sound pressure level is the level calculated in accordance with the method described in 8.1.2 and then corrected as described in 8.6.1, 8.6.3 and 8.6.4.
8.5 Calculation of the sound power level LWA
The sound power level LWA of the sound source is calculated by means of the following equation:
where:
LWA = the sound power level of the source tested, expressed in dB (see 3.4);
LpAm = the surface sound pressure level, expressed in dB, as defined in 3.3;
S = the area of the measuring surface in m2, calculated in accordance with the method described in 8.3;
S0 = reference area of 1 m2;
K2 = correction term for the test area, expressed in dB. See last paragraph of 8.6.2.
Note(see 6.4.1)
8.6 Corrections to be made to measurements
8.6.1 Extraneous noise
The average sound pressure level over the measuring surface, calculated in accordance with the method described in 8.1, shall be corrected, if necessary, to take account of the extraneous noise determined in accordance with the method described in 8.2. The correction K1, in dB, which shall be subtracted from the average sound pressure level over the measuring surface is given in Table II.
Table II
| Difference (in dB) between the sound pressure level calculated when the sound source is operating and the sound pressure level due to extraneous noise alone | Correction K1 in dB |
|---|---|
| less than 6 | no valid measurement |
| 6 | 1.0 |
| 7 | 1.0 |
| 8 | 1.0 |
| 9 | 0.5 |
| 10 | 0.5 |
| more than 10 | no correction |
8.6.2 Acoustic properties of test area
The constant C, which indicates the acoustic properties of the test area, is determined by the following equation:
C = LWAr - LWAs
where:
LWAr = nominal sound power level of the reference source, expressed in dB;
LWAs = sound power level of the reference source, calculated on the basis of measurements made on the test area, account being taken of 7.1((a), (b) and (c)).
If the ground surface of the test area is rigid and made of concrete or non-porous asphalt and if there are no reflecting objects on the measuring site, there is no need to determine any environmental constant C.
In the case of a partially reflecting ground surface, the value of C must be between limit values laid down below. The effective value of C, which indicates the acoustic properties of the measuring site used, is determined by the above equation.
This value is used as K2 for fixing the sound power level of the source.
Further corrections relating to the operation of the sound source (e.g. the altitude of the measuring site) should also be made.
For lawnmowers the constant C determined in accordance with this section shall be between 0.5 and 2 dB. Then K2 is put equal to zero in the equation in Section 8.5.
8.6.3 Disturbances: temperature, humidity, altitude of site, etc.
Measuring apparatus
The manufacturer’s instructions should be followed in order to take account of any effects of all the disturbances mentioned by him, such as temperature, barometric pressure, humidity.
Sound source:
See 8.6.1, 8.6.2 and 8.6.4.
8.6.4 Wind interference
The maximum permissible wind speed is 8m/sec.
Above the wind speed indicated by the manufacturer, microphones shall be equipped with a wind-screen. Any corrections to be made to the calculations referred to in 8.4 are indicated by the wind-screen manufacturer.
9 DATA TO BE RECORDED
In principle, the following information shall be compiled and recorded in a report concerning all measurements made in accordance with the specification for this method of measurement.
9.1 Sound source under test
(a)description of the sound source under test (including dimensions);
(b)operating conditions of the sound source during the tests;
(c)conditions for installation on the test area;
(d)location of sound source on measuring site;
(e)if the machine tested has multiple noise sources, description of sources in operation during measurement;
(f)width of cut;
(g)speed of rotation of the cutting device.
9.2 Acoustic environment
(a)description of the measuring site, including physical characteristics of the test area; diagram showing the location of the sound sources and any reflecting objects on the measuring site;
(b)meteorological conditions: weather (e.g. sunshine, cloud, rain, fog), air tempera ture, barometric pressure, wind speed and direction, humidity;
(c)correction constant representing the acoustic properties of the test area.
9.3 Instrumentation
(a)equipment used for the measurements, including the name of the equipment, type, serial number and name of manufacturer;
(b)method used to calibrate the measuring equipment in accordance with 5.5.1.
Name of laboratory which carried out the calibration required in 5.5.2 and date of last calibration.
9.4 Acoustic data
(a)shape and dimensions of measuring surface, location of microphones. Numbers of measuring points and wind direction shall be indicated in the diagram required under 9.2(a);
(b)value of
(c)place, date and time of measurements;
(d)sound pressure levels recorded at measuring points (see 8.1.1);
(e)average sound pressure level over measuring surface (see 8.1.2);
(f)any dB corrections (see 8.6.1, 8.6.3 and 8.6.4);
(g)surface sound pressure level LpAm (see 8.4);
(h)environmental constant C (see 8.6.2);
(i)sound power level (see 8.5);
(j)directivity index and number of the measuring point at which LpAmax was recorded (see 3.6);
(k)nature of noise (see 7.3);
(l)where applicable, sound pressure levels at operator’s position (see Part 2).
10. DATA TO BE INCLUDED IN THE REPORT LAID DOWN IN SECTION 9
Only those data recorded in accordance with section 9 and required for the purposes of the measurements shall be reported. The report shall state clearly that the sound power levels were obtained in full compliance with this measuring method. It shall specify that these sound power levels are given in A-weighted dB, reference 1 pW.
11. METHOD OF CALCULATING THE AVERAGE LEVEL CORRESPONDING TO THE ROOT MEAN SQUARE VALUE OF THE VARIOUS SOUND PRESSURE LEVELS
The root mean square value of the various sound pressure levels resulting either from a series of measurements made at a single point (root mean square in time) or from a series of measurements made at different points on the measuring surface (root mean square in space) can be determined by the following formula:
where:
LpAi equals the sound pressure level of the i-th measurement;
LpAo is an auxiliary sound pressure level to simplify the calculation (for example, the smallest of the LpAi values);
gi is the auxiliary variable for the i-th measurement:
gm is the mean value of the gi variables:
The quantity ΔL is defined by:
ΔL = LpAi - LpAo
Table III gives the values of g for different values of ΔL.
Table III
Value of g as a function of ΔL
The table may be extended in either direction.
| ΔL dB | g |
|---|---|
| −20.0 | 0.010 |
| −19.5 | 0.011 |
| −19.0 | 0.013 |
| −18.5 | 0.014 |
| −18.0 | 0.016 |
| −17.5 | 0.018 |
| −17.0 | 0.020 |
| −16.5 | 0.022 |
| −16.0 | 0.025 |
| −15.5 | 0.028 |
| −15.0 | 0.032 |
| −14.5 | 0.035 |
| −14.0 | 0.040 |
| −13.5 | 0.045 |
| −13.0 | 0.050 |
| −12.5 | 0.056 |
| −12.0 | 0.063 |
| −11.5 | 0.071 |
| −11.0 | 0.079 |
| −10.5 | 0.089 |
| −10.0 | 0.100 |
| −9.5 | 0.112 |
| −9.0 | 0.126 |
| −8.5 | 0.141 |
| −8.0 | 0.158 |
| −7.5 | 0.178 |
| −7.0 | 0.2 |
| −6.5 | 0.224 |
| −6.0 | 0.251 |
| −5.5 | 0.282 |
| −5.0 | 0.316 |
| −4.5 | 0.355 |
| −4.0 | 0.398 |
| −3.5 | 0.447 |
| −3.0 | 0.501 |
| −2.5 | 0.562 |
| −2.0 | 0.631 |
| −1.5 | 0.708 |
| −1.0 | 0.794 |
| −0.5 | 0.891 |
| −0.0 | 1 |
| 0.0 | 1 |
| 0.5 | 1.12 |
| 1.0 | 1.26 |
| 1.5 | 1.41 |
| 2.0 | 1.58 |
| 2.5 | 1.78 |
| 3.0 | 2.00 |
| 3.5 | 2.24 |
| 4.0 | 2.51 |
| 4.5 | 2.82 |
| 5.0 | 3.16 |
| 5.5 | 3.55 |
| 6.0 | 3.98 |
| 6.5 | 4.47 |
| 7.0 | 5.01 |
| 7.5 | 5.62 |
| 8.0 | 6.31 |
| 8.5 | 7.08 |
| 9.0 | 7.94 |
| 9.5 | 8.91 |
| 10.0 | 10 |
| 10.0 | 10.0 |
| 10.5 | 11.2 |
| 11.0 | 12.6 |
| 11.5 | 14.1 |
| 12.0 | 15.8 |
| 12.5 | 17.8 |
| 13.0 | 20.0 |
| 13.5 | 22.4 |
| 14.0 | 25.1 |
| 14.5 | 28.2 |
| 15.0 | 31.6 |
| 15.5 | 35.5 |
| 16.0 | 39.8 |
| 16.5 | 44.7 |
| 17.0 | 50.1 |
| 17.5 | 56.2 |
| 18.0 | 63.1 |
| 18.5 | 70.8 |
| 19.0 | 79.4 |
| 19.5 | 89.1 |
| 20.0 | 100 |
| 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 20.5 | 112.0 |
| 21.0 | 125.9 |
| 21.5 | 141.3 |
| 22.0 | 158.5 |
| 22.5 | 177.8 |
| 23.0 | 199.5 |
| 23.5 | 223.9 |
| 24.0 | 251.2 |
| 24.5 | 281.8 |
| 25.0 | 316.2 |
| 25.5 | 354.8 |
| 26.0 | 398.1 |
| 26.5 | 446.7 |
| 27.0 | 501.2 |
| 27.5 | 562.3 |
| 28.0 | 631.0 |
| 28.5 | 707.9 |
| 29.0 | 794.3 |
| 29.5 | 891.3 |
| 30.0 | 1000.0 |
ANNEX AARTIFICIAL FLOORING
1. DIMENSIONS AND MATERIALS
1.1 Dimensions
The artificial flooring shall have a size of 360 × 360 cm.
1.2 Materials
The artificial flooring is composed of a cover of absorptive material of which the absorption coefficients α, measured in accordance with ISO 354 first edition, 1985-02-01, are within the limits given in the following table:
| Frequency/Hz | 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α minimum | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 0.70 | 0.80 |
| α maximum | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 1.00 |
Note:
An example of a material and construction which can be expected to fulfil these requirements is given in Annex B.
ANNEX BARTIFICIAL FLOORING
EXAMPLE OF MATERIAL AND CONSTRUCTION
Mineral fibre of thickness 20 mm, airflow resistance 11 kNs/m4 and density 25 kg/m3.
For convenience the artificial flooring can be built of abutting panels (see Figure 1 of this Annex).
The cut edges of the chipboard are to be made non-absorbtive and to be protected against moisture. This can be done by applying a coat of plastic paint.
The outsides are bordered by aluminium U-sections of size 3 × 20 mm. In general, these panels come in two types:
(A) panels not to be loaded;
(B) panels to carry the lawnmower and the test personnel.
On the panels mentioned under (B) aluminium T-sections size 3 × 20 mm are mounted as spacers (see Figure 1 of this Annex).
The prepared boards are then covered with the absorbtive material cut to size.
The panels mentioned under (A) are covered with a wire mesh with a wire thickness of 0.8 mm and a mesh width of 10 mm (aviary wire).
The panels under (B) are covered with wire grating of corrugated steel wire with a diameter of 3.1 mm and a mesh width of 30 mm.
These wire covers are fastened to the aluminium U-sections.
PART 2METHOD OF DETERMINING AIRBORNE NOISE EMITTED BY LAWNMOWERS (ALSO REFERRED TO AS MOWERS IN THIS SCHEDULE) WITH A CUTTING WIDTH OF MORE THAN 120 CM AT THE OPERATOR POSITION
1. AIM
The aim of this method is to determine the noise emitted at the operator’s position(s) by all categories of lawnmowers with a cutting width exceeding 120 cm and having a seat attached in a suitable way to a structural component of the lawnmower.
It is not applicable for measurements to determine directly the level of an operator’s exposure at his post.
The values obtained by this method represent the data that make it possible to determine the equivalent continuous sound pressure level emitted by lawnmowers to the operator’s position(s). Save as otherwise indicated, these values include all tolerances.
2 SCOPE
2.1 Type of noise
This method is applicable to all types of noise emitted by lawnmowers at the operator’s position(s).
2.2 Type of lawnmowers
This method is applicable to all lawnmowers with one or more operator’s positions.
3 DEFINITIONS
3.1 Sound pressure level LpA
See Section 3.1 in Part 1.
3.2 Equivalent continuous sound pressure level LAeq:(t1, t2)
The equivalent continuous sound pressure level LAeq:(t1, t2) is obtained by applying the A-weighting as defined in IEC publication 651, first edition, 1979 to the equivalent continuous sound pressure level Leq:(t1, t2) defined below. This weighting is obtained inter alia by using the A-weighting filter in the measuring system.
The equivalent continuous sound pressure level for a limited period between intervals t1 and t2, Leq:(t1, t2), expressed in decibels, of a noise at a given point is defined by:
where:
p(t) is the instantaneous value of the sound pressure at this point, expressed in Pa;
p0 is the reference sound pressure, equivalent to 20 μPa;
Lp(t) is the sound pressure level at a given time at that point, expressed in dB;
t1 and t2 are the points indicating respectively the beginning and end of the reference period determining the Leq
t1 − t2 is the measurement interval.
4 CRITERION TO BE USED TO EXPRESS RESULTS
The acoustic criterion for the operator’s position(s) of lawnmowers is expressed by the equivalent continuous A-weighted sound pressure level LAeq(t1, t2).
5 MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
The specifications laid down in Section 5 of Annex I are to be used, with the extra requirement added to point 5.3 that the external diameter of the microphone must not exceed 13 mm.
6 PRESENCE OF THE OPERATOR
An operator shall occupy the operator’s position.
6.1 Clothing specifications
When he is present during the measurements, the operator must wear normal working clothes and all the equipment (e.g. safety helmet) normally prescribed for the post in question.
6.2 Height specifications of the operator(s)
6.2.1 Seated operator
The height of the operator(s) when seated (h) must be 0.93 ± 0.05 m, as shown in Figure 1.
7 MICROPHONE LOCATIONS
7.1 General
The microphone shall be located as specified in Section 7.2.
7.2 Microphone locations with operator present
The microphone is placed at 200 ± 20 mm from the median plane of the head and in line with the eyes and to the side of the head where the LAeq:(t1, t2) is highest.
Note:
To facilitate the placing of the microphone, it can conveniently be mounted on a frame or the helmet or a shoulder harness worn by the operator. For measurements when the operator is seated, the seat must be adjusted to allow the operator to reach the machine controls comfortably.
8 ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS
8.1 Measuring site
The machine must, as far as possible, be installed in conditions identical to those specified in Sections 6.3 of Part 1.
8.2 Background noise
Background noise at each measuring point must be at least 10 dB(A) lower than the noise emitted by the machine.
9 INSTALLATION AND OPERATING CONDITIONS
9.1 General
The conditions required for installing and operating the lawnmower are laid down in point 6.2 of Part 1.
10 MEASUREMENTS AND CALCULATION OF RESULTS
10.1 Measurement interval T(= t2 − t1)
The measurement interval T must in principle be at least 15 seconds; in the case of a work cycle, it must be equal to the duration of a whole number of work cycles.
10.2 Determination of the equivalent continuous A-weighted sound pressure level (LAeq:(t1, t2)
This level is obtained either directly by integrating p (t) or by sampling of the pressure level LpA.
10.2.1 By integrating p2(t)
LAeq:(t1, t2) may be directly obtained by integrating the square of the A-weighted sound pressure during a period equal to t2 − t1 in accordance with the formula given in Section 3.2.
Digital or analogue integration may be used, e.g., with an integrating sound level meter.
10.2.2 Using the A-weighted sound pressure levels LpA
If a sound level meter is used, T is five seconds.
The number of measurements is 5.
10.3 Measurement of disturbances
The requirements are laid down in Section 7.1.3 of Part I.
10.4 Corrections to be made to measurements
10.4.1. Disturbances (temperature, humidity, altitude, etc)
The requirements are laid down in Section 8.6.3 of Part I.
10.4.2 Background noise
No correction is to be made for background noise.
11 DATA TO BE RECORDED
The report must contain the necessary data relating to the measurement of noise at operator’s position in accordance with Section 10 of Part 1.
Additional information must be given on the layout of the operator’s position during the measurements.
The report must also confirm that the equivalent continuous A-weighted sound pressure levels LAeq:(t1, t2) were obtained strictly according to this method of measurement.
Note:
If the measurements of sound pressure level at the operator’s position are carried out when the sound power level of the machine is determined, the data must be recorded in a single report.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Instrument
PrintThis Schedule only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As Enacted or Made): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was enacted or made. No changes have been applied to the text.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as enacted version that was used for the print copy
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources