Statutory Instruments
2001 No. 25
ROAD TRAFFIC
The Motor Vehicles (Approval) Regulations 2001
Made
9th January 2001
Laid before Parliament
10th January 2001
Coming into force
1st February 2001
The Secretary of State for the Environment, Transport and the Regions, in exercise of the powers conferred by sections 54, 61, 63 and 66 of the Road Traffic Act 1988(1) and of all other powers enabling him in that behalf, and after consultation with representative organisations in accordance with section 195(2) of that Act, hereby makes the following Regulations:—
PART IGENERAL
Citation and commencement
1. These Regulations may be cited as the Motor Vehicles (Approval) Regulations 2001 and shall come into force on 1st February 2001.
Revocation
2. The instruments specified in Schedule 1 are hereby revoked.
Interpretation
3.—(1) In these Regulations, unless the context otherwise requires—
“the 1970 Directive” means Council Directive 70/156/EEC of 6th February 1970 on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to the type-approval of motor vehicles and their trailers(2) as last amended by Directive 98/14/EC of 25th March 1998(3);
“the 1982 Regulations” means the Motor Vehicles (Type Approval for Goods Vehicles) (Great Britain) Regulations 1982(4);
“the 1984 Regulations” means the Motor Vehicles (Type Approval) (Great Britain) Regulations 1984(5);
“the 1988 Act” means the Road Traffic Act 1988;
“ambulance”, “armoured vehicle”, “hearse” and “motor caravan” have the meanings given by paragraph 1 of Schedule 2;
“approval requirements”, in relation to a vehicle, means the requirements prescribed by section 54 of the 1988 Act as they apply to that vehicle and which are set out in regulation 5(1);
“axle weight”, “gross weight”, “kerbside weight”, “maximum gross weight” and “maximum permitted axle weight” have the meanings given in regulation 3(2) of the Construction and Use Regulations;
“the Construction and Use Regulations” means the Road Vehicles (Construction and Use) Regulations 1986(6);
“design gross weight” means the weight which the vehicle is designed or adapted not to exceed when in normal use and travelling on a road laden;
“EEA State” means a State which is a contracting party to the Agreement on the European Economic Area signed at Oporto on 2nd May 1992 as adjusted by the Protocol signed at Brussels on 17th March 1993(7);
“family of types” has the same meaning as in Annex XII of the 1970 Directive;
“goods vehicle” means a vehicle of a kind specified in regulation 4(1)(b);
“kg” means kilograms;
“kph” means kilometres per hour;
“the Lighting Regulations” means the Road Vehicles Lighting Regulations 1989(8);
“mm” means millimetres;
“mph” means miles per hour;
“registered” means registered under the Vehicle Excise and Regulation Act 1994(9);
“relevant vehicle” has the meaning given in regulation 4(3);
“Schedule 2 vehicle” has the meaning given in Schedule 2;
“subject matter” means a subject matter in relation to which approval requirements are specified in Schedule 3 or 4 and “applicable subject matter” in relation to a vehicle means a subject matter as respects which approval requirements are applicable to the vehicle in accordance with these Regulations;
“wheel” has the meaning given in regulation 3(2) of the Construction and Use Regulations.
(2) References to vehicles of categories M1, M2, M3, N1, N2 and N3 are to vehicles of those categories as defined in Annex II.A of the 1970 Directive.
(3) A reference in any provision of these Regulations to a prescribed fee is a reference to the fee (if any) for the time being prescribed for the purposes of that provision in regulations made under section 61 of the 1988 Act.
(4) Paragraphs (7) and (8) of regulation 3 of the Construction and Use Regulations (determination of the numbers of wheels and axles of a vehicle) shall apply for the purposes of these Regulations other than item 16 of Schedule 3 as they apply for the purposes of the Construction and Use Regulations other than regulations 26 and 27.
(5) For the purposes of these Regulations, a vehicle is to be regarded as being manufactured on or after a particular date if it is first assembled on or after that date, even if it includes one or more parts which were manufactured before that date.
(6) Schedule 6 of these Regulations—
(a)defines expressions relating to Community instruments and ECE Regulations (including references to complying with provisions of such instruments); and
(b)sets out details of Community instruments and ECE Regulations referred to in these Regulations.
PART IIAPPROVAL REQUIREMENTS FOR RELEVANT VEHICLES
Application of Regulations
4.—(1) These Regulations apply to every motor vehicle—
(a)to which the 1984 Regulations apply; or
(b)to which the 1982 Regulations apply and which either has a design gross weight not exceeding 3,500 kg or complies with the requirements specified in paragraph (2).
(2) The requirements referred to in paragraph (1)(b) are that the vehicle in question—
(a)has a design gross weight exceeding 3,500 kg but not exceeding 5,500 kg;
(b)has a kerbside weight not exceeding 3,425 kg; and
(c)belongs to the same family of types as at least one vehicle to which these Regulations apply by virtue of paragraph (1) and which has been granted a Minister’s approval certificate on the basis that it complies with the approval requirements by virtue of these Regulations or the Motor Vehicles (Approval) Regulations 1996(10).
(3) In these Regulations, “relevant vehicle” means a vehicle to which these Regulations apply.
Approval requirements for relevant vehicles
5.—(1) Subject to the following provisions of this regulation, the following are prescribed under section 54 of the 1988 Act as requirements as to the design, construction, equipment and marking of relevant vehicles—
(a)in the case of any relevant vehicle, compliance with the requirements set out in column 3 of the Table in Schedule 3; and
(b)in the case of any relevant vehicle which is not a Schedule 2 vehicle, and in relation to each item in the Table in Schedule 4 for which is specified in column 3(a) of that Table a date which is, or falls before, the date of manufacture of the vehicle, compliance with the requirements of the Community instruments set out in column 3(b) of that Table in relation to that item, or with any equivalent requirement of the ECE Regulations set out in column 3(c) of that Table.
(2) Subject to paragraph (3), the requirements of paragraph (1)(b) shall not apply to a relevant vehicle until 1st August 2001.
(3) Where, in the case of any relevant vehicle which is of category M1 and to which the requirements of paragraph (1)(b) would not otherwise apply, a person making an application in accordance with regulation 6 requests the Secretary of State in writing at the time of making the application that the provisions of paragraph (1)(b) be applied for the purposes of the application, those provisions shall so apply.
(4) The items in Schedule 3 numbered 1, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 14, 15, 16 and 19 and the items in Schedule 4 numbered 3, 8, 10, 11, 26, 27 and 28 shall not apply to goods vehicles.
(5) The requirements set out or referred to in column 3 of the Tables in Schedules 3 and 4 have effect subject to the exceptions and modifications set out in column 5 of those Tables.
(6) An entry in column 4 of an item in the Table in Schedules 3 and 4 shall have effect for the purposes of interpreting or otherwise supplementing the entries in that item and, for convenience, expressions that are defined in that column are printed in bold type.
(7) Where a provision of any Community instrument or ECE Regulation is applied by Schedule 4, that provision as so applied shall (except in so far as the contrary intention appears) have effect in relation to—
(a)a vehicle to which the 1984 Regulations apply as it has effect in relation to a vehicle of category M1; and
(b)a vehicle to which the 1982 Regulations apply as it has effect in relation to a vehicle of category N1.
(8) A relevant vehicle shall be regarded as complying with all the requirements prescribed under section 54 of the 1988 Act if at least one of the following three conditions are satisfied in relation to each applicable subject matter mentioned in Schedule 3 or 4—
(a)that the vehicle complies with the requirements set out in paragraph (1);
(b)that requirements applicable to the vehicle are prescribed by regulation 4 of the 1984 Regulations or by regulation 4 of the 1982 Regulations in relation to the subject matter and the vehicle complies with those requirements;
(c)that there is produced to the Secretary of State evidence that satisfies him that the vehicle has been found by a competent authority in another EEA State to comply with requirements applicable to the vehicle equivalent to those prescribed in relation to the subject matter.
(9) For the purposes of paragraph (8)(b), the requirements prescribed by regulation 4 of the 1984 Regulations in relation to the subject matter mentioned in item 6 of column 2 of the Table in Schedule 3 to these Regulations (lamps, reflectors and devices) shall be regarded as the requirements prescribed in relation to—
(a)installation of lighting and signalling equipment;
(b)direction indicators;
(c)headlamps and filament lamps;
(d)side, rear and stop lamps;
(e)rear reflectors; and
(f)rear fog lamps.
(10) For the purposes of paragraph (8), regulation 4(1A) of the 1984 Regulations shall have effect as if—
(a)for sub-paragraph (a), there were substituted—
“(a)an entry in column (6) of Part I of Schedule 1 shall not apply to the vehicle if the vehicle was manufactured before the date specified or having effect as if specified in that entry;”; and
(b)the words after sub-paragraph (b) were omitted.
(11) For the purposes of paragraph (8), regulation 4(2A) of the 1982 Regulations shall have effect as if—
(a)for sub-paragraph (a), there were substituted—
“(a)an entry in column (6) of Part I of Schedule 1 shall not apply to the vehicle if the vehicle was manufactured before the date specified or having effect as if specified in that entry;”; and
(b)the words after sub-paragraph (b) were omitted.
(12) If a relevant vehicle complies with all the requirements prescribed by—
(a)regulation 4 of the 1984 Regulations (disregarding paragraph (9)); or
(b)regulation 4 of the 1982 Regulations (disregarding paragraph (10)),
that are applicable to it, the requirements prescribed by this regulation shall not apply to it.
PART IIIMISCELLANEOUS
Application for Minister’s approval certificate
6.—(1) An application for the issue for a Minister’s approval certificate on the basis that the vehicle complies with the approval requirements by virtue of these Regulations shall be made to the Secretary of State.
(2) The application shall be in a form which—
(a)has been approved by the Secretary of State; and
(b)has been duly completed so as to furnish all the information required by that form.
(3) The application shall be accompanied by—
(a)the documents mentioned in the form as being required in connection with the application; and
(b)the prescribed fee.
(4) As soon as reasonably practicable after he receives the application, the Secretary of State shall send to the applicant a notice stating the time when and the place where an examination for the purposes of the application is to be carried out.
(5) The Secretary of State may by notice to the applicant alter the time when or the place where the examination is to be carried out, but he shall not alter the time to an earlier time without the consent of the applicant.
(6) Where an application (“the original application”) made in accordance with the paragraphs (1) to (3) is refused other than by virtue of regulation 10 or on the grounds that the vehicle is not a relevant vehicle, a further application by the same applicant in respect of the vehicle shall be regarded as having been made in accordance with and pursuant to those paragraphs if—
(a)it is made (orally or in writing) to the Secretary of State during the period of six months beginning with the date on which the original application was refused; and
(b)at the time that he makes the further application, the applicant requests an examination to be carried out for the purpose of the further application—
(i)during that period of six months; and
(ii)except in the case of a Schedule 2 vehicle other than a left hand drive vehicle or a personally imported vehicle, at the place where the examination took place for the purposes of the original application.
(7) Paragraphs (4) and (5) shall not apply to an application made in accordance with paragraph (6); and in the case of such an application—
(a)the Secretary of State shall inform the applicant in such manner as he thinks fit of the time when and the place where the examination is to be carried out;
(b)the Secretary of State may alter the time when or the place where the examination is to be carried out, but he shall not alter the time to an earlier time without the consent of the applicant;
(c)if the Secretary of State so alters the time or place, he shall inform the applicant in such manner as he thinks fit of the time when and the place where the examination is to be carried out; and
(d)the applicant shall pay the prescribed fee to the Secretary of State before the examination is carried out.
(8) Paragraphs (4) to (7) shall not apply to an application for the issue of a Minister’s approval certificate under section 58(4) of the 1988 Act.
Assignment of vehicle identification numbers
7.—(1) Where it appears to the Secretary of State when an application is made for a Minister’s approval certificate in accordance with paragraphs (1) to (3) of regulation 6 that the vehicle to which the application relates does not have a vehicle identification number which—
(a)complies with paragraph 3.1.1 of the Annex to Directive 76/114/EEC(11) or that Directive as last amended by Directive 78/507/EEC(12);
(b)has been previously assigned to the vehicle under this regulation; or
(c)does not fall within sub-paragraph (a) or (b), but is adequate for the purpose of enabling the vehicle to be identified,
he shall assign a vehicle identification number to the vehicle.
(2) Where an application is made under regulation 6 for the issue of a Minister’s approval certificate under section 58(4) of the 1988 Act, paragraph (1) shall have effect as if the words “in accordance with paragraphs (1) to (3) of regulation 6” were omitted.
Criteria for determining design weights
8. For the purposes of section 54(2) of the 1988 Act, where an application is made pursuant to regulation 6, the criteria for determining, as design weights, the axle weights and gross weights which in the opinion of the Secretary of State should not be exceeded in the case of a vehicle to which these Regulations apply are as follows—
(a)the design of the vehicle, its construction and equipment and the stresses to which it is likely to be subject when used on a road;
(b)any information which is available about the weight which a vehicle of that type was designed by the manufacturer to carry when used on a road; and
(c)any information obtained from an examination of a vehicle of that type or a similar type with a view to ascertaining whether at the time of the examination, it complied with any requirement prescribed under section 54 of the 1988 Act and applicable to it.
Appeals
9.—(1) An appeal under section 60 of the 1988 Act by a person aggrieved by a determination made by the Secretary of State pursuant to an application under regulation 6 shall be made by including with the documents submitted a form which—
(a)has been provided by the Secretary of State; and
(b)has been completed so as to include a description of the grounds upon which the appeal is made and such other information as may be reasonably required by that form.
(2) The appeal shall be accompanied by the prescribed fee.
(3) The prescribed time within which an appeal against such a determination may be made is 14 days beginning with the date of the determination.
(4) As soon as reasonably practicable after the date of the receipt of the appeal the Secretary of State shall send to the appellant a notice stating the time when and the place where the re-examination for the purpose of determining the issues raised on the appeal is to be carried out.
(5) The Secretary of State may by notice to the applicant alter the time when or the place where the re-examination is to be carried out, but he shall not alter the time to an earlier time without the consent of the applicant.
Refusal of application or appeal without an examination or a complete examination
10.—(1) In this regulation—
“appeal” means an appeal under section 60 of the 1988 Act in respect of the determination of an application;
“application” means an application under regulation 6 for the issue of a Minister’s approval certificate under section 58(1) of the 1988 Act;
“examination” means an examination for the purposes of an application or appeal; and
“examiner”, in relation to an examination, means the person appointed by the Secretary of State to conduct the examination.
(2) The Secretary of State may refuse an application or appeal even though an examination has not been carried out if—
(a)the vehicle is not submitted for examination at the time and place fixed under these Regulations for the examination;
(b)the fee in respect of the examination is not paid at or before the time fixed under these Regulations for the examination;
(c)the examiner is not able, with the facilities and apparatus available to him at the place at which the examination would otherwise be carried out, to complete the examination without the vehicle being driven or the engine run and the vehicle is not when submitted for examination, either for want of fuel or oil or for any other reason, fit to be driven or for the engine to be run to such extent as may be necessary for the purposes of carrying out the examination;
(d)when the vehicle is submitted for the examination, the vehicle or any item which forms part of the vehicle or its equipment is so dirty or dangerous as to make it unreasonable for the examination to be carried out;
(e)any things which are on the vehicle when it is submitted for the examination, and are not part of its equipment or accessories, are required by the examiner to be removed from the vehicle or to be secured in such a manner as he may think necessary and those things are not removed or secured accordingly;
(f)when the vehicle is submitted for the examination, a proper examination cannot be carried out as a consequence of any door, tailgate, boot lid, engine cover, fuel cap or other device designed to be capable of being readily opened, being locked or otherwise fixed so that it cannot readily be opened;
(g)when the vehicle is submitted for the examination, its condition is such that, in the opinion of the examiner, a proper examination of the vehicle would involve a danger of—
(i)injury to any person, or
(ii)damage to the vehicle or any other property;
(h)when the vehicle is submitted for the examination, there is not permanently fixed to the chassis or main structure of the vehicle in a conspicuous and easily accessible position so as to readily legible, a vehicle identification number which—
(i)complies with paragraph 3.1.1 of Annex to Directive 76/114/EEC or that Directive as last amended by Directive 78/507/EEC;
(ii)has been assigned to the vehicle under regulation 7(1); or
(iii)does not fall within sub-paragraph (i) or (ii), but appears to the Secretary of State to be adequate for the purpose of enabling the vehicle to be identified; or
(i)the person who is the driver of the vehicle at the time it is submitted for the examination is requested to remain in it or its vicinity throughout the examination, to drive it, to operate its controls or to remove or refit its panels and he declines to do so.
(3) Nothing in this regulation shall affect any power of the Secretary of State to refuse an application or to reject an appeal otherwise than under this regulation.
Form of certificate
11.—(1) Subject to the following paragraphs, where a Minister’s approval certificate is issued under section 58(1) of the 1988 Act on the basis that the vehicle complies with the approval requirements by virtue of these Regulations, the certificate shall be in the form set out in Schedule 5 to these Regulations or in a form to the like effect.
(2) Where the certificate is issued on the basis that it relates to a vehicle falling within a class specified in column (2) of an item in the Table below there shall be inserted in the box under the words “Class Code” the letter specified in column (3) of that item.
TABLE
| (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|
| Item | Class of vehicle | Letter |
| 1. | Left hand drive vehicle | N |
| 2. | Personally imported vehicle | P |
| 3. | Amateur built vehicle | A |
| 4. | Vehicle manufactured in very low volume | L |
| 5. | Vehicle manufactured using parts from a registered vehicle | C |
| 6. | Disabled persons vehicle | D |
| 7. | Rebuilt vehicle | S |
| 8. | Motor caravan, ambulance or hearse | M |
| 9. | Armoured vehicle | T |
| 10. | Vehicle not falling within any of the preceding classes specified in this Table | R |
| 11. | Vehicle which meets the condition set out in regulation 5(8)(c) | E |
(3) Any letter or letters inserted pursuant to paragraph (2) may be followed by a zero and then by any letters or numbers that the Secretary of State thinks fit to insert.
(4) Expressions used in this regulation which are the subject of definitions in Schedule 2 shall have the meanings given by those definitions.
(5) This regulation shall apply to a Minister’s approval certificate issued under section 58(4) of the 1988 Act as it applies to such a certificate issued under section 58(1) of that Act as if for the words “section 58(1)” in the form set out in Schedule 5 to these Regulations there were substituted the words “section 58(4)”.
Replacement certificates
12.—(1) If a Minister’s approval certificate has been lost or defaced, an application for issue of a replacement for the original certificate may be made, either orally or in writing, to the Secretary of State at the place from which the original certificate was issued.
(2) The application shall—
(a)specify the identification number of the vehicle in respect of which the original certificate was issued; and
(b)be accompanied by the prescribed fee.
(3) As soon as reasonably practicable after he receives the application and fee, the Secretary of State shall issue to the applicant a replacement for the certificate to which the application relates and any such replacement shall have the same effect as the certificate which it replaces and shall be marked “replacement”.
Notices
13. Except as otherwise provided by these Regulations, every notice under them shall be in writing and may be given by post.
Obligatory certificates
14.—(1) Subject to paragraph (2) below, this regulation applies to all relevant vehicles.
(2) This regulation does not apply—
(a)to any ambulance or a motor caravan;
(b)to any registered vehicle;
(c)to a vehicle more than 10 years after the time when it was manufactured; or
(d)to a vehicle that meets the requirements specified in paragraph (3).
(3) The requirements referred to in paragraph (2)(d) are that—
(a)the person by whom the vehicle is kept (“the keeper”) is a member of a visiting force or of a member of the civilian component of a visiting force;
(b)the vehicle has been imported into the United Kingdom for the personal use of the keeper or of his dependants;
(c)there is not in force with respect to the vehicle—
(i)a Minister’s approval certificate issued in pursuance of these Regulations;
(ii)a certificate of conformity;
(iii)a Minister’s approval certificate in a form prescribed by regulation 14 of the 1982 Regulations or regulation 9 of the 1984 Regulations; or
(iv)an EC certificate of conformity; and
(d)not more than one other vehicle which meets the requirements of sub-paragraphs (a), (b) and (c) is kept in the United Kingdom by the keeper.
(4) In paragraph (3) the expressions “member of a visiting force” and “member of a civilian component of a visiting force” shall bear the same meanings as in Part I of the Visiting Forces Act 1952(13).
(5) The day appointed for the purposes of section 63(1) of the 1988 Act in relation to every vehicle—
(a)to which this regulation applies; but
(b)which is not of a class for which a day had previously been appointed for those purposes,
is 1st February 2001.
(6) Without prejudice to any other Regulations having effect by virtue of section 63(1) of the 1988 Act, all vehicles to which this regulation applies are vehicles of a prescribed class for the purposes of that section.
(7) The type approval requirements prescribed for the purposes of section 63(1) of the 1988 Act, in relation to every vehicle to which this regulation applies, are the approval requirements.
(8) Section 63(1) of the 1988 Act shall not apply to the use of a relevant vehicle—
(a)for the purpose of submitting it (by previous arrangement for a specified time on a specified date) before it is registered for an examination pursuant to an application under these Regulations;
(b)for the purpose of bringing it away, before it is registered, from such an examination;
(c)by an authorised person for the purpose of—
(i)taking it to, or bringing it away from, a place where a part of such an examination is to be, or has been, carried out, or
(ii)carrying out a part of such an examination, or
(iii)warming up its engine in preparation for such an examination, before it is registered;
(d)where an application under regulation 6 is refused following such an examination, for the purpose of—
(i)delivering it (by previous arrangement for a specified time on a specified date) at a place where relevant work is to be done on it, or
(ii)bringing it away from a place where relevant work has been done on it, before it is registered.
(9) In this regulation—
“authorised person” means an examiner appointed under section 66A of the 1988 Act or a person carrying out such an examination under the direction of such an examiner;
“relevant work” means work done or to be done to remedy the defects on the grounds of which the application was refused (including work to alter the vehicle in some aspect of design, construction, equipment or marking on account of which the certificate was refused).
Licences not to be issued for vehicles unless appropriate certificates are in force
15. Where application is made for a licence under the Vehicle Excise and Registration Act 1994(14) for a vehicle to which regulation 14 applies, the licence shall not be granted unless on the first application after the day appointed by Regulations made by virtue of the 1988 Act for a licence for that vehicle, there is produced evidence that there are one or more certificates in force for the vehicle under sections 54 to 58 of the 1988 Act from which it appears that the vehicle complies with the approval requirements.
Signed by authority of the Secretary of State
Gus Macdonald
Minister of State,
Department of the Environment, Transport and the Regions
9th January 2001
Regulation 2
SCHEDULE 1INSTRUMENTS REVOKED
| Instrument | Number |
|---|---|
| The Motor Vehicles (Approval) Regulations 1996 | S.I. 1996/3013 |
| The Motor Vehicles (Approval) (Amendment) Regulations 1997 | S.I. 1997/1366 |
| The Motor Vehicles (Approval) (Amendment) (No. 2) Regulations 1997 | S.I. 1997/2934 |
| The Motor Vehicles (Approval) (Amendment) Regulations 1998 | S.I. 1998/1008 |
| The Motor Vehicles (Approval) (Amendment) Regulations 1999 | S.I. 1999/2082 |
| The Motor Vehicles (Approval) (Amendment) (No. 2) Regulations 1999 | S.I. 1999/3226 |
| The Motor Vehicles (Approval) (Amendment) Regulations 2000 | S.I. 2000/1972 |
Regulation 3(1)
SCHEDULE 2SCHEDULE 2 VEHICLES
Meaning of “Schedule 2 vehicle”
1. A Schedule 2 vehicle is a relevant vehicle which is—
(a)a left hand drive vehicle;
(b)a personally imported vehicle;
(c)an amateur built vehicle;
(d)a vehicle manufactured in very low volume;
(e)a vehicle manufactured using parts of a registered vehicle;
(f)a disabled person’s vehicle;
(g)a rebuilt vehicle;
(h)a motor caravan as defined in Annex II.A of the 1970 Directive;
(i)an ambulance as defined in Annex II.A of the 1970 Directive;
(j)a hearse as defined in Annex II.A of the 1970 Directive; or
(k)an armoured vehicle as defined in Annex II.A of the 1970 Directive.
Personally imported vehicles
2.—(1) A vehicle is a personally imported vehicle if—
(a)it has been imported by a person entering the United Kingdom;
(b)that person had, at the time the vehicle was imported, been normally resident in a country other than the United Kingdom for a continuous period of at least 12 months;
(c)that person intends to become normally resident in the United Kingdom;
(d)the vehicle has been in the possession of that person and used by him in the country where he has been normally resident for a period of at least 6 months before its importation; and
(e)the vehicle is intended for his personal or household use in the United Kingdom.
(2) For the purposes of this paragraph a person shall be treated as being normally resident in the country where he usually lives—
(a)for a period of, or periods together amounting to, at least 185 days in a period of 12 months;
(b)because of his occupational ties; and
(c)because of his personal ties.
(3) In the case of a person with no occupational ties, sub-paragraph (2) shall apply with the omission of paragraph (b), provided that his personal ties show close links with that country.
(4) Where a person has his occupational ties in one country and his personal ties in another country, he will be treated, for the purposes of this paragraph, as being normally resident in that latter country provided that either—
(a)his stay in the former country is in order to carry out a task of a definite duration, or
(b)he returns regularly to the country where he has his personal ties.
(5) Notwithstanding paragraph (4), a United Kingdom citizen whose personal ties are in the United Kingdom but whose occupational ties are in a country other than the United Kingdom shall be treated for the purpose of this paragraph as normally resident in the country of his occupational ties, provided that he has lived there for a period of, or periods together amounting to, at least 185 days in a period of 12 months.
Amateur built vehicles
3.—(1) A vehicle is an amateur built vehicle if—
(a)the vehicle was constructed or assembled for the personal use of a relevant individual; and
(b)the construction or assembly or a substantial part of the construction or assembly was carried out by—
(i)the individual referred to in paragraph (a),
(ii)one or more relevant individuals acting on his behalf and under his direction, or
(iii)the individual referred to in paragraph (a) and one or more relevant individuals acting on his behalf and under his direction.
(2) For the purposes of this paragraph, a reference to a relevant individual, in relation to a motor vehicle, is a reference to an individual who did not, at any time during the period when the construction or assembly of the vehicle was being carried out, carry on a business in the course of which motor vehicles are normally constructed or assembled.
Vehicles manufactured in very low volume
4.—(1) A vehicle is a vehicle manufactured in very low volume if the condition specified in either paragraph (2) or paragraph (3) is complied with.
(2) The condition specified in this paragraph is that the total number of vehicles of the family of types to which the vehicle in question belongs which are manufactured in the world for any period of 12 months falling within the period of 36 months immediately preceding the month in which the vehicle was manufactured does not exceed 200.
(3) The condition specified in this paragraph is that the number of vehicles of the type variant to which the vehicle in question belongs which are manufactured in the world for any period of 12 months falling within the period of 36 months immediately preceding the month in which the vehicle was manufactured does not exceed 20.
(4) For the purposes of sub-paragraph (3), a type variant consists exclusively of vehicles which do not differ in at least the following essential respects—
(a)the manufacturer;
(b)essential aspects of construction and design, that is to say in:
(i)obvious and fundamental differences in the chassis, floor pan or other parts of the vehicle’s structure, or
(ii)the power plant (whether internal combustion, electric or hybrid);
(c)body style (by way of example, saloon, hatchback, coupe, cabriolet or estate);
(d)the following further characteristics of the power plant:
(i)its working principle (whether positive ignition or compression ignition, and whether four stroke or two stroke),
(ii)the number and arrangement of its cylinders,
(iii)differences in maximum power of more than 30% (the highest is more than 1.3 times the lowest), or
(iv)engine capacity differences of more than 20% (the highest is more than 1.2 times the lowest);
(e)number, position or interconnection of the powered axles; or
(f)number or position of the steered axles.
Vehicles manufactured using parts of a registered vehicle
5. A vehicle is a vehicle manufactured using parts of a registered vehicle if—
(a)it is constructed or assembled by a person carrying on a business in the course of which motor vehicles are normally constructed or assembled;
(b)it is equipped with an engine which has previously been used as the engine of another vehicle which had been registered under the Vehicle Excise and Registration Act 1994 or any earlier Act relating to the registration of mechanically propelled vehicles; and
(c)it is equipped with one or more of the following components taken from the same vehicle as the engine—
(i)chassis;
(ii)body;
(iii)suspension;
(iv)an axle;
(v)transmission; or
(vi)steering assembly.
Disabled person’s vehicle
6.—(1) A vehicle is a disabled person’s vehicle if it is adapted or specially constructed so as to enable a person who has a disability to travel in the vehicle, whether as the driver or a passenger, in safety and reasonable comfort.
(2) In sub-paragraph (1), “disability” has the meaning given by section 1 of the Disability Discrimination Act 1995(15).
Rebuilt vehicles
7. A vehicle is a rebuilt vehicle if it—
(a)is a vehicle to which the Secretary of State is required by regulation 7 to assign a vehicle identification number;
(b)does not fall within either of the classes defined by paragraphs 3 or 5; and
(c)has been rebuilt using a replacement chassis, or an integral chassis body, which is of the same design and construction as that of the original vehicle and which—
(i)was supplied for the purpose without having been previously used, or
(ii)previously formed part of a registered vehicle.
Regulation 5(1)(a)
SCHEDULE 3APPROVAL REQUIREMENTS FOR RELEVANT VEHICLES
(References to paragraphs (unless otherwise provided) mean references to the numbered paragraph in column 3 of the item in which the reference appears, and the expressions in bold type are defined in column 4)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Subject matter | Requirement | Definitions and supplementary provisions | Exemptions and modifications |
| 1 | Doors, their latches and hinges | 1. All doors, provided on the vehicle for the entry and exit of occupants, shall be designed as to allow easy and safe use. Doors shall have both intermediate and fully latched positions and their latches shall be designed to prevent the doors from opening accidentally. However, latching in an intermediate position is not required if a safety-bolt with an audible warning device is provided as specified in paragraph 2(b) below. | For the purposes of this item, “longitudinal plane” means a vertical plane parallel to the longitudinal axis of a vehicle. | Paragraph 3 shall not apply to doors which do not give direct access to a seat designed for normal use while a vehicle is travelling on a road. This includes any door, for which the longitudinal plane passing through the extreme inboard projecting point of such a door is more than 300mm distant from the longitudinal plane passing through the nearest edge of such a seat. |
2. Where hinges are used, the hinges shall be fitted at the front edge of the door. However, they may be fitted at the top or rear edge if either— (a)a device is fitted which automatically closes the door at least to the intermediate latched position if it is unlatched when the vehicle is moving in the forward direction; or (b)a safety-bolt is fitted to prevent such unlatching and an audible warning device is provided which activates an audible warning if the vehicle is driven without the bolt in place. | The latching requirements in paragraphs 1 and 3 shall not apply to any power-operated door if the force applied by the power actuator is sufficient to keep the door completely closed even when any load is applied as described in paragraph 3. | |||
3. On hinged doors, the latch and striker assembly shall be capable of withstanding any load which is likely to be applied in the course of normal driving (i.e. excluding crash impacts) in both the intermediate and fully latched positions. However if a safety-bolt with an audible warning device is provided as specified in paragraph 2(b) above, the requirement need be met only with the bolt in place. | ||||
| 2 | Radio-interference suppression | The vehicle shall comply with the design, construction and fitting requirements of paragraph 6.1 of Annex 1 to Directive 72/245/EEC as last amended by Directive 89/491/EEC, or of paragraph 6.1 of ECE Regulation 10.01. | This item shall only apply to vehicles propelled by a spark ignition engine. | |
| 3 | Protective Steering | 1. No part of the steering control surface directed towards the driver which can be contacted by a sphere of 165mm in diameter shall present any roughness or sharp edges with a radius of curvature of less than 2.5mm. 2. The steering control shall be designed, constructed and fitted so as not to embody components or accessories, including the horn control and other assemblies, capable of catching in the driver’s clothing or jewellery in normal driving movements. 3. The steering control and column assembly as fitted to the vehicle or the steering control itself shall offer a degree of protection to the driver in the event of a frontal impact by absorbing energy. This requirement shall be treated as met if either— (a)the vehicle complies with the requirements of paragraph 5.2 of Annex 1 of Directive 74/297/EEC; or (b)the steering control complies with the requirements of paragraphs 5.2, 5.4.3, 5.4.4 and 5.4.5 of Directive 74/297/EEC as last amended by Directive 91/662/EEC. 4. The vehicle shall comply with the requirements of paragraph 5.1 of Annex 1 of Directive 74/297/EEC. | For the purposes of this item— “driver’s air-bag” means a flexible bag fitted to a vehicle and designed to be filled with gas under pressure in order to protect the driver in the event of a collision involving the front end of the vehicle. “steering control” has the same meaning as in Directive 74/297/EEC. | This item shall not apply to— (a) vehicles, the steering control of which has been specially constructed for the use of a person suffering from some physical defect or disability; (b) vehicles manufactured before 1 October 1997 in which the centre of the steering control is in the forward quarter of the total length of the vehicle, including any bumpers and overriders; (c) goods vehicles having a maximum gross weight of not less than 1500kg and goods vehicles manufactured before 1 October 1997; (d) ambulances, motor caravans and hearses (in each case) having a maximum gross weight of more than 2,500 kg if the vehicle has been derived from a goods vehicle either having a maximum gross weight of not less than 1,500 kg or manufactured before 1st October 1997; and (e) armoured vehicles. Paragraph 1 shall not apply to a vehicle if— (a) it is a Schedule 2 vehicle but not— (i) an amateur-built vehicle; (ii) a vehicle manufactured using parts of a registered vehicle; or (iii) a rebuilt vehicle; (b) it is fitted with a driver’s air bag; and (c) the driver’s air bag was fitted at the time the vehicle was manufactured. Paragraph 1 shall not apply to any switch fitted to the steering control of a vehicle if— (a) it is a Schedule 2 vehicle but not— (i) an amateur-built vehicle; (ii) a vehicle manufactured using parts of a registered vehicle; or (iii) a rebuilt vehicle; and (b) the switch is an integral part of the steering control as originally fitted to the vehicle by its manufacturer and it can be depressed into the steering control by finger pressure. |
| 4 | Exhaust emissions | 1. The vehicle shall not emit any avoidable smoke or avoidable visible vapour. 2. When the engine by which it is propelled is running without load at a normal idling speed, the carbon monoxide content of the exhaust emissions from the engine shall not exceed— (a)if the vehicle has an effective date before 1st August 1986, 4.5%; or (b)if the vehicle has an effective date on or after 1st August 1986 and not being a vehicle to which sub-paragraph (c) or (d) below applies, 3.5%; or (c)if the vehicle is of a description mentioned in the Annex to the emissions publication and is either— (i)a passenger car having an effective date on or after 1st August 1992; or (ii)any other vehicle having four or more wheels and an effective date on or after 1st August 1994, the relevant percentage; or (d)if the vehicle is not of a description mentioned in the Annex to the emissions publication and is either— (i)a passenger car having an effective date on or after 1st August 1995; or (ii)any other vehicle having four or more wheels and an effective date on or after 1st August 1997, 0.5%; of the total exhaust emissions from the engine by volume. 3. If the engine by which the vehicle is propelled is run without a load at a rotational speed of 2,000 revolutions per minute, the hydrocarbon content of the exhaust emission from the engine shall not exceed 0.12% if the vehicle either— (a)has not more than three wheels; or (b)is a vehicle to which paragraph 2(a) or (b) applies; 4. If the vehicle is one to which paragraph 2(c) or (d) applies and the engine by which it is propelled is run without a load at a fast idling speed— (a)the carbon monoxide content of the exhaust emissions from the engine shall not exceed 0.3% of the total exhaust emissions from the engine by volume; (b)the hydrocarbon content of the exhaust emissions from the engine shall not exceed 0.02% of the total exhaust emissions from the engine by volume; and (c)the lambda value shall be between the relevant limits. | For the purposes of this item— “effective date” means the date of manufacture of the vehicle, except that in the case of a vehicle which for the time being meets the requirements of paragraph 3, 5 or 6 of Schedule 2 to these Regulations, it shall mean the 1st January immediately preceding the date of manufacture of the engine by which it is propelled, if that date is earlier; “the emissions publication” is the publication entitled “In-service Exhaust Emissions Standards for Road Vehicles” (ISBN 0-9526457-5-0) published by the Department of the Environment, Transport and the Regions; “a fast idling speed” means— (a) in the case of a vehicle of a description mentioned in the Annex to the emissions publication, a rotational speed between the minimum and maximum limits shown against that description of vehicle in columns 3(e) and (f) respectively of that Annex; or (b) in any other case, a rotational speed of between 2,500 and 3,000 revolutions per minute; “the lambada value” means the ratio by mass of air to petrol vapour in the mixture entering the combustion chambers divided by 14.7; “a normal idling speed” means in the case of a vehicle of a description mentioned in the Annex to the emissions publication, a rotational speed between the minimum and maximum limits shown against that description of vehicle in columns 2(b) and 2(c) respectively of that Annex; “passenger car” means a motor vehicle which— (a) is constructed or adapted for use for the carriage of passengers and is not a goods vehicle; (b) has no nore than five seats in addition to the driver’s seat; (c) has a weight not exceeding 2,500 kg maximum gross; and (d) has four or more wheels; “the relevant limits” means— (a) in the case of a vehicle of a description mentioned in the Annex to the emissions publication, the minimum and maximum limits shown against that description of vehicle in columns 3(c) and 3(d) respectively of that Annex; or (b) in any other case, 0.97 and 1.03; “the relevant percentage” means in the case of a vehicle of a description mentioned in the Annex to the emissions publication, the percentage shown against that description of vehicle in column 2(a) of that Annex; and “rotary piston engine” means an engine in which the torque is provided by means of one or more rotary pistons and not by any reciprocating piston; and any rotary piston engine shall be deemed to be a four-stroke engine. | Paragraphs 2, 3 and 4 shall not apply to— (a) vehicles not propelled by a spark ignition engine; (b) vehicles having an effective date before 1st August 1975; and (c) vehicles having an effective date before 1st August 1987 and propelled by a rotary piston engine. Paragraphs 2(a) and (b) and 3 shall not apply to vehicles propelled by a 2-stroke engine. Paragraphs 2(c) and 2(d) shall not apply to vehicles having an effective date before 1st January 1999 which are either— (i) fuelled solely by either liquid petroleum gas or natural gas, or (ii) bi-fuelled vehicles when controlled to operate on either of those gases. Paragraphs 3 and 4(b) shall not apply to vehicles fuelled solely by natural gas or to bi-fuelled vehicles when controlled to operate on either liquid petroleum gas or natural gas. Paragraph 4(c) shall not apply to vehicles fuelled by liquid petroleum gas or natural gas. |
| 5 | Smoke Emissions | If the vehicle has an effective date on or after 1 August 1979, when the engine by which it is propelled is subject to the free-acceleration test, the coefficient of absorption of the exhaust emissions from the engine immediately after leaving the exhaust shall not exceed— (a) if the engine of the vehicle is turbo-charged, 3.0 per metre, or (b) in any other case, 2.5 per metre. | For the purposes of this item—
| This item shall only apply to vehicles propelled by a compression ignition engine. |
| 6 | Lamps, reflectors and devices | The construction and equipment of the vehicle shall be such that its use on a road between sunset and sunrise would not constitute a contravention or a failure to comply with— (a) regulations 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19 or 20 of the Lighting Regulations; or (b) regulation 18 of those Regulations except in so far as it requires a vehicle— (i) to comply with paragraph 12(c) of Part 1 of Schedule 4 to those Regulations; and (ii) to be fitted with a dim-dip device or running lamp. | For the purpose of this item, the Lighting Regulations shall have effect as if for every reference to the date on which a vehicle is first used there were substituted a reference to the date of manufacture of the vehicle. For the purposes of this item—
| This item, in so far as it requires any lamp (not being a filament lamp), reflector or device to bear a particular standard mark (or one of two or more standard marks), shall not apply to a vehicle if— (a) in the case of a lamp or device, it meets the requirements as to intensity; and (b) in the case of a reflector, it meets the standards as to coefficient of luminous intensity, of the instrument to which the standard mark (or as the case may be one of those standard marks) relates. This item, in so far as it requires compliance with regulation 14 of the Lighting Regulations (filament lamps), shall not apply to a lamp, if by virtue of the preceding paragraphs, it could comply with this item without bearing any standard mark. This item, in so far as it requires the headlamps (including a filament lamp fitted to a headlamp) fitted to a vehicle to bear a particular standard mark (or one of two or more standard marks), shall not apply to headlamps that emit sufficient light to illuminate the road in front of the vehicle on both main and dipped beam. In the case of a rear direction indicator which is one of a number of lamps having a common housing and fitted to a left-hand drive vehicle, paragraph 2(b)(i) in Part 1 of Schedule 7 of the Lighting Regulations shall apply as if for “400 mm” there were substituted “480 mm”. In the case of an ambulance, motor caravan, hearse or armoured vehicle, exemptions shall be permitted in so far as the special purpose of the vehicle makes it impossible fully to comply, provided that all obligatory lamps, reflectors and devices are installed and the angles of visibility are not affected. |
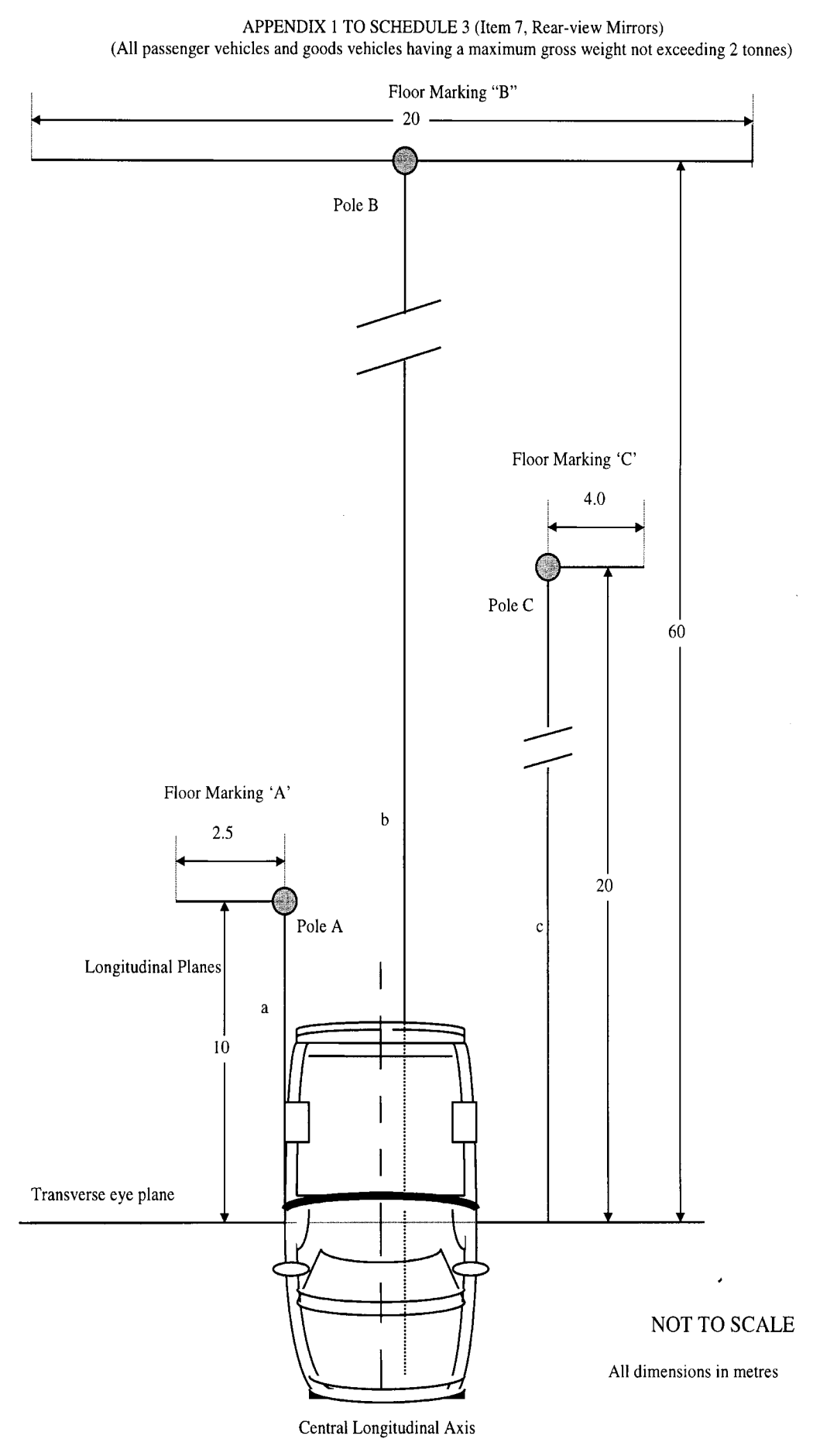
| 7 | Rear-view mirrors | 1. The vehicle shall be fitted with at least one offside exterior mirror which meets— (a)if the vehicle is right hand drive or has a central driving position, the adjustment, rear view, and vibration requirements; or (b)if the vehicle is left hand drive, the rear view, and vibration requirements. 2 It shall also be fitted with at least one interior mirror which meets the adjustment, rear view and vibration requirements unless no interior mirror could provide any view to the rear. 3. If no interior mirror is fitted or if no interior mirror meets the rear view requirements, a nearside exterior mirror shall be fitted which meets— (a)if the vehicle is right hand drive or has a central driving position, the rear view and vibration requirements; or (b)if the vehicle is left hand drive, the adjustment, rear view, and vibration requirements. 4. Each rear view mirror fitted to the vehicle shall either— (a)comply with the requirements (including marking requirements) of Annex II to Directive 71/127/EEC as last amended by Directive 88/321/EEC or of Part I of ECE Regulation 46.01 for a Class I mirror in the case of an interior mirror and a Class III or a Class II mirror in the case of an exterior mirror; or (b)comply with the dimension requirements and the following requirements— (i)the edge of the reflective surface shall be enclosed within a protective housing; (ii)all parts of the external surface of the mirror which are, in the case of an interior mirror, contactable by a sphere of 165 mm diameter, and in the case of an exterior mirror, by a sphere of 100 mm diameter, shall have a radius of curvature of not less than 2.5 mm, with the exception of fixing holes or recesses less than 12 mm wide if these are blunted; (iii)exterior mirrors shall be capable of rotating inwards towards the vehicle when a force of 10 kg is applied horizontally at the extreme outer edge in a longitudinal plane from both the front and the rear. The axis of rotation shall lie within 50 mm of the surface at which the mirror is attached to the vehicle bodywork. | For the purposes of this item—
“the adjustment requirements” In order to meet the adjustment requirements—
Provided that a mirror shall be regarded as meeting the requirements of sub-paragraph (a) above whether or not— (a) it can meet those requirements only with the window in the driver’s door being open; or (b) the mirror is capable of being locked in position from the outside of the vehicle. “The dimension requirements” In order for an exterior mirror to meet the dimension requirements, the dimensions of the reflecting surface must be such that an orthogonal projection onto a vertical surface accommodates a vertical line with a length of 70 mm and a rectangle with vertical sides of40 mm and horizontal sides of 70 mm. In order for an interior mirror to meet the dimension requirements, the dimensions of the reflecting surface must be such that an orthogonal projection onto a vertical surface accommodates a rectangle with vertical sides of40 mm and horizontal sides of 80 mm. “The rear view requirements” (see the Appendices 1 and 2 to this Schedule) In order for a mirror to meet the rear view requirements, it must be such that when the vehicle is positioned such that its longitudinal axis is parallel to the longitudinal planes a, b and c, with the driver seated in his normal upright driving position such that his eyes lie in the transverse eye plane and with the mirror correctly adjusted, he shall be able to see in that mirror— (a) in the case of an offside exterior mirror, with the offside extreme outer edge of the vehicle positioned so that it is tangential to the longitudinal plane a, the whole of floor marking A and pole A; and (b) in the case of an interior mirror, with the central longitudinal axis of the vehicle positioned so that it lies on the longitudinal plane b, the whole of floor marking B and pole B; or (c) in the case of a nearside exterior mirror, with the nearside extreme outer edge of the vehicle positioned so that it is tangential to the longitudinal plane c, the whole of floor marking C and pole C.
In order to comply with the vibration requirements, a mirror shall be fixed to the vehicle in such a way that under normal driving conditions, it neither moves so as to change the field of vision, nor vibrate to an extent which would cause the driver to misinterpret the nature of the image received. | This item shall not apply to vehicles having not more than three wheels, if they comply with the requirements for motor-tricycles in Annex III to Directive 97/24/EC. The requirements of paragraph 2 shall not apply to motor caravans, ambulances, hearses or armoured vehicles (in each case) having a maximum gross weight exceeding 2,500 kg if the vehicle has been derived from a vehicle of category M2, M3, N2 or N3. Paragraph 4(b)(iii) shall not apply— (a) to any mirror, no part of which is less than 2,000 mm above the ground, or (b) to any mirror which does not protrude beyond an extreme outer edge of the vehicle, or (c) any left hand drive vehicle. |
| 8 | Anti-theft devices | 1. The vehicle shall be fitted with some form of anti-theft device, that is to say, a mechanical, electrical or electronic immobiliser or a combination of these (in addition to any key operated switch normally used to start the engine) that prevents the vehicle being driven or moved under its own power. 2. No anti-theft device shall operate on the braking system. 3. If any anti-theft device is, or incorporates, any mechanical device that acts upon a system that affects the control of the vehicle (e.g. the steering control)— (a)it shall not be possible to start the engine in the normal way until every such mechanical device has been deactivated, (b)it shall not be possible to activate any such mechanical device while the engine is running, and (c)the action of activating any such mechanical device shall be distinct and separate from that of stopping the engine. | This item shall not apply to disabled person’s vehicles | |
| 9 | Seat belts | 1. Every adult belt fitted to the vehicle, not being a harness belt or a passive belt, shall comply with the requirements of regulation 47(7) of Construction and Use Regulations to the extent (if any) that it would apply were the said paragraph 7 to apply to all motor vehicles. 2. If the vehicle is fitted with one or more passive belts, every such belt shall— (a)bear a mark as described in regulation 47(4)(c)(i) of the Construction and Use Regulations; or (b)meet the requirements referred to in regulation 47(4)(c)(iii) of those Regulations. 3. If the vehicle is fitted with one or more harness belts, every such belt shall— (a)bear a mark as described in regulation 47(4)(c)(ii) of the Construction and Use Regulations; or (b)meet the requirements referred to in regulation 47(4)(c)(iv) of those Regulations. | For the purposes of this item— “adult belt” means a seat belt for an adult not being a disabled person’s belt; “disabled person’s belt”, “lap belt” and “seat belt” have the same meanings as in regulation 47(8) of the Construction and Use Regulations; “harness belt” means an adult belt which is a harness belt comprising a lap belt and shoulder straps; “passive belt” means an adult belt comprised in a passive belt system. | This item shall not apply to an adult belt fitted to a vehicle if the belt provides a level of safety equivalent to that provided by an adult belt which complies with the requirements of this item as they would otherwise apply to the belt but disregarding paragraph 2(b) and 3(b). |
| 10 | Seat belt anchorages | 1. The vehicle shall comply with the requirements of paragraph 4.3 of Annex I to Directive 76/115/EEC. For outboard seating positions other than in the front, two lower anchorages are allowed. 2. Without prejudice to paragraph 1, the vehicle shall be fitted with an anchorage in every position required to hold securely every adult belt or any part of an adult belt fitted to the vehicle. 3. Every anchorage intended for an adult belt shall comply with the requirements of paragraphs 4.2, 4.4 and 4.5 of Annex I to Directive 76/115/EEC. 4. The vehicle shall comply with the requirements of paragraph 5 of Annex I to Directive 76/115/EEC. | For the purposes of this item—
Annex I to Directive 76/115/EEC Directive shall have effect as if for paragraph 4.4.1 there were substituted— “4.4.1 Every belt anchorage shall comply with the following requirements.”. | Paragraph 3 shall not apply to anchorages which are so located that when used with an adult belt of a type for which they are intended to be used, if they provide a level of safety equivalent to that provided by anchorages that meet the requirements of that paragraph when used with an adult belt of a type for which they are intended. For motor caravans, ambulances and hearses, paragraph 1 shall apply only to seating positions where there is a seat intended for use while the vehicle is travelling on a road. An armoured vehicle shall be exempted from any requirement of paragraph 1 if it can be demonstrated to the satisfaction of the Secretary of State that it is impossible for the vehicle to comply due to its special purpose. |
| 11 | Installation of seat belts | 1. The vehicle shall be fitted with, a harness belt, a passive belt or a three point belt for the driver’s seat and the specified passenger seat (if any). 2. If the vehicle has an effective date on or after 1st April 1987, in addition to the seat belts required by paragraph 1 above, it shall be fitted with an appropriate belt for every other forward-facing seat in the front alongside the driver’s seat, not being a specified passenger’s seat. 3. If the vehicle has an effective date on or after 1st April 1987, in addition to the seat belts required by paragraph 1 and 2 above, it shall be fitted with a harness belt, a lap belt, a passive belt or three-point belt for every other forward-facing seat. 4. Every adult belt and every disabled person’s belt fitted to the vehicle shall be properly secured to anchorages provided for it and installed so that it can be used properly to restrain an occupant (e.g. in the case of a lap belt by passing over the pelvic region and in the case of a harness belt, a passive belt or a three-point belt by also restraining the upper torso and not being liable to slip off the shoulder). Also, there shall be no sharp edges liable to cause abrasion or damage to the belts in normal use. In the case of every lap belt, passive belt and three point belt, provision shall be made for their safe and convenient storage. | For the purposes of this item—
| The requirements of paragraphs 1, 2 and 3 shall not apply in relation to a seat fitted to a disabled person’s vehicle if the vehicle is fitted with a disabled person’s belt for that seat. Paragraph 2 shall have effect in relation to motor caravans, ambulances and hearses as if for “1st April 1987” there were substituted “1st October 1988”. Paragraph 3 shall have effect in relation to motor caravans, ambulances and hearses as if— (a) for “1st April 1987” there were substituted “1st April 1997”; and (b) there were added at the end the words “intended for use while the vehicle is travelling on a road”. An armoured vehicle shall be exempted from any requirement of paragraphs 1, 2 or 3 if it can be demonstrated to the satisfaction of the Secretary of State that it is impossible for the vehicle to comply on account of its special purpose. |
| 12 | Brakes | 1. The vehicle shall comply with the requirements of paragraph 2.1 and 2.2 of Annex 1 of Directive 71/320/EEC as last amended by Directive 85/647/EEC; but in the application of that Annex (as so amended) for these purposes— (a)the second sentence of paragraph 2.2.1.2.4 shall not apply; and (b)paragraph 2.2.1.4.2 shall not apply in relation to a vehicle which is fitted with a braking device having a split-circuit transmission which enables braking of not less than one wheel on each side of the vehicle, in the event of failure in a part of the transmission of the service braking; (c)paragraph 2.2.1.5.1 shall apply as if for the last sentence there were substituted the words “This condition must be met by automatic means”. 2. If the vehicle is equipped with an anti-lock device it shall comply with paragraph 2.2.1.23 of 71/320/EEC as last amended by Directive 88/194/EEC. 3. The vehicle shall comply with the requirements of paragraphs 2.2.1.11.1 and 2.2.1.11.2 of Directive 71/320/EEC as last amended by Directive 91/422/EEC. 4. The secondary braking and service braking shall have the same control. 5. The brake efficiency shall be not less than— (a)for the service braking (i)in the case of a passenger vehicle, 60%; or (ii)in the case of a goods vehicle, 50% (b)for the secondary braking in the case when the servo-assistance provided for the service braking (if any) fails and a force is applied to the control (i)in the case of a passenger vehicle, 30% when the force applied is 50kg; or (ii)in the case of a goods vehicle, 25% when the force applied is 70kg. (c)18% for the parking braking. | For the purpose of this item—
| The requirements in paragraph 1 for the driver to be able to operate the service braking system while keeping both hands on the steering control, and the secondary braking system while keeping at least one hand on the steering control, shall not apply to a disabled person’s vehicle, provided that the vehicle is adapted to allow the driver to control the steering at all times while operating either braking system. Paragraphs 1 to 4 shall not apply to vehicles having not more than three wheels, if they comply with the requirments for motor-tricycles in the following provisions of Directive 93/14/EEC— (a) paragraph 2.1 of the Annex; (b) paragraphs 2.2.4 to 2.2.8 of the Annex; and (c) in the case of vehicles equipped with anti-lock devices, Appendix 2 to the Annex; In relation to vehicles having not more than three wheels, paragraph 5 shall have effect as if— (a) for “60%” and “30%” there were substituted “50%” and “25%” respectively, and (b) for “50 kg” and “70 kg” there were substituted “40 kg”, if a manual control is used to apply the secondary braking. Paragraph 7 shall not apply to a Schedule 2 vehicle other than:— (a) an amateur-built vehicle; (b) a vehicle manufactured using parts of a registered vehicle; (c) a rebuilt vehicle; and (d) the brakes acting on its rear wheels are fitted with an anti-lock device and were so fitted at the time of its manufacture. |
6. The lateral brake distribution for the service braking shall— (a)in relation to each steering axle; and (b)for all values of total breaking force and vehicle speed, be not less than 70%. 7. The longitudinal brake distribution for the service braking shall, for all values of total braking force, vehicle speed and adjustment settings (if any), be greater than the ratio of the vertical forces transmitted to the road through the front and rear wheels respectively when the vehicle is in running order and being braked on a level surface. 8. The capacity of the braking device to absorb and dissipate energy shall be sufficient to ensure that all the required aspects of braking performance can be maintained under all normal operating conditions of the vehicle, including long hill descents, taking account of the vehicle’s speed capability, weight and weight distribution. | ||||
| 13 | Noise and silencers | 1. The vehicle shall be fitted with an exhaust system including a silencer such that the exhaust gases shall not escape into the atmosphere without first passing through the silencer. 2. When— (a)the vehicle is held stationary on a level surface such that there is an unobstructed area not less than 3 metres wide all around the vehicle; and (b)the engine by which the vehicle is propelled is run at a constant rotational speed of 3/4 S, the noise measured at 0.5 metres from the exhaust outlet at 45 degrees to the axis of the outlet pipe in a horizonatal plane, shall not exceed 101db(A). | For the purposes of this item, “S” means the rotational speed at which maximum power is produced. | Paragraph 1 shall only apply to vehicles propelled by an internal combustion engine. |
| 14 | Glass in windscreens and other windows outside | The windows of the vehicle shall be fitted with glazing which complies with the requirements of regulations 31 and 32 of the Construction and Use Regulations to the extent (if any) that they apply to the vehicle. However, side screens may be constructed of safety glazing. | For the purposes of this item, the Construction and Use Regulations shall have effect as if every reference to the date on which a vehicle is first used were a reference to its effective date. For the purposes of this item—
| The requirements of regulation 32(2) and (7) of the Construction and Use Regulations shall not apply to the glazing fitted to any window, if that glazing provides a level of safety equivalent to glazing which complies with the requirements set out in column 3 of this item. In relation to a vehicle fitted with a near-side exterior mirror (in addition to the obligatory off-side exterior mirror) which meets the requirements of item 7 (rear-view mirrors), the requirements of regulation 32(10) of those Regulations shall not apply to the glazing fitted to any window every part of which is behind the driver. In relation to any glass fitted in a window of an armoured vehicle, the requirements of regulation 32(10) of those Regulations shall apply as if the values in column 4 of Table II of that regulation (minimum light transmission) were all 60 per cent. |
| 15 | Seats and their anchorages | 1. Every seat and seat back adjustment and displacement system provided shall incorporate a locking system which operates automatically in all positions provided for normal use and all seats, including those which can be tipped forward or have fold-down backs, shall lock automatically in their normal upright position. 2. The unlocking controls for displacement systems which facilitate access by passengers shall be accessible from outside the vehicle when the door is open. They shall be easily accessible, even to the occupant of the seat immediately behind the seat concerned if such a seat is designated as suitable for an adult. 3. Seats shall be constructed and firmly attached to the vehicle such that they and their anchorages comply with the design, construction and fitting requirements of paragraph 6.2 to Annex I of Directive 74/408/EEC. | This item does not apply to seats not intended for normal use while the vehicle is travelling on a road (including seats exempt from Directive 74/408/EEC as last amended by Directive 81/577/EEC). This item does not apply to any seat designed for a person with a disability and fitted in a disabled person’s vehicle. | |
| 16 | Tyres | 1. Every tyre (not being a retreaded tyre) fitted to the vehicle shall bear an approval mark in accordance with the requirements of Directive 92/23/EEC or ECE Regulation 30. 2. Every retreaded tyre fitted to the vehicle shall bear a mark in accordance with paragraph 6 of BS AU 144e–1988 or a corresponding standard and the indication given by the mark must not be false in a material particular. 3. Each tyre fitted to the vehicle shall bear marks that were moulded on to or into the tyre at the time that it was manufactured which provide the following service information— (a)nominal size; (b)construction type (e.g. radial ply); (c)load capacity; and (d)speed capability. 4. Each tyre fitted to the vehicle shall be of a nominal size appropriate to the wheel to which it is fitted. 5. Tyres on the same axle shall be of the same nominal size and of the same construction type. If radial tyres are fitted to the front axle, they shall also be fitted to the rear and if bias-belted tyres are fitted to the front axle, radial or bias-belted tyres shall be fitted to the rear. 6. Each wheel on each axle shall be equipped with a tyre which has a load capacity such that when the axle is loaded to its maximum permitted axle weight, the weight transmitted to the road surface by that tyre does not exceed that load capacity. 7. The speed capability of all tyres fitted shall be not less than the maximum design speed of the vehicle. | For the purpose of this item—
| Paragraph 1 shall not apply to a tyre fitted to a vehicle, if the tyre provides a level of safety equivalent to a tyre that meets the requirements of that paragraph. Paragraph 2 shall not apply to a tyre fitted to a vehicle, if the tyre provides a level of safety equivalent to that provided by a tyre that complies with the requirements of that paragraph so far as it relates to BS AU 144e–1988. Paragraph 3(c) and (d) shall not apply to a tyre fitted to a vehicle for which information on the load capacity and speed capability have been separately provided. |
| 17 | Interior fittings | 1. No surface (other than a surface of a window) of the vehicle interior which can be contacted by a sphere of 165mm diameter and which is within the specified zone, shall include any fittings (e.g. controls and instruments) or design features which have any dangerous roughness or sharp edges. 2. Switches and other controls mounted on the instrument panel which project by more than 9.5mm from the surface of the panel, can be contacted by a sphere of 165mm diameter and which are within the specified zone, shall be so constructed and mounted that they would either retract into the surface of the panel or become detached from the panel when a horizontal force of 40kg is applied to them. 3. The lower edge of the instrument panel shall be rounded to a radius of curvature of not less than 19mm, or if it is covered with non-rigid material, not less than 5mm. 4. The rearward and upward-facing parts of seat frames behind which there is a designated seating position, shall be both covered with non-rigid material and have a radius of curvature of not less than 5mm. 5. The handbrake control in the fully released position and the gear-lever control in any forward gear position shall not have any radius of curvature of less than 3.2mm on surfaces which can be contacted by a sphere of 165mm diameter. 6. Shelves and other similar items shall be so constructed that their supports have no protruding edges and that all parts facing into the vehicle present a surface not less than 25mm high with edges rounded to a radius of curvature of not less than 3.2mm. This surface shall also be covered with non-rigid material. 7. On that part of the inner surface of the roof which is situated above or forward of the occupants and can be contacted by a sphere of 165mm diameter, the width of projecting parts made of rigid material, shall not be less than the length of their projection from the surface and their edges shall have a radius of curvature of not less than 5mm. Roof sticks or ribs made of rigid material with the exception of the header rail of the glazed surfaces and door frames, shall not project downwards by more than 19mm. | For the purposes of this item— “air bag” means a flexible bag fitted to a vehicle and designed to be filled with gas under pressure in order to protect the driver or a front seat passenger in the event of a collision involving the front of the vehicle; “designated seating position” means a position where there is a seat designed for normal use while the vehicle is travelling on the road; “head impact zone” has the same meaning as in Directive 74/60/EEC; “non-rigid material” means a material which has a hardness of less than 50 shore A; “rigid material” means a material which has a hardness of no less than 50 shore A; “sharp edge” means an edge of rigid material having a radius of curvature of less than 2.5mm, except in the case of projections of less than 3.2mm from the panel. In this case, the minimum radius of curvature shall not apply provided that the height of the projection is not more than half its width and its edges are blunted; “special purpose” has the same meaning as in item 6; “specified zone” means the zone which— (a) is forward of the transverse plane of the torso reference line of the manikin as defined in paragraph 2.5 and appendix 1 of Annex 3 to Directive 77/649/EEC as last amended by Directive 90/630/EEC with the manikin positioned in the rearmost designated seating position; (b) is above the horizontal plane passing through the point 150mm above the lowest part of the top of the front seat cushions; and (c) is outside the areas defined by paragraphs 2.3.1, 2.3.2 and 2.3.3 of Annex I to Directive 74/60/EEC as last amended by Directive 78/632/EEC. | This item shall not apply to a goods vehicle. This item shall not apply to any area inside a motor caravan, an ambulance or a hearse which is not inside the head impact zone for any designated seating position. An armoured vehicle shall be exempted from any requirement of this item if it can be demonstrated to the satisfaction of the Secretary of State that it is impossible for the vehicle to comply due to its special purpose Paragraphs 1 and 2 shall not apply to any switches, controls or associated equipment designed for the use of a person with a disability and fitted in a disabled person’s vehicle Paragraph 4 shall not apply to any seat designed for a person with a disability and fitted in a disabled person’s vehicle Paragraph 5 shall not apply to— (a) any floor-mounted hand-brake control if, in the fully released position, no part of the control is in the specified zone; or (b) any hand-brake control mounted on or under the instrument panel, if in the fully released position, there is no possibility of the occupants of the vehicle contacting it in the event of a frontal impact. Paragraph 7 shall not apply to parts covered with a non-rigid material and the hood-frames of convertible vehicles. For opening roofs, the requirements shall apply to parts, including devices for opening, closing and adjusting the roof, with the roof in the closed position. Paragraph 1 (in so far as it relates to the surface of an instrument panel) and paragraph 2 shall not apply to a vehicle if— (a) it is a Schedule 2 vehicle but not one of the following classes— (i) an amateur-built vehicle; (ii) a vehicle manufactured using parts of a registered vehicle; (iii) a rebuilt vehicle; (b) it is fitted with air bags for the protection of the driver and the front seat passenger; and (c) those air bags were fitted at the time the vehicle was manufactured. |
| 18 | External projections | 1. The vehicle shall not be fitted with any mascot, emblem or other ornamental object unless it complies with the requirements of regulation 53 of the Construction and Use Regulations. 2. The radius of curvature of all hard parts on or protruding from the external surface of the vehicle and which can be contacted by a sphere of 100 mm diameter, shall be not less than 2.5 mm. 3. Headlamp visors and rims shall not project more than30 mm beyond the lens surface. 4. The ends of bumpers shall be turned inwards or recessed or integrated within the bodywork. 5. Handles, hinges, push buttons and fuel tank filler caps shall not project more than 40 mm from the external surface unless they cannot under any circumstance project beyond the extreme outer edge of the vehicle, in which case they may project by up to 50 mm from the external surface. All handles shall be enclosed in a protective surround or be recessed, unless they cannot in any circumstances project beyond the extreme outer edge of the vehicle. 6. The open ends of door handles which rotate parallel to the plane of the door shall be turned back towards the plane of the door. Such open ends shall be directed rearwards unless the handles cannot under any circumstances project beyond the extreme outer edge of the vehicle and at least one of the following requirements is met— (a)the open end of the handle is shielded to the front by a protective surround, or (b)the open end of the handle is recessed into the vehicle bodywork, or (c)the gap measured laterally between the open end of the handle and the vehicle body is no more than 2 mm when the handle is in its normal position with the door latched. 7. The open ends of handles which pivot outwards in any direction shall face either rearwards or downwards, unless they have an independent return mechanism and cannot project more than 15 mm from the external surface should the return mechanism fail. 8. Windows which open outwards from the external surface of the vehicle shall have no forward facing exposed edge and shall not project beyond the extreme outer edge of the vehicle. 9. No jacking bracket shall project by more than 10 mm beyond the vertical projection of the floor line lying directly above it. 10. No exhaust pipe shall project by more than 10 mm beyond the vertical projection of the floor line lying directly above it, unless it terminates in a rounded edge having a radius of curvature of no less than 2.5 mm. | For the purposes of this item—
| This item shall not apply to a goods vehicle. Those parts of a motor caravan, ambulance or hearse other than the driver’s cabin shall be exempted from any requirement of this item if it can be demonstrated to the satisfaction of the Secretary of State that it is impossible for the vehicle to comply due to its special purpose. An armoured vehicle shall be exempted from any requirement of this item if it can be demonstrated to the satisfaction of the Secretary of State that it is impossible for the vehicle to comply due to its special purpose. Paragraph 2 shall not apply to— (a) parts which protrude by less than 5.0 mm but by not less than 1.5 mm, if the outward facing angles of such parts are blunted and any parts which protrude by less than 1.5 mm; (b) grills such as air intakes, having gaps of not more than 40 mm but more than 25 mm, if they have radii of curvature of not less than 1 mm; and those having gaps of not more than 25 mm but more than 10 mm, if they have radii of curvature of not less than 0.5 mm; and those having gaps of not more than 10 mm; if they are blunted; (c) wind screen, head lamp and rear window wiper blades and supports, provided that they are blunted; (d) wheels, if there are no pointed or sharp features which projects beyond the external plane of the wheel rim, no wing nuts are fitted above the horizontal plane passing through the axis of rotation of the wheels, and there are no projections beyond the vehicle body plan form apart from tyres and wheel discs, (including central wheel securing nuts) if the latter have a radius of curvature of not less than 30 mm and do not project by more than 30 mm beyond the vehicle body plan-form; (e) sheet metal edges if they are folded back by about 180 degrees; (f) folds in body panels; (g) lateral air or rain deflectors, if their edges which are capable of being directed outwards have a radius of curvature of not less than 1 mm; and (h) in the case of a Schedule 2 vehicle other than— (i) an amateur-built vehicle; (ii) a vehicle manufactured using parts of a registered vehicle, or (iii) a rebuilt vehicle, any part of the external surface of the body (including without prejudice to the generality of this paragraph cosmetic features such as trim and badges) of the vehicle as originally manufactured, or as subsequently altered in a manner approved by the manufacturer, and which it is not reasonably practicable to remove. |
| 19 | Speed-ometers | 1. The vehicle shall be fitted with a speedometer capable of indicating speed in mph at uniform intervals not exceeding 20 mph at all speeds up to the maximum speed of the vehicle and capable of being read by the driver at all times of the day or night. 2. For all true speeds up to the design speed of the vehicle, the true speed shall not exceed the indicated speed. 3. For all true speeds of between 25 mph and 70 mph (or the maximum speed if lower), the difference between the indicated speed and the true speed shall not exceed— V/10 + 6.25 mph where V = the true speed of the vehicle in mph. | In this item “maximum speed” has the meaning given in regulation 3(2) of the Construction and Use Regulations. | This item shall not apply to vehicles having a maximum speed of less than 25 mph. |
| 20 | Wiper and washer system | 1. The vehicle shall be fitted with one or more wipers which when switched on, operate automatically to clear the windscreen of water so that the driver has an adequate view of the road ahead, both directly in front of the vehicle and in front of both sides of the vehicle, in wet weather. 2. The wiper or wipers shall have at least one operating frequency at which it or they shall operate continuously at no less than 45 cycles per minute. 3. The wiper blade or blades shall return automatically to a position of rest which shall be at or beyond the outer edge of the area swept by the wiper and shall be capable of being displaced from this position on the windscreen to allow for windscreen cleaning. 4. The vehicle shall be fitted with a windscreen washer system capable of cleaning, in conjunction with the wiper or wipers, the area of windscreen swept by the wiper or wipers. 5. When this system is actuated with the nozzles plugged, it shall be capable of withstanding the pressures produced. 6. The capacity of the liquid reservoir for this system shall not be less than 1 litre. | This item shall not apply to a goods vehicle. This item shall not apply to vehicles not equipped with a windscreen through which the driver must look to obtain an adequate view of the road ahead, both directly in front of the vehicle and in front of both sides of the vehicle, from all normal seating positions. | |
| 21 | Defrosting and demisting system | 1. The vehicle shall be equipped with a system for removing frost and ice from the glazed surfaces of the windscreen. This system shall be effective enough to ensure that the driver has an adequate view of the road ahead, both directly in front of the vehicle and in front of both sides of the vehicle, in cold weather. 2. The vehicle shall be equipped with a system for removing mist from the interior glazed surface of the windscreen. This system shall be effective enough to ensure that the driver has an adequate view of the road ahead, both directly in front of the vehicle and in front of both sides of the vehicle, in wet and humid weather. | This item shall not apply to a goods vehicle. This item shall not apply to vehicles not equipped with a windscreen through which the driver must look to obtain an adequate view of the road ahead, both directly in front of the vehicle and in front of both sides of the vehicle, from all normal seating positions. | |
| 22 | Fuel input | The vehicle shall be fitted with a fuel tank so constructed that it cannot readily be filled from a petrol pump delivery nozzle which has an external diameter of not less than 23.6mm without the aid of a device (such as a funnel) not fitted to the vehicle. | This item shall not apply to vehicles to which paragraph 2(c) or (d) in column 3 of item 4 (exhaust emissions) do not apply. | |
| 23 | Design weights | 1. The maximum gross weight of the vehicle shall be no less than the sum of the kerbside weight, and— (a)in the case of a vehicle other than a motor caravan, 75kg for each seat; and (b)in the case of a motor caravan, 85kg for each seat and 10kg for each metre of the total length of the vehicle. 2. For all vehicles— (a)the sum of the maximum permitted axle weights must not be less than the maximum gross weight of the vehicle; (b)when the vehicle is loaded to its maximum gross weight by placing a weight of 68kg in each seat and by distributing the remaining weight evenly in the areas designed to accommodate luggage (all in accordance with paragraph 2 of the Appendix to Directive 92/21/EEC as last amended by Directive 95/48/EC), the axle weight of each axle shall not exceed the maximum permitted axle weight; and (c)when the vehicle is loaded to its maximum gross weight, and at the same time, its rear axle is loaded to its maximum permitted axle weight, the front axle weight shall not be less than 30% of the maximum gross weight. | For the purposes of this item— “seat” means any seat, including the driver’s seat, designed for use while the vehicle is travelling on the road. | This item shall not apply to a goods vehicle. |
| 24 | General vehicle construction | 1. All aspects of the design and construction of the vehicle and its equipment which are not covered by other subject matters in this Schedule, shall be such that no danger is caused or likely to be caused to any person in the vehicle or on a road. 2. In particular, under all normal conditions likely to be encountered while the vehicle is being driven on a road, including when the vehicle is loaded to its maximum gross weight and the axle weight of any one axle equals its maximum permitted axle weight— (a)it shall be possible to control the vehicle safely, taking account of the vehicle’s speed and acceleration capabilities; (b)it shall at all times be possible for the driver, while controlling the vehicle, to have a full view of the road and traffic ahead of the vehicle; (c)the clearance between any of the following parts of the vehicle, namely the tyres, wheels, other rotating components associated with the transmission of engine power or braking, moveable parts of the steering mechanism and fixed parts shall be sufficient to ensure no risk of fouling and the wheels and wheel fixings shall be compatible; (d)the vehicle structure (chassis or integral chassis-body), shall be so designed and constructed as to withstand the forces and vibration to which it is likely to be subject; (e)all entries and exits provided for the vehicle occupants (other than doors) shall be so designed as to allow easy and safe use. (f)all aperture covers (other than doors) including tail gates, boot and bonnet lids, shall be capable of being securely latched in the fully closed position; (g)the steering, suspension, axles and wheels shall be so designed, constructed and fitted as to withstand the forces and vibration to which they are likely to be subject; (h)the fuel system, including the fuel tank, shall be so designed, constructed and fitted as to withstand the forces, vibration and corrosive environment to which it is likely to be subject. It shall also be so fitted as to avoid the risk of damage, such as abrasion, due to fouling of other parts, and to minimise the risk of fire in the event of any leakage of fuel. The fuel tank shall comply with regulation 39 of the Construction and Use Regulations, except that it need not be made of metal. (i)the electrical system, including the battery, electrical components and wires, shall be securely attached to the vehicle. In particular, the maximum distance between attachments of wires, except those contained within hollow components, shall be 300 mm and wires shall be so fitted and protected as to avoid the risk of damage to insulation, such as abrasion. All components shall be so constructed and fitted as to minimise the risk of corrosion and fire. | ||
| 25 | Plate for goods vehicles | Every goods vehicle shall comply with the requirements of paragraphs (2) and (3) of regulation 66 of the Construction and Use Regulations. |
Regulation 5(1)(b)
SCHEDULE 4APPROVAL REQUIREMENTS FOR RELEVANT VEHICLES EXCEPT SCHEDULE 2 VEHICLES
(The expressions in bold type are defined in column 4)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Subject matter | Design, construction and equipment requirements | Definitions and supplementary provisions | Exemptions and modifications | ||
(a) Date of manufacture of the vehicle | (b) Community Instrument | (c) ECE Regulation | ||||
| 3 | Protective steering | 1st July 1991 | Directive 74/297/EEC, annex 1, paragraphs 5 and 6 | ECE Regulation 12.01, paragraphs 5 and 6 | This item shall not apply to— (a) vehicles, the steering control of which has been specially constructed for the use of a person suffering from some physical defect or disability; (b) ambulances, motor caravans and hearses (in each case) having a maximum gross weight of more than 2,500 kg if the vehicle has been derived from a goods vehicle which either had a maximum gross weight of not less than 1,500 kg or was manufactured before 1st October 1997; and (c) armoured vehicles. | |
| 1st October 1996 | Directive 74/297/EEC as last amended by Directive 91/662/EEC, annex 1, paragraphs 5 and 6 | ECE Regulation 12.03, paragraphs 5 and 6 | ||||
| 4 | Exhaust emissions | 1st January 1993 | Directive 70/220/EEC as last amended by: Directive 91/441/EEC, annex 1, paragraphs 5, 7 and 8 (applies only to passenger cars) | ECE Regulation 83.01, paragraphs 5, 8 amd 13 | For the purposes of this item—
| |
| 1st October 1994 | Directive 93/59/EEC, annex 1, paragraphs 5, 7 and 8 (applies only to vehicles other than passenger cars) | ECE Regulation 83.01, paragraphs 5, 8 and 13 | ||||
| 1st January 1997 | Directive 94/12/EC, annex 1, paragraph 5 (applies only to passenger cars) | ECE Regulation 83.02, paragraph 5 | “Reference mass” has the same meaning as in Directive 70/220/EEC as last amended by Directive 96/69/EC. | |||
| 1st October 1997 (applies from this date to Class I vehicles) | Directive 96/69/EC, annex 1, paragraph 5 | ECE Regulation 83.03, paragraph 5 | “Class I vehicle” means a goods vehicle (category N1) which has a reference mass not exceeding 1,250 kg (1,305 kg from 1st January 2001). | |||
| 1st October 1998 (applies from this date to vehicles of category M1 other than passenger cars, Class II and Class III vehicles) | “ | “ | “Class II vehicle” means a goods vehicle (category N1) which has a reference mass exceeding 1,250 kg (1,305 kg from 2001) but not exceeding 1,700 kg (1,760 kg from 2001). | |||
| 1st October 1999 | Directive 98/77/EC, annex 1, paragraph 5 (applies to vehicles fuelled by liquid petroleum gas or compressed natural gas) | ECE Regulation 83.04, paragraph 5 | “Class III vehicle” means a goods vehicle (category N1) which has a reference mass exceeding 1,700 kg (1,760 kg from 2001). | |||
| 1st January 2001 (applies from this date to passenger cars and Class I vehicles) | Directive 98/69/EC, annex 1, paragraph 5 (Phase I limits) | Does not apply until 1st January 2002 providing the vehicle is registered before that date. | ||||
| 1st January 2002 (applies from this date to vehicles of category M1 other than passenger cars, Class II and Class III vehicles) | “ | “Diesel passenger vehicle” means a vehicle of category M1 the maximum mass of which exceeds 2,000 kg, fitted with a compression ignition engine, and which is: | Does not apply until 1st January 2003 providing the vehicle is registered before that date. | |||
| 1st January 2003 (until this date, a diesel passenger vehicle is treated as a vehicle of category N1) | “ | (a)construct-ed or adapted to carry more than 6 occupants including the driver, or (b)an off-road vehicle as defined in Annex II to the 1970 Directive. | ||||
| 1st January 2006 (applies from this date to passenger cars and Class I vehicles) 1st January 2007 (applies from this date to vehicles of category M1 other than passenger cars, Class II and Class III vehicles) | Directive 98/69/EC annex 1, paragraph 5 (Phase 2 limits) “ | |||||
| 8 | Anti-theft devices | 1st October 1998 | Directive 74/61/EEC as last amended by Directive 95/56/EC, annex V (electronic immobiliser) and annex VI (alarm system) | ECE Regulation 18.02, paragraph 7 and ECE Regulation 97.01 paragraphs 5,6 and 7 (alarm system) and paragraphs 31, 32 and 33 (immobiliser) | ||
| 10 | Seat belt anchorages | Directive 76/115/EEC as last amended by: | ||||
| 1st July 1991 | Directive 82/318/EEC, annex 1, paragraphs 4 and 5 | ECE Regulation 14.02, paragraphs 5, 6 and 7 | ||||
| 1st July 1997 | Directive 90/629/EEC, annex 1, paragraphs 4 and 5 | ECE Regulation 14.03, paragraphs 5, 6 and 7 | ||||
| 11 | Installation of seat belts | 1st July 1997 | Directive 77/541/EEC as last amended by: Directive 90/628/EEC, annex 1, paragraphs 3.1 to 3.1.9 | “disabled person’s belt” has the same meaning as in regulation 47(8) of the Construction and Use Regulations. | The requirements shall not apply in relation to a seat fitted to a disabled person’s vehicle if the vehicle is fitted with a disabled person’s belt for that seat. | |
| 1st October 1999 | Directive 96/36/EC, annex 1, paragraphs 3.1 to 3.1.10 and 3.1.11 and 3.1.12 | ECE Regulation 16.04, (Supplement 8) paragraphs 8.1 to 8.1.10.3 and 8.1.11 to 8.1.12 | ||||
| 12 | Brakes | Directive 71/320/EEC as last amended by: | ||||
1st April 1995 1st October 1999 | Directive 91/442/EEC, annex 1, paragraph 2 Directive 98/12/EC, annex 1, paragraph 2.1.1.3 (Requirements for asbestos-free brake linings only) | ECE Regulation 13.06 paragraph 5 ECE Regulation 13.09, paragraph 5.1.1.3 or ECE Regulation 13H, paragraph 5.1.1.3 (Requirements for asbestos-free brake linings only) | ||||
| 31st March 2001 | Directive 98/12/EC, annex 1, paragraph 2 (All requirements) | ECE Regulation 13.09, paragraph 5 or ECE Regulation 13H, paragraph 5 (All requirements) | ||||
| 13 | Noise and silencers | 1st July 1991 | Directive 70/157/EEC as last amended by: Directive 84/424/EEC, annex 1, paragraph 5 | ECE Regulation 51.01, paragraph 5 | ||
| 1st January 1997 | Directive 92/97/EEC or Directive 96/20/EC, annex 1, paragraph 5 | ECE Regulation 51.02, paragraph 5 | ||||
| 26 | Carbon dioxide emissions and fuel consumption | 1st January 1997 | Directive 80/1269/EEC as last amended by Directive 93/116/EC, annex 1, paragraph 5 | ECE Regulation 101, paragraph 5 | ||
| 27 | Frontal impact | 1st October 2003 | Directive 96/79/EC, annex 2, paragraph 3 | ECE Regulation 94.01, paragraph 5 | ||
| 28 | Side impact | 1st October 2003 | Directive 96/27/EC, annex 2, paragraph 3 | ECE Regulation 95.01, paragraph 5 | ||
Regulation 11
SCHEDULE 5FORM OF APPROVAL CERTIFICATE
Regulation 3(6)
SCHEDULE 6COMMUNITY INSTRUMENTS AND ECE REGULATIONS
PART I
References to Community Instruments
1.—(1) The Directives referred to in these Regulations are set out in Part II of this Schedule; those marked with an asterisk are Commission Directives, those marked with a cross are Directives of the European Parliament and the Council and the other Directives are Council Directives.
(2) A reference in these Regulations to a Directive shown in column 2 of Part II of this Schedule as last amended by a Directive shown in column 3 against that Directive shall be read as follows.
(3) The reference shall be read as a reference to the Directive shown in column 2 as amended by the Directives shown in column 3 against that Directive down as far as (and including) the Directive referred to as the last amending Directive.
2.—(1) For the purposes of these Regulations, where a vehicle does not comply with an item in Schedule 3 or 4 of these Regulations, it shall nevertheless be regarded as complying with that item if—
(a)that item contains a reference to a Directive (“the base Directive”) not followed by the words “as last amended by”; and
(b)the vehicle would comply with that item were there substituted for that reference, a reference to the base Directive as last amended by a Directive shown against the base Directive in column 3 of Part II of this Schedule.
(2) For the purposes of these Regulations, where a vehicle does not comply with an item in Schedule 3 or 4 of these Regulations, it shall nevertheless be regarded as complying with that item if—
(a)that item contains a reference to a Directive (“the base Directive”) as last amended by another Directive (“the amending Directive”); and
(b)the vehicle would comply with that item were there substituted for that reference, a reference to the base Directive as last amended by a Directive shown—
(i)against the base Directive, and
(ii)below the amending Directive in column 3 of Part II of this Schedule.
References to ECE Regulations
3.—(1) A reference in these Regulations to an ECE Regulation followed by a number which is not itself followed by a full-stop and 2 digits (for example “ECE Regulation 30”) shall be read as a reference to the ECE Regulation of that number which came into force on the date shown against that number in column (4) of Part III of this Schedule.
(2) A reference in these Regulations to an ECE Regulation followed by a number which is itself followed by a full-stop and 2 digits (for example “ECE Regulation 30.01”) shall be read as a reference to the ECE Regulation of that number with the amendments in force on the dates shown against the number in column (4) of Part III of this Schedule.
4.—(1) For the purposes of these Regulations, where a vehicle does not comply with an item in Schedule 3 or 4 of these Regulations, it shall nevertheless be regarded as complying with that item if—
(a)that item contains a reference to an ECE Regulation (“the base Regulation”) that is not followed by a full-stop and 2 digits; and
(b)the vehicle would comply with that item were there substituted for that reference, a reference to an entry in column (3) of Part III of this Schedule shown against that Regulation.
(2) For the purposes of these Regulations, where a vehicle does not comply with an item in Schedule 3 or 4 of these Regulations, it shall nevertheless be regarded as complying with that item if—
(a)that item contains a reference to an ECE Regulation (“the base Regulation”) that is followed by a full-stop and 2 digits; and
(b)the vehicle would comply with that item were there substituted for that reference, a reference to an entry in column 3 of Part III of this Schedule shown—
(i)against that Regulation, and
(ii)below the entry in that column for that ECE Regulation and those 2 digits.
5. In these Regulations, “ECE Regulation” means a Regulation annexed to the Agreement concerning the adoption of uniform conditions of approval for motor vehicle equipment and parts and reciprocal recognition thereof concluded at Geneva on 20th March 1958(17) as amended(18) to which the United Kingdom is a party(19).
PART IIREFERENCES TO COMMUNITY DIRECTIVES
References in Schedule 3
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject matter of Directive | Principal Directive | Amending Directive | Official Journal reference |
| Radio interference suppression | 72/245/EEC | L152, 6.7.72, p. 15 | |
| 89/491/EEC* | L238, 15.8.89, p. 43 | ||
| 95/54/EC | L226, 8.11.95, p. 1 | ||
| Protective steering | 74/297/EEC | L165, 20.6.74, p. 16 | |
| 91/662/EEC* | L366, 31.12.91, p. 1 | ||
| Diesel smoke | 72/306/EEC | L190, 20.8.72, p. 1 | |
| 97/20/EC* | L125, 16.5.97, p. 21 | ||
| Roadworthiness | 77/143/EEC | L47, 18.2.77, p. 47 | |
| 88/449/EEC | L222, 12.8.88, p. 10 | ||
| 91/225/EEC | L103, 24.4.91, p. 3 | ||
| 91/328/EEC | L178, 6.7.91, p. 29 | ||
| 92/55/EEC | L225, 10.8.92, p. 68 | ||
| Rear view mirrors | 71/127/EEC | L68, 22.3.71, p. 1 | |
| 79/795/EEC* | L239, 22.9.79, p. 1 | ||
| 85/205/EEC* | L90, 29.3.85, p. 1 | ||
| 86/562/EEC* | L327, 02.11.86, p. 49 | ||
| 88/321/EEC* | L147, 14.6.88, p. 77 | ||
| Seat belt anchorages | 76/115/EEC | L24, 30.1.76, p. 6 | |
| 81/575/EEC | L209, 29.7.81, p. 30 | ||
| 82/318/EEC* | L139, 19.5.82, p. 9 | ||
| 90/629/EEC* | L341, 6.12.90, p. 14 | ||
| 96/38/EC* | L187, 26.7.96, p. 95 | ||
| Seat belts | 77/541/EEC | L220, 29.8.77, p. 95 | |
| 81/576/EEC | L209, 29.7.81, p. 32 | ||
| 82/319/EEC* | L139, 19.5.82, p. 17 | ||
| 90/628/EEC* | L341, 6.12.90, p. 1 | ||
| 96/36/EC* | L178. 17.7.96, p. 15 | ||
| Braking | 71/320/EEC | L202, 6.9.71, p. 37 | |
| 74/132/EEC* | L74, 19.3.74, p. 7 | ||
| 75/524/EEC* | L236, 8.9.75, p. 3 | ||
| 79/489/EEC* | L128, 26.5.79, p. 12 | ||
| 85/647/EEC* | L38, 31.12.85, p. 1 | ||
| 88/194/EEC* | L92, 9.4.88, p. 47 | ||
| 91/422/EEC* | L233, 22.9.91. p. 21 | ||
| 98/12/EC* | L81, 18.3.98, p. 1 | ||
| Braking of 2/3 wheeled vehicles | 93/14/EEC | L121, 15.5.93, p. 1 | |
| Seat strength | 74/408/EEC | L221, 12.8.74, p. 1 | |
| 81/577/EEC | L209, 29.7.81, p. 34 | ||
| 96/37/EC* | L187, 25.7.96, p. 28 | ||
| Tyres | 92/23/EEC | L129, 14.5.92, p. 95 | |
| Interior fittings | 74/60/EEC | L38, 11.2.74, p. 2 | |
| 78/632/EEC* | L206, 29.7.68, p. 26 | ||
| Forward vision | 77/649/EEC | L267, 19.10.77, p. 1 | |
| 81/643/EEC* | L231, 15.8.81, p. 41 | ||
| 88/366/EEC* | L181, 12.7.88, p. 40 | ||
| 90/630/EEC* | L341, 6.12.90, p. 20 | ||
| External projections | 74/483/EEC | L266, 2.10.74, p. 4 | |
| 79/488/EEC* | L128, 26.5.79, p. 1 | ||
| Masses and dimensions | 92/21/EEC | L129, 14.5.92, p. 1 | |
| 95/48/EEC* | L233, 30.9.95, p. 73 |
References in Schedule 4
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject matter of Directive | Principal Directive | Amending Directive | Official Journal reference |
| Protective steering | 74/297/EEC | L165, 20.6.74, p. 16 | |
| 91/662/EEC* | L366, 31.12.91, p. 1 | ||
| Exhaust emissions | 70/220/EEC | L76, 6.4.70, p. 1 | |
| 91/441/EEC | L242, 30.8.91, p. 1 | ||
| 93/59/EEC | L186, 28.7.93, p. 21 | ||
| 94/12/EC+ | L100, 19.4.94, p. 42 | ||
| 96/69/EC+ | L282, 1.11.96, p. 64 | ||
| 98/77/EC+ | L286, 23.10.98, p. 34 | ||
| 98/69/EC+ | L350, 28.12.98, p. 1 | ||
| Anti-theft devices | 74/61/EEC | L38, 11.2.70, p. 22 | |
| 95/56/EC* | L286, 29.11.95, p. 1 | ||
| Seat belt anchorages | 76/115/EEC | L24, 30.1.76, p. 1 | |
| 82/318/EEC* | L139, 19.5.82, p. 9 | ||
| 90/629/EEC* | L341, 6.12.90, p. 14 | ||
| 96/38/EC* | L187, 26.7.96, p. 95 | ||
| Seat belts | 77/541/EEC | L220, 29.8.77, p. 45 | |
| 90/628/EEC | L341, 6.12.90, p. 1 | ||
| 96/36/EC* | L178, 17.7.90, p. 15 | ||
| Braking | 71/320/EEC | L202, 6.9.71, p. 37 | |
| 91/422/EEC* | L238, 27.8.91, p. 25 | ||
| 98/12/EC* | L81, 18.3.98, p. 1 | ||
| Noise and silencers | 70/157/EEC | L42, 23.2.70, p. 16 | |
| 84/424/EEC | L238, 6.9.84, p. 31 | ||
| 92/97/EEC | L371, 19.12.92, p. 1 | ||
| Carbon dioxide emissions and fuel consumption | 80/1268/EEC | L375, 31.12.80, p. 46 | |
| 93/116/EC* | L329, 30.12.93, p. 39 | ||
| Frontal impact | 96/79/EC+ | L18, 21.1.97, p. 7 | |
| Side impact | 96/27/EC+ | L169, 8.7.96, p. 1 |
PART IIIREFERENCES TO ECE REGULATIONS
References in Schedule 3
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject matter of Regulation | ECE Regulation | Amending Series | Date |
| Radio interference suppression | 10 | 17 Dec 1968 | |
| 10.01 | 23 June 1978 | ||
| 10.02 | 3 Sept 1997 | ||
| Rear reflectors | 3 | 1 Nov 1963 | |
| 3.01 | 18 Aug 1982 | ||
| 3.02 | 11 July 1985 | ||
| Rear view mirrors | 46 | 29 Sept 1975 | |
| 46.01 | 5 Oct 1987 | ||
| Tyres | 30 | 1 April 1975 | |
| 30.01 | 10 Oct 1977 | ||
| 30.02 | 21 April 1981 |
References in Schedule 4
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject matter of Regulation | ECE Regulation | Amending Series | Date |
| Protective steering | 12 | 1 June 1969 | |
| 12.01 | 8 Oct 1980 | ||
| 12.02 | 14 Nov 1982 | ||
| 12.03 | 24 Aug 1993 | ||
| Exhaust emissions | 83 | 5 Nov 1989 | |
| 83.01 | 30 Dec 1992 | ||
| 83.02 | 7 Dec 1996 | ||
| 83.04 | 13 Nov 1999 | ||
| Anti-theft devices | 18 | 1 March 1971 | |
| 18.02 | 3 Sept 1997 | ||
| Alarm systems | 97 | 1 Jan 1996 | |
| 97.01 | 13 Jan 2000 | ||
| Seat belt anchorages | 14 | 1 April 1970 | |
| 14.02 | 22 Nov 1984 | ||
| 14.03 | 29 Jan 1992 | ||
| 14.04 | 18 Jan 1998 | ||
| 14.05 | 4 Feb 1999 | ||
| Seat belts | 16 | 1 Dec 1970 | |
| 16.04 | 22 Dec 1985 | ||
| Braking | 13 | 1 June 1970 | |
| 13.06 | 22 Nov 1990 | ||
| 13.07 | 18 Sep 1994 | ||
| 13.08 | 26 March 1995 | ||
| 13.09 | 28 Aug 1996 | ||
| 13H | 11 May 1998 | ||
| Noise and silencers | 51 | 15 July 1982 | |
| 51.01 | 27 April 1988 | ||
| 51.02 | 18 April 1995 | ||
| Carbon dioxide emissions from fuel consumption | 101 | 1 Jan 1997 | |
| Frontal impact | 94 | 1 Oct 1995 | |
| 94.01 | 2 Aug 1998 | ||
| Side impact | 95 | 6 July 1995 | |
| 95.01 | 12 Aug 1998 |
Explanatory Note
(This note is not part of the Regulations)
These Regulations, which replace the Motor Vehicles (Approval) Regulations 1996 as amended, establish a revised system for approving the construction of single vehicles before they enter into service.
The Regulations apply to passenger vehicles and dual-purpose vehicles constructed to carry no more than 8 passengers excluding the driver (equivalent to EC category M1), certain 3 wheeled vehicles having a maximum unladen weight of more than 410 kg (ie not motorcycles), light goods vehicles (maximum gross weight not exceeding 3,500 kg, equivalent to EC category N1) and certain other goods vehicles with a design gross weight not exceeding 5,500 kg.
Part II concerns the approval requirements. Regulation 4 defines the vehicles to which the Regulations apply by reference to the regulations concerning national (Great Britain) type approval. Regulation 5 specifies two sets of approval requirements, namely basic requirements (Schedule 3) and, as from 1st August 2001, enhanced requirements (Schedule 4). However, the special classes of vehicle specified in Schedule 2 need only comply with the basic requirements and certain basic and enhanced requirements do not apply to goods vehicles. Regulation 5(3) allows persons applying for the approval of any vehicle of category M1 which would not otherwise be subject to the enhanced requirements to opt for them to be subject to those requirements. Regulation 5(8) provides for the recognition of equivalent approvals granted in other EEA States.
Part III deals with administrative arrangements. Regulation 6 relates to applications to the Secretary of State for a Minister’s approval certificate and regulation 7 provides for the assignment of vehicle identification numbers to vehicles not having a number which meets the requirements specified in regulation 7(1).
Regulation 8 specifies criteria for determining design weights. The procedure for appeals under section 60 by persons aggrieved by a determination made on behalf of the Secretary of State following an application under regulation 6 is governed by regulation 9. Provision is made in regulation 10 for an application or appeal to be refused without an examination of the vehicle to which the application relates in the circumstances specified in regulation 10(2).
The form of a Minister’s approval certificate is prescribed by regulation 11 and Schedule 5. Regulation 12 provides for the provision of replacement certificates. Regulation 13 requires notices under the Regulations generally to be given in writing and permits them to be given by post.
Regulation 14 specifies the dates appointed for the purposes of section 63(1) of the Road Traffic Act 1988, on or after which it is an offence to use a vehicle of a relevant class without the appropriate certificate in force under sections 54 to 58 of that Act. Regulations 14(2) to (4) and (8) disapply this requirement in respect of specified types of vehicle or types of use.
Regulation 14(5) specifies 1st February 2001 as the day appointed for all other vehicles to which these Regulations apply which are not of a class for which a day had previously been appointed.
Regulation 15 provides that a licence under the Vehicles Excise and Registration Act 1994 is not to be granted in respect of a vehicle to which regulation 14 applies unless, in the first application made for it after the relevant appointed day, there is produced evidence that a certificate (or certificates) is in force for the vehicle under sections 54 to 58 of the 1988 Act from which it appears that the vehicle complies with the approval requirements.
These Regulations have been notified to the European Commission and the other Member States in accordance with Directive 98/34/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ No. L204, 21.7.98, p.37), as amended by Directive 98/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ No. L217, 5.8.98, p.18).
1988 c. 52; section 61 was amended by the Road Traffic Act 1991 (c. 40), Schedule 8 and section 63 was amended by S.I. 1992/3107.
O.J.L42.23.02.70,p.1.
O.J.L91.25.03.98,p.1.
S.I.1982/1271; relevant amending instruments are S.I.1987/1508,1988/1523, 1989/1579, 1991/1021, 1992/25, 1342 and 3084, 1993/2200 and 1995/1323.
S.I. 1984/981; relevant amending instruments are S.I. 1984/1761, 1987/1509, 1988/1522, 1989/1580, 1991/1022, 1992/1341, 2161 and 2908, 1993/2201 and 1995/1322.
S.I. 1986/1078; relevant amending instruments are S.I. 1987/676 and 1333, 1988/1178, 1989/1478, 1990/2212, 1992/2016, 3088 and 3285 and 1994/3270.
Cmnd. 2972 and 2183.
S.I. 1989/1796; the relevant amending instrument is S.I. 1994/2280.
S.I. 1996/3013; relevant amending instruments are set out in Schedule 1.
O.J.L24, 18.12.75, p.1.
O.J. L155 19.05.78, p.31.
1952 c. 67. See sections 10 and 12.
Cmnd. 2535.
Cmnd. 3562.
By an instrument of accession dated 14th January 1963 deposited with the Secretary General of the United Nations on 15th January 1963.