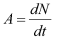Regulation 4
SCHEDULEDIRECTIVE DEFINITIONS
Activity (A): the activity, A, of an amount of a radionuclide in a particular energy state at a given time is the quotient of dN by dt, where dN is the expectation value of the number of spontaneous nuclear transitions from that energy state in the time interval dt:
the unit of activity is the becquerel.
Apprentice: a person receiving training or instruction within an undertaking with a view to exercising a specific skill.
Artificial sources: radiation sources other than natural radiation sources.
Becquerel (Bq): is the special name of the unit of activity. One becquerel is equivalent to one transition per second:
1 Bq = 1 s-1.
Dose limits: maximum references laid down in Title IV for the doses resulting from the exposure of workers, apprentices and students and members of the public to ionizing radiation covered by this Directive that apply to the sum of the relevant doses from external exposures in the specified period and the 50-year committed doses (up to age 70 for children) from intakes in the same period.
Emergency exposure: an exposure of individuals implementing the necessary rapid action to bring help to endangered individuals, prevent exposure of a large number of people or save a valuable installation or goods, whereby one of the individual dose limits equal to that laid down for exposed workers could be exceeded. Emergency exposure shall apply only to volunteers.
Exposed workers: persons, either self-employed or working for an employer, subject to an exposure incurred at work from practices covered by this Directive and liable to result in doses exceeding one or other of the dose levels equal to the dose limits for members of the public.
Exposure: the process of being exposed to ionizing radiation.
Health detriment: an estimate of the risk of reduction in length and quality of life occurring in a population following exposure to ionizing radiations. This includes loss arising from somatic effects, cancer and severe genetic disorder.
Intake: the activities of radionuclides entering the body from the external environment.
Intervention: a human activity that prevents or decreases the exposure of individuals to radiation from sources which are not part of a practice or which are out of control, by acting on sources, transmission pathways and individuals themselves.
Ionizing radiation: the transfer of energy in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves of a wavelength of 100 nanometers or less or a frequency of 3 x 1015 Hertz or more capable of producing ions directly or indirectly.
Members of the public: individuals in the population, excluding exposed workers, apprentices and students during their working hours and individuals during the exposures referred to in Article 6(4)(a), (b) and (c).
Natural radiation sources: sources of ionizing radiation from natural terrestrial or cosmic origin.
Practice: a human activity that can increase the exposure of individuals to radiation from an artificial source, or from a natural radiation source where natural radionuclides are processed for their radioactive, fissile or fertile properties, except in the case of an emergency exposure.
Radioactive substance: any substance that contains one or more radionuclides the activity or concentration of which cannot be disregarded as far as radiation protection is concerned.
Radiological emergency: a situation that requires urgent action in order to protect workers, members of the public or the population either partially or as a whole.
Source: an apparatus, a radioactive substance or an installation capable of emitting ionizing radiation or radioactive substances.
Undertaking: any natural or legal person who carries out the practices or work activities referred to in Article 2 of this Directive and who has the legal responsibility under national law for such practices or work activities.