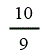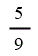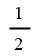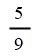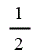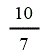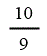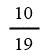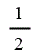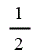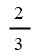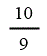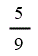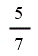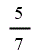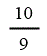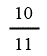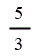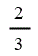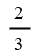- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (20/07/2018)
- Original (As made)
The Renewables Obligation Order 2015
You are here:
- UK Statutory Instruments
- 2015 No. 1947
- SCHEDULE 5
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Status:
Point in time view as at 20/07/2018.
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects for the The Renewables Obligation Order 2015, SCHEDULE 5.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
Articles 14, 32, 33, 34, 35,36, 37, 42 and 57
SCHEDULE 5E+WELECTRICITY TO BE STATED IN ROCs
Article 36
PART 1E+WINTERPRETATION
1.—(1) In this Schedule—E+W
“2009/11 dedicated biomass station” means a generating station which has, in any month after March 2009 and before November 2011, generated electricity—
only from biomass, and
in respect of which ROCs were issued for all or part of the electricity so generated during that month;
“AD” means electricity generated from gas formed by the anaerobic digestion of material which is neither sewage nor material in a landfill;
“advanced gasification/pyrolysis” means electricity generated from an advanced fuel which—
in the case of a gaseous fuel, has a gross calorific value of at least 4 megajoules per metre cubed at 25 degrees Celsius and 0.1 megapascals when measured at the inlet to the generating station, and
in the case of a liquid fuel, has a gross calorific value of at least 10 megajoules per kilogram at 25 degrees Celsius and 0.1 megapascals when measured at the inlet to the generating station;
“building mounted solar PV” means electricity generated from the direct conversion of sunlight into electricity by equipment not installed on the ground either—
directly, or
on a frame, plinth or other structure installed—
on the ground, and
wholly or mainly for the purpose of supporting that equipment;
“closed landfill gas” means electricity generated—
from landfill gas (other than electricity generated using the heat from a turbine or engine), and
in a month in which the generating station generates electricity only from gas formed by the digestion of material in a landfill which has finally ceased to accept waste for disposal;
“co-firing of regular bioliquid” means electricity generated from regular bioliquid burned in a combustion unit in a month in which—
the energy content of the biomass burned in that combustion unit is less than 100% of the energy content of all of the energy sources burned in that combustion unit during that month, and
the generating station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources;
“co-firing of regular bioliquid with CHP” means electricity generated from regular bioliquid burned by a qualifying CHP station in a combustion unit in a month in which—
the energy content of the biomass burned in that combustion unit is less than 100% of the energy content of all of the energy sources burned in that combustion unit during that month,
the station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources, and
the fossil fuel and regular bioliquid have been burned in separate combustion units;
“dedicated biomass” means electricity generated from regular bioliquid or regular biomass by a generating station—
which is not a relevant fossil fuel station, and
in a month in which it generates electricity only from biomass;
“dedicated biomass with CHP” means electricity generated from regular bioliquid or regular biomass by a qualifying CHP station—
which is not a relevant fossil fuel station, and
in a month in which it generates electricity only from biomass;
“dedicated energy crops” means electricity generated from energy crops by a generating station—
which is not a relevant fossil fuel station, and
in a month in which the station generates electricity only from energy crops or only from biomass;
“energy from waste with CHP” means electricity generated from the combustion of waste (other than an advanced fuel or a fuel produced by means of anaerobic digestion) in a qualifying CHP station in a month in which the station generates electricity only from renewable sources and those renewable sources include waste which is not biomass;
“geopressure” means electricity generated using naturally occurring subterranean pressure;
“geothermal” means electricity generated using naturally occurring subterranean heat;
“ground mounted solar PV” means electricity generated from the direct conversion of sunlight into electricity by equipment installed on the ground either—
directly, or
on a frame, plinth or other structure installed—
on the ground, and
wholly or mainly for the purpose of supporting that equipment;
“high-range co-firing” means electricity generated from energy crops or regular biomass burned in a combustion unit in a month in which—
the energy content of the biomass burned in that combustion unit is at least 85% but is less than 100% of the energy content of all of the energy sources burned in that combustion unit during that month, and
the generating station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources;
“high-range co-firing with CHP” means electricity generated from energy crops or regular biomass burned by a qualifying CHP station in a combustion unit in a month in which—
the energy content of the biomass burned in that combustion unit is at least 85% but is less than 100% of the energy content of all of the energy sources burned in that combustion unit during that month,
the station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources, and
the fossil fuel has been burned in a separate combustion unit from the energy crops or regular biomass;
“hydroelectric” means electricity generated by a hydro generating station;
“landfill gas heat recovery” means electricity generated using the heat from a turbine or engine, where that turbine or engine is generating electricity from landfill gas;
“low-range co-firing” means electricity generated from energy crops or regular biomass burned in a combustion unit in a month in which—
the energy content of the biomass burned in that combustion unit is less than 50% of the energy content of all of the energy sources burned in that combustion unit during that month, and
the generating station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources;
“low-range co-firing with CHP” means electricity generated from energy crops or regular biomass burned by a qualifying CHP station in a combustion unit in a month in which—
the energy content of the biomass burned in that combustion unit is less than 50% of the energy content of all of the energy sources burned in that combustion unit during that month,
the station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources, and
the fossil fuel has been burned in a separate combustion unit from the energy crops or regular biomass;
“mid-range co-firing” means electricity generated from energy crops or regular biomass burned in a combustion unit in a month in which—
the energy content of the biomass burned in that combustion unit is at least 50% but is less than 85% of the energy content of all of the energy sources burned in that combustion unit during that month, and
the generating station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources;
“mid-range co-firing with CHP” means electricity generated from energy crops or regular biomass burned by a qualifying CHP station in a combustion unit in a month in which—
the energy content of the biomass burned in that combustion unit is at least 50% but is less than 85% of the energy content of all of the energy sources burned in that combustion unit during that month,
the station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources, and
the fossil fuel has been burned in a separate combustion unit from the energy crops or regular biomass;
“offshore wind” means electricity generated from wind by a generating station that is offshore;
“onshore wind” means electricity generated from wind by a generating station that is not offshore;
“regular bioliquid” means bioliquid other than—
advanced fuel,
fuel produced by means of anaerobic digestion,
energy crops;
“regular biomass” means biomass other than—
advanced fuel,
fuel produced by means of anaerobic digestion,
bioliquid,
energy crops,
landfill gas,
sewage gas;
“relevant fossil fuel CHP station” means a relevant fossil fuel station which is a qualifying CHP station;
“relevant fossil fuel station” means—
a generating station—
which is not a 2009/11 dedicated biomass station, and
which has, in any 6 month period since it was first commissioned, generated electricity from fossil fuel, where the energy content of the fossil fuel was more than 15% of the energy content of all of the energy sources used by the station to generate electricity during that 6 month period, or
a generating station—
which is a 2009/11 dedicated biomass station, and
which has, in any 6 month period since 1st November 2011, generated electricity from fossil fuel, where the energy content of the fossil fuel was more than 15% of the energy content of all of the energy sources used by the station to generate electricity during that 6 month period;
“solar photovoltaic” means electricity generated from the direct conversion of sunlight into electricity;
“standard gasification/pyrolysis” means electricity generated from an advanced fuel which—
in the case of a gaseous fuel, has a gross calorific value which is at least 2 megajoules per metre cubed but is less than 4 megajoules per metre cubed at 25 degrees Celsius and 0.1 megapascals when measured at the inlet to the generating station, and
in the case of a liquid fuel, has a gross calorific value which is less than 10 megajoules per kilogram at 25 degrees Celsius and 0.1 megapascals when measured at the inlet to the generating station;
“station conversion” means electricity generated—
from regular bioliquids, energy crops or regular biomass,
by a relevant fossil fuel station, and
in a month in which the station generates electricity only from biomass or only from energy crops;
“station conversion with CHP” means electricity generated—
from regular bioliquids, energy crops or regular biomass,
by a relevant fossil fuel CHP station, and
in a month in which the station generates electricity only from biomass or only from energy crops;
“tidal impoundment” means electricity generated by a generating station driven by the release of water impounded behind a barrier using the difference in tidal levels where the station has a declared net capacity of less than 1 gigawatt;
“tidal stream” means electricity generated from the capture of the energy created from the motion of naturally occurring tidal currents in water;
“unit conversion” means electricity generated from regular bioliquids, energy crops or regular biomass burned in a combustion unit in a month in which—
that combustion unit burns only biomass or burns only energy crops, and
the generating station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources;
“unit conversion with CHP” means electricity generated from regular bioliquids, energy crops or regular biomass burned by a qualifying CHP station in a combustion unit in a month in which—
that combustion unit burns only biomass or burns only energy crops, and
the station generates electricity partly from fossil fuel and partly from renewable sources;
“wave” means electricity generated from the capture of the energy created from the motion of naturally occurring waves on water.
(2) For the purposes of this Schedule—
(a)fossil fuel does not include waste which is a renewable source;
(b)in determining how electricity has been generated, no account is to be taken of any fossil fuel or waste which a generating station uses for permitted ancillary purposes;
(c)in determining the energy content of the energy sources used by a generating station to generate electricity, no account is to be taken of any fossil fuel or waste which the station uses for permitted ancillary purposes; and
(d)in determining the energy content of the energy sources burned in a combustion unit, no account is to be taken of any fossil fuel or waste which is used in that combustion unit for permitted ancillary purposes.
Article 33
PART 2E+WAMOUNT OF ELECTRICITY TO BE STATED IN ROCs ISSUED FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATED USING PRE-2013 CAPACITY
| Way of generating electricity | Amount of electricity (in megawatt hours) to be stated in a ROC issued for electricity generated using pre-2013 capacity |
|---|---|
| AD | |
| Advanced gasification/pyrolysis | |
| Co-firing of regular bioliquid | 2 |
| Dedicated biomass | |
| Dedicated energy crops | |
| Electricity generated from landfill gas | 4 |
| Electricity generated from sewage gas | 2 |
| Energy from waste with CHP | 1 |
| Geopressure | 1 |
| Geothermal | |
| High-range co-firing | |
| Hydroelectric | 1 |
| Low-range co-firing | 2 |
| Mid-range co-firing | |
| Offshore wind | |
| Onshore wind | 1 |
| Solar photovoltaic | |
| Standard gasification/pyrolysis | 1 |
| Station conversion | 1 |
| Tidal impoundment | |
| Tidal stream | |
| Unit conversion | 1 |
| Wave |
Articles 33 and 42
PART 3E+WAMOUNT OF ELECTRICITY TO BE STATED IN ROCs ISSUED FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATED USING 2013/14 CAPACITY, 2014/15 CAPACITY, 2015/16 CAPACITY OR POST-2016 CAPACITY
| Way of generating electricity | Amount of electricity (in megawatt hours) to be stated in a ROC issued for electricity generated using— | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013/14 capacity | 2014/15 capacity | 2015/16 capacity | post-2016 capacity | |
| AD | ||||
| Advanced gasification/ pyrolysis | ||||
| Building mounted solar PV | ||||
| Closed landfill gas | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Co-firing of regular bioliquid | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Dedicated biomass | ||||
| Dedicated energy crops | ||||
| Electricity generated from sewage gas | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Energy from waste with CHP | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Geopressure | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Geothermal | ||||
| Ground mounted solar PV | ||||
| High-range co-firing | ||||
| Hydroelectric | ||||
| Landfill gas heat recovery | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Low-range co-firing | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Mid-range co-firing | ||||
| Offshore wind | ||||
| Onshore wind | ||||
| Standard gasification/ pyrolysis | ||||
| Station conversion | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Tidal impoundment | ||||
| Tidal stream | ||||
| Unit conversion | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Wave | ||||
Article 34
PART 4E+WAMOUNT OF ELECTRICITY TO BE STATED IN ROCs ISSUED FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATED BY MICROGENERATORS TO WHICH ARTICLE 34 APPLIES
Article 35
PART 5E+WAMOUNT OF ELECTRICITY TO BE STATED IN ROCs ISSUED FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATED USING PRE-2013 CAPACITY OR 2013/15 CAPACITY WHERE ARTICLE 35(3) OR (4) APPLIES
| Way of generating electricity | Amount of electricity (in megawatt hours) to be stated in a ROC issued in respect of the qualifying proportion of electricity generated using pre-2013 capacity or 2013/15 capacity | Amount of electricity (in megawatt hours) to be stated in a ROC issued in respect of the remainder of the electricity generated using pre-2013 capacity or 2013/15 capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Co-firing of regular bioliquid with CHP | 1 | 2 |
| Dedicated biomass with CHP | ||
| High-range co-firing with CHP | ||
| Low-range co-firing with CHP | 1 | 2 |
| Mid-range co-firing with CHP | ||
| Station conversion with CHP | 1 | |
| Unit conversion with CHP | 1 |
Article 35
PART 6E+WAMOUNT OF ELECTRICITY TO BE STATED IN ROCs ISSUED FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATED USING 2015/16 CAPACITY WHERE ARTICLE 35(5) APPLIES
| Way of generating electricity | Amount of electricity (in megawatt hours) to be stated in a ROC issued in respect of the qualifying proportion of electricity generated using 2015/16 capacity | Amount of electricity (in megawatt hours) to be stated in a ROC issued in respect of the remainder of the electricity generated using 2015/16 capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Co-firing of regular bioliquid with CHP | 1 | 2 |
| Dedicated biomass with CHP | ||
| High-range co-firing with CHP | ||
| Low-range co-firing with CHP | 1 | 2 |
| Mid-range co-firing with CHP | ||
| Station conversion with CHP | 1 | |
| Unit conversion with CHP | 1 |
Article 35
PART 7E+WAMOUNT OF ELECTRICITY TO BE STATED IN ROCs ISSUED FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATED USING POST-2016 CAPACITY WHERE ARTICLE 35(6) APPLIES
| Way of generating electricity | Amount of electricity (in megawatt hours) to be stated in a ROC issued in respect of the qualifying proportion of electricity generated using post-2016 capacity | Amount of electricity (in megawatt hours) to be stated in a ROC issued in respect of the remainder of the electricity generated using post-2016 capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Co-firing of regular bioliquid with CHP | 1 | 2 |
| Dedicated biomass with CHP | ||
| High-range co-firing with CHP | ||
| Low-range co-firing with CHP | 1 | 2 |
| Mid-range co-firing with CHP | ||
| Station conversion with CHP | 1 | |
| Unit conversion with CHP | 1 |
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Instrument
PrintThis Schedule only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As Enacted or Made): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was enacted or made. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Explanatory Memorandum
Explanatory Memorandum sets out a brief statement of the purpose of a Statutory Instrument and provides information about its policy objective and policy implications. They aim to make the Statutory Instrument accessible to readers who are not legally qualified and accompany any Statutory Instrument or Draft Statutory Instrument laid before Parliament from June 2004 onwards.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as enacted version that was used for the print copy
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Impact Assessments
Impact Assessments generally accompany all UK Government interventions of a regulatory nature that affect the private sector, civil society organisations and public services. They apply regardless of whether the regulation originates from a domestic or international source and can accompany primary (Acts etc) and secondary legislation (SIs). An Impact Assessment allows those with an interest in the policy area to understand:
- Why the government is proposing to intervene;
- The main options the government is considering, and which one is preferred;
- How and to what extent new policies may impact on them; and,
- The estimated costs and benefits of proposed measures.
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different points in time where a change occurred. The dates will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. The first date in the timeline will usually be the earliest date when the provision came into force. In some cases the first date is 01/02/1991 (or for Northern Ireland legislation 01/01/2006). This date is our basedate. No versions before this date are available. For further information see the Editorial Practice Guide and Glossary under Help.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as made version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources