- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser (07/04/2005)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Commission Decision of 18 December 1996 laying down provisions for the implementation of Council Directive 96/16/EC on statistical surveys of milk and milk products (Text with EEA relevance) (97/80/EC)
You are here:
- Penderfyniadau yn deillio o’r UE
- 1997 No. 80
- Annexes only
- Dangos Graddfa Ddaearyddol(e.e. Lloegr, Cymru, Yr Alban aca Gogledd Iwerddon)
- Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Rhagor o Adnoddau
PDF o Fersiynau Diwygiedig
- ddiwygiedig 24/03/20110.68 MB
- ddiwygiedig 07/04/20050.64 MB
- ddiwygiedig 17/10/19980.49 MB
Pan adawodd y DU yr UE, cyhoeddodd legislation.gov.uk ddeddfwriaeth yr UE a gyhoeddwyd gan yr UE hyd at ddiwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.). Ar legislation.gov.uk, mae'r eitemau hyn o ddeddfwriaeth yn cael eu diweddaru'n gyson ag unrhyw ddiwygiadau a wnaed gan y DU ers hynny.
Mae'r eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth yn tarddu o'r UE
Mae legislation.gov.uk yn cyhoeddi fersiwn y DU. Mae EUR-Lex yn cyhoeddi fersiwn yr UE. Mae Archif Gwe Ymadael â’r UE yn rhoi cipolwg ar fersiwn EUR-Lex o ddiwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Commission Decision of 18 December 1996 laying down provisions for the implementation of Council Directive 96/16/EC on statistical surveys of milk and milk products (Text with EEA relevance) (97/80/EC) (Annexes only)
Version Superseded: 24/03/2011
Alternative versions:
Status:
Point in time view as at 07/04/2005.
Changes to legislation:
There are outstanding changes by UK legislation not yet made to Commission Decision of 18 December 1996 laying down provisions for the implementation of Council Directive 96/16/EC on statistical surveys of milk and milk products (Text with EEA relevance) (97/80/EC). Any changes that have already been made to the legislation appear in the content and are referenced with annotations.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Changes and effects yet to be applied by the editorial team are only applicable when viewing the latest version or prospective version of legislation. They are therefore not accessible when viewing legislation as at a specific point in time. To view the ‘Changes to Legislation’ information for this provision return to the latest version view using the options provided in the ‘What Version’ box above.
ANNEX IU.K.LIST OF MILK PRODUCTS
| a [F1Data collection and transfer optional.] | |
| Product code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Fresh products |
| 11 | Drinking milk |
| 111 | Raw milk |
| 112 | Whole milk |
| 1121 | Pasteurized |
| 1122 | Sterilized |
| 1123 | Uperized |
| 113 | Semi-skimmed milk |
| 1131 | Pasteurized |
| 1132 | Sterilized |
| 1133 | Uperized (i.e. UHT) |
| 114 | Skimmed milk |
| 1141 | Pasteurized |
| 1142 | Sterilized |
| 1143 | Uperized |
| 12 | Buttermilk |
| 13 | Cream |
| Of fat content by weight | |
| 131 | Not exceeding 29 % |
| 132 | Over 29 % |
| 14 | Acidified milk (Yoghurts, drinking yoghurts and other) |
| 141 | With additives |
| 142 | Without additives |
| 15 | Drinks with a milk base |
| 16 | Other milk products (Milk jelly and others) |
| 2 | Manufactured products |
| 21 | Concentrated milk |
| 211 | Unsweetened |
| 212 | Sweetened |
| 22 | Powdered dairy products |
| 221 | Cream milk powder |
| 222 | Whole milk powder |
| 223 | Partly skimmed-milk powder |
| 224 | Skimmed-milk powder |
| 225 | Buttermilk |
| 226 | Other powder products |
| [F223 | Total butter and other yellow fat dairy products |
| 231 | Butter |
| 2311 | Traditional butter a |
| 2312 | Recombined butter a |
| 2313 | Whey butter a |
| 232 | Rendered butter and butteroil |
| 233 | Other yellow fat products |
| 2331 | Reduced-fat butter a |
| 2332 | Other] a |
| 24 | Cheese |
| 241 | Cheese by milk category: |
| 2411 | Cheese from cows' milk only |
| 2412 | Cheese from ewes' milk only |
| 2413 | Cheese from goats' milk only |
| 2414 | Others (mixed or cheese from buffalos' milk only) |
| 242 | Cheese (all milks) by category: |
| 2421 | Soft cheese |
| 2422 | Semi-soft cheese |
| 2423 | Semi-hard cheese |
| 2424 | Hard cheese |
| 2425 | Extra hard cheese |
| 2426 | Fresh cheese |
| 25 | Processed cheese |
| 26 | Caseins and caseinates |
| 27 | Whey, total |
| 271 | Whey delivered in the liquid state |
| 272 | Whey delivered in the concentrated state |
| 273 | Whey in powder or block |
| 274 | Lactose (milk sugar) |
| 275 | Lactalbumin |
| 28 | Other manufactured products |
Textual Amendments
EXPLANATORY NOTESU.K.
DRINKING MILK (11)U.K.
Drinking milk: raw milk, whole milk, semi-skimmed and skimmed milk containing no additives.
Relates only to milk directly intended for consumption, normally in containers of 2 l or less,
Also includes milk with vitamin additives.
Raw milk (111): milk produced by the secretion of the mammary glands of one or more cows, ewes, goats or buffalos, which has not been heated beyond 40 oC or undergone any treatment that has an equivalent effect (Council Directive 92/46/EEC of 16 June 1992, OJ No L 268, 14. 9. 1992, p. 3).
Whole milk (112): milk which has been subject to one heat treatment or an authorized treatment of equivalent effect by a milk processor and whose fat content is either at least 3,50 % naturally or has been brought to at least 3,5 % (Council Regulation (EEC) No 1411/71 of 29 June 1971, OJ No L 148, 3. 7. 1971, p. 4).
Also includes Swedish drinking milk types designated as ‘Gammaldags mjölk’ and ‘Standardmjölk’ whose milk fat contents are 4,2 % and 3 % respectively.
Semi-skimmed milk (113): milk which has been subject to at least one heat treatment or an authorized treatment of equivalent effect by a milk processor and whose fat content has been brought to at least 1,50 % and at most 1,80 % (Council Regulation (EEC) No 1411/71 of 29 June 1971, OJ No L 148, 3. 7. 1971, p. 4).
Also includes Finnish drinking milk designated as ‘ykkösmaito/ettans mjölk’ whose milk fat content is 1 %,
Also includes the Swedish drinking milk types designated as ‘Ekologisk mjölk’ and ‘Mellanmjölk’ whose milk fat contents are 2 % and 1,5 % respectively,
Also includes Austrian drinking milk whose milk fat content is between 2 % and 2,5 %.
Skimmed milk (114): milk which has been subject to at least one heat treatment or an authorized treatment of equivalent effect by a milk processor and whose fat content has been brought to not more than 0,30 % (Council Regulation (EEC) No 1411/71 of 29 June 1971, OJ No L 148, 3. 7. 1971, p. 4).
Also includes the Swedish drinking milk types designated as ‘Lättmjölk’ and ‘Minimjölk’ whose milk fat contents are 0,5 % and 0,07 % respectively,
Also includes Austrian drinking milk whose milk fat content is 0,5 %.
Pasteurized: pasteurized milk must have been obtained by means of a treatment involving a high temperature for a short time (at least 71,7 oC for 15 seconds or any equivalent combination) or pasteurization process using different time and temperature combinations to obtain an equivalent effect (Council Directive 92/46/EEC of 16 June 1992, OJ No L 268, 14. 9. 1992, p. 24).
Sterilized: sterilized milk must:
have been heated and sterilized in hermetically sealed wrappings or containers, the seal of which must remain intact,
in the event of random sampling, be of preservability such that no deterioration can be observed after it has spent 15 days in a closed container at a temperature of + 30 oC (Council Directive 92/46/EEC of 16 June 1992, OJ No L 268, 14. 9. 1992, p. 25).
Uperized: uperized milk (or UHT milk) must be produced by applying a continuous flow of heat using a high temperature for a short time (not less than 135 oC for not less than 1 second) (Council Directive 92/46/EEC of 16 June 1992, OJ No L 268, 14. 9. 1992, p. 24).
Member States which make no distinction between sterilized and uperized milk may group them together.
BUTTERMILK (12)U.K.
Buttermilk: Residual product (may even be acid or acidified) of the processing of milk or cream into butter (by continuous churning and separation of the solid fats).
Buttermilk with additives must be included in drinks with a milk base.
CREAM (13)U.K.
Cream: a film of fat which forms naturally on the surface of the milk by slow agglomeration of emulsifying fat globules. If it is removed by skimming it from the surface of the milk or extracted from the milk by centrifuging in a cream separator, it has, in addition to the other components of the milk, a relatively high fat content (usually exceeding 10 % of the weight of the product).
Cream (13): cream which has been processed and is available for delivery outside dairies (i.e. for human consumption, as raw material for manufacturers of chocolate, ice cream, etc.). In the same way as for other products, does not include intermediate production intended for the manufacture of other dairy products.
Cream of a fat content by weight not exceeding 29 % (131).
Cream of a fat content by weight over 29 % (132).
Table A/ ‘Collection’: raw material (in milk equivalent) delivered to dairies by agricultural holdings.
Table B/ ‘Availabilities’: cream separated at the farm and delivered to a dairy.
Table A/ ‘Products obtained’ and Table B/ ‘Utilization’:
pasteurized, sterilized or uperized;
also includes acidified cream;
also includes cream in cartons or tins.
ACIDIFIED MILK (14)U.K.
Acidified milk: milk products with a pH of between 3,8 and 5,5.
Relates to yoghurts, drinkable yoghurts, prepared yoghurts, heat-treated fermented milk and others,
Also includes products based on or containing bifidus.
Acidified milk with additives (141): sweetened acidified milk should be included under heading 142.
Acidified milk without additives (142): also includes acidified milk with the addition of sugar and/or sweeteners.
DRINKS WITH A MILK BASE (15)U.K.
Drinks with a milk base: other liquid products containing at least 50 % milk products, including products based on whey.
Includes chocolate milk, buttermilk with additives or flavoured, etc.
OTHER FRESH PRODUCTS (16)U.K.
Relates to fresh milk products not elsewhere specified, mainly milk-based desserts (jellied milks, custard tarts, cream desserts, mousses, etc.) and ice cream (and similar products) manufactured in the reporting enterprises,
Also includes desserts in tins,
Also includes fresh farm products collected from agricultural holdings (under heading Availability/III.4) and placed on the market without processing (excluding packaging).
CONCENTRATED MILK (21)U.K.
Concentrated milk: a product obtained by partial elimination of water, from whole milk, semi-skimmed or skimmed milk only.
Also includes evaporated milk (heat-treated) and concentrated milk with added sugar,
Also includes concentrated milk used for the manufacture of ‘Chocolate crumb’; dried product consisting of milk, sugar and cocoa paste in the following proportions:
milkfat: more than 6,5 % (content by weight) but less than 11 % (content by weight),
cocoa: more than 6,5 % (content by weight) but less than 15 % (content by weight),
sucrose (including invert sugar calculated as sucrose) more than 50 % (content by weight) but less than 60 % (content by weight),
non-fat dry matter of milk: more than 17 % (content by weight) but less than 30 % (content by weight),
water: more than 0,5 % (content by weight) but less than 3,5 % (content by weight).
Its composition is as given in Annex I to Commission Regulation (EEC) No 380/84 of 15 February 1984 (OJ No L 46 16. 2. 1984, p. 26).
POWDERED DAIRY PRODUCTS (22)U.K.
Powdered dairy products: product obtained by eliminating water from cream, whole milk, semi-skimmed milk, skimmed milk, buttermilk and acidified milk.
Also includes additives to the raw material before the product is made into powder,
Also includes milk powder manufactured in dairies and contained in powders for infants and in animal feeds.
Cream milk powder (221): milk powder with a milk fat content of not less than 42 % by weight of the product.
Whole milk powder (222): milk powder with a milk fat content of not less than 26 % and less than 42 % by weight of the product.
Partly skimmed-milk powder (223): milk powder with a milk fat content of more than 1,5 % and less than 26 % by weight of the product.
Skimmed-milk powder (224): milk powder with a maximum milk fat content of 1,5 % by weight of the product.
Buttermilk powder (225): powder product made from buttermilk.
Other powdered products (226): curdled milk and cream, kephir and other fermented or acidified milk and cream, whether or not containing added sugar or other sweetening matter or flavoured or containing added fruit or cocoa.
Also includes mixtures of powdered cream, milk, buttermilk and/or whey,
Also includes protein-based powdered products.
[F2BUTTER (23) U.K.
Butter, total and other yellow fat dairy products (23): includes butter, traditional butter, recombined butter, whey butter, rendered butter and butteroil, and other yellow fat products, expressed in butter equivalent with a milk fat content equal to 82 % by weight of the product.
Table A: Denmark: includes only butter (231),
Table B: the headings 231 (butter), 2311 (traditional butter), 2312 (recombined butter), 2313 (whey butter), 232 (rendered butter and butteroil), 233 (other yellow fat dairy products), 2331 (reduced-fat butter) and 2332 (other) must be recorded in product weight. Only item 23 must be given in its butter equivalent.
Butter (231): a product with a milk fat content of not less than 80 % and less than 90 %, a maximum water content of 16 % and a maximum dry non-fat milk-material content of 2 %.
Includes also butter which contains small amounts of herbs, spices, aromatic substances, etc. on the condition that the product retains the characteristics of butter.
Traditional butter (2311): a product obtained directly and exclusively from pasteurised cream, with a milk fat content of not less than 80 % and less than 90 %, a maximum water content of 16 % and a maximum dry non-fat milk-material content of 2 %.
Recombined butter (2312): a product obtained from butteroil, non-fat dry milk extract and water, with a milk fat content of not less than 80 % and less than 90 % and maximum water content of 16 % and a maximum dry non-fat milk-material content of 2 %.
Whey butter (2313): a product obtained from whey cream or a mixture of whey cream and cream with a milk fat content of not less than 80 % and less than 90 % and maximum water content of 16 % and a maximum dry non-fat milk-material content of 2 %.
Headings 2311, 2312 and 2313 also include butter which contains small amounts of herbs, spices, aromatic substances, etc. on the condition that the product retains the characteristics of butter.
Rendered butter and butteroil (232): U.K.
Rendered butter: renderd butters have a milk fat content exceeding 85 % by weight. The term frequently covers, in addition to rendered butter as such, a number of other similar dehydrated butters which are known generically under various names, such as ‘dehydrated butter’, ‘anhydrous butter’, ‘butteroil’, ‘butyric fat’ (milk fat) and ‘concentrated butter’.
Butteroil: a product obtained from milk, cream or butter by processes which eliminate the water and the dry non-fat extract with a minimum content of milk fat of 99,3 % of the total weight and a maximum water content of 0,5 % of the total weight.
Also includes ‘ ghee ’ .
To avoid double counting, ‘ butteroil ’ relates only to direct production from cream.
Other yellow fat products (233): U.K.
Reduced-fat butter (2331): product similar to butter with a milk-fat content of less than 80 % by weight (excluding all other fat) (sales description according to section A of the Annex to Regulation (EC) No 2991/94 (1) : ‘three-quarter-fat butter’, ‘half-fat butter’ and ‘dairy spread’).
Other (2332): in particular fats composed of plant and/or animal products: products in the form of a solid, malleable emulsion principally of the water-in-oil type, derived from solid and/or liquid vegetable and/or animal fats suitable for human consumption, with a milk-fat content of between 10 and 80 % of the fat content (sales description according to section C of the Annex to Regulation (EC) No 2291/94: ‘blend’, ‘three-quarter-fat blend’, ‘half-fat blend’ and ‘blended spread’).
Table B: if the reduced-fat butter (2331) and/or ‘ other ’ (2332) are producted from butter manufactured in the same dairy and the type of butter is not identifiable (2311, 2312 or 2313) the data are taken from heading 23, indicating the quantity of butter concerned.]
CHEESE (24)U.K.
Cheese: shall be a fresh or matured, solid or semi-solid product, obtained by coagulating milk, skimmed milk, partly skimmed milk, cream, whey cream or buttermilk, alone or in combination, by the action of rennet or other suitable coagulating agents, and by partly draining the whey resulting from such coagulation. (Codex Alimentarius — FAO, Volume XVI, Standard A-6).
Soft cheese (2421): cheese in which the MFFB when refined is in general not less than 68 %.
Semi-soft cheese (2422): cheese in which the MFFB when refined is in general not less than 62 % and less than 68 %.
Semi-hard cheese (2423): cheese in which the MFFB when refined is in general not less than 55 % and less than 62 %.
Hard cheese (2424): cheese in which the MFFB when refined is in general not less than 47 % and less than 55 %.
Very hard cheese (2425): cheese in which the MFFB when refined is in general less than 47 %.
Fresh cheese (2426): product obtained from sour milk from which most of the serum has been removed (e.g. by draining or pressing). Also includes curds (other than in powder form) containing up to 30 % by weight in the form of sugar and added fruits.
Includes fresh whey cheese (obtained by concentrating whey and adding milk or milk fat).
PROCESSED CHEESE (25)U.K.
Processed cheese: product obtained by grinding, mixing, melting and emulsifying under the action of heat and with the aid of emulsifying agents one or more varieties of cheese, with or without the addition of milk components and/or other foodstuffs. (Codex Alimentarius — FAO, Volume XVI, Standard A-8 (b)).
CASEIN AND CASEINATES (26)U.K.
Casein: is the main protein constituent of milk. It is obtained from skimmed milk by precipitation (curdling), generally with acids or rennet. The heading covers various types of casein which differ according to the method of curdling, e.g. acid casein and rennet casein (paracasein). (Explanatory notes to the harmonized system — SectionVI, Chapter 35 (No 35.01)).
Caseinates: (salts of casein) include the sodium and ammonium salts known as ‘soluble caseins’; these salts are normally used to prepare concentrated foods and pharmaceutical products. Calcium caseinate is used in the preparation of foodstuffs or as a glue, depending on its character. (Explanatory notes to the harmonized system — SectionVI, Chapter 35 (No 35.01)).
WHEY (27)U.K.
Whey: by-product obtained during the manufacture of cheese or casein. In the liquid state, whey contains natural constituents (on average 4,8 % lactose, 0,8 % protein and 0,2 % fats by weight of the product) which remain when the casein and the majority of the fat have been removed from the milk.
Total whey (27): also includes the whey used in the dairy for manufacturing animal feedingstuffs.
Items 271 (whey delivered in the liquid state), 272 (whey used in the concentrated state), 273 (whey in powder or block form), 274 (lactose), 275 (lactalbumin) are to be given in their effective weight. Only item 27 (total whey) is to be given in its liquid whey equivalent and must in no event be the sum of the abovementioned quantities.
Whey delivered in the liquid state (271): whey delivered to be used mainly for animal feeds. Quantities used as raw materials for other processes must be excluded.
Whey delivered in the concentrated state (272).
Whey in powdered or block form (273).
Lactose (milk sugar) (274).
Lactalbumin (275): one of the main components of whey protein.
OTHER MANUFACTURED PRODUCTS (28)U.K.
This heading relates to manufactured milk products (to be specified) not designated elsewhere, mainly lactoferrins.
Also includes manufactured farm products collected from agricultural holdings (under heading Availability/III.4) and placed on the market without processing (excluding packaging or maturing).
ANNEX IIU.K.
TABLE AU.K.
Table BU.K.
TABLE CU.K.
TABLE DU.K.
TABLE EU.K.
TABLE FU.K.
TABLE G.1U.K.
TABLE G.2U.K.
TABLE G.3U.K.
TABLE G.4U.K.
TABLE G.5U.K.
[F3TABLE H
Dairies’ activities
Protein content of cows’ milk in the main milk products
| Country: … Year: … | |||
| a Column 1: quantities produced in thousand tonnes over the period under consideration (year). Definition : See Annex II to Decision 97/80/EC, Table B, column 1. | |||
| Code | Product | Quantity a ( 1 000 t) | Protein content (t) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | ||
| 1 | Fresh products | ||
| 11 | Drinking milk | ||
| 112 | Whole milk | ||
| 113 | Semi-skimmed milk | ||
| 114 | Skimmed milk | ||
| 12 | Buttermilk | ||
| 13 | Cream | ||
| 2 | Manufactured products | ||
| 21 | Concentrated milk | ||
| 221 | Cream milk powder | ||
| 222 | Whole milk powder | ||
| 223 | Partially skimmed-milk powder | ||
| 224 | Skimmed-milk powder | ||
| 225 | Buttermilk powder | ||
| 23 | Butter and other yellow fat dairy products | ||
| 2411 | Cheese from cows' milk | ||
| 25 | Processed cheese | ||
| 26 | Casein and caseinates | ||
| 27 | Whey | ||
Textual Amendments
TABLE I
Regional data on production of cows' milk
| Country: … Year: … | ||
| a This covers all cows’ milk other than milk directly suckled by calves; it includes all milk obtained from milking (including colostrum) and fed to animals (e.g. in buckets or by other means).] | ||
| Region | NUTS 2 code | Annual production of cows’ milk ( 1 000 t) a |
|---|---|---|
| Country total | ||
EXPLANATORY NOTESU.K.
TABLE AU.K.
The data concerning this Table refer only to cows' milk, for both collection and the products obtained (mixtures are therefore excluded).
In the case of weekly returns, the data for the weeks running into the next month must be divided and broken down in accordance with the number of working days in each of the two months.
| Fat content: |
|
| Protein content: |
|
Products obtained: quantities of processed fresh milk products shall be understood to be available for delivery outside dairies.
TABLE BU.K.
To avoid double counting, milk products used within the same dairy for the manufacture of other milk products are not taken into account.
Likewise, the data in this table refer to the concept of the ‘national dairy’. Accordingly, all trade in raw materials or products between dairies in the Member State concerned must be excluded from national production figures.
Availability/I and II: collected milk: relates to purchases of all types of whole milk (cows', ewes', goats' and buffalos' milk) and milk products collected directly from agricultural holdings.
Availability/II.6: relates to other milk products (such as cheese, butter and yoghurt) collected from agricultural holdings. These products, irrespective of whether or not they are processed, are intended for input in the dairies' manufacturing process and must be included in part B (Use) of the table.
Availability/III.4: relates to other milk products (such as cheese, butter and yoghurt) imported from other countries. These products, irrespective of whether or not they are intended for input in the dairies' manufacturing process, must be included in part B (Use) of the table.
If they are intended to be placed on the market without processing (excluding packaging or maturing), these products must be entered under heading 16 (in the case of fresh farm products) or 28 (in the case of manufactured farm products).
Availability/III-Imports and intra-Community arrivals: in bulk or in containers of 2 l or more.
Column 1 — Quantities: unless otherwise indicated, the quantities to be recorded refer to the net weight of the raw material/finished product (in 1 000 tonnes).
Quantities of processed fresh milk products shall be understood to be available for delivery outside dairies.
Column 2/B. Use — milk fat content: quantities (in tonnes) of milk fat used to manufacture the product concerned, including possible losses occurring during the manufacturing process.
Column 3/A. Availabilities — milk protein: quantities (in tonnes) of milk protein contained in the cows' milk collected.
Column 3/B. Use — input of whole milk: quantities (in 1 000 tonnes) of whole milk used in the manufacture of the product in question, including possible losses occurring during the manufacturing process.
Column 4/B. Use — input of skimmed milk:
positive: quantities (in 1 000 tonnes) of skimmed milk used in the manufacture of the product in question, including possible losses occurring during the manufacturing process,
negative: quantities (in 1 000 tonnes) of skimmed milk recovered during the manufacturing process for the product in question (for example: skimmed milk recovered during the manufacture of butter from whole milk or cream).
Other uses (codes 3-6):U.K.
Skimmed milk and buttermilk returned to the farm (3): the skimmed milk and buttermilk returned to farms.
Exports and consignments of milk and cream in bulk (4): exports and Community dispatches of whole milk, skimmed milk and liquid cream in bulk or in containers of 2 l or more by the dairies.
Other uses (5): includes whole and skimmed milk in bulk or in containers of more than 2 l delivered to food industries (e.g. for ice cream) or intended for use as animal feedingstuffs in all forms, except item 3.
Differences (6): relates to the statistical differences.
TABLE CU.K.
Agricultural holding: a techno-economic unit under a single management producing agricultural products.
A:Availabilities:U.K.
Cows' milk: relates to all cows' milk, excluding milk directly suckled but including that obtained by milking (including colostrum) used for animal feedingstuffs (for example in buckets or by other means).
Dairy cows: cows which are used exclusively or mainly for the production of milk for human consumption and/or processing into dairy products, including cull dairy cows (whether or not fattened between their last lactation and their slaughter).
Whole milk column: relates to the quantities of milk obtained.
Skimmed milk and buttermilk column:U.K.
returned by the dairies (1): see definition Table B/3.
balance of cream deliveries (2).
B.Use:U.K.
Whole milk/home consumption: whole milk consumed by the holder's household (therefore for human consumption only).
Whole milk/direct sales: whole milk for human consumption sold direct to consumers.
Whole milk/farm butter and cream: whole milk (all milks) used to produce farm butter and cream.
Whole milk/farm cheese: whole milk (all milks) used to produce farm cheese.
Whole milk/other products: whole milk (all milks) used for the manufacture of milk products for human consumption (e.g. yoghurt).
Whole milk/animal feedingstuffs: whole milk used on the farm for animal feedingstuffs, in whatever form (as they are or as compound animal feedingstuffs manufactured on the farm).
Whole milk/delivered to dairies:U.K.
includes deliveries:
of all types of whole milk (from cows, ewes, goats and buffalos) to dairies (within or outside the Member State) and to the agricultural holdings referred to in Article 2 of Directive 96/16/EC;
other products (specify), in milk equivalent,
deliveries of cream must be expressed in milk equivalent.
Whole milk/differences and losses:U.K.
refers to the statistical difference and the quantities lost during manufacturing,
the total for the ‘whole milk use column’ should be equal to the total available.
Skimmed milk and buttermilk/drinking milk: skimmed milk and buttermilk used on agricultural holdings for human consumption, in particular home consumption on holdings and direct sales to consumers.
Skimmed milk and buttermilk/farm cheese: quantity of skimmed milk and buttermilk used to produce farm cheese.
C.Products obtained:U.K.
The quantities reported shall refer to the net weight of the finished product (in 1 000 tonnes).
Drinking milk: home consumption and direct sales.
Farm cream: cream produced on agricultural holdings.
Farm butter: butter produced on agricultural holdings.
Farm cheese: cheese produced on the agricultural holding.
Other products: other products (to be specified) produced on the agricultural holding.
Of which delivered to dairies: relates to deliveries of cream, butter, cheese and other farm products to dairies (within or outside the Member State).
TABLES D AND EU.K.
Milk collected: quantities of milk and cream (in milk equivalent) collected direct from farms.
TABLE EU.K.
Collection centres: relates only to those enterprises which purchase milk from agricultural holdings and sell it in their own name to dairies. Collection centres which are local units dependent on dairies are thus excluded.
The accounting centres for national accounting of quantities of milk collected in the national territory by an enterprise (dairy) from another Member State must therefore also be included in this table.
TABLE FU.K.
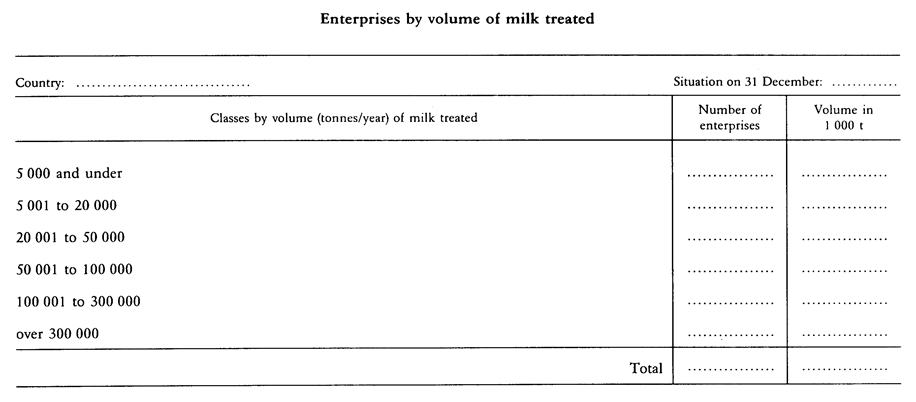
Volume: total volume of raw material processed = quantities of whole milk (or whole milk equivalent) used for the manufacture of milk products in the enterprise.
TABLES D, E, F AND GU.K.
Enterprise: the enterprise is the smallest combination of legal units that is an organizational unit producing goods or services, which benefits from a certain degree of autonomy in decision-making, especially for the allocation of its current resources. An enterprise carries out one or more activities at one or more locations. An enterprise may be a sole legal unit. (Council Regulation (EEC) No 696/93 of 15 March 1993, OJ No L 76, 30. 3. 1993).
Transmitted data which are subject to statistical confidentiality must be clearly identified as such.
The tables must be completed for all enterprises in operation on 31 December of the reference year. They relate to the dairies' activities, including the activities of dairies taken over by them in the course of the year.
[F4ANNEX III] U.K.
Textual Amendments
Options/Cymorth
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Decision
PrintThe Annexes only
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
Gweler y wybodaeth ychwanegol ochr yn ochr â’r cynnwys
Rhychwant ddaearyddol: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Mae’r llinell amser yma yn dangos y fersiynau gwahanol a gymerwyd o EUR-Lex yn ogystal ag unrhyw fersiynau dilynol a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig.
Cymerir dyddiadau fersiynau’r UE o ddyddiadau’r dogfennau ar EUR-Lex ac efallai na fyddant yn cyfateb â’r adeg pan ddaeth y newidiadau i rym ar gyfer y ddogfen.
Ar gyfer unrhyw fersiynau a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig, bydd y dyddiad yn cyd-fynd â’r dyddiad cynharaf y daeth y newid (e.e. ychwanegiad, diddymiad neu gyfnewidiad) a weithredwyd i rym. Am ragor o wybodaeth gweler ein canllaw i ddeddfwriaeth ddiwygiedig ar Ddeall Deddfwriaeth.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill