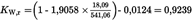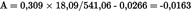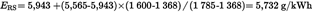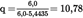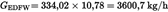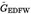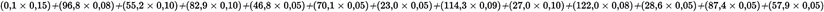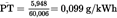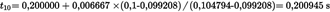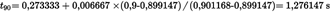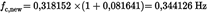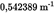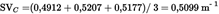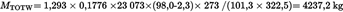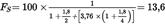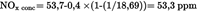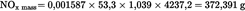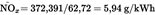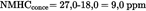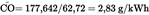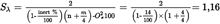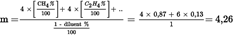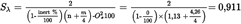- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser (19/12/2005)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Directive 2005/55/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (repealed)Dangos y teitl llawn
Directive 2005/55/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 28 September 2005 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to the measures to be taken against the emission of gaseous and particulate pollutants from compression-ignition engines for use in vehicles, and the emission of gaseous pollutants from positive-ignition engines fuelled with natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas for use in vehicles (Text with EEA relevance) (repealed)
You are here:
- Dangos Graddfa Ddaearyddol(e.e. Lloegr, Cymru, Yr Alban aca Gogledd Iwerddon)
- Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Rhagor o Adnoddau
PDF o Fersiynau Diwygiedig
- ddiwygiedig 31/12/20130.45 MB
- ddiwygiedig 08/08/20082.04 MB
- ddiwygiedig 10/06/20064.30 MB
- ddiwygiedig 19/12/20052.67 MB
Pan adawodd y DU yr UE, cyhoeddodd legislation.gov.uk ddeddfwriaeth yr UE a gyhoeddwyd gan yr UE hyd at ddiwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.). Ar legislation.gov.uk, mae'r eitemau hyn o ddeddfwriaeth yn cael eu diweddaru'n gyson ag unrhyw ddiwygiadau a wnaed gan y DU ers hynny.
Mae'r eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth yn tarddu o'r UE
Mae legislation.gov.uk yn cyhoeddi fersiwn y DU. Mae EUR-Lex yn cyhoeddi fersiwn yr UE. Mae Archif Gwe Ymadael â’r UE yn rhoi cipolwg ar fersiwn EUR-Lex o ddiwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: ANNEX VII
Version Superseded: 31/12/2013
Alternative versions:
Status:
Cyhoeddir Cyfarwyddebau’r UE ar y wefan hon i gynorthwyo croesgyfeirio o ddeddfwriaeth y DU. Ers diwrnod cwblhau’r cyfnod gweithredu (31 Rhagfyr 2020 11.00 p.m.) nid oes unrhyw ddiwygiadau wedi'u cymhwyso i'r fersiwn hon.
ANNEX VIIU.K.EXAMPLE OF CALCULATION PROCEDURE
1.ESC TESTU.K.
1.1.Gaseous emissionsU.K.
The measurement data for the calculation of the individual mode results are shown below. In this example, CO and NOx are measured on a dry basis, HC on a wet basis. The HC concentration is given in propane equivalent (C3) and has to be multiplied by 3 to result in the C1 equivalent. The calculation procedure is identical for the other modes.
| P(kW) | Ta(K) | Ha(g/kg) | GEXH(kg) | GAIRW(kg) | GFUEL(kg) | HC(ppm) | CO(ppm) | NOx(ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 82,9 | 294,8 | 7,81 | 563,38 | 545,29 | 18,09 | 6,3 | 41,2 | 495 |
Calculation of the dry to wet correction factor KW,r (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 4.2):U.K.
Calculation of the wet concentrations:U.K.
Calculation of the NOx humidity correction factor KH,D (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 4.3):U.K.
Calculation of the emission mass flow rates (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 4.4):U.K.
Calculation of the specific emissions (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 4.5):U.K.
The following example calculation is given for CO; the calculation procedure is identical for the other components.
The emission mass flow rates of the individual modes are multiplied by the respective weighting factors, as indicated in Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 2.7.1, and summed up to result in the mean emission mass flow rate over the cycle:
The engine power of the individual modes is multiplied by the respective weighting factors, as indicated in Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 2.7.1, and summed up to result in the mean cycle power:
Calculation of the specific NOx emission of the random point (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 4.6.1):U.K.
Assume the following values have been determined on the random point:
=
1 600 min-1
=
495 Nm
=
487,9 g/h (calculated according to the previous formulae)
=
83 kW
=
487,9/83 = 5,878 g/kWh
Determination of the emission value from the test cycle (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 4.6.2):U.K.
Assume the values of the four enveloping modes on the ESC to be as follows:
| nRT | nSU | ER | ES | ET | EU | MR | MS | MT | MU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 368 | 1 785 | 5,943 | 5,565 | 5,889 | 4,973 | 515 | 460 | 681 | 610 |
Comparison of the NOx emission values (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 4.6.3):U.K.
1.2.Particulate emissionsU.K.
Particulate measurement is based on the principle of sampling the particulates over the complete cycle, but determining the sample and flow rates (MSAM and GEDF) during the individual modes. The calculation of GEDF depends on the system used. In the following examples, a system with CO2 measurement and carbon balance method and a system with flow measurement are used. When using a full flow dilution system, GEDF is directly measured by the CVS equipment.
Calculation of GEDF (Annex III, Appendix 1, Sections 5.2.3 and 5.2.4):U.K.
Assume the following measurement data of mode 4. The calculation procedure is identical for the other modes.
| GEXH(kg/h) | GFUEL(kg/h) | GDILW(kg/h) | GTOTW(kg/h) | CO2D(%) | CO2A(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 334,02 | 10,76 | 5,4435 | 6,0 | 0,657 | 0,04 |
Calculation of the mass flow rate (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 5.4):U.K.
The GEDFW flow rates of the individual modes are multiplied by the respective weighting factors, as indicated in Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 2.7.1, and summed up to result in the mean GEDF over the cycle. The total sample rate MSAM is summed up from the sample rates of the individual modes.
Assume the particulate mass on the filters to be 2,5 mg, then
Background correction (optional)U.K.
Assume one background measurement with the following values. The calculation of the dilution factor DF is identical to Section 3.1 of this Annex and not shown here.
Calculation of the specific emission (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 5.5):U.K.
Calculation of the specific weighting factor (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 5.6):U.K.
Assume the values calculated for mode 4 above, then
This value is within the required value of 0,10 ± 0,003.
2.ELR TESTU.K.
Since Bessel filtering is a completely new averaging procedure in European exhaust legislation, an explanation of the Bessel filter, an example of the design of a Bessel algorithm, and an example of the calculation of the final smoke value is given below. The constants of the Bessel algorithm only depend on the design of the opacimeter and the sampling rate of the data acquisition system. It is recommended that the opacimeter manufacturer provide the final Bessel filter constants for different sampling rates and that the customer use these constants for designing the Bessel algorithm and for calculating the smoke values.
2.1.General remarks on the Bessel filterU.K.
Due to high frequency distortions, the raw opacity signal usually shows a highly scattered trace. To remove these high frequency distortions a Bessel filter is required for the ELR-test. The Bessel filter itself is a recursive, second-order low-pass filter which guarantees the fastest signal rise without overshoot.
Assuming a real time raw exhaust plume in the exhaust tube, each opacimeter shows a delayed and differently measured opacity trace. The delay and the magnitude of the measured opacity trace is primarily dependent on the geometry of the measuring chamber of the opacimeter, including the exhaust sample lines, and on the time needed for processing the signal in the electronics of the opacimeter. The values that characterise these two effects are called the physical and the electrical response time which represent an individual filter for each type of opacimeter.
The goal of applying a Bessel filter is to guarantee a uniform overall filter characteristic of the whole opacimeter system, consisting of:
physical response time of the opacimeter (tp),
electrical response time of the opacimeter (te),
filter response time of the applied Bessel filter (tF).
The resulting overall response time of the system tAver is given by:
and must be equal for all kinds of opacimeters in order to give the same smoke value. Therefore, a Bessel filter has to be created in such a way, that the filter response time (tF) together with the physical (tp) and electrical response time (te) of the individual opacimeter must result in the required overall response time (tAver). Since tp and te are given values for each individual opacimeter, and tAver is defined to be 1,0 s in this Directive, tF can be calculated as follows:
By definition, the filter response time tF is the rise time of a filtered output signal between 10 % and 90 % on a step input signal. Therefore the cut-off frequency of the Bessel filter has to be iterated in such a way, that the response time of the Bessel filter fits into the required rise time.
In Figure a, the traces of a step input signal and Bessel filtered output signal as well as the response time of the Bessel filter (tF) are shown.
Designing the final Bessel filter algorithm is a multi step process which requires several iteration cycles. The scheme of the iteration procedure is presented below.
2.2.Calculation of the Bessel algorithmU.K.
In this example a Bessel algorithm is designed in several steps according to the above iteration procedure which is based upon Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 6.1.
For the opacimeter and the data acquisition system, the following characteristics are assumed:
physical response time tp 0,15 s
electrical response time te 0,05 s
overall response time tAver 1,00 s (by definition in this Directive)
sampling rate 150 Hz
Step 1Required Bessel filter response time tF:U.K.
Step 2Estimation of cut-off frequency and calculation of Bessel constants E, K for first iteration:U.K.
=
1/150 = 0,006667 s
This gives the Bessel algorithm:
where Si represents the values of the step input signal (either ‘0’ or ‘1’) and Yi represents the filtered values of the output signal.
Step 3Application of Bessel filter on step input:U.K.
The Bessel filter response time tF is defined as the rise time of the filtered output signal between 10 % and 90 % on a step input signal. For determining the times of 10 % (t10) and 90 % (t90) of the output signal, a Bessel filter has to be applied to a step input using the above values of fc, E and K.
The index numbers, the time and the values of a step input signal and the resulting values of the filtered output signal for the first and the second iteration are shown in Table B. The points adjacent to t10 and t90 are marked in bold numbers.
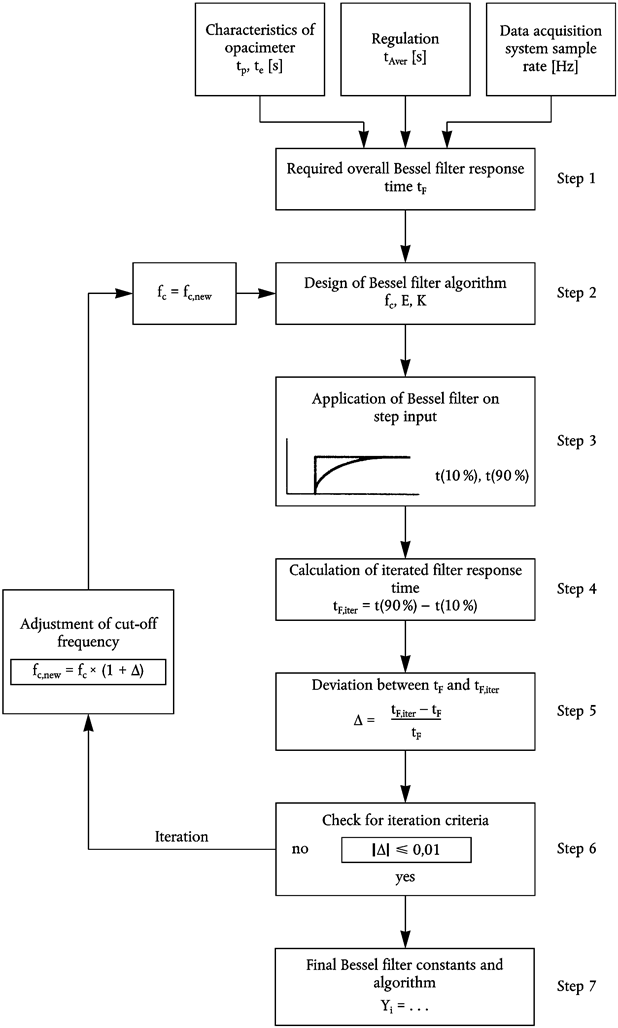
In Table B, first iteration, the 10 % value occurs between index number 30 and 31 and the 90 % value occurs between index number 191 and 192. For the calculation of tF,iter the exact t10 and t90 values are determined by linear interpolation between the adjacent measuring points, as follows:
where outupper and outlower, respectively, are the adjacent points of the Bessel filtered output signal, and tlower is the time of the adjacent time point, as indicated in Table B.
Step 4Filter response time of first iteration cycle:U.K.
Step 5Deviation between required and obtained filter response time of first iteration cycle:U.K.
Step 6Checking the iteration criteria:U.K.
|Δ| ≤ 0,01 is required. Since 0,081641 > 0,01, the iteration criteria is not met and a further iteration cycle has to be started. For this iteration cycle, a new cut-off frequency is calculated from fc and Δ as follows:
This new cut-off frequency is used in the second iteration cycle, starting at step 2 again. The iteration has to be repeated until the iteration criteria is met. The resulting values of the first and second iteration are summarised in Table A.
Table A
Values of the first and second iteration
| Parameter | 1. Iteration | 2. Iteration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| fc | (Hz) | 0,318152 | 0,344126 |
| E | (-) | 7,07948 E-5 | 8,272777 E-5 |
| K | (-) | 0,970783 | 0,96841 |
| t10 | (s) | 0,200945 | 0,185523 |
| t90 | (s) | 1,276147 | 1,179562 |
| tF,iter | (s) | 1,075202 | 0,994039 |
| Δ | (-) | 0,081641 | 0,006657 |
| fc,new | (Hz) | 0,344126 | 0,346417 |
Step 7Final Bessel algorithm:U.K.
As soon as the iteration criteria has been met, the final Bessel filter constants and the final Bessel algorithm are calculated according to step 2. In this example, the iteration criteria has been met after the second iteration (Δ = 0,006657 ≤ 0,01). The final algorithm is then used for determining the averaged smoke values (see next Section 2.3).
Table B
Values of step input signal and Bessel filtered output signal for the first and second iteration cycle
| Index i[-] | Time[s] | Step input signal Si[-] | Filtered output signal Yi[-] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Iteration | 2. Iteration | |||
| - 2 | - 0,013333 | 0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| - 1 | - 0,006667 | 0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| 0 | 0,0 | 1 | 0,000071 | 0,000083 |
| 1 | 0,006667 | 1 | 0,000352 | 0,000411 |
| 2 | 0,013333 | 1 | 0,000908 | 0,00106 |
| 3 | 0,02 | 1 | 0,001731 | 0,002019 |
| 4 | 0,026667 | 1 | 0,002813 | 0,003278 |
| 5 | 0,033333 | 1 | 0,004145 | 0,004828 |
| ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| 24 | 0,16 | 1 | 0,067877 | 0,077876 |
| 25 | 0,166667 | 1 | 0,072816 | 0,083476 |
| 26 | 0,173333 | 1 | 0,077874 | 0,089205 |
| 27 | 0,18 | 1 | 0,083047 | 0,095056 |
| 28 | 0,186667 | 1 | 0,088331 | 0,101024 |
| 29 | 0,193333 | 1 | 0,093719 | 0,107102 |
| 30 | 0,2 | 1 | 0,099208 | 0,113286 |
| 31 | 0,206667 | 1 | 0,104794 | 0,11957 |
| 32 | 0,213333 | 1 | 0,110471 | 0,125949 |
| 33 | 0,22 | 1 | 0,116236 | 0,132418 |
| 34 | 0,226667 | 1 | 0,122085 | 0,138972 |
| 35 | 0,233333 | 1 | 0,128013 | 0,145605 |
| 36 | 0,24 | 1 | 0,134016 | 0,152314 |
| 37 | 0,246667 | 1 | 0,140091 | 0,159094 |
| ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| 175 | 1,166667 | 1 | 0,862416 | 0,895701 |
| 176 | 1,173333 | 1 | 0,864968 | 0,897941 |
| 177 | 1,18 | 1 | 0,867484 | 0,900145 |
| 178 | 1,186667 | 1 | 0,869964 | 0,902312 |
| 179 | 1,193333 | 1 | 0,87241 | 0,904445 |
| 180 | 1,2 | 1 | 0,874821 | 0,906542 |
| 181 | 1,206667 | 1 | 0,877197 | 0,908605 |
| 182 | 1,213333 | 1 | 0,87954 | 0,910633 |
| 183 | 1,22 | 1 | 0,881849 | 0,912628 |
| 184 | 1,226667 | 1 | 0,884125 | 0,914589 |
| 185 | 1,233333 | 1 | 0,886367 | 0,916517 |
| 186 | 1,24 | 1 | 0,888577 | 0,918412 |
| 187 | 1,246667 | 1 | 0,890755 | 0,920276 |
| 188 | 1,253333 | 1 | 0,8929 | 0,922107 |
| 189 | 1,26 | 1 | 0,895014 | 0,923907 |
| 190 | 1,266667 | 1 | 0,897096 | 0,925676 |
| 191 | 1,273333 | 1 | 0,899147 | 0,927414 |
| 192 | 1,28 | 1 | 0,901168 | 0,929121 |
| 193 | 1,286667 | 1 | 0,903158 | 0,930799 |
| 194 | 1,293333 | 1 | 0,905117 | 0,932448 |
| 195 | 1,3 | 1 | 0,907047 | 0,934067 |
| ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
2.3.Calculation of the smoke valuesU.K.
In the scheme below the general procedure of determining the final smoke value is presented.
In Figure b, the traces of the measured raw opacity signal, and of the unfiltered and filtered light absorption coefficients (k-value) of the first load step of an ELR-Test are shown, and the maximum value Ymax1,A (peak) of the filtered k trace is indicated. Correspondingly, Table C contains the numerical values of index i, time (sampling rate of 150 Hz), raw opacity, unfiltered k and filtered k. Filtering was conducted using the constants of the Bessel algorithm designed in Section 2.2 of this Annex. Due to the large amount of data, only those sections of the smoke trace around the beginning and the peak are tabled.
The peak value (i = 272) is calculated assuming the following data of Table C. All other individual smoke values are calculated in the same way. For starting the algorithm, S-1, S-2, Y-1 and Y-2 are set to zero.
| LA (m) | 0,43 |
| Index i | 272 |
| N ( %) | 16,783 |
| S271 (m-1) | 0,427392 |
| S270 (m-1) | 0,427532 |
| Y271 (m-1) | 0,542383 |
| Y270 (m-1) | 0,542337 |
Calculation of the k-value (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 6.3.1):U.K.
This value corresponds to S272 in the following equation.
Calculation of Bessel averaged smoke (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 6.3.2):U.K.
In the following equation, the Bessel constants of the previous Section 2.2 are used. The actual unfiltered k-value, as calculated above, corresponds to S272 (Si). S271 (Si-1) and S270 (Si-2) are the two preceding unfiltered k-values, Y271 (Yi-1) and Y270 (Yi-2) are the two preceding filtered k-values.
This value corresponds to Ymax1,A in the following equation.
Calculation of the final smoke value (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 6.3.3):U.K.
From each smoke trace, the maximum filtered k-value is taken for the further calculation.
Assume the following values
| Speed | Ymax (m-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle 1 | Cycle 2 | Cycle 3 | |
| A | 0,5424 | 0,5435 | 0,5587 |
| B | 0,5596 | 0,54 | 0,5389 |
| C | 0,4912 | 0,5207 | 0,5177 |
Cycle validation (Annex III, Appendix 1, Section 3.4)U.K.
Before calculating SV, the cycle must be validated by calculating the relative standard deviations of the smoke of the three cycles for each speed.
| Speed | Mean SV(m-1) | Absolute standard deviation(m-1) | Relative standard deviation(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0,5482 | 0,0091 | 1,7 |
| B | 0,5462 | 0,0116 | 2,1 |
| C | 0,5099 | 0,0162 | 3,2 |
In this example, the validation criteria of 15 % are met for each speed.
Table C
Values of opacity N, unfiltered and filtered k-value at beginning of load step
| Index i[-] | Time[s] | Opacity N[%] | Unfiltered k-value[m-1] | Filtered k-value[m-1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - 2 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| - 1 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| 0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| 1 | 0,006667 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,0 |
| 2 | 0,013333 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,0 |
| 3 | 0,02 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,0 |
| 4 | 0,026667 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000001 |
| 5 | 0,033333 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000002 |
| 6 | 0,04 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000002 |
| 7 | 0,046667 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000003 |
| 8 | 0,053333 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000004 |
| 9 | 0,06 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000005 |
| 10 | 0,066667 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000006 |
| 11 | 0,073333 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000008 |
| 12 | 0,08 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000009 |
| 13 | 0,086667 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000011 |
| 14 | 0,093333 | 0,02 | 0,000465 | 0,000012 |
| 15 | 0,1 | 0,192 | 0,004469 | 0,000014 |
| 16 | 0,106667 | 0,212 | 0,004935 | 0,000018 |
| 17 | 0,113333 | 0,212 | 0,004935 | 0,000022 |
| 18 | 0,12 | 0,212 | 0,004935 | 0,000028 |
| 19 | 0,126667 | 0,343 | 0,00799 | 0,000036 |
| 20 | 0,133333 | 0,566 | 0,0132 | 0,000047 |
| 21 | 0,14 | 0,889 | 0,020767 | 0,000061 |
| 22 | 0,146667 | 0,929 | 0,021706 | 0,000082 |
| 23 | 0,153333 | 0,929 | 0,021706 | 0,000109 |
| 24 | 0,16 | 1,263 | 0,029559 | 0,000143 |
| 25 | 0,166667 | 1,455 | 0,034086 | 0,000185 |
| 26 | 0,173333 | 1,697 | 0,039804 | 0,000237 |
| 27 | 0,18 | 2,03 | 0,047695 | 0,000301 |
| 28 | 0,186667 | 2,081 | 0,048906 | 0,000378 |
| 29 | 0,193333 | 2,081 | 0,048906 | 0,000469 |
| 30 | 0,2 | 2,424 | 0,057067 | 0,000573 |
| 31 | 0,206667 | 2,475 | 0,058282 | 0,000693 |
| 32 | 0,213333 | 2,475 | 0,058282 | 0,000827 |
| 33 | 0,22 | 2,808 | 0,066237 | 0,000977 |
| 34 | 0,226667 | 3,01 | 0,071075 | 0,001144 |
| 35 | 0,233333 | 3,253 | 0,076909 | 0,001328 |
| 36 | 0,24 | 3,606 | 0,08541 | 0,001533 |
| 37 | 0,246667 | 3,96 | 0,093966 | 0,001758 |
| 38 | 0,253333 | 4,455 | 0,105983 | 0,002007 |
| 39 | 0,26 | 4,818 | 0,114836 | 0,002283 |
| 40 | 0,266667 | 5,02 | 0,119776 | 0,002587 |
Values of opacity N, unfiltered and filtered k-value around Ymax1,A (≡ peak value, indicated in bold number)
| Index i[-] | Time[s] | Opacity N[%] | Unfiltered k-value[m-1] | Filtered k-value[m-1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 259 | 1,726667 | 17,182 | 0,438429 | 0,538856 |
| 260 | 1,733333 | 16,949 | 0,431896 | 0,539423 |
| 261 | 1,74 | 16,788 | 0,427392 | 0,539936 |
| 262 | 1,746667 | 16,798 | 0,427671 | 0,540396 |
| 263 | 1,753333 | 16,788 | 0,427392 | 0,540805 |
| 264 | 1,76 | 16,798 | 0,427671 | 0,541163 |
| 265 | 1,766667 | 16,798 | 0,427671 | 0,541473 |
| 266 | 1,773333 | 16,788 | 0,427392 | 0,541735 |
| 267 | 1,78 | 16,788 | 0,427392 | 0,541951 |
| 268 | 1,786667 | 16,798 | 0,427671 | 0,542123 |
| 269 | 1,793333 | 16,798 | 0,427671 | 0,542251 |
| 270 | 1,8 | 16,793 | 0,427532 | 0,542337 |
| 271 | 1,806667 | 16,788 | 0,427392 | 0,542383 |
| 272 | 1,813333 | 16,783 | 0,427252 | 0,542389 |
| 273 | 1,82 | 16,78 | 0,427168 | 0,542357 |
| 274 | 1,826667 | 16,798 | 0,427671 | 0,542288 |
| 275 | 1,833333 | 16,778 | 0,427112 | 0,542183 |
| 276 | 1,84 | 16,808 | 0,427951 | 0,542043 |
| 277 | 1,846667 | 16,768 | 0,426833 | 0,54187 |
| 278 | 1,853333 | 16,01 | 0,40575 | 0,541662 |
| 279 | 1,86 | 16,01 | 0,40575 | 0,541418 |
| 280 | 1,866667 | 16,0 | 0,405473 | 0,541136 |
| 281 | 1,873333 | 16,01 | 0,40575 | 0,540819 |
| 282 | 1,88 | 16,0 | 0,405473 | 0,540466 |
| 283 | 1,886667 | 16,01 | 0,40575 | 0,54008 |
| 284 | 1,893333 | 16,394 | 0,416406 | 0,539663 |
| 285 | 1,9 | 16,394 | 0,416406 | 0,539216 |
| 286 | 1,906667 | 16,404 | 0,416685 | 0,538744 |
| 287 | 1,913333 | 16,394 | 0,416406 | 0,538245 |
| 288 | 1,92 | 16,394 | 0,416406 | 0,537722 |
| 289 | 1,926667 | 16,384 | 0,416128 | 0,537175 |
| 290 | 1,933333 | 16,01 | 0,40575 | 0,536604 |
| 291 | 1,94 | 16,01 | 0,40575 | 0,536009 |
| 292 | 1,946667 | 16,0 | 0,405473 | 0,535389 |
| 293 | 1,953333 | 16,01 | 0,40575 | 0,534745 |
| 294 | 1,96 | 16,212 | 0,411349 | 0,534079 |
| 295 | 1,966667 | 16,394 | 0,416406 | 0,533394 |
| 296 | 1,973333 | 16,394 | 0,416406 | 0,532691 |
| 297 | 1,98 | 16,192 | 0,410794 | 0,531971 |
| 298 | 1,986667 | 16,0 | 0,405473 | 0,531233 |
| 299 | 1,993333 | 16,0 | 0,405473 | 0,530477 |
| 300 | 2,0 | 16,0 | 0,405473 | 0,529704 |
3.ETC TESTU.K.
3.1.Gaseous emissions (diesel engine)U.K.
Assume the following test results for a PDP-CVS system
| V0 (m3/rev) | 0,1776 |
| Np (rev) | 23 073 |
| pB (kPa) | 98,0 |
| p1 (kPa) | 2,3 |
| T (K) | 322,5 |
| Ha (g/kg) | 12,8 |
| NOx conce (ppm) | 53,7 |
| NOx concd (ppm) | 0,4 |
| COconce (ppm) | 38,9 |
| COconcd (ppm) | 1,0 |
| HCconce (ppm) | 9,0 |
| HCconcd (ppm) | 3,02 |
| CO2,conce (%) | 0,723 |
| Wact (kWh) | 62,72 |
Calculation of the diluted exhaust gas flow (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.1):U.K.
Calculation of the NOx correction factor (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.2):U.K.
Calculation of the background corrected concentrations (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.3.1.1):U.K.
Assuming a diesel fuel of the composition C1H1,8
Calculation of the emissions mass flow (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.3.1):U.K.
Calculation of the specific emissions (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.4):U.K.
3.2.Particulate emissions (diesel engine)U.K.
Assume the following test results for a PDP-CVS system with double dilution
| MTOTW (kg) | 4 237,2 |
| Mf,p (mg) | 3,03 |
| Mf,b (mg) | 0,044 |
| MTOT (kg) | 2,159 |
| MSEC (kg) | 0,909 |
| Md (mg) | 0,341 |
| MDIL (kg) | 1,245 |
| DF | 18,69 |
| Wact (kWh) | 62,72 |
Calculation of the mass emission (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 5.1):U.K.
Calculation of the background corrected mass emission (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 5.1):U.K.
Calculation of the specific emission (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 5.2):U.K.
3.3.Gaseous emissions (CNG engine)U.K.
Assume the following test results for a PDP-CVS system with double dilution
| MTOTW (kg) | 4 237,2 |
| Ha (g/kg) | 12,8 |
| NOx conce (ppm) | 17,2 |
| NOx concd (ppm) | 0,4 |
| COconce (ppm) | 44,3 |
| COconcd (ppm) | 1,0 |
| HCconce (ppm) | 27,0 |
| HCconcd (ppm) | 3,02 |
| CH4 conce (ppm) | 18,0 |
| CH4 concd (ppm) | 1,7 |
| CO2,conce ( %) | 0,723 |
| Wact (kWh) | 62,72 |
Calculation of the NOx, correction factor (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.2):U.K.
Calculation of the NMHC concentration (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.3.1):U.K.
Calculation of the background corrected concentrations (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.3.1.1):U.K.
Assuming a G20 reference fuel (100 % methane) of the composition C1H4:
For NMHC, the background concentration is the difference between HCconcd and CH4concd U.K.
Calculation of the emissions mass flow (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.3.1):U.K.
Calculation of the specific emissions (Annex III, Appendix 2, Section 4.4):U.K.
4.λ-SHIFT FACTOR (Sλ)U.K.
4.1.Calculation of the λ-shift factor (Sλ)(1) U.K.
where:
=
λ-shift factor;
=
% by volume of inert gases in the fuel (i.e. N2, CO2, He, etc.);
=
% by volume of original oxygen in the fuel;
where:
=
% by volume of methane in the fuel;
=
% by volume of all C2 hydrocarbons (e.g. C2H6, C2H4, etc.) in the fuel;
=
% by volume of all C3 hydrocarbons (e.g. C3H8, C3H6, etc.) in the fuel;
=
% by volume of all C4 hydrocarbons (e.g. C4H10, C4H8, etc.) in the fuel
=
% by volume of all C5 hydrocarbons (e.g. C5H12, C5H10, etc.) in the fuel;
=
% by volume of dilution gases in the fuel (i.e. O2 *, N2, CO2, He etc.).
4.2.Examples for the calculation of the λ-shift factor Sλ U.K.
Example 1: G25: CH4 = 86 %, N2 = 14 % (by volume)U.K.
Example 2: GR: CH4 = 87 %, C2H6 = 13 % (by vol)U.K.
Example 3: USA: CH4 = 89 %, C2H6 = 4,5 %, C3H8 = 2,3 %, C6H14 = 0,2 %, O2 = 0,6 %, N2 = 4 %U.K.
Stoichiometric Air/Fuel ratios of automotive fuels - SAE J1829, June 1987. John B. Heywood, Internal combustion engine fundamentals, McGraw-Hill, 1988, Chapter 3.4 ‘Combustion stoichiometry’ (pp. 68 to 72).
Options/Cymorth
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThis Annex only
You have chosen to open the Whole Directive
The Whole Directive you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
Y Rhestrau you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
Gweler y wybodaeth ychwanegol ochr yn ochr â’r cynnwys
Rhychwant ddaearyddol: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Mae’r llinell amser yma yn dangos y fersiynau gwahanol a gymerwyd o EUR-Lex yn ogystal ag unrhyw fersiynau dilynol a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig.
Cymerir dyddiadau fersiynau’r UE o ddyddiadau’r dogfennau ar EUR-Lex ac efallai na fyddant yn cyfateb â’r adeg pan ddaeth y newidiadau i rym ar gyfer y ddogfen.
Ar gyfer unrhyw fersiynau a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig, bydd y dyddiad yn cyd-fynd â’r dyddiad cynharaf y daeth y newid (e.e. ychwanegiad, diddymiad neu gyfnewidiad) a weithredwyd i rym. Am ragor o wybodaeth gweler ein canllaw i ddeddfwriaeth ddiwygiedig ar Ddeall Deddfwriaeth.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill