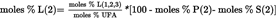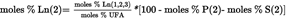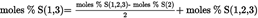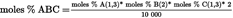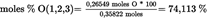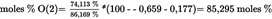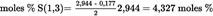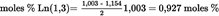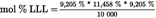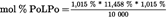- Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (Diwygiedig)
- Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser (01/01/2008)
- Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE)
Commission Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91Dangos y teitl llawn
Commission Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91 of 11 July 1991 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis
You are here:
- Rheoliadau yn deillio o’r UE
- 1991 No. 2568
- ANNEX XVIII
- Dangos Graddfa Ddaearyddol(e.e. Lloegr, Cymru, Yr Alban aca Gogledd Iwerddon)
- Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Rhagor o Adnoddau
PDF o Fersiynau Diwygiedig
- ddiwygiedig 20/10/20193.52 MB
- ddiwygiedig 04/12/20163.60 MB
- ddiwygiedig 11/10/20163.55 MB
- ddiwygiedig 04/08/20163.60 MB
- ddiwygiedig 16/10/20153.42 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/01/20153.68 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/03/20143.69 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/01/20142.84 MB
- ddiwygiedig 09/08/20122.49 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/04/20112.46 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/10/20081.42 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/01/20081.42 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/11/20035.95 MB
- ddiwygiedig 22/05/20020.48 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/11/20010.66 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/07/20010.66 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/06/19990.65 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/11/19980.65 MB
- ddiwygiedig 10/02/19980.65 MB
- ddiwygiedig 31/10/19950.59 MB
- ddiwygiedig 28/05/19950.59 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/11/19940.55 MB
- ddiwygiedig 19/02/19940.55 MB
- ddiwygiedig 05/02/19940.55 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/05/19930.55 MB
- ddiwygiedig 21/03/19930.56 MB
- ddiwygiedig 20/02/19930.56 MB
- ddiwygiedig 01/11/19920.55 MB
- ddiwygiedig 21/07/19920.55 MB
- ddiwygiedig 03/07/19920.54 MB
- ddiwygiedig 05/06/19920.54 MB
- ddiwygiedig 21/12/19910.52 MB
- ddiwygiedig 06/09/19910.52 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
Mae hon yn eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n deillio o’r UE
Mae unrhyw newidiadau sydd wedi cael eu gwneud yn barod gan y tîm yn ymddangos yn y cynnwys a chyfeirir atynt gydag anodiadau.Ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael bydd tair fersiwn o’r ddeddfwriaeth yma i’w gwirio at ddibenion gwahanol. Y fersiwn legislation.gov.uk yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn y Deyrnas Unedig. Y Fersiwn UE sydd ar EUR-lex ar hyn o bryd yw’r fersiwn sy’n weithredol yn yr UE h.y. efallai y bydd arnoch angen y fersiwn hon os byddwch yn gweithredu busnes yn yr UE. EUR-Lex Y fersiwn yn yr archif ar y we yw’r fersiwn swyddogol o’r ddeddfwriaeth fel yr oedd ar y diwrnod ymadael cyn cael ei chyhoeddi ar legislation.gov.uk ac unrhyw newidiadau ac effeithiau a weithredwyd yn y Deyrnas Unedig wedyn. Mae’r archif ar y we hefyd yn cynnwys cyfraith achos a ffurfiau mewn ieithoedd eraill o EUR-Lex. The EU Exit Web Archive legislation_originated_from_EU_p3
Changes over time for: ANNEX XVIII
Version Superseded: 01/10/2008
Status:
Point in time view as at 01/01/2008.
Changes to legislation:
There are outstanding changes not yet made to Commission Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91. Any changes that have already been made to the legislation appear in the content and are referenced with annotations.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Changes and effects yet to be applied by the editorial team are only applicable when viewing the latest version or prospective version of legislation. They are therefore not accessible when viewing legislation as at a specific point in time. To view the ‘Changes to Legislation’ information for this provision return to the latest version view using the options provided in the ‘What Version’ box above.
[F1ANNEX XVIII U.K. DETERMINATION OF TRIACYLGLYCEROLS WITH ECN 42 (DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HPLC DATA AND THEORETICAL CONTENT)
Textual Amendments
F1 Inserted by Commission Regulation (EC) No 2472/97 of 11 December 1997 amending Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis and Council Regulation (EEC) No 2658/87 on the tariff and statistical nomenclature and on the Common Customs Tariff.
1. Scope U.K.
Determination of the composition of triacylglycerols (TAGs) in olive oils, in terms of their equivalent carbon number by differences between the analytical results obtained by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and the theoretical content, calculated starting from the fatty acid composition.
2. Field application U.K.
The standard is applicable to olive oils. The method is applicable to the detection of the presence of small amounts of seed oils (rich in linoleic acid) in every class of olive oils.
3. Principle U.K.
The content of triacylglycerols with ECN42 determined by HPLC analysis and the theoretical content of triacylglycerols with ECN42 (calculated on the basis of GLC determination of fatty acid composition) correspond within a certain limit for pure oils. A difference larger than the values stated in the Regulation for each type of oil points out that the oil contains seed oils.
4. Method U.K.
The method for calculation of theoretical content of triacylglycerols with ECN42 and of the difference between the HPLC data and this one essentially is made by the coordination of analytical data obtained by means of other methods: it is possible to distinguish three phases: determination of fatty acid composition by capillary gas chromatography, calculation of theoretical composition of triacylglycerols with ECN42, HPLC determination of ECN42 triacylglycerols
4.1. Apparatus U.K.
4.1.1. Round bottom flasks, 250 and 500 ml. U.K.
4.1.2. Beakers 100 ml. U.K.
4.1.3. Glass chromatographic column, 21 mm internal diameter, 450 mm length, with cock and normalized cone (female) at the top. U.K.
4.1.4. Separator funnels, 250 ml, with normalized cone (male) at the bottom, suitable to be connected with the top of the column. U.K.
4.1.5. Glass rod, 600 mm length. U.K.
4.1.6. Glass funnel, 80 mm diameter. U.K.
4.1.7. Volumetric flasks, 50 ml. U.K.
4.1.8. Volumetic flasks, 20 ml. U.K.
4.1.9. Rotative evaporator. U.K.
4.1.10. High performance liquid chromatography, allowing thermostatic control of column temperature. U.K.
4.1.11. Injection units for 10 μl delivery. U.K.
4.1.12. Detector: differential refractometer. The full scale sensitivity should be at least 10 -4 units of refractive index. U.K.
4.1.13. Column: stainless steel tube 250 mm length and 4,5 mm internal diameter packed with 5 μm diameter particles of slica with 22 to 23 % carbon in the form of octadecylsilane (note 2). U.K.
4.1.14. Recorder and/or integrator. U.K.
4.2. Reagents U.K.
The reagents should be of analytical purity. Elution solvents should be de-gassed, and may be recycled several times without effect on the separations.
4.2.1. Petroleum ether 40 to 60 °C chromatographic grade. U.K.
4.2.2. Ethil ether, peroxides free, freshly distilled. U.K.
4.2.3. Glass chromatographic elution solvent: mixture petroleum ether/ethil ether 87/13 (v/v). U.K.
4.2.4. Silicagel, 70-230 mesh, type Merck 7734, with water content standardized at 5 % (w/w). U.K.
4.2.5. Glass wool. U.K.
4.2.6. Acetone. U.K.
4.2.7. Acetonitrile. U.K.
4.2.8. HPLC elution solvent: acetonitrile + acetone (proportions to be adjusted to obtain the desired separation; begin with 50:50 mixture). U.K.
4.2.9. Solubilization solvent: acetone. U.K.
4.2.10. Reference triglycerides commercial triglycerides tripalmitin, triolein, etc.) may be used and the retention times thence plotted in accordance with the equivalent carbon number, or alternatively reference chromatograms obtained from soya oil, mixture 30:70 soya oil/olive oil and pure olive oil (see notes 3 and 4 and figure 1, 2, 3, 4). U.K.
4.3. Sample preparation U.K.
As a number of interfering substances can rise false positive results, the sample must always be purified according to IUPAC method 2.507, used for determination of polar substances in oxidised oils.
4.3.1. Chromatographic column preparation U.K.
Fill the column (4.1.3) with about 30 ml of elution solvent (4.2.3), then introduce inside the column some glass wool (4.2.5) pushing it to the bottom of the column by means of the glass rod (4.1.5).
In a 100 ml beaker, suspend 25 g of silicagel (4.2.4) in 80 ml of elution mixture (4.2.3), then transfer it inside the column, by means of a glass funnel (4.1.6).
To ensure the complete transfer of silicagel inside the column, wash the beaker with the elution mixture and transfer the washing portions inside the column, too.
Open the cock and let solvent elute from the column until its level is about 1 cm over the silicagel.
4.3.2. Column chromatography U.K.
Weigh with the accuracy of 0,001 g, 2,5 ± 0,1 g of oil, previously filtered, homogenized and anhydrified, if necessary, in a 50 ml volumetric flask (4.1.7). Solve it in about 20 ml of elution solvent (4.2.3), if necessary, slightly heat it to make the dissolution easily. Cool at room temperature and adjust the volume with elution solvent.
By means of a volumetric pipette, introduce 20 ml of solution inside the column prepared according to 4.3.1, open the cock and let solvent elute to the silicagel layer level.
Then elute with 150 ml of elution solvent (4.2.3), adjusting the solvent rate at about 2 ml/min (150 ml will take about 60 to 70 minutes to pass through the column).
The eluated is recovered in a 250 ml round bottom flask (4.1.1) previously tared in an oven and exactly weighted. Eliminate solvent at reduce pressure (Rotavapor) and weigh the residue that will be used to prepare the solution for HPLC analysis and for methyl ester preparation.
The sample recovery from the column must be 90 % at least for extra virgin, virgin, ordinary refined and olive oil categories, and a minimum of 80 % for lampante and residue olive oils.
4.4. HPLC analysis U.K.
4.4.1. Preparation of the samples for chromatographic analysis U.K.
A 5 % solution of the sample to be analysed is prepared by weighing 0,5 ± 0,001 g of the sample into a 10 ml graduated flask and making up to 10 ml with the solubilization solvent (4.2.9).
4.4.2. Procedure U.K.
Set up the chromatographic system. Pump elution solvent (4.2.8) at a rate of 1,5 ml/min to purge the entire system. Wait until a stable base line is obtained. Inject 10 μl of the sample prepared as in 4.3.
4.4.3. Calculation and expression of results U.K.
Use the area normalization method, i.e. assume that the sum of the areas of the peaks corresponding to TAGs from ECN42 up to ECN52 is equal to 100 %. Calculate the relative percentage of each triglyceride using the formula:
% triglyceride = area of peak × 100/ sum of peak areas.
The results are to be given to within at least two decimal places.
Note 1: U.K.
The elution order can be determined by calculating the equivalent carbon numbers, often defined by the relation ECN = CN-2n, where CN is the carbon number and n is the number of double bounds, it can be calculated more precisely by taking into account the origin of the double bond. If n o , n l and n ln are the numbers of double bonds attributed to oleic, linoleic and linolenic acids respectively, the equivalent carbon number can be calculated by means of the relation of the formula: U.K.
ECN = CN - d o n o - d l n l - d ln n ln ,
where the coefficient do, d l and d ln can be calculated by means of the reference triglycerides. Under the conditions specified in this method, the relation obtained will be close in:
ECN = CN - (2,60 n o ) - (2,35 n l ) - (2,17 n ln )
Note 2: U.K.
| Examples: | Lichrosorb (Merck) RP 18 Art 50333 |
| Lichrosphere or equivalent (Merck) 100 CH18 Art 50377. |
Note 3: U.K.
With several reference triglycerides, it is also possible to calculate the resolution with respect to triolein: U.K.
α = RT' / RT triolein
by use of the reduced retention time RT' = RT - RT solvent.
The graph of log α against f (number of double bonds) enables the retention values to be determined for all the triglycerides of fatty acids contained in the reference triglycerides — see figure 2.
Note 4: U.K.
The efficiency of the column should permit clear separation of the peak of trilinoein from the peaks of the triglycerides with an adjacent RT. The elution is carried out up to ECN52 peak. U.K.
Note 5: U.K.
A correct measure of the areas of all peaks of interest for the present determination is ensured if the second peak corresponding to ECN50 is 50 % of full scale of the recorder. U.K.
4.5. Calculation of triacylglycerols composition U.K.
4.5.1. Determination of fatty acid composition U.K.
Fatty acid composition is carried out by means of the EEC gas chromatographic method reported in Annex X A of Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91, by means of a capillary column. The methyl esters preparation is carried out according to Annex X B (sodium methylate alcohol solution).
4.5.2. Fatty acids for calculation U.K.
Glycerides are grouped by their equivalent carbon number (ECN), taking into account the following equivalencies between ECN and fatty acids. Only fatty acids with 16 and 18 carbon atoms were taken in consideration, because only these are important for olive oil.
| Fatty acid (FA) | Abbreviation | Molecular weight (MW) | ECN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Palmatic acid | P | 256,4 | 16 |
| Palmatoleic acid | Po | 254,4 | 14 |
| Stearic acid | S | 284,5 | 18 |
| Oleic acid | O | 282,5 | 16 |
| Linoleic acid | L | 280,4 | 14 |
| Linolenic acid | Ln | 278,4 | 12 |
4.5.3. Conversion of area % into moles for all fatty acids U.K.
4.5.4. Normalization of fatty acids to 100 % U.K.
The result gives the percentage of each fatty acid in moles % in the overall (1,2,3-) position of the TAGs.
Then the sum of the saturated fatty acids P and S (SFA) and the unsaturated fatty acids Po, O, L and Ln (UFA) are calculated:
| moles % SFA = moles % P + moles % S | (3) |
| moles UFA = 100 - moles % SFA |
4.5.5. Calculation of the fatty acid composition in 2- and 1,3- positions of TAGs U.K.
The fatty acids are distributed to three pools as follows: two identical for 1- and 3- positions and one for 2- position, with different coefficients for the saturated (P and S) and unsaturated acids (Po, O, L and Ln).
4.5.5.1. Saturated fatty acids in 2- position [P(2) and S(2)] U.K.
| moles % P(2) = moles % P (1,2,3) * 0,06 | (4) |
| moles % S(2) = moles % S (1,2,3) * 0,06 |
4.5.5.2. Unsaturated fatty acids in 2- position [Po(2), O(2), L(2) and Ln(2)]: U.K.
4.5.5.3. Fatty acids in 1,3-positions [P(1,3), S(1,3), Po(1,3) O(1,3), L(1,3) and Ln(1,3)]: U.K.
4.5.6. Calculation of triacylglycerols U.K.
4.5.6.1. TAGs with one fatty acid (AAA, here LLL, PoPoPo) U.K.
4.5.6.2. TAGs with two fatty acids (AAB, here PoPoL, PoLL) U.K.
4.5.6.3. TAGs with three different fatty acids (ABC, here OLLn, PLLn, PoOLn, PPoLn) U.K.
4.5.6.4. Triacylglycerides with ECN42 U.K.
The following triglycerides with ECN42 are calculated according equation 7, 8 and 9 in order of expected elution in HPLC (normally only three peaks).
LLL
PoLL and the positional isomer LPoL
OLLn and the positional isomers OLnL and LnOL
PoPoL and the positional isomer PoLPo
PoOLn and the positional isomers OPoLn and OLnPo
PLLn and the positional isomers LLnP and LnPL
PoPoPo
SLnLn and the positional isomer LnSLn
PPoLn and the positional isomers PLnPo and PoPLn
The triacylglycerides with ECN42 are given by the sum of the nine triacylglycerols including their positional isomers. The results to be given with at least two decimal places.
5. Evaluation of the results U.K.
The calculated theoretical content and the content determined by the HPLC analysis are compared. If the difference between HLPC data minus theoretical data is greater than the values states for the appropriate oil category in the Regulation, the sample contains seed oil.
Note: U.K.
Results are given to within one decimal figure. U.K.
6. Example (The numbers refer to the sections in the text of the method) U.K.
4.5.1. Calculation of moles % fatty acids from GLC data (area %) U.K.
The following data are obtained for the fatty acid composition by GLC:
| FA MW | P 256,4 | S 284,5 | Po 254,4 | O 282,5 | L 280,4 | Ln 278,4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| area % | 10,0 | 3,0 | 1,0 | 75,0 | 10,0 | 1,0 |
4.5.3. Conversion of area % into moles for all fatty acids U.K.
4.5.4. Normalization of fatty acids to 100 % U.K.
Sum of the saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in the 1,2,3- position of TAGs
| moles % SFA = 10,888 % + 2,944 % = 13,831 % | See formula (3) |
| moles % UFA = 100,000 % — 13,831 % = 86,169 % | See formula (3) |
4.5.5. Calculation of the fatty acid composition in 2- and 1,3- positions of the TAGs U.K.
4.5.5.1. Saturated fatty acids in 2- position [P(2) and S(2)] U.K.
| moles % P(2) = 10,888 % * 0,06 = 0,653 moles % | See formula (4) |
| moles % S(2) = 2,944 % * 0,06 = 0,177 moles % | See formula (4) |
4.5.5.2. Unsaturated fatty acids in 1,3-position [Po(1,3), O(1,3), L(1,3) and Ln(1,3)] U.K.
4.5.5.3. Fatty acids in 1,3-positions [P(1,3), S(1,3), Po(1,3), O(1,3), L(1,3) and Ln(1,3)] U.K.
4.5.6. Calculation of triacylglycerols U.K.
From the calculated fatty acid composition in sn-2- and sn-1,3- positions (see above):
| FA in | 1,3-pos. | 2-pos. |
|---|---|---|
| P | 16,005 % | 0,653 % |
| S | 4,327 % | 0,177 % |
| Po | 1,015 % | 1,263 % |
| O | 68,522 % | 85,295 % |
| L | 9,205 % | 11,458 % |
| Ln | 0,927 % | 1,154 % |
| Sum | 100,0 % | 100,0 % |
the following triacylglycerols are calculated:
LLL
PoPoPo
PoLL with 1 positional isomer
SLnLn with 1 positional isomer
PoPoL with 1 positional isomer
PPoLn with 2 positional isomers
OLLn with 2 positional isomers
PLLn with 2 positional isomers
PoOLn with 2 positional isomers.
4.5.6.1. TAGs with one fatty acid (LLL, PoPoPo) See formula (7) U.K.
4.5.6.2. TAGs with two fatty acids (PoLL, SLnLn, PoPoL) See formula (8) U.K.
4.5.6.3. TAGs with three different fatty acids (PoPLn, OLLn, PLLn, PoOLn) See formula (9) U.K.
[F2Note: U.K.
La = lauric acid; My = myristic acid; P = palmitic acid; St = stearic acid; O = oleic acid; L = linoleic acid; Ln = linolenic acid.] ] U.K.
Textual Amendments
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThis Annex only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
Y Rhestrau you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Mae deddfwriaeth ar gael mewn fersiynau gwahanol:
Y Diweddaraf sydd Ar Gael (diwygiedig):Y fersiwn ddiweddaraf sydd ar gael o’r ddeddfwriaeth yn cynnwys newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth ddilynol ac wedi eu gweithredu gan ein tîm golygyddol. Gellir gweld y newidiadau nad ydym wedi eu gweithredu i’r testun eto yn yr ardal ‘Newidiadau i Ddeddfwriaeth’.
Gwreiddiol (Fel y’i mabwysiadwyd gan yr UE): Mae'r wreiddiol version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Pwynt Penodol mewn Amser: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
Gweler y wybodaeth ychwanegol ochr yn ochr â’r cynnwys
Rhychwant ddaearyddol: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Dangos Llinell Amser Newidiadau: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Gallwch wneud defnydd o ddogfennau atodol hanfodol a gwybodaeth ar gyfer yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth o’r tab hwn. Yn ddibynnol ar yr eitem ddeddfwriaeth sydd i’w gweld, gallai hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- slipiau cywiro
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill
Llinell Amser Newidiadau
Mae’r llinell amser yma yn dangos y fersiynau gwahanol a gymerwyd o EUR-Lex yn ogystal ag unrhyw fersiynau dilynol a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig.
Cymerir dyddiadau fersiynau’r UE o ddyddiadau’r dogfennau ar EUR-Lex ac efallai na fyddant yn cyfateb â’r adeg pan ddaeth y newidiadau i rym ar gyfer y ddogfen.
Ar gyfer unrhyw fersiynau a grëwyd ar ôl y diwrnod ymadael o ganlyniad i newidiadau a wnaed gan ddeddfwriaeth y Deyrnas Unedig, bydd y dyddiad yn cyd-fynd â’r dyddiad cynharaf y daeth y newid (e.e. ychwanegiad, diddymiad neu gyfnewidiad) a weithredwyd i rym. Am ragor o wybodaeth gweler ein canllaw i ddeddfwriaeth ddiwygiedig ar Ddeall Deddfwriaeth.
Rhagor o Adnoddau
Defnyddiwch y ddewislen hon i agor dogfennau hanfodol sy’n cyd-fynd â’r ddeddfwriaeth a gwybodaeth am yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth. Gan ddibynnu ar yr eitem o ddeddfwriaeth sy’n cael ei gweld gall hyn gynnwys:
- y PDF print gwreiddiol y fel adopted fersiwn a ddefnyddiwyd am y copi print
- slipiau cywiro
liciwch ‘Gweld Mwy’ neu ddewis ‘Rhagor o Adnoddau’ am wybodaeth ychwanegol gan gynnwys
- rhestr o newidiadau a wnaed gan a/neu yn effeithio ar yr eitem hon o ddeddfwriaeth
- manylion rhoi grym a newid cyffredinol
- pob fformat o’r holl ddogfennau cysylltiedig
- dolenni i ddeddfwriaeth gysylltiedig ac adnoddau gwybodaeth eraill