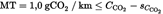- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (31/01/2020)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/160Show full title
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/160 of 5 February 2016 on the approval of the Toyota Motor Europe efficient exterior lighting using light emitting diodes as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Decisions originating from the EU
- 2016 No. 160
- Whole Decision
- Previous
- Next
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Status:
Point in time view as at 31/01/2020.
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects by UK legislation for Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/160.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/160
of 5 February 2016
on the approval of the Toyota Motor Europe efficient exterior lighting using light emitting diodes as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council
(Text with EEA relevance)
THE EUROPEAN COMMISSION,
Having regard to the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union,
Having regard to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 setting emissions performance standards for new passenger cars as part of the Community's integrated approach to reduce CO2 emissions from light-duty vehicles(1), and in particular Article 12(4) thereof,
Whereas:
(1) The manufacturer Toyota Motor Europe NV/SA (the ‘Applicant’) submitted an application for the approval of an efficient exterior lighting system with the use of light emitting diodes (LEDs) as an innovative technology on 15 April 2015. The completeness of that application was assessed in accordance with Article 4 of Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011(2). The Commission identified certain relevant information as missing in the original application and requested the applicant to complete it. The applicant provided the required information on 26 May 2015. The application was found to be complete and the period for the Commission's assessment of the application started on the day following the date of official receipt of the complete information, i.e. 27 May 2015.
(2) The application has been assessed in accordance with Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 443/2009, Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 and the Technical Guidelines for the preparation of applications for the approval of innovative technologies pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 (the Technical Guidelines, version February 2013)(3).
(3) The application refers to an efficient exterior lighting system including low-beam headlamp, high-beam headlamp, front position, front fog, rear fog, front turn signal, rear turn signal, licence plate and reversing lamps fitted with LEDs..
(4) The Commission finds that the information provided in the application demonstrates that the conditions and criteria referred to in Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 and in Articles 2 and 4 of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 have been met.
(5) The applicant has demonstrated that the use of the LEDs in the in the low-beam headlamp, the high-beam headlamp, the front position, front fog lamp, rear fog lamp, front turn signal, rear turn signal, licence plate and reversing lamp did not exceed 3 % of the new passenger cars registered in the reference year 2009. In support of this the applicant has referred to the Technical Guidelines, which provides for the summary of the CLEPA Light Sight Safety report. The applicant has used predefined functions and averaged data in line with the simplified approach specified in the Technical Guidelines (version February 2013).
(6) The applicant has in accordance with the simplified approach described in the Technical Guidelines used halogen lighting as baseline technology for demonstrating the CO2-reducing capacity of the efficient exterior lighting system with the use of LEDs in the low-beam headlamp, the high-beam headlamp, the front position, front fog lamp, rear fog lamp, front turn signal, rear turn signal, licence plate and reversing lamp.
(7) The applicant has provided a methodology for testing the CO2 reductions which includes formulae that are consistent with the formulae described in the Technical Guidelines for the simplified approach with regard to lighting functions. The Commission considers that the testing methodology will provide testing results that are verifiable, repeatable and comparable and that it is capable of demonstrating in a realistic manner the CO2 emissions benefits of the innovative technology with strong statistical significance in accordance with Article 6 of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011.
(8) Against that background the Commission finds that the applicant has demonstrated satisfactorily that the emission reduction achieved by the efficient exterior lighting system including the low-beam headlamp, high-beam headlamp, front position lamp, front fog lamp, rear fog lamp and licence plate lamp is at least 1 gCO2/km. It should therefore also be concluded that an efficient exterior lighting system including not only those lamps but also the front turn signal, rear turn signal and the reversing lamps fitted with LEDs or another appropriate combination of those lamps could achieve a CO2 reduction of at least 1 gCO2/km.
(9) Since the activation of the exterior lighting is not required for the CO2 emissions type-approval test referred to in Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council(4) and Commission Regulation (EC) No 692/2008(5), the Commission is satisfied that the lighting functions in question are not covered by the standard test cycle.
(10) The activation of the lighting functions concerned is mandatory to ensure the safe operation of the vehicle and as a consequence not dependent on the choice of the driver. On that basis the Commission finds that the manufacturer should be considered accountable for the CO2 emission reduction due to the use of the innovative technology.
(11) The Commission finds that the verification report has been prepared by Vehicles Certification Agency which is an independent and certified body and that the report supports the findings set out in the application.
(12) Against that background, the Commission finds that no objections should be raised as regards the approval of the innovative technology in question.
(13) Any manufacturer wishing to benefit from a reduction of its average specific CO2 emissions for the purpose of meeting its specific emissions target by means of the CO2 savings from the use of the innovative technology approved by this Decision, should in accordance with Article 11(1) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011, refer to this Decision in its application for an EC type-approval certificate for the vehicles concerned.
(14) For the purposes of determining the general eco-innovation code to be used in the relevant type-approval documents in accordance with Annexes I, VIII and IX to Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council(6), the individual code to be used for the innovative technology approved through this Implementing Decision should be specified,
HAS ADOPTED THIS DECISION:
Article 1U.K.
1.The efficient exterior lighting system including low-beam headlamp, high-beam headlamp, front position, front fog, rear fog, front turn signal, rear turn signal, licence plate and reversing lamp fitted with light emitting diodes (LEDs) intended for use in M1 vehicles is approved as an innovative technology within the meaning of Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 443/2009.
2.The CO2 emissions reduction from the use of the efficient exterior lighting system including all, or an appropriate combination of the lighting functions referred to in paragraph 1 shall be determined using the methodology set out in the Annex.
3.The individual eco-innovation code to be entered into type-approval documentation to be used for the innovative technology approved through this Implementing Decision shall be ‘15’.
Article 2U.K.
This Decision shall enter into force on the twentieth day following that of its publication in the Official Journal of the European Union.
Done at Brussels, 5 February 2016.
For the Commission
The President
Jean-Claude Juncker
ANNEXU.K.
1. Testing methodology — Introduction U.K.
In order to determine the CO2 emission reductions that can be attributed to the efficient exterior lighting system including all, or an appropriate combination of low-beam headlamps, high-beam headlamps, front position, front fog, rear fog, front turn signal, rear turn signal, licence plate and reversing lamps fitted with light emitting diodes (LED) in an M1 vehicle, it is necessary to establish the following:
the testing conditions;
the test procedure;
the formulae for calculating the CO2 savings;
the formulae for calculating the standard deviation;
the determination of the CO2 savings for the certification by type approval authorities.
2. Testing conditions U.K.
The requirements of Regulation UN/ECE No 112(7) on uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or light-emitting diode (LED) modules shall apply. For determining the power consumption, the reference is to be made to point 6.1.4 of Regulation No 112, and points 3.2.1 and 3.2.2 of Annex 10 to Regulation No 112.
3. The testing procedure U.K.
Measurements are to be performed as shown in the figure. The following equipment is to be used:
a power supply unit (i.e. variable voltage supplier),
two digital multi-meters, one for measuring the DC current, and the other for measuring the DC voltage. In the figure the test set-up shows the possible case of the DC voltage meter integrated in the power supply unit.
Test set-up U.K.
In total, five measurements on the current should be done at 13,2 V for each type of lighting used in the vehicle (i.e. low-beam headlamp, high-beam headlamp, front position, front fog, rear fog, front turn signal, rear turn signal, licence plate and reversing lamps). LED module(s) operated by an electronic light source control gear, shall be measured as specified by the applicant.
As an alternative, other measurements on the current can be done at other additional voltages. The manufacturer must hand over verified documentation on the necessity to perform these other measurements to the type-approval authority. In total, five measurements on the current are to be done at each of these additional voltages.
The exact installed voltages and the measured current are to be recorded in four decimals.
4. Formulae U.K.
The following steps are to be taken to determine the CO2 savings and to determine whether the threshold value of 1 gCO2/km is met:
Step 1: Calculation of the power savings
Step 2: Calculation of the CO2 savings
Step 3: Calculation of the error in the CO2 savings
Step 4: Verification of the threshold value.
4.1 Calculation of the power savings U.K.
For each of the five measurements the power which is used is to be calculated by multiplying the installed voltage with the measured current. When a stepper motor or electronic controller is used for the supply of the electricity to the LED lamps, then the electric load of this component part is to be excluded from the measurement. This will result in five values. Each value must be expressed in four decimals. Then the mean value of the used power will be calculated, which is the sum of the five values for the power divided by five.
The resulting power savings are to be calculated with the following formula:
Formula (1):
ΔP = Pbaseline – Peco-innovation
Where:
Power savings [W];
Power of the baseline, specified in Table 1 [W];
Mean value of the used power of the eco-innovation [W].
Table 1
Power requirements for different baseline types of lighting
| Type of lighting | Total electric power [W] |
|---|---|
| Low-beam headlamp | 137 |
| High-beam headlamp | 150 |
| Front position | 12 |
| Licence plate | 12 |
| Front fog lamp | 124 |
| Rear fog lamp | 26 |
| Front turn signal lamp | 13 |
| Rear turn signal lamp | 13 |
| Reversing lamp | 52 |
4.2 Calculation of the CO2 savings U.K.
The total CO2 savings of the innovative technology (efficient exterior lighting system) are to be calculated by formulae (2), (3) and (4).
For a petrol-fuelled vehicle:
Formula(2):
For a diesel-fuelled vehicle:
Formula(3)
For a petrol-fuelled vehicle with turbo charger:
Formula(4)
These formulae present the total CO2 savings of the innovative technology (efficient exterior lighting system) in gCO2/km.
The input data for the formulae (2), (3) and (4) are:
Saved electrical power in W of the type of lighting j, which is the result of step 1
Usage factor of the type of lighting j, specified in Table 2
Number of types of lighting in the innovative technology package
Mean driving speed of the NEDC, which is 33,58 km/h
Consumption of effective power for petrol-fuelled vehicles, which is 0,264 l/kWh
Consumption of effective power for diesel-fuelled vehicles, which is 0,22 l/kWh
Consumption of effective power for petrol-fuelled vehicles with turbo charger, which is 0,28 l/kWh
Efficiency of the alternator, which is 0,67
Conversion factor for petrol fuel, which is 2 330 gCO2/l
Conversion factor for diesel fuel, which is 2 640 gCO2/l
Table 2
Usage factor for different types of lighting
| Type of lighting | Usage factor UF |
|---|---|
| Low-beam headlamp | 0,33 |
| High-beam headlamp | 0,03 |
| Front position | 0,36 |
| Licence plate | 0,36 |
| Front fog lamp | 0,01 |
| Rear fog lamp | 0,01 |
| Front turn signal lamp | 0,15 |
| Rear turn signal lamp | 0,15 |
| Reversing lamp | 0,01 |
4.3 Calculation of the statistical error in the CO2 savings U.K.
The statistical error in the CO2 savings is to be determined in two steps. In the first step the error value of the power is to be determined as a standard deviation being equivalent to a confidence interval of 68 % around the mean.
This is to be done by formula (5).
Formula (5):
Where:
Sample data [W]
Number of observations of the sample, which is five.
In order to calculate the error in the CO2 savings for petrol, petrol turbo and diesel-fuelled vehicles, the propagation law, expressed in formula (6), is to be applied.
Formula (6):
Where:
Number of types of lighting in the innovative technology package
Substituting formula (2) in formula (6) results in formula (7) for calculating the error in CO2 savings for petrol-fuelled vehicles.
Formula (7)
Substituting formula (3) in formula (6) results in formula (8) for calculating the error in CO2 savings for diesel-fuelled vehicles.
Formula(8):
Substituting formula (4) in formula (6) results in formula (9) for calculating the error in CO2 savings for petrol-fuelled vehicles with turbo charger.
Formula (9):
4.4 Verification of the threshold value U.K.
In order to demonstrate that the 1,0 gCO2/km threshold is exceeded with statistical relevance, the following formula (10) should be used.
Formula 10:
Where:
Minimum threshold [gCO2/km],
Where the total CO2 emission savings of the innovative technology (efficient exterior lighting system), as a result of the calculation using formula (10), are below the threshold specified in Article 9(1) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011, the second subparagraph of Article 11(2) of that Regulation shall apply.
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011of 25 July 2011 establishing a procedure for the approval and certification of innovative technologies for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars (OJ L 194, 26.7.2011, p. 19).
https://circabc.europa.eu/w/browse/42c4a33e-6fd7-44aa-adac-f28620bd436f
Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2007 on type approval of motor vehicles with respect to emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro 5 and Euro 6) and on access to vehicle repair and maintenance information (OJ L 171, 29.6.2007, p. 1).
Commission Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 of 18 July 2008 implementing and amending Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council on type-approval of motor vehicles with respect to emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro 5 and Euro 6) and on access to vehicle repair and maintenance information (OJ L 199, 28.7.2008, p. 1).
Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 September 2007 establishing a framework for the approval of motor vehicles and their trailers, and of systems, components and separate technical units intended for such vehicles (Framework Directive) (OJ L 263, 9.10.2007, p. 1).
E/ECE/324/Rev.2/Add.111/Rev.3 — E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.2/Add.111/Rev.3, 9 January 2013.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Decision
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources