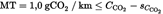- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/160Show full title
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/160 of 5 February 2016 on the approval of the Toyota Motor Europe efficient exterior lighting using light emitting diodes as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Decisions originating from the EU
- 2016 No. 160
- Annexes only
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/160 (Annexes only)
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects by UK legislation for Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/160.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
ANNEXU.K.
1. Testing methodology — Introduction U.K.
In order to determine the CO2 emission reductions that can be attributed to the efficient exterior lighting system including all, or an appropriate combination of low-beam headlamps, high-beam headlamps, front position, front fog, rear fog, front turn signal, rear turn signal, licence plate and reversing lamps fitted with light emitting diodes (LED) in an M1 vehicle, it is necessary to establish the following:
the testing conditions;
the test procedure;
the formulae for calculating the CO2 savings;
the formulae for calculating the standard deviation;
the determination of the CO2 savings for the certification by type approval authorities.
2. Testing conditions U.K.
The requirements of Regulation UN/ECE No 112(1) on uniform provisions concerning the approval of motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or light-emitting diode (LED) modules shall apply. For determining the power consumption, the reference is to be made to point 6.1.4 of Regulation No 112, and points 3.2.1 and 3.2.2 of Annex 10 to Regulation No 112.
3. The testing procedure U.K.
Measurements are to be performed as shown in the figure. The following equipment is to be used:
a power supply unit (i.e. variable voltage supplier),
two digital multi-meters, one for measuring the DC current, and the other for measuring the DC voltage. In the figure the test set-up shows the possible case of the DC voltage meter integrated in the power supply unit.
Test set-up U.K.
In total, five measurements on the current should be done at 13,2 V for each type of lighting used in the vehicle (i.e. low-beam headlamp, high-beam headlamp, front position, front fog, rear fog, front turn signal, rear turn signal, licence plate and reversing lamps). LED module(s) operated by an electronic light source control gear, shall be measured as specified by the applicant.
As an alternative, other measurements on the current can be done at other additional voltages. The manufacturer must hand over verified documentation on the necessity to perform these other measurements to the type-approval authority. In total, five measurements on the current are to be done at each of these additional voltages.
The exact installed voltages and the measured current are to be recorded in four decimals.
4. Formulae U.K.
The following steps are to be taken to determine the CO2 savings and to determine whether the threshold value of 1 gCO2/km is met:
Step 1: Calculation of the power savings
Step 2: Calculation of the CO2 savings
Step 3: Calculation of the error in the CO2 savings
Step 4: Verification of the threshold value.
4.1 Calculation of the power savings U.K.
For each of the five measurements the power which is used is to be calculated by multiplying the installed voltage with the measured current. When a stepper motor or electronic controller is used for the supply of the electricity to the LED lamps, then the electric load of this component part is to be excluded from the measurement. This will result in five values. Each value must be expressed in four decimals. Then the mean value of the used power will be calculated, which is the sum of the five values for the power divided by five.
The resulting power savings are to be calculated with the following formula:
Formula (1):
ΔP = Pbaseline – Peco-innovation
Where:
Power savings [W];
Power of the baseline, specified in Table 1 [W];
Mean value of the used power of the eco-innovation [W].
Table 1
Power requirements for different baseline types of lighting
| Type of lighting | Total electric power [W] |
|---|---|
| Low-beam headlamp | 137 |
| High-beam headlamp | 150 |
| Front position | 12 |
| Licence plate | 12 |
| Front fog lamp | 124 |
| Rear fog lamp | 26 |
| Front turn signal lamp | 13 |
| Rear turn signal lamp | 13 |
| Reversing lamp | 52 |
4.2 Calculation of the CO2 savings U.K.
The total CO2 savings of the innovative technology (efficient exterior lighting system) are to be calculated by formulae (2), (3) and (4).
For a petrol-fuelled vehicle:
Formula(2):
For a diesel-fuelled vehicle:
Formula(3)
For a petrol-fuelled vehicle with turbo charger:
Formula(4)
These formulae present the total CO2 savings of the innovative technology (efficient exterior lighting system) in gCO2/km.
The input data for the formulae (2), (3) and (4) are:
Saved electrical power in W of the type of lighting j, which is the result of step 1
Usage factor of the type of lighting j, specified in Table 2
Number of types of lighting in the innovative technology package
Mean driving speed of the NEDC, which is 33,58 km/h
Consumption of effective power for petrol-fuelled vehicles, which is 0,264 l/kWh
Consumption of effective power for diesel-fuelled vehicles, which is 0,22 l/kWh
Consumption of effective power for petrol-fuelled vehicles with turbo charger, which is 0,28 l/kWh
Efficiency of the alternator, which is 0,67
Conversion factor for petrol fuel, which is 2 330 gCO2/l
Conversion factor for diesel fuel, which is 2 640 gCO2/l
Table 2
Usage factor for different types of lighting
| Type of lighting | Usage factor UF |
|---|---|
| Low-beam headlamp | 0,33 |
| High-beam headlamp | 0,03 |
| Front position | 0,36 |
| Licence plate | 0,36 |
| Front fog lamp | 0,01 |
| Rear fog lamp | 0,01 |
| Front turn signal lamp | 0,15 |
| Rear turn signal lamp | 0,15 |
| Reversing lamp | 0,01 |
4.3 Calculation of the statistical error in the CO2 savings U.K.
The statistical error in the CO2 savings is to be determined in two steps. In the first step the error value of the power is to be determined as a standard deviation being equivalent to a confidence interval of 68 % around the mean.
This is to be done by formula (5).
Formula (5):
Where:
Sample data [W]
Number of observations of the sample, which is five.
In order to calculate the error in the CO2 savings for petrol, petrol turbo and diesel-fuelled vehicles, the propagation law, expressed in formula (6), is to be applied.
Formula (6):
Where:
Number of types of lighting in the innovative technology package
Substituting formula (2) in formula (6) results in formula (7) for calculating the error in CO2 savings for petrol-fuelled vehicles.
Formula (7)
Substituting formula (3) in formula (6) results in formula (8) for calculating the error in CO2 savings for diesel-fuelled vehicles.
Formula(8):
Substituting formula (4) in formula (6) results in formula (9) for calculating the error in CO2 savings for petrol-fuelled vehicles with turbo charger.
Formula (9):
4.4 Verification of the threshold value U.K.
In order to demonstrate that the 1,0 gCO2/km threshold is exceeded with statistical relevance, the following formula (10) should be used.
Formula 10:
Where:
Minimum threshold [gCO2/km],
Where the total CO2 emission savings of the innovative technology (efficient exterior lighting system), as a result of the calculation using formula (10), are below the threshold specified in Article 9(1) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011, the second subparagraph of Article 11(2) of that Regulation shall apply.
E/ECE/324/Rev.2/Add.111/Rev.3 — E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.2/Add.111/Rev.3, 9 January 2013.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Decision
PrintThe Annexes only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources