- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (31/01/2020)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2017/785Show full title
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2017/785 of 5 May 2017 on the approval of efficient 12 V motor-generators for use in conventional combustion engine powered passenger cars as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: ANNEX
Alternative versions:
Status:
Point in time view as at 31/01/2020.
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects by UK legislation for Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2017/785, ANNEX.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
ANNEXU.K. METHODOLOGY TO DETERMINE THE CO2 SAVINGS OF EFFICIENT 12 V MOTOR-GENERATORS FOR CONVENTIONAL COMBUSTION ENGINE POWERED M1 VEHICLES
1. Introduction U.K.
In order to determine the CO2 emission reductions that can be attributed to the generator function of a 12 V motor generator, hereinafter referred to as an efficient 12 V motor generator or motor generator, for use in an M1 vehicle powered by a combustion engine, it is necessary to establish the following:
the testing conditions;
the test equipment;
the determination of the peak power output;
the calculation of the CO2 savings;
the calculation of the statistical margin of the CO2 savings.
2. Symbols, parameters and units U.K.
Latin symbols U.K.
—
Carbon dioxide
—
Conversion factor (l/100 km) — (g CO2/km) [g CO2/l] as defined in Table 3
—
Frequency as defined in Table 1
—
Current intensity at which the measurement shall be carried out [A]
—
Number of measurements of the sample
—
Torque [Nm]
—
Rotational frequency [min– 1] as defined in Table 1
—
Power [W]
—
Test voltage at which the measurement shall be carried out [V]
—
Mean driving speed of the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) [km/h]
—
Consumption of effective power [l/kWh] as defined in Table 2
Greek symbols U.K.
—
Difference
—
Baseline alternator efficiency [%]
—
Motor generator efficiency [%]
Subscripts U.K.
Index (i) refers to operating point
Index (j) refers to measurement of the sample
—
Motor generator
—
Mechanical
—
Real-world conditions
—
Type approval conditions
—
Baseline
3. Measurements and determination of the efficiency U.K.
The efficiency of the 12 V motor generator shall be determined in accordance with ISO 8854:2012, with the exception of the elements specified in this point.
Evidence shall be provided to the type approval authority that the speed ranges of the efficient 12 V motor generator are consistent with those set out in Table 1. The measurements shall be conducted at different operating points, as set out in Table 1. The efficient 12 V motor generator current intensity shall be defined as half of the rated current for all operating points. For each speed the voltage and the output current of the alternator shall be kept constant at 14,3 V.
Table 1
Operating points
| Operating pointi | Holding time[s] | Rotational frequencyni[min– 1] | Frequencyhi |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 200 | 1 800 | 0,25 |
| 2 | 1 200 | 3 000 | 0,40 |
| 3 | 600 | 6 000 | 0,25 |
| 4 | 300 | 10 000 | 0,10 |
The efficiency at each operating point shall be calculated in accordance with the following Formula 1:
Formula 1 U.K.
All efficiency measurements are to be performed consecutively at least five (5) times. The average of the measurements at each operating point ( 
The efficiency of the motor generator (ηMG) shall be calculated in accordance with the following Formula 2:
Formula 2 U.K.
The motor generator leads to saved mechanical power under real-world conditions (ΔPmRW) and type approval conditions (ΔPmTA) as set out in Formula 3.
Formula 3 U.K.
Where the saved mechanical power under real-world conditions (ΔPmRW) shall be calculated in accordance with Formula 4 and the saved mechanical power under type-approval conditions (ΔPmTA) in accordance with the following Formula 5:
Formula 4 U.K.
Formula 5 U.K.
where
:
Power requirement under ‘real-world’ conditions [W], which is 750W
:
Power requirement under type-approval conditions [W], which is 350W
:
Efficiency of the baseline alternator [%], which is 67 %
4. Calculation of the CO2 savings U.K.
The CO2 savings of the efficient 12 V motor generator shall be calculated in accordance with the following Formula 6:
Formula 6 U.K.
where
:
Mean driving speed of the NEDC [km/h], which is 33,58 km/h
:
Consumption of effective power specified in Table 2
Table 2
Consumption of effective power
| Type of engine | Consumption of effective power (VPe)[l/kWh] |
|---|---|
| Petrol | 0,264 |
| Petrol Turbo | 0,280 |
| Diesel | 0,220 |
:
Conversion factor (l/100 km) — (g CO2/km) [g CO2/l] as defined in Table 3
Table 3
Fuel conversion factor
| Type of fuel | Conversion factor (l/100 km) — (g CO2/km) (CF)[g CO2/l] |
|---|---|
| Petrol | 2 330 |
| Diesel | 2 640 |
5. Calculation of the statistical error U.K.
The statistical errors in the results of the testing methodology caused by the measurements shall be quantified. For each operating point the standard deviation shall be calculated in accordance with the following Formula 7:
Formula 7 U.K.
The standard deviation of the efficiency value of the efficient 12 V motor generator ( 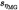
Formula 8 U.K.
The standard deviation of the motor generator efficiency ( 

Formula 9 U.K.
6. Statistical significance U.K.
It has to be demonstrated for each type, variant and version of a vehicle fitted with the efficient 12 V motor generator that the error in the CO2 savings calculated in accordance with Formula 9 is not greater than the difference between the total CO2 savings and the minimum savings threshold specified in Article 9(1) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 (see Formula 10).
Formula 10 U.K.
Where:
:
minimum threshold [g CO2/km]
:
CO2 correction coefficient due to the positive mass difference between the efficient 12 V motor generator and the baseline alternator. For 
Δm (in Table 4) is the extra mass due to the installation of the motor generator. It is the positive difference between the mass of the efficient 12 V motor generator and the mass of baseline alternator. The mass of the baseline alternator is 7 kg. The extra mass is to be verified and confirmed in the verification report to be submitted to the type approval authority together with the application for certifications.
7. The efficient 12 V motor generator to be fitted in vehicles U.K.
The type approval authority is to certify the CO2 savings based on measurements of the 12 V motor generator and the baseline alternator using the test methodology set out in this Annex. Where the CO2 emission savings are below the threshold specified in Article 9(1) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 the second subparagraph of Article 11(2) of that Regulation shall apply.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Decision
PrintThis Annex only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources