ANNEX 1U.K.ESSENTIAL REQUIREMENTS
I.GENERAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
1.The devices must be designed and manufactured in such a way that, when implanted under the conditions and for the purposes laid down, their use does not compromise the clinical condition or the safety of patients. They must not present any risk to the persons implanting them or, where applicable, to other persons.U.K.
2.The devices must achieve the performances intended by the manufacturer, viz. be designed and manufactured in such a way that they are suitable for one or more of the functions referred to in Article 1 (2) (a) as specified by him.U.K.
3.The characteristics and performances referred to in sections 1 and 2 must not be adversely affected to such a degree that the clinical condition and safety of the patients or, as appropriate, of other persons are compromised during the lifetime of the device anticipated by the manufacturer, where the device is subjected to stresses which may occur during normal conditions of use.U.K.
4.The devices must be designed, manufactured and packed in such a way that their characteristics and performances are not adversely affected in the storage and transport conditions laid down by the manufacturer (temperature, humidity, etc.).U.K.
5.Any side effects or undesirable conditions must constitute acceptable risks when weighed against the performances intended.U.K.
[5a. Demonstration of conformity with the essential requirements must include a clinical evaluation in accordance with Annex 7.] U.K.
II.REQUIREMENTS REGARDING DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTIONU.K.
6.The solutions adopted by the manufacturer for the design and construction of the devices must comply with safety principles taking account of the generally acknowledged state of the art.U.K.
7.Implantable devices must be designed, manufactured and packed in a non-reusable pack according to appropriate procedures to ensure they are sterile when placed on the market and, in the storage and transport conditions stipulated by the manufacturer, remain so until the packaging is removed and they are implanted.U.K.
8.Devices must be designed and manufactured in such a way as to remove or minimize as far as possible:U.K.
the risk of physical injury in connection with their physical, including dimensional, features,
risks connected with the use of energy sources with particular reference, where electricity is used, to insulation, leakage currents and overheating of the devices,
risks connected with reasonably foreseeable environmental conditions such as magnetic fields, external electrical influences, electrostatic discharge, pressure or variations in pressure and acceleration,
risks connected with medical treatment, in particular those resulting from the use of defibrillators or high-frequency surgical equipment,
[risks connected with ionising radiation from radioactive substances included in the device, in compliance with the protection requirements laid down in Council Directive 96/29/Euratom of 13 May 1996 laying down basic safety standards for the protection of the health of workers and the general public against the dangers arising from ionising radiation () and Council Directive 97/43/Euratom of 30 June 1997 on health protection of individuals against the dangers of ionising radiation in relation to medical exposure () ,]
risks which may arise where maintenance and calibration are impossible, including:
excessive increase of leakage currents,
ageing of the materials used,
excess heat generated by the device,
decreased accuracy of any measuring or control mechanism.
9.The devices must be designed and manufactured in such a way as to guarantee the characteristics and performances referred to in I. ‘General requirements’, with particular attention being paid to:U.K.
the choice of materials used, particularly as regards toxicity aspects,
mutual compatibility between the materials used and biological tissues, cells and body fluids, account being taken of the anticipated use of the device,
compatibility of the devices with the substances they are intended to administer,
the quality of the connections, particularly in respect of safety,
the reliability of the source of energy,
if appropriate, that they are leakproof,
proper functioning of the programming and control systems, including software.[ For devices which incorporate software or which are medical software in themselves, the software must be validated according to the state of the art taking into account the principles of development lifecycle, risk management, validation and verification.]
[10. Where a device incorporates, as an integral part, a substance which, if used separately, may be considered to be a medicinal product as defined in Article 1 of Directive 2001/83/EC, and which is liable to act upon the body with action ancillary to that of the device, the quality, safety and usefulness of the substance must be verified by analogy with the methods specified in Annex I to Directive 2001/83/EC. U.K.
For the substances referred to in the first paragraph, the notified body shall, having verified the usefulness of the substance as part of the medical device and taking account of the intended purpose of the device, seek a scientific opinion from one of the competent authorities designated by the Member States or the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) acting particularly through its committee in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 () on the quality and safety of the substance including the clinical benefit/risk profile of the incorporation of the substance into the device. When issuing its opinion, the competent authority or the EMEA shall take into account the manufacturing process and the data related to the usefulness of incorporation of the substance into the device as determined by the notified body.
Where a device incorporates, as an integral part, a human blood derivative, the notified body shall, having verified the usefulness of the substance as part of the device and taking account of the intended purpose of the device, seek a scientific opinion from the EMEA, acting particularly through its committee, on the quality and safety of the substance, including the clinical benefit/risk profile of the incorporation of the human blood derivative into the device. When issuing its opinion, the EMEA shall take into account the manufacturing process and the data related to the usefulness of incorporation of the substance into the device as determined by the notified body.
Where changes are made to an ancillary substance incorporated in a device, in particular related to its manufacturing process, the notified body shall be informed of the changes and shall consult the relevant medicines competent authority (i.e. the one involved in the initial consultation), in order to confirm that the quality and safety of the ancillary substance are maintained. The competent authority shall take into account the data related to the usefulness of the incorporation of the substance into the device as determined by the notified body, in order to ensure that the changes have no negative impact on the established benefit/risk profile of the addition of the substance in the device.
When the relevant medicines competent authority (i.e. the one involved in the initial consultation) has obtained information on the ancillary substance, which could have an impact on the established benefit/risk profile of the addition of the substance to the device, it shall provide the notified body with advice, whether this information has an impact on the established benefit/risk profile of the addition of the substance to the device or not. The notified body shall take the updated scientific opinion into account in reconsidering its assessment of the conformity assessment procedure.]
11.The devices and, if appropriate, their component parts must be identified to allow any necessary measure to be taken following the discovery of a potential risk in connection with the devices and their component parts.U.K.
12.Devices must bear a code by which they and their manufacturer can be unequivocably identified (particularly with regard to the type of device and year of manufacture); it must be possible to read this code, if necessary, without the need for a surgical operation.U.K.
13.When a device or its accessories bear instructions required for the operation of the device or indicate operating or adjustment parameters, by means of a visual system, such information must be understandable to the user and, as appropriate, the patient.U.K.
14.Every device must bear, legibly and indelibly, the following particulars, where appropriate in the form of generally recognized symbols:U.K.
14.1.On the sterile pack:U.K.
the method of sterilization,
an indication permitting this packaging to be recognized as such,
the name and address of the manufacturer,
a description of the device,
if the device is intended for clinical investigations, the words: ‘exclusively for clinical investigations’,
if the device is custom-made, the words ‘custom-made device’,
a declaration that the implantable device is in a sterile condition,
the month and year of manufacture,
an indication of the time limit for implanting a device safely.
14.2.On the sales packaging:U.K.
[the name and address of the manufacturer and the name and address of the authorised representative, where the manufacturer does not have a registered place of business in the Community,]
a description of the device,
the purpose of the device,
the relevant characteristics for its use,
if the device is intended for clinical investigations, the words: ‘exclusively for clinical investigations’,
if the device is custom-made, the words: ‘custom-made device’,
a declaration that the implantable device is in a sterile condition,
the month and year of manufacture,
an indication of the time limit for implanting a device safely,
the conditions for transporting and staring the device[,]
[in the case of a device within the meaning of Article 1(4a), an indication that the device contains a human blood derivative.]
15.When placed on the market, each device must be accompanied by instructions for use giving the following particulars:U.K.
the year of authorization to affix the CE mark,
the details referred to in 14,1 and 14.2, with the exception of those referred to in the eighth and ninth indents,
the performances referred to in section 2 and any undesirable side effects,
information allowing the physician to select a suitable device and the corresponding software and accessories,
information constituting the instructions for use allowing the physician and, where appropriate, the patient to use the device, its accessories and software correctly, as well as information on the nature, scope and times for operating controls and trials and, where appropriate, maintenance measures,
information allowing, if appropriate, certain risks in connection with implantation of the device to be avoided,
information regarding the risks of reciprocal interference() in connection with the presence of the device during specific investigations or treatment,
the necessary instructions in the event of the sterile pack being damaged and, where appropriate, details of appropriate methods of resterilization,
an indication, if appropriate, that a device can be reused only if it is reconditioned under the responsibility of the manufacturer to comply with the essential requirements.
The instruction leaflet must also include details allowing the physician to brief the patient on the contra-indications and the precautions to be taken. These details should cover in particular:
information allowing the lifetime of the energy source to be established,
precautions to be taken should changes occur in the device's performance,
precautions to be taken as regards exposure, in reasonably foreseeable environmental conditions, to magnetic fields, external electrical influences, electrostatic discharge, pressure or variations in pressure, acceleration, etc.,
adequate information regarding the medicinal products which the device in question is designed to administer[,]
[date of issue or the latest revision of the instructions for use.]
16.Confirmation that the device satisfies the requirements in respect of characteristics and performances, as referred to in I. ‘General requirements’, in normal conditions of use, and the evaluation of the side effects or undesirable effects must be based on clinical data established in accordance with Annex 7.U.K.
ANNEX 2U.K.EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY(Complete quality assurance system)
1.The manufacturer shall apply the quality system approved for the design, manufacture and final inspection of the products concerned as specified in sections 3 and 4 and shall be subject to EC surveillance as specified in section 5.U.K.
2.The declaration of conformity is the procedure by means of which the manufacturer who satisfies the obligations of section 1 ensures and declares that the products concerned meet the provisions of this Directive which apply to them.U.K.
[The manufacturer or his authorized representative established within the Community shall affix the CE marking in accordance with Article 12 and shall draw up a written declaration of conformity.
[This declaration shall cover one or more clearly identified devices by means of product name, product code or other unambiguous reference and must be kept by the manufacturer.]
The CE marking shall be accompanied by the identification number of the notified body responsible.]
3.Quality systemU.K.
3.1.The manufacturer shall make an application for evaluation of his quality system to a notified body.U.K.
The application shall include:
all the appropriate items of information for the category of products manufacture of which is envisaged,
the quality-system documentation,
an undertaking to fulfil the obligations arising from the quality system as approved,
an undertaking to maintain the approved quality system in such a way that it remains adequate and efficacious,
[an undertaking by the manufacturer to institute and keep updated a post-marketing surveillance system including the provisions referred to in Annex 7.] The undertaking shall include an obligation for the manufacturer to notify the competent authorities of the following incidents immediately on learning of them:
(i)
any deterioration in the characteristics or performances, and any inaccuracies in the instruction leaflet for a device which might lead to or have led to the death of a patient or a deterioration in his state of health;
(ii)
any technical or medical reason resulting in withdrawal of a device from the market by the manufacturer.
3.2.The application of the quality system must ensure that the products conform to the provisions of this Directive which apply to them at every stage, from design to final controls.U.K.
All the elements, requirements and provisions adopted by the manufacturer for his quality system shall be documented in a systematic and orderly manner in the form of written policies and procedures. This quality-system documentation must make possible a uniform interpretation of the quality policies and procedures such as quality programmes, quality plans, quality manuals and quality records.[ It shall include in particular the corresponding documentation, data and records arising from the procedures referred to in point (c).]
It shall include in particular an adequate description of:
(a)
the manufacturer's quality objectives;
(b)
the organization of the business and in particular:
the organizational structures, the responsibilities of the managerial staff and their organizational authority where quality of design and manufacture of the products is concerned,
the methods of monitoring the efficient operation of the quality system and in particular its ability to achieve the desired quality of the design and of the products, including control of products which do not conform[,]
[where the design, manufacture and/or final inspection and testing of the products, or elements thereof, is carried out by a third party, the methods of monitoring the efficient operation of the quality system and in particular the type and extent of control applied to the third party;]
(c)
the procedures for monitoring and verifying the design of the products and in particular:
the design specifications, including the standards which will be applied and a description of the solutions adopted to fulfil the essential requirements which apply to the products when the standards referred to in Article 5 are not applied in full,
the techniques of control and verification of the design, the processes and systematic actions which will be used when the products are being designed[,]
[a statement indicating whether or not the device incorporates, as an integral part, a substance or a human blood derivative referred to in Section 10 of Annex 1 and the data on the tests conducted in this connection required to assess the safety, quality and usefulness of that substance or human blood derivative, taking account of the intended purpose of the device,
the pre-clinical evaluation,
the clinical evaluation referred to in Annex 7;]
(d)
the techniques of control and of quality assurance at the manufacturing stage and in particular:
the processes and procedures which will be used, particularly as regards sterilization, purchasing and the relevant documents,
product-identification procedures drawn up and kept up to date from drawings, specifications or other relevant documents at every stage of manufacture;
(e)
the appropriate tests and trials which will be effected before, during and after production, the frequency with which they will take place, and the test equipment used.
3.3.Without prejudice to Article 13 of this Directive, the notified body shall effect an audit of the quality system to determine whether it meets the requirements referred to in 3.2. It shall presume conformity with these requirements for the quality systems which use the corresponding harmonized standards.U.K.
The team entrusted with the evaluation shall include at least one member who has already had experience of evaluations of the technology concerned. [The evaluation procedure shall include an inspection on the manufacturer's premises and, in duly substantiated cases, on the premises of the manufacturer's suppliers and/or subcontractors to inspect the manufacturing processes.]
The decision shall be notified to the manufacturer after the final inspection. It shall contain the conclusions of the control and a reasoned evaluation.
3.4.The manufacturer shall inform the notified body which has approved the quality system of any plan to alter the quality system.U.K.
The notified body shall evaluate the proposed modifications and shall verify whether the quality system so modified would meet the requirements referred to in 3.2; it shall notify the manufacturer of its decision. This decision shall contain the conclusions of the control and a reasoned evaluation.
4.Examination of the design of the productU.K.
4.1.In addition to the obligations incumbent on him under section 3, the manufacturer shall make an application for examination of the design dossier relating to the product which he plans to manufacture and which falls into the category referred to in 3.1.U.K.
4.2. [The application shall describe the design, manufacture and performances of the product in question, and it must include the documents needed to assess whether the product conforms to the requirements of this Directive, and in particular Annex 2, Section 3.2, third paragraph, points (c) and (d).] U.K.
It shall include inter alia:
the design specifications, including the standards which have been applied,
the necessary proof of their appropriations, in particular where the standards referred to in Article 5 have not been applied in full. This proof must include the results of the appropriate tests carried out by the manufacturer or carried out under his responsibility,
a statement as to whether or not the device incorporates, as an integral part, a substance as referred to in section 10 of Annex 1, whose action in combination with the device may result in its bioavailability, together with data on the relevant trials conducted,
the clinical [evaluation] referred to in Annex 7,
the draft instruction leaflet.
4.3.The notified body shall examine the application and, where the product complies with the relevant provisions of this Directive, shall issue the applicant with an EC design examination certificate. The notified body may require the application to be supplemented by further tests or proof so that compliance with the requirements of the Directive may be evaluated. The certificate shall contain the conclusions of the examination, the conditions of its validity, the data needed for identification of the approved design and, where appropriate, a description of the intended use of the product.U.K.
[In the case of devices referred to in Annex 1, Section 10, second paragraph, the notified body shall, as regards the aspects referred to in that section, consult one of the competent authorities designated by the Member States in accordance with Directive 2001/83/EC or the EMEA before taking a decision. The opinion of the competent national authority or the EMEA shall be drawn up within 210 days after receipt of valid documentation. The scientific opinion of the competent national authority or the EMEA must be included in the documentation concerning the device. The notified body will give due consideration to the views expressed in this consultation when making its decision. It will convey its final decision to the competent body concerned.
In the case of devices referred to in Annex 1, Section 10, third paragraph, the scientific opinion of the EMEA must be included in the documentation concerning the device. The opinion shall be drawn up within 210 days after receipt of valid documentation. The notified body will give due consideration to the opinion of the EMEA when making its decision. The notified body may not deliver the certificate if the EMEA's scientific opinion is unfavourable. It will convey its final decision to the EMEA.]
4.4.The applicant shall inform the notified body which issued the EC design examination certificate of any modification made to the approved design. Modifications made to the approved design must obtain supplementary approval from the notified body which issued the EC design examination certificate where such modifications may affect conformity with the essential requirements of this Directive or the conditions prescribed for the use of the product. This supplementary approval shall be given in the form of an addendum to the EC design examination certificate.U.K.
5.SurveillanceU.K.
5.1.The aim of surveillance is to ensure that the manufacturer duly fulfils the obligations arising from the approved quality system.U.K.
5.2.The manufacturer shall authorize the notified body to carry out all necessary inspections and shall supply it with all appropriate information, in particular:U.K.
the quality-system documentation,
[the data stipulated in the part of the quality system relating to design, such as the results of analyses, calculations, tests, pre-clinical and clinical evaluation, post-market clinical follow-up plan and the results of the post-market clinical follow-up, if applicable, etc.,]
the data stipulated in the part of the quality system relating to manufacture, such as reports concerning inspections, tests, standardizations/calibrations and the qualifications of the staff concerned, etc.
5.3.The notified body shall periodically carry out appropriate inspections and evaluations in order to ascertain that the manufacturer is applying the approved quality system, and shall supply the manufacturer with an evaluation report.U.K.
5.4.In addition, the notified body may make unannounced visits to the manufacturer, and shall supply him with an inspection report.U.K.
[6. Administrative provisions U.K.
[6.1. For at least 15 years from the last date of manufacture of the product, the manufacturer or his authorised representative shall keep available for the national authorities: U.K.
the declaration of conformity,
the documentation referred to in the second indent of Section 3.1, and in particular the documentation, data and records referred to in the second paragraph of Section 3.2,
the amendments referred to in Section 3.4,
the documentation referred to in Section 4.2,
the decisions and reports of the notified body referred to in Sections 3.4, 4.3, 5.3 and 5.4.]
6.2. On request, the notified body shall make available to the other notified bodies and the competent authority all relevant information on approvals of quality systems issued, refused or withdrawn.] U.K.
6.3.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .U.K.
[7. Application to the devices referred to in Article 1(4a): U.K.
Upon completing the manufacture of each batch of devices referred to in Article 1(4a), the manufacturer shall inform the notified body of the release of the batch of devices and send to it the official certificate concerning the release of the batch of human blood derivative used in the device, issued by a State laboratory or a laboratory designated for that purpose by a Member State in accordance with Article 114(2) of Directive 2001/83/EC.]
ANNEX 3U.K.EC TYPE-EXAMINATION
1.EC type-examination is the procedure whereby a notified body observes and certifies that a representative sample of the production envisaged satisfies the relevant provisions of this Directive.U.K.
2.The application for EC type-examination shall be made by the manufacturer, or by his authorized representative established in the Community, to a notified body.U.K.
The application shall include:
the name and address of the manufacturer and the name and address of the authorized representative if the application is made by the latter,
a written declaration specifying that an application has not been made to any other notified body,
the documentation described in section 3 needed to allow an evaluation to be made of the conformity of a representative sample of the production in question, hereinafter referred to as ‘type’, with the requirements of this Directive.
The applicant shall make a ‘type’ available to the notified body. The notified body may request other samples as necessary.
3.The documentation must make it possible to understand the design, the manufacture and the performances of the product. The documentation shall contain the following items in particular:U.K.
[a general description of the type, including any variants planned, and its intended use(s),]
design drawings, methods of manufacture envisaged, in particular as regards sterilization, and diagrams of parts, sub-assemblies, circuits, etc.,
the descriptions and explanations necessary for the understanding of the abovementioned drawings and diagrams and of the operation of the product,
a list of the standards referred to in Article 5, applied in full or in part, and a description of the solutions adopted to satisfy the essential requirements where the standards referred to in Article 5 have not been applied,
[the results of design calculations, risk analysis, investigations and technical tests carried out, etc.,
a declaration stating whether or not the device incorporates, as an integral part, a substance or a human blood derivative as referred to in Section 10 of Annex 1 and the data on the tests conducted in this connection required to assess the safety, quality and usefulness of that substance or human blood derivative, taking account of the intended purpose of the device,
the pre-clinical evaluation,
the clinical evaluation referred to in Annex 7,
the draft instruction leaflet.]
4.The notified body shall:U.K.
4.1.examine and evaluate the documentation, verify that the type has been manufactured in accordance with that documentation; it shall also record the items which have been designed in accordance with the applicable provisions of the standards referred to in Article 5, as well as the items for which the design is not based on the relevant provisions of the said standards;U.K.
4.2.carry out or have carried out the appropriate inspections and the tests necessary to verify whether the solutions adopted by the manufacturer satisfy the essential requirements of this Directive where the standards referred to in Article 5 have not been applied;U.K.
4.3.carry out or have carried out the appropriate inspections and the tests necessary to verify whether, where the manufacturer has chosen to apply the relevant standards, these have actually been applied;U.K.
4.4.agree with the applicant on the place where the necessary inspections and tests will be carried out.U.K.
5.Where the type meets the provisions of this Directive, the notified body shall issue an EC type-examination certificate to the applicant. The certificate shall contain the name and address of the manufacturer, the conclusions of the control, the conditions under which the certificate is valid and the information necessary for identification of the type approved.U.K.
The significant parts of the documentation shall be attached to the certificate and a copy shall be kept by the notified body.
[In the case of devices referred to in Annex 1, Section 10, second paragraph, the notified body shall, as regards the aspects referred to in that section, consult one of the competent authorities designated by the Member States in accordance with Directive 2001/83/EC or the EMEA before taking a decision. The opinion of the competent national authority or the EMEA shall be drawn up within 210 days after receipt of valid documentation. The scientific opinion of the competent national authority or the EMEA must be included in the documentation concerning the device. The notified body will give due consideration to the views expressed in this consultation when making its decision. It will convey its final decision to the competent body concerned.
In the case of devices referred to in Annex 1, Section 10, third paragraph, the scientific opinion of the EMEA must be included in the documentation concerning the device. The opinion shall be drawn up within 210 days after receipt of valid documentation. The notified body will give due consideration to the opinion of the EMEA when making its decision. The notified body may not deliver the certificate if the EMEA's scientific opinion is unfavourable. It will convey its final decision to the EMEA.]
6.The applicant shall inform the notified body which issued the EC type-examination certificate of any modification made to the approved product.U.K.
Modifications to the approved product must receive further approval from the notified body which issued the EC type-examination certificate where such modifications may affect conformity with the essential requirements or with the conditions of use specified for the product. This new approval shall be issued, where appropriate, in the form of a supplement to the initial EC type-examination certificate.
[7. Administrative provisions U.K.
7.1. On request, each notified body shall make available to the other notified bodies and the competent authority, all relevant information on EC type-examination certificates and addenda issued, refused or withdrawn. U.K.
7.2. Other notified bodies may obtain a copy of the EC type-examination certificates and/or the addenda to them. The annexes to the certificates shall be made available to the other notified bodies when a reasoned application is made and after the manufacturer has been informed. U.K.
7.3. The manufacturer or his authorized representative shall keep with the technical documentation a copy of the EC type-examination certificates and the supplements to them for a period of at least [15 years from the manufacture of the last product] .] U.K.
7.4.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .U.K.
[ANNEX 4 U.K. EC VERIFICATION
1. EC verification is the procedure whereby the manufacturer or his authorized representative established within the Community ensures and declares that the products subject to the provisions of section 3 are in conformity with the type as described in the EC type-examination certification and satisfy the requirements of this Directive that apply to them. U.K.
2. The manufacturer or his authorized representative established within the Community shall take all measures necessary in order that the manufacturing process ensures conformity of the products to the type as described in the EC type-examination certification and to the requirements of this Directive that apply to them. The manufacturer or his authorized representative established within the Community shall affix the CE marking to each product and draw up a written declaration of conformity. U.K.
3. The manufacturer shall, before the start of manufacture, prepare documents defining the manufacturing processes, in particular as regards sterilization, together with all the routine, pre-established provisions to be implemented to ensure uniformity of production and conformity of the products with the type as described in the EC type-examination certificate as well as with the relevant requirements of this Directive. U.K.
4. The manufacturer shall undertake to institute and keep updated a [post-marketing surveillance system including the provisions referred to in Annex 7] . This undertaking shall include the obligation on the part of the manufacturer to notify the competent authorities of the following events immediately on learning of them: U.K.
(i)
any change in the characteristics or performances and any inaccuracies in the instruction leaflet for a device which might lead to or have led to the death of a patient or deterioration in his state of health;
(ii)
any technical or medical reason resulting in the withdrawal of a device from the market by a manufacturer.
5. The notified body shall carry out the appropriate examinations and tests in order to check the conformity of the product to the requirements of this Directive by examination and testing of products on a statistical basis, as specified in section 6. The manufacturer must authorize the notified body to evaluate the efficiency of the measures taken pursuant to section 3, by audit where appropriate. U.K.
6. Statistical verification U.K.
6.1. Manufacturers shall present the products manufactured in the form of uniform batches and shall take all necessary measures in order that the manufacturing process ensures the uniformity of each batch produced. U.K.
6.2. A random sample shall be taken from each batch. Products in a sample shall be individually examined and appropriate tests, as set out in the standard(s) referred to in Article 5, or equivalent tests shall be carried out to verify their conformity to the type as described in the EC type-examination certificate and thereby determine whether a batch is to be accepted or rejected. U.K.
[6.3. Statistical control of products will be based on attributes and/or variables, entailing sampling schemes with operational characteristics which ensure a high level of safety and performance according to the state of the art. The sampling schemes will be established by the harmonised standards referred to in Article 5, taking account of the specific nature of the product categories in question.] U.K.
6.4. Where batches are accepted, the notified body shall affix, or cause to be affixed, its identification number to each product and draw up a written certificate of conformity relating to the tests carried out. All products in the batch may be placed on the market except for those products from the sample which were found not to be in conformity. U.K.
Where a batch is rejected, the notified body shall take appropriate measures to prevent the placing on the market of that batch. In the event of frequent rejection of batches the notified body may suspend the statistical verification.
The manufacturer may, under the responsibility of the notified body, affix the latter's identification number during the manufacturing process.
6.5. The manufacturer or his authorized representative shall ensure that he is able to supply the notified body's certificates of conformity on request. U.K.
[7. Application to the devices referred to in Article 1(4a): U.K.
Upon completing the manufacture of each batch of devices referred to in Article 1(4a), the manufacturer shall inform the notified body of the release of the batch of devices and send to it the official certificate concerning the release of the batch of human blood derivative used in the device, issued by a State laboratory or a laboratory designated for that purpose by a Member State in accordance with Article 114(2) of Directive 2001/83/EC.] ]
ANNEX 5U.K.EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY TO TYPE(Assurance of production quality)
1.The manufacturer shall apply the quality system approved for the manufacture and shall conduct the final inspection of the products concerned as specified in 3; he shall be subject to the surveillance referred to in section 4.U.K.
2.This declaration of conformity is the procedural element whereby the manufacturer who satisfies the obligations of section 1 guarantees and declares that the products concerned conform to the type described in the EC type-examination certificate and meet the provisions of the Directive which apply to them.U.K.
[The manufacturer or his authorized representative established within the Community shall affix the CE marking in accordance with Article 12 and draw up a written declaration of conformity. This declaration shall cover one or more [devices manufactured, clearly identified by means of product name, product code or other unambiguous reference and must be kept by the manufacturer] . The CE marking shall be accompanied by the identification number of the notified body responsible.]
3.Quality systemU.K.
3.1.The manufacturer shall make an application for evaluation of his quality system to a notified body.U.K.
The application shall include:
all appropriate information concerning the products which it is intended to manufacture,
the quality-system documentation,
an undertaking to fulfil the obligations arising from the quality system as approved,
an undertaking to maintain the approved quality system in such a way that it remains adequate and efficacious,
where appropriate, the technical documentation relating to the approved type and a copy of the EC type-examination certificate,
an undertaking by the manufacturer to institute and keep up-dated a [post-marketing surveillance system including the provisions referred to in Annex 7]. The undertaking shall include an obligation for the manufacturer to notify the competent authorities of the following incidents immediately on learning of them:
(i)
any deterioration in the characteristics or performances, and any inaccuracies in the instruction leaflet for a device which might lead to or have led to the death of a patient or a deterioration in his state of health;
(ii)
any technical or medical reason resulting in withdrawal of a device from the market by the manufacturer.
3.2.Application of the quality system must ensure that the products conform to the type described in the EC type-examination certificate.U.K.
All the elements, requirements and provisions adopted by the manufacturer for his quality system shall be documented in a systematic and orderly manner in the form of written policies and procedures. This quality-system documentation must make possible a uniform interpretation of the quality policies and procedures such as quality programmes, quality plans, quality manuals and quality records.
It shall include in particular an adequate description of:
(a)
the manufacturer's quality objectives;
(b)
the organization of the business and in particular:
the organizational structures, the responsibilities of the managerial staff and their organizational authority where manufacture of the products is concerned,
the methods of monitoring the efficient operation of the quality system and in particular its ability to achieve the desired quality[of the design and] of the products, including control of products which do not conform[,]
[where the manufacture and/or final inspection and testing of the products, or elements thereof, are carried out by a third party, the methods of monitoring the efficient operation of the quality system and in particular the type and extent of control applied to the third party;]
(c)
the techniques of control and of quality assurance at the manufacturing stage and in particular:
the processes and procedures which will be used, particularly as regards sterilization, purchasing and the relevant documents,
product identification procedures drawn up and kept up-to-date from drawings, specifications or other relevant documents at every stage of manufacture;
(d)
the appropriate tests and trials which will be effected before, during and after production, the frequency with which they will take place, and the test equipment used.
3.3.Without prejudice to Article 13, the notified body shall effect an audit of the quality system to determine whether it meets the requirements referred to in 3.2. It shall presume conformity with these requirements for the quality systems which use the corresponding harmonized standards.U.K.
The team entrusted with the evaluation shall include at least one member who has already had experience of evaluations of the technology concerned. The evaluation procedure shall include an inspection on the manufacturer's premises.
The decision shall be notified to the manufacturer after the final inspection. It shall contain the conclusions of the control and a reasoned evaluation.
3.4.The manufacturer shall inform the notified body which has approved the quality system of any plan to alter that system.U.K.
The notified body shall evaluate the proposed modifications and shall verify whether the quality system so modified would meet the requirements referred to in 3.2; it shall notify the manufacturer of its decision. This decision shall contain the conclusions of the control and a reasoned evaluation.
4.SurveillanceU.K.
4.1.The aim of surveillance is to ensure that the manufacturer duly fulfils the obligations which arise from the approved quality system.U.K.
4.2.The manufacturer shall authorize the notified body to carry out all necessary inspections and shall supply it with all appropriate information, in particular:U.K.
the quality-system documentation,
[the technical documentation,]
the data stipulated in the part of the quality system relating to manufacture, such as reports concerning inspections, tests, standardizations/calibrations and the qualifications of the staff concerned, etc.
4.3.The notified body shall periodically carry out appropriate inspections and evaluations in order to ascertain that the manufacturer is applying the approved quality system, and shall supply the manufacturer with an evaluation report.U.K.
4.4.In addition, the notified body may make unannounced visits to the manufacturer, and shall supply him with an inspection report.U.K.
5.The notified body shall communicate to the other notified bodies all relevant information concerning approvals of quality systems issued, refused or withdrawn.U.K.
[6. Application to the devices referred to in Article 1(4a): U.K.
Upon completing the manufacture of each batch of devices referred to in Article 1(4a), the manufacturer shall inform the notified body of the release of the batch of devices and send to it the official certificate concerning the release of the batch of human blood derivative used in the device, issued by a State laboratory or a laboratory designated for that purpose by a Member State in accordance with Article 114(2) of Directive 2001/83/EC.]
ANNEX 6U.K.STATEMENT CONCERNING DEVICES INTENDED FOR SPECIAL PURPOSES
1.The manufacturer or his authorized representative established within the Community shall draw up for custom-made devices or for devices intended for clinical investigations the statement comprising the elements stipulated in section 2.U.K.
2.The statement shall comprise the following information:U.K.
2.1.For custom-made devices:U.K.
[the name and address of the manufacturer,
the information necessary for the identification of the product in question,]
a statement affirming that the device is intended for exclusive use by a particular patient, together with his name,
the name of the [duly qualified medical practitioner] who drew up the prescription and, if applicable, the name of the clinic concerned,
[the specific characteristics of the product revealed by the prescription,]
a statement affirming that the device complies with the essential requirements given in Annex 1 and, where applicable, indicating which essential requirements have not been wholly met, together with the grounds.
[2.2. For devices intended for clinical investigations covered in Annex 7: U.K.
data allowing the devices in question to be identified,
the clinical investigation plan,
the investigator's brochure,
the confirmation of insurance of subjects,
the documents used to obtain informed consent,
a statement indicating whether or not the device incorporates, as an integral part, a substance or human blood derivative referred to in Section 10 of Annex 1,
the opinion of the ethics committee concerned and details of the aspects covered by its opinion,
the name of the duly qualified medical practitioner or other authorised person and of the institution responsible for the investigations,
the place, date of commencement and duration scheduled for the investigations,
a statement affirming that the device in question complies with the essential requirements apart from the aspects constituting the object of the investigations and that, with regard to these aspects, every precaution has been taken to protect the health and safety of the patient.]
3.The manufacturer shall undertake to keep available for the competent national authorities:U.K.
3.1. [For custom-made devices, documentation, indicating manufacturing site(s) and enabling the design, manufacture and performances of the product, including the expected performances, to be understood, so as to allow conformity with the requirements of this Directive to be assessed.] U.K.
The manufacturer shall take all necessary measures to see that the manufacturing process ensures that the products manufactured conform to the documentation referred to in the first paragraph.
3.2.For devices intended for clinical investigations, the documentation shall also contain:U.K.
[a general description of the product and its intended use,]
design drawings, manufacturing methods, in particular as regards sterilization, and diagrams of parts, sub-assemblies, circuits, etc.,
the descriptions and explanations necessary for the understanding of the said drawings and diagrams and of the operation of the product,
[the results of the risk analysis and a list of the standards] laid down in Article 5, applied in full or in part, and a description of the solutions adopted to satisfy the essential requirements of the Directive where the standards in Article 5 have not been applied,
[if the device incorporates, as an integral part, a substance or human blood derivative referred to in Section 10 of Annex 1, the data on the tests conducted in this connection which are required to assess the safety, quality and usefulness of that substance, or human blood derivative, taking account of the intended purpose of the device,]
the results of the design calculations, checks and technical tests carried out, etc.
The manufacturer shall take all necessary measures to see that the manufacturing process ensures that the products manufactured conform to the documentation referred to in 3.1 and in the first paragraph of this section.
The manufacturer may authorize the evaluation, by audit where necessary, of the effectiveness of these measures.
[4. The information included in the declarations covered by this Annex shall be kept for a period of at least 15 years from the date of manufacture of the last product. U.K.
5. For custom-made devices, the manufacturer must undertake to review and to document experience gained in the post-production phase, including the provisions referred to in Annex 7, and to implement appropriate means to apply any necessary corrective action. This undertaking must include an obligation for the manufacturer to notify the competent authorities of the following incidents immediately on learning of them and the relevant corrective actions: U.K.
(i)
any malfunction or deterioration in the characteristics and/or performance of a device, as well as any inadequacy in the labelling or the instructions for use which might lead to or might have led to the death of a patient or user or to a serious deterioration in his state of health;
(ii)
any technical or medical reason connected with the characteristics or performance of a device for the reasons referred to in point (i) leading to systematic recall of devices of the same type by the manufacturer.]
ANNEX 7U.K.CLINICAL EVALUATION
[1. General provisions U.K.
1.1. As a general rule, confirmation of conformity with the requirements concerning the characteristics and performances referred to in Sections 1 and 2 of Annex 1 under the normal conditions of use of the device and the evaluation of the side-effects and of the acceptability of the benefit/risk ratio referred to in Section 5 of Annex 1, must be based on clinical data. The evaluation of this data (hereinafter referred to as clinical evaluation), where appropriate taking account of any relevant harmonised standards, must follow a defined and methodologically sound procedure based on: U.K.
1.1.1. Either a critical evaluation of the relevant scientific literature currently available relating to the safety, performance, design characteristics and intended purpose of the device where: U.K.
there is demonstration of equivalence of the device to the device to which the data relates and,
the data adequately demonstrate compliance with the relevant essential requirements.
1.1.2. Or a critical evaluation of the results of all the clinical investigations made, U.K.
1.1.3. Or a critical evaluation of the combined clinical data provided in 1.1.1 and 1.1.2. U.K.
1.2. Clinical investigations shall be performed unless it is duly justified to rely on existing clinical data. U.K.
1.3. The clinical evaluation and its outcome shall be documented. This documentation shall be included and/or fully referenced in the technical documentation of the device. U.K.
1.4. The clinical evaluation and its documentation must be actively updated with data obtained from the post-market surveillance. Where post-market clinical follow-up as part of the post-market surveillance plan for the device is not deemed necessary, this must be duly justified and documented. U.K.
1.5. Where demonstration of conformity with essential requirements based on clinical data is not deemed appropriate, adequate justification for any such exclusion has to be given based on risk management output and under consideration of the specifics of the device/body interaction, the clinical performances intended and the claims of the manufacturer. Adequacy of demonstration of conformity with the essential requirements by performance evaluation, bench testing and pre-clinical evaluation alone has to be duly substantiated. U.K.
1.6. All data must remain confidential unless it is deemed essential that they be divulged.] U.K.
2.Clinical investigationU.K.
2.1.PurposeU.K.
The purpose of clinical investigation is to:
verify that, under normal conditions of use, the performances of the device comply with those indicated in section 2 of Annex 1,
determine any undesirable side effects, under normal conditions of use, and assess whether they are acceptable risks having regard to the intended performance of the device.
2.2.Ethical considerationU.K.
Clinical investigations shall be made in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki approved by the 18th World Medical Assembly in Helsinki, Finland, in 1964, and amended by the 29th World Medical Assembly in Tokyo, Japan, in 1975 and the 35th World Medical Assembly in Venice, Italy, in 1983. It is mandatory that all measures relating to the protection of human subjects are carried out in the spirit of the Declaration of Helsinki. This includes every step in the clinical investigation from first consideration of need and justification of the study to publication of results.
2.3.MethodsU.K.
2.3.1.Clinical investigations shall be performed according to an appropriate state of the art plan of investigation defined in such a way as to confirm or refute the manufacturer's claims for the device; the investigations shall include an adequate number of observations to guarantee the scientific validity of the conclusions.U.K.
2.3.2.The procedures utilized to perform the investigations shall be appropriate to the device under examination.U.K.
2.3.3.Clinical investigations shall be performed in circumstances equivalent to those which would be found in normal conditions of use of the device.U.K.
2.3.4.All appropriate features, including those involving the safety and performances of the device, and its effects on the patients, shall be examined.U.K.
[2.3.5. All serious adverse events must be fully recorded and immediately notified to all competent authorities of the Member States in which the clinical investigation is being performed.] U.K.
2.3.6.The investigations shall be performed under the responsibility of an [duly qualified medical practitioner or authorised person], in an appropriate environment.U.K.
The medical specialist shall have access to the technical data regarding the device.
2.3.7.The written report, signed by the responsible medical specialist, shall comprise a critical evaluation of all the data collected during the clinical investigation.U.K.
ANNEX 8U.K.MINIMUM CRITERIA TO BE MET WHEN DESIGNATING INSPECTION BODIES TO BE NOTIFIED
1.The body, its director and the staff responsible for carrying out the evaluation and verification operations shall not be the designer, manufacturer, supplier or installer of devices which they control, nor the authorized representative of any of those parties. They may not become directly involved in the design, construction, marketing or maintenance of the devices, nor represent the parties engaged in these activities. This does not preclude the possibility of exchanges of technical information between the manufacturer and the body.U.K.
2.The body and its staff must carry out the evaluation and verification operations with the highest degree of professional integrity and technical competence and must be free from all pressures and inducements, particularly financial, which might influence their judgement or the results of the inspection, especially from persons or groups of persons with an interest in the results of verifications.U.K.
3.The body must be able to carry out all the tasks in one of Annexes 2 to 5 assigned to such a body and for which it has been notified, whether those tasks are carried out by the body itself or under its responsibility. In particular, it must have at its disposal the necessary staff and possess the necessary facilities to enable it to perform properly the technical and administrative tasks connected with evaluation and verification; it must also have access to the equipment necessary for the verifications required.U.K.
4.The staff responsible for control operations must have:U.K.
sound vocational training covering all the evaluation and verification operations for which the body has been designated,
satisfactory knowledge of the requirements of the controls they carry out and adequate experience of such operations,
the ability required to draw up the certificates, records and reports to demonstrate that the controls have been carried out.
5.The impartiality of inspection staff must be guaranteed. Their remuneration must not depend on the number of controls carried out, nor on the results of such controls.U.K.
6.The body must take out liability insurance unless liability is assumed by the State in accordance with national law, or the Member State itself is directly responsible for controls.U.K.
7.The staff of the body are bound to observe professional secrecy with regard to all information gained in carrying out their tasks (except vis-à-vis the competent administrative authorities of the State in which their activities are carried out) under this Directive or any provision of national law giving effect to it.U.K.
[ANNEX 9 U.K. CE CONFORMITY MARKING
The CE conformity marking shall consist of the initials ‘ CE ’ taking the following form:
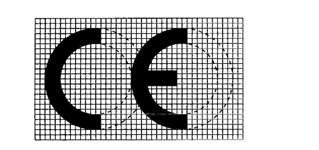
If the CE marking is reduced or enlarged the proportions given in the above graduated drawing must be respected.
The various components of the CE marking must have substantially the same vertical dimension, which may not be less than 5 mm.
This minimum dimension may be waived for small-scale devices.]


