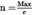- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (01/01/2013)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Directive 2009/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (repealed)Show full title
Directive 2009/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on non-automatic weighing instruments (Codified version) (Text with EEA relevance) (repealed)
You are here:
- Directives originating from the EU
- 2009 No. 23
- Annexes only
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 01/01/20130.54 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Directive 2009/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (repealed) (Annexes only)
Version Superseded: 20/04/2016
Alternative versions:
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
ANNEX IU.K.
ESSENTIAL REQUIREMENTS U.K.
The terminology used is that of the International Organisation of Legal Metrology.
Preliminary observation U.K.
Where an instrument includes, or is connected to, more than one indicating or printing device used for the applications listed in point (a) of Article 1(2), those devices which repeat the results of the weighing operation and which cannot influence the correct functioning of the instrument shall not be subject to the essential requirements if the weighing results are printed or recorded correctly and indelibly by a part of the instrument which meets the essential requirements and the results are accessible to both parties concerned by the measurement. However, in the case of instruments used for direct sales to the public, display and printing devices for the vendor and the customer must fulfil the essential requirements.
METROLOGICAL REQUIREMENTS U.K.
1.Units of massU.K.
The units of mass used shall be the legal units within the meaning of Council Directive 80/181/EEC of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to units of measurement(1).
Subject to compliance with this condition, the following units are permitted:
SI units: kilogram, microgram, milligram, gram, tonne,
imperial unit: troy ounce, if weighing precious metals,
other non-SI unit: metric carat, if weighing precious stones.
For instruments that make use of the imperial unit of mass referred to above, the relevant essential requirements specified below shall be converted to that unit, using simple interpolation.
2.Accuracy classesU.K.
2.1.The following accuracy classes have been defined:U.K.
special
high
medium
ordinary
The specifications of these classes are given in Table 1.
Table 1
Accuracy classes
The minimum capacity is reduced to 5 e for instruments in classes II and III for determining a conveying tariff.
2.2.Scale intervalsU.K.
2.2.1.The actual scale interval (d) and the verification scale interval (e) shall be in the form:U.K.
1 × 10k, 2 × 10k, or 5 × 10k mass units,
k being any integer or zero.
2.2.2.For all instruments other than those with auxiliary indicating devices:U.K.
d = e.
2.2.3.For instruments with auxiliary indicating devices the following conditions apply:U.K.
e = 1 × 10k g,
d < e ≤ 10 d,
except for instruments of class I with d < 10–4 g, for which e = 10–3 g.
3.ClassificationU.K.
3.1.Instruments with one weighing rangeU.K.
Instruments equipped with an auxiliary indicating device shall belong to class I or class II. For these instruments the minimum capacity lower limits for these two classes are obtained from Table 1 by replacement in column 3 of the verification scale interval (e) by the actual scale interval (d).
If d < 10–4 g, the maximum capacity of class I may be less than 50 000 e.
3.2.Instruments with multiple weighing rangesU.K.
Multiple weighing ranges are permitted, provided they are clearly indicated on the instrument. Each individual weighing range is classified according to point 3.1. If the weighing ranges fall into different accuracy classes the instrument shall comply with the severest of the requirements that apply for the accuracy classes in which the weighing ranges fall.
3.3.Multi-interval instrumentsU.K.
3.3.1.Instruments with one weighing range may have several partial weighing ranges (multi-interval instruments).U.K.
Multi-interval instruments shall not be equipped with an auxiliary indicating device.
3.3.2.Each partial weighing range i of multi-interval instruments is defined by:U.K.
where:
=
1, 2, … r,
=
partial weighing range number,
=
the total number of partial weighing ranges.
All capacities are capacities of net load, irrespective of the value of any tare used.
3.3.3.The partial weighing ranges are classified according to Table 2. All partial weighing ranges shall fall into the same accuracy class, that class being the instrument’s accuracy class.U.K.
Table 2
Multi-interval instruments
| i = 1, 2, … r i = partial weighing range number r = total number of partial weighing ranges | |||||
| a For i = r, the corresponding column of Table 1 applies, with e replaced by er. | |||||
| Class | Verification scale interval (e) | Minimum capacity (Min) | Number of verification scale intervals | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum value | Minimum valuea  | Maximum value  | |||
| I | 0,001 | g ≤ ei | 100 e1 | 50 000 | — |
| II | 0,001 | g ≤ ei ≤ 0,05 g | 20 e1 | 5 000 | 100 000 |
| 0,1 | g ≤ ei | 50 e1 | 5 000 | 100 000 | |
| III | 0,1 | g ≤ ei | 20 e1 | 500 | 10 000 |
| IIII | 5 | g ≤ ei | 10 e1 | 50 | 1 000 |
4.AccuracyU.K.
4.1.On implementation of the procedures laid down in Article 9, the error of indication shall not exceed the maximum permissible error of indication as shown in Table 3. In case of digital indication the error of indication shall be corrected for the rounding error.U.K.
The maximum permissible errors apply to the net value and tare value for all possible loads, excluding preset tare values.
Table 3
Maximum permissible errors
| Load | Maximum permissible error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | Class II | Class III | Class IIII | |
| 0 ≤ m ≤ 50 000 e | 0 ≤ m ≤ 5 000 e | 0 ≤ m ≤ 500 e | 0 ≤ m ≤ 50 e | ± 0,5 e |
| 50 000 e < m ≤ 200 000 e | 5 000 e < m ≤ 20 000 e | 500 e < m ≤ 2 000 e | 50 e < m ≤ 200 e | ± 1,0 e |
| 200 000 e < m | 20 000 e < m ≤ 100 000 e | 2 000 e < m ≤ 10 000 e | 200 e < m ≤ 1 000 e | ± 1,5 e |
4.2.The maximum permissible errors in service are twice the maximum permissible errors fixed in Section 4.1.U.K.
5.Weighing results of an instrument shall be repeatable, and shall be reproducible by the other indicating devices used and in accordance with other methods of balancing used.U.K.
The weighing results shall be sufficiently insensitive to changes in the position of the load on the load receptor.
6.The instrument shall react to small variations in the load.U.K.
7.Influence quantities and timeU.K.
7.1.Instruments of classes II, III and IIII, liable to be used in a tilted position, shall be sufficiently insensitive to the degree of tilting that can occur in normal use.U.K.
7.2.The instruments shall meet the metrological requirements within the temperature range specified by the manufacturer. The value of this range shall be at least equal to:U.K.
5 °C for an instrument in class I,
15 °C for an instrument in class II,
30 °C for an instrument in class III or IIII.
In the absence of a manufacturer’s specification, the temperature range of – 10 °C to + 40 °C applies.
7.3.Instruments operated from a mains power supply shall meet the metrological requirements under conditions of power supply within the limits of normal fluctuation.U.K.
Instruments operated from battery power shall indicate whenever the voltage drops below the minimum required value and shall under those circumstances either continue to function correctly or be automatically put out of service.
7.4.Electronic instruments, except those in class I and in class II if e is less than 1 g, shall meet the metrological requirements under conditions of high relative humidity at the upper limit of their temperature range.U.K.
7.5.Loading an instrument in class II, III or IIII for a prolonged period of time shall have a negligible influence on the indication at load or on the zero indication immediately after removal of the load.U.K.
7.6.Under other conditions the instruments shall either continue to function correctly or be automatically put out of service.U.K.
Design and construction U.K.
8.General requirementsU.K.
8.1.Design and construction of the instruments shall be such that the instruments will preserve their metrological qualities when properly used and installed and when used in an environment for which they are intended. The value of the mass must be indicated.U.K.
8.2.When exposed to disturbances, electronic instruments shall not display the effects of significant faults, or shall automatically detect and indicate them.U.K.
Upon automatic detection of a significant fault, electronic instruments shall provide a visual or audible alarm that shall continue until the user takes corrective action or the fault disappears.
8.3.The requirements of points 8.1 and 8.2 shall be met on a lasting basis during a period of time that is normal in view of the intended use of such instruments.U.K.
Digital electronic devices shall always exercise adequate control of the correct operation of the measuring process, of the indicating device, and of all data storage and data transfer.
Upon automatic detection of a significant durability error, electronic instruments shall provide a visual or audible alarm that shall continue until the user takes corrective action or the error disappears.
8.4.When external equipment is connected to an electronic instrument through an appropriate interface the metrological qualities of the instrument shall not be adversely influenced.U.K.
8.5.The instruments shall have no characteristics likely to facilitate fraudulent use, whereas possibilities for unintentional misuse shall be minimal. Components that may not be dismantled or adjusted by the user shall be secured against such actions.U.K.
8.6.Instruments shall be designed to permit ready execution of the statutory controls laid down by this Directive.U.K.
9.Indication of weighing results and other weight valuesU.K.
The indication of the weighing results and other weight values shall be accurate, unambiguous and non-misleading and the indicating device shall permit easy reading of the indication under normal conditions of use.
The names and symbols of the units referred to in point 1 of this Annex shall comply with the provisions of Directive 80/181/EEC with the addition of the symbol for the metric carat which shall be the symbol ‘ct’.
Indication shall be impossible above the maximum capacity (Max), increased by 9 e.
An auxiliary indicating device is permitted only to the right of the decimal mark. An extended indicating device may be used only temporarily, and printing shall be inhibited during its functioning.
Secondary indications may be shown, provided that they cannot be mistaken for primary indications.
10.Printing of weighing results and other weight valuesU.K.
Printed results shall be correct, suitably identified and unambiguous. The printing shall be clear, legible, non-erasable and durable.
11.LevellingU.K.
When appropriate, instruments shall be fitted with a levelling device and a level indicator, sufficiently sensitive to allow proper installation.
12.ZeroingU.K.
Instruments may be equipped with zeroing devices. The operation of these devices shall result in accurate zeroing and shall not cause incorrect measuring results.
13.Tare devices and preset tare devicesU.K.
The instruments may have one or more tare devices and a preset tare device. The operation of the tare devices shall result in accurate zeroing and shall ensure correct net weighing. The operation of the preset tare device shall ensure correct determination of the calculated net value.
14.Instruments for direct sales to the public, with a maximum capacity not greater than 100 kg: additional requirementsU.K.
Instruments for direct sale to the public shall show all essential information about the weighing operation and, in the case of price-indicating instruments, shall clearly show the customer the price calculation of the product to be purchased.
The price to pay, if indicated, shall be accurate.
Price-computing instruments shall display the essential indications long enough for the customer to read them properly.
Price-computing instruments may perform functions other than per-article weighing and price computation only if all indications related to all transactions are printed clearly and unambiguously and are conveniently arranged on a ticket or label for the customer.
Instruments shall bear no characteristics that can cause, directly or indirectly, indications the interpretation of which is not easy or straightforward.
Instruments shall safeguard customers against incorrect sales transactions due to their malfunctioning.
Auxiliary indicating devices and extended indicating devices are not permitted.
Supplementary devices are permitted only if they cannot lead to fraudulent use.
Instruments similar to those normally used for direct sales to the public which do not satisfy the requirements of this Section must carry near to the display the indelible marking ‘Not to be used for direct sale to the public’.
15.Price labelling instrumentsU.K.
Price labelling instruments shall meet the requirements of price indicating instruments for direct sale to the public, as far as applicable to the instrument in question. The printing of a price label shall be impossible below a minimum capacity.
ANNEX IIU.K. CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES
1.EC type-examinationU.K.
1.1.EC type-examination is the procedure whereby a notified body verifies and certifies that an instrument, representative of the production envisaged, meets the requirements of this Directive.U.K.
1.2.The application for EC type-examination shall be lodged with a single notified body by the manufacturer or his authorised representative established within the Community.U.K.
The application shall include:
the name and address of the manufacturer and, if the application is lodged by the authorised representative, his name and address in addition,
a written declaration that the application has not been lodged with any other notified body,
the design documentation, as described in Annex III.
The applicant shall place at the disposal of the notified body an instrument, representative of the production envisaged, hereinafter the ‘type’.
1.3.The notified body shall:U.K.
1.3.1.examine the design documentation and verify that the type has been manufactured in accordance with that documentation;U.K.
1.3.2.agree with the applicant on the location where the examinations and/or tests shall be carried out;U.K.
1.3.3.perform or have performed the appropriate examinations and/or tests to check whether the solutions adopted by the manufacturer meet the essential requirements where the harmonised standards referred to in Article 6(1) have not been applied;U.K.
1.3.4.perform or have performed the appropriate examinations and/or tests to check whether, where the manufacturer has chosen to apply the relevant standards, these standards have been applied effectively, thereby assuring conformity with the essential requirements.U.K.
1.4.Where the type complies with the provisions of this Directive, the notified body shall issue an EC type-approval certificate to the applicant. The certificate shall contain the conclusions of the examination, conditions (if any) for its validity, the necessary data for identification of the approved instrument and, if relevant, a description of its functioning. All the relevant technical elements such as drawings and layouts shall be annexed to the EC type-approval certificate.U.K.
The certificate shall have a validity period of 10 years from the date of its issue, and may be renewed for subsequent periods of 10 years each.
In the event of fundamental changes to the design of the instrument, e.g. as a result of the application of new techniques, the validity of the certificate may be limited to two years and extended by three years.
1.5.Each notified body shall periodically make available to all Member States the list of:U.K.
applications received for EC type-examination,
EC type-approval certificates issued,
applications for type-certificates refused,
additions and amendments relating to documents already issued.
Each notified body shall moreover inform all the Member States forthwith of withdrawals of EC type-approval certificates.
Each Member State shall make this information available to the bodies which it has notified.
1.6.The other notified bodies may receive a copy of the certificates together with the annexes to them.U.K.
1.7.The applicant shall keep the notified body that has issued the EC type-approval certificate informed of any modification to the approved type.U.K.
Modifications to the approved type must receive additional approval from the notified body that issued the EC type-approval certificate where such changes influence conformity with the essential requirements of this Directive or the prescribed conditions for use of the instrument. This additional approval is given in the form of an addition to the original EC type-approval certificate.
2.EC declaration of type conformity (guarantee of production quality)U.K.
2.1.The EC declaration of type conformity (guarantee of production quality) is the procedure whereby the manufacturer who satisfies the obligations of point 2.2 declares that the instruments concerned are, where applicable, in conformity with the type as described in the EC type-approval certificate and that they satisfy the requirements of this Directive.U.K.
The manufacturer or his authorised representative established within the Community shall affix the ‘CE’ conformity marking to each instrument and the inscriptions provided for in Annex IV and shall draw up a written declaration of conformity.
The ‘CE’ conformity marking shall be accompanied by the identification number of the notified body responsible for the EC surveillance referred to in point 2.4.
2.2.The manufacturer shall have adequately implemented a quality system as specified in point 2.3 and shall be subject to EC surveillance as specified in point 2.4.U.K.
2.3.Quality systemU.K.
2.3.1.The manufacturer shall lodge an application for approval of his quality system with a notified body.U.K.
The application shall include:
an undertaking to carry out the obligations arising from the approved quality system,
an undertaking to maintain the approved quality system to ensure its continuing suitability and effectiveness.
The manufacturer shall make available to the notified body all relevant information, in particular the quality system’s documentation and the design documentation of the instrument.
2.3.2.The quality system shall ensure conformity of the instruments with the type as described in the EC type-approval certificate and with the requirement(s) of this Directive.U.K.
All the elements, requirements and provisions adopted by the manufacturer shall be documented in a systematic and orderly manner in the form of written rules, procedures and instructions. This quality system documentation shall ensure a proper understanding of the quality programmes, plans, manuals and records.
It shall contain in particular an adequate description of:
the quality objectives and the organisational structure, responsibilities and powers of the management with regard to product quality,
the manufacturing process, the quality control and assurance techniques and the systematic measures that will be used,
the examinations and tests that will be carried out before, during and after manufacture, and the frequency with which they will be carried out,
the means to monitor the achievement of the required product quality and the effective operation of the quality system.
2.3.3.The notified body shall examine and evaluate the quality system to determine whether it satisfies the requirements referred to in point 2.3.2. It shall presume conformity with these requirements in respect of quality systems that implement the corresponding harmonised standard.U.K.
It shall notify its decision to the manufacturer and inform the other notified bodies thereof. The notification to the manufacturer shall contain the conclusions of the examination and, in the event of refusal, the justification for the decision.
2.3.4.The manufacturer or his authorised representative shall keep the notified body that has approved the quality system informed of any updating of the quality assurance system in relation to changes brought about by, e.g. new technologies and new quality concepts.U.K.
2.3.5.Any notified body that withdraws approval of a quality system shall so inform the other notified bodies.U.K.
2.4.EC surveillanceU.K.
2.4.1.The purpose of EC surveillance is to make sure that the manufacturer duly fulfils the obligations arising out of the approved quality system.U.K.
2.4.2.The manufacturer shall grant the notified body access for inspection purposes to the manufacture, inspection, testing and storage premises and shall provide it with all necessary information, in particular:U.K.
the quality system documentation,
the design documentation,
the quality records, e.g. the inspection reports and tests and calibration data, reports on the qualifications of the personnel concerned, etc.
The notified body shall periodically carry out audits in order to ensure that the manufacturer is maintaining and applying the quality system; it shall provide the manufacturer with an audit report.
In addition, the notified body may carry out unscheduled visits to the manufacturer. During such visits, the notified body may carry out full or partial audits. It shall provide the manufacturer with a report on the visit, and, where appropriate, an audit report.
2.4.3.The notified body shall ensure that the manufacturer maintains and applies the approved quality system.U.K.
3.EC verificationU.K.
3.1.EC verification is the procedure whereby the manufacturer or his authorised representative established within the Community ensures and declares that the instruments which have been checked in accordance with point 3.3 are, where applicable, in conformity with the type described in the EC type-examination certificate and that they satisfy the requirements of this Directive.U.K.
3.2.The manufacturer shall take all necessary measures in order that the manufacturing process ensures conformity of the instruments, where applicable, with the type as described in the EC type-examination certificate and with the requirements of this Directive which apply to them. The manufacturer or his authorised representative established within the Community shall affix the ‘CE’ conformity marking to each instrument and draw up a written declaration of conformity.U.K.
3.3.The notified body shall carry out the appropriate examinations and tests in order to check the conformity of the product to the requirements of this Directive by examination and testing of every instrument, as specified in point 3.5.U.K.
3.4.For instruments not subject to EC type-approval, the documents relating to the design of the instrument, as set out in Annex III, must be accessible to the notified body should the latter so request.U.K.
3.5.Verification by checking and testing of each instrumentU.K.
3.5.1.All instruments shall be individually examined and appropriate tests, as set out in the relevant harmonised standards referred to in Article 6(1), or equivalent tests, shall be carried out in order to verify their conformity, where applicable, with the type as described in the EC type-examination certificate and the requirements of this Directive.U.K.
3.5.2.The notified body shall affix, or cause to be affixed, its identification number on each instrument the conformity of which to requirements has been established, and shall draw up a written certificate of conformity relating to the tests carried out.U.K.
3.5.3.The manufacturer or his authorised representative shall ensure that he is able to supply the notified body’s certificates of conformity on request.U.K.
4.EC unit verificationU.K.
4.1.EC unit verification is the procedure whereby the manufacturer or his authorised representative established within the Community ensures and declares that the instrument, generally designed for a specific application, which has been issued with the certificate referred to in point 4.2 conforms to the requirements of this Directive that apply to it. The manufacturer or his authorised representative shall affix the ‘CE’ conformity marking to the instrument and shall draw up a written declaration of conformity.U.K.
4.2.The notified body shall examine the instrument and carry out the appropriate tests, as set out in the relevant harmonised standard(s) referred to in Article 6(1), or equivalent tests, in order to ensure its conformity with the relevant requirements of this Directive.U.K.
The notified body shall affix, or cause to be affixed, its identification number to the instrument the conformity of which to requirements has been established, and shall draw up a written certificate of conformity concerning the tests carried out.
4.3.The aim of the technical documentation relating to the design of the instrument, as referred to in Annex III, is to enable conformity with the requirements of this Directive to be assessed and the design, manufacture and operation of the instrument to be understood. It must be accessible to the notified body.U.K.
4.4.The manufacturer or his authorised representative shall ensure that he is able to supply the notified body’s certificates of conformity on request.U.K.
5.Common provisionsU.K.
5.1.The EC declaration of type conformity (guarantee of production quality), the EC verification, and the EC unit verification may be carried out at the manufacturer’s works or any other location if transport to the place of use does not require dismantling of the instrument, if the putting into service at the place of use does not require assembly of the instrument or other technical installation work likely to affect the instrument’s performance, and if the gravity value at the place of putting into service is taken into consideration or if the instrument’s performance is insensitive to gravity variations. In all other cases, they shall be carried out at the place of use of the instrument.U.K.
5.2.If the instrument’s performance is sensitive to gravity variations the procedures referred to in point 5.1 may be carried out in two stages, with the second stage comprising all examinations and tests of which the outcome is gravity-dependent, and the first stage all other examinations and tests. The second stage shall be carried out at the place of use of the instrument. If a Member State has established gravity zones on its territory the expression ‘at the place of use of the instrument’ may be read as ‘in the gravity zone of use of the instrument’.U.K.
5.2.1.Where a manufacturer has opted for execution in two stages of one of the procedures mentioned in point 5.1, and where these two stages will be carried out by different parties, an instrument which has undergone the first stage of the procedure shall bear the identification number of the notified body involved in that stage.U.K.
5.2.2.The party which has carried out the first stage of the procedure shall issue for each of the instruments a certificate containing the data necessary for identification of the instrument and specifying the examinations and tests that have been carried out.U.K.
The party which carries out the second stage of the procedure shall carry out those examinations and tests that have not yet been carried out.
The manufacturer or his authorised representative shall ensure that he is able to supply the notified body’s certificates of conformity on request.
5.2.3.A manufacturer who has opted for the EC declaration of type conformity (guarantee of production quality) in the first stage may either use this same procedure in the second stage or decide to continue in the second stage with EC verification.U.K.
5.2.4.The ‘CE’ conformity marking shall be affixed to the instrument on completion of the second stage, along with the identification number of the notified body which took part in the second stage.U.K.
ANNEX IIIU.K. DESIGN TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION
The technical documentation must render the design, manufacture and operation of the product intelligible and enable an assessment to be made of its conformity with the requirements of this Directive.
The documentation shall include in so far as relevant for assessment:
a general description of the type,
conceptual designs and manufacturing drawings and plans of components, sub-assemblies, circuits, etc.,
descriptions and explanations necessary for the understanding of the above, including the operation of the instrument,
a list of the harmonised standards referred to in Article 6(1), applied in full or in part, and descriptions of the solutions adopted to meet the essential requirements where the harmonised standards referred to in Article 6(1) have not been applied,
results of design calculations made and of examinations, etc.,
test reports,
the EC type-approval certificates and the results of relevant tests on instruments containing parts identical to those in the design.
ANNEX IVU.K. ‘CE’ CONFORMITY MARKING AND INSCRIPTIONS
1.Instruments subject to the EC conformity assessment procedureU.K.
1.1.These instruments must bear:U.K.
the ‘CE’ conformity marking comprising the ‘CE’ symbol as described in Annex VI,
the identification number(s) of the notified body/bodies that has/have carried out the EC surveillance or the EC verification.
The abovementioned marking and inscriptions shall be affixed to the instrument and distinctly grouped together;
a green sticker at least 12,5 mm × 12,5 mm square bearing a capital letter ‘M’ printed in black;
the following inscriptions:
the number of the EC type-approval certificate, where appropriate,
the manufacturer’s mark or name,
the accuracy class, enclosed in an oval or in two horizontal lines joined by two half circles,
maximum capacity, in the form Max …,
minimum capacity, in the form Min …,
verification scale interval, in the form e = …,
the last two digits of the year in which the ‘CE’ conformity marking was affixed,
plus, when applicable:
serial number,
for instruments consisting of separate but associated units: identification mark on each unit,
scale interval if it is different from e, in the form d = …,
maximum additive tare effect, in the form T = + …,
maximum subtractive tare effect if it is different from Max, in the form T = – …,
tare interval if it is different from d, in the form dT = …,
maximum safe load if it is different from Max, in the form Lim …,
the special temperature limits, in the form … °C/… °C,
ratio between load receptor and load.
1.2.The instruments shall have adequate facilities for the affixing of the ‘CE’ conformity marking and/or inscriptions. These shall be such that it shall be impossible to remove the marking and inscriptions without damaging them, and that the marking and inscriptions shall be visible when the instrument is in its regular operating position.U.K.
1.3.Where a data plate is used it shall be possible to seal the plate unless it cannot be removed without being destroyed. If the data plate is sealable it shall be possible to apply a control mark to it.U.K.
1.4.The inscriptions Max, Min, e, and d, shall also be shown near the display of the result if they are not already located there.U.K.
1.5.Each load measuring device which is connected or can be connected to one or more load receptors shall bear the relevant inscriptions relating to the said load receptors.U.K.
2.Other instrumentsU.K.
The other instruments must bear:
the manufacturer’s mark or name,
maximum capacity, in the form Max ….
Those instruments may not bear the stickers provided for in point 1.1(b).
3.Restrictive use symbol specified in Article 13U.K.
That symbol shall be constituted by a capital letter ‘M’ printed in black on a red background at least 25 mm × 25 mm square with two intersecting diagonals forming a cross.
ANNEX VU.K. The minimum criteria to be applied by member states when designating bodies for the carrying-out of tasks pertaining to the procedures referred to in article 9
1.The bodies shall have at their disposal the necessary personnel, means and equipment.U.K.
2.The personnel of the bodies shall have technical competence and professional integrity.U.K.
3.The bodies shall work independently of all circles, groups or persons having a direct or indirect interest in non-automatic weighing instruments as regards the carrying-out of the tests, the preparation of the reports, the issuing of the certificates and the surveillance required by this Directive.U.K.
4.The personnel of the bodies shall respect professional confidentiality.U.K.
5.The bodies shall take out a civil liability insurance if their civil liability is not covered by the State under national law.U.K.
The fulfilment of the conditions under points 1 and 2 shall be periodically verified by the Member States.
ANNEX VIU.K. ‘CE’ CONFORMITY MARKING
The ‘CE’ conformity marking shall consist of the initials ‘CE’ taking the following form:
If the ‘CE’ conformity marking is reduced or enlarged the proportions given in the above graduated drawing must be respected.
The various components of the ‘CE’ conformity marking must have substantially the same vertical dimension, which may not be less than 5 mm.
ANNEX VIIU.K.
PART A U.K.
Repealed Directive with its amendment
(referred to in Article 17)
| Council Directive 90/384/EEC | |
| Council Directive 93/68/EEC | Article 1, point 7, and Article 8 only |
PART B U.K.
List of time limits for transposition into national law and application
(referred to in Article 17)
| a In accordance with Article 15(3) of Directive 90/384/EEC Member States shall permit, during a period of 10 years from the date on which they apply the laws, regulations and administrative provisions adopted by the Member States in order to transpose that Directive into national law, the placing on the market and/or putting into service of instruments which conform to the rules in force before 1 January 1993. | ||
| b In accordance with Article 14(2) of Directive 93/68/EEC: ‘Until 1 January 1997, Member States shall allow the placing on the market and the bringing into service of products which comply with the marking arrangements in force before 1 January 1995’. | ||
| Directive | Time limit for transposition | Date of application |
|---|---|---|
| 90/384/EEC | 30 June 1992 | 1 January 1993a |
| 93/68/EEC | 30 June 1994 | 1 January 1995b |
ANNEX VIIIU.K.
CORRELATION TABLE
| Directive 90/384/EEC | This Directive |
|---|---|
| Recital 5, last sentence | Article 2, point (3) |
| Article 1(1), first subparagraph | Article 2, point (1) |
| Article 1(1), second subparagraph | Article 2, point (2) |
| Article 1(1), third subparagraph | Article 1(1) |
| Article 1(2), introductory wording | Article 1(2), introductory wording |
| Article 1(2), point (a)(1) | Article 1(2), point (a)(i) |
| Article 1(2), point (a)(2) | Article 1(2), point (a)(ii) |
| Article 1(2), point (a)(3) | Article 1(2), point (a)(iii) |
| Article 1(2), point (a)(4) | Article 1(2), point (a)(iv) |
| Article 1(2), point (a)(5) | Article 1(2), point (a)(v) |
| Article 1(2), point (a)(6) | Article 1(2), point (a)(vi) |
| Article 1(2), point (b) | Article 1(2), point (b) |
| Article 2 | Article 3 |
| Article 3 | Article 4 |
| Article 4 | Article 5 |
| Article 5 | Article 6 |
| Article 6, first paragraph, first sentence | Article 7, first paragraph |
| Article 6, first paragraph, second sentence | Article 7, second paragraph |
| Article 6, second paragraph | Article 7, third paragraph |
| Article 7 | Article 8 |
| Article 8(1) and (2) | Article 9(1) and (2) |
| Article 8(3), point (a) | Article 9(3), first subparagraph |
| Article 8(3), point (b) | Article 9(3), second subparagraph |
| Article 9 | Article 10 |
| Article 10 | Article 11 |
| Article 11 | Article 12 |
| Article 12 | Article 13 |
| Article 13 | Article 14 |
| Article 14, first sentence | Article 15, first paragraph |
| Article 14, second sentence | Article 15, second paragraph |
| Article 15(1) to (3) | — |
| Article 15(4) | Article 16 |
| Article 15(5) | — |
| — | Article 17 |
| — | Article 18 |
| Article 16 | Article 19 |
| Annexes I to VI | Annexes I to VI |
| — | Annex VII |
| — | Annex VIII |
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThe Annexes only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources