- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (04/07/2012)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Directive 2012/19/EU of the European Parliament and of the CouncilShow full title
Directive 2012/19/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 July 2012 on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) (recast) (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Directives originating from the EU
- 2012 No. 19
- Annexes only
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 04/07/20180.42 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Directive 2012/19/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council (Annexes only)
Alternative versions:
Status:
EU Directives are published on this site to aid cross referencing from UK legislation. Since IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.) no amendments have been applied to this version.
ANNEX IU.K. Categories of EEE covered by this Directive during the transitional period as provided for in Article 2(1)(a)
1.Large household appliancesU.K.
2.Small household appliancesU.K.
3.IT and telecommunications equipmentU.K.
4.Consumer equipment and photovoltaic panelsU.K.
5.Lighting equipmentU.K.
6.Electrical and electronic tools (with the exception of large-scale stationary industrial tools)U.K.
7.Toys, leisure and sports equipmentU.K.
8.Medical devices (with the exception of all implanted and infected products)U.K.
9.Monitoring and control instrumentsU.K.
10.Automatic dispensersU.K.
ANNEX IIU.K. Indicative list of EEE which falls within the categories of Annex I
1.LARGE HOUSEHOLD APPLIANCESU.K.
Large cooling appliances
Refrigerators
Freezers
Other large appliances used for refrigeration, conservation and storage of food
Washing machines
Clothes dryers
Dish washing machines
Cookers
Electric stoves
Electric hot plates
Microwaves
Other large appliances used for cooking and other processing of food
Electric heating appliances
Electric radiators
Other large appliances for heating rooms, beds, seating furniture
Electric fans
Air conditioner appliances
Other fanning, exhaust ventilation and conditioning equipment
2.SMALL HOUSEHOLD APPLIANCESU.K.
Vacuum cleaners
Carpet sweepers
Other appliances for cleaning
Appliances used for sewing, knitting, weaving and other processing for textiles
Irons and other appliances for ironing, mangling and other care of clothing
Toasters
Fryers
Grinders, coffee machines and equipment for opening or sealing containers or packages
Electric knives
Appliances for hair cutting, hair drying, tooth brushing, shaving, massage and other body care appliances
Clocks, watches and equipment for the purpose of measuring, indicating or registering time
Scales
3.IT AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENTU.K.
Centralised data processing:
Mainframes
Minicomputers
Printer units
Personal computing:
Personal computers (CPU, mouse, screen and keyboard included)
Laptop computers (CPU, mouse, screen and keyboard included)
Notebook computers
Notepad computers
Printers
Copying equipment
Electrical and electronic typewriters
Pocket and desk calculators
and other products and equipment for the collection, storage, processing, presentation or communication of information by electronic means
User terminals and systems
Facsimile machine (fax)
Telex
Telephones
Pay telephones
Cordless telephones
Cellular telephones
Answering systems
and other products or equipment of transmitting sound, images or other information by telecommunications
4.CONSUMER EQUIPMENT AND PHOTOVOLTAIC PANELSU.K.
Radio sets
Television sets
Video cameras
Video recorders
Hi-fi recorders
Audio amplifiers
Musical instruments
and other products or equipment for the purpose of recording or reproducing sound or images, including signals or other technologies for the distribution of sound and image than by telecommunications
Photovoltaic panels
5.LIGHTING EQUIPMENTU.K.
Luminaires for fluorescent lamps with the exception of luminaires in households
Straight fluorescent lamps
Compact fluorescent lamps
High intensity discharge lamps, including pressure sodium lamps and metal halide lamps
Low pressure sodium lamps
Other lighting or equipment for the purpose of spreading or controlling light with the exception of filament bulbs
6.ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TOOLS (WITH THE EXCEPTION OF LARGE-SCALE STATIONARY INDUSTRIAL TOOLS)U.K.
Drills
Saws
Sewing machines
Equipment for turning, milling, sanding, grinding, sawing, cutting, shearing, drilling, making holes, punching, folding, bending or similar processing of wood, metal and other materials
Tools for riveting, nailing or screwing or removing rivets, nails, screws or similar uses
Tools for welding, soldering or similar use
Equipment for spraying, spreading, dispersing or other treatment of liquid or gaseous substances by other means
Tools for mowing or other gardening activities
7.TOYS, LEISURE AND SPORTS EQUIPMENTU.K.
Electric trains or car racing sets
Hand-held video game consoles
Video games
Computers for biking, diving, running, rowing, etc.
Sports equipment with electric or electronic components
Coin slot machines
8.MEDICAL DEVICES (WITH THE EXCEPTION OF ALL IMPLANTED AND INFECTED PRODUCTS)U.K.
Radiotherapy equipment
Cardiology equipment
Dialysis equipment
Pulmonary ventilators
Nuclear medicine equipment
Laboratory equipment for in vitro diagnosis
Analysers
Freezers
Fertilization tests
Other appliances for detecting, preventing, monitoring, treating, alleviating illness, injury or disability
9.MONITORING AND CONTROL INSTRUMENTSU.K.
Smoke detector
Heating regulators
Thermostats
Measuring, weighing or adjusting appliances for household or as laboratory equipment
Other monitoring and control instruments used in industrial installations (e.g. in control panels)
10.AUTOMATIC DISPENSERSU.K.
Automatic dispensers for hot drinks
Automatic dispensers for hot or cold bottles or cans
Automatic dispensers for solid products
Automatic dispensers for money
All appliances which deliver automatically all kinds of products
ANNEX IIIU.K. CATEGORIES OF EEE COVERED BY THIS DIRECTIVE
1.Temperature exchange equipmentU.K.
2.Screens, monitors, and equipment containing screens having a surface greater than 100 cm2 U.K.
3.LampsU.K.
4.Large equipment (any external dimension more than 50 cm) including, but not limited to:U.K.
Household appliances; IT and telecommunication equipment; consumer equipment; luminaires; equipment reproducing sound or images, musical equipment; electrical and electronic tools; toys, leisure and sports equipment; medical devices; monitoring and control instruments; automatic dispensers; equipment for the generation of electric currents. This category does not include equipment included in categories 1 to 3.
5.Small equipment (no external dimension more than 50 cm) including, but not limited to:U.K.
Household appliances; consumer equipment; luminaires; equipment reproducing sound or images, musical equipment; electrical and electronic tools; toys, leisure and sports equipment; medical devices; monitoring and control instruments; automatic dispensers; equipment for the generation of electric currents. This category does not include equipment included in categories 1 to 3 and 6.
6.Small IT and telecommunication equipment (no external dimension more than 50 cm)U.K.
ANNEX IVU.K. Non-exhaustive list of EEE which falls within the categories listed in Annex III
1.Temperature exchange equipmentU.K.
Refrigerators, Freezers, Equipment which automatically delivers cold products, Air conditioning equipment, Dehumidifying equipment, Heat pumps, Radiators containing oil and other temperature exchange equipment using fluids other than water for the temperature exchange.
2.Screens, monitors, and equipment containing screens having a surface greater than 100 cm2 U.K.
Screens, Televisions, LCD photo frames, Monitors, Laptops, Notebooks.
3.LampsU.K.
Straight fluorescent lamps, Compact fluorescent lamps, Fluorescent lamps, High intensity discharge lamps - including pressure sodium lamps and metal halide lamps, Low pressure sodium lamps, LED.
4.Large equipmentU.K.
Washing machines, Clothes dryers, Dish washing machines, Cookers, Electric stoves, Electric hot plates, Luminaires, Equipment reproducing sound or images, Musical equipment (excluding pipe organs installed in churches), Appliances for knitting and weaving, Large computer-mainframes, Large printing machines, Copying equipment, Large coin slot machines, Large medical devices, Large monitoring and control instruments, Large appliances which automatically deliver products and money, Photovoltaic panels.
5.Small equipmentU.K.
Vacuum cleaners, Carpet sweepers, Appliances for sewing, Luminaires, Microwaves, Ventilation equipment, Irons, Toasters, Electric knives, Electric kettles, Clocks and Watches, Electric shavers, Scales, Appliances for hair and body care, Calculators, Radio sets, Video cameras, Video recorders, Hi-fi equipment, Musical instruments, Equipment reproducing sound or images, Electrical and electronic toys, Sports equipment, Computers for biking, diving, running, rowing, etc., Smoke detectors, Heating regulators, Thermostats, Small Electrical and electronic tools, Small medical devices, Small Monitoring and control instruments, Small Appliances which automatically deliver products, Small equipment with integrated photovoltaic panels.
6.Small IT and telecommunication equipment (no external dimension more than 50 cm)U.K.
Mobile phones, GPS, Pocket calculators, Routers, Personal computers, Printers, Telephones.
ANNEX VU.K. MINIMUM RECOVERY TARGETS REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 11
Part 1:U.K.Minimum targets applicable by category from 13 August 2012 until 14 August 2015 with reference to the categories listed in Annex I:
for WEEE falling within category 1 or 10 of Annex I,
80 % shall be recovered, and
75 % shall be recycled;
for WEEE falling within category 3 or 4 of Annex I,
75 % shall be recovered, and
65 % shall be recycled;
for WEEE falling within category 2, 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9 of Annex I,
70 % shall be recovered, and
50 % shall be recycled;
for gas discharge lamps, 80 % shall be recycled.
Part 2:U.K.Minimum targets applicable by category from 15 August 2015 until 14 August 2018 with reference to the categories listed in Annex I:
for WEEE falling within category 1 or 10 of Annex I,
85 % shall be recovered, and
80 % shall be prepared for re-use and recycled;
for WEEE falling within category 3 or 4 of Annex I,
80 % shall be recovered, and
70 % shall be prepared for re-use and recycled;
for WEEE falling within category 2, 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9 of Annex I,
75 % shall be recovered, and
55 % shall be prepared for re-use and recycled;
for gas discharge lamps, 80 % shall be recycled.
Part 3:U.K.Minimum targets applicable by category from 15 August 2018 with reference to the categories listed in Annex III:
for WEEE falling within category 1 or 4 of Annex III,
85 % shall be recovered, and
80 % shall be prepared for re-use and recycled;
for WEEE falling within category 2 of Annex III,
80 % shall be recovered, and
70 % shall be prepared for re-use and recycled;
for WEEE falling within category 5 or 6 of Annex III,
75 % shall be recovered, and
55 % shall be prepared for re-use and recycled;
for WEEE falling within category 3 of Annex III, 80 % shall be recycled.
ANNEX VIU.K. MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR SHIPMENTS
1.In order to distinguish between EEE and WEEE, where the holder of the object claims that he intends to ship or is shipping used EEE and not WEEE, Member States shall require the holder to have available the following to substantiate this claim:U.K.
a copy of the invoice and contract relating to the sale and/or transfer of ownership of the EEE which states that the equipment is destined for direct re-use and that it is fully functional;
evidence of evaluation or testing in the form of a copy of the records (certificate of testing, proof of functionality) on every item within the consignment and a protocol containing all record information according to point 3;
a declaration made by the holder who arranges the transport of the EEE that none of the material or equipment within the consignment is waste as defined by Article 3(1) of Directive 2008/98/EC; and
appropriate protection against damage during transportation, loading and unloading in particular through sufficient packaging and appropriate stacking of the load.
2.By way of derogation, point 1(a) and (b) and point 3 do not apply where it is documented by conclusive proof that the shipment is taking place in the framework of a business-to-business transfer agreement and that:U.K.
the EEE is sent back to the producer or a third party acting on his behalf as defective for repair under warranty with the intention of re-use; or
the used EEE for professional use is sent to the producer or a third party acting on his behalf or a third-party facility in countries to which Decision C(2001)107/Final of the OECD Council concerning the revision of Decision C(92)39/Final on control of transboundary movements of wastes destined for recovery operations applies, for refurbishment or repair under a valid contract with the intention of re-use; or
the defective used EEE for professional use, such as medical devices or their parts, is sent to the producer or a third party acting on his behalf for root cause analysis under a valid contract, in cases where such an analysis can only be conducted by the producer or third parties acting on his behalf.
3.In order to demonstrate that the items being shipped constitute used EEE rather than WEEE, Member States shall require the following steps for testing and record keeping for used EEE to be carried out:U.K.
Step 1: Testing
(a)Functionality shall be tested and the presence of hazardous substances shall be evaluated. The tests to be conducted depend on the kind of EEE. For most of the used EEE a functionality test of the key functions is sufficient.
(b)Results of evaluation and testing shall be recorded.
Step 2: Record
(a)The record shall be fixed securely but not permanently on either the EEE itself (if not packed) or on the packaging so it can be read without unpacking the equipment.
(b)The record shall contain the following information:
name of item (name of the equipment if listed in Annex II or Annex IV, as appropriate, and category set out in Annex I or Annex III, as appropriate),
identification number of the item (type No) where applicable,
year of production (if available),
name and address of the company responsible for evidence of functionality,
result of tests as described in step 1 (including date of the functionality test),
kind of tests performed.
4.In addition to the documentation requested in points 1, 2 and 3, every load (e.g. shipping container, lorry) of used EEE shall be accompanied by:U.K.
a relevant transport document, e.g. CMR or waybill;
a declaration by the liable person on its responsibility.
5.In the absence of proof that an object is used EEE and not WEEE through the appropriate documentation required in points 1, 2, 3 and 4 and of appropriate protection against damage during transportation, loading and unloading in particular through sufficient packaging and appropriate stacking of the load, which are the obligations of the holder who arranges the transport, Member State authorities shall consider that an item is WEEE and presume that the load comprises an illegal shipment. In these circumstances the load will be dealt with in accordance with Articles 24 and 25 of Regulation (EC) No 1013/2006.U.K.
ANNEX VIIU.K. Selective treatment for materials and components of waste electrical and electronic equipment referred to in Article 8(2)
1.As a minimum the following substances, mixtures and components have to be removed from any separately collected WEEE:U.K.
polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) containing capacitors in accordance with Council Directive 96/59/EC of 16 September 1996 on the disposal of polychlorinated biphenyls and polychlorinated terphenyls (PCB/PCT)(1),
mercury containing components, such as switches or backlighting lamps,
batteries,
printed circuit boards of mobile phones generally, and of other devices if the surface of the printed circuit board is greater than 10 square centimetres,
toner cartridges, liquid and paste, as well as colour toner,
plastic containing brominated flame retardants,
asbestos waste and components which contain asbestos,
cathode ray tubes,
chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFC) or hydrofluorocarbons (HFC), hydrocarbons (HC),
gas discharge lamps,
liquid crystal displays (together with their casing where appropriate) of a surface greater than 100 square centimetres and all those back-lighted with gas discharge lamps,
external electric cables,
components containing refractory ceramic fibres as described in Commission Directive 97/69/EC of 5 December 1997 adapting to technical progress for the 23rd time Council Directive 67/548/EEC on the approximation of the laws, regulations and administrative provisions relating to the classification, packaging and labelling of dangerous substances(2),
components containing radioactive substances with the exception of components that are below the exemption thresholds set in Article 3 of and Annex I to Council Directive 96/29/Euratom of 13 May 1996 laying down basic safety standards for the protection of the health of workers and the general public against the dangers arising from ionizing radiation(3),
electrolyte capacitors containing substances of concern (height > 25 mm, diameter > 25 mm or proportionately similar volume).
These substances, mixtures and components shall be disposed of or recovered in compliance with Directive 2008/98/EC.
2.The following components of WEEE that is separately collected have to be treated as indicated:U.K.
cathode ray tubes: the fluorescent coating has to be removed,
equipment containing gases that are ozone depleting or have a global warming potential (GWP) above 15, such as those contained in foams and refrigeration circuits: the gases must be properly extracted and properly treated. Ozone-depleting gases must be treated in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1005/2009,
gas discharge lamps: the mercury shall be removed.
3.Taking into account environmental considerations and the desirability of preparation for re-use and recycling, points 1 and 2 shall be applied in such a way that environmentally-sound preparation for re-use and recycling of components or whole appliances is not hindered.U.K.
ANNEX VIIIU.K. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 8(3)
1.Sites for storage (including temporary storage) of WEEE prior to its treatment (without prejudice to the requirements of Council Directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the landfill of waste(4)):U.K.
impermeable surfaces for appropriate areas with the provision of spillage collection facilities and, where appropriate, decanters and cleanser-degreasers,
weatherproof covering for appropriate areas.
2.Sites for treatment of WEEE:U.K.
scales to measure the weight of the treated waste,
impermeable surfaces and waterproof covering for appropriate areas with the provision of spillage collection facilities and, where appropriate, decanters and cleanser-degreasers,
appropriate storage for disassembled spare parts,
appropriate containers for storage of batteries, PCBs/PCTs containing capacitors and other hazardous waste such as radioactive waste,
equipment for the treatment of water in compliance with health and environmental regulations.
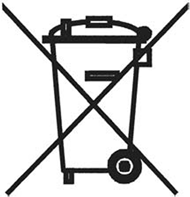
ANNEX IXU.K. SYMBOL FOR THE MARKING OF EEE
The symbol indicating separate collection for EEE consists of the crossed-out wheeled bin, as shown below. The symbol must be printed visibly, legibly and indelibly.
ANNEX XU.K. INFORMATION FOR REGISTRATION AND REPORTING REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 16
A. Information to be submitted upon registration: U.K.
Name and address of the producer or of the authorised representative where appointed under Article 17 (postal code and location, street name and number, country, telephone and fax number, e-mail, as well as a contact person). In the case of an authorised representative as defined in Article 17, also the contact details of the producer that is represented.
National identification code of the producer, including European tax number or national tax number of the producer.
Category of EEE set out in Annex I or III, as appropriate.
Type of EEE (household or other than household equipment).
Brand name of EEE.
Information on how the producer meets its responsibilities: individual or collective scheme, including information on financial guarantee.
Selling technique used (e.g. distance selling).
Declaration stating that the information provided is true.
B. Information to be submitted for reporting: U.K.
National identification code of the producer.
Reporting period.
Category of EEE set out in Annex I or III, as appropriate.
Quantity of EEE placed on the national market, by weight.
Quantity, by weight, of waste of EEE separately collected, recycled (including prepared for re-use), recovered and disposed of within the Member State or shipped within or outside the Union.
Note: information set out in points 4 and 5 must be given by category.U.K.
ANNEX XIU.K.
PART A U.K.
Repealed Directive with its successive amendments
(referred to in Article 25)
| Directive 2002/96/EC on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) | (OJ L 37, 13.2.2003, p. 24) |
| Directive 2003/108/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council | (OJ L 345, 31.12.2003, p. 106) |
| Directive 2008/34/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council | (OJ L 81, 20.3.2008, p. 65) |
PART B U.K.
List of time limits for transposition into national law
(referred to in Article 25)
| Directive | Deadline for transposition |
|---|---|
| 2002/96/EC | 13 August 2004 |
| 2003/108/EC | 13 August 2004 |
| 2008/34/EC | — |
ANNEX XIIU.K.
CORRELATION TABLE
| Directive 2002/96/EC | This Directive |
|---|---|
| Article 1 | — |
| — | Article 1 |
| Article 2(1) | Article 2(1) |
| Article 2(2) | Article 2(2) |
| Article 2(3) | Article 2(3)(a) |
| Article 2(1) (partly) | Article 2(3)(b) |
| Annex IB, point 5, last item | Article 2(3)(c) |
| Annex IB, point 8 | Article 2(4)(g) |
| — | Article 2(4)(a) to (f) and 2(5) |
| Article 3(a) | Article 3(1)(a) |
| — | Article 3(1)(b) to (d) |
| Article 3(b) | Article 3(1)(e) |
| Article 3(c) to (h) | Article 3(2) |
| Article 3(i) | Article 3(1)(f) |
| Article 3(j) | Article 3(1)(g) |
| Article 3(k) | Article 3(1)(h) |
| Article 3(l) | — |
| Article 3(m) | Article 3(1)(i) |
| — | Article 3(1)(j) to (o) |
| Article 4 | Article 4 |
| Article 5(1) to (2) | Article 5(1) to (2) |
| — | Article 5(3) to (4) |
| Article 5(3) | Article 5(5) |
| — | Article 6(1) |
| Article 5(4) | Article 6(2) |
| Article 5(5) | Article 7(1) and (2) |
| — | Article 8(1) |
| Article 6(1), first and second subparagraphs, and (3) | Article 8(2), (3) and (4) |
| Annex II(4) | Article 8(4), second subparagraph, first sentence |
| Article 6(1), third subparagraph | Article 8(5) |
| Article 6(6) | Article 8(6) |
| Article 6(2) | Article 9(1) and (2) |
| Article 6(4) | Article 9(3) |
| Article 6(5) | Article 10(1) and (2) |
| — | Article 10(3) |
| Article 7(1) | — |
| Article 7(2) | Article 11(1) and Annex V |
| — | Article 11(2) |
| — | Article 11(3) |
| Article 7(3), first subparagraph | Article 11(4) |
| Article 7(3), second subparagraph | — |
| Article 7(4) | — |
| Article 7(5) | Article 11(5) |
| — | Article 11(6) |
| Article 8(1) | Article 12(1) |
| — | Article 12(2) |
| Article 8(2), first and second subparagraphs | Article 12(3) |
| Article 8(2), third subparagraph | Article 14(1) (partly) |
| Article 8(3), first subparagraph | Article 12(4) |
| — | Article 12(5) |
| Article 8(3), second subparagraph | Article 14(1) (partly) |
| Article 8(4) | — |
| Article 9(1), first subparagraph | Article 13(1), first subparagraph |
| Article 9(1), second subparagraph | — |
| Article 9(1), third subparagraph | Article 13(1), second subparagraph |
| Article 9(1), fourth subparagraph | Article 13(1), third subparagraph |
| Article 9(2) | Article 13(2) |
| Article 10(1) | Article 14(2) |
| Article 10(2) | Article 14(3) |
| Article 10(3) | Article 14(4) |
| Article 10(4) | Article 14(5) |
| Article 11 | Article 15 |
| Article 12(1) (partly) | Article 16(1) to (3) |
| Article 12(1), first subparagraph (partly) | Article 16(4) |
| Article 12(1), second subparagraph | Article 16(1) and (2) and Article 17(2) and (3) |
| Article 12(1), third subparagraph | Article 16(3) and (5) |
| — | Article 17(1) |
| Article 12(1), fourth subparagraph | Article 18 |
| Article 12(2) | Article 16(5) |
| Article 13 | Article 19 |
| — | Article 20 |
| Article 14 | Article 21 |
| Article 15 | Article 22 |
| Article 16 | Article 23(1) |
| — | Article 23(2) to (4) |
| Article 17(1) to (3) | Article 24(1) to (3) |
| Article 17(4) | Article 7(3) |
| Article 17(5) | Article 7(4) to (7), Article 11(6) and Article 12(6) |
| — | Article 25 |
| Article 18 | Article 26 |
| Article 19 | Article 27 |
| Annex IA | Annex I |
| Annex IB | Annex II |
| — | Annexes III, IV and VI |
| Annexes II to IV | Annexes VII to IX |
| — | Annexes X and XI |
| — | Annex XII |
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Directive
PrintThe Annexes only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources