- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Regulation (EC) No 798/2008Show full title
Commission Regulation (EC) No 798/2008 of 8 August 2008 laying down a list of third countries, territories, zones or compartments from which poultry and poultry products may be imported into and transit through the Community and the veterinary certification requirements (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Regulations originating from the EU
- 2008 No. 798
- Annexes only
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 10/08/20207.16 MB
- Revised 11/05/20207.16 MB
- Revised 23/04/20207.19 MB
- Revised 15/03/20207.13 MB
- Revised 07/03/20207.12 MB
- Revised 14/12/20197.16 MB
- Revised 11/11/20197.16 MB
- Revised 14/09/20197.17 MB
- Revised 24/02/20197.14 MB
- Revised 09/11/20187.09 MB
- Revised 07/08/20177.27 MB
- Revised 24/03/20177.13 MB
- Revised 07/02/20177.11 MB
- Revised 31/01/20174.93 MB
- Revised 26/03/20164.84 MB
- Revised 08/02/20164.84 MB
- Revised 05/02/20164.84 MB
- Revised 28/01/20164.85 MB
- Revised 08/12/20154.84 MB
- Revised 24/10/20154.42 MB
- Revised 25/08/20154.43 MB
- Revised 28/07/20154.40 MB
- Revised 18/07/20154.39 MB
- Revised 16/06/20154.39 MB
- Revised 25/05/20154.38 MB
- Revised 21/04/20154.38 MB
- Revised 31/03/20158.86 MB
- Revised 07/03/201510.88 MB
- Revised 03/10/201416.98 MB
- Revised 14/03/201421.70 MB
- Revised 17/12/201323.37 MB
- Revised 30/09/201323.38 MB
- Revised 01/07/20137.48 MB
- Revised 17/05/201323.36 MB
- Revised 26/03/201323.41 MB
- Revised 21/02/201332.57 MB
- Revised 25/06/201222.34 MB
- Revised 29/05/201222.32 MB
- Revised 13/02/201222.32 MB
- Revised 01/02/201222.34 MB
- Revised 29/11/201122.33 MB
- Revised 09/10/201122.35 MB
- Revised 01/07/201122.32 MB
- Revised 01/12/201021.97 MB
- Revised 05/11/201023.42 MB
- Revised 13/04/201022.15 MB
- Revised 23/05/200919.49 MB
- Revised 01/01/20096.72 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Status:
This is the original version as it was originally adopted in the EU.
This legislation may since have been updated - see the latest available (revised) version
ANNEX IPOULTRY, HATCHING EGGS, DAY-OLD CHICKS, SPECIFIED PATHOGEN-FREE EGGS, MEAT, MINCED MEAT, MECHANICALLY SEPARATED MEAT, EGGS AND EGG PRODUCTS
PART 1
List of third countries, territories, zones or compartments
| a Commodities, including those transported on the high seas, produced before this date may be imported into the Community during a period of 90 days from this date. | ||||||||||
| b Only commodities produced after this date may be imported into the Community. | ||||||||||
| c Certificates in accordance with the agreement between the European Community and the Swiss Confederation on trade in agricultural products (OJ L 114, 30.4.2002, p. 132 as last amended). | ||||||||||
| d The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia; provisional code that does not prejudge in any way the definitive nomenclature for this country, which will be agreed following the conclusion of negotiations currently taking place on this subject in the United Nations. | ||||||||||
| e Not including Kosovo, as defined by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1244 of 10 June 1999. | ||||||||||
| ISO code and name of third country or territory | Code of third country, territory, zone or compartment | Description of third country, territory, zone or compartment | Veterinary certificate | Specific conditions | Specific conditions | Avian influenza surveillance status | Avian influenza vaccination status | Salmonella control status | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model(s) | Additional guarantees | Closing datea | Opening dateb | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6A | 6B | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| AL — Albania | AL-0 | Whole country | EP, E | |||||||
| AR — Argentina | AR-0 | Whole country | SPF | A | ||||||
| POU, RAT, EP, E | ||||||||||
| WGM | VIII | |||||||||
| AU — Australia | AU-0 | Whole country | SPF | P1 | ||||||
| EP, E | ||||||||||
| BPP, DOC, HEP, SRP | ||||||||||
| BPR | I | |||||||||
| DOR | II | |||||||||
| HER | III | |||||||||
| POU | VI | |||||||||
| RAT | VII | |||||||||
| BR — Brazil | BR-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| BR-1 | States of: Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, Paraná, São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul | RAT, BPR, DOR, HER, SRA | P1 | |||||||
| BR-2 | States of: Mato Grosso, Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina and São Paulo | BPP, DOC, HEP, SRP | ||||||||
| BR-3 | Distrito Federal and States of: Goiás, Minas Gerais, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina and São Paulo | WGM | VIII | |||||||
| EP, E, POU | ||||||||||
| BW — Botswana | BW-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| EP, E | ||||||||||
| BPR | I | |||||||||
| DOR | II | |||||||||
| HER | III | |||||||||
| RAT | VII | |||||||||
| CA — Canada | CA-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| EP, E | ||||||||||
| BPR, BPP, DOC, DOR, HEP, HER, SRA, SRP | IV | |||||||||
| WGM | VIII | |||||||||
| POU, RAT | ||||||||||
| CH — Switzerland | CH-0 | Whole country | c | |||||||
| CL — Chile | CL-0 | Whole country | SPF | P1 | ||||||
| EP, E, | ||||||||||
| BPR, BPP, DOC, DOR, HEP, HER, SRA, SRP | ||||||||||
| WGM | VIII | |||||||||
| POU, RAT | ||||||||||
| CN — China (People's Republic of) | CN-0 | Whole country | EP | |||||||
| CN-1 | Province of Shandong | POU, E | VI | P2 | 6.2.2004 | — | ||||
| GL — Greenland | GL-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| EP, WGM | ||||||||||
| HK — Hong Kong | HK-0 | The whole territory of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region | EP | |||||||
| HR — Croatia | HR-0 | Whole country | SPF | P1 | ||||||
| BPR, BPP, DOR, DOC, HEP, HER, SRA, SRP | ||||||||||
| EP, E, POU, RAT, WGM | ||||||||||
| IL — Israel | IL-0 | Whole country | SPF | A | ||||||
| BPR, BPP, DOC, DOR, HEP, HER, SRP | IV | |||||||||
| WGM | VIII | |||||||||
| EP, E POU, RAT | ||||||||||
| IN — India | IN-0 | Whole country | EP | |||||||
| IS — Iceland | IS-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| EP, E | ||||||||||
| KR — Korea (Rep) | KR-0 | Whole country | EP, E | |||||||
| ME — Montenegro | ME-O | Whole country | EP | |||||||
| MG — Madagascar | MG-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| EP, E, WGM | ||||||||||
| MY — Malaysia | MY-0 | — | — | |||||||
| MY-1 | Western Peninsular | EP | ||||||||
| E | P2 | 6.2.2004 | ||||||||
| MK — Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedoniad | MK-0d | Whole country | EP | |||||||
| MX — Mexico | MX-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| EP | ||||||||||
| NA — Namibia | NA-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| BPR | I | |||||||||
| DOR | II | |||||||||
| HER | III | |||||||||
| RAT, EP, E | VII | |||||||||
| NC — New Caledonia | NC-0 | Whole country | EP | |||||||
| NZ — New Zealand | NZ-0 | Whole country | SPF | P1 | ||||||
| BPR, BPP, DOC, DOR, HEP, HER, SRA, SRP | ||||||||||
| WGM | VIII | |||||||||
| EP, E, POU, RAT | ||||||||||
| PM — St Pierre and Miquelon | PM-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| RS — Serbiae | XS-0e | Whole country | EP | |||||||
| RU — Russian Federation | RU-0 | Whole country | EP | |||||||
| SG — Singapore | SG-0 | Whole country | EP | |||||||
| TH — Thailand | TH-0 | Whole country | SPF, EP | |||||||
| WGM | VIII | P2 | 23.1.2004 | |||||||
| E, POU, RAT | P2 | 23.1.2004 | ||||||||
| TN — Tunisia | TN-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| DOR, BPR, BPP, HER | IV | |||||||||
| WGM | VIII | |||||||||
| EP, E, POU, RAT | ||||||||||
| TR — Turkey | TR-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| E, EP | ||||||||||
| US — United States | US-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| BPR, BPP, DOC, DOR, HEP, HER, SRA, SRP | IV | |||||||||
| WGM | VIII | |||||||||
| EP, E, POU, RAT | ||||||||||
| UY — Uruguay | UY-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| EP, E, RAT | ||||||||||
| ZA — South Africa | ZA-0 | Whole country | SPF | |||||||
| EP, E | ||||||||||
| BPR | I | |||||||||
| DOR | II | |||||||||
| HER | III | |||||||||
| RAT | VII | |||||||||
| ZW — Zimbabwe | ZW-0 | Whole country | RAT | VII | ||||||
| EP, E | ||||||||||
PART 2
Model veterinary certificates
Model(s):
:
Model veterinary certificate for breeding or productive poultry other than ratites
:
Model veterinary certificate for breeding or productive ratites
:
Model veterinary certificate for day-old chicks other than of ratites
:
Model veterinary certificate for day-old chicks of ratites
:
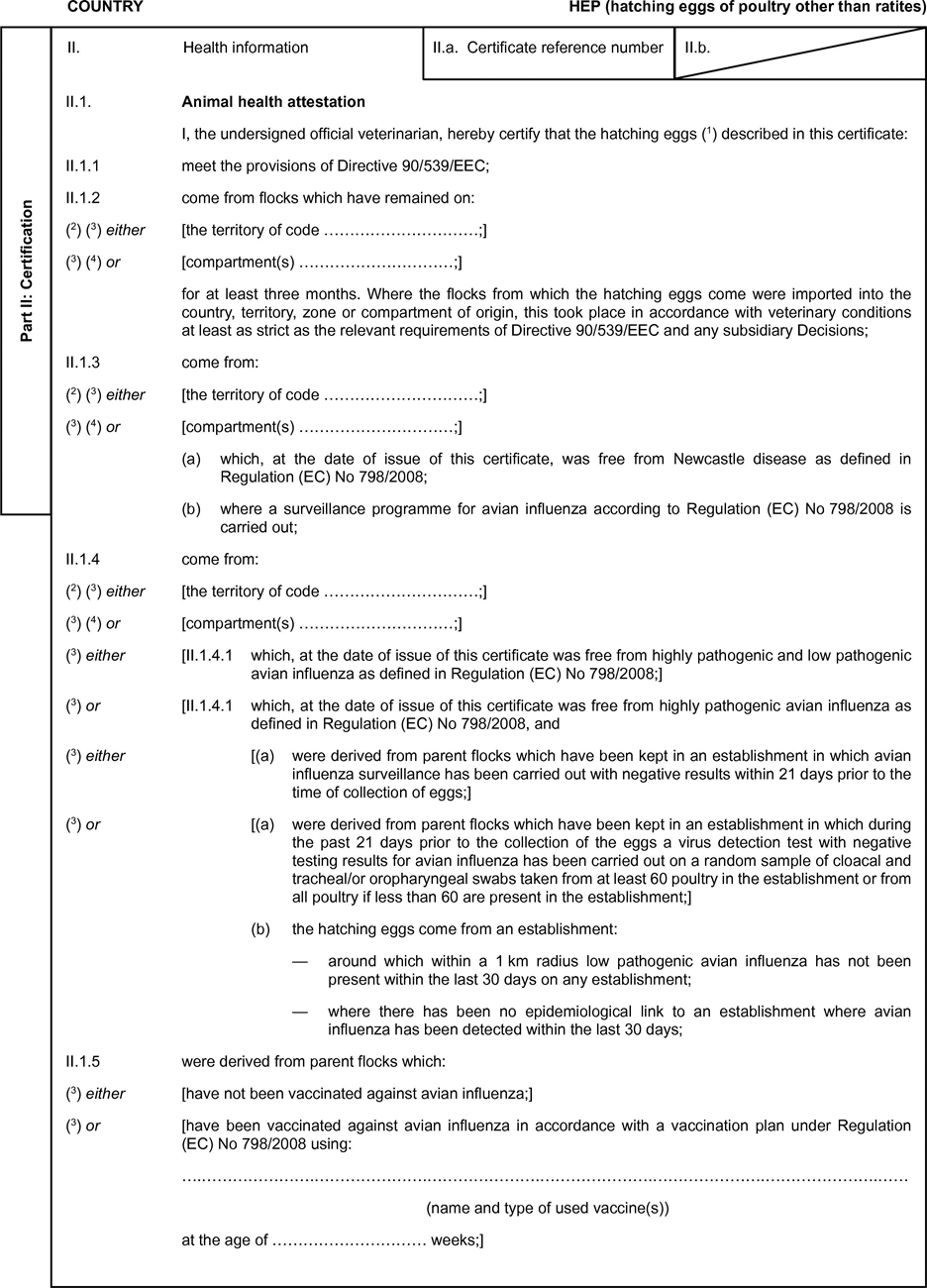
Model veterinary certificate for hatching eggs of poultry other than ratites
:
Model veterinary certificate for hatching eggs of ratites
:
Model veterinary certificate for specified pathogen-free eggs
:
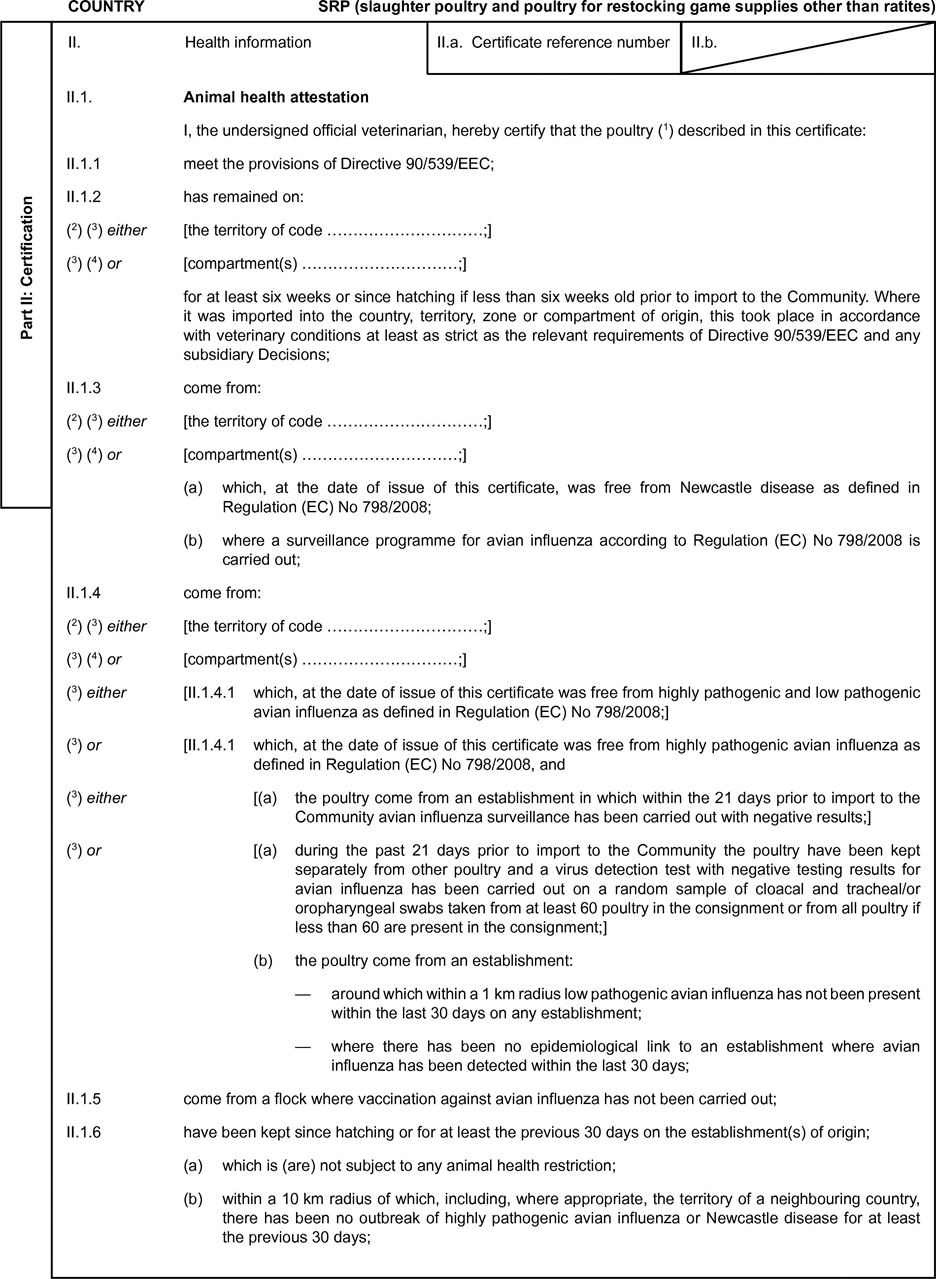
Model veterinary certificate for slaughter poultry and poultry for restocking game supplies other than ratites
:
Model veterinary certificate for slaughter ratites
:
Model veterinary certificate for meat of poultry
:
Model veterinary certificate for minced meat and mechanically separated meat of poultry
:
Model veterinary certificate for meat of farmed ratites for human consumption
:
Model veterinary certificate for minced meat and mechanically separated meat of farmed ratites for human consumption
:
Model veterinary certificate for wild game-bird meat
:
Model veterinary certificate for wild game-bird minced meat and mechanically separated meat
:
Model veterinary certificate for eggs
:
Model veterinary certificate for egg products
Additional guarantees (AG):
:
Guarantees for breeding and productive ratites coming from a third country, territory or zone not free from Newcastle disease, certified in accordance with model BPR
:
Guarantees for day-old chicks of ratites coming from a third country, territory or zone not free from Newcastle disease, certified in accordance with model DOR
:
Guarantees for hatching eggs of ratites coming from a third country, territory or zone not free from Newcastle disease certified in accordance with model HER
:
Relevant guarantees for breeding poultry of Gallus gallus, day-old chicks of Gallus gallus intended for breeding purposes and hatching eggs of Gallus gallus in accordance with EU provisions on the control of Salmonella, have been provided and shall be certified in accordance with model BPP, DOC and HEP respectively
:
Guarantees for slaughter ratites coming from a third country, territory or zone not free from Newcastle disease, certified in accordance with model SRA
:
additional guarantees covering poultrymeat certified in accordance with model POU
:
additional guarantees covering meat of farmed ratites for human consumption certified in accordance with model RAT
:
additional guarantees for wild game-bird meat certified in accordance with model WGM
Salmonella control programme:
:
Prohibition to import into the Community breeding poultry of Gallus gallus, day-old chicks of Gallus gallus intended for breeding purposes and hatching eggs of Gallus gallus because a Salmonella control programme in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 has not been submitted to the Commission or approved by it.
Specific conditions:
:
Prohibition to import into or transit through the Community due to restrictions related to a HPAI outbreak
:
Prohibition to import into or transit through the Community due to restrictions related to a ND outbreak
Avian influenza surveillance programme and avian influenza vaccination plan:
:
Third country, territory, zone or compartment carries out an avian influenza surveillance programme in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 798/2008
:
Third country, territory, zone or compartment carries out vaccination against avian influenza in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 798/2008
Notes
General notes:
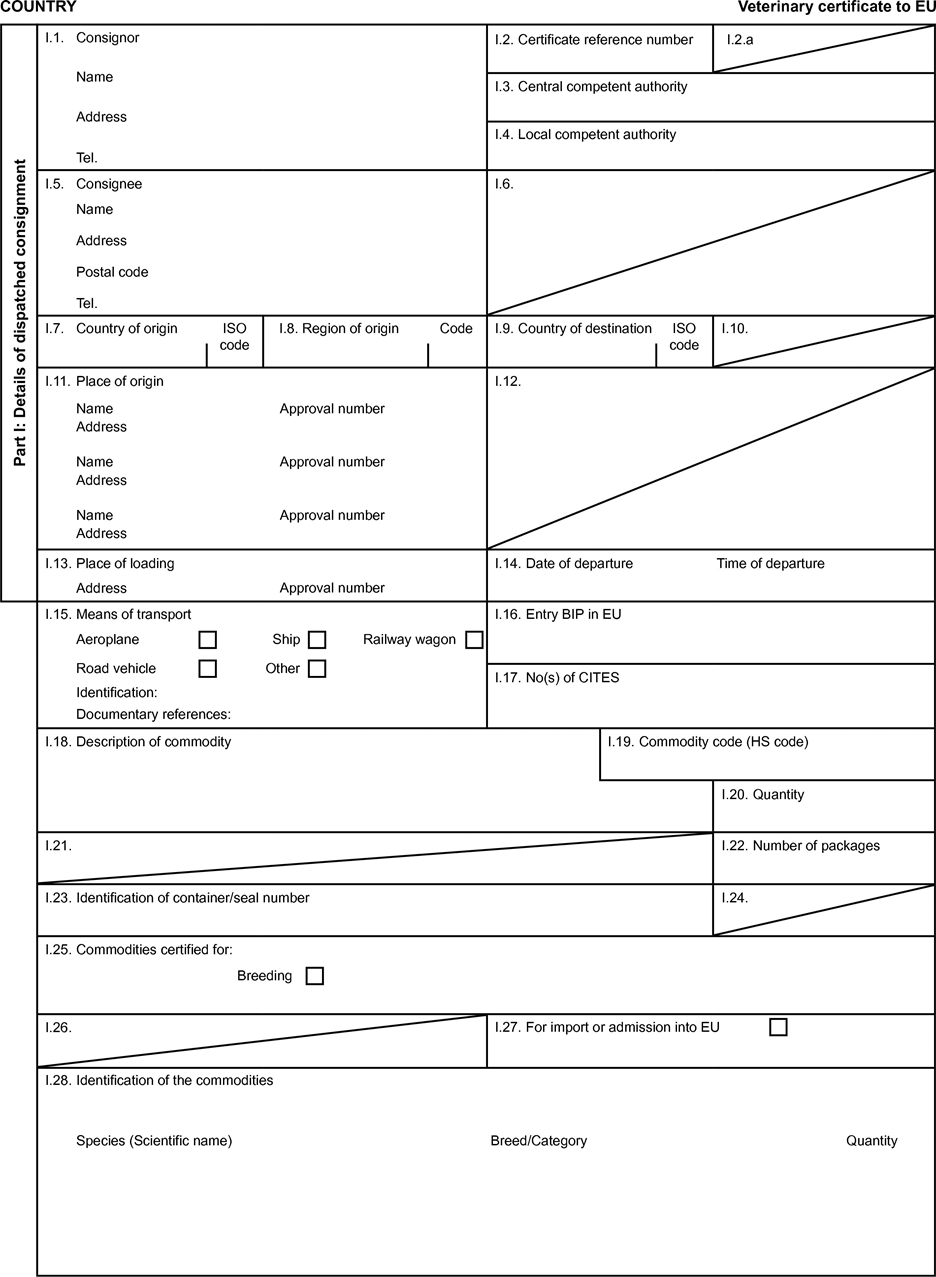
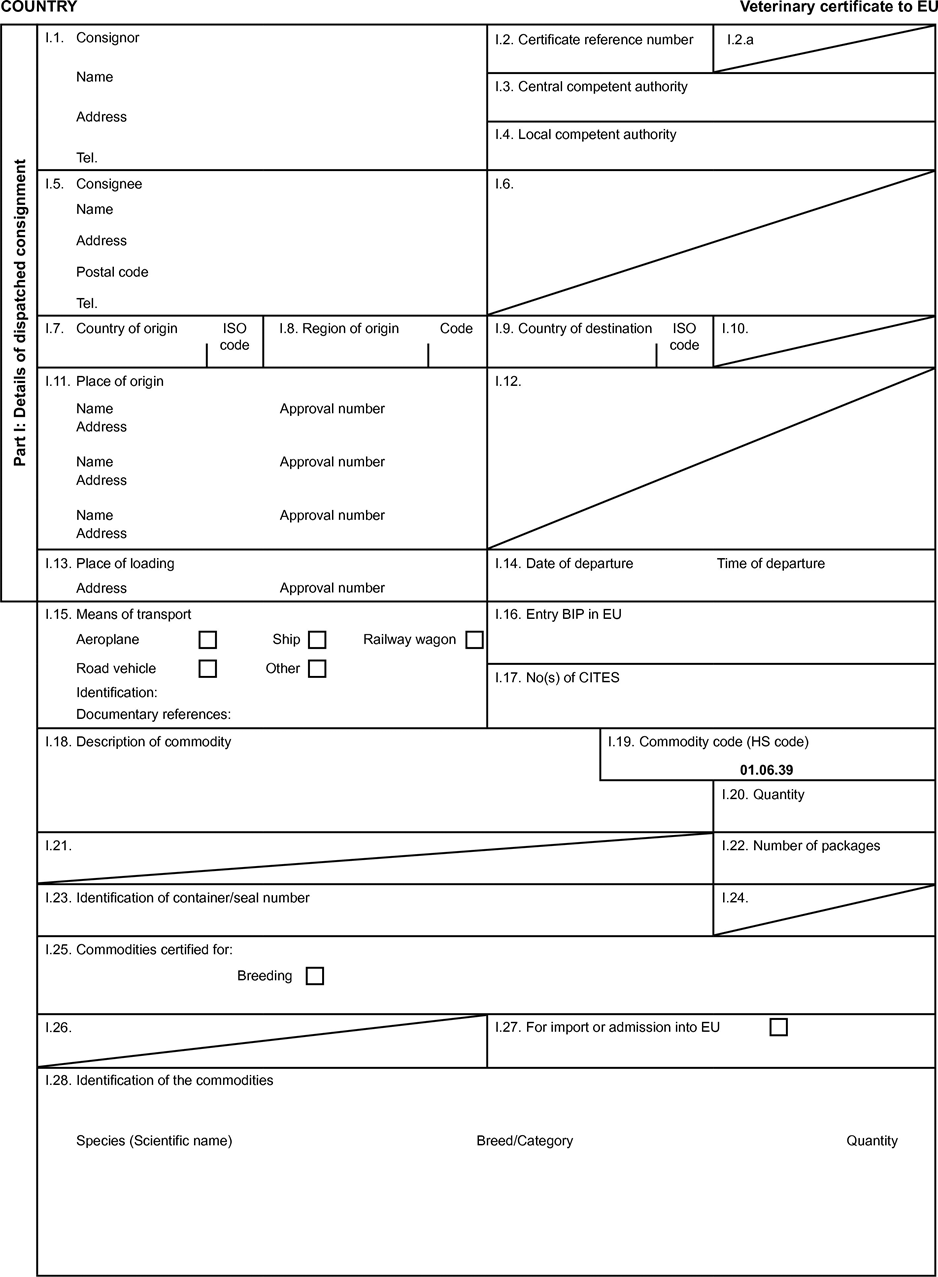
(a)Veterinary certificates based on the models in Part 2 of this Annex and following the layout of the model that corresponds to the commodity concerned shall be issued by the exporting country, territory, zone or compartment. They shall contain, in the order appearing in the model, the attestations that are required for any third country and, where applicable, those additional health requirements required for the exporting country, territory, zone or compartment.
Where additional guarantees are required by the EU Member State of destination for the commodity concerned, these shall also be entered on the original of the veterinary certificate.
(b)A separate, single certificate must be presented for each consignment of the commodity concerned, exported to the same destination from a territory appearing in columns 2 and 3 of Part 1 of this Annex and transported in the same railway wagon, lorry, aircraft or ship.
(c)The original of certificates shall consist of a single page printed on both sides or, where more text is required, such that all the pages form a whole and cannot be separated.
(d)The certificate shall be drawn up in at least one official language of the EU Member State where the border inspection takes place and in one official language of the EU Member State of destination. However, those Member States may allow another Community language instead of their own, accompanied, if necessary, by an official translation.
(e)Where additional pages are attached to the certificate for the purposes of identifying the items making up the consignment, such additional pages shall also be considered to form part of the original of the certificate, provided the signature and stamp of the certifying official veterinarian appear on each page.
(f)Where the certificate, including any additional pages as provided for in (e), comprises more than one page, each page shall be numbered ‘–x(page number) of y(total number of pages)–’ on the bottom and shall bear the code number of the certificate allocated by the competent authority on the top.
(g)The original of the certificate must be completed and signed by an official veterinarian not more than 24 hours prior to loading of the consignment for imports to the Community, unless otherwise stated. To that end, the competent authorities of the exporting country shall ensure that principles of certification equivalent to those laid down in Directive 96/93/EC are followed.
The colour of the signature shall be different from that of the printing. The same rule shall apply to stamps other than embossed stamps or watermarks.
(h)The original of the certificate must accompany the consignment as far as the EU border inspection post.
Additional notes for poultry and day-old chicks:
(i)The certificate shall be valid for 10 days from the date of issue, unless otherwise stated.
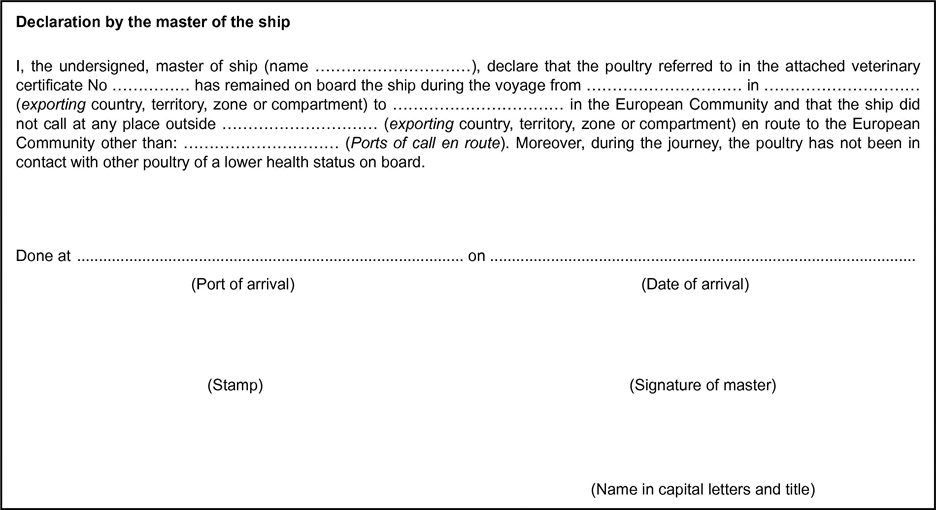
In the case of transport by ship, the term of validity shall be extended by the time taken by the voyage. To that end, the original of a declaration by the ship's master, drawn up in accordance with Annex II, shall be attached to the veterinary certificate.
(j)Poultry and day-old chicks shall not be transported with other poultry and day-old chicks that are either not intended for the European Community or of a lower health status.
(k)Poultry and day-old chicks shall not in the course of transport to the Community be moved through nor unloaded in a third country, territory, zone or compartment from which imports of such poultry and day-old chicks into the Community are not authorised.
Model veterinary certificate for breeding or productive poultry other than ratites (BPP)
Model veterinary certificate for breeding or productive ratites (BPR)
Model veterinary certificate for day-old chicks other than of ratites (DOC)
Model veterinary certificate for day-old chicks of ratites (DOR)
Model veterinary certificate for hatching eggs of poultry other than ratites (HEP)
Model veterinary certificate for hatching eggs of ratites (HER)
Model veterinary certificate for specified pathogen-free eggs (SPF)
Model veterinary certificate for slaughter poultry and poultry for restocking game supplies other than ratites (SRP)
Model veterinary certificate for slaughter ratites (SRA)
Model veterinary certificate for meat of poultry (POU)
Model veterinary certificate for minced meat and mechanically separated meat of poultry (POU-MI/MSM)
(Not yet established)
Model veterinary certificate for meat of farmed ratites for human consumption (RAT)
Model veterinary certificate for minced meat and mechanically separated meat of farmed ratites for human consumption (RAT-MI/MSM)
(Not yet established)
Model veterinary certificate for wild game-bird meat (WGM)
Model veterinary certificate for wild game-bird minced meat and mechanically separated meat (WGM-MI/MSM)
(Not yet established)
Model veterinary certificate for eggs (E)
Model veterinary certificate for egg products (EP)
ANNEX II(as referred to in Article 4)
(To be completed and attached to the veterinary certificate where transport of poultry and day-old chicks to the European Community border includes transport by ship, even for part of the journey.)
ANNEX IIICOMMUNITY ACTS, INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS AND PROCEDURES FOR EXAMINATION, SAMPLING AND TESTING AS REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 6
I.Before import into the Community
Methods for standardisation of materials and procedures for examination, sampling and testing for:
Avian influenza
Newcastle disease
Annex III to Council Directive 92/66/EEC(3); or
Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals of the World Organisation for animal Health (OIE);
Where Article 12 of Directive 90/539/EEC applies, the sampling and testing methods must comply with the methods described in Annexes to Commission Decision 92/340/EEC(4).
Salmonella pullorum and Salmonella gallinarum
Chapter III of Annex II to Directive 90/539/EEC; or
Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals of the World Organisation for animal Health (OIE).
Salmonella arizonae
Serological examination: 60 birds must be sampled at the point of lay with methods described in the Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals of the World Organisation for animal Health (OIE).
Mycoplasma gallisepticum
Chapter III of Annex II to Directive 90/539/EEC; or
Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals of the World Organisation for animal Health (OIE).
Mycoplasma meleagridis
Chapter III of Annex II to Directive 90/539/EEC.
Salmonella of public health significance
The detection method recommended by the Community reference laboratory (CRL) for Salmonella in Bilthoven, the Netherlands, or an equivalent method shall be used. That method is described in the current version of draft Annex D of ISO 6579 (2002): ‘Detection of Salmonella spp. in animal faeces and in samples of the primary production stage’. In that detection method, a semi-solid medium (modified semi-solid Rappaport-Vassiladis medium, MSRV) is used as the single selective enrichment medium.
Serotyping shall be carried out following the Kauffmann-White scheme or an equivalent method.
II.After import into the Community
Sampling and testing procedures for avian influenza and Newcastle disease:
During the period referred to in point II.1 of Annex VIII, the official veterinarian shall take samples from the imported poultry for virological examination, to be tested as follows:
Between the seventh and the fifteenth day following the date of commencement of the isolation period, cloacal swabs must be taken from all birds where the consignment contains less than 60 birds, and from at least 60 birds where consignments contain more than 60 birds;
Testing of samples must be carried out in official laboratories designated by the competent authority, using diagnostic procedures for:
(i)avian influenza as laid down in the diagnostic manual in Commission Decision 2006/437/EC;
(ii)Newcastle disease as laid down in Annex III to Council Directive 92/66/EEC.
III.General requirements
Samples may be pooled, subject to a maximum of five samples from individual birds in each pool.
Virus isolates must be sent without delay to the national reference laboratory.
ANNEX IV(as referred to in Article 8(2)(d), Article 9(2)(b) and Article 10REQUIREMENTS FOR AVIAN INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE PROGRAMMES AND INFORMATION TO BE SUBMITTED(5)
I.Requirements for avian influenza surveillance in poultry carried out in third countries, territories, zones or compartments as referred to in Article 10.
A.surveillance for avian influenza in poultry:
Description of objectives
Third country, territory, zone or compartment (keep as appropriate):
Type of surveillance:
Serological surveillance
Virological surveillance
Targeted avian influenza subtypes
Sampling criteria:
Targeted species (for example, turkeys, chicken, partridges)
Targeted categories (for example, breeders, layers)
Targeted husbandry systems (for example, commercial establishments, backyard flocks)
Statistical basis for number of establishments sampled:
Number of establishments in area
Number of establishments per category
Number of establishments to be sampled per poultry category
Frequency of sampling
Number of samples taken per establishment/shed
Time period for sampling
Type of samples taken (tissue, faeces, cloacal/oropharyngeal/tracheal swabs)
Laboratory tests used (for example, AGID, PCR, HI, Virus isolation.)
Indication of laboratories carrying out testing at central, regional or local level (keep as appropriate)
Indication of reference laboratory carrying out confirmatory testing (avian influenza national reference laboratory, OIE or Community reference laboratory for avian influenza)
Reporting system/protocol used for avian influenza surveillance results (include results where available)
Follow-up investigations of positive results for subtypes H5 and H7.
B.where available information on surveillance for avian influenza in wild birds to assess risk factors for avian influenza introduction into poultry:
Type of surveillance:
Serological surveillance
Virological surveillance
Targeted avian influenza subtypes
Sampling criteria
Targeting of wild bird species (indicate species names in Latin)
Targeting of selected areas
Information referred to in point 6 and points 8 to 12 of Part I.A.
II.Avian influenza surveillance to be carried out following the occurrence of an outbreak of that disease in a third country, territory, zone or compartment previously free from that disease, as referred to in Articles 8(2)(d) and 9(2)(b)
Surveillance for avian influenza must provide at least the confidence by a randomised representative sample of the populations at risk to demonstrate the absence of infection taking into account the specific epidemiological circumstances in relation to the occurred outbreak(s).
ANNEX V(as referred to in Article 11(a))INFORMATION TO BE SUBMITTED BY A THIRD COUNTRY VACCINATING AGAINST AVIAN INFLUENZA(6)
I.Requirements for vaccination plans carried out in a third country, territory, zone or compartment as referred to in Article 11
Country, territory, zone or compartment (keep as appropriate)
Disease history (previous outbreaks in poultry or cases in wild birds of HPAI/LPAI)
Description of the reasons for the decision on the introduction of vaccination
Risk assessment based on:
Avian influenza outbreak within that third country, territory, zone or compartment (keep as appropriate)
Avian influenza outbreak in a nearby country
Other risk factors such as certain areas, type of poultry husbandry or categories of poultry or other captive birds
Geographical area where vaccination is carried out
Number of establishments in vaccination area
Number of establishments where vaccination is carried out, if different from number in point 6
Species and categories of poultry or other captive birds in vaccination territory, zone or compartment
Approximate number of poultry or other captive birds in the establishments referred to in point 7
Summary of the vaccine characteristics
Authorisation, handling, manufacture, storage, supply, distribution and sale of avian influenza vaccines on national territory
Implementation of a DIVA strategy
Envisaged duration of vaccination campaign
Provisions and restrictions on the movements of vaccinated poultry and poultry products derived from vaccinated poultry or vaccinated other captive birds
Clinical and laboratory tests carried out in the establishments vaccinated and/or located in the vaccination area (e.g. efficacy and pre-movement testing etc.)
Means of record keeping (e.g. for the detailed information referred to point 15) and registration of holdings where vaccination is carried out.
II.Surveillance for third countries, territories, zones or compartments that carry out vaccination against avian influenza as referred to in Article 11
Where vaccination is carried out in a third country, territory, zone or compartment all commercial establishments that are vaccinated against avian influenza must be required to undergo laboratory testing and the following information, in addition to the information referred to in Part I.A to Annex IV, shall be submitted:
Number of vaccinated establishments in area per category
Number of vaccinated establishments to be sampled per poultry category
Use of sentinel birds (indicate species and number of sentinel birds used per shed)
Number of samples taken per establishment and/or shed
Data on vaccine efficacy.
ANNEX VI(as referred to in Article 12(1)(b) and (2)(c)(ii) and Article 13(1)(a))CRITERIA FOR RECOGNISED NEWCASTLE DISEASE VACCINES
I.General criteria
Vaccines must be registered by the competent authorities of the third country concerned before being allowed to be distributed and used. For such registration, the competent authorities must rely on a complete file containing data about efficacy and innocuity; for imported vaccines the competent authorities may rely on data checked by the competent authorities of the country where the vaccine is produced, as far as these checks have been carried out in conformity with internationally accepted standards.
In addition, imports or production and distribution of the vaccines must be controlled by the competent authorities of the third country concerned.
Before distribution is allowed, each batch of vaccines must be tested on innocuity, in particular regarding attenuation or inactivation and absence of undesired contaminating agents, and on efficacy on behalf of the competent authorities.
II.Specific criteria
Live Newcastle disease vaccines shall be prepared from a Newcastle disease virus strain for which the master seed has been tested and shown to have an intracerebral pathogenicity index (ICPI) of either:
less than 0,4, if not less than 107 EID50 are administered to each bird in the ICPI test; or
less than 0,5, if not less than 108 EID50 are administered to each bird in the ICPI test.
Inactivated Newcastle disease vaccines shall be prepared from a Newcastle disease virus strain with an intracerebral pathogenicity index (ICPI) in one-day-old chicks of less than 0,7, if not less than 108 EID50 are administered to each bird in the ICPI test.
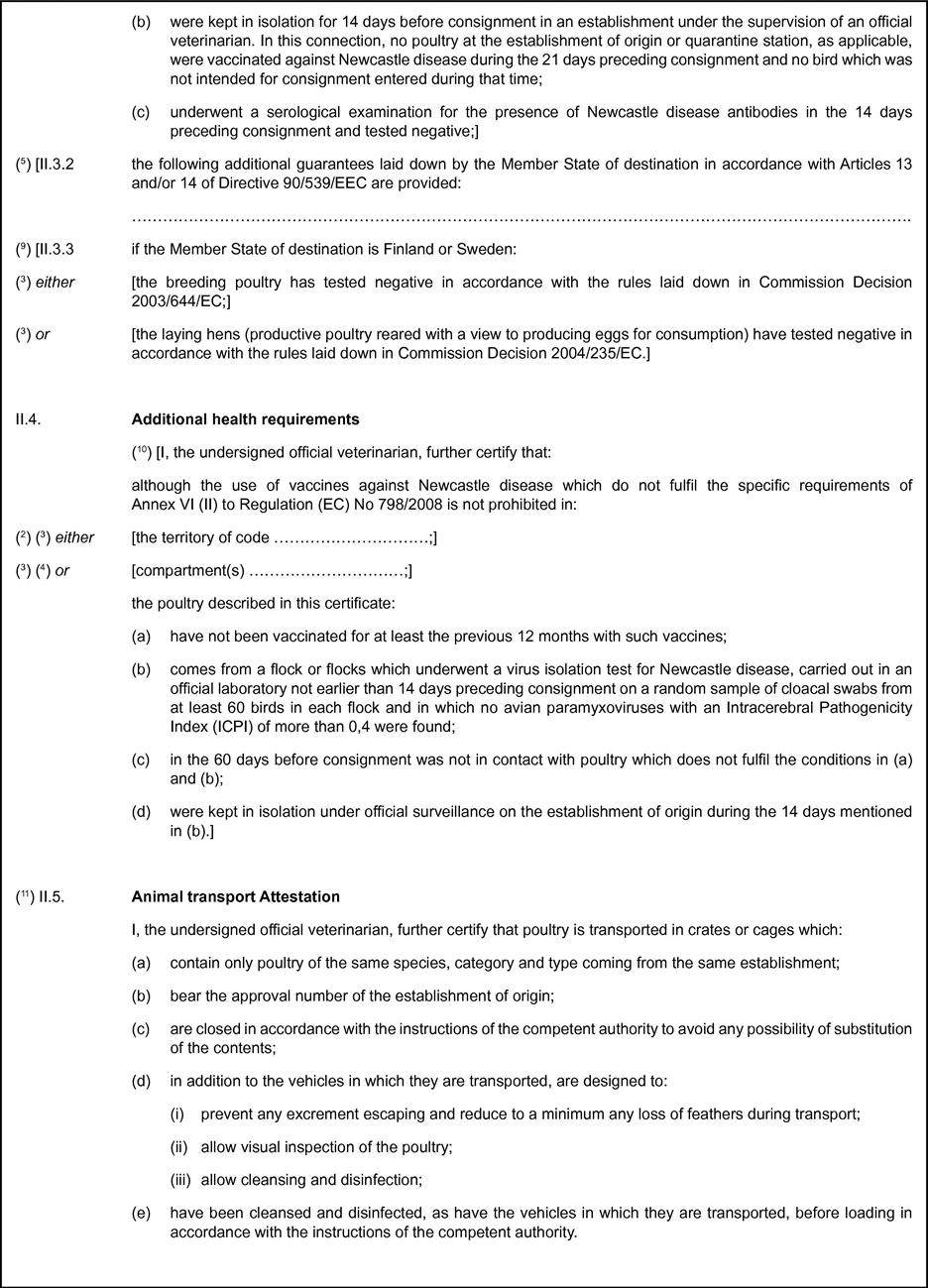
ANNEX VII(as referred to in Article 13)ADDITIONAL HEALTH REQUIREMENTS
I.For poultry, day-old chicks and hatching eggs coming from a third country, Territory, zone or compartment where vaccines used against Newcastle disease do not meet THE criteria of Annex VI
Where the third country, territory, zone or compartment does not prohibit the use of Newcastle disease vaccines that do not meet the specific criteria set out in Annex VI the following additional health requirements shall apply to:
poultry, including day-old chicks must not have been vaccinated with such vaccines for at least 12 months preceding the date of import to the Community;
the flock or flocks must have undergone a virus isolation test for Newcastle disease not earlier than two weeks before the date of import into the Community or, in the case of hatching eggs, not earlier than two weeks before the date of collection of the eggs:
carried out in an official laboratory;
on a random sample of cloacal swabs from at least 60 birds in each flock;
in which no avian paramyxoviruses with an Intracerebral Pathogenicity Index of more than 0,4 have been found.
poultry must have been kept in isolation under official surveillance on the establishment of origin during the two-week period referred to in (b);
poultry must not have been in contact with poultry not meeting the requirements set out in (a) and (b) during a period of 60 days before the date of import into the Community or, in the case of hatching eggs, during a period of 60 days before the date of collection of the eggs.
Where day-old chicks are imported from a third country, territory, zone or compartment as referred to in point 1, the day-old chicks and the hatching eggs from which the day-old chicks are derived must not have been in contact in the hatchery or during transport with poultry or hatching eggs not meeting the requirements set out in point 1(a) to (d).
II.For meat of poultry
Meat of poultry must come from slaughter poultry that:
has not been vaccinated with vaccines prepared from a Newcastle disease virus master seed showing a higher pathogenicity than lentogenic strains of the virus within 30 days preceding slaughter;
underwent a virus isolation test for Newcastle disease, carried out in an official laboratory at the time of slaughter on a random sample of cloacal swabs from at least 60 birds in each flock concerned and in which no avian paramyxoviruses with an Intracerebral Pathogenicity Index (ICPI) of more than 0,4 were found;
has not been in contact in 30 days preceding the date of slaughter with poultry that does not fulfil the conditions set out in (a) and (b).
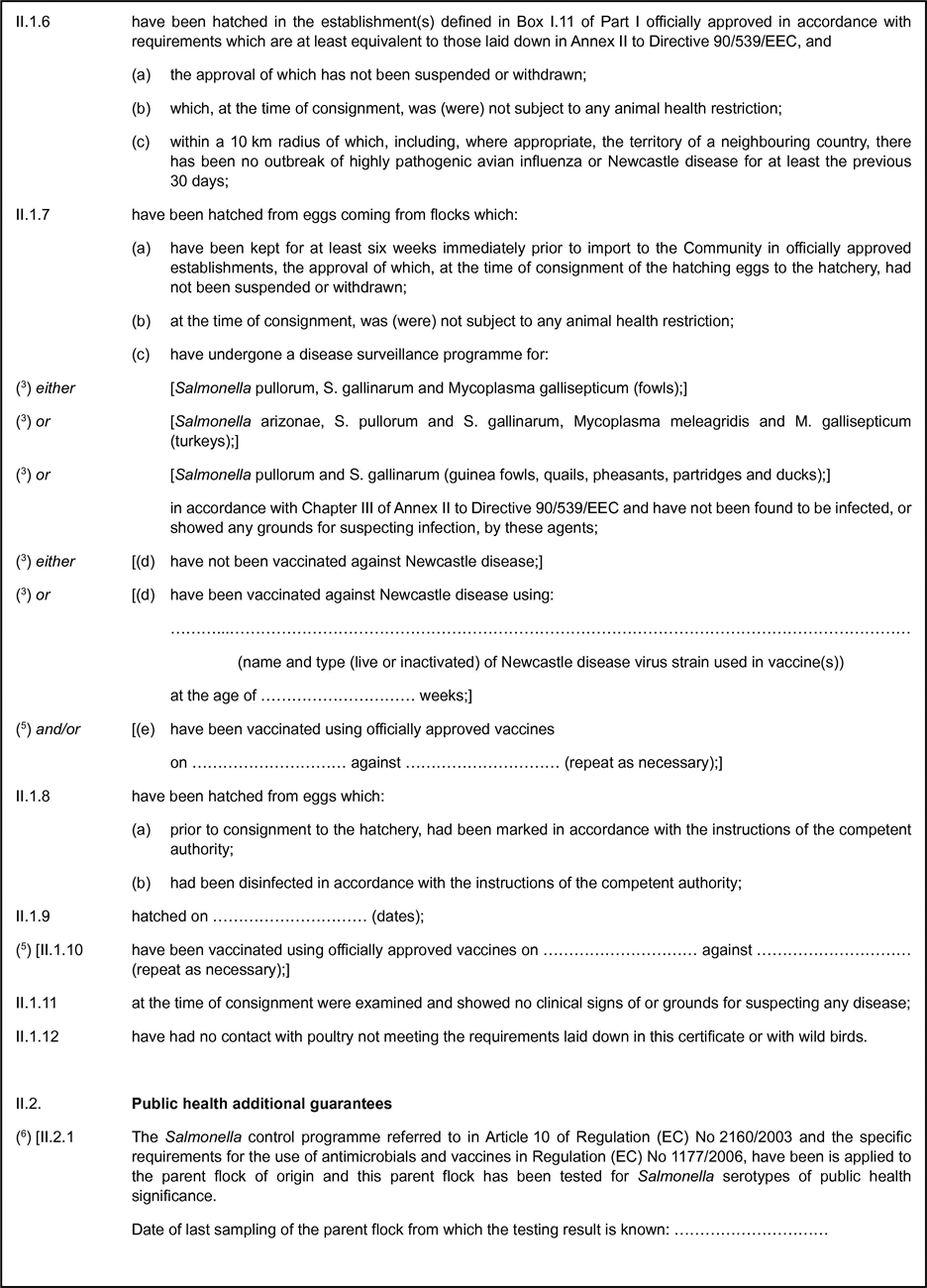
ANNEX VIII(as referred to in Article 14(1)(a))BREEDING AND PRODUCTIVE POULTRY OTHER THAN RATITES, HATCHING EGGS AND DAY-OLD CHICKS OTHER THAN OF RATITES
I.Requirements applicable before import
Breeding and productive poultry other than ratites, hatching eggs and day-old chicks other than of ratites for import into the Community shall only come from establishments which have been approved by the competent authority of the third country concerned in accordance with conditions that are at least as strict as those laid down in Annex II to Directive 90/539/EEC and where such approval has not been suspended or withdrawn.
Where breeding and productive poultry other than ratites, hatching eggs and day-old chicks other than of ratites and/or their flocks of origin are to undergo testing to meet the requirements of the relevant veterinary certificates laid down in this Regulation, sampling for testing and the testing itself must be carried out in accordance with Annex III.
Hatching eggs for import into the Community shall bear the name of the third country of origin and the word ‘hatching’ that is more than 3mm high in one of the official languages of the Community.
Each package of hatching eggs as referred to in point 3 shall contain only eggs of a single species, category and type of poultry from the same third country, territory, zone or compartment of origin and consignor, and shall bear at least the following particulars:
the information shown on the eggs as provided for in point 3;
the species of poultry from which the eggs come;
the consignor's name or business name and address.
Each box of imported day-old chicks shall contain only a single species, category and type of poultry from the same third country, territory, zone or compartment of origin, hatchery and consignor and shall bear at least the following particulars:
the name of the third country, territory, zone or compartment of origin;
the species of poultry to which the day-old chicks belong;
the distinguishing number of the hatchery;
the consignor's name or business name and address.
II.Requirements applicable after imports
Imported breeding and productive poultry other than ratites and day-old chicks other than of ratites shall be kept on the establishment(s) of destination from their date of arrival:
for a period of at least six weeks; or
where the birds are slaughtered before the expiry of the period referred to in (a), until the day of slaughter.
However, the period provided for in (a) may be reduced to three weeks, provided that sampling and testing in accordance with Annex III have been carried out with favourable results.
Breeding and productive poultry other than ratites which have been hatched from imported hatching eggs shall be kept for at least three weeks from the date of hatching in the hatchery or for at least three weeks on the establishment(s) to which the poultry has been sent after hatching.
Where day-old chicks are not reared in the Member State which imported the hatching eggs, they shall be transported directly to the final destination (as specified in points 1.10 and 1.11 of the health certificate, Model 2 in Annex IV to Directive 90/539/EEC) and kept there for at least three weeks from the date of hatching.
During the relevant periods, as referred to in points 1 and 2, imported breeding and productive poultry and day-old chicks and breeding and productive poultry other than ratites which have hatched from imported hatching eggs shall be kept in isolation in poultry houses where no other flocks are present.
However, they may be introduced into poultry houses where breeding and productive poultry and day-old chicks are already present.
In that case, the relevant periods referred to in points 1 and 2 shall commence from the date of introduction of the last imported bird and no poultry present shall be moved from the poultry houses before the end of those periods.
Imported hatching eggs shall be hatched in separate incubators and hatchers.
However, imported hatching eggs may be introduced into incubators and hatchers where other hatching eggs are already present.
In that case, the periods referred to in points 1 and 2 shall commence from the date of introduction of the last imported hatching egg.
No later than the date of expiry of the relevant periods as provided for in point 1 or 2, imported breeding and productive poultry and day-old chicks shall undergo a clinical examination carried out by the official veterinarian and, where necessary, samples shall be taken to monitor their state of health.
ANNEX IX(as referred to in Article 14(1)(b))RATITES FOR BREEDING AND PRODUCTION, HATCHING EGGS AND DAY-OLD CHICKS THEREOF
I.Requirements applicable before import
Imported ratites for breeding and production (ratites) shall be identified by neck-tags and/or microchips bearing the ISO code of the third country of origin. Such microchips must comply with ISO standards.
Imported hatching eggs of ratites shall be marked with a stamp indicating the ISO code of the third country of origin and the approval number of the establishment of origin.
Each package of hatching eggs as referred to in point 2 shall contain only eggs of ratites from the same third country, territory, zone or compartment of origin and consignor, and shall bear at least the following particulars:
the information shown on the eggs as provided for in point 2;
a clearly visible and legible indication that the consignment contains hatching eggs of ratites;
the consignor’s name or business name and address.
Each box of imported day-old chicks of ratites for breeding and production shall contain only ratites from the same third country, territory, zone or compartment of origin, establishment and consignor, and shall bear at least the following particulars:
the ISO code of the third country of origin and the approval number of the establishment of origin;
a clearly visible and legible indication that the consignment contains day-old chicks of ratites;
the consignor’s name or business name and address.
II.Requirements applicable after import
After the import controls have been carried out in accordance with Directive 91/496/EEC, consignments of ratites and hatching eggs and day-old chicks thereof shall be transported directly to the final destination.
Imported ratites and day-old chicks thereof shall be kept on the establishment(s) of destination from their date of arrival:
for a period at least six weeks; or
where the birds are slaughtered before the expiry of the period referred to in (a), until the day of slaughter.
Ratites which have hatched from imported hatching eggs shall be kept for a period of at least three weeks from the date of hatching in the hatchery or for at least three weeks on the establishment(s) to which they have been sent after hatching.
During the relevant periods as referred to in points 2 and 3, imported ratites and ratites which have hatched from imported hatching eggs shall be kept in isolation in poultry houses where no other ratites or poultry are present.
However, they may be introduced into poultry houses where other ratites or poultry are already present. In that case, the periods referred to in points 2 and 3 shall commence from the date of introduction of the last imported ratite and no ratites or poultry present shall be moved from the poultry housing before the end of those periods.
Imported hatching eggs shall be hatched in separate incubators and hatchers.
However, imported hatching eggs may be introduced into incubators and hatchers where other hatching eggs are already present. In that case, the periods referred to in points 2 and 3 shall commence from the date of introduction of the last imported hatching egg and the measures as provided for in those points shall apply.
No later than the date of expiry of the relevant periods as referred to in point 2 or 3, imported ratites and day-old chicks thereof shall undergo a clinical examination carried out by an official veterinarian and, where necessary, samples shall be taken to monitor their state of health.
III.Requirements for ratites for breeding and production and day-old chicks thereof from Asia and Africa applicable on their import into the Community
The protective measures for Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever set out in Part I of Annex X shall apply to ratites for breeding and production and day-old chicks thereof coming from third countries, territories, zones or compartments in Asia and Africa.
All ratites testing positive to the competitive ELISA test for antibodies to Crimean Congo haemorrhagic fever provided for therein shall be destroyed.
All birds of the same consignment shall be retested by the competitive ELISA test 21 days after the date of the original sampling. Where any bird tests positive all birds in the same consignment shall be destroyed.
IV.Requirements for ratites for breeding and production from a third country, territory or zone considered to be infected with Newcastle disease
The following rules shall apply to ratites and hatching eggs thereof coming from a third country, territory or zone considered as infected with Newcastle disease and to day-old chicks that have hatched from such eggs:
before the date the isolation period begins, the competent authority shall check the isolation facilities as referred to in point 4 of Part II of this Annex to verify whether they are satisfactory;
during the relevant periods as referred to in points 2 and 3 of Part II of this Annex a virus isolation test for Newcastle disease shall be carried out on a cloacal swab or faeces sample from each ratite;
where ratites are to be sent to a Member State, the status of which has been established in accordance with Article 12(2) of Directive 90/539/EEC, a serological test shall be carried out on each ratite, in addition to the virus isolation test provided for in point (b) of this Part;
negative results of the tests provided for in points (b) and (c) shall be available before any bird is released from isolation.
ANNEX X(as referred to in Article 17)PROTECTIVE MEASURES IN RELATION TO CRIMEAN-CONGO HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER
I.For ratites
The competent authority shall ensure that the ratites are isolated in rodent-proof, tick-free surroundings for at least 21 days prior to the date of import into the Community.
Before moving to the tick-free surroundings, the ratites shall be treated to ensure that all ectoparasites on them are destroyed. After 14 days in tick-free surroundings, the ratites shall undergo the competitive ELISA test for antibodies to Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Every animal put into isolation must test negative to the test. On the ratites' arrival in the Community, the treatment for ectoparasites and the serological test shall be repeated.
II.For ratites from which meat for import is derived
The competent authority shall ensure that the ratites are isolated in rodent-proof, tick-free surroundings for at least 14 days prior to the date of slaughter.
Before moving to the tick-free surroundings, the ratites shall either be examined to verify that they are tick-free or treated to ensure that all ticks on them are destroyed. The treatment used must be specified on the import certificate. Any treatment used shall not result in any detectable residues in the ratite meat.
Each batch of ratites shall be examined for ticks prior to slaughter. If any ticks are detected, the entire batch shall again be put into pre-slaughter isolation.
ANNEX XI(as referred to in Article 18(2)
Model veterinary certificate for transit/storage of specified pathogen-free eggs, meat, minced meat and mechanically separated meat of poultry, ratites and wild game-birds, eggs and egg products
ANNEX XII(as referred to in Article 20)CORRELATION TABLE
| This Regulation | Decision 2006/696/EC | Decision 94/438/EC | Decision 93/342/EEC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Article 1(1) first subparagraph | Article 1 first subparagraph | ||
| Article 1(1) second subparagraph | Article 5 | ||
| Article 1(2) | Article 1 second subparagraph | ||
| Article 1(3) | Annex I and II (part1) | ||
| Article 2 (1-5) | Article 2 (a-e) | ||
| Article 2 (6) | Article 2 (m) | ||
| Article 2 (7) | Article 2 (j) | ||
| Article 2 (8) | Article 2 (k) | ||
| Article 2 (9) | Article 2 (l) | ||
| Article 2 (10) | |||
| Article 2 (11) | |||
| Article 2 (12) (a-c) | Article 2 (g) | ||
| Article 2 (12) (d) | |||
| Article 2 (13) | Article 2 (h) | ||
| Article 2 (14) | Article 2 (f) | ||
| Article 2 (15) | |||
| Article 2 (16) | |||
| Article 2 (17) | |||
| Article 2 (18) | |||
| Article 2 (19) | |||
| Article 2 (20) | |||
| Article 3 | Article 5 | ||
| Article 4 first subparagraph | Article 5 and 3 | ||
| Article 4 second subparagraph | Annex I part 3 | ||
| Article 4 third subparagraph | Article 3 second subparagraph | ||
| Article 5 | Article 4 | ||
| Article 6 | |||
| Article 7 (a) | Article 2 (h) | ||
| Article 7 (b) | Article 2 (g) | ||
| Article 7 (c) | Article 2 (i) | ||
| Article 8 | |||
| Article 9 | |||
| Article 10 | |||
| Article 11 | |||
| Article 12 | Article 4 (1) (2) | Article 4 (1) (2) | |
| Article 13 | Article 4 (3) | Article 4 (4) | |
| Article 14 (1) (a) | Article 9 | ||
| Article 14 (1) (b) | Article 11 | ||
| Article 14 (2) | |||
| Article 15 | Article 18 | ||
| Article 16 | Article 8 | ||
| Article 17 | Article 16 (2) | ||
| Article 18 (1) | |||
| Article 18 (2) | Article 19 (b) | ||
| Article 18 (3) | Article 19 | ||
| Article 19 | Article 20 | ||
| Article 20 | |||
| Article 21 | |||
| Article 22 | |||
| Annex I | Annex I and II | ||
| Annex II | Annex I part 3 | ||
| Annex III (I) (1-6) | Annex I part 4 (A) | ||
| Annex III (I) (7) | |||
| Annex III (II), (III) | Annex I part 4 (B) | ||
| Annex IV | |||
| Annex V | |||
| Annex VI | Annex B | ||
| Annex VII (I) | Article 7 | ||
| Annex VII (II) | Annex | ||
| Annex VIII (I) | Article 9 | ||
| Annex VIII (II) | Article 10 | ||
| Annex IX (I) | Article 11 | ||
| Annex IX (II) | Article 12 | ||
| Annex IX (III) | Article 13 | ||
| Annex IX (IV) | Article 14 | ||
| Annex X | Annex V | ||
| Annex XI | Annex IV | ||
| Annex XII |
http://www.oie.int/eng/normes/mmanual/A_summry.htm
OJ L 260, 5.9.1992, p. 1. Directive as last amended by Directive 2006/104/EC (OJ L 363, 20.12.2006, p. 352).
Please give as much detailed information as necessary to allow proper assessment of the programme.
Please give as much detailed information as necessary to allow proper assessment of the programme.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThe Annexes only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources