- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (31/12/2020)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011Show full title
Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 of 14 January 2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Regulations originating from the EU
- 2011 No. 10
- Annexes only
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 23/09/20201.11 MB
- Revised 29/08/20191.05 MB
- Revised 08/07/20191.04 MB
- Revised 19/05/20191.04 MB
- Revised 31/01/20190.96 MB
- Revised 14/09/20180.95 MB
- Revised 26/06/20180.95 MB
- Revised 08/02/20180.94 MB
- Revised 19/05/20170.94 MB
- Revised 14/09/20160.93 MB
- Revised 26/02/20151.40 MB
- Revised 24/03/20142.59 MB
- Revised 01/01/20130.69 MB
- Revised 30/12/20110.65 MB
- Revised 22/04/20110.65 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 (Annexes only)
Alternative versions:
- 14/01/2011- Amendment
- 22/04/2011- Amendment
- 30/12/2011- Amendment
- 01/01/2013- Amendment
- 24/03/2014- Amendment
- 26/02/2015- Amendment
- 14/09/2016- Amendment
- 19/05/2017- Amendment
- 08/02/2018- Amendment
- 26/06/2018- Amendment
- 14/09/2018- Amendment
- 31/01/2019- Amendment
- 19/05/2019- Amendment
- 29/08/2019- Amendment
- Exit day: start of implementation period31/01/2020 11pm- Amendment
- 23/09/2020- Amendment
- End of implementation period31/12/2020- Amendment
- 31/12/2020
Point in time
Status:
Point in time view as at 31/12/2020.
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects by UK legislation for Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
ANNEX IU.K.Substances
1.F1... List of authorised monomers, other starting substances, macromolecules obtained from microbial fermentation, additives and polymer production aidsU.K.
Table 1 contains the following information:
Column 1 (FCM substance No): the unique identification number of the substance
Column 2 (Ref. No): the EEC packaging material reference number
Column 3 (CAS No): the Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) registry number
Column 4 (Substance Name): the chemical name
Column 5 (Use as additive or polymer production aid (PPA) (yes/no)): an indication if the substance is authorised to be used as additive or polymer production aid (yes) or if the substance is not authorised to be used as additive or polymer production aid (no). If the substance is only authorised as PPA it is indicated (yes) and in the specifications the use is restricted to PPA.
Column 6 (Use as monomer or other starting substance or macromolecule obtained from microbial fermentation (yes/no)): an indication if the substance is authorised to be used as monomer or other starting substance or macromolecule obtained from microbial fermentation (yes) or if the substance is not authorised to be used as monomer or other starting substance or macromolecule obtained from microbial fermentation (no). If the substance is authorised as macromolecule obtained from microbial fermentation it is indicated (yes) and in the specifications it is indicated that the substance is a macromolecule obtained from microbial fermentation.
Column 7 (FRF applicable (yes/no)): an indication if for the substance the migration results can be corrected by the Fat Consumption Reduction Factor (FRF) (yes) or if they cannot be corrected by the FRF (no).
[F2Column 8 (SML [mg/kg]): the specific migration limit applicable for the substance. It is expressed in mg substance per kg food. It is marked as ND ( ‘ not-detectable ’ ) if the substance is one in respect of which no migration is permitted, to be determined in accordance with Article 11(4).]
Textual Amendments
Column 9 (SML(T) [mg/kg] (group restriction No)): contains the identification number of the group of substances for which the group restriction in Column 1 in Table 2 of this Annex applies.
Column 10 (Restrictions and specifications): contains other restrictions than the specific migration limit specifically mentioned and it contains specifications related to the substance. In case detailed specifications are set out a reference to Table 4 is included.
Column 11 (Notes on verification of compliance): contains the Notes number which refers to the detailed rules applicable for verification of compliance for this substance included in Column 1 in Table 3 of this Annex.
If a substance appearing on the list as an individual compound is also covered by a generic term, the restrictions applying to this substance shall be those indicated for the individual compound.
F3...
Textual Amendments
Table 1
d [F4Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 of 9 March 2012 laying down specifications of food additives listed in Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council ( OJ L 83, 22.3.2012, p. 1 ).] | ||||||||||
f [F5[F6Infant as defined in Article 2(2)(a) of Regulation (EU) No 609/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 June 2013 on food intended for infants and young children, food for special medical purposes, and total diet replacement for weight control and repealing Council Directive 92/52/EEC, Commission Directives 96/8/EC, 1999/21/EC, 2006/125/EC and 2006/141/EC, Directive 2009/39/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and Commission Regulations (EC) No 41/2009 and (EC) No 953/2009 ( OJ L 181, 29.6.2013, p. 35 ).] | ||||||||||
g This restriction is applicable from 1 May 2011 as regards the manufacture and from 1 June 2011 as regards the placing on the market and importation into the Union.] | ||||||||||
i [F8Infant as defined in Article 2(2)(a) of Regulation (EU) No 609/2013. | ||||||||||
j Young children as defined in Article 2(2)(b) of Regulation (EU) No 609/2013.] | ||||||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) |
| FCM substance No | Ref. No | CAS No | Substance name | Use as additive or polymer production aid(yes/no) | Use as monomer or other starting substance or macromolecule obtained from microbial fermentation(yes/no) | FRF applicable(yes/no) | SML[mg/kg] | SML(T)[mg/kg](Group restriction No) | Restrictions and specifications | Notes on verification of compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12310 | 0266309-43-7 | albumin | no | yes | no | ||||
| 2 | 12340 | — | albumin, coagulated by formaldehyde | no | yes | no | ||||
| 3 | 12375 | — | alcohols, aliphatic, monohydric, saturated, linear, primary (C4-C22) | no | yes | no | ||||
| 4 | 22332 | — | mixture of (40 % w/w) 2,2,4-trimethylhexane-1,6-diisocyanate and (60 % w/w) 2,4,4-trimethylhexane-1,6-diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety. | (10) | |
| 5 | 25360 | — | trialkyl(C5-C15)acetic acid, 2,3-epoxypropyl ester | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as epoxygroup. Molecular weight is 43 Da. | ||
| 6 | 25380 | — | trialkyl acetic acid (C7-C17), vinyl esters | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (1) | ||
| 7 | 30370 | — | acetylacetic acid, salts | yes | no | no | ||||
| 8 | 30401 | — | acetylated mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids | yes | no | no | (32) | |||
| 9 | 30610 | — | acids, C2-C24, aliphatic, linear, monocarboxylic from natural oils and fats, and their mono-, di- and triglycerol esters (branched fatty acids at naturally occuring levels are included) | yes | no | no | ||||
| 10 | 30612 | — | acids, C2-C24, aliphatic, linear, monocarboxylic, synthetic and their mono-, di- and triglycerol esters | yes | no | no | ||||
| 11 | 30960 | — | acids, aliphatic, monocarboxylic (C6-C22), esters with polyglycerol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 12 | 31328 | — | acids, fatty, from animal or vegetable food fats and oils | yes | no | no | ||||
| 13 | 33120 | — | alcohols, aliphatic, monohydric, saturated, linear, primary (C4-C24) | yes | no | no | ||||
| 14 | 33801 | — | n-alkyl(C10-C13)benzenesulphonic acid | yes | no | no | 30 | |||
| 15 | 34130 | — | alkyl, linear with even number of carbon atoms (C12-C20) dimethylamines | yes | no | yes | 30 | |||
| 16 | 34230 | — | alkyl(C8-C22)sulphonic acids | yes | no | no | 6 | |||
| 17 | 34281 | — | alkyl(C8-C22)sulphuric acids, linear, primary with an even number of carbon atoms | yes | no | no | ||||
| 18 | 34475 | — | aluminium calcium hydroxide phosphite, hydrate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 19 | 39090 | — | N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)alkyl(C8-C18)amine | yes | no | no | (7) | |||
| 20 | 39120 | — | N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)alkyl(C8-C18)amine hydrochlorides | yes | no | no | (7) | SML(T) expressed excluding HCl | ||
| 21 | 42500 | — | carbonic acid, salts | yes | no | no | ||||
| 22 | 43200 | — | castor oil, mono- and diglycerides | yes | no | no | ||||
| 23 | 43515 | — | chlorides of choline esters of coconut oil fatty acids | yes | no | no | 0,9 | (1) | ||
| 24 | 45280 | — | cotton fibers | yes | no | no | ||||
| 25 | 45440 | — | cresols, butylated, styrenated | yes | no | no | 12 | |||
| 26 | 46700 | — | 5,7-di-tert-butyl-3-(3,4- and 2,3-dimethylphenyl)-3H-benzofuran-2-one containing: a) 5,7-di-tert-butyl-3-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-3H-benzofuran-2-one (80 to 100 % w/w) and b) 5,7-di-tert-butyl-3-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)-3H-benzofuran-2-one (0 to 20 % w/w) | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 27 | 48960 | — | 9,10-dihydroxy stearic acid and its oligomers | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 28 | 50160 | — | di-n-octyltin bis(n-alkyl(C10-C16) mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 29 | 50360 | — | di-n-octyltin bis(ethyl maleate) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 30 | 50560 | — | di-n-octyltin 1,4-butanediol bis(mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 31 | 50800 | — | di-n-octyltin dimaleate, esterified | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 32 | 50880 | — | di-n-octyltin dimaleate, polymers (n = 2-4) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 33 | 51120 | — | di-n-octyltin thiobenzoate 2-ethylhexyl mercaptoacetate | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 34 | 54270 | — | ethylhydroxymethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 35 | 54280 | — | ethylhydroxypropylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 36 | 54450 | — | fats and oils, from animal or vegetable food sources | yes | no | no | ||||
| 37 | 54480 | — | fats and oils, hydrogenated, from animal or vegetable food sources | yes | no | no | ||||
| 38 | 55520 | — | glass fibers | yes | no | no | ||||
| 39 | 55600 | — | glass microballs | yes | no | no | ||||
| 40 | 56360 | — | glycerol, esters with acetic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 41 | 56486 | — | glycerol, esters with acids, aliphatic, saturated, linear, with an even number of carbon atoms (C14-C18) and with acids, aliphatic, unsaturated, linear, with an even number of carbon atoms (C16-C18) | yes | no | no | ||||
| 42 | 56487 | — | glycerol, esters with butyric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 43 | 56490 | — | glycerol, esters with erucic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 44 | 56495 | — | glycerol, esters with 12-hydroxystearic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 45 | 56500 | — | glycerol, esters with lauric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 46 | 56510 | — | glycerol, esters with linoleic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 47 | 56520 | — | glycerol, esters with myristic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 48 | 56535 | — | glycerol, esters with nonanoic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 49 | 56540 | — | glycerol, esters with oleic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 50 | 56550 | — | glycerol, esters with palmitic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 51 | 56570 | — | glycerol, esters with propionic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 52 | 56580 | — | glycerol, esters with ricinoleic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 53 | 56585 | — | glycerol, esters with stearic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 54 | 57040 | — | glycerol monooleate, ester with ascorbic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 55 | 57120 | — | glycerol monooleate, ester with citric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 56 | 57200 | — | glycerol monopalmitate, ester with ascorbic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 57 | 57280 | — | glycerol monopalmitate, ester with citric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 58 | 57600 | — | glycerol monostearate, ester with ascorbic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 59 | 57680 | — | glycerol monostearate, ester with citric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 60 | 58300 | — | glycine, salts | yes | no | no | ||||
| 62 | 64500 | — | lysine, salts | yes | no | no | ||||
| 63 | 65440 | — | manganese pyrophosphite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 64 | 66695 | — | methylhydroxymethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 65 | 67155 | — | mixture of 4-(2-benzoxazolyl)-4′-(5-methyl-2-benzoxazolyl)stilbene, 4,4′-bis(2-benzoxazolyl) stilbene and 4,4′-bis(5-methyl-2-benzoxazolyl)stilbene | yes | no | no | Not more than 0,05 % (w/w) (quantity of substance used/quantity of the formulation). Mixture obtained from the manufacturing process in the typical ratio of (58-62 %):(23-27 %):(13-17 %). | |||
| 66 | 67600 | — | mono-n-octyltin tris(alkyl(C10-C16) mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (11) | |||
| 67 | 67840 | — | montanic acids and/or their esters with ethyleneglycol and/or with 1,3-butanediol and/or with glycerol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 68 | 73160 | — | phosphoric acid, mono- and di-n-alkyl (C16 and C18) esters | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | |||
| 69 | 74400 | — | phosphorous acid, tris(nonyl-and/or dinonylphenyl) ester | yes | no | yes | 30 | |||
| 70 | 76463 | — | polyacrylic acid, salts | yes | no | no | (22) | |||
| 71 | 76730 | — | polydimethylsiloxane, γ-hydroxypropylated | yes | no | no | 6 | |||
| 72 | 76815 | — | polyester of adipic acid with glycerol or pentaerythritol, esters with even numbered, unbranched C12-C22 fatty acids | yes | no | no | (32) | The fraction with molecular weight below 1 000 Da [F2shall] not exceed 5 % (w/w) | ||
| 73 | 76866 | — | polyesters of 1,2-propanediol and/or 1,3- and/or 1,4-butanediol and/or polypropyleneglycol with adipic acid, which may be end-capped with acetic acid or fatty acids C12-C18 or n-octanol and/or n-decanol | yes | no | yes | (31) (32) | |||
| 74 | 77440 | — | polyethyleneglycol diricinoleate | yes | no | yes | 42 | |||
| 75 | 77702 | — | polyethyleneglycol esters of aliph. monocarb. acids (C6-C22) and their ammonium and sodium sulphates | yes | no | no | ||||
| 76 | 77732 | — | polyethylene glycol (EO = 1-30, typically 5) ether of butyl 2-cyano 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) acrylate | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Only for use in PET | ||
| 77 | 77733 | — | polyethyleneglycol (EO = 1-30, typically 5) ether of butyl-2-cyano-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acrylate | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Only for use in PET | ||
| 78 | 77897 | — | polyethyleneglycol (EO = 1-50) monoalkylether (linear and branched, C8-C20) sulphate, salts | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 79 | 80640 | — | polyoxyalkyl (C2-C4) dimethylpolysiloxane | yes | no | no | ||||
| 80 | 81760 | — | powders, flakes and fibres of brass, bronze, copper, stainless steel, tin, iron and alloys of copper, tin and iron | yes | no | no | ||||
| 81 | 83320 | — | propylhydroxyethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 82 | 83325 | — | propylhydroxymethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 83 | 83330 | — | propylhydroxypropylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 84 | 85601 | — | silicates, natural (with the exception of asbestos) | yes | no | no | ||||
| 85 | 85610 | — | silicates, natural, silanated (with the exception of asbestos) | yes | no | no | ||||
| 86 | 86000 | — | silicic acid, silylated | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F287 | 86285 | Silicon dioxide, silanated | yes | no | no | For synthetic amorphous silicon dioxide, silanated: primary particles of 1–100 nm which are aggregated to a size of 0,1–1 μm and may form agglomerates within the size distribution of 0,3 μm to the mm size. ] | ||||
| 88 | 86880 | — | sodium monoalkyl dialkylphenoxybenzenedisulphonate | yes | no | no | 9 | |||
| 89 | 89440 | — | stearic acid, esters with ethyleneglycol | yes | no | no | (2) | |||
| 90 | 92195 | — | taurine, salts | yes | no | no | ||||
| 91 | 92320 | — | tetradecyl-polyethyleneglycol(EO = 3-8) ether of glycolic acid | yes | no | yes | 15 | |||
| 92 | 93970 | — | tricyclodecanedimethanol bis(hexahydrophthalate) | yes | no | no | 0,05 | |||
| 93 | 95858 | — | waxes, paraffinic, refined, derived from petroleum based or synthetic hydrocarbon feedstocks, low viscosity | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. Average molecular weight not less than 350 Da. Viscosity at 100 °C not less than 2,5 cSt (2,5 × 10-6 m2/s). Content of hydrocarbons with Carbon number less than 25, not more than 40 % (w/w). | ||
| 94 | 95859 | — | waxes, refined, derived from petroleum based or synthetic hydrocarbon feedstocks, high viscosity | yes | no | no | Average molecular weight not less than 500 Da. Viscosity at 100 °C not less than 11 cSt (11 × 10-6 m2/s). Content of mineral hydrocarbons with Carbon number less than 25, not more than 5 % (w/w). | |||
| 95 | 95883 | — | white mineral oils, paraffinic, derived from petroleum based hydrocarbon feedstocks | yes | no | no | Average molecular weight not less than 480 Da. Viscosity at 100 °C not less than 8,5 cSt (8,5 × 10-6 m2/s). Content of mineral hydrocarbons with Carbon number less than 25, not more than 5 % (w/w). | |||
| 96 | 95920 | — | wood flour and fibers, untreated | yes | no | no | ||||
| 97 | 72081/10 | — | petroleum hydrocarbon resins (hydrogenated) | yes | no | no | Petroleum hydrocarbon resins, hydrogenated are produced by the catalytic or thermalpolymerisation of dienes and olefins of the aliphatic, alicyclic and/or monobenzenoidarylalkene types from distillates of cracked petroleum stocks with a boiling range not greater than 220 °C, as well as the pure monomers found in these distillation streams, subsequently followed by distillation, hydrogenation and additional processing. Properties:
| |||
| 98 | 17260 | 0000050-00-0 | formaldehyde | yes | yes | no | (15) | |||
| 54880 | ||||||||||
| 99 | 19460 | 0000050-21-5 | lactic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 62960 | ||||||||||
| 100 | 24490 | 0000050-70-4 | sorbitol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 88320 | ||||||||||
| 101 | 36000 | 0000050-81-7 | ascorbic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 102 | 17530 | 0000050-99-7 | glucose | no | yes | no | ||||
| 103 | 18100 | 0000056-81-5 | glycerol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 55920 | ||||||||||
| 104 | 58960 | 0000057-09-0 | hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide | yes | no | no | 6 | |||
| 105 | 22780 | 0000057-10-3 | palmitic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 70400 | ||||||||||
| 106 | 24550 | 0000057-11-4 | stearic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 89040 | ||||||||||
| 107 | 25960 | 0000057-13-6 | urea | no | yes | no | ||||
| 108 | 24880 | 0000057-50-1 | sucrose | no | yes | no | ||||
| 109 | 23740 | 0000057-55-6 | 1,2-propanediol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 81840 | ||||||||||
| 110 | 93520 | 0000059-02-9 0010191-41-0 | α-tocopherol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 111 | 53600 | 0000060-00-4 | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 112 | 64015 | 0000060-33-3 | linoleic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 113 | 16780 | 0000064-17-5 | ethanol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 52800 | ||||||||||
| 114 | 55040 | 0000064-18-6 | formic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 115 | 10090 | 0000064-19-7 | acetic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 30000 | ||||||||||
| 116 | 13090 | 0000065-85-0 | benzoic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 37600 | ||||||||||
| 117 | 21550 | 0000067-56-1 | methanol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 118 | 23830 | 0000067-63-0 | 2-propanol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 81882 | ||||||||||
| 119 | 30295 | 0000067-64-1 | acetone | yes | no | no | ||||
| 120 | 49540 | 0000067-68-5 | dimethyl sulphoxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 121 | 24270 | 0000069-72-7 | salicylic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 84640 | ||||||||||
| 122 | 23800 | 0000071-23-8 | 1-propanol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 123 | 13840 | 0000071-36-3 | 1-butanol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 124 | 22870 | 0000071-41-0 | 1-pentanol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 125 | 16950 | 0000074-85-1 | ethylene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 126 | 10210 | 0000074-86-2 | acetylene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 127 | 26050 | 0000075-01-4 | vinyl chloride | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product | ||
| 128 | 10060 | 0000075-07-0 | acetaldehyde | no | yes | no | (1) | |||
| 129 | 17020 | 0000075-21-8 | ethylene oxide | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product | (10) | |
| 130 | 26110 | 0000075-35-4 | vinylidene chloride | no | yes | no | ND | (1) | ||
| 131 | 48460 | 0000075-37-6 | 1,1-difluoroethane | yes | no | no | ||||
| 132 | 26140 | 0000075-38-7 | vinylidene fluoride | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 133 | 14380 | 0000075-44-5 | carbonyl chloride | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product | (10) | |
| 23155 | ||||||||||
| 134 | 43680 | 0000075-45-6 | chlorodifluoromethane | yes | no | no | 6 | Content of chlorofluoromethane less than 1 mg/kg of the substance | ||
| 135 | 24010 | 0000075-56-9 | propylene oxide | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product | ||
| 136 | 41680 | 0000076-22-2 | camphor | yes | no | no | (3) | |||
| 137 | 66580 | 0000077-62-3 | 2,2′-methylenebis(4-methyl-6-(1-methylcyclohexyl)phenol) | yes | no | yes | (5) | |||
| 138 | 93760 | 0000077-90-7 | tri-n-butyl acetyl citrate | yes | no | no | (32) | |||
| 139 | 14680 | 0000077-92-9 | citric acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 44160 | ||||||||||
| 140 | 44640 | 0000077-93-0 | citric acid, triethyl ester | yes | no | no | (32) | |||
| 141 | 13380 | 0000077-99-6 | 1,1,1-trimethylolpropane | yes | yes | no | 6 | |||
| 25600 | ||||||||||
| 94960 | ||||||||||
| 142 | 26305 | 0000078-08-0 | vinyltriethoxysilane | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used as a surface treatment agent | [F9(1)] | |
| 143 | 62450 | 0000078-78-4 | isopentane | yes | no | no | ||||
| 144 | 19243 | 0000078-79-5 | 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product | ||
| 21640 | ||||||||||
| 145 | 10630 | 0000079-06-1 | acrylamide | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 146 | 23890 | 0000079-09-4 | propionic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 82000 | ||||||||||
| 147 | 10690 | 0000079-10-7 | acrylic acid | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 148 | 14650 | 0000079-38-9 | chlorotrifluoroethylene | no | yes | no | ND | (1) | ||
| 149 | 19990 | 0000079-39-0 | methacrylamide | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 150 | 20020 | 0000079-41-4 | methacrylic acid | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| [F6151 | 13480 | 0000080-05-7 | 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Not to be used for the manufacture of polycarbonate infant f feeding bottles g . Not to be used for the manufacture of polycarbonate drinking cups or bottles which, due to their spill proof characteristics, are intended for infants i and young children j . | ||
| 13607] | ||||||||||
| 152 | 15610 | 0000080-07-9 | 4,4′-dichlorodiphenyl sulphone | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 153 | 15267 | 0000080-08-0 | 4,4′-diaminodiphenyl sulphone | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 154 | 13617 | 0000080-09-1 | 4,4′-dihydroxydiphenyl sulphone | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 16090 | ||||||||||
| 155 | 23470 | 0000080-56-8 | α-pinene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 156 | 21130 | 0000080-62-6 | methacrylic acid, methyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 157 | 74880 | 0000084-74-2 | phthalic acid, dibutyl ester | yes | no | no | 0,3 | (32) | Only to be used as: (a) plasticiser in repeated use materials and articles contacting non-fatty foods; (b) technical support agent in polyolefins in concentrations up to 0,05 % in the final product. | (7) |
| 158 | 23380 | 0000085-44-9 | phthalic anhydride | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 76320 | ||||||||||
| 159 | 74560 | 0000085-68-7 | phthalic acid, benzyl butyl ester | yes | no | no | 30 | (32) | Only to be used as: (a) plasticiser in repeated use materials and articles; (b) plasticiser in single-use materials and articles contacting non-fatty foods except for infant formulae and follow-on formulae as defined by Directive 2006/141/EC or processed cereal-based foods and baby foods for infants and young children as defined by Directive 2006/125/EC; (c) technical support agent in concentrations up to 0,1 % in the final product. | (7) |
| 160 | 84800 | 0000087-18-3 | salicylic acid, 4-tert-butylphenyl ester | yes | no | yes | 12 | |||
| [F10161 | 92160 | 000087-69-4 | L-(+)-tartaric acid | yes | no | no ] | ||||
| 162 | 65520 | 0000087-78-5 | mannitol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 163 | 66400 | 0000088-24-4 | 2,2′-methylene bis(4-ethyl-6-tert-butylphenol) | yes | no | yes | (13) | |||
| 164 | 34895 | 0000088-68-6 | 2-aminobenzamide | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Only for use in PET for water and beverages | ||
| 165 | 23200 | 0000088-99-3 | o-phthalic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 74480 | ||||||||||
| 166 | 24057 | 0000089-32-7 | pyromellitic anhydride | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 167 | 25240 | 0000091-08-7 | 2,6-toluene diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 168 | 13075 | 0000091-76-9 | 2,4-diamino-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine | no | yes | no | 5 | [F9(1)] | ||
| 15310 | ||||||||||
| 169 | 16240 | 0000091-97-4 | 3,3′-dimethyl-4,4′-diisocyanatobiphenyl | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 170 | 16000 | 0000092-88-6 | 4,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl | no | yes | no | 6 | |||
| 171 | 38080 | 0000093-58-3 | benzoic acid, methyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 172 | 37840 | 0000093-89-0 | benzoic acid, ethyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 173 | 60240 | 0000094-13-3 | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, propyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 174 | 14740 | 0000095-48-7 | o-cresol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 175 | 20050 | 0000096-05-9 | methacrylic acid, allyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 176 | 11710 | 0000096-33-3 | acrylic acid, methyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 177 | 16955 | 0000096-49-1 | ethylene carbonate | no | yes | no | 30 | SML expressed as ethyleneglycol. Residual content of 5 mg ethylene carbonate per kg of hydrogel with max 10 g of hydrogel in contact with 1 kg of food. | ||
| 178 | 92800 | 0000096-69-5 | 4,4′-thiobis(6-tert-butyl-3-methylphenol) | yes | no | yes | 0,48 | |||
| 179 | 48800 | 0000097-23-4 | 2,2′-dihydroxy-–5,5′-dichlorodiphenylmethane | yes | no | yes | 12 | |||
| [F11180 | 17160 | 0000097-53-0 | eugenol | no | yes | no | (33) ] | |||
| 181 | 20890 | 0000097-63-2 | methacrylic acid, ethyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 182 | 19270 | 0000097-65-4 | itaconic acid | no | yes | no | ||||
| 183 | 21010 | 0000097-86-9 | methacrylic acid, isobutyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 184 | 20110 | 0000097-88-1 | methacrylic acid, butyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 185 | 20440 | 0000097-90-5 | methacrylic acid, diester with ethyleneglycol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 186 | 14020 | 0000098-54-4 | 4-tert-butylphenol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 187 | 22210 | 0000098-83-9 | α-methylstyrene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 188 | 19180 | 0000099-63-8 | isophthalic acid dichloride | no | yes | no | (27) | |||
| 189 | 60200 | 0000099-76-3 | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, methyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 190 | 18880 | 0000099-96-7 | p-hydroxybenzoic acid | no | yes | no | ||||
| 191 | 24940 | 0000100-20-9 | terephthalic acid dichloride | no | yes | no | (28) | |||
| 192 | 23187 | — | phthalic acid | no | yes | no | (28) | |||
| 193 | 24610 | 0000100-42-5 | styrene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 194 | 13150 | 0000100-51-6 | benzyl alcohol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 195 | 37360 | 0000100-52-7 | benzaldehyde | yes | no | no | (3) | |||
| 196 | 18670 | 0000100-97-0 | hexamethylenetetramine | yes | yes | no | (15) | |||
| 59280 | ||||||||||
| 197 | 20260 | 0000101-43-9 | methacrylic acid, cyclohexyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 198 | 16630 | 0000101-68-8 | diphenylmethane-4,4′-diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 199 | 24073 | 0000101-90-6 | resorcinol diglycidyl ether | no | yes | no | ND | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. For indirect food contact only, behind a PET layer. | (8) | |
| 200 | 51680 | 0000102-08-9 | N,N′-diphenylthiourea | yes | no | yes | 3 | |||
| 201 | 16540 | 0000102-09-0 | diphenyl carbonate | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 202 | 23070 | 0000102-39-6 | (1,3-phenylenedioxy)diacetic acid | no | yes | no | 0,05 | [F9(1)] | ||
| 203 | 13323 | 0000102-40-9 | 1,3-bis(2-hydroxyethoxy)benzene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 204 | 25180 | 0000102-60-3 | N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-hydroxypropyl)ethylenediamine | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 92640 | ||||||||||
| 205 | 25385 | 0000102-70-5 | triallylamine | no | yes | no | 40 mg/kg hydrogel at a ratio of 1 kg food to a maximum of 1,5 grams of hydrogel. Only to be used in hydrogels intended for non-direct food contact use. | |||
| 206 | 11500 | 0000103-11-7 | acrylic acid, 2-ethylhexyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 207 | 31920 | 0000103-23-1 | adipic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester | yes | no | yes | 18 | (32) | (2) | |
| 208 | 18898 | 0000103-90-2 | N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acetamide | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 209 | 17050 | 0000104-76-7 | 2-ethyl-1-hexanol | no | yes | no | 30 | |||
| 210 | 13390 | 0000105-08-8 | 1,4-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane | no | yes | no | ||||
| 14880 | ||||||||||
| 211 | 23920 | 0000105-38-4 | propionic acid, vinyl ester | no | yes | no | (1) | |||
| 212 | 14200 | 0000105-60-2 | caprolactam | yes | yes | no | (4) | |||
| 41840 | ||||||||||
| 213 | 82400 | 0000105-62-4 | 1,2-propyleneglycol dioleate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 214 | 61840 | 0000106-14-9 | 12-hydroxystearic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 215 | 14170 | 0000106-31-0 | butyric anhydride | no | yes | no | ||||
| 216 | 14770 | 0000106-44-5 | p-cresol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 217 | 15565 | 0000106-46-7 | 1,4-dichlorobenzene | no | yes | no | 12 | |||
| 218 | 11590 | 0000106-63-8 | acrylic acid, isobutyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 219 | 14570 | 0000106-89-8 | epichlorohydrin | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product | (10) | |
| 16750 | ||||||||||
| 220 | 20590 | 0000106-91-2 | methacrylic acid, 2,3-epoxypropyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,02 | (10) | ||
| 221 | 40570 | 0000106-97-8 | butane | yes | no | no | ||||
| 222 | 13870 | 0000106-98-9 | 1-butene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 223 | 13630 | 0000106-99-0 | butadiene | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product | ||
| 224 | 13900 | 0000107-01-7 | 2-butene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 225 | 12100 | 0000107-13-1 | acrylonitrile | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 226 | 15272 | 0000107-15-3 | ethylenediamine | no | yes | no | 12 | |||
| 16960 | ||||||||||
| 227 | 16990 | 0000107-21-1 | ethyleneglycol | yes | yes | no | (2) | |||
| 53650 | ||||||||||
| 228 | 13690 | 0000107-88-0 | 1,3-butanediol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 229 | 14140 | 0000107-92-6 | butyric acid | no | yes | no | ||||
| 230 | 16150 | 0000108-01-0 | dimethylaminoethanol | no | yes | no | 18 | |||
| 231 | 10120 | 0000108-05-4 | acetic acid, vinyl ester | no | yes | no | 12 | |||
| 232 | 10150 | 0000108-24-7 | acetic anhydride | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 30280 | ||||||||||
| 233 | 24850 | 0000108-30-5 | succinic anhydride | no | yes | no | ||||
| 234 | 19960 | 0000108-31-6 | maleic anhydride | no | yes | no | (3) | |||
| 235 | 14710 | 0000108-39-4 | m-cresol | no | yes | no | ||||
| [F12236 | 23050 | 0000108-45-2 | 1,3-phenylenediamine | no | yes | no | ND | (28)] | ||
| 237 | 15910 | 0000108-46-3 | 1,3-dihydroxybenzene | no | yes | no | 2,4 | |||
| 24072 | ||||||||||
| 238 | 18070 | 0000108-55-4 | glutaric anhydride | no | yes | no | ||||
| [F13239 | 19975 | 0000108-78-1 | 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine | yes | yes | no | 2,5 | |||
| 25420 | ||||||||||
| 93720] | ||||||||||
| 240 | 45760 | 0000108-91-8 | cyclohexylamine | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F10241 | 22960 | 0000108-95-2 | phenol | no | yes | no | 3 ] | |||
| 242 | 85360 | 0000109-43-3 | sebacic acid, dibutyl ester | yes | no | no | (32) | |||
| 243 | 19060 | 0000109-53-5 | isobutyl vinyl ether | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (10) | ||
| 244 | 71720 | 0000109-66-0 | pentane | yes | no | no | ||||
| 245 | 22900 | 0000109-67-1 | 1-pentene | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 246 | 25150 | 0000109-99-9 | tetrahydrofuran | no | yes | no | 0,6 | |||
| 247 | 24820 | 0000110-15-6 | succinic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 90960 | ||||||||||
| 248 | 19540 | 0000110-16-7 | maleic acid | yes | yes | no | (3) | |||
| 64800 | ||||||||||
| 249 | 17290 | 0000110-17-8 | fumaric acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 55120 | ||||||||||
| 250 | 53520 | 0000110-30-5 | N,N′-ethylenebisstearamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 251 | 53360 | 0000110-31-6 | N,N′-ethylenebisoleamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 252 | 87200 | 0000110-44-1 | sorbic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 253 | 15250 | 0000110-60-1 | 1,4-diaminobutane | no | yes | no | ||||
| 254 | 13720 | 0000110-63-4 | 1,4-butanediol | yes | yes | no | (30) | |||
| 40580 | ||||||||||
| 255 | 25900 | 0000110-88-3 | trioxane | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 256 | 18010 | 0000110-94-1 | glutaric acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 55680 | ||||||||||
| [F11257 | 13550 | 0000110-98-5 | dipropyleneglycol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 16660 | 0025265-71-8 | |||||||||
| 51760 ] | ||||||||||
| 258 | 70480 | 0000111-06-8 | palmitic acid, butyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 259 | 58720 | 0000111-14-8 | heptanoic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 260 | 24280 | 0000111-20-6 | sebacic acid | no | yes | no | ||||
| 261 | 15790 | 0000111-40-0 | diethylenetriamine | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 262 | 35284 | 0000111-41-1 | N-(2-aminoethyl)ethanolamine | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. For indirect food contact only, behind a PET layer. | ||
| 263 | 13326 | 0000111-46-6 | diethyleneglycol | yes | yes | no | (2) | |||
| 15760 | ||||||||||
| 47680 | ||||||||||
| 264 | 22660 | 0000111-66-0 | 1-octene | no | yes | no | 15 | |||
| 265 | 22600 | 0000111-87-5 | 1-octanol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 266 | 25510 | 0000112-27-6 | triethyleneglycol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 94320 | ||||||||||
| 267 | 15100 | 0000112-30-1 | 1-decanol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 268 | 16704 | 0000112-41-4 | 1-dodecene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 269 | 25090 | 0000112-60-7 | tetraethyleneglycol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 92350 | ||||||||||
| 270 | 22763 | 0000112-80-1 | oleic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 69040 | ||||||||||
| 271 | 52720 | 0000112-84-5 | erucamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 272 | 37040 | 0000112-85-6 | behenic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 273 | 52730 | 0000112-86-7 | erucic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 274 | 22570 | 0000112-96-9 | octadecyl isocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 275 | 23980 | 0000115-07-1 | propylene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 276 | 19000 | 0000115-11-7 | isobutene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 277 | 18280 | 0000115-27-5 | hexachloroendomethylenetetrahydrophthalic anhydride | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 278 | 18250 | 0000115-28-6 | hexachloroendomethylenetetrahydrophthalic acid | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 279 | 22840 | 0000115-77-5 | pentaerythritol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 71600 | ||||||||||
| 280 | 73720 | 0000115-96-8 | phosphoric acid, trichloroethyl ester | yes | no | no | ND | |||
| 281 | 25120 | 0000116-14-3 | tetrafluoroethylene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 282 | 18430 | 0000116-15-4 | hexafluoropropylene | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 283 | 74640 | 0000117-81-7 | phthalic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester | yes | no | no | 1,5 | (32) | Only to be used as: (a) plasticiser in repeated use materials and articles contacting non-fatty foods; (b) technical support agent in concentrations up to 0,1 % in the final product. | (7) |
| 284 | 84880 | 0000119-36-8 | salicylic acid, methyl ester | yes | no | no | 30 | |||
| 285 | 66480 | 0000119-47-1 | 2,2′-methylene bis(4-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol) | yes | no | yes | (13) | |||
| 286 | 38240 | 0000119-61-9 | benzophenone | yes | no | yes | 0,6 | |||
| 287 | 60160 | 0000120-47-8 | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, ethyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 288 | 24970 | 0000120-61-6 | terephthalic acid, dimethyl ester | no | yes | no | ||||
| 289 | 15880 | 0000120-80-9 | 1,2-dihydroxybenzene | no | yes | no | 6 | |||
| 24051 | ||||||||||
| 290 | 55360 | 0000121-79-9 | gallic acid, propyl ester | yes | no | no | (20) | |||
| 291 | 19150 | 0000121-91-5 | isophthalic acid | no | yes | no | (27) | |||
| 292 | 94560 | 0000122-20-3 | triisopropanolamine | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 293 | 23175 | 0000122-52-1 | phosphorous acid, triethyl ester | no | yes | no | ND | 1 mg/kg in final product | (1) | |
| 294 | 93120 | 0000123-28-4 | thiodipropionic acid, didodecyl ester | yes | no | yes | (14) | |||
| 295 | 15940 | 0000123-31-9 | 1,4-dihydroxybenzene | yes | yes | no | 0,6 | |||
| 18867 | ||||||||||
| 48620 | ||||||||||
| 296 | 23860 | 0000123-38-6 | propionaldehyde | no | yes | no | ||||
| 297 | 23950 | 0000123-62-6 | propionic anhydride | no | yes | no | ||||
| 298 | 14110 | 0000123-72-8 | butyraldehyde | no | yes | no | ||||
| 299 | 63840 | 0000123-76-2 | levulinic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 300 | 30045 | 0000123-86-4 | acetic acid, butyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 301 | 89120 | 0000123-95-5 | stearic acid, butyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 302 | 12820 | 0000123-99-9 | azelaic acid | no | yes | no | ||||
| 303 | 12130 | 0000124-04-9 | adipic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 31730 | ||||||||||
| 304 | 14320 | 0000124-07-2 | caprylic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 41960 | ||||||||||
| 305 | 15274 | 0000124-09-4 | hexamethylenediamine | no | yes | no | 2,4 | |||
| 18460 | ||||||||||
| 306 | 88960 | 0000124-26-5 | stearamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 307 | 42160 | 0000124-38-9 | carbon dioxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 308 | 91200 | 0000126-13-6 | sucrose acetate isobutyrate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 309 | 91360 | 0000126-14-7 | sucrose octaacetate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 310 | 16390 | 0000126-30-7 | 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 22437 | ||||||||||
| 311 | 16480 | 0000126-58-9 | dipentaerythritol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 51200 | ||||||||||
| 312 | 21490 | 0000126-98-7 | methacrylonitrile | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 313 | 16650 | 0000127-63-9 | diphenyl sulphone | yes | yes | no | 3 | |||
| 51570 | ||||||||||
| 314 | 23500 | 0000127-91-3 | β-pinene | no | yes | no | ||||
| 315 | 46640 | 0000128-37-0 | 2,6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol | yes | no | no | 3 | |||
| 316 | 23230 | 0000131-17-9 | phthalic acid, diallyl ester | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 317 | 48880 | 0000131-53-3 | 2,2′-dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone | yes | no | yes | (8) | |||
| 318 | 48640 | 0000131-56-6 | 2,4-dihydroxybenzophenone | yes | no | no | (8) | |||
| 319 | 61360 | 0000131-57-7 | 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone | yes | no | yes | (8) | |||
| 320 | 37680 | 0000136-60-7 | benzoic acid, butyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 321 | 36080 | 0000137-66-6 | ascorbyl palmitate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 322 | 63040 | 0000138-22-7 | lactic acid, butyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 323 | 11470 | 0000140-88-5 | acrylic acid, ethyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 324 | 83700 | 0000141-22-0 | ricinoleic acid | yes | no | yes | 42 | |||
| 325 | 10780 | 0000141-32-2 | acrylic acid, n-butyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 326 | 12763 | 0000141-43-5 | 2-aminoethanol | yes | yes | no | 0,05 | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. For indirect food contact only, behind a PET layer. | ||
| 35170 | ||||||||||
| 327 | 30140 | 0000141-78-6 | acetic acid, ethyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 328 | 65040 | 0000141-82-2 | malonic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 329 | 59360 | 0000142-62-1 | hexanoic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 330 | 19470 | 0000143-07-7 | lauric acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 63280 | ||||||||||
| 331 | 22480 | 0000143-08-8 | 1-nonanol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 332 | 69760 | 0000143-28-2 | oleyl alcohol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 333 | 22775 | 0000144-62-7 | oxalic acid | yes | yes | no | 6 | |||
| 69920 | ||||||||||
| 334 | 17005 | 0000151-56-4 | ethyleneimine | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 335 | 68960 | 0000301-02-0 | oleamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 336 | 15095 | 0000334-48-5 | n-decanoic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 45940 | ||||||||||
| 337 | 15820 | 0000345-92-6 | 4,4′-difluorobenzophenone | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 338 | 71020 | 0000373-49-9 | palmitoleic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 339 | 86160 | 0000409-21-2 | silicon carbide | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F14340 | 47440 | 0000461-58-5 | dicyanodiamide | yes | no | no | 60 ] | |||
| 341 | 13180 | 0000498-66-8 | bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 22550 | ||||||||||
| 342 | 14260 | 0000502-44-3 | caprolactone | no | yes | no | (29) | |||
| 343 | 23770 | 0000504-63-2 | 1,3-propanediol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| [F10344 | 13810 | 0000505-65-7 | 1,4-butanediol formal | no | yes | no | 0,05 | 15 30 | (21) | |
| 21821] | ||||||||||
| 345 | 35840 | 0000506-30-9 | arachidic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 346 | 10030 | 0000514-10-3 | abietic acid | no | yes | no | ||||
| 347 | 13050 | 0000528-44-9 | trimellitic acid | no | yes | no | (21) | |||
| 25540 | ||||||||||
| 348 | 22350 | 0000544-63-8 | myristic acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 67891 | ||||||||||
| 349 | 25550 | 0000552-30-7 | trimellitic anhydride | no | yes | no | (21) | |||
| 350 | 63920 | 0000557-59-5 | lignoceric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 351 | 21730 | 0000563-45-1 | 3-methyl-1-butene | no | yes | no | ND | Only to be used in polypropylene | (1) | |
| 352 | 16360 | 0000576-26-1 | 2,6-dimethylphenol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 353 | 42480 | 0000584-09-8 | carbonic acid, rubidium salt | yes | no | no | 12 | |||
| 354 | 25210 | 0000584-84-9 | 2,4-toluene diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 355 | 20170 | 0000585-07-9 | methacrylic acid, tert-butyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 356 | 18820 | 0000592-41-6 | 1-hexene | no | yes | no | 3 | |||
| 357 | 13932 | 0000598-32-3 | 3-buten-2-ol | no | yes | no | ND | Only to be used as a co-monomer for the preparation of polymeric additive | (1) | |
| 358 | 14841 | 0000599-64-4 | 4-cumylphenol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 359 | 15970 | 0000611-99-4 | 4,4′-dihydroxybenzophenone | yes | yes | no | (8) | |||
| 48720 | ||||||||||
| 360 | 57920 | 0000620-67-7 | glycerol triheptanoate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 361 | 18700 | 0000629-11-8 | 1,6-hexanediol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 362 | 14350 | 0000630-08-0 | carbon monoxide | no | yes | no | ||||
| 363 | 16450 | 0000646-06-0 | 1,3-dioxolane | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| [F10364 | 15404 | 0000652-67-5 | 1,4:3,6-dianhydrosorbitol | no | yes | no | 5 | Only to be used as: (a) a co-monomer in poly(ethylene-co-isosorbide terephthalate); (b) a co-monomer at levels of up to 40 mole % of the diol component in combination with ethylene glycol and/or 1,4-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane, for the production of polyesters. Polyesters made using dianhydrosorbitol together with 1,4-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane shall not be used in contact with foods containing more than 15 % alcohol. ] | ||
| 365 | 11680 | 0000689-12-3 | acrylic acid, isopropyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 366 | 22150 | 0000691-37-2 | 4-methyl-1-pentene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 367 | 16697 | 0000693-23-2 | n-dodecanedioic acid | no | yes | no | ||||
| 368 | 93280 | 0000693-36-7 | thiodipropionic acid, dioctadecyl ester | yes | no | yes | (14) | |||
| 369 | 12761 | 0000693-57-2 | 12-aminododecanoic acid | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 370 | 21460 | 0000760-93-0 | methacrylic anhydride | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 371 | 11510 | 0000818-61-1 | acrylic acid, monoester with ethyleneglycol | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 11830 | ||||||||||
| 372 | 18640 | 0000822-06-0 | hexamethylene diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 373 | 22390 | 0000840-65-3 | 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid, dimethyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 374 | 21190 | 0000868-77-9 | methacrylic acid, monoester with ethyleneglycol | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 375 | 15130 | 0000872-05-9 | 1-decene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| [F13376 | 66905 | 0000872-50-4 | N-methylpyrrolidone | yes | no | no | 60 ] | |||
| 377 | 12786 | 0000919-30-2 | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Residual extractable content of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane to be less than 3 mg/kg filler when used for the reactive surface treatment of inorganic fillers. SML = 0,05 mg/kg when used for the surface treatment of materials and articles. | ||
| 378 | 21970 | 0000923-02-4 | N-methylolmethacrylamide | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 379 | 21940 | 0000924-42-5 | N-methylolacrylamide | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 380 | 11980 | 0000925-60-0 | acrylic acid, propyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 381 | 15030 | 0000931-88-4 | cyclooctene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used in polymers contacting foods for which simulant A is laid down | ||
| 382 | 19490 | 0000947-04-6 | laurolactam | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 383 | 72160 | 0000948-65-2 | 2-phenylindole | yes | no | yes | 15 | |||
| 384 | 40000 | 0000991-84-4 | 2,4-bis(octylmercapto)-6-(4-hydroxy-3,5-di-tert-butylanilino)-1,3,5-triazine | yes | no | yes | 30 | |||
| 385 | 11530 | 0000999-61-1 | acrylic acid, 2-hydroxypropyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | SML expressed as the sum of acrylic acid, 2-hydroxypropyl ester and acrylic acid, 2-hydroxyisopropyl ester. It may contain up to 25 % (m/m) of acrylic acid, 2-hydroxyisopropyl ester (CAS No 0002918-23-2). | (1) | |
| 386 | 55280 | 0001034-01-1 | gallic acid, octyl ester | yes | no | no | (20) | |||
| 387 | 26155 | 0001072-63-5 | 1-vinylimidazole | no | yes | no | 0,05 | [F9(1)] | ||
| 388 | 25080 | 0001120-36-1 | 1-tetradecene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 389 | 22360 | 0001141-38-4 | 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 390 | 55200 | 0001166-52-5 | gallic acid, dodecyl ester | yes | no | no | (20) | |||
| [F2391 | 22932 | 0001187-93-5 | perfluoromethyl perfluorovinyl ether | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used in:
| ||
| 392 | 72800 | 0001241-94-7 | phosphoric acid, diphenyl 2-ethylhexyl ester | yes | no | yes | 2,4 | |||
| 393 | 37280 | 0001302-78-9 | bentonite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 394 | 41280 | 0001305-62-0 | calcium hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 395 | 41520 | 0001305-78-8 | calcium oxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 396 | 64640 | 0001309-42-8 | magnesium hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 397 | 64720 | 0001309-48-4 | magnesium oxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F12398 | 35760 | 0001309-64-4 | antimony trioxide | yes | no | no | (6)] | |||
| 399 | 81600 | 0001310-58-3 | potassium hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 400 | 86720 | 0001310-73-2 | sodium hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 401 | 24475 | 0001313-82-2 | sodium sulphide | no | yes | no | ||||
| 402 | 96240 | 0001314-13-2 | zinc oxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 403 | 96320 | 0001314-98-3 | zinc sulphide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 404 | 67200 | 0001317-33-5 | molybdenum disulphide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 405 | 16690 | 0001321-74-0 | divinylbenzene | no | yes | no | ND | SML expressed as the sum of divinylbenzene and ethylvinylbenzene. It may contain up to 45 % (m/m) of ethylvinylbenzene. | (1) | |
| 406 | 83300 | 0001323-39-3 | 1,2-propyleneglycol monostearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 407 | 87040 | 0001330-43-4 | sodium tetraborate | yes | no | no | (16) | |||
| 408 | 82960 | 0001330-80-9 | 1,2-propyleneglycol monooleate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 409 | 62240 | 0001332-37-2 | iron oxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F10410 | 62720 | 0001332-58-7 | kaolin | yes | no | no | Particles can be thinner than 100 nm only if incorporated at a quantity of less than 12 % w/w in an ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) inner layer of a multi-layer structure, in which the layer in direct contact with the food provides a functional barrier preventing migration of particles into the food. ] | |||
| 411 | 42080 | 0001333-86-4 | carbon black | yes | no | no | Primary particles of 10 – 300 nm which are aggregated to a size of 100 – 1 200 nm which may form agglomerates within the size distribution of 300 nm – mm. Toluene extractables: maximum 0,1 %, determined according to ISO method 6209. UV absorption of cyclohexane extract at 386 nm: < 0,02 AU for a 1 cm cell or < 0,1 AU for a 5 cm cell, determined according to a generally recognised method of analysis. Benzo(a)pyrene content: max 0,25 mg/kg carbon black. Maximum use level of carbon black in the polymer: 2,5 % w/w. | |||
| 412 | 45200 | 0001335-23-5 | copper iodide | yes | no | no | (6) | |||
| 413 | 35600 | 0001336-21-6 | ammonium hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 414 | 87600 | 0001338-39-2 | sorbitan monolaurate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 415 | 87840 | 0001338-41-6 | sorbitan monostearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 416 | 87680 | 0001338-43-8 | sorbitan monooleate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 417 | 85680 | 0001343-98-2 | silicic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 418 | 34720 | 0001344-28-1 | aluminium oxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 419 | 92150 | 0001401-55-4 | tannic acids | yes | no | no | According to the JECFA specifications | |||
| 420 | 19210 | 0001459-93-4 | isophthalic acid, dimethyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| [F14421 | 13000 | 0001477-55-0 | 1,3-benzenedimethanamine | no | yes | no | (34) ] | |||
| 422 | 38515 | 0001533-45-5 | 4,4′-bis(2-benzoxazolyl)stilbene | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | (2) | ||
| 423 | 22937 | 0001623-05-8 | perfluoropropylperfluorovinyl ether | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 424 | 15070 | 0001647-16-1 | 1,9-decadiene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 425 | 10840 | 0001663-39-4 | acrylic acid, tert-butyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 426 | 13510 | 0001675-54-3 | 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane bis(2,3-epoxypropyl) ether | no | yes | no | In compliance with Commission Regulation (EC) No 1895/2005a | |||
| 13610 | ||||||||||
| 427 | 18896 | 0001679-51-2 | 4-(hydroxymethyl)-1-cyclohexene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 428 | 95200 | 0001709-70-2 | 1,3,5-trimethyl-2,4,6-tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)benzene | yes | no | no | ||||
| 429 | 13210 | 0001761-71-3 | bis(4-aminocyclohexyl)methane | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 430 | 95600 | 0001843-03-4 | 1,1,3-tris(2-methyl-4-hydroxy-5-tert-butylphenyl) butane | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 431 | 61600 | 0001843-05-6 | 2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxybenzophenone | yes | no | yes | (8) | |||
| 432 | 12280 | 0002035-75-8 | adipic anhydride | no | yes | no | ||||
| 433 | 68320 | 0002082-79-3 | octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate | yes | no | yes | 6 | |||
| 434 | 20410 | 0002082-81-7 | methacrylic acid, diester with 1,4-butanediol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 435 | 14230 | 0002123-24-2 | caprolactam, sodium salt | no | yes | no | (4) | |||
| 436 | 19480 | 0002146-71-6 | lauric acid, vinyl ester | no | yes | no | ||||
| 437 | 11245 | 0002156-97-0 | acrylic acid, dodecyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (2) | ||
| [F13438 | 13303 | 0002162-74-5 | bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl) carbodiimide | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Expressed as the sum of bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)carbodiimide and its hydrolysis product 2,6-diisopropylaniline ] | ||
| 439 | 21280 | 0002177-70-0 | methacrylic acid, phenyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 440 | 21340 | 0002210-28-8 | methacrylic acid, propyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 441 | 38160 | 0002315-68-6 | benzoic acid, propyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 442 | 13780 | 0002425-79-8 | 1,4-butanediol bis(2,3-epoxypropyl)ether | no | yes | no | ND | Residual content = 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as epoxygroup. Molecular weight is 43 Da. | (10) | |
| 443 | 12788 | 0002432-99-7 | 11-aminoundecanoic acid | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 444 | 61440 | 0002440-22-4 | 2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methylphenyl)benzotriazole | yes | no | no | (12) | |||
| 445 | 83440 | 0002466-09-3 | pyrophosphoric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 446 | 10750 | 0002495-35-4 | acrylic acid, benzyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 447 | 20080 | 0002495-37-6 | methacrylic acid, benzyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 448 | 11890 | 0002499-59-4 | acrylic acid, n-octyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| [F11449 | 49840 | 0002500-88-1 | dioctadecyl disulphide | yes | no | yes | 0,05 ] | |||
| 450 | 24430 | 0002561-88-8 | sebacic anhydride | no | yes | no | ||||
| 451 | 66755 | 0002682-20-4 | 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one | yes | no | no | 0,5 | Only to be used in aqueous polymer dispersions and emulsions | ||
| [F13452 | 38885 | 0002725-22-6 | 2,4-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-6-(2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxyphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine | yes | no | no | 5 ] | |||
| 453 | 26320 | 0002768-02-7 | vinyltrimethoxysilane | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (10) | ||
| 454 | 12670 | 0002855-13-2 | 1-amino-3-aminomethyl-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexane | no | yes | no | 6 | |||
| 455 | 20530 | 0002867-47-2 | methacrylic acid, 2-(dimethylamino)-ethyl ester | no | yes | no | ND | |||
| 456 | 10810 | 0002998-08-5 | acrylic acid, sec-butyl ester | no | yes | no | (22) | |||
| 457 | 20140 | 0002998-18-7 | methacrylic acid, sec-butyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 458 | 36960 | 0003061-75-4 | behenamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 459 | 46870 | 0003135-18-0 | 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzylphosphonic acid, dioctadecyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 460 | 14950 | 0003173-53-3 | cyclohexyl isocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 461 | 22420 | 0003173-72-6 | 1,5-naphthalene diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 462 | 26170 | 0003195-78-6 | N-vinyl-N-methylacetamide | no | yes | no | 0,02 | [F9(1)] | ||
| 463 | 25840 | 0003290-92-4 | 1,1,1-trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 464 | 61280 | 0003293-97-8 | 2-hydroxy-4-n-hexyloxybenzophenone | yes | no | yes | (8) | |||
| 465 | 68040 | 0003333-62-8 | 7-[2H-naphtho-(1,2-D)triazol-2-yl]-3-phenylcoumarin | yes | no | no | ||||
| 466 | 50640 | 0003648-18-8 | di-n-octyltin dilaurate | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| [F15467 | 14800 | 3724-65-0 | crotonic acid | yes | yes | no | (35) | |||
| 45600] | ||||||||||
| 468 | 71960 | 0003825-26-1 | perfluorooctanoic acid, ammonium salt | yes | no | no | Only to be used in repeated use articles, sintered at high temperatures | |||
| 469 | 60480 | 0003864-99-1 | 2-(2′-hydroxy-3,5′-di-tert-butylphenyl)-5-chlorobenzotriazole | yes | no | yes | (12) | |||
| 470 | 60400 | 0003896-11-5 | 2-(2′-hydroxy-3′-tert-butyl-5′-methylphenyl)-5-chlorobenzotriazole | yes | no | yes | (12) | |||
| 471 | 24888 | 0003965-55-7 | 5-sulphoisophthalic acid, monosodium salt, dimethyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 472 | 66560 | 0004066-02-8 | 2,2′-methylenebis(4-methyl-6-cyclohexylphenol) | yes | no | yes | (5) | |||
| 473 | 12265 | 0004074-90-2 | adipic acid, divinyl ester | no | yes | no | ND | 5 mg/kg in final product. Only to be used as co-monomer. | (1) | |
| 474 | 43600 | 0004080-31-3 | 1-(3-chloroallyl)-3,5,7-triaza-1-azoniaadamantane chloride | yes | no | no | 0,3 | |||
| 475 | 19110 | 0004098-71-9 | 1-isocyanato-3-isocyanatomethyl-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexane | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 476 | 16570 | 0004128-73-8 | diphenylether-4,4′-diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 477 | 46720 | 0004130-42-1 | 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol | yes | no | yes | 4,8 | (1) | ||
| 478 | 60180 | 0004191-73-5 | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, isopropyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 479 | 12970 | 0004196-95-6 | azelaic anhydride | no | yes | no | ||||
| 480 | 46790 | 0004221-80-1 | 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 481 | 13060 | 0004422-95-1 | 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid trichloride | no | yes | no | 0,05 | SML expressed as 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid | [F9(1)] | |
| 482 | 21100 | 0004655-34-9 | methacrylic acid, isopropyl ester | no | yes | no | (23) | |||
| 483 | 68860 | 0004724-48-5 | n-octylphosphonic acid | yes | no | no | 0,05 | |||
| 484 | 13395 | 0004767-03-7 | 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)propionic acid | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (1) | ||
| 485 | 13560 | 0005124-30-1 | dicyclohexylmethane-4,4′-diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 15700 | ||||||||||
| 486 | 54005 | 0005136-44-7 | ethylene-N-palmitamide-N′-stearamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 487 | 45640 | 0005232-99-5 | 2-cyano-3,3-diphenylacrylic acid, ethyl ester | yes | no | no | 0,05 | |||
| 488 | 53440 | 0005518-18-3 | N,N′-ethylenebispalmitamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 489 | 41040 | 0005743-36-2 | calcium butyrate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 490 | 16600 | 0005873-54-1 | diphenylmethane-2,4′-diisocyanate | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 491 | 82720 | 0006182-11-2 | 1,2-propyleneglycol distearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 492 | 45650 | 0006197-30-4 | 2-cyano-3,3-diphenylacrylic acid, 2-ethylhexyl ester | yes | no | no | 0,05 | |||
| 493 | 39200 | 0006200-40-4 | bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-hydroxypropyl-3-(dodecyloxy)methylammonium chloride | yes | no | no | 1,8 | |||
| 494 | 62140 | 0006303-21-5 | hypophosphorous acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 495 | 35160 | 0006642-31-5 | 6-amino-1,3-dimethyluracil | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 496 | 71680 | 0006683-19-8 | pentaerythritol tetrakis[3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-propionate] | yes | no | no | ||||
| 497 | 95020 | 0006846-50-0 | 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate | yes | no | no | 5 | Only to be used in single-use gloves | ||
| 498 | 16210 | 0006864-37-5 | 3,3′-dimethyl-4,4′-diaminodicyclohexylmethane | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used in polyamides | (5) | |
| 499 | 19965 | 0006915-15-7 | malic acid | yes | yes | no | In case of use as a monomer only to be used as a co-monomer in aliphatic polyesters up to maximum level of 1 % on a molar basis | |||
| 65020 | ||||||||||
| 500 | 38560 | 0007128-64-5 | 2,5-bis(5-tert-butyl-2-benzoxazolyl)thiophene | yes | no | yes | 0,6 | |||
| 501 | 34480 | — | aluminium fibers, flakes and powders | yes | no | no | ||||
| 502 | 22778 | 0007456-68-0 | 4,4′-oxybis(benzenesulphonyl azide) | no | yes | no | 0,05 | [F9(1)] | ||
| 503 | 46080 | 0007585-39-9 | β-dextrin | yes | no | no | ||||
| 504 | 86240 | 0007631-86-9 | silicon dioxide | yes | no | no | For synthetic amorphous silicon dioxide: primary particles of 1 – 100 nm which are aggregated to a size of 0,1 – 1 μm which may form agglomerates within the size distribution of 0,3 μm to the mm size. | |||
| 505 | 86480 | 0007631-90-5 | sodium bisulphite | yes | no | no | (19) | |||
| 506 | 86920 | 0007632-00-0 | sodium nitrite | yes | no | no | 0,6 | |||
| 507 | 59990 | 0007647-01-0 | hydrochloric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 508 | 86560 | 0007647-15-6 | sodium bromide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 509 | 23170 | 0007664-38-2 | phosphoric acid | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 72640 | ||||||||||
| 510 | 12789 | 0007664-41-7 | ammonia | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 35320 | ||||||||||
| 511 | 91920 | 0007664-93-9 | sulphuric acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 512 | 81680 | 0007681-11-0 | potassium iodide | yes | no | no | (6) | |||
| 513 | 86800 | 0007681-82-5 | sodium iodide | yes | no | no | (6) | |||
| 514 | 91840 | 0007704-34-9 | sulphur | yes | no | no | ||||
| 515 | 26360 | 0007732-18-5 | water | yes | yes | no | In compliance with Directive 98/83/ECb | |||
| 95855 | ||||||||||
| 516 | 86960 | 0007757-83-7 | sodium sulphite | yes | no | no | (19) | |||
| 517 | 81520 | 0007758-02-3 | potassium bromide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 518 | 35845 | 0007771-44-0 | arachidonic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 519 | 87120 | 0007772-98-7 | sodium thiosulphate | yes | no | no | (19) | |||
| 520 | 65120 | 0007773-01-5 | manganese chloride | yes | no | no | ||||
| 521 | 58320 | 0007782-42-5 | graphite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 522 | 14530 | 0007782-50-5 | chlorine | no | yes | no | ||||
| 523 | 45195 | 0007787-70-4 | copper bromide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 524 | 24520 | 0008001-22-7 | soybean oil | no | yes | no | ||||
| 525 | 62640 | 0008001-39-6 | japan wax | yes | no | no | ||||
| 526 | 43440 | 0008001-75-0 | ceresin | yes | no | no | ||||
| 527 | 14411 | 0008001-79-4 | castor oil | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 42880 | ||||||||||
| 528 | 63760 | 0008002-43-5 | lecithin | yes | no | no | ||||
| 529 | 67850 | 0008002-53-7 | montan wax | yes | no | no | ||||
| 530 | 41760 | 0008006-44-8 | candelilla wax | yes | no | no | ||||
| 531 | 36880 | 0008012-89-3 | beeswax | yes | no | no | ||||
| 532 | 88640 | 0008013-07-8 | soybean oil, epoxidised | yes | no | no | 60 30(*) | (32) | (*)In the case of PVC gaskets used to seal glass jars containing infant formulae and follow-on formulae as defined by Directive 2006/141/EC or processed cereal-based foods and baby foods for infants and young children as defined by Directive 2006/125/EC, the SML is lowered to 30 mg/kg.Oxirane < 8 %, iodine number < 6. | |
| 533 | 42720 | 0008015-86-9 | carnauba wax | yes | no | no | ||||
| 534 | 80720 | 0008017-16-1 | polyphosphoric acids | yes | no | no | ||||
| 535 | 24100 | 0008050-09-7 | rosin | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 24130 | ||||||||||
| 24190 | ||||||||||
| 83840 | ||||||||||
| 536 | 84320 | 0008050-15-5 | rosin, hydrogenated, ester with methanol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 537 | 84080 | 0008050-26-8 | rosin, ester with pentaerythritol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 538 | 84000 | 0008050-31-5 | rosin, ester with glycerol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 539 | 24160 | 0008052-10-6 | rosin tall oil | no | yes | no | ||||
| 540 | 63940 | 0008062-15-5 | lignosulphonic acid | yes | no | no | 0,24 | Only to be used as dispersant for plastics dispersions | ||
| 541 | 58480 | 0009000-01-5 | gum arabic | yes | no | no | ||||
| 542 | 42640 | 0009000-11-7 | carboxymethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 543 | 45920 | 0009000-16-2 | dammar | yes | no | no | ||||
| 544 | 58400 | 0009000-30-0 | guar gum | yes | no | no | ||||
| 545 | 93680 | 0009000-65-1 | tragacanth gum | yes | no | no | ||||
| 546 | 71440 | 0009000-69-5 | pectin | yes | no | no | ||||
| 547 | 55440 | 0009000-70-8 | gelatin | yes | no | no | ||||
| 548 | 42800 | 0009000-71-9 | casein | yes | no | no | ||||
| 549 | 80000 | 0009002-88-4 | polyethylene wax | yes | no | no | ||||
| 550 | 81060 | 0009003-07-0 | polypropylene wax | yes | no | no | ||||
| 551 | 79920 | 0009003-11-6 0106392-12-5 | poly(ethylene propylene) glycol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 552 | 81500 | 0009003-39-8 | polyvinylpyrrolidone | yes | no | no | The substance shall meet the purity criteria as laid down in Commission Directive 2008/84/ECc | |||
| 553 | 14500 | 0009004-34-6 | cellulose | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 43280 | ||||||||||
| 554 | 43300 | 0009004-36-8 | cellulose acetate butyrate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 555 | 53280 | 0009004-57-3 | ethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 556 | 54260 | 0009004-58-4 | ethylhydroxyethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 557 | 66640 | 0009004-59-5 | methylethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 558 | 60560 | 0009004-62-0 | hydroxyethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 559 | 61680 | 0009004-64-2 | hydroxypropylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 560 | 66700 | 0009004-65-3 | methylhydroxypropylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 561 | 66240 | 0009004-67-5 | methylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 562 | 22450 | 0009004-70-0 | nitrocellulose | no | yes | no | ||||
| 563 | 78320 | 0009004-97-1 | polyethyleneglycol monoricinoleate | yes | no | yes | 42 | |||
| 564 | 24540 | 0009005-25-8 | starch, edible | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 88800 | ||||||||||
| 565 | 61120 | 0009005-27-0 | hydroxyethyl starch | yes | no | no | ||||
| 566 | 33350 | 0009005-32-7 | alginic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 567 | 82080 | 0009005-37-2 | 1,2-propyleneglycol alginate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 568 | 79040 | 0009005-64-5 | polyethyleneglycol sorbitan monolaurate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 569 | 79120 | 0009005-65-6 | polyethyleneglycol sorbitan monooleate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 570 | 79200 | 0009005-66-7 | polyethyleneglycol sorbitan monopalmitate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 571 | 79280 | 0009005-67-8 | polyethyleneglycol sorbitan monostearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 572 | 79360 | 0009005-70-3 | polyethyleneglycol sorbitan trioleate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 573 | 79440 | 0009005-71-4 | polyethyleneglycol sorbitan tristearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 574 | 24250 | 0009006-04-6 | rubber, natural | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 84560 | ||||||||||
| 575 | 76721 | 0063148-62-9 | polydimethylsiloxane (Mw > 6 800 Da) | yes | no | no | Viscosity at 25 °C not less than 100 cSt (100 × 10-6 m2/s) | |||
| 576 | 60880 | 0009032-42-2 | hydroxyethylmethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 577 | 62280 | 0009044-17-1 | isobutylene-butene copolymer | yes | no | no | ||||
| 578 | 79600 | 0009046-01-9 | polyethyleneglycol tridecyl ether phosphate | yes | no | no | 5 | For materials and articles intended for contact with aqueous foods only. Polyethyleneglycol (EO ≤ 11) tridecyl ether phosphate (mono-and dialkyl ester) with a maximum 10 % content of polyethyleneglycol (EO ≤ 11) tridecylether. | ||
| 579 | 61800 | 0009049-76-7 | hydroxypropyl starch | yes | no | no | ||||
| 580 | 46070 | 0010016-20-3 | α-dextrin | yes | no | no | ||||
| 581 | 36800 | 0010022-31-8 | barium nitrate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 582 | 50240 | 0010039-33-5 | di-n-octyltin bis(2-ethylhexyl maleate) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 583 | 40400 | 0010043-11-5 | boron nitride | yes | no | no | (16) | |||
| 584 | 13620 | 0010043-35-3 | boric acid | yes | yes | no | (16) | |||
| 40320 | ||||||||||
| 585 | 41120 | 0010043-52-4 | calcium chloride | yes | no | no | ||||
| 586 | 65280 | 0010043-84-2 | manganese hypophosphite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 587 | 68400 | 0010094-45-8 | octadecylerucamide | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 588 | 64320 | 0010377-51-2 | lithium iodide | yes | no | no | (6) | |||
| 589 | 52645 | 0010436-08-5 | cis-11-eicosenamide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 590 | 21370 | 0010595-80-9 | methacrylic acid, 2-sulphoethyl ester | no | yes | no | ND | (1) | ||
| 591 | 36160 | 0010605-09-1 | ascorbyl stearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 592 | 34690 | 0011097-59-9 | aluminium magnesium carbonate hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 593 | 44960 | 0011104-61-3 | cobalt oxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 594 | 65360 | 0011129-60-5 | manganese oxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 595 | 19510 | 0011132-73-3 | lignocellulose | no | yes | no | ||||
| 596 | 95935 | 0011138-66-2 | xanthan gum | yes | no | no | ||||
| 597 | 67120 | 0012001-26-2 | mica | yes | no | no | ||||
| 598 | 41600 | 0012004-14-7 0037293-22-4 | calcium sulphoaluminate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 599 | 36840 | 0012007-55-5 | barium tetraborate | yes | no | no | (16) | |||
| 600 | 60030 | 0012072-90-1 | hydromagnesite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 601 | 35440 | 0012124-97-9 | ammonium bromide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 602 | 70240 | 0012198-93-5 | ozokerite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 603 | 83460 | 0012269-78-2 | pyrophyllite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 604 | 60080 | 0012304-65-3 | hydrotalcite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 605 | 11005 | 0012542-30-2 | acrylic acid, dicyclopentenyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (1) | ||
| 606 | 65200 | 0012626-88-9 | manganese hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 607 | 62245 | 0012751-22-3 | iron phosphide | yes | no | no | Only to be used in PET polymers and copolymers | |||
| 608 | 40800 | 0013003-12-8 | 4,4′-butylidene-bis(6-tert-butyl-3-methylphenyl-ditridecyl phosphite) | yes | no | yes | 6 | |||
| 609 | 83455 | 0013445-56-2 | pyrophosphorous acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 610 | 93440 | 0013463-67-7 | titanium dioxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 611 | 35120 | 0013560-49-1 | 3-aminocrotonic acid, diester with thiobis (2-hydroxyethyl) ether | yes | no | no | ||||
| 612 | 16694 | 0013811-50-2 | N,N′-divinyl-2-imidazolidinone | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (10) | ||
| 613 | 95905 | 0013983-17-0 | wollastonite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 614 | 45560 | 0014464-46-1 | cristobalite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 615 | 92080 | 0014807-96-6 | talc | yes | no | no | ||||
| 616 | 83470 | 0014808-60-7 | quartz | yes | no | no | ||||
| 617 | 10660 | 0015214-89-8 | 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulphonic acid | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 618 | 51040 | 0015535-79-2 | di-n-octyltin mercaptoacetate | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 619 | 50320 | 0015571-58-1 | di-n-octyltin bis(2-ethylhexyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 620 | 50720 | 0015571-60-5 | di-n-octyltin dimaleate | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 621 | 17110 | 0016219-75-3 | 5-ethylidenebicyclo[2,2,1]hept-2-ene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (9) | ||
| 622 | 69840 | 0016260-09-6 | oleylpalmitamide | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 623 | 52640 | 0016389-88-1 | dolomite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 624 | 18897 | 0016712-64-4 | 6-hydroxy-2-naphthalenecarboxylic acid | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 625 | 36720 | 0017194-00-2 | barium hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 626 | 57800 | 0018641-57-1 | glycerol tribehenate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 627 | 59760 | 0019569-21-2 | huntite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 628 | 96190 | 0020427-58-1 | zinc hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 629 | 34560 | 0021645-51-2 | aluminium hydroxide | yes | no | no | ||||
| 630 | 82240 | 0022788-19-8 | 1,2-propyleneglycol dilaurate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 631 | 59120 | 0023128-74-7 | 1,6-hexamethylene-bis(3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionamide) | yes | no | yes | 45 | |||
| 632 | 52880 | 0023676-09-7 | 4-ethoxybenzoic acid, ethyl ester | yes | no | no | 3,6 | |||
| 633 | 53200 | 0023949-66-8 | 2-ethoxy-2′-ethyloxanilide | yes | no | yes | 30 | |||
| 634 | 25910 | 0024800-44-0 | tripropyleneglycol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 635 | 40720 | 0025013-16-5 | tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole | yes | no | no | 30 | |||
| 636 | 31500 | 0025134-51-4 | acrylic acid, acrylic acid, 2-ethylhexyl ester, copolymer | yes | no | no | 0,05 | (22) | SML expressed as acrylic acid, 2-ethylhexyl ester | |
| 637 | 71635 | 0025151-96-6 | pentaerythritol dioleate | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down | ||
| 638 | 23590 | 0025322-68-3 | polyethyleneglycol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 76960 | ||||||||||
| 639 | 23651 | 0025322-69-4 | polypropyleneglycol | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 80800 | ||||||||||
| 640 | 54930 | 0025359-91-5 | formaldehyde-1-naphthol, copolymer | yes | no | no | 0,05 | |||
| [F2641 | 22331 | 0025513-64-8 | mixture of (35-45 % w/w) 1,6-diamino-2,2,4-trimethylhexane and (55-65 % w/w)1,6-diamino-2,4,4-trimethylhexane | no | yes | no | 0,05 ] | |||
| 642 | 64990 | 0025736-61-2 | maleic anhydride-styrene, copolymer, sodium salt | yes | no | no | The fraction with molecular weight below 1 000 Da [F2shall] not exceed 0,05 % (w/w) | |||
| 643 | 87760 | 0026266-57-9 | sorbitan monopalmitate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 644 | 88080 | 0026266-58-0 | sorbitan trioleate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 645 | 67760 | 0026401-86-5 | mono-n-octyltin tris(isooctyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (11) | |||
| 646 | 50480 | 0026401-97-8 | di-n-octyltin bis(isooctyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 647 | 56720 | 0026402-23-3 | glycerol monohexanoate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 648 | 56880 | 0026402-26-6 | glycerol monooctanoate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 649 | 47210 | 0026427-07-6 | dibutylthiostannoic acid polymer | yes | no | no | Molecular unit = (C8H18S3Sn2)n (n = 1,5-2) | |||
| 650 | 49600 | 0026636-01-1 | dimethyltin bis(isooctyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (9) | |||
| 651 | 88240 | 0026658-19-5 | sorbitan tristearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 652 | 38820 | 0026741-53-7 | bis(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) pentaerythritol diphosphite | yes | no | yes | 0,6 | |||
| 653 | 25270 | 0026747-90-0 | 2,4-toluene diisocyanate dimer | no | yes | no | (17) | 1 mg/kg in final product expressed as isocyanate moiety | (10) | |
| 654 | 88600 | 0026836-47-5 | sorbitol monostearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 655 | 25450 | 0026896-48-0 | tricyclodecanedimethanol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 656 | 24760 | 0026914-43-2 | styrenesuphonic acid | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 657 | 67680 | 0027107-89-7 | mono-n-octyltin tris(2-ethylhexyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (11) | |||
| 658 | 52000 | 0027176-87-0 | dodecylbenzenesulphonic acid | yes | no | no | 30 | |||
| 659 | 82800 | 0027194-74-7 | 1,2-propyleneglycol monolaurate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 660 | 47540 | 0027458-90-8 | di-tert-dodecyl disulphide | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | |||
| 661 | 95360 | 0027676-62-6 | 1,3,5-tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 662 | 25927 | 0027955-94-8 | 1,1,1-tris(4-hydroxyphenol)ethane | no | yes | no | 0,005 | Only to be used in polycarbonates | [F9(1)] | |
| 663 | 64150 | 0028290-79-1 | linolenic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 664 | 95000 | 0028931-67-1 | trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate-methyl methacrylate copolymer | yes | no | no | ||||
| 665 | 83120 | 0029013-28-3 | 1,2-propyleneglycol monopalmitate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 666 | 87280 | 0029116-98-1 | sorbitan dioleate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 667 | 55190 | 0029204-02-2 | gadoleic acid | yes | no | no | ||||
| 668 | 80240 | 0029894-35-7 | polyglycerol ricinoleate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 669 | 56610 | 0030233-64-8 | glycerol monobehenate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 670 | 56800 | 0030899-62-8 | glycerol monolaurate diacetate | yes | no | no | (32) | |||
| 671 | 74240 | 0031570-04-4 | phosphorous acid, tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl)ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 672 | 76845 | 0031831-53-5 | polyester of 1,4-butanediol with caprolactone | yes | no | no | (29) (30) | The fraction with molecular weight below 1 000 Da [F2shall] not exceed 0,5 % (w/w) | ||
| 673 | 53670 | 0032509-66-3 | ethylene glycol bis[3,3-bis(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)butyrate] | yes | no | yes | 6 | |||
| 674 | 46480 | 0032647-67-9 | dibenzylidene sorbitol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 675 | 38800 | 0032687-78-8 | N,N′-bis(3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionyl)hydrazide | yes | no | yes | 15 | |||
| 676 | 50400 | 0033568-99-9 | di-n-octyltin bis(isooctyl maleate) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 677 | 82560 | 0033587-20-1 | 1,2-propyleneglycol dipalmitate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 678 | 59200 | 0035074-77-2 | 1,6-hexamethylene-bis(3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate) | yes | no | yes | 6 | |||
| 679 | 39060 | 0035958-30-6 | 1,1-bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-di-tert-butylphenyl)ethane | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 680 | 94400 | 0036443-68-2 | triethyleneglycol bis[3-(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl) propionate] | yes | no | no | 9 | |||
| 681 | 18310 | 0036653-82-4 | 1-hexadecanol | no | yes | no | ||||
| 682 | 53270 | 0037205-99-5 | ethylcarboxymethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 683 | 66200 | 0037206-01-2 | methylcarboxymethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 684 | 68125 | 0037244-96-5 | nepheline syenite | yes | no | no | ||||
| 685 | 85950 | 0037296-97-2 | silicic acid, magnesium-sodium-fluoride salt | yes | no | no | 0,15 | SML expressed as fluoride. Only to be used in layers of multi-layer materials not coming into direct contact with food. | ||
| 686 | 61390 | 0037353-59-6 | hydroxymethylcellulose | yes | no | no | ||||
| 687 | 13530 | 0038103-06-9 | 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane bis(phthalic anhydride) | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 13614 | ||||||||||
| 688 | 92560 | 0038613-77-3 | tetrakis(2,4-di-tert-butyl-phenyl)-4,4′-biphenylylene diphosphonite | yes | no | yes | 18 | |||
| 689 | 95280 | 0040601-76-1 | 1,3,5-tris(4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylbenzyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione | yes | no | yes | 6 | |||
| 690 | 92880 | 0041484-35-9 | thiodiethanol bis(3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy phenyl) propionate) | yes | no | yes | 2,4 | |||
| 691 | 13600 | 0047465-97-4 | 3,3-bis(3-methyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)2-indolinone | no | yes | no | 1,8 | |||
| 692 | 52320 | 0052047-59-3 | 2-(4-dodecylphenyl)indole | yes | no | yes | 0,06 | |||
| 693 | 88160 | 0054140-20-4 | sorbitan tripalmitate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 694 | 21400 | 0054276-35-6 | methacrylic acid, sulphopropyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (1) | ||
| 695 | 67520 | 0054849-38-6 | monomethyltin tris(isooctyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (9) | |||
| 696 | 92205 | 0057569-40-1 | terephthalic acid, diester with 2,2′-methylenebis(4-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol) | yes | no | no | ||||
| 697 | 67515 | 0057583-34-3 | monomethyltin tris(ethylhexyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (9) | |||
| 698 | 49595 | 0057583-35-4 | dimethyltin bis(ethylhexyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (9) | |||
| 699 | 90720 | 0058446-52-9 | stearoylbenzoylmethane | yes | no | no | ||||
| 700 | 31520 | 0061167-58-6 | acrylic acid, 2-tert-butyl-6-(3-tert-butyl-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzyl)-4-methylphenyl ester | yes | no | yes | 6 | |||
| 701 | 40160 | 0061269-61-2 | N,N′-bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl)hexamethylenediamine-1,2-dibromoethane, copolymer | yes | no | no | 2,4 | |||
| 702 | 87920 | 0061752-68-9 | sorbitan tetrastearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 703 | 17170 | 0061788-47-4 | fatty acids, coco | no | yes | no | ||||
| 704 | 77600 | 0061788-85-0 | polyethyleneglycol ester of hydrogenated castor oil | yes | no | no | ||||
| 705 | 10599/90A | 0061788-89-4 | acids, fatty, unsaturated (C18), dimers, non hydrogenated, distilled and non-distilled | no | yes | no | (18) | (1) | ||
| 10599/91 | ||||||||||
| 706 | 17230 | 0061790-12-3 | fatty acids, tall oil | no | yes | no | ||||
| 707 | 46375 | 0061790-53-2 | diatomaceous earth | yes | no | no | ||||
| 708 | 77520 | 0061791-12-6 | polyethyleneglycol ester of castor oil | yes | no | no | 42 | |||
| 709 | 87520 | 0062568-11-0 | sorbitan monobehenate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 710 | 38700 | 0063397-60-4 | bis(2-carbobutoxyethyl)tin-bis(isooctyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | yes | 18 | |||
| 711 | 42000 | 0063438-80-2 | (2-carbobutoxyethyl)tin-tris(isooctyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | yes | 30 | |||
| 712 | 42960 | 0064147-40-6 | castor oil, dehydrated | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F10713 | 43480 | 0064365-11-3 | charcoal, activated | yes | no | no | Only for use in PET at maximum 10 mg/kg of polymer. Same purity requirements as for Vegetable Carbon (E 153) set out by Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 d with exception of ash content which can be up to 10 % (w/w). | |||
| 0007440-44-0] | ||||||||||
| 714 | 84400 | 0064365-17-9 | rosin, hydrogenated, ester with pentaerythritol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 715 | 46880 | 0065140-91-2 | 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzylphosphonic acid, monoethyl ester, calcium salt | yes | no | no | 6 | |||
| 716 | 60800 | 0065447-77-0 | 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl piperidine-succinic acid, dimethyl ester, copolymer | yes | no | no | 30 | |||
| 717 | 84210 | 0065997-06-0 | rosin, hydrogenated | yes | no | no | ||||
| 718 | 84240 | 0065997-13-9 | rosin, hydrogenated, ester with glycerol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 719 | 65920 | 0066822-60-4 | N-methacryloyloxyethyl-N,N-dimethyl-N-carboxymethylammonium chloride, sodium salt -octadecyl methacrylate-ethyl methacrylate-cyclohexyl methacrylate-N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone, copolymers | yes | no | no | ||||
| 720 | 67360 | 0067649-65-4 | mono-n-dodecyltin tris(isooctyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (25) | |||
| 721 | 46800 | 0067845-93-6 | 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, hexadecyl ester | yes | no | no | ||||
| 722 | 17200 | 0068308-53-2 | fatty acids, soya | no | yes | no | ||||
| 723 | 88880 | 0068412-29-3 | starch, hydrolysed | yes | no | no | ||||
| 724 | 24903 | 0068425-17-2 | syrups, hydrolysed starch, hydrogenated | no | yes | no | In compliance with the purity criteria for maltitol syrup E 965(ii) as laid down in Commission Directive 2008/60/ECe | |||
| F16 | ||||||||||
| 726 | 83599 | 0068442-12-6 | reaction products of oleic acid, 2-mercaptoethyl ester, with dichlorodimethyltin, sodium sulphide and trichloromethyltin | yes | no | yes | (9) | |||
| 727 | 43360 | 0068442-85-3 | cellulose, regenerated | yes | no | no | ||||
| 728 | 75100 | 0068515-48-0 0028553-12-0 | phthalic acid, diesters with primary, saturated C8-C10 branched alcohols, more than 60 % C9 | yes | no | no | (26) (32) | Only to be used as: (a) plasticiser in repeated use materials and articles; (b) plasticiser in single-use materials and articles contacting non-fatty foods except for infant formulae and follow-on formulae as defined by Directive 2006/141/EC or processed cereal-based foods and baby foods for infants and young children as defined by Directive 2006/125/EC; (c) technical support agent in concentrations up to 0,1 % in the final product. | (7) | |
| 729 | 75105 | 0068515-49-1 0026761-40-0 | phthalic acid, diesters with primary, saturated C9-C11 alcohols more than 90 % C10 | yes | no | no | (26) (32) | Only to be used as: (a) plasticiser in repeated use materials and articles; (b) plasticiser in single-use materials and articles contacting non-fatty foods except for infant formulae and follow-on formulae as defined by Directive 2006/141/EC or processed cereal-based foods and baby foods for infants and young children as defined by Directive 2006/125/EC; (c) technical support agent in concentrations up to 0,1 % in the final product. | (7) | |
| 730 | 66930 | 0068554-70-1 | methylsilsesquioxane | yes | no | no | Residual monomer in methylsilsesquioxane: < 1 mg methyltrimethoxysilane/kg of methylsilsesquioxane | |||
| 731 | 18220 | 0068564-88-5 | N-heptylaminoundecanoic acid | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (2) | ||
| 732 | 45450 | 0068610-51-5 | p-cresol-dicyclopentadiene-isobutylene, copolymer | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 733 | 10599/92A | 0068783-41-5 | acids, fatty, unsaturated (C18), dimers, hydrogenated, distilled and non-distilled | no | yes | no | (18) | (1) | ||
| 10599/93 | ||||||||||
| 734 | 46380 | 0068855-54-9 | diatomaceous earth, soda ash flux-calcined | yes | no | no | ||||
| 735 | 40120 | 0068951-50-8 | bis(polyethyleneglycol)hydroxymethylphosphonate | yes | no | no | 0,6 | |||
| 736 | 50960 | 0069226-44-4 | di-n-octyltin ethyleneglycol bis(mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | no | (10) | |||
| 737 | 77370 | 0070142-34-6 | polyethyleneglycol-30 dipolyhydroxystearate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 738 | 60320 | 0070321-86-7 | 2-[2-hydroxy-3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylbenzyl)phenyl]benzotriazole | yes | no | yes | 1,5 | |||
| 739 | 70000 | 0070331-94-1 | 2,2′-oxamidobis[ethyl-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-propionate] | yes | no | no | ||||
| 740 | 81200 | 0071878-19-8 | poly[6-[(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diyl]-[(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl)-imino]hexamethylene[(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl) imino] | yes | no | yes | 3 | |||
| 741 | 24070 | 0073138-82-6 | resin acids and rosin acids | yes | yes | no | ||||
| 83610 | ||||||||||
| 742 | 92700 | 0078301-43-6 | 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-20-(2,3-epoxypropyl)-7-oxa-3,20-diazadispiro-[5.1.11.2]-heneicosan-21-one, polymer | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 743 | 38950 | 0079072-96-1 | bis(4-ethylbenzylidene)sorbitol | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F15744 | 18888 | 080181-31-3 | 3-hydroxybutanoic acid-3- hydroxypentanoic acid, copolymer | no | yes | no | (35) | The substance is used as product obtained by bacterial fermentation. In compliance with the specifications mentioned in the Table 4 of Annex I. ] | ||
| 745 | 68145 | 0080410-33-9 | 2,2′,2′-nitrilo(triethyl tris(3,3′,5,5′-tetra-tert-butyl-1,1′-bi-phenyl-2,2′-diyl)phosphite) | yes | no | yes | 5 | SML expressed as sum of phosphite and phosphate | ||
| 746 | 38810 | 0080693-00-1 | bis(2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenyl)pentaerythritol diphosphite | yes | no | yes | 5 | SML expressed as sum of phosphite and phosphate | ||
| 747 | 47600 | 0084030-61-5 | di-n-dodecyltin bis(isooctyl mercaptoacetate) | yes | no | yes | (25) | |||
| 748 | 12765 | 0084434-12-8 | N-(2-aminoethyl)-β-alanine, sodium salt | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 749 | 66360 | 0085209-91-2 | 2,2′-methylene bis(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl) sodium phosphate | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 750 | 66350 | 0085209-93-4 | 2,2′-methylenebis(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl) lithium phosphate | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 751 | 81515 | 0087189-25-1 | poly(zinc glycerolate) | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F2752 | 39890 | 0087826-41-3 0069158-41- 4 0054686-97-4 0081541-12-0 | bis(methylbenzylidene)sorbitol | yes | no | no ] | ||||
| 753 | 62800 | 0092704-41-1 | kaolin, calcined | yes | no | no | ||||
| 754 | 56020 | 0099880-64-5 | glycerol dibehenate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 755 | 21765 | 0106246-33-7 | 4,4′-methylenebis(3-chloro-2,6-diethylaniline) | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (1) | ||
| 756 | 40020 | 0110553-27-0 | 2,4-bis(octylthiomethyl)-6-methylphenol | yes | no | yes | (24) | |||
| 757 | 95725 | 0110638-71-6 | vermiculite, reaction product with citric acid, lithium salt | yes | no | no | ||||
| 758 | 38940 | 0110675-26-8 | 2,4-bis(dodecylthiomethyl)-6-methylphenol | yes | no | yes | (24) | |||
| 759 | 54300 | 0118337-09-0 | 2,2′-ethylidenebis(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl) fluorophosphonite | yes | no | yes | 6 | |||
| 760 | 83595 | 0119345-01-6 | reaction product of di-tert-butylphosphonite with biphenyl, obtained by condensation of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol with Friedel Craft reaction product of phosphorous trichloride and biphenyl | yes | no | no | 18 | Composition:
(*)Quantity of substance used/quantity of formulationOther specifications:
| ||
| 761 | 92930 | 0120218-34-0 | thiodiethanolbis(5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate) | yes | no | no | 6 | |||
| 762 | 31530 | 0123968-25-2 | acrylic acid, 2,4-di-tert-pentyl-6-(1-(3,5-di-tert-pentyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl)phenyl ester | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 763 | 39925 | 0129228-21-3 | 3,3-bis(methoxymethyl)-2,5-dimethylhexane | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | |||
| 764 | 13317 | 0132459-54-2 | N,N′-bis[4-(ethoxycarbonyl)phenyl]-1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxydiimide | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Purity > 98,1 % (w/w). Only to be used as co-monomer (max 4 %) for polyesters (PET, PBT). | ||
| 765 | 49485 | 0134701-20-5 | 2,4-dimethyl-6-(1-methylpentadecyl)phenol | yes | no | yes | 1 | |||
| 766 | 38879 | 0135861-56-2 | bis(3,4-dimethylbenzylidene)sorbitol | yes | no | no | ||||
| 767 | 38510 | 0136504-96-6 | 1,2-bis(3-aminopropyl)ethylenediamine, polymer with N-butyl-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinamine and 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 768 | 34850 | 0143925-92-2 | amines, bis(hydrogenated tallow alkyl) oxidised | yes | no | no | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. Only to be used in: (a) polyolefins at 0,1 % (w/w) concentration and in (b) PET at 0,25 % (w/w) concentration. | (1) | ||
| 769 | 74010 | 0145650-60-8 | phosphorous acid, bis(2,4-di-tert-butyl-6-methylphenyl) ethyl ester | yes | no | yes | 5 | SML expressed as sum of phosphite and phosphate | ||
| 770 | 51700 | 0147315-50-2 | 2-(4,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-5-(hexyloxy)phenol | yes | no | no | 0,05 | |||
| 771 | 34650 | 0151841-65-5 | aluminium hydroxybis [2,2′-methylenebis (4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphate] | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 772 | 47500 | 0153250-52-3 | N,N′-dicyclohexyl-2,6-naphthalene dicarboxamide | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 773 | 38840 | 0154862-43-8 | bis(2,4-dicumylphenyl)pentaerythritol-diphosphite | yes | no | yes | 5 | SML expressed as sum of the substance itself, its oxidised form bis(2,4-dicumylphenyl)pentaerythritol-phosphate and its hydrolysis product (2,4-dicumylphenol) | ||
| 774 | 95270 | 0161717-32-4 | 2,4,6-tris(tert-butyl)phenyl-2-butyl-2-ethyl-1,3-propanediol phosphite | yes | no | yes | 2 | SML expressed as sum of phosphite, phosphate and the hydrolysis product = TTBP | ||
| 775 | 45705 | 0166412-78-8 | 1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid, diisononyl ester | yes | no | no | (32) | |||
| 776 | 76723 | 0167883-16-1 | polydimethylsiloxane, 3-aminopropyl terminated, polymer with dicyclohexylmethane-4,4′-diisocyanate | yes | no | no | The fraction with molecular weight below 1 000 Da [F2shall] not exceed 1,5 % (w/w) | |||
| 777 | 31542 | 0174254-23-0 | acrylic acid, methyl ester, telomer with 1-dodecanethiol, C16-C18 alkyl esters | yes | no | no | 0,5 % in final product | (1) | ||
| 778 | 71670 | 0178671-58-4 | pentaerythritol tetrakis (2-cyano-3,3-diphenylacrylate) | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | |||
| [F2779 | 39815 | 0182121-12-6 | 9,9-bis(methoxymethyl)fluorene | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | [F9(2)]] | ||
| 780 | 81220 | 0192268-64-7 | poly-[[6-[N-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl)-n-butylamino]-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diyl][(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl)imino]-1,6-hexanediyl[(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl)imino]]-α-[N,N,N′,N′-tetrabutyl-N"-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl)-N"-[6-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinylamino)-hexyl]-[1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine]-ω-N,N,N′,N′-tetrabutyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine] | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 781 | 95265 | 0227099-60-7 | 1,3,5-tris(4-benzoylphenyl) benzene | yes | no | no | 0,05 | |||
| 782 | 76725 | 0661476-41-1 | polydimethylsiloxane, 3-aminopropyl terminated, polymer with 1-isocyanato-3-isocyanatomethyl-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexane | yes | no | no | The fraction with molecular weight below 1 000 Da [F2shall] not exceed 1 % (w/w) | |||
| 783 | 55910 | 0736150-63-3 | glycerides, castor-oil mono-, hydrogenated, acetates | yes | no | no | (32) | |||
| [F10784 | 95420 | 0745070-61-5 | 1,3,5-tris (2,2-di-methylpropanamido) benzene | yes | no | no | 5 ] | |||
| 785 | 24910 | 0000100-21-0 | terephthalic acid | no | yes | no | (28) | |||
| 786 | 14627 | 0000117-21-5 | 3-chlorophthalic anhydride | no | yes | no | 0,05 | SML expressed as 3-chlorophthalic acid | ||
| 787 | 14628 | 0000118-45-6 | 4-chlorophthalic anhydride | no | yes | no | 0,05 | SML expressed as 4-chlorophthalic acid | ||
| 788 | 21498 | 0002530-85-0 | [3-(methacryloxy)propyl]trimethoxysilane | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used as a surface treatment agent of inorganic fillers | (1) (11) | |
| 789 | 60027 | — | hydrogenated homopolymers and/or copolymers made of 1-hexene and/or 1-octene and/or 1-decene and/or 1-dodecene and/or 1-tetradecene (Mw: 440–12 000) | yes | no | no | Average molecular weight not less than 440 Da. Viscosity at 100 °C not less than 3,8 cSt (3,8 × 10-6 m2/s). | (2) | ||
| 790 | 80480 | 0090751-07-8 0082451-48-7 | poly(6-morpholino-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diyl)-[(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl)imino)] hexa-methylene-[(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl)imino)] | yes | no | no | 5 | Average molecular weight not less than 2 400 Da. Residual content of morpholine ≤ 30 mg/kg, of N,N′-bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-4-yl)hexane-1,6-diamine < 15 000 mg/kg, and of 2,4-dichloro-6-morpholino-1,3,5-triazine ≤ 20 mg/kg. | (16) | |
| 791 | 92470 | 0106990-43-6 | N,N′,N″,N″-tetrakis(4,6-bis(N-butyl-(N-methyl-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-4-yl)amino)triazin-2-yl)-4,7-diazadecane-1,10-diamine | yes | no | no | 0,05 | |||
| 792 | 92475 | 0203255-81-6 | 3,3′,5,5′-tetrakis(tert-butyl)-2,2′-dihydroxybiphenyl, cyclic ester with [3-(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)propyl]oxyphosphonous acid | yes | no | yes | 5 | SML expressed as the sum of phosphite and phosphate form of the substance and the hydrolysis products | ||
| 793 | 94000 | 0000102-71-6 | triethanolamine | yes | no | no | 0,05 | SML expressed as the sum of triethanolamine and the hydrochloride adduct expressed as triethanolamine | ||
| [F13794 | 18117 | 0000079-14-1 | glycolic acid | no | yes | no | Only to be used for manufacture of polyglycolic acid (PGA) for (i) indirect food contact behind polyesters such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polylactic acid (PLA); and (ii) direct food contact of a blend of PGA up to 3 % w/w in PET or PLA. ] | |||
| 795 | 40155 | 0124172-53-8 | N,N′-bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl)-N,N′-diformylhexamethylenediamine | yes | no | no | 0,05 | (2) (12) | ||
| 796 | 72141 | 0018600-59-4 | 2,2′-(1,4-phenylene)bis[4H-3,1-benzoxazin-4-one] | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | SML including the sum of its hydrolysis products | ||
| [F13797 | 76807 | 0073018-26-5 | polyester of adipic acid with 1,3-butanediol, 1,2-propanediol and 2-ethyl-1-hexanol | yes | no | yes | (31) (32) ] | |||
| 798 | 92200 | 0006422-86-2 | terephthalic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl)ester | yes | no | no | 60 | (32) | ||
| [F10799 | 77708 | polyethyleneglycol (EO = 1-50) ethers of linear and branched primary (C 8 -C 22 ) alcohols | yes | no | no | 1,8 | In compliance with the maximum ethylene oxide content as laid down in the purity criteria for food additives in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012. ] | |||
| 800 | 94425 | 0000867-13-0 | triethyl phosphonoacetate | yes | no | no | Only for use in PET | |||
| 801 | 30607 | — | acids, C2-C24, aliphatic, linear, monocarboxylic, from natural oils and fats, lithium salt | yes | no | no | ||||
| 802 | 33105 | 0146340-15-0 | alcohols, C12-C14 secondary, β-(2-hydroxyethoxy), ethoxylated | yes | no | no | 5 | (12) | ||
| 803 | 33535 | 0152261-33-1 | α-alkenes(C20-C24) copolymer with maleic anhydride, reaction product with 4-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine | yes | no | no | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. Not to be used in contact with alcoholic foods. | (13) | ||
| 804 | 80510 | 1010121-89-7 | poly(3-nonyl-1,1-dioxo-1-thiopropane-1,3-diyl)-block-poly(x-oleyl-7-hydroxy-1,5-diiminooctane-1,8-diyl), process mixture with x = 1 and/or 5, neutralised with dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid | yes | no | no | Only to be used as polymer production aid in polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) and polystyrene (PS) | |||
| 805 | 93450 | — | titanium dioxide, coated with a copolymer of n-octyltrichlorosilane and [aminotris(methylenephosphonic acid), penta sodium salt] | yes | no | no | The content of the surface treatment copolymer of the coated titanium dioxide is less than 1 % w/w | |||
| 806 | 14876 | 0001076-97-7 | 1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid | no | yes | no | 5 | Only to be used for manufacture of polyesters | ||
| [F11807 | 93485 | — | titanium nitride, nanoparticles | yes | no | no | No migration of titanium nitride nanoparticles. Only to be used in polyethylene terephthalate (PET) up to 20 mg/kg. In the PET, the agglomerates have a diameter of 100-500 nm consisting of primary titanium nitride nanoparticles; primary particles have a diameter of approximately 20 nm. ] | |||
| 808 | 38550 | 0882073-43-0 | bis(4-propylbenzylidene)propylsorbitol | yes | no | no | 5 | SML including the sum of its hydrolysis products | ||
| 809 | 49080 | 0852282-89-4 | N-(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-6-[4-(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenoxy]-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-1,3(2H)-dione | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | Only for use in PET | (6) (14) (15) | |
| 810 | 68119 | neopentyl glycol, diesters and monoesters with benzoic acid and 2-ethylhexanoic acid | yes | no | no | 5 | (32) | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. | ||
| 811 | 80077 | 0068441-17-8 | polyethylene waxes, oxidised | yes | no | no | 60 | |||
| [F13812 | 80350 | 0124578-12-7 | poly(12-hydroxystearic acid)-polyethyleneimine copolymer | yes | no | no | Only to be used in plastics up to 0,1 % w/w. Prepared by the reaction of poly(12-hydroxystearic acid) with polyethyleneimine. ] | |||
| 813 | 91530 | — | sulphosuccinic acid alkyl (C4-C20) or cyclohexyl diesters, salts | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 814 | 91815 | — | sulphosuccinic acid monoalkyl (C10-C16) polyethyleneglycol esters, salts | yes | no | no | 2 | |||
| 815 | 94985 | — | trimethylolpropane, mixed triesters and diesters with benzoic acid and 2-ethylhexanoic acid | yes | no | no | 5 | (32) | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down | |
| 816 | 45704 | — | cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid, salts | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| 817 | 38507 | — | cis-endo-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2,3-dicarboxylic acid, salts | yes | no | no | 5 | Not to be used with polyethylene in contact with acidic foods. Purity ≥ 96 %. | ||
| 818 | 21530 | — | methallylsulphonic acid, salts | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 819 | 68110 | — | neodecanoic acid, salts | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Not to be used in polymers contacting fatty foods. Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. SML expressed as neodecanoic acid. | ||
| 820 | 76420 | — | pimelic acid, salts | yes | no | no | ||||
| 821 | 90810 | — | stearoyl-2-lactylic acid, salts | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F17822 | 71938 | Perchloric acid, salts | yes | no | no | 0,002 | (4)] | |||
| 823 | 24889 | — | 5-Sulphoisophthalic acid, salts | no | yes | no | 5 | |||
| 854 | 71943 | 0329238-24-6 | perfluoro acetic acid, α-substituted with the copolymer of perfluoro-1,2-propylene glycol and perfluoro-1,1-ethylene glycol, terminated with chlorohexafluoropropyloxy groups | yes | no | no | Only to be used in concentrations up to 0,5 % w/w in the polymerisation of fluoropolymers that are processed at temperatures at or above 340 °C and are intended for use in repeated use articles | |||
| [F18855 | 40560 | (butadiene, styrene, methyl methacrylate) copolymer cross-linked with 1,3-butanediol dimethacrylate | yes | no | no | Only to be used in rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) at a maximum level of 12 % at room temperature or below. | ||||
| [F19856 | 40563 | 25101-28-4 | (butadiene, styrene, methyl methacrylate, butyl acrylate) copolymer cross-linked with divinylbenzene or 1,3-butanediol dimethacrylate | yes | no | no | Only to be used in:
| |||
| 857 | 66765 | 0037953-21-2 | (methyl methacrylate, butyl acrylate, styrene, glycidyl methacrylate) copolymer | yes | no | no | Only to be used in rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) at a maximum level of 2 % at room temperature or below. ] | |||
| [F7[X1858 | 38565 | 0090498-90-1 | 3,9-bis[2-(3-(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)propionyloxy)-1,1-dimethylethyl]-2,4,8,10-tetraoxaspiro[5,5]undecane | yes | no | yes | 0,05 | SML expressed as the sum of the substance and its oxidation product 3-[(3-(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)prop-2-enoyloxy)-1,1-dimethylethyl]-9-[(3-(3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)propionyloxy)-1,1-dimethylethyl]-2,4,8,10-tetraoxaspiro[5,5]-undecane in equilibrium with its para quinone methid tautomer. | (2)]] | |
| [F4859 | (butadiene, ethyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate, styrene) copolymer crosslinked with divinylbenzene, in nanoform | yes | no | no | Only to be used as particles in non-plasticised PVC up to 10 % w/w in contact with all food types at room temperature or below including long-term storage. When used together with the substance with FCM No 998 and/or the substance with FCM No 1043, the restriction of 10 % w/w applies to the sum of those substances. The diameter of particles shall be > 20 nm, and for at least 95 % by number it shall be > 40 nm. ] | |||||
| 860 | 71980 | 0051798-33-5 | perfluoro[2-(poly(n-propoxy))propanoic acid] | yes | no | no | Only to be used in the polymerisation of fluoropolymers that are processed at temperatures at or above 265 °C and are intended for use in repeated use articles | |||
| 861 | 71990 | 0013252-13-6 | perfluoro[2-(n-propoxy)propanoic acid] | yes | no | no | Only to be used in the polymerisation of fluoropolymers that are processed at temperatures at or above 265 °C and are intended for use in repeated use articles | |||
| [F13862 | 15180 | 0018085-02-4 | 3,4-diacetoxy-1-butene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | SML including the hydrolysis product 3,4-dihydroxy-1-butene Only to be used as a co-monomer for ethylvinylalcohol (EVOH) and polyvinylalcohol (PVOH) copolymers. | (17) (19)] | |
| [F18863 | 15260 | 0000646-25-3 | 1,10-decanediamine | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used as a co-monomer for manufacturing polyamide articles for repeated use in contact with aqueous, acidic and dairy foodstuffs at room temperature or for short term contact up to 150 °C. ] | ||
| 864 | 46330 | 0000056-06-4 | 2,4-diamino-6-hydroxypyrimidine | yes | no | no | 5 | Only to be used in rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) in contact with non-acidic and non-alcoholic aqueous food | ||
| [F11865 | 40619 | 0025322-99-0 | (butyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate, butyl methacrylate) copolymer | yes | no | no | Only to be used in: (a) rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) at a maximum level of 1 % w/w; (b) polylactic acid (PLA) at a maximum level of 5 % w/w. ] | |||
| 866 | 40620 | — | (butyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate) copolymer, cross-linked with allyl methacrylate | yes | no | no | Only to be used in rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) at a maximum level of 7 % | |||
| 867 | 40815 | 0040471-03-2 | (butyl methacrylate, ethyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate) copolymer | yes | no | no | Only to be used in rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) at a maximum level of 2 % | |||
| [F11868 | 53245 | 0009010-88-2 | (ethyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate) copolymer | yes | no | no | Only to be used in: (a) rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) at a maximum level of 2 % w/w; (b) polylactic acid (PLA) at a maximum level of 5 % w/w; (c) polyethylene terephthalate (PET) at a maximum level of 5 % w/w. ] | |||
| 869 | 66763 | 0027136-15-8 | (butyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate, styrene) copolymer | yes | no | no | Only to be used in rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) at a maximum level of 3 % | |||
| 870 | 95500 | 0160535-46-6 | N,N′,N″-tris(2-methylcyclohexyl)-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxamide | yes | no | no | 5 | |||
| [F20871 | 0287916-86-3 | dodecanoic acid, 12-amino-, polymer with ethene, 2,5-furandione, α-hydro-ω-hydroxypoly (oxy-1,2-ethanediyl) and 1-propene | yes | no | no | Only to be used in polyolefins at levels of up to 20 weight %. These polyolefins shall only be used in contact with foods for which Table 2 of Annex III assigns food simulant E, at ambient temperature or below, and when migration of the total oligomeric fraction of less than 1 000 Da does not exceed 50 μg/kg food. | (23)] | |||
| [F21872 | 0006607-41-6 | 2-phenyl-3,3-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)phthalimidine | no | yes | no | 0,05 | To be used only as a co-monomer in polycarbonate copolymers | (20)] | ||
| [F18873 | 93460 | titanium dioxide reacted with octyltriethoxysilane | yes | no | no | Reaction product of titanium dioxide with up to 2 % w/w surface treatment substance octyltriethoxysilane, processed at high temperatures. ] | ||||
| [F7874 | 16265 | 0156065-00-8 | α-dimethyl-3-(4’-hydroxy-3’-methoxyphenyl)propylsilyloxy, ω-3-dimethyl-3-(4’-hydroxy-3’-methoxyphenyl)propylsilyl polydimethylsiloxane | no | yes | no | 0,05 | (33) | Only to be used as comonomer in siloxane modified polycarbonate. The oligomeric mixture shall be characterised by the formula C 24 H 38 Si 2 O 5 (SiOC 2 H 6 )n (50 > n ≥ 26). ] | |
| 875 | 80345 | 0058128-22-6 | poly(12-hydroxystearic acid) stearate | yes | no | yes | 5 | |||
| 878 | 31335 | — | acids, fatty (C8-C22) from animal or vegetable fats and oils, esters with branched alcohols, aliphatic, monohydric, saturated, primary (C3-C22) | yes | no | no | ||||
| 879 | 31336 | — | acids, fatty (C8-C22) from animal or vegetable fats and oils, esters with alcohols, linear, aliphatic, monohydric, saturated, primary (C1-C22) | yes | no | no | ||||
| [F10880 | 31348 | acids, fatty (C 8 -C 22 ), esters with pentaerythritol' | yes | no | no | |||||
| 881 | 25187 | 0003010-96-6 | 2,2,4,4-tetramethylcyclobutane-1,3-diol | no | yes | no | 5 | Only for: (a) repeated use articles for long term storage at room temperature or below and hotfill; (b) single use materials and articles as a co-monomer at a maximum use level of 35 mole % of the diol component of polyesters, and if such materials and articles are for long term storage at room temperature or below of food types which have an alcohol content of up to 10 % and for which Table 2 of Annex III does not assign simulant D2. Hot fill conditions are allowed for such single use materials and articles. ] | ||
| 882 | 25872 | 0002416-94-6 | 2,3,6-trimethylphenol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | |||
| 883 | 22074 | 0004457-71-0 | 3-methyl-1,5-pentanediol | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used in materials in contact with food at a surface to mass ratio up to 0,5 dm2/kg | ||
| 884 | 34240 | 0091082-17-6 | alkyl(C10-C21)sulphonic acid, esters with phenol | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Not to be used for articles in contact with fatty foods for which [F2simulant D1 and/or D2] is laid down. | ||
| 885 | 45676 | 0263244-54-8 | cyclic oligomers of (butylene terephthalate) | yes | no | no | Only to be used in poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET), poly(butylene terephthalate) (PBT), polycarbonate (PC), polystyrene (PS) and rigid poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) plastics in concentrations up to 1 % w/w, in contact with aqueous, acidic and alcoholic foods, for long term storage at room temperature. | |||
| [F18894 | 93360 | 0016545-54-3 | thiodipropionic acid, ditetradecyl ester | yes | no | no | (14) | |||
| 895 | 47060 | 0171090-93-0 | 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid, esters with C13-C15 branched and linear alcohols | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Only to be used in polyolefins in contact with foods other than fatty/high-alcoholic and dairy products. | ||
| 896 | 71958 | 0958445-44-8 | 3H-perfluoro-3-[(3-methoxy-propoxy)propanoic acid], ammonium salt | yes | no | no | Only to be used in the polymerisation of fluoropolymers when:
| |||
| [F7902 | 0000128-44-9 | 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one 1,1-dioxide, sodium salt | yes | no | no | The substance shall comply with the specific purity criteria as set out in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 h . ] | ||||
| [F4903 | 37486-69-4 | 2H-perfluoro-[(5,8,11,14-tetramethyl)-tetraethyleneglycol ethyl propyl ether] | yes | no | no | Only to be used as a polymer production aid in the polymerisation of fluoropolymers intended for: (a) repeated and single use materials and articles when sintered or processed (non-sintered) at temperatures at or above 360 °C for at least 10 minutes or at higher temperatures for equivalent shorter times; (b) repeated use materials and articles when processed (non-sintered) at temperatures from 300 °C and up to 360 °C for at least 10 minutes. ] | ||||
| 923 | 39150 | 0000120-40-1 | N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)dodecanamide | yes | no | no | 5 | The residual amount of diethanolamine in plastics, as an impurity and decomposition product of the substance, [F2shall] not result in a migration of diethanolamine higher than 0,3 mg/kg food. | (18) | |
| 924 | 94987 | trimethylolpropane, mixed triesters and diesters with n-octanoic and n-decanoic acids | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Only for use in PET in contact with all types of foods other than fatty, high-alcoholic and dairy products. | |||
| 926 | 71955 | 0908020-52-0 | perfluoro[(2-ethyloxy-ethoxy)acetic acid], ammonium salt | yes | no | no | Only to be used in the polymerisation of fluoropolymers that are processed at temperatures higher than 300 °C for at least 10 minutes. | |||
| [F4969 | 24937-78-8 | ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer wax | yes | no | no | Only to be used as a polymeric additive up to 2 % w/w in polyolefins. The migration of low molecular weight oligomeric fraction below 1 000 Da shall not exceed 5 mg/kg food. ] | ||||
| 971 | 25885 | 0002459-10-1 | trimethyl trimellitate | no | yes | no | Only to be used as a co-monomer up to 0,35 % w/w to produce modified polyesters intended to be used in contact with aqueous and dry foodstuffs containing no free fat at the surface. | (17) | ||
| 972 | 45197 | 0012158-74-6 | copper hydroxide phosphate | yes | no | no | ||||
| 973 | 22931 | 0019430-93-4 | (perfluorobutyl)ethylene | no | yes | no | Only to be used as a co-monomer up to 0,1 % w/w in the polymerisation of fluoropolymers, sintered at high temperatures. | |||
| [F17974 | 74050 | 939402-02-5 | phosphorous acid, mixed 2,4-bis(1,1- dimethylpropyl)phenyl and 4-(1,1- dimethylpropyl)phenyl triesters | yes | no | yes | 10 | SML expressed as the sum of the phosphite and phosphate forms of the substance, 4-tert-amylphenol and 2,4-di-tert-amylphenol. The migration of 2,4-di-tert- amylphenol shall not exceed 1 mg/kg food. ]] | ||
| [F7979 | 79987 | — | (polyethylene terephthalate, hydroxylated polybutadiene, pyromellitic anhydride) copolymer | yes | no | no | Only to be used in polyethylene terephthalate (PET) at a maximum level of 5 % w/w. ] | |||
| [F21988 | 3634-83-1 | 1,3-bis(isocyanatomethyl)benzene | no | yes | no | (34) | SML(T) applies to the migration of its hydrolysis product, 1,3-benzenedimethanamine To be used only as co-monomer in the manufacture of a middle layer coating on a poly(ethylene terephthalate) polymer film in a multilayer film ] | |||
| [F4998 | (butadiene, ethyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate, styrene) copolymer not cross-linked, in nanoform | yes | no | no | Only to be used as particles in non-plasticised PVC up to 10 % w/w in contact with all food types at room temperature or below including long-term storage. When used together with the substance with FCM No 859 and/or the substance with FCM No 1043, the restriction of 10 % w/w applies to the sum of those substances. The diameter of particles shall be > 20 nm, and for at least 95 % by number it shall be > 40 nm. | |||||
| [F221007 | 976-56-7 | diethyl[[3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]methyl]phosphonate | no | yes | no | Only to be used up to 0,2 % w/w based on the final polymer weight in the polymerisation process to manufacture poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET). | ||||
| 1016 | (methacrylic acid, ethyl acrylate, n-butyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate and butadiene) copolymer in nanoform | yes | no | no | Only to be used up to: (a) 10 % w/w in non-plasticised PVC; (b) 15 % w/w in non-plasticised PLA. The final material shall be used at room temperature or below. ] | |||||
| 1017 | 25618-55-7 | polyglycerol | yes | no | no | To be processed under conditions preventing the decomposition of the substance and up to a maximum temperature of 275 °C. | ||||
| [F221030 | montmorillonite clay modified by dimethyldialkyl(C16-C18)ammonium chloride | yes | no | no | Only to be used up to 12 % (w/w) in polyolefins in contact with dry foods to which simulant E is assigned in table 2 of Annex III at room temperature or below. The sum of the specific migration of 1-chlorohexadecane and 1-chlorooctadecane shall not exceed 0,05 mg/kg food. Can contain platelets in the nanoform that are only in one dimension thinner than 100 nm. Such platelets shall be oriented parallel to the polymer surface and shall be fully embedded in the polymer. ] | |||||
| [F201031 | 3238-40-2 | furan-2,5-dicarboxylic acid | no | yes | no | 5 | Only to be used as a monomer in the production of polyethylene furanoate. The migration of the oligomeric fraction of less than 1 000 Da shall not exceed 50 μg/kg food (expressed as furan-2,5-dicarboxylic acid). | (22) (23) | ||
| 1034 | 3710-30-3 | 1,7-octadiene | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used as a crosslinking co-monomer in the manufacture of polyolefins for contact with any type of foods for long term storage at room temperature, including when packaged under hot-fill conditions. ] | |||
| 1043 | (butadiene, ethyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate, styrene) copolymer crosslinked with 1,3-butanediol dimethacrylate, in nanoform | yes | no | no | Only to be used as particles in non-plasticised PVC up to 10 % w/w in contact with all food types at room temperature or below including long-term storage. When used together with the substance with FCM No 859 and/or the substance with FCM No 998, the restriction of 10 % w/w applies to the sum of those substances. The diameter of particles shall be > 20 nm, and for at least 95 % by number it shall be > 40 nm. ] | |||||
| [F201045 | 1190931-27-1 | perfluoro{acetic acid, 2-[(5-methoxy-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)oxy]}, ammonium salt | yes | no | no | Only to be used as a polymer production aid during the manufacture of fluoropolymers under high temperature conditions of at least 370 °C. | ||||
| 1046 | zinc oxide, nanoparticles, coated with [3-(methacryloxy)propyl] trimethoxysilane (FCM No 788) | yes | no | no | Only to be used in unplasticised polymers. The restrictions and specifications specified for FCM substance No 788 shall be respected. | |||||
| 1048 | 624-03-3 | ethylene glycol dipalmitate | yes | no | no | (2) | Only to be used when produced from a fatty acid precursor that is obtained from edible fats or oils. | |||
| 1050 | zinc oxide, nanoparticles, uncoated | yes | no | no | Only to be used in unplasticised polymers. | |||||
| 1051 | 42774-15-2 | N,N′-bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl) isophthalamide | yes | no | no | 5 | ||||
| 1052 | 1455-42-1 | 2,4,8,10-tetraoxaspiro[5,5]undecane-3,9-diethanol,β3,β3,β9,β9-tetramethyl- ( ‘ SPG ’ ) | no | yes | no | 5 | Only to be used as a monomer in the production of polyesters. The migration of oligomers of less than 1 000 Da shall not exceed 50 μg/kg food (expressed as SPG). | (22) (23) | ||
| 1053 | fatty acids, C16–18 saturated, esters with dipentaerythritol | yes | no | no | Only to be used when produced from a fatty acid precursor that is obtained from edible fats or oils ] | |||||
| [F221055 | 7695-91-2 58-95-7 | α-tocopherol acetate | yes | no | no | Only to be used as antioxidant in polyolefins. | (24) | |||
| [F231059 | 147398-31-0 | Poly((R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyhexanoate) | no | yes | no | (35) | Only to be used either alone or blended with other polymers in contact with all foods under contact conditions of up to 6 months and/or 6 months and more, at room temperature or below, including hot fill or a short heating up phase. The migration of all oligomers with a molecular weight below 1 000 Da shall not exceed 5,0 mg/kg food. | (23)] | ||
| 1060 | ground sunflower seed hulls | yes | no | no | Only to be used at room temperature or below in contact with foods for which Table 2 of Annex III assigns food simulant E. The seed hulls shall be obtained from sunflower seeds that are fit for human consumption. The processing temperature of the plastic containing the additive shall not exceed 240 °C. | |||||
| [F241061 | 80512-44-3 | 2,4,4′-trifluorobenzophenone | no | yes | no | Only to be used as a co-monomer in the manufacture of polyether ether ketone plastics up to 0,3 % w/w of the final material. ] | ||||
| 1062 | mixture composed of 97 % tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) with CAS No 78-10-4 and 3 % hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) with CAS No 999-97-3 | no | yes | no | Only to be used for the production of recycled PET and at up to 0,12 % (w/w). ] | |||||
| [F241063 | 1547-26-8 | 2,3,3,4,4,5,5-heptafluoro-1-pentene | no | yes | no | Only to be used together with tetrafluoroethylene and/or ethylene co-monomers to manufacture fluorocopolymers for application as polymer processing aid at up to 0,2 % w/w of the food contact material, and when the low-molecular mass fraction below 1 500 Da in the fluorocopolymer does not exceed 30 mg/kg. | ||||
| 1064 | 39318-18-8 | tungsten oxide | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Stoichiometry: WO n , n = 2,72-2,90 | (25) | ||
| 1065 | 85711-28-0 | mixture of methyl-branched and linear C 14 -C 18 alkanamides, derived from fatty acids | yes | no | no | 5 | Only to be used in the manufacture of articles made of polyolefins, and which do not come into contact with foods for which food simulant D2 is assigned in Table 2 of Annex III. | (26)] | ||
| [F151066 | 23985-75-3 | 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylic acid, dimethyl ester | no | yes | no | 0,05 | Only to be used as a co-monomer in the manufacture of a polyester non-food contact layer in a plastic multilayer material, which is to be used only in contact with foods for which food simulants A, B, C and/or D1 are assigned in Table 2 of Annex III. The specific migration limit in column 8 refers to the sum of the substance and of its dimers (cyclic and open chain). ] | |||
| [F251067 | 616-38-6 | dimethyl carbonate | no | yes | no | Only to be used: a) with 1,6-hexanediol in the manufacture of polycarbonate pre-polymers that are used at up to 30 % to manufacture thermoplastic polyurethanes with 4,4′-methylenediphenyldiisocyanate and diols, such as polypropylene glycol and 1,4-butanediol. The resulting material shall only be applied in repeated use articles intended to come into short–term contact (≤ 30 min at room temperature) with food for which simulants A and/or B are assigned in Table 2 of Annex III; or b) for the production of other polycarbonates and/or under other conditions provided that the migration of dimethyl carbonate does not exceed 0,05 mg/kg food and that the migration of all polycarbonate oligomers with a molecular weight below 1 000 Da together does not exceed 0,05 mg/kg food. | (27)] | |||
| [F151068 | 2530-83-8 | [3-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)propyl]trimethoxy silane | no | yes | no | Only to be used as a component of a sizing agent to treat glass fibres to be embedded in glass-fibre-reinforced low diffusivity plastics (polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polycarbonate (PC), polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), thermoset polyesters and epoxy bisphenol vinylester) in contact with all foodstuffs. In treated glass fibres, residues of the substance must not be detectable at 0,01 mg/kg for the substance and 0,06 mg/kg for each of the reaction products (hydrolysed monomers and epoxy-containing cyclic dimer, trimer and tetramer). ] | ||||
| [F251069 | 75-28-5 | isobutane | yes | no | no | Only to be used as a blowing agent. ] | ||||
| [F261075 | Montmorillonite clay modified with hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide | yes | no | no | Only to be used as additive at up to 4,0 % w/w in polylactic acid plastics intended for long-term storage of water at ambient temperature or below. Can form platelets in the nanoform that are in one or two dimensions thinner than 100 nm. Such platelets shall be oriented parallel to the polymer surface and shall be fully embedded in the polymer. | |||||
| 1076 | 1227937-46-3 | Phosphorous acid, triphenyl ester, polymer with alpha-hydro-omega-hydroxypoly[oxy(methyl-1,2-ethanediyl)], C10-16 alkyl ester | yes | no | no | 0,05 | Only to be used as an additive at up to 0,2 % w/w in high impact polystyrene materials and articles intended contact with food at room temperature and below, including hot-fill and/or heating up to 100 °C for up to 2 hours. It shall not be used in contact with foods for which simulant C and/or D1 is assigned in Annex III. | |||
| 1077 | Titanium dioxide surface-treated with fluoride-modified alumina | yes | no | no | Only to be used at up to 25,0 % w/w, including in the nanoform. | 29] | ||||
Editorial Information
X1Substituted by Corrigendum to Commission Regulation (EU) No 1183/2012 of 30 November 2012 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Official Journal of the European Union L 338 of 12 December 2012).
Textual Amendments
F4Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/174 of 5 February 2015 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F5Inserted by Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 321/2011 of 1 April 2011 amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as regards the restriction of use of Bisphenol A in plastic infant feeding bottles (Text with EEA relevance).
F6Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/213 of 12 February 2018 on the use of bisphenol A in varnishes and coatings intended to come into contact with food and amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as regards the use of that substance in plastic food contact materials (Text with EEA relevance).
F7Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) No 1183/2012 of 30 November 2012 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F8Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/213 of 12 February 2018 on the use of bisphenol A in varnishes and coatings intended to come into contact with food and amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as regards the use of that substance in plastic food contact materials (Text with EEA relevance).
F9Deleted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/752 of 28 April 2017 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F10Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/174 of 5 February 2015 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F11Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) No 1183/2012 of 30 November 2012 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F12Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2020/1245 of 2 September 2020 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F13Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) No 1282/2011 of 28 November 2011 amending and correcting Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F14Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) No 202/2014 of 3 March 2014 amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F15Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/37 of 10 January 2019 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F16Deleted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/174 of 5 February 2015 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F17Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/831 of 5 June 2018 amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F18Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) No 1282/2011 of 28 November 2011 amending and correcting Commission Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F19Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/79 of 18 January 2018 amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F20Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/1416 of 24 August 2016 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F21Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) No 202/2014 of 3 March 2014 amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F22Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/752 of 28 April 2017 amending and correcting Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F23Substituted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/1338 of 8 August 2019 amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
F24Inserted by Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/79 of 18 January 2018 amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance).
Textual Amendments
F1Word in Annex 1 point 1 omitted (31.12.2020) by virtue of The Materials and Articles in Contact with Food (Amendment) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/704), regs. 1, 76; 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
2.Group restriction of substancesU.K.
Table 2 on Group restrictions contains the following information:
Column 1 (Group restriction No): contains the identification number of the group of substances for which the group restriction applies. It is the number referred to in Column 9 in Table 1 of this Annex.
Column 2 (FCM substance No): contains the unique identification numbers of the substances for which the group restriction applies. It is the number referred to in Column 1 in Table 1 of this Annex.
Column 3 (SML (T) [mg/kg]): contains the total specific migration limit for the sum of substances applicable to this group. It is expressed in mg substance per kg food. It is indicated ND if the substance shall not migrate in detectable quantities.
Column 4 (Group restriction specification): contains an indication of the substance whose molecular weight forms the basis for expression of the result.
Table 2
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
| Group Restriction No | FCM substance No | SML (T)[mg/kg] | Group restriction specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 128 211 | 6 | expressed as acetaldehyde |
| [F22 | 89 227 263 1048 | 30 | expressed as ethyleneglycol] |
| 3 | 234 248 | 30 | expressed as maleic acid |
| 4 | 212 435 | 15 | expressed as caprolactam |
| 5 | 137 472 | 3 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| 6 | 412 512 513 588 | 1 | expressed as iodine |
| 7 | 19 20 | 1,2 | expressed as tertiary amine |
| 8 | 317 318 319 359 431 464 | 6 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| 9 | 650 695 697 698 726 | 0,18 | expressed as tin |
| 10 | 28 29 30 31 32 33 466 582 618 619 620 646 676 736 | 0,006 | expressed as tin |
| 11 | 66 645 657 | 1,2 | expressed as tin |
| 12 | 444 469 470 | 30 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| 13 | 163 285 | 1,5 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| [F1314 | 294 | 5 | expressed as the sum of the substances and their oxidation products |
| 368 | |||
| 894] | |||
| [F1015 | 98 196 344 | 15 | expressed as formaldehyde] |
| 16 | 407 583 584 599 | 6 | expressed as boron Without prejudice to the provisions of Directive 98/83/EC |
| 17 | 4 167 169 198 274 354 372 460 461 475 476 485 490 653 | ND | expressed as isocyanate moiety |
| 18 | 705 733 | 0,05 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| 19 | 505 516 519 | 10 | expressed as SO2 |
| 20 | 290 386 390 | 30 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| 21 | 347 349 | 5 | expressed as trimellitic acid |
| 22 | 70 147 176 218 323 325 365 371 380 425 446 448 456 636 | 6 | expressed as acrylic acid |
| 23 | 150 156 181 183 184 355 370 374 439 440 447 457 482 | 6 | expressed as methacrylic acid |
| 24 | 756 758 | 5 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| 25 | 720 747 | 0,05 | sum of mono-n-dodecyltin tris(isooctylmercaptoacetate), di-n-dodecyltin bis(isooctyl mercaptoacetate), mono-dodecyltin trichloride and di-dodecyltin dichloride) expressed as the sum of mono- and di-dodecyltin chloride |
| 26 | 728 729 | 9 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| 27 | 188 291 | 5 | expressed as isophthalic acid |
| 28 | 191 192 785 | 7,5 | expressed as terephthalic acid |
| 29 | 342 672 | 0,05 | expressed as the sum of 6-hydroxyhexanoic acid and caprolactone |
| [F1030 | 254 344 672 | 5 | expressed as 1,4-butanediol] |
| 31 | 73 797 | 30 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| 32 | 8 72 73 138 140 157 159 207 242 283 532 670 728 729 775 783 797 798 810 815 | 60 | expressed as the sum of the substances |
| [F733 | 180 874 | ND | expressed as eugenol] |
| [F2134 | 421 988 | 0,05 | Expressed as 1,3-benzenedimethanamine] |
| [F2535 | 467 744 1059 | 0,05 | expressed as crotonic acid] |
3.Notes on verification of complianceU.K.
Table 3 on notes on verification of compliance contains the following information:
Column 1 (Note No): contains the identification number of the Note. It is the number referred to in Column 11 in Table 1 of this Annex.
Column 2 (Notes on verification of compliance): contains rules that shall be respected when testing for compliance of the substance with specific migration limits or other restrictions or it contains remarks on situations where there is a risk of non-compliance.
Table 3
| (1) | (2) |
| Note No | Notes on verification of compliance |
|---|---|
| (1) | Verification of compliance by residual content per food contact surface area (QMA) pending the availability of an analytical method. |
| (2) | There is a risk that the SML or OML could be exceeded in fatty food simulants. |
| (3) | There is a risk that the migration of the substance deteriorates the organoleptic characteristics of the food in contact and then, that the final product does not comply with Article 3(1) c of the Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. |
| [F11(4) | Compliance testing when there is a fat contact [F2shall] be performed using saturated fatty food simulants as simulant D2.] |
| (5) | Compliance testing when there is a fat contact [F2shall] be performed using isooctane as substitute of simulant D2 (unstable). |
| (6) | Migration limit might be exceeded at very high temperature. |
| (7) | If testing in food is performed, Annex V 1.4 shall be taken into account. |
| (8) | Verification of compliance by residual content per food contact surface area (QMA); QMA = 0,005 mg/6 dm2. |
| (9) | Verification of compliance by residual content per food contact surface area (QMA) pending the availability of analytical method for migration testing. The ratio surface to quantity of food shall be lower than 2dm2/kg. |
| (10) | Verification of compliance by residual content per food contact surface area (QMA) in case of reaction with food or simulant. |
| (11) | Only a method of analysis for the determination of the residual monomer in the treated filler is available. |
| (12) | There is a risk that the SML could be exceeded from polyolefins. |
| (13) | Only a method for determination of the content in polymer and a method for determination of the starting substances in food simulants are available. |
| (14) | There is a risk that the SML could be exceeded from plastics containing more than 0,5 % w/w of the substance. |
| (15) | There is a risk that the SML could be exceeded in contact with foods with high alcoholic content. |
| (16) | There is a risk that the SML could be exceeded from low-density polyethylene (LDPE) containing more than 0,3 % w/w of the substance when in contact with fatty foods |
| (17) | Only a method for determination of the residual content of the substance in the polymer is available |
| [F18(18) | There is a risk that the SML could be exceeded from low-density polyethylene (LDPE) |
| (19) | There is a risk that the OML could be exceeded in direct contact with aqueous foods from ethylvinylalcohol (EVOH) and polyvinylalcohol (PVOH) copolymers] |
| [F21(20) | The substance contains aniline as an impurity; verification of compliance with the restriction set for primary aromatic amines in Annex II (2) is necessary] |
| [F4(21) | In case of reaction with foods or simulants verification of compliance shall include verification that the migration limits of the hydrolysis products, formaldehyde and 1,4-butanediol, are not exceeded.] |
| [F20(22) | When used in contact with non-alcoholic foods for which Table 2 of Annex III assigns food simulant D1, food simulant C shall be used for verification of compliance instead of food simulant D1. |
| (23) | When a final material or article containing this substance is placed on the market, a well described method to determine whether the oligomer migration complies with the restrictions specified in column 10 of Table 1 shall form part of the supporting documentation referred to in Article 16. This method shall be suitable for use by a competent authority to verify compliance. If an adequate method is publicly available, reference shall be made to that method. If the method requires a calibration sample, a sufficient sample shall be supplied to the competent authority on its request.] |
| [F22(24) | The substance or its hydrolysis products are authorised food additives and compliance with Article 11(3) shall be verified.] |
| [F24(25) | When used as reheat agent in polyethylene terephthalate (PET) verification of compliance with the specific migration limit is not required; in all other cases compliance with the specific migration limit shall be verified in accordance with Article 18; the specific migration limit is expressed as mg tungsten/kg food. |
| (26) | Migration of stearamide, listed in Table 1 under FCM substance No 306 to which no specific migration limit applies, shall be excluded from verification of the compliance of the migration of the mixture with the specific migration limit laid down for the mixture.] |
| [F25(27) | When a final material or article containing this substance and produced under conditions other than those described in point (a) column 10 of Table 1 is placed on the market, a well described method to determine whether the oligomer migration complies with the restrictions specified in point (b) column 10 of Table 1 shall form part of the supporting documentation referred to in Article 16. This method shall be suitable for use by a competent authority to verify compliance. If an adequate method is publicly available, reference shall be made to that method. If the method requires a calibration sample, a sufficient sample shall be supplied to the competent authority on its request.] |
| [F26(28) | A detection limit of 0,002 mg/kg food or food simulant applies |
| (29) | In polar polymers which swell in contact with foods for which simulant B is assigned in Annex III, there is a risk that under severe contact conditions the migration limits for aluminium and fluoride are exceeded. Under contact conditions above 4 hours at 100 °C this exceedance can be high.] |
4.Detailed specification on substancesU.K.
Table 4 on detailed specifications on substances contains the following information
Column 1 (FCM substance No): contains the unique identification number of the substances referred to in Column 1 in Table 1 of Annex I to which the specification applies.
Column 2 (Detailed specification on the substance): contains the specification on the substance.
Table 4
| (1) | (2) | |
| FCM substance No | Detailed specification on the substance | |
|---|---|---|
| 744 | Definition | The copolymers are produced by the controlled fermentation of Alcaligenes eutrophus using mixtures of glucose and propanoic acid as carbon sources. The organism used has not been genetically engineered and has been derived from a single wildtype organism Alcaligenes eutrophus strain H16 NCIMB 10442. Master stocks of the organism are stored as freeze-dried ampoules. A submaster/working stock is prepared from the master stock and stored in liquid nitrogen and used to prepare inocula for the fermenter. Fermenter samples will be examined daily both microscopically and for any changes in colonial morphology on a variety of agars at different temperatures. The copolymers are isolated from heat treatment bacteria by controlled digestion of the other cellular components, washing and drying. These copolymers are normally offered as formulated, melt formed granules containing additives such as nucleating agents, plasticisers, fillers, stabilisers and pigments which all conform to the general and individual specifications |
| Chemical name | Poly(3-D-hydroxybutanoate-co-3-D-hydroxypentanoate) | |
| CAS number | 0080181-31-3 | |
| Structural formula | 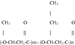 where n/(m + n) greater than 0 and less or equal to 0,25 | |
| Average molecular weight | Not less than 150 000 Daltons (measured by gel permeation chromatography) | |
| Assay | Not less than 98 % poly(3-D-hydroxybutanoate-co-3-D-hydoxy-pentanoate) analysed after hydrolysis as a mixture of 3-D-hydro-xybutanoic and 3-D-hydroxypentanoic acids | |
| Description | White to off-white powder after isolation | |
| Characteristics | ||
| Identification tests: | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chlorinated hydrocarbons such as chloroform or dichloromethane but practically insoluble in ethanol, aliphatic alkanes and water | |
| [F15Restriction | Specific migration limit for crotonic acid is 0,05 mg/kg food] | |
| Purity | Prior to granulation the raw material copolymer powder must contain: | |
| Not more than 2 500 mg/kg of plastic | |
| Not more than 100 mg/kg of plastic | |
| Not more than 5 mg/kg of plastic | |
| Not more than 2 mg/kg of plastic | |
| Not more than 1 mg/kg of plastic | |
| Not more than 1 mg/kg of plastic | |
[F12ANNEX II U.K. Restrictions on plastic materials and articles
The following restrictions on plastic materials and articles apply:
Plastic materials and articles shall not release the substances in Table 1 below in quantities exceeding the specific migration limits expressed in mg/kg food or simulant specified in column (3), and subject to the remarks in Column (4).
Substances listed in Table 1 shall only be used in accordance with the compositional requirements set out in Chapter II. If Chapter II does not provide a basis for the authorised use of such a substance, that substance may only be present as an impurity subject to the restrictions specified in Table 1.
| Table 1 | |||
| General list of migration limits for substances migrating from plastic materials and articles | |||
| ND: Not Detectable; detection limit assigned in accordance with second subparagraph of Article 11(4); LOD: specified Limit of Detection. | |||
| Remarks | |||
| (1) The migration is subject to Article 11(3) and Article 12 | |||
| (2) The note in Annex I, Table 1, FCM No 398 applies: SML might be exceeded at very high temperature | |||
| (3) To verify compliance with the Regulation, the detection limit of 0,01 mg/kg shall apply for total chromium. However if the operator that placed the material on the market can prove on the basis of pre-existing documentary evidence that the presence of hexavalent chromium in the material is excluded because it is not used or formed or during the entire production process, a limit for the total chromium of 3,6 mg/kg food shall apply. | |||
| (4) The lanthanide substances europium, gadolinium, lanthanum, and/or terbium can be used in accordance with Article 6(3)(a) provided that: (a) The sum of all lanthanide substances migrating to the food or food simulant does not exceed the specific migration limit of 0,05 mg/kg; and (b) analytical evidence using a well described methodology demonstrating that the lanthanide substance(s) used are present in dissociated ionic form in the food or the food simulant, forms part of the documentation referred to in Article 16. | |||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Salts allowed in accordance with Article 6(3)(a) | SML [mg/kg food or food simulant] | Remark |
| Aluminium | yes | 1 | |
| Ammonium | yes | - | (1) |
| Antimony | no | 0,04 | (2) |
| Arsenic | no | ND | |
| Barium | yes | 1 | |
| Cadmium | no | ND (LOD 0,002) | |
| Calcium | yes | - | (1) |
| Chromium | no | ND | (3) |
| Cobalt | yes | 0,05 | |
| Copper | yes | 5 | |
| Europium | yes | 0,05 | (4) |
| Gadolinium | yes | 0,05 | (4) |
| Iron | yes | 48 | |
| Lanthanum | yes | 0,05 | (4) |
| Lead | no | ND | |
| Lithium | yes | 0,6 | |
| Magnesium | yes | - | (1) |
| Manganese | yes | 0,6 | |
| Mercury | no | ND | |
| Nickel | no | 0,02 | |
| Potassium | yes | - | (1) |
| Sodium | yes | - | (1) |
| Terbium | yes | 0,05 | (4) |
| Zinc | yes | 5 | |
Primary aromatic amines (‘PAAs’) listed in entry 43 to Appendix 8 of Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council (1) and for which no migration limit is specified in Table 1 of Annex I shall not migrate or shall not otherwise be released from plastic materials and articles into food or food simulant. They shall not be detectable using analytical equipment with a limit of detection of 0,002 mg/kg food or food simulant applied to each individual primary aromatic amine (‘PAA’), in accordance with Article 11(4).
For PAAs not listed in entry 43 to Appendix 8 of Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006, but for which no specific migration limit is specified in Annex I, compliance with Article 3 of Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 shall be verified in accordance with Article 19. The sum of those PAAs shall however not exceed 0,01 mg/kg in food or food simulant.]
ANNEX IIIU.K.Food simulants
1.Food simulantsU.K.
For demonstration of compliance for plastic materials and articles not yet in contact with food the food simulants listed in Table 1 below are assigned.
[F2Table 1
List of food simulants
| Food simulant | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Ethanol 10 % (v/v) | Food simulant A |
| Acetic acid 3 % (w/v) | Food simulant B |
| Ethanol 20 % (v/v) | Food simulant C |
| Ethanol 50 % (v/v) | Food simulant D1 |
| Any vegetable oil containing less than 1 % unsaponifiable matter | Food simulant D2 |
| poly(2,6-diphenyl-p-phenylene oxide), particle size 60-80 mesh, pore size 200 nm | Food simulant E] |
2.General assignment of food simulants to foodsU.K.
Food simulants A, B and C are assigned for foods that have a hydrophilic character and are able to extract hydrophilic substances. Food simulant B shall be used for those foods which have a pH below 4.5. Food simulant C shall be used for alcoholic foods with an alcohol content of up to 20 % and those foods which contain a relevant amount of organic ingredients that render the food more lipophilic.
Food simulants D1 and D2 are assigned for foods that have a lipophilic character and are able to extract lipophilic substances. Food simulant D1 shall be used for alcoholic foods with an alcohol content of above 20 % and for oil in water emulsions. Food simulant D2 shall be used for foods which contain free fats at the surface.
Food simulant E is assigned for testing specific migration into dry foods.
[F23. Specific assignment of food simulants to foods for migration testing of materials and articles not yet in contact with food U.K.
For testing migration from materials and articles not yet in contact with food the food simulants that corresponds to a certain food category shall be chosen according to Table 2 below.
For testing migration from materials and articles intended to come into contact with foods not listed in Table 2 below, or a combination of foods, the general food simulant assignments in point 2 shall be used for specific migration testing, and for overall migration testing the food simulant assignments in point 4 shall be applicable.
Table 2 contains the following information:
Column 1 (Reference number): contains the reference number of the food category
Column 2 (Description of food): contains a description of the foods covered by the food category
Column 3 (Food simulants): contains sub-columns for each of the food simulants
The food simulant for which a cross is contained in the respective sub-column of column 3 shall be used when testing migration of materials and articles not yet in contact with food.
For food categories where in sub-column D2 or E the cross is followed by an oblique stroke and a figure, the migration test result shall be corrected by dividing the result by this figure. The corrected test result shall then be compared to the migration limit to establish compliance. The test results for substances that shall not migrate in detectable quantities shall not be corrected in this way.
For food category 01.04 food simulant D2 shall be replaced by 95 % ethanol.
For food categories where in sub-column B the cross is followed by (*) the testing in food simulant B can be omitted if the food has a pH of more than 4,5.
For food categories where in sub-column D2 the cross is followed by (**) the testing in food simulant D2 can be omitted if it can be demonstrated that there is no ‘ fatty contact ’ with the plastic food contact material.]
Table 2
food category specific assignment of food simulants
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference number | Description of food | Food simulants | |||||
| A | B | C | D1 | D2 | E | ||
| 01 | Beverages | ||||||
| 01.01 | Non-alcoholic beverages or alcoholic beverages of an alcoholic strength lower than or equal to 6 % vol.: | ||||||
A.Clear drinks:Water, ciders, clear fruit or vegetable juices of normal strength or concentrated, fruit nectars, lemonades, syrups, bitters, infusions, coffee, tea, beers, soft drinks, energy drinks and the like, flavoured water, liquid coffee extract | X(*) | X | |||||
B.cloudy drinks:juices and nectars and soft drinks containing fruit pulp, musts containing fruit pulp, liquid chocolate | X(*) | X | |||||
| 01.02 | Alcoholic beverages of an alcoholic strength of between 6 %vol and 20 %. | X | |||||
| 01.03 | Alcoholic beverages of an alcoholic strength above 20 % and all cream liquors | X | |||||
| 01.04 | Miscellaneous: undenaturated ethyl alcohol | X(*) | Substitute 95 % ethanol | ||||
| 02 | Cereals, cereal products, pastry, biscuits, cakes and other bakers’ wares | ||||||
| 02.01 | Starches | X | |||||
| 02.02 | Cereals, unprocessed, puffed, in flakes (including popcorn, corn flakes and the like) | X | |||||
| 02.03 | Cereal flour and meal | X | |||||
| 02.04 | Dry pasta e.g. macaroni, spaghetti and similar products and fresh pasta | X | |||||
| 02.05 | Pastry, biscuits, cakes, bread, and other bakers’ wares, dry: | ||||||
A.With fatty substances on the surface | X/3 | ||||||
B.Other | X | ||||||
| 02.06 | Pastry, cakes, bread, dough and other bakers’ wares, fresh: | ||||||
A.With fatty substances on the surface | X/3 | ||||||
B.Other | X | ||||||
| 03 | Chocolate, sugar and products thereof Confectionery products | ||||||
| 03.01 | Chocolate, chocolate-coated products, substitutes and products coated with substitutes | X/3 | |||||
| 03.02 | Confectionery products: | ||||||
A.In solid form: | |||||||
I.With fatty substances on the surface | X/3 | ||||||
II.Other | X | ||||||
B.In paste form: | |||||||
I.With fatty substances on the surface | X/2 | ||||||
II.Moist | X | ||||||
| 03.03 | Sugar and sugar products | ||||||
A.In solid form: crystal or powder | X | ||||||
B.Molasses, sugar syrups, honey and the like | X | ||||||
| 04 | Fruit, vegetables and products thereof | ||||||
| [F204.01 | Fruit, fresh or chilled: | ||||||
A. unpeeled and uncut | X/10 | ||||||
B. peeled and/or cut | X | X (*) | ] | ||||
| 04.02 | Processed fruit: | ||||||
A.Dried or dehydrated fruits, whole, sliced, flour or powder | X | ||||||
B.Fruit in the form of purée, preserves, pastes or in its own juice or in sugar syrup (jams, compote, and similar products) | X(*) | X | |||||
C.Fruit preserved in a liquid medium: | |||||||
I.In an oily medium | X | ||||||
II.In an alcoholic medium | X | ||||||
| 04.03 | Nuts (peanuts, chestnuts, almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, pine kernels and others): | ||||||
A.Shelled, dried, flaked or powdered | X | ||||||
B.Shelled and roasted | X | ||||||
C.In paste or cream form | X | X | |||||
| [F204.04 | Vegetables, fresh or chilled: | ||||||
A. unpeeled and uncut | X/10 | ||||||
B. peeled and/or cut | X | X (*) | ] | ||||
| [F204.05 | Processed vegetables: A. Dried or dehydrated vegetables whole, sliced or in the form of flour or powder. | X | |||||
B. ( obsolete ) | |||||||
C. Vegetables in the form of purée, preserves, pastes or in its own juice (including pickled and in brine). | X (*) | X | |||||
D. Preserved vegetables: | |||||||
I. In an oily medium | X | X | |||||
II. In an alcoholic medium | X | ] | |||||
| 05 | Fats and oils | ||||||
| 05.01 | Animals and vegetable fats and oils, whether natural or treated (including cocoa butter, lard, resolidified butter) | X | |||||
| 05.02 | Margarine, butter and other fats and oils made from water emulsions in oil | X/2 | |||||
| 06 | Animal products and eggs | ||||||
| 06.01 | Fish: | ||||||
A.Fresh, chilled, processed, salted or smoked including fish eggs | X | X/3(**) | |||||
B.Preserved fish: | |||||||
I.In an oily medium | X | X | |||||
II.In an aqueous medium | X(*) | X | |||||
| 06.02 | Crustaceans and molluscs (including oysters, mussels, snails) | ||||||
A.Fresh within the shell | |||||||
B.Shell removed, processed, preserved or cooked with the shell | |||||||
I.In an oily medium | X | X | |||||
II.In an aqueous medium | X(*) | X | |||||
| 06.03 | Meat of all zoological species (including poultry and game): | ||||||
A.Fresh, chilled, salted, smoked | X | X/4(**) | |||||
B.Processed meat products (such as ham, salami, bacon, sausages, and other) or in the form of paste, creams | X | X/4(**) | |||||
C.Marinated meat products in an oily medium | X | X | |||||
| 06.04 | Preserved meat: | ||||||
A.In an fatty or oily medium | X | X/3 | |||||
B.In an aqueous medium | X(*) | X | |||||
| 06.05 | Whole eggs, egg yolk, egg white | ||||||
A.Powdered or dried or frozen | X | ||||||
B.Liquid and cooked | X | ||||||
| 07 | Milk products | ||||||
| 07.01 | Milk | ||||||
A.Milk and milk based drinks whole, partly dried and skimmed or partly skimmed | X | ||||||
B.Milk powder including infant formula (based on whole milk powder) | X | ||||||
| 07.02 | Fermented milk such as yoghurt, buttermilk and similar products | X(*) | X | ||||
| 07.03 | Cream and sour cream | X(*) | X | ||||
| 07.04 | Cheeses: | ||||||
A.Whole, with not edible rind | X | ||||||
B.Natural cheese without rind or with edible rind (gouda, camembert, and the like) and melting cheese | X/3(**) | ||||||
C.Processed cheese (soft cheese, cottage cheese and similar) | X(*) | X | |||||
D.Preserved cheese: | |||||||
I.In an oily medium | X | X | |||||
II.In an aqueous medium (feta, mozarella, and similar) | X(*) | X | |||||
| 08 | Miscellaneous products | ||||||
| 08.01 | Vinegar | X | |||||
| 08.02 | Fried or roasted foods: | ||||||
A.Fried potatoes, fritters and the like | X | X/5 | |||||
B.Of animal origin | X | X/4 | |||||
| 08.03 | Preparations for soups, broths, sauces, in liquid, solid or powder form (extracts, concentrates); homogenised composite food preparations, prepared dishes including yeast and raising agents | ||||||
A.Powdered or dried: | |||||||
I.With fatty character | X/5 | ||||||
II.Other | X | ||||||
B.any other form than powdered or dried: | |||||||
I.With fatty character | X | X(*) | X/3 | ||||
II.Other | X(*) | X | |||||
| 08.04 | Sauces: | ||||||
A.With aqueous character | X(*) | X | |||||
B.With fatty character e.g. mayonnaise, sauces derived from mayonnaise, salad creams and other oil/water mixtures e.g. coconut based sauces | X | X(*) | X | ||||
| 08.05 | Mustard (except powdered mustard under heading 08.14) | X | X(*) | X/3(**) | |||
| 08.06 | Sandwiches, toasted bread pizza and the like containing any kind of foodstuff | ||||||
A.With fatty substances on the surface | X | X/5 | |||||
B.Other | X | ||||||
| 08.07 | Ice-creams | X | |||||
| 08.08 | Dried foods: | ||||||
A.With fatty substances on the surface | X/5 | ||||||
B.Other | X | ||||||
| 08.09 | Frozen or deep-frozen foods | X | |||||
| 08.10 | Concentrated extracts of an alcoholic strength equal to or exceeding 6 % vol. | X(*) | X | ||||
| 08.11 | Cocoa: | ||||||
A.Cocoa powder, including fat-reduced and highly fat reduced | X | ||||||
B.Cocoa paste | X/3 | ||||||
| 08.12 | Coffee, whether or not roasted, decaffeinated or soluble, coffee substitutes, granulated or powdered | X | |||||
| 08.13 | Aromatic herbs and other herbs such as camomile, mallow, mint, tea, lime blossom and others | X | |||||
| 08.14 | Spices and seasonings in the natural state such as cinnamon, cloves, powdered mustard, pepper, vanilla, saffron, salt and other | X | |||||
| 08.15 | Spices and seasoning in oily medium such as pesto, curry paste | X | |||||
[F274. Food simulant assignment for testing overall migration U.K.
For tests to demonstrate compliance with the overall migration limit food simulants shall be chosen as set out in Table 3:
Table 3
Food simulant assignment for demonstrating compliance with the overall migration limit
| Foods covered | Food simulants in which testing shall be performed |
|---|---|
| all types of food | 1. distilled water or water of equivalent quality or food simulant A;2. food simulant B; and3. food simulant D2. |
| all types of food except for acidic foods | 1. distilled water or water of equivalent quality or food simulant A; and2. food simulant D2. |
| [F15all aqueous and alcoholic foods and milk products with a pH ≥ 4,5 | food simulant D1 |
| all aqueous and alcoholic foods and milk products with a pH < 4,5 | food simulant D1 and food simulant B] |
| all aqueous foods and alcoholic foods up to an alcohol content of 20 % | food simulant C |
| all aqueous and acidic foods and alcoholic foods up to an alcohol content of 20 % | 1. food simulant C; and2. food simulant B.] |
Textual Amendments
[F205. General derogation to the assignment of food simulants U.K.
By derogation from the assignments of food simulants in points 2 to 4 of this Annex, where testing with several food simulants is required, a single food simulant shall be sufficient if on the basis of evidence acquired using generally recognised scientific methods this food simulant is shown to be the most severe food simulant for the particular material or article being tested under the applicable time and temperature conditions selected in accordance with Chapters 2 and 3 of Annex V.
The scientific basis on which this derogation is used shall in such cases form part of the documentation required under Article 16 of this Regulation.]
ANNEX IVU.K.Declaration of compliance
The written declaration referred to in Article 15 shall contain the following information:
the identity and address of the business operator issuing the declaration of compliance;
the identity and address of the business operator which manufactures or imports the plastic materials or articles or products from intermediate stages of their manufacturing or the substances intended for the manufacturing of those materials and articles;
the identity of the materials, the articles, products from intermediate stages of manufacture or the substances intended for the manufacturing of those materials and articles;
the date of the declaration;
[F2confirmation that the plastic materials or articles, products from intermediate stages of manufacture or the substances meet the relevant requirements laid down in this Regulation and in Article 3, 11(5), 15 and 17 of Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004;]
[F12adequate information relative to the substances used or products of degradation thereof for which restrictions and/or specifications are set out in Annex I and II to the Regulation to allow the downstream business operators to ensure compliance with the Regulation.
At intermediate stages, this information shall include the identification and amount of substances in the intermediate material,
that are subject to restrictions in Annex II, or
for which genotoxicity has not been ruled out, and which originate from an intentional use during a manufacturing stage of that intermediate material and which could be present in an amount that foreseeably gives rise to a migration from the final material exceeding 0,00015 mg/kg food or food simulant;]
adequate information relative to the substances which are subject to a restriction in food, obtained by experimental data or theoretical calculation about the level of their specific migration and, where appropriate, purity criteria in accordance with Directives 2008/60/EC, 95/45/EC and 2008/84/EC to enable the user of these materials or articles to comply with the F28... provisions applicable to food;
specifications on the use of the material or article, such as:
type or types of food with which it is intended to be put in contact;
time and temperature of treatment and storage in contact with the food;
[F27the highest food contact surface area to volume ratio for which compliance has been verified in accordance with Article 17 and 18 or equivalent information;]
when a functional barrier is used in a multi-layer material or article, the confirmation that the material or article complies with the requirements of Article 13(2), (3) and (4) or Article 14(2) and (3) of this Regulation.
Textual Amendments
F28Words in Annex 4 para. 7 omitted (31.12.2020) by virtue of The Materials and Articles in Contact with Food (Amendment) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (S.I. 2019/704), regs. 1, 77; 2020 c. 1, Sch. 5 para. 1(1)
ANNEX VU.K.COMPLIANCE TESTING
For testing compliance of migration from plastic food contact materials and articles the following general rules apply.U.K.
CHAPTER 1U.K.Testing for specific migration of materials and articles already in contact with food
1.1.Sample preparationU.K.
The material or article shall be stored as indicated on the packaging label or under conditions adequate for the packaged food if no instructions are given. The food shall be removed from contact with the material or article before its expiration date or any date by which the manufacturer has indicated the product should be used for reasons of quality or safety.
1.2.Conditions of testingU.K.
The food shall be treated in accordance with the cooking instructions on the package if the food is to be cooked in the package. Parts of the food which are not intended to be eaten shall be removed and discarded. The remainder shall be homogenised and analysed for migration. The analytical results shall always be expressed on the basis of the food mass that is intended to be eaten, in contact with the food contact material.
1.3.Analysis of migrated substancesU.K.
The specific migration is analysed in the food using an analytical method in accordance with the requirements of Article 11 of Regulation (EC) No 882/2004.
[F21.4. Account of substances originating from other sources U.K.
In case there is evidence linked to the food sample that a substance partially or wholly originates from a source or sources other than the material or article for which the test is being carried out, the test results shall be corrected for the amount of that substance originating from the other source or sources before comparing the test results to the applicable specific migration limit.]
CHAPTER 2U.K.Testing for specific migration of materials and articles not yet in contact with food
2.1.Verification methodU.K.
Verification of compliance of migration into foods with the migration limits shall be carried out under the most extreme conditions of time and temperature foreseeable in actual use taking into account paragraphs 1.4, 2.1.1, 2.1.6 and 2.1.7.U.K.
Verification of compliance of migration into food simulants with the migration limits shall be carried out using conventional migration tests according to the rules set out in paragraphs 2.1.1 to 2.1.7.
2.1.1.Sample preparationU.K.
The material or article shall be treated as described by accompanying instructions or by provisions given in the declaration of compliance.
Migration is determined on the material or article or, if this is impractical, on a specimen taken from the material or article, or a specimen representative of this material or article. For each food simulant or food type, a new test specimen is used. Only those parts of the sample which are intended to come into contact with foods in actual use shall be placed in contact with the food simulant or the food.
2.1.2.Choice of food simulantU.K.
Materials and articles intended for contact with all types of food shall be tested with food simulant A, B and D2. However, if substances that may react with acidic food simulant or foods are not present testing in food simulant B can be omitted.
Materials and articles intended only for specific types of foods shall be tested with the food simulants indicated for the food types in Annex III.
2.1.3.Conditions of contact when using food simulantsU.K.
[F2The sample shall be placed in contact with the food simulant in a manner representing the worst of the foreseeable conditions of use as regard contact time in Table 1 and as regard contact temperature in Table 2.
By way of derogation to the conditions set out in Tables 1 and 2, the following rules apply:
If it is found that carrying out the tests under the combination of contact conditions specified in Tables 1 and 2 causes physical or other changes in the test specimen which do not occur under worst foreseeable conditions of use of the material or article under examination, the migration tests shall be carried out under the worst foreseeable conditions of use in which these physical or other changes do not take place;
if the material or article during it intended use is subjected only to precisely controlled time and temperature conditions in food processing equipment, either as part of food packaging or as part of the processing equipment itself, testing may be done using the worst foreseeable contact conditions that can occur during the processing of the food in that equipment;
if the material or article is intended to be employed only for hot-fill conditions, only a 2-hour test at 70 °C shall be carried out. However, if the material or article is intended to be used also for storage at room temperature or below, the test conditions set out in Tables 1 and 2 of this Section or in Section 2.1.4 of this Chapter apply depending on the duration of storage.
[F26if the plastic material or article intended to come into contact with food of which the compliance must be verified becomes in its final application part of a food processing equipment or an appliance, or a part thereof, the migration tests may be carried out by determining the specific migration into the food or food simulant produced or processed by the whole equipment or appliance, or the part thereof, as appropriate, subject to the following conditions:
the food or food simulant is processed during testing by the equipment or part thereof in accordance with the worst foreseeable conditions that can be achieved if the equipment or its part is operated in accordance with its operating instructions, and
the migration from parts used for storage such as from reservoirs, containers, or capsules or pads which are part of the equipment during the processing of the food, is determined using conditions representative for their use, unless the applied testing conditions for the whole tested equipment or appliance are representative also of their use.
When migration testing is done under the above conditions, and the transfer of constituents from the equipment or appliance as a whole does not exceed the migration limits, the plastic parts or materials present in the equipment or appliance shall be considered to comply with Article 11(1).
The testing of the parts used for storage or supply such as reservoirs, containers, capsules or pads shall be under conditions representative of their use, and shall include the foreseeable storage conditions of the food in these parts.
The supporting documentation referred to in Article 16 shall clearly document the testing on the whole food processing and/or food producing equipment or appliance, or on parts thereof. It shall demonstrate that the testing was representative of its foreseeable use, and shall indicate for which substances migration testing was carried out and provide all testing results. The manufacturer of individual plastic parts shall ensure the absence of migration for substances for which the Regulation specifies that their migration shall not be detectable at a specified level of detection in accordance with Article 11(4).
Compliance documentation supplied in accordance with the Regulation to the producer of the final equipment or appliance, or part thereof, shall list all substances subject to migration limits that might be exceeded under the foreseeable use of the supplied part or material.
When the result is not in compliance with the Regulation it shall be determined whether the source of the non-compliance is a plastic part subject to the Regulation or a part made from another material not subject to the Regulation on the basis of documentary evidence or analytical testing. Without prejudice to Article 3 of Regulation (EU) No 1935/2004, non-compliance to the Regulation shall only be established if the migration originates from a plastic part.]
If the testing conditions representative for the worst foreseeable conditions of intended use of the material or article, are not technically feasible in food simulant D2, migration tests shall be done using ethanol 95 % and isooctane. In addition a migration test shall be done using food simulant E if the temperature under the worst foreseeable conditions of intended use exceeds 100 °C. The test that results in the highest specific migration shall be used to establish compliance with this Regulation.]
Table 1
[F2Selection of test time]
| Contact time in worst foreseeable use | [F2Time to be selected for testing] |
|---|---|
| t ≤ 5 min | 5 min |
| 5 min < t ≤ 0,5 hour | 0,5 hour |
| 0,5 hours < t ≤ 1 hour | 1 hour |
| 1 hour < t ≤ 2 hours | 2 hours |
| 2 hours < t ≤ 6 hours | 6 hours |
| 6 hours < t ≤ 24 hours | 24 hours |
| 1 day < t ≤ 3 days | 3 days |
| 3 days < t ≤ 30 days | 10 days |
| Above 30 days | See specific conditions |
[F2Table 2
Selection of test temperature
| a This temperature shall be used only for food simulants D2 and E. For applications heated under pressure, migration testing under pressure at the relevant temperature may be performed. For food simulants A, B, C or D1 the test may be replaced by a test at 100 °C or at reflux temperature for duration of four times the time selected according to the conditions in Table 1.] | |
| Worst foreseeable contact temperature | Contact temperature to be selected for testing |
|---|---|
| T ≤ 5 °C | 5 °C |
| 5 °C < T ≤ 20 °C | 20 °C |
| 20 °C < T ≤ 40 °C | 40 °C |
| 40 °C < T ≤ 70 °C | 70 °C |
| 70 °C < T ≤ 100 °C | 100 °C or reflux temperature |
| 100 °C < T ≤ 121 °C | 121 °C a |
| 121 °C < T ≤ 130 °C | 130 °C a |
| 130 °C < T ≤ 150 °C | 150 °C a |
| 150 °C < T < 175 °C | 175 °C a |
| 175 °C < T ≤ 200 °C | 200 °C a |
| T > 200 °C | 225 °C a |
[F22.1.4. Specific conditions for contact times above 30 days at room temperature and below U.K.
For contact times above 30 days (long term) at room temperature and below, the specimen shall be tested in accelerated test conditions at elevated temperature for a maximum of 10 days at 60 °C (2) .
Testing for 10 days at 20 °C shall cover all storage times at frozen condition. This test can include the freezing and defrosting processes if labelling or other instructions ensure that 20 °C is not exceeded and the total time above – 15 °C does not exceed 1 day in total during the foreseeable intended use of the material or article.
Testing for 10 days at 40 °C shall cover all storage times at refrigerated and frozen conditions including hot-fill conditions and/or heating up to 70 °C ≤ T ≤ 100 °C for maximum t = 120/2^((T-70)/10) minutes.
Testing for 10 days at 50 °C shall cover all storage times of up to 6 months at room temperature, including hot-fill conditions and/or heating up to 70 °C ≤ T ≤ 100 °C for maximum t = 120/2^((T-70)/10) minutes.
Testing for 10 days at 60 °C shall cover storage above 6 months at room temperature and below, including hot-fill conditions and/or heating up to 70 °C ≤ T ≤ 100 °C for maximum t = 120/2^((T-70)/10) minutes.
For storage at room temperature the testing conditions can be reduced to 10 days at 40 °C if it is shown by scientific evidence that migration of the respective substance in the polymer has reached equilibration under this test condition.
For worst foreseeable conditions of intended use not covered by the test conditions set out in points (a) to (e), the testing time and temperature conditions shall be based on the following formula:
t2 = t1 * Exp (9627 * (1/T2 – 1/T1))
t1 is the contact time
t2 is the testing time
T1 is the contact temperature in Kelvin. For room temperature storage this is set at 298K (25 °C). For refrigerated conditions it is set at 278K (5 °C). For frozen storage it is set at 258 K (– 15 °C).
T2 is the testing temperature in Kelvin.]
2.1.5.Specific conditions for combinations of contact times and temperatureU.K.
[F2If a material or article is intended for different applications covering different combinations of contact time and temperature the testing shall be restricted to the test conditions which are recognised to be the most severe on the basis of scientific evidence.]
If the material or article is intended for a food contact application where it is successively subject to a combination of two or more times and temperatures, the migration test shall be carried out subjecting the test specimen successively to all the applicable worst foreseeable conditions appropriate to the sample, using the same portion of food simulant.
[F122.1.6. Repeated use materials and articles U.K.
If the material or article is intended to come into repeated contact with foods, the migration test(s) shall be carried out three times on a single sample using another portion of food simulant on each occasion. The specific migration in the second test shall not exceed the level observed in the first test, and the specific migration in the third test shall not exceed the level observed in the second test.
Compliance of the material or article shall than be verified on the basis of the level of the migration found in the third test and on the basis of the stability of the material or article from the first to the third migration test. The stability of the material shall be considered insufficient if migration is observed above the level of detection in any of the three migration tests, and increases from the first migration test to the third migration test. In case of insufficient stability, compliance of the material shall not be established even in case the specific migration limit is not exceeded in any of the three tests.
However, if there is conclusive scientific proof that the level of the migration decreases in the second and third tests and if the migration limits are not exceeded on the first test, no further test is necessary.
Irrespective of the above rules, a material or article shall never be considered to comply with this Regulation if in the first test a substance that is prohibited from migrating or from being released in detectable quantities under Article 11(4) is detected.]
2.1.7.Analysis of migrating substancesU.K.
At the end of the prescribed contact time, the specific migration is analysed in the food or food simulant using an analytical method in accordance with the requirements of Article 11 of Regulation (EC) No 882/2004.
2.1.8.Verification of compliance by residual content per food contact surface area (QMA)U.K.
For substances which are unstable in food simulant or food or for which no adequate analytical method is available it is indicated in Annex I that verification of compliance shall be undertaken by verification of residual content per 6 dm2 of contact surface. For materials and articles between 500 ml and 10 l the real contact surface is applied. For materials and articles below 500 ml and above 10 l as well as for articles for which it is impractical to calculate the real contact surface the contact surface is assumed to be 6 dm2 per kg food.
2.2.Screening approachesU.K.
[F2To screen if a material or article complies with the migration limits any of the following approaches can be applied which are considered at least as severe as the verification method described in section 2.1.] U.K.
2.2.1.Replacing specific migration by overall migrationU.K.
To screen for specific migration of non-volatile substances, determination of overall migration under test conditions at least as severe as for specific migration can be applied.
2.2.2.Residual contentU.K.
To screen for specific migration the migration potential can be calculated based on the residual content of the substance in the material or article assuming complete migration.
[F22.2.3. Migration modelling U.K.
To screen for specific migration, the migration potential can be calculated based on the residual content of the substance in the material or article applying generally recognised diffusion models based on scientific evidence that are constructed in a way that must never underestimate real levels of migration.]
[F22.2.4. Food simulant substitutes U.K.
To screen for specific migration, food simulants can be replaced by substitute food simulants if it is based on scientific evidence that the substitute food simulants result in migration that is at least as severe as migration that would be obtained using the food simulants specified in Section 2.1.2.]
[F202.2.5. Single test for successive combinations of time and temperature U.K.
If the material or article is intended for a food contact application where it is successively subject to two or more time and temperature combinations, a single migration contact test time can be defined based on the highest contact test temperature from Section 2.1.3 and/or 2.1.4 by using the equation as described in point (f) of Section 2.1.4. The reasoning justifying that the resulting single test is at least as severe as the combined time and temperature combinations shall be documented in the supporting documentation provided for in Article 16.]
CHAPTER 3U.K.Testing for overall migration
Overall migration testing shall be performed under the standardised testing conditions set out in this chapter.U.K.
3.1.Standardised testing conditionsU.K.
The overall migration test for materials and articles intended for the food contact conditions described in column 3 of Table 3 shall be performed for the time specified and at the temperature specified in column 2. For test OM5 the test can be performed either for 2 hours at 100 °C (food simulant D2) or at reflux (food simulant A, B, C, D1) or for 1 hour at 121 °C. The food simulant shall be chosen in accordance with Annex III.
If it is found that carrying out the tests under the contact conditions specified in Table 3 causes physical or other changes in the test specimen which do not occur under worst foreseeable conditions of use of the material or article under examination, the migration tests shall be carried out under the worst foreseeable conditions of use in which these physical or other changes do not take place.
[F12Table 3
Standardised conditions for testing the overall migration
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Test number | Contact time in days [d] or hours [h] at Contact temperature in [°C] for testing | Intended food contact conditions |
| OM0 | 30 min at 40 °C | Any food contact at cold or ambient temperatures and for a short duration (≤ 30 minutes). |
| OM1 | 10 d at 20 °C | Any food contact at frozen and refrigerated conditions |
| OM2 | 10 d at 40 °C | Any long-term storage at room temperature or below, including when packaged under hot-fill conditions, and/or heating up to a temperature T where 70 °C ≤ T ≤ 100 °C for a maximum of t = 120/2^((T-70)/10) minutes. |
| OM3 | 2 h at 70 °C | Any food contact conditions that include hot-fill and/or heating up to a temperature T where 70 °C ≤ T ≤ 100 °C for maximum of t = 120/2^((T-70)/10) minutes, which are not followed by long-term room temperature or refrigerated storage. |
| OM4 | 1 h at 100 °C or at reflux | High temperature applications for all types of food at temperature up to 100 °C. |
| OM5 | 2 h at 100 °C or at reflux or alternatively 1 h at 121 °C | High temperature applications up to 121 °C. |
| OM6 | 4 h at 100 °C or at reflux | Any food contact conditions at a temperature exceeding 40 °C, and with foods for which point 4 of Annex III assigns simulants A, B, C or D1. |
| OM7 | 2 h at 175 °C | High temperature applications with fatty foods exceeding the conditions of OM5. |
Test OM 7 covers also food contact conditions described for OM0, OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, OM5. It represents the worst case conditions for fatty food simulants in contact with non-polyolefins. In case it is technically not feasible to perform OM 7 with food simulant D2 the test can be replaced as set out in paragraph 3.2.
Test OM 6 covers also food contact conditions described for OM0, OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5. It represents worst case conditions for food simulants A, B and C in contact with non-polyolefins.
Test OM 5 covers also food contact conditions described for OM0, OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4. It represents the worst case conditions for all food simulants in contact with polyolefins.
Test OM 2 covers also food contact conditions described for OM0, OM1 and OM3.]
[F23.2. Substitute overall migration tests for tests with food simulant D2 U.K.
[F12If it is not technically feasible to perform one or more of the tests OM0 to OM6 in food simulant D2, migration tests shall be done using ethanol 95 % and isooctane. In addition a test shall be done using food simulant E in case the worst foreseeable conditions of use exceed 100 °C. The test that results in the highest overall migration shall be used to establish compliance with the Regulation.
In case it is technically not feasible to perform OM7 with food simulant D2, either test OM8 or test OM9 shall be selected as a replacement test by selecting the most appropriate of these two tests on the basis of the intended and the foreseeable use of the material or article that is being tested. Subsequently, a migration test shall be done at each of the two test conditions specified for the selected test, using a new test sample for each test condition. The test condition that results in the higher overall migration shall be used to establish compliance with the Regulation.]
| Test number | Test conditions | Intended food contact conditions | Covers the intended food contact conditions described in |
|---|---|---|---|
| OM8 | Food simulant E for 2 hours at 175 °C and food simulant D2 for 2 hours at 100 °C | High temperature applications only | OM1, OM3, OM4, OM5 and OM6 |
| OM9 | Food simulant E for 2 hours at 175 °C and food simulant D2 for 10 days at 40 °C | High temperature applications including long term storage at room temperature | OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, OM5 and OM6] |
[F23.3. Verification of compliance U.K.
3.3.1. Single use articles and materials U.K.
At the end of the prescribed contact time, to verify compliance the overall migration is analysed in the food simulant using an analytical method in accordance with the requirements of Article 11 of Regulation (EC) No 882/2004.
[F123.3.2. Repeated use articles and materials U.K.
The applicable overall migration test shall be carried out three times on a single sample using another portion of food simulant on each occasion. The migration shall be determined using an analytical method in accordance with the requirements of Article 34 of Regulation (EU) 2017/625 of the European Parliament and of the Council (3) . The overall migration in the second test shall be lower than in the first test, and the overall migration in the third test shall be lower than in the second test. Compliance with the overall migration limit shall be verified on the basis of the level of the overall migration found in the third test.
If it is not technically feasible to test the same sample three times, such as when testing in vegetable oil, the overall migration test can be carried out by testing different samples for three different periods of time lasting one, two and three times the applicable contact test time. The difference between the third and the second test results shall be considered to represent the overall migration. Compliance shall be verified on the basis of this difference, which shall not exceed the overall migration limit. In addition, the difference between the second and the first test results shall be lower than the first test results and the difference between the third and the second test results shall be lower than the difference between the second and the first test results.
By derogation from the first paragraph, if, on the basis of scientific evidence, it is established that for the material or article being tested the overall migration decreases in the second and third tests and if the overall migration limit is not exceeded in the first test, the first test alone shall be sufficient.] ]
3.4.Screening approachesU.K.
[F2To screen if a material or article complies with the migration limits, any of the following approaches can be applied which are considered at least as severe as the verification method described in Sections 3.1 and 3.2.] U.K.
3.4.1.Residual contentU.K.
To screen for overall migration the migration potential can be calculated based on the residual content of migratable substances determined in a complete extraction of the material or article.
[F23.4.2. Food simulant substitutes U.K.
To screen for overall migration, food simulants can be replaced if based on scientific evidence the substitute food simulants result in migration that is at least as severe as migration that would be obtained using the food simulants specified in Annex III.]
CHAPTER 4U.K.Correction factors applied when comparing migration test results with migration limits
4.1.Correction of specific migration in foods containing more than 20 % fat by the Fat Reduction Factor (FRF)U.K.
For lipophilic substances for which in Annex I it is indicated in column 7 that the FRF is applicable the specific migration can be corrected by the FRF. The FRF is determined according to the formula FRF = (g fat in food/kg of food)/200 = (% fat × 5)/100.
The FRF shall be applied according to the following rules.
The migration test results shall be divided by the FRF before comparing with the migration limits.
The correction by the FRF is not applicable in the following cases:
when the material or article is or is intended to be brought in contact with food intended for infants and young children as defined by Directives 2006/141/EC and 2006/125/EC;
for materials and articles for which it is impracticable to estimate the relationship between the surface area and the quantity of food in contact therewith, for example due to their shape or use, and the migration is calculated using the conventional surface area/volume conversion factor of 6 dm2/kg.
[F2The specific migration in food or food simulant shall not exceed 60 mg/kg food before application of the FRF.]
[F20When testing is performed in food simulant D2 or E and when the test results are corrected in application of the correction factor laid down in Table 2 of Annex III this correction may be applied in combination with the FRF by multiplying both factors. The combined correction factor shall not exceed 5, unless the correction factor laid down in Table 2 of Annex III exceeds 5.]
F34.2.Correction of migration into food simulant D2U.K.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
F34.3.Combination of correction factors 4.1 and 4.2.U.K.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ANNEX VIU.K.Correlation tables
| Directive 2002/72/EC | This Regulation |
|---|---|
| Article 1(1) | Article 1 |
| Article 1(2), (3) and (4) | Article 2 |
| Article 1a | Article 3 |
| Article 3(1), Article 4(1) and Article 5 | Article 5 |
| Article 4(2), Article 4a(1) and (4), Article 4d, Annex II (2) and (3) and Annex III (2) and (3) | Article 6 |
| Article 4a(3) and (6) | Article 7 |
| Annex II (4) and Annex III (4) | Article 8 |
| Article 3(1) and Article 4(1) | Article 9 |
| Article 6 | Article 10 |
| Article 5a(1) and Annex I (8) | Article 11 |
| Article 2 | Article 12 |
| Article 7a | Article 13 |
| Article 9(1) and (2) | Article 15 |
| Article 9(3) | Article 16 |
| Article 7 and Annex I (5a) | Article 17 |
| Article 8 | Article 18 |
| Annex II (3) and Annex III (3) | Article 19 |
| Annex I, Annex II, Annex IV, Annex IVa, Annex V Part B, and Annex VI | Annex I |
| Annex II (2), Annex III (2) and Annex V, Part A | Annex II |
| Article 8(5) and Annex VIa | Annex IV |
| Annex I | Annex V |
| Directive 93/8/EEC | This Regulation |
|---|---|
| Article 1 | Article 11 |
| Article 1 | Article 12 |
| Article 1 | Article 18 |
| Annex | Annex III |
| Annex | Annex V |
| Directive 97/48/EC | This Regulation |
|---|---|
| Annex | Annex III |
| Annex | Annex V |
[F12Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), establishing a European Chemicals Agency, amending Directive 1999/45/EC and repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 793/93 and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 as well as Council Directive 76/769/EEC and Commission Directives 91/155/EEC, 93/67/EEC, 93/105/EC and 2000/21/EC ( OJ L 396, 30.12.2006, p. 1 ).;]
[F2When testing at these accelerated test conditions the test specimen shall not undergo any physical or other changes compared to the real conditions of use, including a phase transition of the material.]
[F2 [F12Regulation (EU) 2017/625 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 March 2017 on official controls and other official activities performed to ensure the application of food and feed law, rules on animal health and welfare, plant health and plant protection products, amending Regulations (EC) No 999/2001, (EC) No 396/2005, (EC) No 1069/2009, (EC) No 1107/2009, (EU) No 1151/2012, (EU) No 652/2014, (EU) 2016/429 and (EU) 2016/2031 of the European Parliament and of the Council, Council Regulations (EC) No 1/2005 and (EC) No 1099/2009 and Council Directives 98/58/EC, 1999/74/EC, 2007/43/EC, 2008/119/EC and 2008/120/EC, and repealing Regulations (EC) No 854/2004 and (EC) No 882/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council, Council Directives 89/608/EEC, 89/662/EEC, 90/425/EEC, 91/496/EEC, 96/23/EC, 96/93/EC and 97/78/EC and Council Decision 92/438/EEC (Official Controls Regulation) ( OJ L 95, 7.4.2017, p. 1 ).] ]
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThe Annexes only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources
