- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (25/02/2011)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011Show full title
Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011 of 25 February 2011 implementing Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council laying down health rules as regards animal by-products and derived products not intended for human consumption and implementing Council Directive 97/78/EC as regards certain samples and items exempt from veterinary checks at the border under that Directive (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Regulations originating from the EU
- 2011 No. 142
- Whole Regulation
- Previous
- Next
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 08/12/20209.59 MB
- Revised 30/06/20209.58 MB
- Revised 23/06/20209.54 MB
- Revised 08/03/20209.54 MB
- Revised 14/12/20199.44 MB
- Revised 31/07/20199.44 MB
- Revised 16/07/20199.44 MB
- Revised 20/03/20199.75 MB
- Revised 02/08/201710.18 MB
- Revised 01/07/201710.16 MB
- Revised 29/05/20179.92 MB
- Revised 22/02/20179.91 MB
- Revised 23/02/20159.85 MB
- Revised 15/07/20149.35 MB
- Revised 19/03/20149.30 MB
- Revised 01/12/20138.38 MB
- Revised 01/07/20139.54 MB
- Revised 15/03/20139.53 MB
- Revised 14/12/20129.27 MB
- Revised 04/12/20129.27 MB
- Revised 19/08/20118.01 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Status:
Point in time view as at 25/02/2011.
Changes to legislation:
There are currently no known outstanding effects by UK legislation for Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Revised legislation carried on this site may not be fully up to date. At the current time any known changes or effects made by subsequent legislation have been applied to the text of the legislation you are viewing by the editorial team. Please see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’ for details regarding the timescales for which new effects are identified and recorded on this site.
Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011
of 25 February 2011
implementing Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council laying down health rules as regards animal by-products and derived products not intended for human consumption and implementing Council Directive 97/78/EC as regards certain samples and items exempt from veterinary checks at the border under that Directive
(Text with EEA relevance)
THE EUROPEAN COMMISSION,
Having regard to the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union,
Having regard to Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 laying down health rules as regards animal by-products and derived products not intended for human consumption and repealing Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002 (Animal by-products Regulation)(1), and in particular Articles 5(2) and 6(1)(b)(ii) and the second subparagraph of Article 6(1), the second subparagraph of Article 6(2), Article 11(2)(b) and (c) and the second subparagraph of Article 11(2), Article 15(1)(b), (d), (e), (h) and (i) and the second subparagraph of Article 15(1), Articles 17(2) and 18(3), Article 19(4)(a), (b) and (c) and the second subparagraph of Article 19(4), Article 20(10) and (11), Article 21(5) and (6), Articles 22(3) and 23(3), Article 27(a), (b), (c) and (e) to (h) and the second subparagraph of Article 27, Articles 31(2), 32(3), Article 40, the first and third subparagraph of Article 41(3), Article 42, Articles 43(3), 45(4), 47(2), Article 48(2), Article 48(7)(a) and (8)(a) and the second subparagraph of Article 48(8) thereof,
Having regard to Council Directive 97/78/EC of 18 December 1997 laying down the principles governing the organisation of veterinary checks on products entering the Community from third countries(2), and in particular Article 16(3) thereof,
Whereas:
(1) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 lays down animal and public health rules for animal by-products and products derived thereof. That Regulation determines the circumstances under which animal by-products are to be disposed of, in order to prevent the spreading of risks for public and animal health. In addition, that Regulation specifies under which conditions animal by-products may be used for applications in animal feed and for various purposes, such as in cosmetics, medicinal products and technical applications. It also lays down obligations for operators to handle animal by-products within establishments and plants which are subject to official controls.
(2) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 provides that detailed rules for the handling of animal by-products and derived products, such as processing standards, hygiene conditions and the format for documentary evidence which has to accompany consignments of animal by-products and derived products for the purposes of traceability are to be adopted by means of implementing measures.
(3) The detailed rules for the use and disposal of animal by-products in this Regulation should be laid down with a view to the achievement of the objectives of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, notably the sustainable use of animal materials, and a high level of protection of public and animal health in the European Union.
(4) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 does not apply to entire bodies or parts of wild animals, which are not suspected of being infected or affected with a disease communicable to humans or animals, except for aquatic animals landed for commercial purposes. In addition, it does not apply to entire bodies or parts of wild game which are not collected after killing, in accordance with good hunting practice. Regarding those animal by-products from hunting, disposal should be carried out in a way which prevents the transmission of risks, as appropriate for specific hunting practices and in accordance with the good practice as it has been described by the hunting profession.
(5) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 applies to animal by-products for the preparation of game trophies. The preparation of such trophies, as well as the preparations of animals and parts of animals for which other methods, such as plastination, are used, should take place under conditions which prevent the transmission of risks for human or animal health.
(6) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 applies to catering waste if it originates from means of transport operating internationally, such as materials derived from foodstuffs served on board an airplane or a ship arriving in the European Union from a third country destination. Catering waste also falls within the scope of that Regulation, if it is destined for feeding purposes, for processing in accordance with one of the authorised processing methods under this Regulation or for transformation into biogas or for composting. Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 prohibits the feeding of catering waste to farmed animals, other than fur animals. Therefore, in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, catering waste may be processed and subsequently used, provided that the derived product is not fed to such animals.
(7) For the sake of consistency of Union legislation, the definition of feed materials in Regulation (EC) No 767/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 July 2009 on the placing on the market and use of feed, amending European Parliament and Council Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003 and repealing Council Directive 79/373/EEC, Commission Directive 80/511/EEC, Council Directives 82/471/EEC, 83/228/EEC, 93/74/EEC, 93/113/EEC and 96/25/EC and Commission Decision 2004/217/EC(3) should be used as a basis for defining feed materials of animal origin in this Regulation.
(8) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 prohibits the dispatch of animal by-products and of derived products from susceptible species from holdings, establishments, plants or zones which are subject to restrictions due to the presence of a serious transmissible disease. In order to provide for a high level of protection of animal health in the Union, the list of diseases in the Terrestrial and Aquatic Animal Health Codes of the World Organisation of Animal Health (hereinafter referred to as ‘OIE’) should be specified as the list of serious transmissible diseases for the purpose of determining the scope of this prohibition.
(9) Since the incineration and the co-incineration of certain animal by-products do not fall within the scope of Directive 2000/76/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 December 2000 on the incineration of waste(4), adequate rules for the prevention of health risks arising from such operations should be laid down in this Regulation, taking into account the possible effects on the environment. Residues from the operation of the incineration or co-incineration of animal by-products or derived products should be recycled or disposed of, in accordance with Union environmental legislation, since in particular, that legislation allows for the use of the phosphorous component of ashes in fertilisers and for the handover of ashes from the cremation of pet animals to the owners.
(10) Products of animal origin or foodstuffs containing such products, should only be disposed of in a landfill, in accordance with Council Directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the landfill of waste(5), if they have been processed as defined in Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on the hygiene of foodstuffs(6), in order to mitigate potential health risks.
(11) The disposal of animal by-products or derived products via the wastewater stream should be prohibited, since that stream is not subject to requirements which would ensure an appropriate control of public and animal health risks. Appropriate measures should be taken to prevent unacceptable risks from accidental disposal of liquid animal by-products, such as from the cleaning of floors and equipments used for processing.
(12) Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on waste and repealing certain Directives(7) lays down certain measures to protect the environment and human health. Article 2(2)(b) of that Directive provides that certain matters are excluded from the scope of that Directive to the extent that they are covered by other Union legislation, including animal by-products covered by Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 3 October 2002 laying down health rules concerning animal by-products not intended for human consumption(8), except those which are destined for incineration, landfilling or use in a biogas or composting plant. That Regulation has now been repealed and replaced by Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 from 4 March 2011. In the interests of coherency of Union legislation, the processes whereby animal by-products and derived products are transformed into biogas and composted should comply with the health rules laid down in this Regulation, as well as the measures for the protection of the environment laid down in Directive 2008/98/EC.
(13) The competent authority of a Member State should be able to authorise alternative parameters for the transformation of animal by-products into biogas or for their composting on the basis of a validation according to a harmonised model. In that case, it should be possible to place digestion residues and compost on the market in the whole European Union. In addition, the competent authority of a Member State should be able to authorise certain parameters for specific animal by-products, such as catering waste and mixtures of catering waste with certain other materials, which are transformed into biogas or composted. Since such authorisations are not issued according to a harmonised model, digestion residues and compost should only be placed on the market within the Member State where the parameters have been authorised.
(14) In order to prevent the contamination of foodstuffs with pathogenic agents, establishments or plants processing animal by-products should operate on a separate site from slaughterhouses or other establishments in which foodstuffs are processed, in particular in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin(9), unless the processing of the animal by-products takes place under conditions which have been approved by the competent authority, with a view to preventing the transmission of risks to public and animal health into the food-processing establishments.
(15) Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 May 2001 laying down rules for the prevention, control and eradication of certain transmissible spongiform encephalopathies(10) provides that Member States are to carry out annual monitoring programmes for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs). Bodies of animals which are used for feeding to certain species, for the purposes of promotion of bio-diversity, should be included in those monitoring programmes to the extent necessary to ensure that those programmes provide sufficient information regarding the prevalence of TSE in a particular Member State.
(16) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 allows the feeding of certain Category 1 material to endangered or protected species of necrophagous birds and to other species living in their natural habitat, for the promotion of biodiversity. Such feeding should be authorised for certain carnivore species referred to in Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora(11) and for certain species of birds of prey referred to in Directive 2009/147/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on the conservation of wild birds(12), in order to take into account the natural feeding patterns of those species.
(17) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 has introduced a procedure for the authorisation of alternative methods of use or disposal of animal by-products or derived products. Such methods may be authorised by the Commission following receipt of an opinion from the European Food Safety Authority (hereinafter referred to as ‘EFSA’). In order to facilitate the evaluation of applications by EFSA, a standard format should be laid down which illustrates to applicants the nature of the evidence to be submitted. In accordance with the Treaties, it should be possible to submit applications for alternative methods in the official languages of the Union, as laid down in EEC Council Regulation No 1 determining the languages to the used by the European Economic Community(13).
(18) In accordance with Regulation (EC) No 183/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 January 2005 laying down requirements for feed hygiene(14), feed business operators, other than primary producers, are required to store and transport feed under certain hygienic conditions. Since those conditions provide for an equivalent mitigation of potential risks, compound feedingstuffs derived from animal by-products should not be subject to the requirements of this Regulation regarding storage and transport.
(19) For the promotion of science and research and to ensure the best possible use of animal by-products and of derived products in the diagnosis of human or animal diseases, the competent authority should be authorised to lay down conditions for samples of such materials for research, educational and diagnostic purposes. However, those conditions should not be laid down for samples of pathogenic agents for which special rules are provided in Council Directive 92/118/EEC of 17 December 1992 laying down animal health and public health requirements governing trade in and imports into the Community of products not subject to the said requirements laid down in specific Community rules referred to in Annex A (I) to Directive 89/662/EEC and, as regards pathogens, to Directive 90/425/EEC(15).
(20) Directive 97/78/EC exempts animal by-products which are intended for exhibitions, provided that they are not intended to be marketed, and animal by-products intended for particular studies or analyses from veterinary checks in the border inspection post of entry into the Union. That Directive allows for the adoption of implementing measures for those exemptions. In this Regulation, appropriate conditions should be set out for the import of animal by-products and derived products intended for exhibitions and particular studies or analyses, to ensure that no unacceptable risks to public or animal health are spread where such products enter the Union. In the interests of coherency of Union legislation, and in order to provide legal certainty to operators, those conditions and the implementing measures for Directive 97/78/EC should be laid down in this Regulation.
(21) Following collection, animal by-products should be handled under appropriate conditions which ensure that no unacceptable risks to public or animal health are transmitted. Establishments or plants in which certain operations are carried out before animal by-products are submitted to further processing should be constructed and should operate in a manner which prevents such transmission. This should include establishments or plants where operations involving the handling of animal by-products in accordance with Union veterinary legislation, other than the handling of animal by-products in the course of curative activities of private veterinarians, are carried out.
(22) Pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, operators are to ensure that animal by-products and derived products are traceable at all stages of the chain of manufacturing, use and disposal, so as to avoid unnecessary disruptions of the internal market in the case of events which are linked to actual or potential risks to public or animal health. Traceability should therefore not only be ensured by operators generating, collecting or transporting animal by-products, but also by operators disposing of animal by-products or derived products, by incineration, co-incineration or landfilling.
(23) Containers and means of transport which are used for animal by-products or derived products should be maintained in a clean state, so as to prevent contamination. When they are dedicated to the transport of a particular material, such as a liquid animal by-product which does not pose an unacceptable health risk, operators may adjust their measures to ensure the prevention of contamination to the actual risk arising from that material.
(24) Member States should be authorised to require operators to use the integrated computerised veterinary system (Traces) introduced by Commission Decision 2004/292/EC of 30 March 2004 on the introduction of the Traces system and amending Decision 92/486/EEC(16) (hereinafter referred to as ‘the TRACES system’) in order to provide proof for the arrival of consignments of animal by-products or derived products at the place of destination. Alternatively, proof for the arrival of consignments should be provided by way of a fourth copy of the commercial document, which is returned to the producer. The experience with the two alternatives should be evaluated after the first year of implementation of this Regulation.
(25) Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 specifies certain parameters for the treatment of rendered fats, fish oil and egg products which provide an adequate control of possible health risks, when such products are used for purposes other than human consumption. Those parameters should therefore be authorised as alternatives to the treatments for animal by-products which are set out in this Regulation.
(26) Colostrum and colostrum products should originate from bovine herds which are free of certain diseases as referred to in Council Directive 64/432/EEC of 26 June 1964 on animal health problems affecting intra-Community trade in bovine animals and swine(17).
(27) The references to Council Directive 76/768/EEC of 27 July 1976 on the approximation of laws of the Member States relating to cosmetic products(18), to Council Directive 96/22/EC of 29 April 1996 concerning the prohibition on the use in stockfarming of certain substances having a hormonal or thyrostatic action and of beta-agonists(19), to Council Directive 96/23/EC of 29 April 1996 on measures to monitor certain substances and residues thereof in live animals and animal products(20) should be updated and the reference to Council Directive 2009/158/EC of 30 November 2009 on animal health conditions governing intra-Community trade in, and imports from third countries of, poultry and hatching eggs(21) in the health rules for the trade in unprocessed manure should be updated.
(28) Certain imported materials for the production of petfood should be handled and used under conditions which are appropriate to the risk which such materials may pose. In particular, provision should be made for their safe channelling to establishments or plants of destination where such materials, as well as Category 3 material, are incorporated into petfood. With respect to the establishments or plants of destination, the competent authority should be authorised to allow the storage of imported materials together with Category 3 material, provided the imported materials can be traced.
(29) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 refers to certain derived products which may be placed on the market in accordance with conditions laid down in certain other Union legislation. That legislation also lays down conditions for the import, collection and movement of animal by-products and derived products for the manufacture of such derived products. However, Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 applies where that other Union legislation does not lay down conditions concerning risks to public and animal health which may arise from such raw materials. Since such conditions have not been laid down regarding materials which have undergone certain stages of processing prior to their fulfilling the conditions for placing on the market under that other Union legislation, they should be laid down in this Regulation. In particular, the conditions for the import and handling of such materials inside the Union under strict control and documentation requirements should be laid down, so as to prevent the transmission of potential health risks from such materials.
(30) In particular, adequate health conditions should be laid down in this Regulation for materials which are used for the manufacture of medicinal products in accordance with Directive 2001/83/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 November 2001 on the Community code relating to medicinal products for human use(22), of veterinary medicinal products in accordance with Directive 2001/82/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 November 2001 on the Community code relating to veterinary medicinal products(23), of medical devices in accordance with Council Directive 93/42/EEC of 14 June 1993 concerning medical devices(24), of in vitro diagnostic medical devices in accordance with Directive 98/79/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 October 1998 on in vitro diagnostic medical devices(25), active implantable medical devices in accordance with Council Directive 90/385/EEC of 20 June 1990 on the approximation of laws of the Member States relating to active implantable medical devices(26) or laboratory reagents (‘the finished products’). If the risks arising from such materials are mitigated due to the purification, concentration in the product or due to the conditions under which they are handled and disposed of, only the requirements of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and of this Regulation in relation to traceability should apply. In such case, the requirements related to the separation of animal by-products of different categories within the establishment or plant producing the finished products should not apply, since the subsequent use of materials for other purposes, in particular their diversion into food or feed can be excluded by the proper application of the rules by the operator, under the responsibility of the competent authority. Consignments of such materials which are to be imported into the Union should be subject to veterinary checks at the border inspection post of entry in accordance with Directive 97/78/EC, in order to ascertain that those products comply with the requirements for their placing on the market within the Union.
(31) Pursuant to Council Directive 2009/156/EC of 30 November 2009 on animal health conditions governing the movement and import from third countries of equidae(27), certain diseases to which equidae are susceptible are compulsorily notifiable. Blood products from equidae which are intended for purposes other than for feeding, such as blood products intended for veterinary medicinal products, should originate from equidae which did not show clinical signs of those diseases, in order to mitigate the risk of transmission of those diseases.
(32) It should be permissible to place on the market fresh hides and skins for purposes other than human consumption, provided they comply with the animal health conditions for fresh meat laid down in accordance with Council Directive 2002/99/EC of 16 December 2002 laying down the animal health rules governing the production, processing, distribution and introduction of products of animal origin for human consumption(28), since those conditions provide for an appropriate mitigation of possible health risks.
(33) The health rules laid down in this Regulation for the manufacture and placing on the market of game trophies and other preparations from animals which eliminate potential risks should be in addition to the rules for the protection of certain species of wild animals laid down in Council Regulation (EC) No 338/97 of 9 December 1996 on the protection of species of wild fauna and flora by regulating trade therein(29), due to the different objective of that Regulation. Anatomical preparations of animals or animal by-products which have been submitted to a process such as plastination which equally eliminates potential risks should not be subject to animal health restrictions, in order to facilitate the use of such preparations, in particular in education.
(34) Apiculture by-products which are to be placed on the market should be free of certain diseases to which bees are susceptible that are listed in Council Directive 92/65/EEC of 13 July 1992 laying down animal health requirements governing trade in and imports into the Community of animals, semen, ova and embryos not subject to animal health requirements laid down in specific Community rules referred to in Annex A (I) to Directive 90/425/EEC(30).
(35) The European Parliament and the Council have called upon the Commission to determine an end point in the manufacturing chain for oleochemical products, beyond which they are no longer subject to the requirements of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009. The decision regarding that end point should be taken as soon as an assessment has become available which evaluates the capacity of the oleochemical processes to mitigate potential health risks which may be present in animal fats of any category of material which are processed.
(36) Commission Regulation (EU) No 206/2010 of 12 March 2010 laying down lists of third countries, territories or parts thereof authorised for the introduction into the European Union of certain animals and fresh meat and the veterinary certification requirements(31) should be referred to in this Regulation, in so far as those third countries and other territories should be authorised for the importation of certain animal by-products or derived products, since the risks which arise from those products are identical to those which potentially arise from the import of live animals or fresh meat.
(37) Further lists of third countries from which certain materials of animal origin may be imported should be referred to for the purposes of determining the third countries from which animal by-products of the respective species may be imported, on the basis of similar considerations concerning health risks and in order to ensure coherency of Union legislation. Such lists have been laid down in Commission Decision 2004/211/EC of 6 January 2004 establishing the list of third countries and parts of territory thereof from which Member States authorise imports of live equidae and semen, ova and embryos of the equine species and amending Decisions 93/195/EEC and 94/63/EC(32), Commission Regulation (EU) No 605/2010 of 2 July 2010 laying down animal and public health and veterinary certifications conditions for introduction into the European Union of raw milk and dairy products intended for human consumption(33), Commission Decision 2006/766/EC of 6 November 2006 establishing the lists of third countries and territories from which imports of bivalve molluscs, echinoderms, tunicates, marine gastropods and fishery products are permitted(34), Commission Regulation (EC) No 798/2008 of 8 August 2008 laying down a list of third countries, territories, zones or compartments from which poultry and poultry products may be imported into and transit through the Community and the veterinary certification requirements(35) and Commission Regulation (EC) No 119/2009 of 9 February 2009 laying down a list of third countries or parts thereof, for imports into, or transit through, the Community of meat of wild leporidae, of certain wild land mammals and of farmed rabbits and the veterinary certification requirements(36).
(38) Since waste from the photographic industry which uses certain animal by-products such as bovine vertebral column does not only pose risks to public and animal health, but also risks to the environment, it should either be disposed of or exported to the third country of origin of the animal by-products in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1013/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 on shipments of waste(37).
(39) The list of border inspection posts laid down in Commission Decision 2009/821/EC of 28 September 2009 drawing up a list of approved border inspection posts, laying down certain rules on the inspections carried out by Commission veterinary experts and laying down the veterinary units in Traces(38) should be referred to in the rules for the transit of certain animal by-products and derived products through the European Union between territories of the Russian Federation. The Common Veterinary Entry Document laid down in Commission Regulation (EC) No 136/2004 of 22 January 2004 laying down procedures for veterinary checks at Community border inspection posts on products imported from third countries(39) should be used for the purposes of that transit.
(40) This Regulation should provide that the health certificates which are to accompany consignments of animal by-products or derived products at the point of entry into the Union where the veterinary checks take place should be issued in accordance with principles of certification equivalent to those laid down in Council Directive 96/93/EC of 17 December 1996 on the certification of animals and animal products(40).
(41) In the interests of consistency of Union legislation, official controls on the entire chain of animal by-products and derived products should be carried out in accordance with the general obligations for official controls which are laid down in Regulation (EC) No 882/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on official controls performed to ensure the verification of compliance with feed and food law, animal health and animal welfare rules(41).
(42) It is therefore necessary to lay down implementing measures for Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 in this Regulation.
(43) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 repeals Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002 with effect from 4 March 2011.
(44) Following the adoption of Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002, certain implementing acts were adopted, namely Commission Regulation (EC) No 811/2003(42) on the intra-species recycling ban for fish, and the burial and burning of certain animal by-products, Commission Decision 2003/322/EC(43) on the feeding of certain necrophagous birds with certain Category 1 materials, Commission Decision 2003/324/EC(44) on a derogation from the intra-species recycling ban for fur animals, Commission Regulations (EC) No 79/2005(45) on milk and milk-based products, (EC) No 92/2005(46) on means of disposal or uses, (EC) No 181/2006(47) on organic fertilisers and soil improvers other than manure, (EC) No 1192/2006(48) on lists of approved plants and (EC) No 2007/2006(49) on the importation and transit of certain Category 3 intermediate products.
(45) In addition, certain transitional measures were adopted, in particular Commission Regulation (EC) No 878/2004(50) on the import and handling of certain Category 1 and Category 2 materials, Commission Decision 2004/407/EC(51) on the import of certain materials for the production of photogelatine and Commission Regulation (EC) No 197/2006(52) on handling and disposal of former foodstuffs, to lay down risk-proportionate measures for certain specific uses of animal by-products.
(46) In order to further simplify Union rules for animal by-products, as requested by the Presidency of the Council at the time of the adoption of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, those implementing and transitional measures were reviewed. They should now be repealed and replaced, as necessary, by this Regulation, so as to constitute a coherent legal framework for animal by-products and derived products.
(47) Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 applies from 4 March 2011 and accordingly this Regulation should also apply from that date. In addition, it is necessary to provide for a transitional period, in order to give stakeholders time to adjust to the new rules laid down in this Regulation and to place on the market certain products which were produced in accordance with Union health rules applicable before that date, and to allow for a continuation of imports when the requirements of this Regulation become applicable.
(48) The placing on the market and the export of certain products referred to in Regulation (EC) No 878/2004 should continue to be carried out in accordance with national measures, since the associated risks for the limited amount of materials involved currently allow their regulation at national level, pending possible future harmonisation. Pending the adoption of measures for the collection and disposal of certain limited amounts of products of animal origin from the retail sector on the basis of further evidence, the competent authority should continue to be able to authorise the collection and disposal of such products by other means, provided that an equivalent protection of public and animal health is ensured.
(49) In accordance with the request expressed by the European Parliament at the time of its agreement to Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 at first reading, and taking into account the Parliament's more specific suggestions for addressing certain technical issues, a draft of this Regulation has been presented on 27 September 2010 to its Committee for the Environment, Public Health and Food Safety for an exchange of views.
(50) The measures provided for in this Regulation are in accordance with the opinion of the Standing Committee on the Food Chain and Animal Health,
HAS ADOPTED THIS REGULATION:
CHAPTER IU.K. GENERAL PROVISIONS
Article 1U.K.Subject matter and scope
This Regulation lays down implementing measures:
for the public and animal health rules for animal by-products and derived products laid down in Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
concerning certain samples and items exempt from veterinary checks at border inspection posts as provided for in Article 16(1)(e) and (f) of Directive 97/78/EC.
Article 2U.K.Definitions
For the purposes of this Regulation, the definitions set out in Annex I apply.
Article 3U.K.End point in the manufacturing chain for certain derived products
The following derived products may be placed on the market, other than imported, without restrictions, as provided in Article 5(2) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009:
biodiesel which fulfils the requirements for the disposal and use of derived products set out in point 2(b) of Section 3 of Chapter IV of Annex IV;
processed petfood which fulfil the specific requirements for processed petfood set out in point 7(a) of Chapter II of Annex XIII;
dogchews which fulfil the specific requirements for dogchews set out in point 7(b) of Chapter II of Annex XIII;
hides and skins of ungulates which fulfil the specific requirements for the end point for those products set out in point C of Chapter V of Annex XIII;
wool and hair, which fulfil the specific requirements for the end point for those products set out in point B of Chapter VII of Annex XIII;
feathers and down, which fulfil the specific requirements for the end point for those products set out in point C of Chapter VII of Annex XIII;
fur which fulfils the conditions in Chapter VIII of Annex XIII.
Article 4U.K.Serious transmissible diseases
The diseases listed by the OIE in Article 1.2.3 of the Terrestrial Animal Health Code, 2010 edition, and in Chapter 1.3 of the Aquatic Animal Health Code, 2010 edition, shall be regarded as serious transmissible diseases for the purposes of general animal health restrictions, as provided for in Article 6(1)(b)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
CHAPTER IIU.K. DISPOSAL AND USE OF ANIMAL BY-PRODUCTS AND DERIVED PRODUCTS
Article 5U.K.Restrictions on the use of animal by-products and derived products
1.Operators in the Member States referred to in Chapter I of Annex II shall comply with the conditions for the feeding of fur animals with certain materials derived from bodies or parts of animals of the same species set out in the same Chapter.
2.Operators shall comply with the restrictions on the feeding of farmed animals with herbage from land to which certain organic fertilisers or soil improvers have been applied, as set out in Chapter II of Annex II.
Article 6U.K.Disposal by incineration and co-incineration
1.The competent authority shall ensure that incineration and co-incineration of animal by-products and derived products shall only take place:
(a)in incineration plants and co-incineration plants which have been granted a permit in accordance with Directive 2000/76/EC; or
(b)for plants not required to have a permit under Directive 2000/76/EC, in incineration and co-incineration plants which have been approved by the competent authority to carry out disposal by incineration, or disposal or recovery of animal by-products or derived products, if they are waste, by co-incineration, in accordance with Article 24(1)(b) or (c) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
2.The competent authority shall only approve incineration plants and co-incineration plants as referred to in point 1(b), in accordance with Article 24(1)(b) or (c) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, if they comply with the requirements set out in Annex III hereto.
3.Operators of incineration plants and co-incineration plants shall comply with the general requirements for incineration and co-incineration set out in Chapter I of Annex III.
4.Operators of high-capacity incineration and co-incineration plants shall comply with the requirements of Chapter II of Annex III.
5.Operators of low-capacity incineration and co-incineration plants shall comply with the requirements of Chapter III of Annex III.
Article 7U.K.Landfilling of certain Category 1 and 3 materials
By way of derogation from Article 12 and Article 14(c) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the competent authority may authorise the disposal of the following Category 1 and 3 materials in an authorised landfill:
imported petfood or petfood produced from imported materials, from Category 1 material referred to in Article 8(c) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
Category 3 material referred to in Article 10(f) and (g) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, provided that:
such materials have not been in contact with any of the animal by-products referred to in Articles 8 and 9 and Article 10(a) to (e) and (h) to (p) of that Regulation;
at the time when they are destined for disposal, the materials:
referred to in Article 10(f) of that Regulation have undergone processing as defined in Article 2(1)(m) of Regulation (EC) No 852/2004, and
referred to in Article 10(g) of that Regulation have been processed in accordance with Chapter II of Annex X hereto or in accordance with the specific requirements for petfood set out in Chapter II of Annex XIII hereto; and
the disposal of such materials does not pose a risk to public or animal health.
Article 8U.K.Requirements for processing plants and other establishments
1.Operators shall ensure that processing plants and other establishments under their control comply with the following requirements set out in Chapter I of Annex IV:
(a)the general conditions for processing set out in Section 1;
(b)the requirements for wastewater treatment set out in Section 2;
(c)the specific requirements for the processing of Category 1 and 2 materials set out in Section 3;
(d)the specific requirements for the processing of Category 3 materials set out in Section 4.
2.The competent authority shall only approve processing plants and other establishments, if they comply with the conditions laid down in Chapter I of Annex IV.
Article 9U.K.Hygiene and processing requirements for processing plants and other establishments
Operators shall ensure that establishments and plants under their control comply with the following requirements set out in Annex IV:
the hygiene and processing requirements set out in Chapter II;
the standard processing methods set out in Chapter III, provided such methods are used in the establishment or plant;
the alternative processing methods set out in Chapter IV, provided such methods are used in the establishment or plant.
Article 10U.K.Requirements regarding the transformation of animal by-products and derived products into biogas and composting
1.Operators shall ensure that establishments and plants under their control comply with the following requirements for the transformation of animal by-products and derived products into biogas or for composting set out in Annex V:
(a)the requirements applicable to biogas and composting plants set out in Chapter I;
(b)the hygiene requirements applicable to biogas and composting plants set out in Chapter II;
(c)the standard transformation parameters set out in Section 1 of Chapter III;
(d)the standards for digestion residues and compost set out in Section 3 of Chapter III.
2.The competent authority shall only approve biogas and composting plants, if they comply with the requirements laid down in Annex V.
3.The competent authority may authorise the use of alternative transformation parameters for biogas and composting plants subject to the requirements set out in Section 2 of Chapter III of Annex V.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. DEROGATIONS FROM CERTAIN PROVISIONS OF REGULATION (EC) No 1069/2009
Article 11U.K.Special rules on research and diagnostic samples
1.The competent authority may authorise the transport, use and disposal of research and diagnostic samples under conditions which ensure the control of the risks to public and animal health.
The competent authority shall in particular ensure that operators comply with the requirements of Chapter I of Annex VI.
2.Operators shall comply with the special rules on research and diagnostic samples set out in Chapter I of Annex VI.
3.Operators may dispatch research and diagnostic samples which consist of the following animal by-products and derived products to another Member State without informing the competent authority of the Member State of origin in accordance with Article 48(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and without the competent authority of the Member State of destination being informed by means of the TRACES system and agreeing to accept the consignment in accordance with Article 48(1) and (3) of that Regulation:
(a)Category 1 and 2 materials and meat-and-bone meal or animal fat derived from Category 1 and 2 materials;
(b)processed animal protein.
Article 12U.K.Special rules on trade samples and display items
1.The competent authority may authorise the transport, use and disposal of trade samples and display items under conditions which ensure the control of the risks to public and animal health.
The competent authority shall in particular ensure that operators comply with the requirements of points 2, 3 and 4 of Section 1 of Chapter I of Annex VI.
2.Operators shall comply with the special rules on trade samples and display items set out in Section 2 of Chapter I of Annex VI.
3.Operators may dispatch trade samples which consist of the following animal by-products and derived products to another Member State without informing the competent authority of the Member State of origin in accordance with Article 48(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and without the competent authority of the Member State of destination being informed by means of the TRACES system and agreeing to accept the consignment in accordance with Article 48(1) and (3) of that Regulation:
(a)Category 1 and 2 materials and meat-and-bone meal or animal fat derived from Category 1 and 2 materials;
(b)processed animal protein.
Article 13U.K.Special feeding rules
1.Operators may feed Category 2 material to the following animals, provided that such material comes from animals which were not killed or did not die as a result of the presence or suspected presence of a disease communicable to humans or animals, subject to compliance with the general requirements laid down in Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex VI and any other conditions that may be laid down by the competent authority:
(a)zoo animals;
(b)fur animals;
(c)dogs from recognised kennels or packs of hounds;
(d)dogs and cats in shelters;
(e)maggots and worms for fishing bait.
2.Operators may feed Category 3 material to the following animals subject to compliance with the general requirements laid down in Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex VI and any other conditions that may be laid down by the competent authority:
(a)zoo animals;
(b)fur animals;
(c)dogs from recognised kennels or packs of hounds;
(d)dogs and cats in shelters;
(e)maggots and worms for fishing bait.
Article 14U.K.Feeding of certain species in and outside feeding stations and in zoos
1.The competent authority may authorise the use of Category 1 material consisting of entire bodies or parts of dead animals containing specified risk material for the feeding:
(a)in feeding stations, to endangered or protected species of necrophagous birds and other species living in their natural habitat, for the promotion of biodiversity, subject to compliance with the conditions set out in Section 2 of Chapter II of Annex VI;
(b)outside feeding stations, if appropriate without prior collection of the dead animals, to wild animals referred to point 1(a) of Section 2 of Chapter II of Annex VI, subject to compliance with the conditions set out in Section 3 of that Chapter.
2.The competent authority may authorise the use of Category 1 material consisting of entire bodies or parts of dead animals containing specified risk materials and the use of material derived from zoo animals for the feeding of zoo animals subject to compliance with the conditions set out in Section 4 of Chapter II of Annex VI.
Article 15U.K.Special rules on collection and disposal
If the competent authority authorises the disposal of animal by-products by way of the derogation provided for in Article 19(1)(a), (b), (c) and (e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the disposal shall comply with the following special rules set out in Chapter III of Annex VI:
the special disposal rules for animal by-products set out in Section 1;
the rules for the burning and burial of animal by-products in remote areas set out in Section 2;
the rules for the burning and burial of bees and apiculture by-products set out in Section 3.
CHAPTER IVU.K. AUTHORISATIONS OF ALTERNATIVE METHODS
Article 16U.K.Standard format for applications for authorisation of alternative methods
1.Applications for authorisation of alternative methods of use or disposal of animal by-products or derived products, as referred to in Article 20(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, shall be submitted by Member States or interested parties in accordance with the requirements of the standard format for applications for alternative methods set out in Annex VII.
2.Member States shall designate national contact points to provide information on the competent authority responsible for evaluating applications for authorisation of alternative methods of use or disposal of animal by-products.
3.The Commission shall publish a list of national contact points on its website.
CHAPTER VU.K. COLLECTION, TRANSPORT, IDENTIFICATION AND TRACEABILITY
Article 17U.K.Requirements regarding commercial documents and health certificates, identification, the collection and transport of animal by-products and traceability
1.Operators shall ensure that animal by-products and derived products:
(a)comply with the requirements for collection, transport and identification set out in Chapters I and II of Annex VIII;
(b)are accompanied during transport by commercial documents or health certificates in accordance with the requirements set out in Chapter III of Annex VIII.
2.Operators consigning, transporting or receiving animal by-products or derived products shall keep records of consignments and related commercial documents or health certificates in accordance with the requirements set out in Chapter IV of Annex VIII.
3.Operators shall comply with the requirements for the marking of certain derived products set out in Chapter V of Annex VIII.
CHAPTER VIU.K. REGISTRATION AND APPROVAL OF ESTABLISHMENTS AND PLANTS
Article 18U.K.Requirements regarding the approval of one or more establishments and plants handling animal by-products on the same site
The competent authority may grant approval to more than one establishment or plant handling animal by-products on the same site, provided that the transmission of risks to public and animal health between the establishments or plants is excluded by their layout and the handling of animal by-products and derived products within the establishments or plants.
Article 19U.K.Requirements concerning certain approved establishments and plants handling animal by-products and derived products
Operators shall ensure that establishments and plants under their control which have been approved by the competent authority, comply with the requirements set out in the following Chapters of Annex IX hereto where they carry out one or more of the following activities referred to Article 24(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009:
Chapter I, where they manufacture petfood as referred to in Article 24(1)(e) of that Regulation;
Chapter II, where they store animal by-products as referred to in Article 24(1)(i) of that Regulation and where they handle animal by-products after their collection, by way of the following operations referred to in Article 24(1)(h) of that Regulation:
sorting;
cutting;
chilling;
freezing;
salting;
preservation by other processes;
removal of hides and skins or removal of specified risk material;
operations involving the handling of animal by-products which are carried out in compliance with obligations under Union veterinary legislation;
hygienisation/pasteurisation of animal by-products destined for transformation into biogas/composting, prior to such transformation or composting in another establishment or plant in accordance with Annex V hereto;
sieving;
Chapter III, where they store derived products for certain intended purposes as referred to in Article 24(1)(j) of that Regulation.
Article 20U.K.Requirements concerning certain registered establishments and plants handling animal by-products and derived products
1.Operators of registered plants or establishments or other registered operators shall handle animal by-products and derived products under the conditions set out in Chapter IV of Annex IX.
2.Registered operators transporting animal by-products or derived products, other than between premises of the same operator, shall in particular comply with the conditions set out in point 2 of Chapter IV of Annex IX.
3.Paragraphs 1 and 2 shall not apply to:
(a)approved operators who are transporting animal by-products or derived products as an ancillary activity;
(b)operators who have been registered for transport activities in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 183/2005.
4.The competent authority may exempt the following operators from the obligation to notify, referred to in Article 23(1)(a) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009:
(a)operators handling or generating game trophies or other preparations referred to in Chapter VI of Annex XIII hereto for private or non-commercial purposes;
(b)operators handling or disposing research and diagnostic samples for educational purposes.
CHAPTER VIIU.K. PLACING ON THE MARKET
Article 21U.K.Processing and placing on the market of animal by-products and derived products for feeding to farmed animals, excluding fur animals
1.Operators shall comply with the following requirements for the placing on the market, other than the import, of the animal by-products and derived products destined for feeding to farmed animals excluding fur animals, as provided for in Article 31(2) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, set out in Annex X hereto:
(a)the general requirements for the processing and the placing on the market set out in Chapter I;
(b)the specific requirements for processed animal proteins and other derived products set out in Chapter II;
(c)the requirements for certain fish feed and fishing baits set out in Chapter III.
2.The competent authority may authorise the placing on the market, other than the import, of milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products categorised as Category 3 material in accordance with Article 10(e), (f) and (h) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and which have not been processed in accordance with the general requirements set out in Part I of Section 4 of Chapter II of Annex X hereto, provided that those materials comply with the requirements for the derogation for the placing on the market of milk processed in accordance with national standards set out in Part II of that Section.
Article 22U.K.Placing on the market and use of organic fertilisers and soil improvers
1.Operators shall comply with the requirements for the placing on the market, other than the import, of organic fertilisers and soil improvers, and the use of such products, in particular their application to land, as provided for in Articles 15(1)(i) and 32(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, set out in Annex XI hereto.
2.The placing on the market, including the import, of guano from wild sea birds is not subject to any animal health conditions.
3.The competent authority of the Member State where an organic fertiliser or a soil improver, which has been produced from meat-and-bone meal derived from Category 2 material or from processed animal protein, is to be applied to land, shall authorise one or more components which are to be mixed with those materials, in accordance with Article 32(1)(d) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, according to the criteria set out in point 3 of Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex XI hereto.
4.By way of derogation from Article 48(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the competent authorities of a Member State of origin and of a Member State of destination, which share a common border may authorise the dispatch of manure between farms located in border regions of those two Member States subject to appropriate conditions for the control of any possible risks to public or animal health, such as obligations for the operators concerned to keep appropriate records, which are laid down in a bilateral agreement.
5.As provided for in Article 30(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the competent authorities of the Member States shall encourage, where necessary, the development, dissemination and use of national guides for good agricultural practice for the application of organic fertilisers and soil improvers to land.
Article 23U.K.Intermediate products
1.Intermediate products, imported into or in transit through the Union shall comply with the conditions controlling potential risks to public and animal health referred to in Annex XII hereto.
2.Intermediate products which have been transported to an establishment or plant referred to in point 3 of Annex XII hereto, may be handled without further restrictions under Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and under this Regulation, provided that:
(a)the establishment or plant has adequate facilities for the receipt of the intermediate products, which prevent the transmission of diseases communicable to humans or animals;
(b)the intermediate products do not pose any risk of transmission of diseases communicable to humans or animals, due to their purification or to other treatments to which the animal by-products in the intermediate product have been submitted, due to the concentration of animal by-products in the intermediate product or due to adequate bio-security measures for the handling of the intermediate products;
(c)the establishment or plant keeps records on the amount of materials received, their category, if applicable, and the establishment, plant or operator to whom they have supplied their products; and
(d)unused intermediate products or other surplus materials from the establishment or plant, such as expired products, are disposed of in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
3.The operator or owner of the establishment or plant of destination of intermediate products or his representative shall use and/or dispatch the intermediate products exclusively for further mixing, coating, assembling, packaging or labelling.
Article 24U.K.Petfood and other derived products
1.The use of Category 1 material referred to in Article 8(a),(b), (d) and (e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 for the manufacture of derived products which are intended to be ingested by or applied to humans or animals, other than for derived products referred to in Articles 33 and 36 of that Regulation shall be prohibited.
2.Where an animal by-product or a derived product may be used for feeding to farmed animals or for other purposes referred to in Article 36(a) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, they shall be placed on the market, other than imported, in accordance with the specific requirements for processed animal protein and other derived products set out in Chapter II of Annex X hereto, provided that Annex XIII hereto does not set out any specific requirements for such products.
3.Operators shall comply with the requirements for the placing on the market, other than the import, of petfood, as referred to in Article 40 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, set out in Chapters I and II of Annex XIII hereto.
4.Operators shall comply with the requirements for the placing on the market, other than the import, of derived products, as referred to in Article 40 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, set out in Chapter I and Chapters III to XII of Annex XIII hereto.
CHAPTER VIIIU.K. IMPORT, TRANSIT AND EXPORT
Article 25U.K.Import, transit and export of animal by-products and of derived products
1.The importation into and the transit through the Union of the following animal by-products shall be prohibited:
(a)unprocessed manure;
(b)untreated feathers and parts of feathers and down;
(c)beeswax in the form of honeycomb.
2.The importation into and the transit through the Union of the following shall not be subject to any animal health conditions:
(a)wool and hair which has been factory-washed or which has been treated by another method which ensures that no unacceptable risks remain;
(b)furs which have been dried at an ambient temperature of 18°C for a period of at least two days at a humidity of 55 %.
3.Operators shall comply with the following specific requirements for the importation into and the transit through the Union of certain animal by-products and derived products, as referred to in Articles 41(3) and 42 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, set out in Annex XIV hereto:
(a)the specific requirements for the import and transit of Category 3 material and derived products for uses in the feed chain, other than for petfood or feed to fur animals, set out in Chapter I of that Annex;
(b)the specific requirements for the import and transit of animal by-products and derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals, set out in Chapter II of that Annex.
Article 26U.K.Placing on the market, including importation, and export of certain Category 1 materials
The competent authority may authorise the placing on the market, including the importation, and the export of hides and skins derived from animals which have been submitted to an illegal treatment as defined in Article 1(2)(d) of Directive 96/22/EC or in Article 2(b) of Directive 96/23/EC, and of ruminant intestines with or without content and of bones and bone products containing vertebral column and skull, subject to compliance with the following requirements:
those materials must not be Category 1 materials derived from any of the following animals:
animals suspected of being infected by a TSE in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 999/2001;
animals in which the presence of a TSE has been officially confirmed;
animals killed in the context of TSE eradication measures;
those materials must not be intended for any of the following uses:
feeding;
application to land from which farmed animals are fed;
the manufacture of:
cosmetic products as defined in Article 1(1) of Directive 76/768/EEC;
active implantable medical devices as defined in Article 1(2)(c) of Directive 90/385/EEC;
medical devices as defined in Article 1(2)(a) of Directive 93/42/EEC;
in vitro diagnostic medical devices as defined in Article 1(2)(b) of Directive 98/79/EC;
veterinary medicinal products as defined in Article 1(2) of Directive 2001/82/EC;
medicinal products as defined in Article 1(2) of Directive 2001/83/EC;
the materials must be imported with a label and must comply with the specific requirements for certain movements of animal by-products set out in Section 1 of Chapter IV of Annex XIV hereto;
the materials must be imported in accordance with sanitary certification requirements laid down in national legislation.
Article 27U.K.Importation and transit of research and diagnostic samples
1.The competent authority may authorise the importation and the transit of research and diagnostic samples, comprising derived products or animal by-products, including the animal by-products referred to in Article 25(1), in accordance with conditions which ensure the control of risks to public and animal health.
Such conditions shall include at least the following:
(a)the introduction of the consignment must have been authorised in advance by the competent authority of the Member State of destination; and
(b)the consignment must be sent directly from the point of entry into the Union to the authorised user.
2.Operators shall present research and diagnostic samples which are intended to be imported via a Member State, other than the Member State of destination, at an approved Union border inspection post listed in Annex I to Decision 2009/821/EC. At the border inspection post, those research and diagnostic samples shall not be subject to veterinary checks in accordance with Chapter I of Directive 97/78/EC. The competent authority of the border inspection post shall inform the competent authority of the Member State of destination of the introduction of the research and diagnostic samples by means of the TRACES system.
3.Operators handling research samples or diagnostic samples shall comply with the special requirements for disposal of research and diagnostic samples set out in Section 1 of Chapter III of Annex XIV hereto.
Article 28U.K.Importation and transit of trade samples and display items
1.The competent authority may authorise the importation and the transit of trade samples in accordance with the special rules set out in point 1 of Section 2 of Chapter III of Annex XIV hereto.
2.Operators handling trade samples shall comply with the special rules for handling and disposal of trade samples set out in points 2 and 3 of Section 2 of Chapter III of Annex XIV hereto.
3.The competent authority may authorise the importation and the transit of display items in accordance with the special rules for display items set out in Section 3 of Chapter III of Annex XIV hereto.
4.Operators handling display items shall comply with the conditions for packaging, handling and disposal of display items set out in Section 3 of Chapter III of Annex XIV hereto.
Article 29U.K.Specific requirements for certain movements of animal by-products between territories of the Russian Federation
1.The competent authority shall authorise specific movements of consignments of animal by-products coming from and destined to the Russian Federation directly or via another third country, by road or by rail through the Union, between approved Union border inspection posts listed in Annex I to Decision 2009/821/EC, provided that the following conditions are met:
(a)the consignment shall be sealed with a serially numbered seal at the border inspection post of entry to the Union by the veterinary services of the competent authority;
(b)the documents accompanying the consignment and referred to in Article 7 of Directive 97/78/EC shall be stamped ‘ONLY FOR TRANSIT TO RUSSIA VIA THE EU’ on each page by the official veterinarian of the competent authority responsible for the border inspection post;
(c)the procedural requirements provided for in Article 11 of Directive 97/78/EC shall be complied with;
(d)the consignment is certified as acceptable for transit on the Common Veterinary Entry Document provided for in Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 136/2004 by the official veterinarian of the border inspection post of introduction.
2.Unloading or storage, as defined in Article 12(4) or Article 13 of Directive 97/78/EC of such consignments shall not be allowed on the territory of a Member State.
3.Regular audits shall be made by the competent authority to ensure that the number of consignments and the quantities of products leaving the Union territory matches the number and quantities entering.
Article 30U.K.Lists of establishments and plants in third countries
Lists of establishments and plants in third countries shall be entered into the TRACES system in accordance with technical specifications which are published by the Commission on its website.
Each list shall be kept up to date regularly.
Article 31U.K.Models of health certificates and declarations for importation and transit
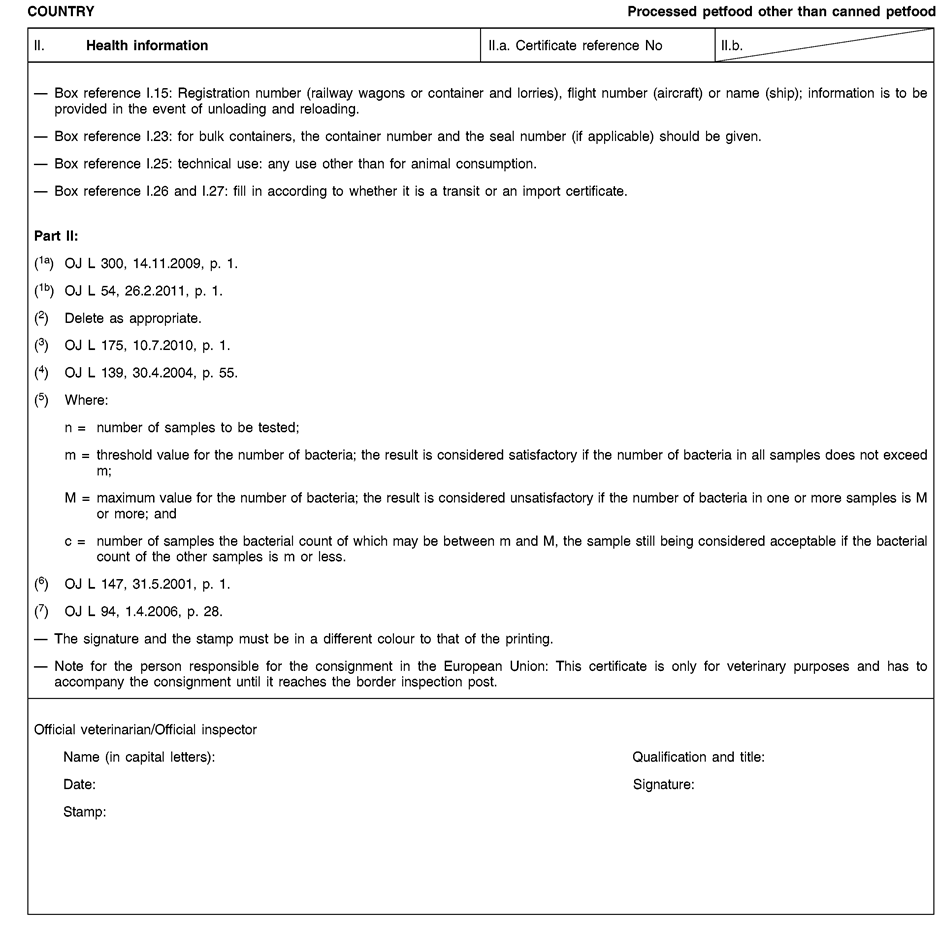
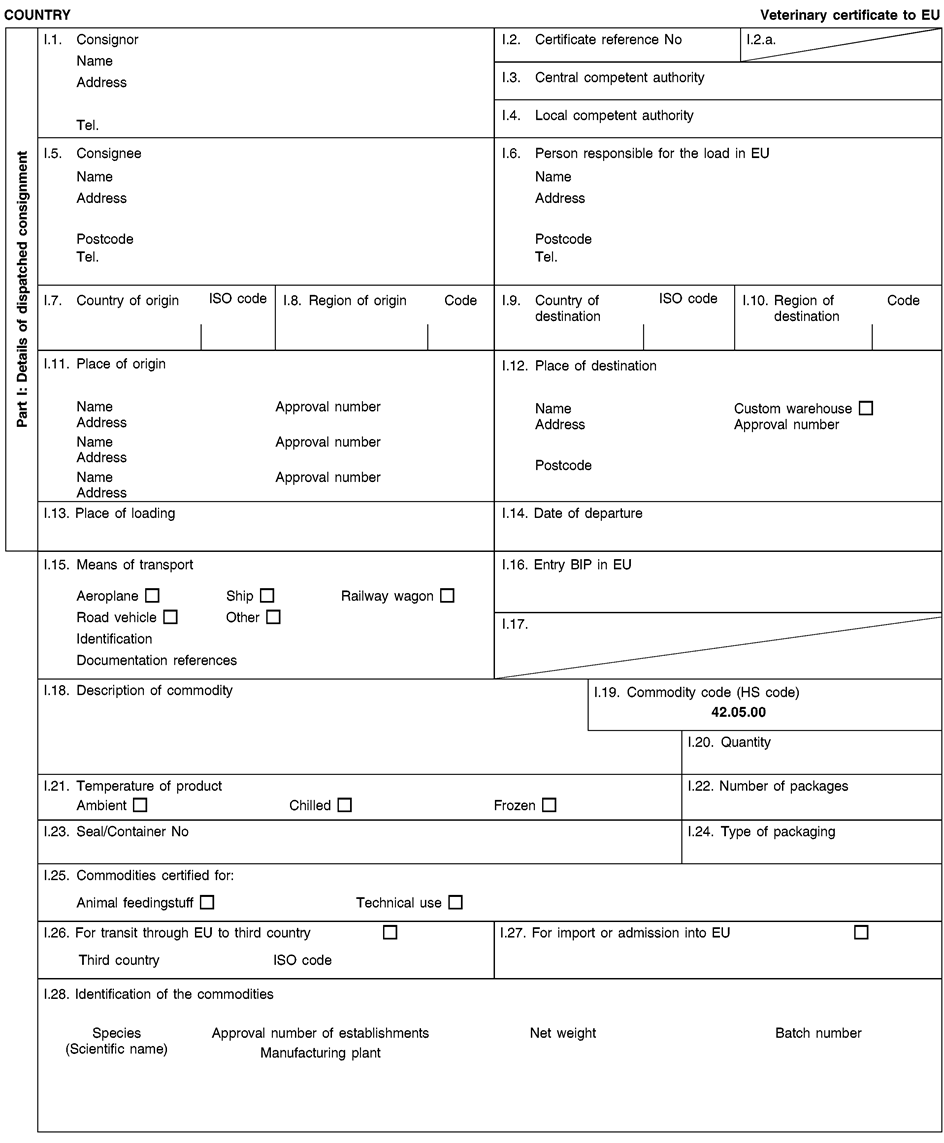
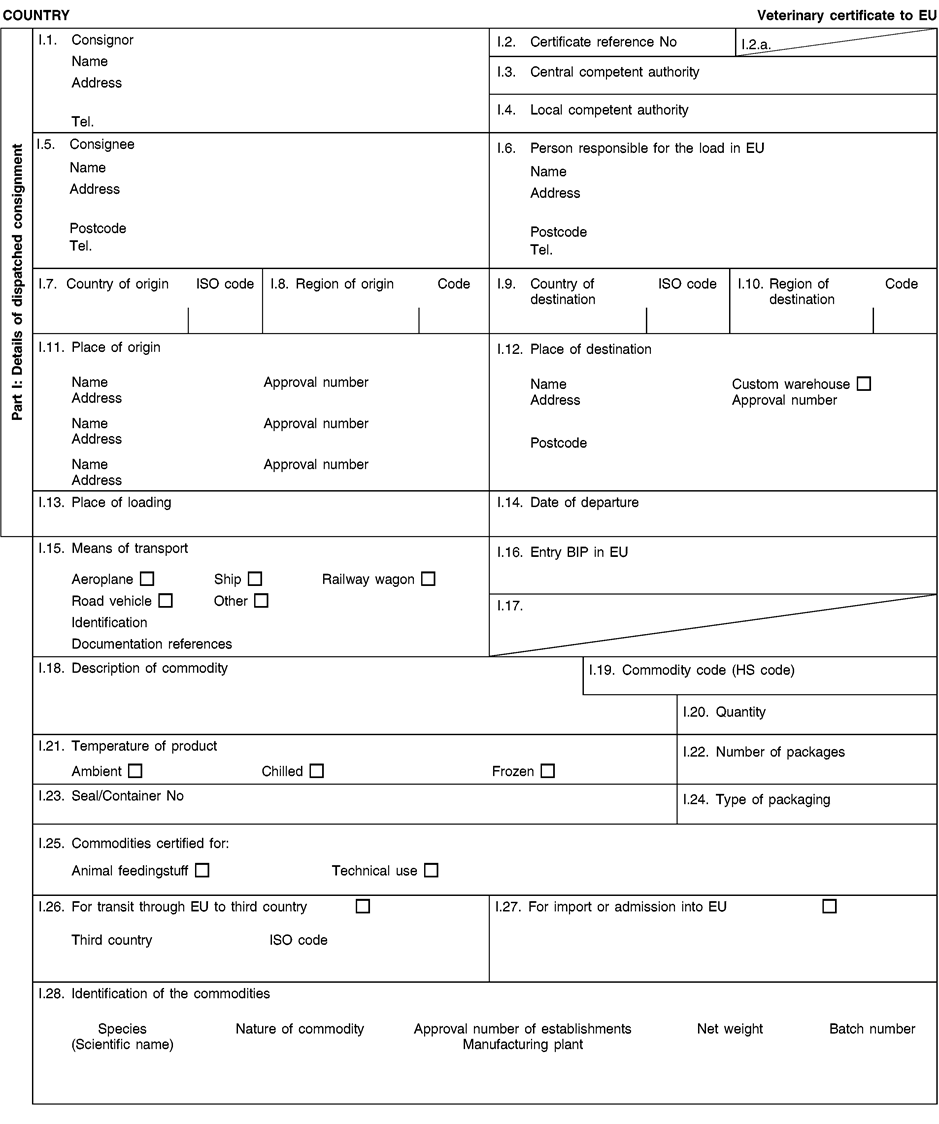
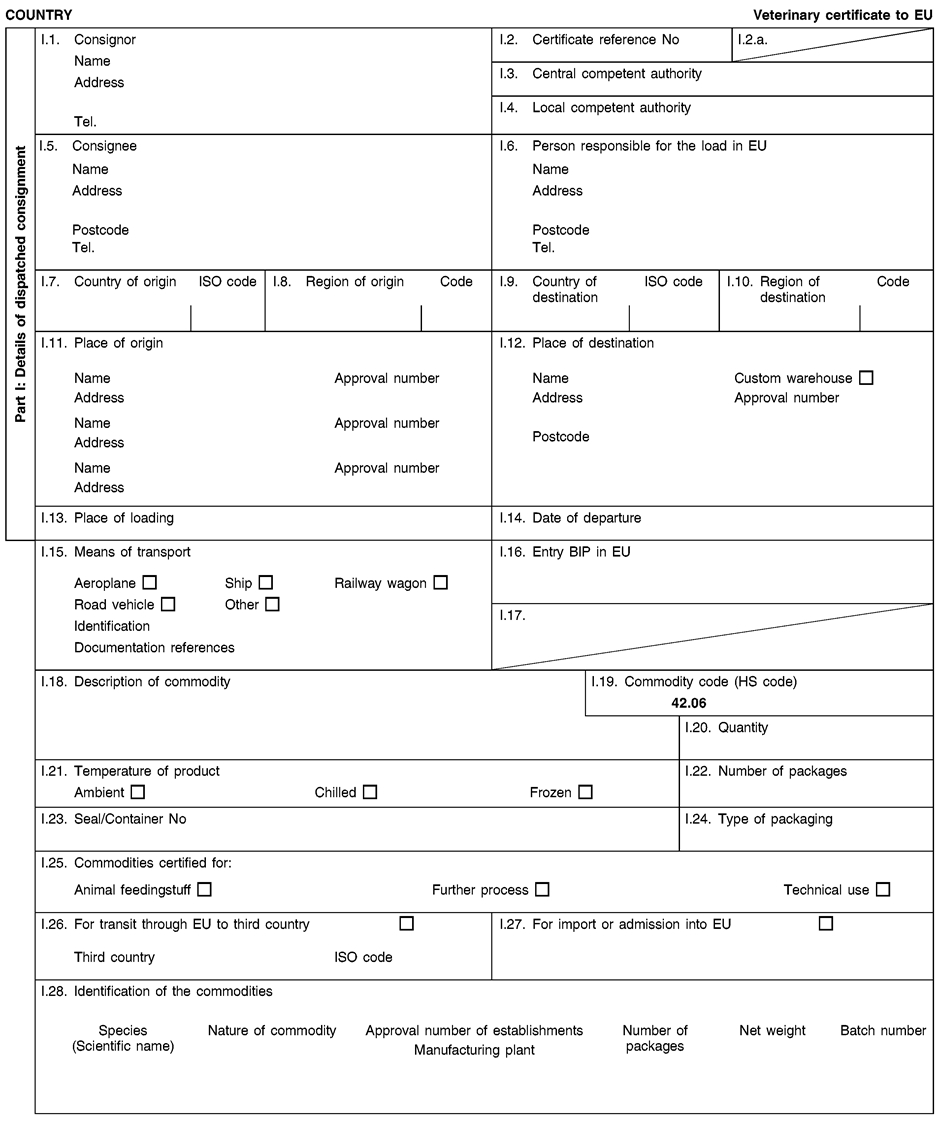
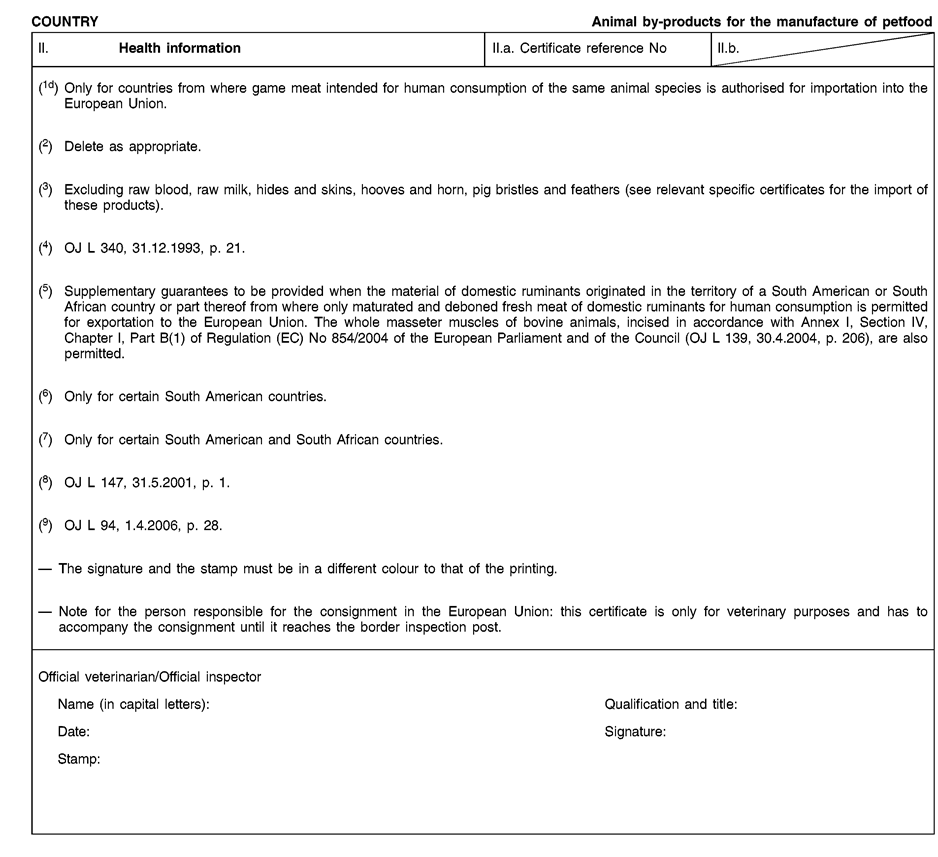
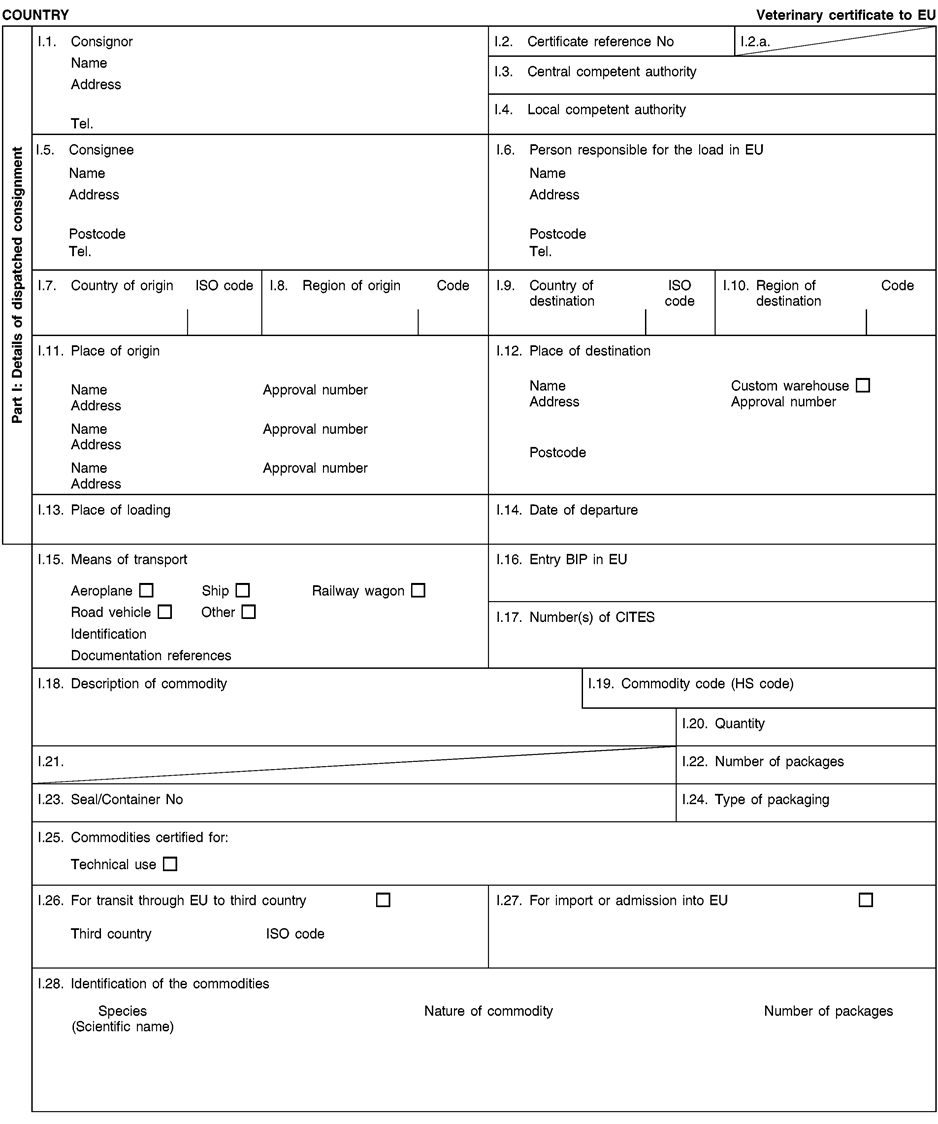
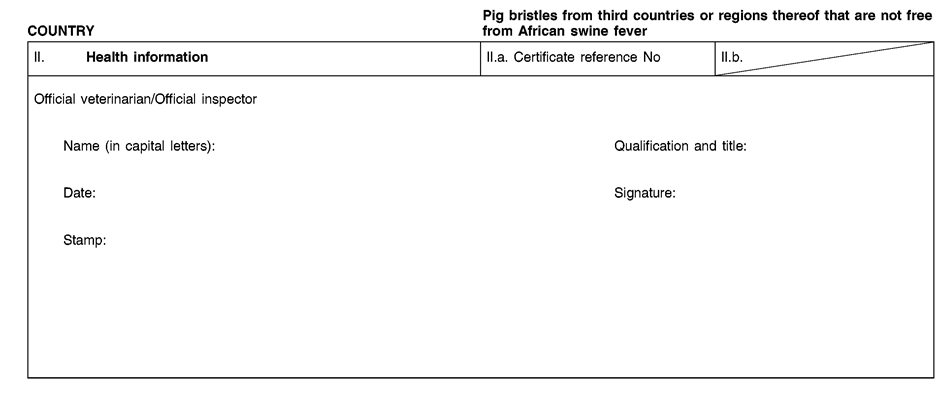
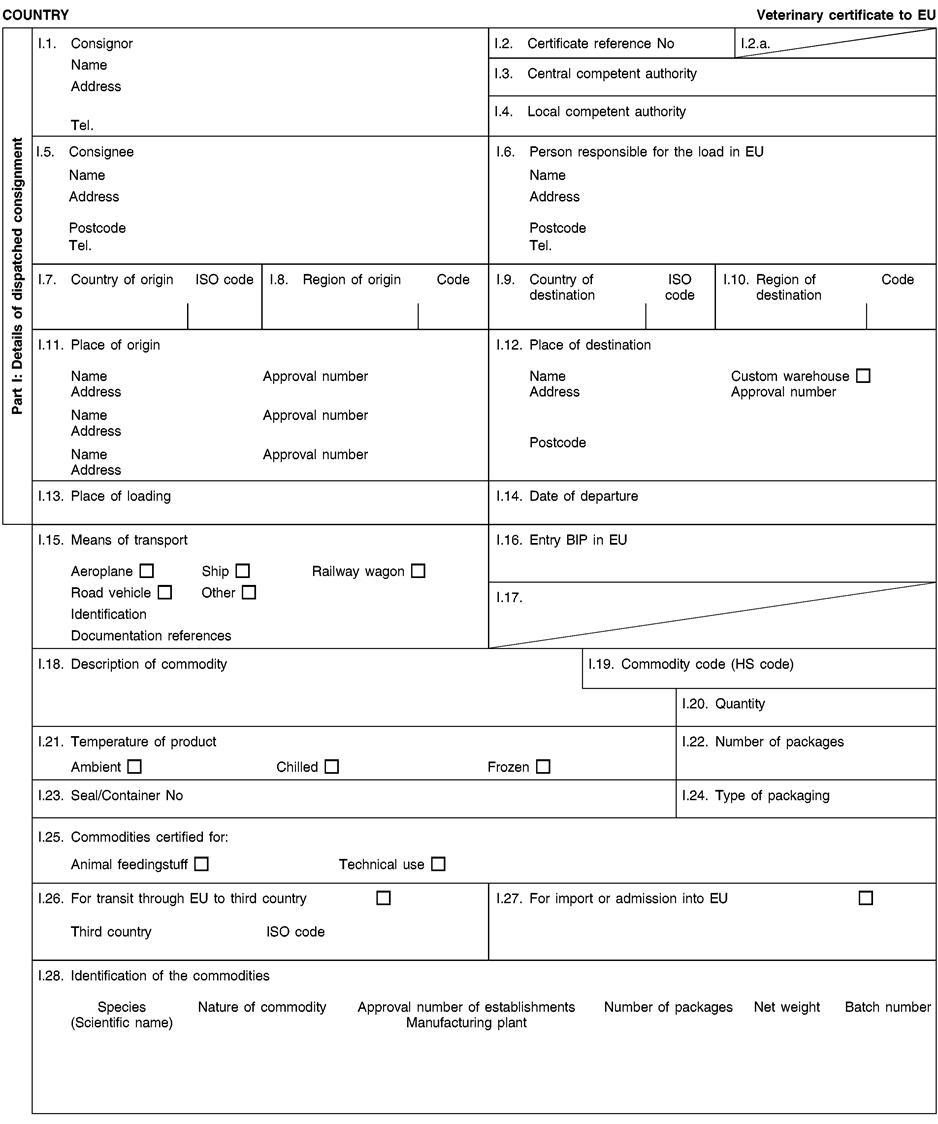
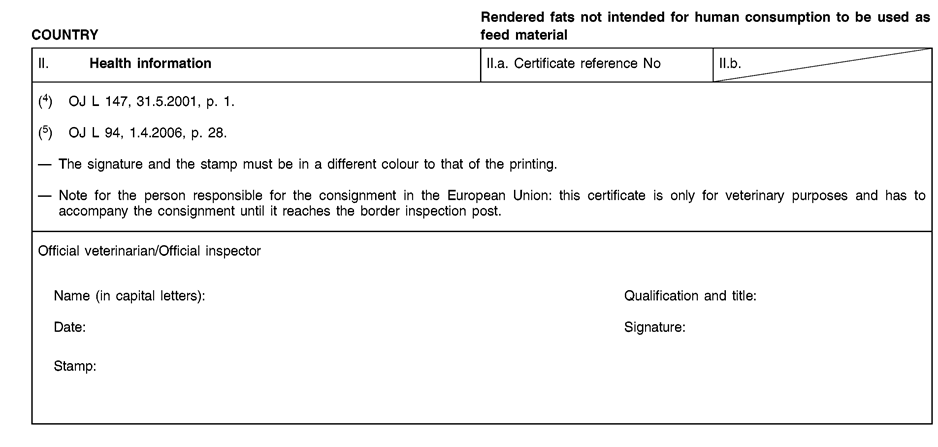
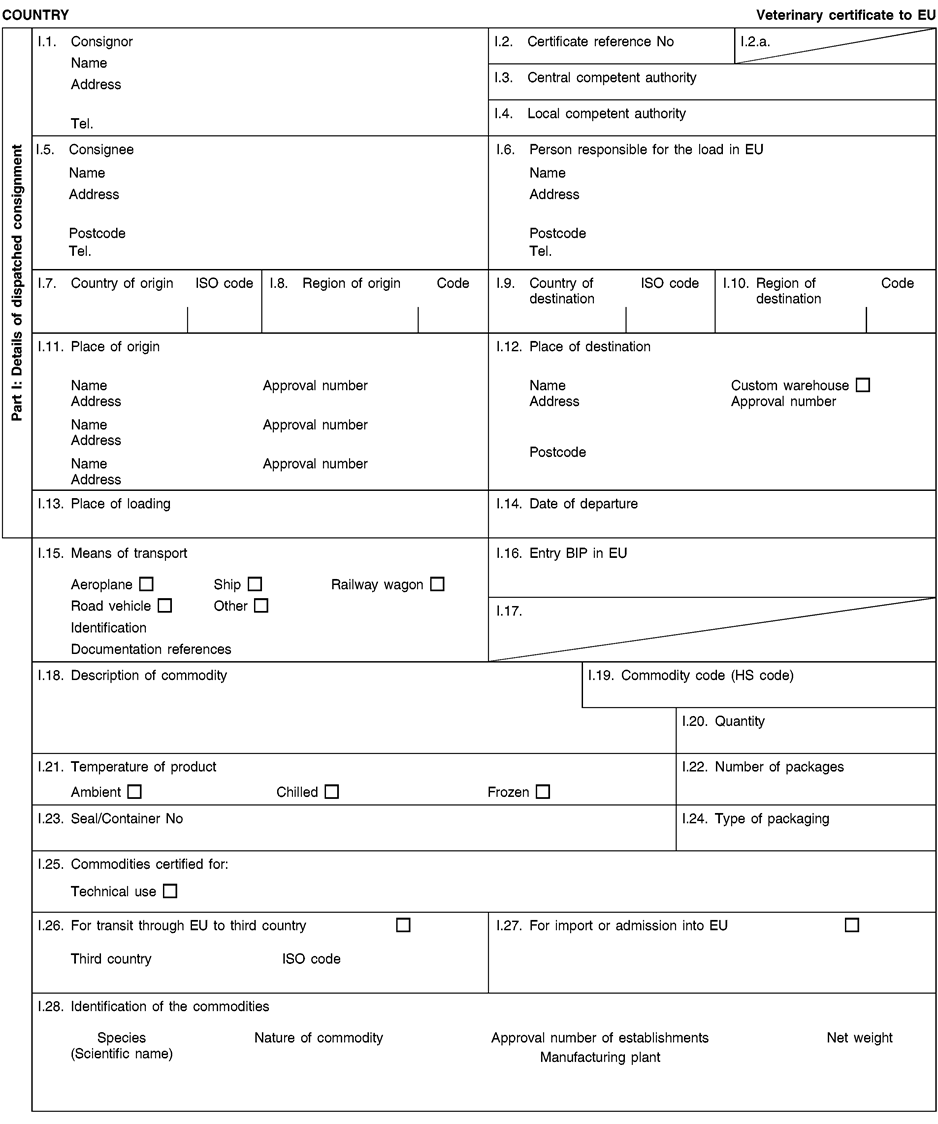
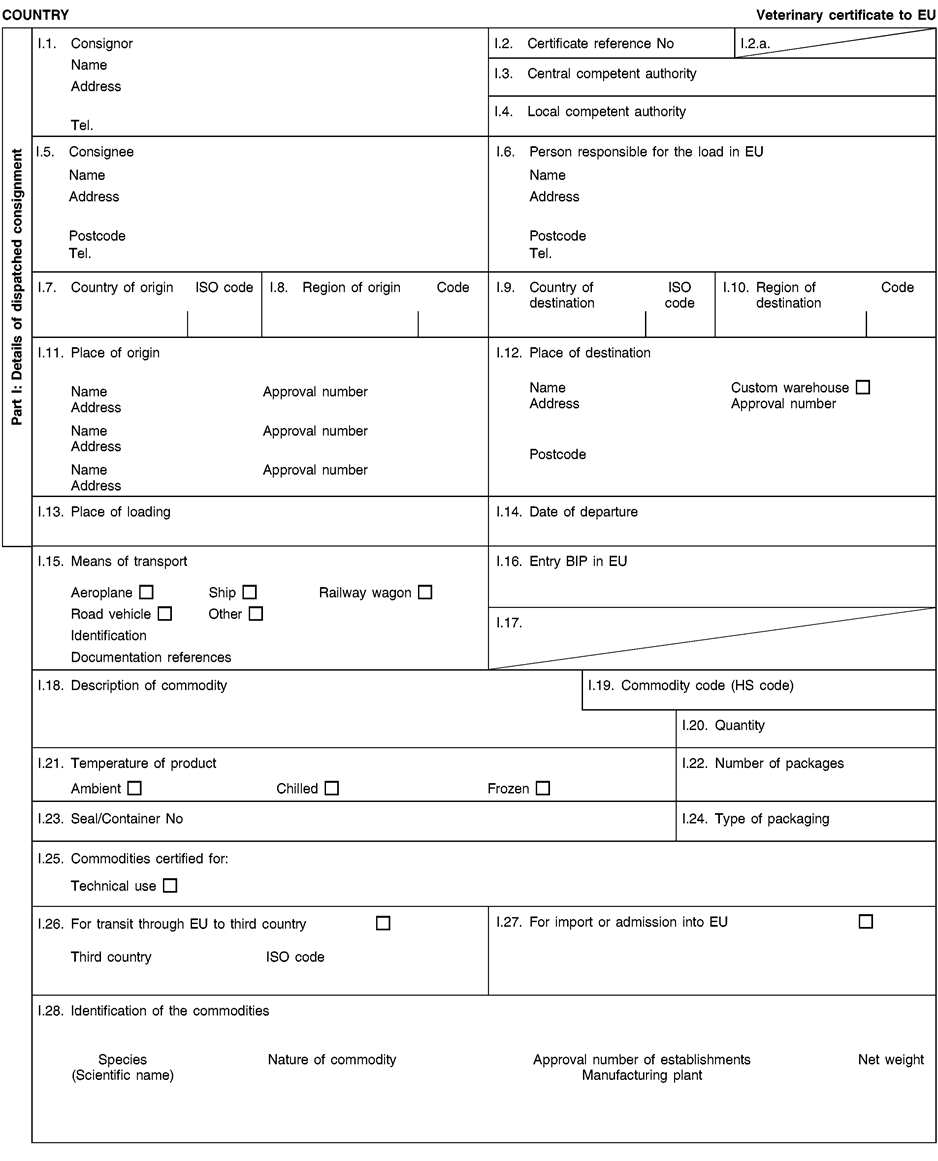
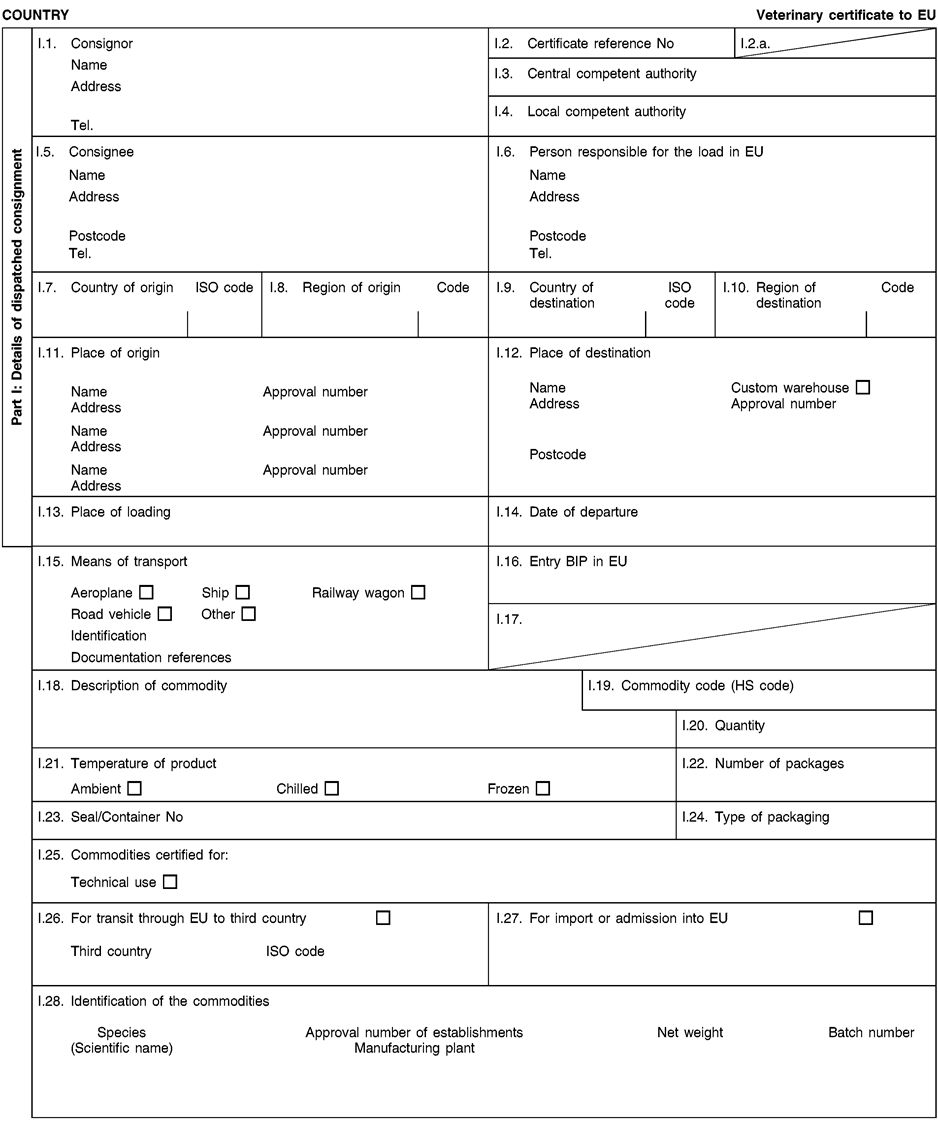
Consignments of animal by-products and derived products for importation into or transit through the Union shall be accompanied by health certificates and declarations, in accordance with the models set out in Annex XV hereto, at the point of entry into the Union where the veterinary checks take place, as provided for in Directive 97/78/EC.
CHAPTER IXU.K. OFFICIAL CONTROLS
Article 32U.K.Official controls
1.The competent authority shall take the necessary measures to control the entire chain of collection, transport, use and disposal of animal by-products and derived products, as referred to in Article 4(2) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
Those measures shall be carried out in accordance with the principles for official controls laid down in Article 3 of Regulation (EC) No 882/2004.
2.The official controls referred to in paragraph 1 shall include checks on the keeping of records and other documents required by the rules laid down in this Regulation.
3.The competent authority shall carry out the following official controls, as referred to in Article 45(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, in accordance with the requirements set out in Annex XVI hereto:
(a)official controls in processing plants as set out in Chapter I;
(b)official controls of other activities which involve the handling of animal by-products, and derived products as set out in Sections 1 to 9 of Chapter III.
4.The competent authority shall carry out checks on seals which are applied to consignments of animal by-products or derived products.
When the competent authority applies a seal to such consignment which is transported to a place of destination, it must inform the competent authority of the place of destination.
5.The competent authority shall draw up the lists of establishments, plants and operators referred to in Article 47(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 in accordance with the format set out in Chapter II of Annex XVI hereto.
6.The competent authority of the Member State of destination shall decide upon the application by an operator concerning the acceptance or refusal of certain Category 1, Category 2 material and meat-and-bone meal or animal fat derived from Category 1 and Category 2 materials, within 20 calendar days from the date of receipt of such application provided that it has been submitted in one of the official languages of that Member State.
7.Operators shall submit applications for the authorisation referred to in paragraph 6 in accordance with the standard format set out in Section 10 of Chapter III of Annex XVI hereto.
Article 33U.K.Reapproval of plants and establishments after the grant of a temporary approval
1.Where a plant or establishment approved for the processing of Category 3 material is subsequently granted temporary approval for the processing of Category 1 or Category 2 material, in accordance with Article 24(2)(b)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, it shall be prohibited from recommencing the processing of Category 3 material, without first obtaining the approval of the competent authority to recommence processing of Category 3 material in accordance with Article 44 of that Regulation.
2.Where a plant or establishment approved for the processing of Category 2 material is subsequently granted temporary approval for the processing of Category 1 material, in accordance with Article 24(2)(b)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, it shall be prohibited from recommencing the processing of Category 2 material, without first obtaining the approval of the competent authority to recommence processing of Category 2 material in accordance with Article 44 of that Regulation.
CHAPTER XU.K. FINAL PROVISIONS
Article 34U.K.Restrictions on the placing on the market of certain animal by-products and derived products for reasons of public and animal health
The competent authority shall not prohibit or restrict the placing on the market of the following animal by-products and derived products for public health or animal health reasons other than the rules laid down in Union legislation, and in particular those laid down in Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and in this Regulation:
processed animal protein and other derived products referred to in Chapter II of Annex X hereto;
petfood and certain other derived products referred to in Annex XIII hereto;
animal by-products and the derived products imported into or in transit through the Union as referred to in Annex XIV hereto.
Article 35U.K.Repeal
1.The following acts are repealed:
(a)Regulation (EC) No 811/2003;
(b)Decision 2003/322/EC;
(c)Decision 2003/324/EC;
(d)Regulation (EC) No 878/2004;
(e)Decision 2004/407/EC;
(f)Regulation (EC) No 79/2005;
(g)Regulation (EC) No 92/2005;
(h)Regulation (EC) No 181/2006;
(i)Regulation (EC) No 197/2006;
(j)Regulation (EC) No 1192/2006;
(k)Regulation (EC) No 2007/2006.
2.References to the repealed acts shall be construed as references to this Regulation.
Article 36U.K.Transitional measures
1.For a transitional period until 31 December 2011, operators may place on the market organic fertilisers and soil improvers which were produced before 4 March 2011 in accordance with Regulations (EC) No 1774/2002 and (EC) No 181/2006:
(a)provided that they have been produced from one of the following:
meat-and-bone meal derived from Category 2 material;
processed animal protein;
(b)even though they have not been mixed with a component to exclude the subsequent use of the mixture for feeding purposes.
2.For a transitional period until 31 January 2012, consignments of animal by-products and of derived products accompanied by a health certificate, declaration or commercial document, which has been completed and signed in accordance with the appropriate model set out in Annex X to Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002 shall continue to be accepted for importation into the Union, provided that such certificates, declarations or documents were completed and signed before 30 November 2011.
3.For a transitional period until 31 December 2012 and by way of derogation from Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, Member States may authorise the collection, transport and disposal of Category 3 materials comprising products of animal origin, or of foodstuffs containing products of animal origin, which are no longer intended for human consumption for commercial reasons or due to problems of manufacturing or packaging defects or other defects from which no risk to public or animal health arise, as referred to in Article 10(f) of that Regulation, by means other than burning or burial on site, as referred to in Article 19(1)(d) of that Regulation, subject to compliance with the requirements for disposal by other means set out in Chapter IV of Annex VI hereto.
Article 37U.K.
This Regulation shall enter into force on the 20th day following its publication in the Official Journal of the European Union.
It shall apply from 4 March 2011.
This Regulation shall be binding in its entirety and directly applicable in all Member States.
Done at Brussels, 25 February 2011.
For the Commission
The President
José Manuel Barroso
ANNEX IU.K. DEFINITIONS AS REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 2
For the purpose of this Regulation, the following definitions shall apply:
‘fur animals’ means animals kept or reared for the production of fur and not used for human consumption;
‘blood’ means fresh whole blood;
‘feed material’ means those feed materials, as defined in Article 3(2)(g) of Regulation (EC) No 767/2009, that are of animal origin, including processed animal proteins, blood products, rendered fats, egg products, fish oil, fat derivatives, collagen, gelatine and hydrolysed proteins, dicalcium phosphate, tricalcium phosphate, milk, milk-based products, milk-derived products, colostrum, colostrum products and centrifuge or separator sludge;
‘blood products’ means derived products from blood or fractions of blood, excluding blood meal; they include dried/frozen/liquid plasma, dried whole blood, dried/frozen/liquid red cells or fractions thereof and mixtures;
‘processed animal protein’ means animal protein derived entirely from Category 3 material, which have been treated in accordance with Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex X (including blood meal and fishmeal) so as to render them suitable for direct use as feed material or for any other use in feedingstuffs, including petfood, or for use in organic fertilisers or soil improvers; however, it does not include blood products, milk, milk-based products, milk-derived products, colostrum, colostrum products, centrifuge or separator sludge, gelatine, hydrolysed proteins and dicalcium phosphate, eggs and egg-products, including eggshells, tricalcium phosphate and collagen;
‘blood meal’ means processed animal protein derived from the heat treatment of blood or fractions of blood in accordance with Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex X;
‘fishmeal’ means processed animal protein derived from aquatic animals, except sea mammals;
‘rendered fats’ means either fats derived from the processing of:
animal by-products; or
products for human consumption, which an operator has destined for purposes other than human consumption;
‘fish oil’ means oil derived from the processing of aquatic animals or oil from the processing of fish for human consumption, which an operator has destined for purposes other than human consumption;
‘apiculture by-products’ means honey, beeswax, royal jelly, propolis or pollen not intended for human consumption;
‘collagen’ means protein-based products derived from hides, skins, bones and tendons of animals;
‘gelatine’ means natural, soluble protein, gelling or non-gelling, obtained by the partial hydrolysis of collagen produced from bones, hides and skins, tendons and sinews of animals;
‘greaves’ means the protein-containing residue of rendering, after partial separation of fat and water;
‘hydrolysed proteins’ means polypeptides, peptides and aminoacids, and mixtures thereof, obtained by the hydrolysis of animal by-products;
‘white water’ means a mixture of milk, milk-based products or products derived thereof with water which is collected during the rinsing of dairy equipment including containers used for dairy products, prior to their cleaning and disinfection;
‘canned petfood’ means heat-processed petfood contained within a hermetically sealed container;
‘dogchews’ means products for pet animals to chew, produced from untanned hides and skins of ungulates or from other material of animal origin;
‘flavouring innards’ means a liquid or dehydrated derived product of animal origin used to enhance the palatability values of petfood;
‘petfood’ means feed for pet animals and dogchews, which
contain Category 3 material, other than material referred to in Article 10(n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, and
may contain imported Category 1 material comprising of animal by-products derived from animals which have been submitted to illegal treatment as defined in Article 1(2)(d) of Directive 96/22/EC or Article 2(b) of Directive 96/23/EC;
‘processed petfood’ means petfood, other than raw petfood, which has been processed in accordance with point 3 of Chapter II of Annex XIII;
‘raw petfood’ means petfood containing certain Category 3 material which has not undergone any preserving process other than chilling or freezing;
‘catering waste’ means all waste food, including used cooking oil originating in restaurants, catering facilities and kitchens, including central kitchens and household kitchens;
‘digestion residues’ means residues resulting from the transformation of animal by-products in a biogas plant;
‘digestive tract content’ means the content of the digestive tract of mammals and ratites;
‘fat derivatives’ means derived products from rendered fats, which, as regards rendered fats of Category 1 or Category 2 material, have been processed in accordance with Chapter XI of Annex XIII;
‘guano’ means a natural product which has been collected from the excrements of bats or wild sea birds and which is not mineralised;
‘meat-and-bone meal’ means animal protein derived from the processing of Category 1 or Category 2 materials in accordance with one of the processing methods set out in Chapter III of Annex IV;
‘treated hides and skins’ means derived products from untreated hides and skins, other than dogchews, that have been:
dried;
dry-salted or wet-salted for a period of at least 14 days prior to dispatch;
salted for a period of at least seven days in sea salt with the addition of 2 % of sodium carbonate;
dried for a period of at least 42 days at a temperature of at least 20 °C; or
subject to a preservation process other than tanning;
‘untreated hides and skins’ means all cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues that have not undergone any treatment, other than cutting, chilling or freezing;
‘untreated feathers and parts of feathers’ means feathers and parts of feathers, other than feathers or parts of feathers, which have been treated:
with a steam current; or
by another method that ensures that no unacceptable risks remain;
‘untreated wool’ means wool, other than wool which has:
undergone factory washing;
been obtained from tanning; or
been treated by another method that ensures that no unacceptable risks remain;
‘untreated hair’ means hair, other than hair which has:
undergone factory washing;
been obtained from tanning; or
been treated by another method that ensures that no unacceptable risks remain;
‘untreated pig bristles’ means pig bristles, other than pig bristles which have:
undergone factory washing;
been obtained from tanning; or
been treated by another method that ensures that no unacceptable risks remain;
‘display item’ means animal by-products or derived products intended for exhibitions or artistic activities;
‘intermediate product’ means a derived product:
which is intended for the manufacture of medicinal products, veterinary medicinal products, medical devices, active implantable medical devices, in vitro diagnostic medical devices or laboratory reagents;
whose design, transformation and manufacturing stages have been sufficiently completed in order to be regarded as a derived product and to qualify the material directly or as a component of a product for that purpose;
which however requires some further handling or transformation, such as mixing, coating, assembling, packaging or labelling to make it suitable for placing the product on the market or putting it into service, as applicable, as a medicinal product, veterinary medicinal product, medical device, active implantable medical device, in vitro diagnostic medical device or laboratory reagent;
‘laboratory reagent’ means a packaged product, ready for use, containing animal by-products or derived products and intended as such or in combination with substances of non-animal origin for specific laboratory use as a reagent or reagent product, calibrator or control material to detect, measure, examine or produce other substances;
‘product used for in vitro diagnosis’ means a packaged product, ready for use, containing a blood product or another animal by-product, and used as a reagent, reagent product, calibrator, kit or any other system, whether used alone or in combination, intended to be used in vitro for the examination of samples of human or animal origin, solely or principally with a view to the diagnosis of a physiological state, state of health, disease or genetic abnormality or to determine safety and compatibility with reagents; it does not include donated organs or blood;
‘research and diagnostic samples’ means animal by-products and derived products intended for the following purposes: examination in the context of diagnostic activities or analysis for the promotion of progress in science and technology, in the context of educational or research activities;
‘trade samples’ means animal by-products or derived products intended for particular studies or analyses with a view to carrying out a production process or developing feedingstuffs or other derived products, including testing of machinery, for use in an establishment or plant which is:
producing feedingstuffs, or products for uses other than food and feed; or
processing animal by-products or derived products;
‘co-incineration’ means the recovery or disposal of animal by-products or derived products, if they are waste, in a co-incineration plant;
‘combustion’ means a process involving the oxidisation of fuel in order to use the energy value of the animal by-products or derived products, if they are not waste;
‘incineration’ means the disposal of animal by-products or derived products as waste, in an incineration plant, as defined in point 4 of Article 3 of Directive 2000/76/EC;
‘incineration and co-incineration residues’ means any residues as defined in point 13 of Article 3 of Directive 2000/76/EC, which are generated by incineration or co-incineration plants treating animal by-products or derived products;
‘colour-coding’ means the systematic use of colours as set out in point 1(c) of Chapter II of Annex VIII for displaying information as provided for in this Regulation on the surface or on part of the surface of a packaging, container or vehicle, or on a label or symbol applied to them;
‘intermediate operations’ means the operations, other than storage, referred to in Article 19(b);
‘tanning’ means the hardening of hides, using vegetable tanning agents, chromium salts or other substances such as aluminium salts, ferric salts, silicic salts, aldehydes and quinones, or other synthetic hardening agents;
‘taxidermy’ means the art of preparing, stuffing and mounting the skins of animals with lifelike effect, so that no unacceptable risks to public and animal health may be transmitted through the mounted skin;
‘trade’ means trade in goods between Member States as referred to in Article 28 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union;
‘processing methods’ means the methods listed in Chapters III and IV of Annex IV;
‘batch’ means a unit of production produced in a single plant using uniform production parameters, such as the origin of the materials, or a number of such units, when produced in continuous order in a single plant and stored together as a shipping unit;
‘hermetically sealed container’ means a container that is designed and intended to be secure against the entry of micro-organisms;
‘biogas plant’ means a plant in which animal by-products or derived products are at least part of the material which is submitted to biological degradation under anaerobic conditions;
‘collection centres’ means premises other than processing plants in which the animal by-products referred to in Article 18(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 are collected with the intention to be used for feeding to the animals referred to in the same Article;
‘composting plant’ means a plant in which animal by-products or derived products are at least part of the material which is submitted to biological degradation under aerobic conditions;
‘co-incineration plant’ means any stationary or mobile plant whose main purpose is the generation of energy or the production of material products as defined in point 5 of Article 3 of Directive 2000/76/EC;
‘incineration plant’ means any stationary or mobile technical unit and equipment dedicated to the thermal treatment of waste as defined in point 4 of Article 3 of Directive 2000/76/EC;
‘petfood plant’ means premises or facilities for the production of petfood or flavouring innards, as referred to in Article 24(1)(e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
‘processing plant’ means premises or facilities for the processing of animal by-products as referred to in Article 24(1)(a) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, in which animal by-products are processed in accordance with Annex IV and/or Annex X.
ANNEX IIU.K. RESTRICTIONS ON THE USE OF ANIMAL BY-PRODUCTS
CHAPTER IU.K. Intra-species recycling of fur animals
1.In Estonia, Latvia and Finland, the following fur animals may be fed with meat-and-bone meal or other products which have been processed in accordance with Chapter III of Annex IV and which are derived from bodies or parts of bodies of animals of the same species:U.K.
foxes (Vulpes vulpes);
raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonides).
2.In Estonia and Latvia, fur animals of the species American mink (Mustela vison) may be fed with meat-and-bone meal or other products which have been processed in accordance with the processing methods set out in Chapter III of Annex IV and which are derived from bodies or parts of bodies of animals of the same species.U.K.
3.The feeding referred to in points 1 and 2 shall take place under the following conditions:U.K.
Feeding shall only take place in farms:
which have been registered by the competent authority on the basis of an application that is accompanied by documentation proving that there is no reason to suspect the presence of the TSE agent in the population of the species covered by the application;
where an appropriate surveillance system for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) in fur animals is in place on the farm and includes regular laboratory testing of samples for TSE;
which have provided appropriate guarantees that no animal by-product or meat-and-bone meal or other products which have been processed in accordance with Chapter III of Annex IV and which are derived from those animals or their offspring may enter the food or feed chain of other animals than fur animals;
which have had no known contact with any farm with a suspected or confirmed outbreak of TSE;
where the operator of the registered farm ensures that:
the carcases of fur animals intended for feeding to animals of the same species are handled and processed separately from carcases not authorised for that purpose,
fur animals fed with meat-and-bone meal or other products which have been processed in accordance with Chapter III of Annex IV and which are derived from animals of the same species are kept separate from animals not being fed with products derived from animals of the same species,
the farm complies with the requirements set out in point 2 of Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex VI and point (2)(b)(ii) of Chapter II of Annex VIII.
The operator of the farm shall ensure that meat-and-bone meal or other products derived from one species and intended for the feeding of the same species must:
have been processed in a processing plant approved under Article 24(1)(a) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and using only processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7 as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV to this Regulation;
have been produced from healthy animals killed for the production of fur.
In the event of any known or suspected contact with any farm with a suspected or confirmed outbreak of TSE, the operator of the farm must immediately:
inform the competent authority of such contact;
cease the dispatch of fur animals to any destination without a written authorisation of the competent authority.
CHAPTER IIU.K. Feeding of farmed animals with herbage
The following conditions shall apply to the feeding of farmed animals with herbage from land, either by direct access of the animals to that land or by using cut herbage as feed, provided that organic fertilisers or soil improvers have been applied to that land:
The waiting period of at least 21 days referred to in Article 11(1)(c) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 must have been observed,
Only organic fertilisers and soil improvers have been used which comply with Article 32(1) and (2) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with Chapter II of Annex XI hereto.
However, those conditions shall not apply, provided only the following organic fertilisers or soil improvers have been applied to land:
manure and guano;
digestive tract content, milk, milk-based products, milk-derived products, colostrum and colostrum products, which the competent authority does not consider to present a risk for the spread of any serious animal disease.
ANNEX IIIU.K. DISPOSAL AND RECOVERY
CHAPTER IU.K. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS FOR INCINERATION AND CO-INCINERATION
Section 1 U.K. General conditions
1.Operators of incineration and co-incineration plants referred to in Article 6(1)(b) of this Regulation shall ensure that the following hygiene conditions are met in the plants under their control:U.K.
Animal by-products and derived products must be disposed of as soon as possible after arrival, in accordance with conditions laid down by the competent authority. They shall be stored properly until disposal, in accordance with conditions laid down by the competent authority.
Plants must have appropriate arrangements for the cleaning and disinfection of containers and vehicles in place, in particular in a designated area from which wastewater is disposed of in accordance with Union legislation, to avoid risks of contamination.
Plants must be located on a well-drained hardstanding.
Plants must have appropriate arrangements for protection against pests, such as insects, rodents and birds. A documented pest control programme must be used for that purpose.
Staff must have access to adequate facilities for personal hygiene such as lavatories, changing rooms and washbasins, if necessary to prevent risks of contamination.
Cleaning procedures must be established and documented for all parts of the premises. Suitable equipment and cleaning agents must be provided for cleaning.
Hygiene control must include regular inspections of the environment and equipment. Inspection schedules and results must be documented and maintained for at least two years.
2.The operator of an incineration or co-incineration plant shall take all necessary precautions concerning the reception of animal by-products or derived products to prevent, or limit as far as practicable, direct risks to human or animal health.U.K.
3.Animals must not have access to the plants, animal by-products and derived products that are awaiting incineration or co-incineration or to ash resulting from the incineration or co-incineration of animal by-products.U.K.
4.If the incineration or co-incineration plant is located on a livestock holding:U.K.
there must be total physical separation between the incineration or co-incineration equipment and the livestock and their feed and bedding, with fencing where necessary;
equipment must be dedicated entirely to the operation of the incinerator and not used elsewhere on the holding or, alternatively, cleaned and disinfected before such use;
personnel working in the plant must change their outer clothing and footwear before handling livestock or livestock feed.
5.The storage of animal by-products and derived products that are awaiting incineration or co-incineration and of ashes must be in covered, correctly identified and, if appropriate, leak proof containers.U.K.
6.Incompletely incinerated animal by-products must be reincinerated or disposed of by other means, other than by disposal in an authorised landfill, in accordance with Articles 12, 13 and 14, as applicable, of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Operating conditions
Incineration or co-incineration plants shall be designed, equipped, built and operated in such a way that the gas resulting from the process is raised in a controlled and homogeneous fashion, even under the most unfavourable conditions, to a temperature of 850 °C for at least 2 seconds or to a temperature of 1 100 °C for 0.2 seconds, as measured near the inner wall or at another representative point of the chamber where the incineration or the co-incineration is carried out, as authorised by the competent authority.
Section 3 U.K. Incineration and co-incineration residues
1.Incineration and co-incineration residues shall be minimised in their amount and harmfulness. Such residues must be recovered, where appropriate, directly in the plant or outside it in accordance with relevant Union legislation or disposed of in an authorised landfill.U.K.
2.Transport and intermediate storage of dry residues, including dust, shall take place in such a way as to prevent dispersal in the environment, such as in closed containers.U.K.
Section 4 U.K. Measurement of temperature and of other parameters
1.Techniques shall be used to monitor the parameters and conditions relevant to the incineration or co-incineration process.U.K.
2.The approval issued by the competent authority, or conditions attached to it, shall lay down temperature measurement requirements.U.K.
3.The functioning of any automated monitoring equipment shall be subject to control and to an annual surveillance test.U.K.
4.Temperature measurement results shall be recorded and presented in an appropriate fashion to enable the competent authority to verify compliance with the permitted operating conditions laid down in this Regulation in accordance with procedures to be decided upon by that authority.U.K.
Section 5 U.K. Abnormal operating
In the case of a breakdown, or abnormal operating conditions of an incineration plant or a co-incineration plant, the operator shall reduce or close down operations as soon as practicable until normal operations can be resumed.
CHAPTER IIU.K. HIGH-CAPACITY INCINERATION AND CO-INCINERATION PLANTS
Section 1 U.K. Specific operating conditions
Incineration or co-incineration plants treating only animal by-products and derived products with a capacity of more than 50 kg per hour (high-capacity plants) and which are not required to have a permit to operate in accordance with Directive 2000/76/EC shall comply with the following conditions:
The plants must be equipped for each line with at least one auxiliary burner. This burner shall be switched on automatically when the temperature of the combustion gases after the last injection of combustion air falls below 850 °C or 1 100 °C, as applicable. It must also be used during plant start-up and shut-down operations to ensure that the temperature of 850 °C or of 1 100 °C, as applicable, is maintained at all times during these operations and as long as unburned material is in the chamber where the incineration or co-incineration is carried out.
When animal by-products or derived products are introduced into the chamber where the incineration or co-incineration is carried out by a continuous process, the plant must operate an automatic system to prevent the introduction of animal by-products or derived products at start-up, until the temperature of 850 °C or of 1 100 °C, as applicable, has been reached, and whenever the temperature is not maintained.
The operator must operate the incineration plant in such manner that a level of incineration is achieved such that the slag and bottom ashes total organic carbon content is less than 3 % or their loss on ignition is less than 5 % of the dry weight of the material. If necessary, appropriate techniques of pre-treatment shall be used.
Section 2 U.K. Water discharges
1.Sites of high capacity plants, including associated storage areas for animal by-products, shall be designed in such a way as to prevent unauthorised and accidental release of any polluting substances into soil, surface water and groundwater.U.K.
2.Storage capacity shall be provided for contaminated rainwater run-off from the plant site or for contaminated water arising from spillage or firefighting operations.U.K.
The operator shall, if necessary, ensure that such rainwater and such water can be tested and treated before discharge, when necessary.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. LOW-CAPACITY INCINERATION AND CO-INCINERATION PLANTS
Incineration and co-incineration plants treating only animal by-products and derived products with a maximum capacity of less than 50 kg of animal by-products per hour or per batch (low-capacity plants) and which are not required to have a permit to operate in accordance with Directive 2000/76/EC shall:
only be used for the disposal of:
dead pet animals referred to in Article 8(a)(iii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; or
Category 1 materials referred to in Article 8(b), (e) and (f), Category 2 materials referred to in Article 9 or Category 3 materials referred to in Article 10 of that Regulation;
when Category 1 materials referred to in Article 8(b) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 are introduced into the low-capacity plant, be equipped with an auxiliary burner;
operate in such way that the animal by-products are completely reduced to ash.
ANNEX IVU.K. PROCESSING
CHAPTER IU.K. REQUIREMENTS FOR PROCESSING PLANTS AND CERTAIN OTHER PLANTS AND ESTABLISHMENTS
Section 1 U.K. General conditions
1.Processing plants shall meet the following requirements, for processing by pressure sterilisation or in accordance with the processing methods referred to in Article 15(1)(b) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009:U.K.
Processing plants must not be situated on the same site as slaughterhouses or other establishments which have been approved or registered in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 or Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, unless the risks to public and animal health resulting from the processing of animal by-products, which originate from such slaughterhouses or other establishments, are mitigated by compliance with at least the following conditions:
the processing plant must be physically separated from the slaughterhouse or other establishment, where appropriate by locating the processing plant in a building that is completely separated from the slaughterhouse or other establishment;
the following must be installed and operated in the processing plant:
a conveyer system which links the processing plant to the slaughterhouse or other establishment and which may not be by-passed,
separate entrances, reception bays, equipment and exits for both the processing plant and the slaughterhouse or establishment;
measures must be taken to prevent the spreading of risks through the operation of personnel which is employed in the processing plant and in the slaughterhouse or other establishment;
unauthorised persons and animals must not have access to the processing plant.
By way of derogation from points (i) to (iv), in the case of processing plants processing Category 3 material, the competent authority may authorise other conditions instead of those set out in those points, aimed at mitigating the risks to public and animal health, including the risks arising from the processing of Category 3 material, which originates from off-site establishments approved or registered in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 or Regulation (EC) No 853/2004.
Member States shall inform the Commission and the other Member States in the framework of the Standing Committee on the Food Chain and Animal Health referred to in Article 52(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the use made of this derogation by their competent authorities;
The processing plant must have a clean and unclean sector, adequately separated. The unclean sector must have a covered place to receive animal by-products and must be constructed in such a way that it is easy to clean and disinfect. Floors must be laid in such a way as to facilitate the draining of liquids;
The processing plant must have adequate facilities including lavatories, changing rooms and washbasins for staff;
The processing plant must have sufficient production capacity for hot water and steam for the processing of animal by-products;
The unclean sector must, if appropriate, contain equipment to reduce the size of animal by-products and equipment for loading the crushed animal by-products into the processing unit;
Where heat treatment is required, all installations must be equipped with:
measuring equipment to monitor temperature against time and, if applicable for the processing method used, pressure at critical points;
recording devices to record continuously the results of these measurements in a way so that they remain accessible for the purpose of checks and official controls;
an adequate safety system to prevent insufficient heating;
To prevent recontamination of the derived product by the introduction of animal by-products, there must be a clear separation between the area of the plant where incoming material for processing is unloaded and the areas set aside for the processing of that product and the storage of the derived product.
2.The processing plant must have adequate facilities for cleaning and disinfecting the containers or receptacles in which animal by-products are received and the means of transport, other than ships, in which they are transported.U.K.
3.Adequate facilities must be provided for the disinfecting of vehicle wheels and the other parts of the vehicle, as appropriate, on leaving the unclean sector of the processing plant.U.K.
4.All processing plants must have a waste-water disposal system meeting the requirements set out by the competent authority in accordance with Union legislation.U.K.
5.The processing plant must have its own laboratory or make use of the services of an external laboratory. The laboratory must be equipped to carry out necessary analyses and be approved by the competent authority on the basis of an assessment of the capacity of the laboratory to carry out those analyses, be accredited according to internationally recognised standards or be subject to regular controls by the competent authority, to assess the capacity of the laboratory to carry out those analyses.U.K.
6.If on the basis of a risk assessment, the volume of products treated requires the regular or permanent presence of the competent authority, the processing plants must have an adequately equipped lockable room for the exclusive use of the inspection service.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Wastewater treatment
1.Processing plants processing Category 1 material and other premises where specified risk material is removed, slaughterhouses and processing plants processing Category 2 material shall have a pre-treatment process for the retention and collection of animal material as an initial step in the treatment of wastewater.U.K.
The equipment used in the pre-treatment process shall consist of drain traps or screens with apertures with a filter pore or a mesh size of no more than 6 mm in the downstream end of the process or equivalent systems that ensure that the solid particles in the wastewater passing through them are no more than 6 mm.
2.Wastewater from the premises as referred to in point 1 must enter a pre-treatment process which shall ensure that all wastewater has been filtered through the process before being drained off the premises. No grinding, maceration or any other processing or application of pressure shall be carried out which could facilitate the passage of solid animal material through the pre-treatment process.U.K.
3.All animal material retained in the pre-treatment process in premises as referred to in point 1 shall be collected and transported as Category 1 or Category 2 material, as appropriate, and disposed of in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.U.K.
4.Wastewater having passed the pre-treatment process in premises referred to in point 1 and wastewater from other premises handling or processing animal by-products shall be treated in accordance with Union legislation, without restrictions in accordance with this Regulation.U.K.
5.In addition to the requirements laid down in point 4, the competent authority may oblige operators to treat wastewater originating in the unclean sector of processing plants and in plants or establishments carrying out intermediate operations with Category 1 material or Category 2 material or storing Category 1 material or Category 2 material, in accordance with conditions which ensure that risks from pathogens are mitigated.U.K.
6.Without prejudice to points 1 to 5, the disposal of animal by-products, including blood and milk, or derived products through the wastewater stream shall be prohibited.U.K.
However, Category 3 material comprising of centrifuge or separator sludge may be disposed of through the wastewater stream, provided that it has been subject to one of the treatments for centrifuge or separator sludge set out in Part III of Section 4 of Chapter II of Annex X hereto.
Section 3 U.K. Specific requirements for the processing of Category 1 and Category 2 materials
The layout of processing plants processing Category 1 and Category 2 materials must ensure the total separation of Category 1 material from Category 2 material from reception of the raw material until dispatch of the resulting derived product, unless a mixture of Category 1 material and Category 2 material is processed as Category 1 material.
Section 4 U.K. Specific requirements for the processing of Category 3 materials
The following requirements shall apply in addition to the general conditions set out in Section 1:
Processing plants processing Category 3 materials shall not be located at the same site as processing plants processing Category 1 or Category 2 materials, unless located in a completely separate building.
However, the competent authority may authorise the processing of Category 3 material on a site where handling or processing of Category 1 or Category 2 material takes place, if cross-contamination is prevented due to:
the layout of the premises, in particular the arrangements for the reception, and by way of the further handling of raw materials;
the layout and the management of the equipment used for processing, including the layout and the management of separate processing lines or of cleaning procedures which are excluding the propagation of any possible risks to public and animal health; and
the layout and the management of the areas for the temporary storage of the end products.
Processing plants processing Category 3 material shall have in place an installation to check the presence of foreign bodies, such as packaging material or metallic pieces, in the animal by-products or derived products, if they are processing materials which are destined for feeding. Such foreign bodies shall be removed before or during processing.
CHAPTER IIU.K. HYGIENE AND PROCESSING REQUIREMENTS
Section 1 U.K. General hygiene requirements
In addition to the general hygiene requirements provided for in Article 25 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, processing plants shall have a documented pest control programme in place for the implementation of the arrangements for protection against pests, such as insects, rodents and birds, referred to in Article 25(1)(c) of that Regulation.
Section 2 U.K. General processing requirements
1.Accurately calibrated gauges/recorders must be used to monitor continuously the processing conditions. Records must be kept to show the date of calibration of gauges/recorders.U.K.
2.Material that may not have received the specified heat treatment, such as material discharged at start up or leakage from cookers, must be recirculated through the heat treatment or collected and reprocessed or disposed of in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.U.K.
Section 3 U.K. Processing methods for Category 1 and Category 2 material
Unless the competent authority requires the application of pressure sterilisation (method 1), Category 1 and Category 2 material shall be processed in accordance with processing methods 2, 3, 4 or 5 as referred to in Chapter III.
Section 4 U.K. Processing of Category 3 material
1.The critical control points that determine the extent of the heat treatments applied in processing shall include for each processing method as specified in Chapter III:U.K.
raw material particle size;
temperature achieved in the heat treatment process;
pressure, if applied to the raw material;
duration of the heat treatment process or feed rate to a continuous system. Minimum processing standards must be specified for each applicable critical control point.
2.In the case of chemical treatments which have been authorised by the competent authority as processing method 7 in accordance with point G of Chapter III, the critical control points that determine the extent of the chemical treatments applied shall include the pH adjustment achieved.U.K.
3.Records shall be maintained for at least two years to show that the minimum process values for each critical control point are applied.U.K.
4.Category 3 material shall be processed in accordance with any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7, or, in the case of material originating from aquatic animals, with any of the processing methods 1 to 7, as referred to in Chapter III.U.K.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. STANDARD PROCESSING METHODS
A.Processing method 1 (pressure sterilisation)U.K.
ReductionU.K.
1.If the particle size of the animal by-products to be processed is more than 50 millimetres, the animal by-products must be reduced in size using appropriate equipment, set so that the particle size after reduction is no greater than 50 millimetres. The effectiveness of the equipment must be checked daily and its condition recorded. If checks disclose the existence of particles larger than 50 millimetres, the process must be stopped and repairs made before the process is resumed.U.K.
Time, temperature and pressureU.K.
2.The animal by-products with the particle size of no greater than 50 millimetres must be heated to a core temperature of more than 133 °C for at least 20 minutes without interruption at a pressure (absolute) of at least 3 bars. The pressure must be produced by the evacuation of all air in the sterilisation chamber and the replacement of the air by steam (‘saturated steam’); the heat treatment may be applied as the sole process or as a pre- or post-process sterilisation phase.U.K.
3.The processing may be carried out in batch or continuous systems.U.K.
B.Processing method 2U.K.
ReductionU.K.
1.If the particle size of the animal by-products to be processed is more than 150 millimetres, the animal by-products must be reduced in size using appropriate equipment, set so that the particle size after reduction is no greater than 150 millimetres. The effectiveness of the equipment must be checked daily and its condition recorded. If checks disclose the existence of particles larger than 150 millimetres, the process must be stopped and repairs made before the process is resumed.U.K.
Time, temperature and pressureU.K.
2.After reduction the animal by-products must be heated in a manner which ensures that a core temperature greater than 100 °C is achieved for at least 125 minutes, a core temperature greater than 110 °C is achieved for at least 120 minutes and a core temperature greater that 120 °C is achieved for at least 50 minutes.U.K.
The core temperatures may be achieved consecutively or through a coincidental combination of the time periods indicated.
3.The processing must be carried out in a batch system.U.K.
C.Processing method 3U.K.
ReductionU.K.
1.If the particle size of the animal by-products to be processed is more than 30 millimetres, the animal by-products must be reduced in size using appropriate equipment, set so that the particle size after reduction is no greater than 30 millimetres. The effectiveness of the equipment must be checked daily and its condition recorded. If checks disclose the existence of particles larger than 30 millimetres, the process must be stopped and repairs made before the process is resumed.U.K.
Time, temperature and pressureU.K.
2.After reduction the animal by-products must be heated in a manner which ensures that a core temperature greater than 100 °C is achieved for at least 95 minutes, a core temperature greater than 110 °C is achieved for at least 55 minutes and a core temperature greater that 120 °C is achieved for at least 13 minutes.U.K.
The core temperatures may be achieved consecutively or through a coincidental combination of the time periods indicated.
3.The processing may be carried out in batch or continuous systems.U.K.
D.Processing method 4U.K.
ReductionU.K.
1.If the particle size of the animal by-products to be processed is more than 30 millimetres, the animal by-products must be reduced in size using appropriate equipment, set so that the particle size after reduction is no greater than 30 millimetres. The effectiveness of the equipment must be checked daily and its condition recorded. If checks disclose the existence of particles larger than 30 millimetres, the process must be stopped and repairs made before the process is resumed.U.K.
Time, temperature and pressureU.K.
2.After reduction the animal by-products must be placed in a vessel with added fat and heated in a manner which ensures that a core temperature greater than 100 °C is achieved for at least 16 minutes, a core temperature greater than 110 °C is achieved for at least 13 minutes, a core temperature greater than 120 °C is achieved for at least eight minutes and a core temperature greater that 130 °C is achieved for at least three minutes.U.K.
The core temperatures may be achieved consecutively or through a coincidental combination of the time periods indicated.
3.The processing may be carried out in batch or continuous systems.U.K.
E.Processing method 5U.K.
ReductionU.K.
1.If the particle size of the animal by-products to be processed is more than 20 millimetres, the animal by-products must be reduced in size using appropriate equipment, set so that the particle size after reduction is no greater than 20 millimetres. The effectiveness of the equipment must be checked daily and its condition recorded. If checks disclose the existence of particles larger than 20 millimetres, the process must be stopped and repairs made before the process is resumed.U.K.
Time, temperature and pressureU.K.
2.After reduction the animal by-products must be heated until they coagulate and then pressed so that fat and water are removed from the proteinaceous material. The proteinaceous material must then be heated in a manner which ensures that a core temperature greater than 80 °C is achieved for at least 120 minutes and a core temperature greater that 100 °C is achieved for at least 60 minutes.U.K.
The core temperatures may be achieved consecutively or through a coincidental combination of the time periods indicated.
3.The processing may be carried out in batch or continuous systems.U.K.
F.Processing method 6 (for Category 3 animal by-products originating from aquatic animal or aquatic invertebrates only)U.K.
ReductionU.K.
1.The animal by-products must be reduced to a particle size which is no greater than:U.K.
50 mm, in case of heat treatment in accordance with point 2(a); or
30 mm, in case of heat treatment in accordance with point 2(b).
They must then be mixed with formic acid to reduce and maintain the pH to 4,0 or lower. The mixture must be stored for at least 24 hours pending further treatment.
Time, temperature and pressureU.K.
2.After reduction, the mixture must be heated to:U.K.
a core temperature of at least 90 °C for at least 60 minutes; or
a core temperature of at least 70 °C for at least 60 minutes.
When using a continuous flow system, the progression of the product through the heat converter must be controlled by means of mechanical commands limiting its displacement in such way that at the end of the heat treatment operation the product has undergone a cycle which is sufficient in both time and temperature.
3.The processing may be carried out in batch or continuous systems.U.K.
G.Processing method 7U.K.
1.Any processing method authorised by the competent authority where the following have been demonstrated by the operator to that authority:U.K.
the identification of relevant hazards in the starting material, in view of the origin of the material, and of the potential risks in view of the animal health status of the Member State or the area or zone where the method is to be used;
the capacity of the processing method to reduce those hazards to a level which does not pose any significant risks to public and animal health;
the sampling of the final product on a daily basis over a period of 30 production days in compliance with the following microbiological standards:
Samples of material taken directly after the treatment:
Clostridium perfringens absent in 1 g of the products
Samples of material taken during or upon withdrawal from storage:
Salmonella: absence in 25g: n=5, c=0, m=0, M=0
Enterobacteriaceae: n=5, c=2; m=10; M=300 in 1 g
where:
=
number of samples to be tested;
=
threshold value for the number of bacteria; the result is considered satisfactory if the number of bacteria in all samples does not exceed m;
=
maximum value for the number of bacteria; the result is considered unsatisfactory if the number of bacteria in one or more samples is M or more; and
=
number of samples the bacterial count of which may be between m and M, the samples still being considered acceptable if the bacterial count of the other samples is m or less.
2.Details of the critical control points under which each processing plant satisfactorily complies with the microbiological standards must be recorded and maintained so that the operator and the competent authority can monitor the operation of the processing plant. The information to be recorded and monitored must include the particle size, and, as appropriate, the critical temperature, the absolute time, pressure profile, raw material feed rate and fat recycling rate.U.K.
3.By way of derogation from point 1, the competent authority may authorise the use of processing methods which have been approved prior to the date of entry into application of this Regulation, in accordance with Chapter III of Annex V to Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002.U.K.
4.The competent authority shall permanently or temporarily suspend the application of processing methods referred to in points 1 and 3, if it obtains evidence that any of the circumstances specified in point 1(a) or (b) have substantially changed.U.K.
5.The competent authority shall inform the competent authority of another Member State upon request about the information at its disposal under points 1 and 2 in relation to an authorised processing method.U.K.
CHAPTER IVU.K. ALTERNATIVE PROCESSING METHODS
Section 1 U.K. General provisions
1.Materials resulting from the processing of Category 1 and 2 materials, except biodiesel produced in accordance with point D of Section 2 of this Chapter, shall be permanently marked in accordance with the requirements for the marking of certain derived products set out in Chapter V of Annex VIII.U.K.
2.The competent authority of a Member State shall make the results of official controls available to the competent authority of another Member State upon request, when an alternative method is used for the first time in that Member State, in order to facilitate the introduction of the new alternative method.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Processing standards
A.Alkaline hydrolysis processU.K.
1.Starting materialU.K.
For this process, animal by-products of all categories may be used.
2.Processing methodU.K.
Alkaline hydrolysis shall be carried out according to the following processing standards:
Either a sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution (or a combination thereof) must be used in an amount that assures approximate molar equivalency to the weight, type and composition of the animal by-products to be digested.
In the case of high fat in the animal by-products that neutralises the base, the added base must be adjusted so that the molar equivalency referred to is achieved.
Animal by-products must be placed in a steel alloy container. The measured amount of alkali must be added either in solid form or as a solution as referred to in point (a).
The container must be closed and the animal by-products and alkali mixture must be heated to a core temperature of at least 150 °C and at a pressure (absolute) of at least 4 bars for at least:
three hours without interruption;
six hours without interruption in case of treatment of animal by-products referred to in Article 8(a)(i) and (ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
However, materials derived from Category 1 materials comprising of animals killed in the context of TSE eradication measures which are either ruminants not requiring TSE testing or ruminants which have been tested with a negative result in accordance with Article 6(1) of Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 may be processed in accordance with point 2(c)(i) of this Section; or
one hour without interruption in the case of animal by-products consisting of fish or of poultry materials.
The process must be carried out in a batch system and the material in the vessel must be constantly mixed in order to facilitate the digestion process until the tissues are dissolved and bones and teeth are softened; and
The animal by-products must be treated in such way that the requirements regarding time, temperature and pressure are achieved at the same time.
B.High pressure high temperature hydrolysis processU.K.
1.Starting materialU.K.
For this process, Category 2 and Category 3 materials may be used.
2.Processing methodU.K.
High pressure high temperature hydrolysis shall be carried out according to the following processing standards:
The animal by-products must be heated to a core temperature of at least 180 °C for at least 40 minutes without interruption at a pressure (absolute) of at least 12 bar, heated by indirect steam application to the biolytic reactor;
The process must be carried out in a batch and the material in the vessel must be constantly mixed; and
The animal by-products must be treated in such a manner that the requirements regarding time, temperature and pressure are achieved at the same time.
C.High pressure hydrolysis biogas processU.K.
1.Starting materialU.K.
For this process, animal by-products of all categories may be used.
2.Processing methodU.K.
The high pressure hydrolysis biogas process shall be carried out according to the following processing standards:
The animal by-products must be first processed using processing method 1 (pressure sterilisation) as set out in Chapter III in an approved processing plant;
Following the process referred to in point (a), the defatted materials must be treated at a temperature of at least 220 °C for at least 20 minutes at a pressure (absolute) of at least 25 bar, heated in a two-step procedure, first by direct steam injection, secondly indirect in a coaxial heat exchanger;
The process must be carried out in a batch or continuous system and the material is constantly mixed;
The animal by-products must be treated in such a manner that the requirements regarding time, temperature and pressure are achieved at the same time;
The resulting material must then be mixed with water and anaerobically fermented (biogas transformation) in a biogas reactor;
In the case of starting material of Category 1, the entire process must take place on the same site and in a closed system and the biogas produced during the process must be combusted rapidly in the same plant at a minimum of 900 °C followed by rapid chilling (‘quenching’).
D.Biodiesel production processU.K.
1.Starting materialU.K.
For this process, a fat fraction derived from animal by-products of all categories may be used.
2.Processing methodU.K.
Biodiesel production shall be carried out according to the following processing standards:
Unless fish oil or rendered fat are used which have been produced in accordance with Sections VIII or XII of Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, respectively, the fat fraction derived from animal by-products must be first processed using:
in the case of Category 1 or 2 materials, processing method 1 (pressure sterilisation) as set out in Chapter III; and
in the case of Category 3 materials, any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7 or, in the case of material derived from fish, processing methods 1 to 7 as set out in Chapter III;
The processed fat must then be processed further using one of the following methods:
a process whereby the processed fat must be separated from the protein and in the case of fat from ruminant origin, insoluble impurities in excess of 0,15 % by weight must be removed, and the processed fat must be subsequently submitted to esterfication and transesterfication.
However, esterfication is not required for processed fat derived from Category 3 material. For esterfication the pH must be reduced to less than 1 by adding sulphuric acid (H2SO4) or an equivalent acid and the mixture must be heated to 72 °C for at least two hours during which it must be intensely mixed.
Transesterfication must be carried out by increasing the pH to about 14 with potassium hydroxide or with an equivalent base at 35 °C to 50 °C for at least 15 minutes. Transesterfication shall be carried out twice under the conditions described in this point using a new base solution. This process must be followed by refinement of the products including vacuum distillation at 150 °C, leading to biodiesel;
a process using equivalent process parameters authorised by the competent authority.
E.Brookes’ gasification processU.K.
1.Starting materialU.K.
For this process, Category 2 and Category 3 material may be used.
2.Processing methodU.K.
Brookes’ gasification shall be carried out according to the following processing standards:
The afterburner chamber must be warmed up using natural gas;
The animal by-products must be loaded into the primary chamber of the gasificator and the door must be closed. The primary chamber must have no burners and must be heated instead by the transfer of heat by conduction from the afterburner, which must be underneath the primary chamber. The only air admitted to the primary chamber must be via three inlet valves mounted on the main door to enhance the efficiency of the process;
The animal by-products must be volatilised into complex hydrocarbons and the resultant gases must pass from the primary chamber via a narrow opening at the top of the back wall to the mixing and cracking zones, where they must be broken down into their constituent elements. Finally the gases must pass into the afterburner chamber where they must be burned in the flame of a natural gas fired burner in the presence of excess air;
Each process unit must have two burners and two secondary air fans for back-up in case of burner or fan failure. The secondary chamber must be designed to give a minimum residence time of two seconds at a temperature of at least 950 °C under all conditions of combustion;
On leaving the secondary chamber the exhaust gases must pass through a barometric damper at the base of the stack, which cools and dilutes them with ambient air, maintaining a constant pressure in the primary and secondary chambers;
The process must be carried out over a 24-hour cycle, which includes loading, processing, cool down and ash removal. At the end of the cycle the residual ash must be removed from the primary chamber by a vacuum extraction system into enclosed bags and sealed before transporting;
The gasification of material other than animal by-products must not be permitted.
F.Combustion of animal fat in a thermal boiler processU.K.
1.Starting materialU.K.
For this process, a fat fraction derived from animal by-products of all categories may be used.
2.Processing methodU.K.
Combustion of animal fat in a thermal boiler shall be carried out according to the following processing standards:
Unless fish oil or rendered fat are used which has been produced in accordance with Sections VIII or XII of Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, respectively, the fat fraction derived from animal by-products must first be processed using:
in the case of fat fraction of Category 1 and 2 materials which is intended to be combusted in another plant,
for the fat fraction from the processing of ruminants which have been tested with a negative result in accordance with Article 6(1) of Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 and from the processing of animals, other than ruminants which require TSE testing, any of the processing methods 1 to 5 as set out in Chapter III of this Annex.
for the fat fraction from the processing of other ruminants, processing method 1 as referred in Chapter III; and
in the case of Category 1 and 2 materials intended for combustion within the same plant and in the case of Category 3 material, any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7; in the case the materials are derived from fish, processing methods 1 to 7 as set out in Chapter III;
The fat fraction must be separated from the protein and in the case of fat from ruminant origin which is intended to be combusted in another plant, insoluble impurities in excess of 0,15 % by weight must be removed;
Following the process referred to in points (a) and (b), the fat must be:
vaporised in a steam-raising boiler and combusted at a temperature of at least 1 100 °C for at least 0,2 seconds; or
processed using equivalent process parameters authorised by the competent authority;
The combustion of material of animal origin other than animal fat must not be permitted;
The combustion of the fat derived from Category 1 and Category 2 materials shall take place in the same plant where the fat is rendered with the aim of utilising the energy generated for the rendering processes. However, the competent authority may authorise the movement of that fat to other plants for combustion provided that:
the plant of destination is authorised for the combustion;
the processing of food or feed in an approved plant on the same premises takes place under strict conditions of separation;
The combustion must be carried out in accordance with Union legislation for the protection of the environment, in particular, with reference to the standards of that legislation regarding best available techniques for the control and monitoring of emissions.
G.Thermomechanical biofuel production processU.K.
1.Starting materialU.K.
For this process, manure and digestive tract content and Category 3 material may be used.
2.Processing methodU.K.
Thermomechanical biofuel production shall be carried out according to the following processing standards:
The animal by-products must be loaded into a converter and subsequently treated at a temperature of 80 °C for a period of eight hours. During this period, the material must be constantly reduced in size using appropriate mechanical abrasion equipment.
The material must be subsequently treated at a temperature of 100 °C for at least two hours.
The particle size of the resulting material must not be larger than 20 millimetres;
The animal by-products must be treated in such a manner that the requirements regarding time, temperature and pressure set out in points (a) and (b) are achieved at the same time;
During the heat treatment of the material, evaporated water must be continually extracted from the air-space above the biofuel and must be passed through a stainless steel condenser. The condensate must be kept at a temperature of at least 70 °C for at least one hour before being discharged as wastewater;
After the heat treatment of the material, the resulting biofuel from the converter must then be discharged and automatically conveyed by a fully covered and interlocked conveyor to incineration or co-incineration on the same site;
The process must be carried out in a batch mode.
Section 3 U.K. Disposal and use of derived products
1.Products derived from the processing of:U.K.
Category 1 material shall be:
disposed of in accordance with Article 12(a) or (b) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
disposed of by burial in an authorised landfill;
transformed into biogas, provided the digestion residues are disposed of in accordance with points (i) or (ii); or
further processed into fat derivatives for uses other than feeding.
Category 2 or Category 3 material shall be:
disposed of as provided for in point 1(a)(i) or (ii), with or without prior processing as provided for in Article 12(a) and (b) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
further processed into fat derivatives for uses other than feeding;
used as an organic fertiliser or soil improver; or
composted or transformed into biogas.
2.Materials resulting from processing in accordance with:U.K.
the alkaline hydrolysis process defined in point A of Section 2 may be transformed in a biogas plant and subsequently combusted rapidly at a minimum of 900°C, followed by rapid chilling (‘quenching’); where material referred to in Article 8(a) and (b) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 has been used as starting material, the transformation into biogas shall take place on the same site as the processing and in a closed system;
the biodiesel production process may be:
in the case of biodiesel and of residues from the distillation of biodiesel, used as a fuel without restrictions under this Regulation (end point);
in the case of potassium sulphate, used for the production of derived products for application to land;
in the case of glycerine:
derived from Category 1 or Category 2 material which has been processed in accordance with processing method 1 as set out in Chapter III, transformed into biogas.
derived from Category 3 material, used for feeding.
3.Any resulting waste from the processing of animal by-products in accordance with this Section, such as sludge, filter contents, ash and digestion residues shall be disposed of in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with this Regulation.U.K.
ANNEX VU.K. TRANSFORMATION OF ANIMAL BY-PRODUCTS AND DERIVED PRODUCTS INTO BIOGAS, COMPOSTING
CHAPTER IU.K. REQUIREMENTS APPLICABLE TO PLANTS
Section 1 U.K. Biogas plants
1.A biogas plant must be equipped with a pasteurisation/hygienisation unit, which cannot be by-passed for the animal by-products or derived products introduced with a maximum particle size of 12 mm before entering the unit, with:U.K.
installations for monitoring that the temperature of 70 °C is reached during the time of one hour;
recording devices to record continuously the results of the monitoring measurements referred to in point (a); and
an adequate system to prevent insufficient heating.
2.By way of derogation from point 1, a pasteurisation /hygienisation unit shall not be mandatory for biogas plants that transform only:U.K.
Category 2 material that has been processed in accordance with processing method 1 as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV;
Category 3 material that has been processed in accordance with any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7, or in the case of material originating from aquatic animals, any of the processing methods 1 to 7, as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV;
Category 3 material that has undergone pasteurisation/hygienisation in another approved plant;
animal by-products which may be used as raw material without processing in accordance with Article 13(e)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with this Regulation;
animal by-products which have been subject to the alkaline hydrolysis process set out in point A of Section 2 of Chapter IV of Annex IV;
the following animal by-products, if authorised by the competent authority:
the animal by-products referred to in Article 10(f) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, which have undergone processing as defined in Article 2(1)(m) of Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 at the time when they are destined for purposes other than human consumption;
the animal by-products referred to in Article 10(g) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; or
animal by-products which are transformed into biogas, where the digestion residues are subsequently composted or processed or disposed of in accordance with this Regulation.
3.If the biogas plant is located on or next to premises where farmed animals are kept and the biogas plant does not only use manure, milk or colostrum which accrues from those animals, the plant shall be located at a distance from the area where such animals are kept.U.K.
That distance shall be determined in a manner which ensures that there is no unacceptable risk for the transmission of a disease communicable to humans or animals from the biogas plant.
In all cases, there must be total physical separation between that biogas plant and the animals and their feed and bedding, with fencing where necessary.
4.Each biogas plant must have its own laboratory or make use of an external laboratory. The laboratory must be equipped to carry out necessary analyses and be approved by the competent authority, be accredited according to internationally recognised standards or be subject to regular controls by the competent authority.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Composting plants
1.A composting plant must be equipped with a closed composting reactor or closed area, which cannot be by-passed for the animal by-products or derived products introduced into the plant, and it must be equipped with the following:U.K.
installations for monitoring temperature against time;
recording devices to record, where appropriate continuously, the results of the monitoring measurements referred to in point (a);
an adequate safety system to prevent insufficient heating.
2.By way of derogation from point 1, other types of composting systems may be allowed provided they:U.K.
are managed in such a way that all the material in the system achieves the required time and temperature parameters, including, where appropriate, continuous monitoring of the parameters; or
transform only materials referred to in point 2 of Section 1; and
comply with all other relevant requirements of this Regulation.
3.If the composting plant is located on or next to premises where farmed animals are kept and the composting plant does not only use manure, milk or colostrum which accrues from those animals, the composting plant shall be located at a distance from the area where animals are kept.U.K.
That distance shall be determined in a manner which ensures that there is no unacceptable risk for the transmission of a disease communicable to humans or animals from the composting plant.
In all cases, there must be total physical separation between that composting plant and the animals and their feed and bedding, with fencing where necessary.
4.Each composting plant must have its own laboratory or make use of an external laboratory. The laboratory must be equipped to carry out necessary analyses and be approved by the competent authority, be accredited according to internationally recognised standards or be subject to regular controls by the competent authority.U.K.
CHAPTER IIU.K. HYGIENE REQUIREMENTS APPLICABLE TO BIOGAS AND COMPOSTING PLANTS
1.Animal by-products must be transformed as soon as possible after arrival at the biogas or composting plant. They must be stored properly until treated.U.K.
2.Containers, receptacles and vehicles used for transporting untreated material must be cleaned and disinfected in a designated area.U.K.
That area must be situated or designed so as to prevent risk of contamination of treated products.
3.Preventive measures against birds, rodents, insects or other vermin must be taken systematically.U.K.
A documented pest-control programme must be used for that purpose.
4.Cleaning procedures must be documented and established for all parts of the premises. Suitable equipment and cleaning agents must be provided for cleaning.U.K.
5.Hygiene control must include regular inspections of the environment and equipment. Inspection schedules and results must be documented.U.K.
6.Installations and equipment must be kept in a good state of repair and measuring equipment must be calibrated at regular intervals.U.K.
7.Digestion residues and compost must be handled and stored at the biogas or composting plant in such way as to prevent recontamination.U.K.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. TRANSFORMATION PARAMETERS
Section 1 U.K. Standard transformation parameters
1.Category 3 material which is used as raw material in a biogas plant equipped with a pasteurisation/hygienisation unit must be submitted to the following minimum requirements:U.K.
maximum particle size before entering the unit: 12 mm;
minimum temperature in all material in the unit: 70 °C; and
minimum time in the unit without interruption: 60 minutes.
However, Category 3 milk, milk-based products, milk-derived products, colostrum and colostrum products may be used without pasteurisation/hygienisation as raw material in a biogas plant, if the competent authority does not consider them to present a risk of spreading any serious transmissible disease to humans or animals.
The minimum requirements set out in points (b) and (c) of this point shall also apply to Category 2 material which is introduced into a biogas plant without prior processing in accordance with Article 13(e)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
2.Category 3 material which is used as raw material in a composting plant must be submitted to the following minimum requirements:U.K.
maximum particle size before entering the composting reactor: 12 mm;
minimum temperature in all material in the reactor: 70 °C; and
minimum time without interruption: 60 minutes.
The minimum requirements set out in points (b) and (c) of this point shall also apply to Category 2 material which is composted without prior processing in accordance with Article 13(e)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
Section 2 U.K. Alternative transformation parameters for biogas and composting plant
1.The competent authority may authorise the use of parameters other than the parameters set out in point 1 of Section 1 of Chapter I and other than the standard transformation parameters, provided that the applicant for such use demonstrates that such parameters ensure adequate reduction of biological risks. That demonstration shall include a validation, which shall be carried out in accordance with the following requirements:U.K.
Identification and analysis of possible hazards, including the impact of input material, based on a full description of the transformation conditions and parameters;
A risk assessment, which evaluates how the specific transformation conditions referred to in point (a) are achieved in practice under normal and atypical situations;
Validation of the intended process by measuring the reduction of viability/infectivity of:
endogenous indicator organisms during the process, where the indicator is:
consistently present in the raw material in high numbers,
not less heat resistant to the lethal aspects of the transformation process, but also not significantly more resistant than the pathogens for which it is being used to monitor,
relatively easy to quantify and to identify and to confirm; or
a well-characterised test organism or virus, during exposure, introduced in a suitable test body into the starting material.
The validation of the intended process referred to in point (c) must demonstrate that the process achieves the following overall risk reduction:
for thermal and chemical processes by:
a reduction of 5 log10 of Enterococcus faecalis or Salmonella Senftenberg (775W, H2S negative),
reduction of infectivity titre of thermoresistant viruses such as parvovirus by at least 3 log10, whenever they are identified as a relevant hazard; and
as regards chemical processes also by:
a reduction of resistant parasites such as eggs of Ascaris sp. by at least 99,9 % (3 log10) of viable stages;
Designing a complete control programme including procedures for monitoring the functioning of the process referred to in point (c);
Measures ensuring continuous monitoring and supervision of the relevant process parameters fixed in the control programme when operating the plant.
Details on the relevant process parameters used in a biogas or composting plant as well as other critical control points must be recorded and maintained so that the owner, operator or their representative and the competent authority can monitor the operation of the plant.
Records must be made available by the operator to the competent authority on request. Information relating to a process authorised under this point must be made available to the Commission on request.
2.By way of derogation from point 1, pending the adoption of rules as referred to in Article 15(2)(a)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the competent authority may authorise the use of specific requirements other than those laid down in this Chapter, provided that they guarantee an equivalent effect regarding the reduction of pathogens, for:U.K.
catering waste used as the only animal by-product in a biogas or composting plant; and
mixtures of catering waste with the following materials:
manure;
digestive tract content separated from the digestive tract;
milk;
milk-based products;
milk-derived products;
colostrum;
colostrum products;
eggs;
egg products;
animal by-products referred to in Article 10(f) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, which have undergone processing as defined in Article 2(1)(m) of Regulation (EC) No 852/2004.
3.Where the materials referred to in point 2(b) or derived products referred to in Article 10(g) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 are the only starting material of animal origin being treated in a biogas or composting plant, the competent authority may authorise the use of specific requirements other than those specified in this Chapter provided that it:U.K.
does not consider that those materials present a risk of spreading any serious transmissible disease to humans or animals;
considers that the digestion residues or compost are unprocessed material and obliges operators to handle them in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with this Regulation.
4.Operators may place on the market digestion residues and compost, which have been produced according to parameters which have been authorised by the competent authority:U.K.
in accordance with point 1;
in accordance with points 2 and 3, only within the Member State where those parameters have been authorised.
Section 3 U.K. Standards for digestion residues and compost
1.
Representative samples of the digestion residues or compost taken during or immediately after transformation at the biogas plant or composting at the composting plant in order to monitor the process must comply with the following standards:
Escherichia coli: n = 5, c = 1, m = 1 000, M = 5 000 in 1 g;
or
Enterococcaceae: n = 5, c = 1, m = 1 000, M = 5 000 in 1 g;
and
Representative samples of the digestion residues or compost taken during or on withdrawal from storage must comply with the following standards:
Salmonella: absence in 25 g: n = 5; c = 0; m = 0; M = 0
Where in the case of point (a) or (b):
=
number of samples to be tested;
=
threshold value for the number of bacteria; the result is considered satisfactory if the number of bacteria in all samples does not exceed m;
=
maximum value for the number of bacteria; the result is considered unsatisfactory if the number of bacteria in one or more samples is M or more; and
=
number of samples the bacterial count of which may be between m and M, the sample still being considered acceptable if the bacterial count of the other samples is m or less.
2.Digestion residues or compost, which do not comply with the requirements set out in this Section, shall be resubmitted to transformation or composting, and in the case of Salmonella handled or disposed of in accordance with the instructions of the competent authority.U.K.
ANNEX VIU.K. SPECIAL RULES ON RESEARCH, FEEDING AND COLLECTION AND DISPOSAL
CHAPTER IU.K. SPECIAL RULES ON SAMPLES FOR RESEARCH AND OTHER PURPOSES
Section 1 U.K. Research and diagnostic samples
1.Operators shall ensure that consignments of research and diagnostic samples are accompanied by a commercial document, which must specify:U.K.
the description of the material and the animal species of origin;
the category of the material;
the quantity of the material;
the place of origin and the place of dispatch of the material;
the name and the address of the consignor;
the name and the address of the consignee and/or user.
2.Users that handle research and diagnostic samples shall take all necessary measures to avoid the spreading of diseases communicable to humans or animals during the handling of the materials under their control, in particular by way of the application of good laboratory practice.U.K.
3.Any subsequent use of research and diagnostic samples for purposes other than those referred to in point 38 of Annex I shall be prohibited.U.K.
4.Unless they are kept for reference purposes, research and diagnostic samples and any products derived from the use of those samples shall be disposed of:U.K.
as waste by incineration or co-incineration;
in case of the animal by-products or derived products referred to in Article 8 (a)(iv), Article 8(c) and (d) and Article 9 and Article 10 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 which are part of cell cultures, laboratory kits or laboratory samples, by a treatment under conditions which are at least equivalent to the validated method for steam autoclaves(53) and subsequent disposal as waste or wastewater in accordance with relevant Union legislation;
by pressure sterilisation and subsequent disposal or use in accordance with Articles 12, 13 and 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
5.Users that handle research and diagnostic samples shall keep a register of consignments of such samples.U.K.
The register shall include the information referred to in point 1 and the date and method of disposal of the samples and of any derived products.
6.By way of derogation from points 1, 4 and 5, the competent authority may accept the handling and disposal of research and diagnostic samples for educational purposes under other conditions which ensure that no unacceptable risks for public or animal health arise.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Trade samples and display items
1.Trade samples and display items may only be transported, used and disposed of in accordance with points 1 to 4 and 6 of Section 1.U.K.
2.Unless trade samples are kept for reference purposes, they shall be, after the particular studies or analyses have been concluded:U.K.
redispatched to the Member State of origin;
dispatched to another Member State or third country, if such dispatch has been authorised by the competent authority of the Member State or third country of destination in advance; or
disposed of or used in accordance with Articles 12, 13 and 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
3.After the exhibition or after the artistic activity has been concluded, display items shall be redispatched to the Member State of origin, dispatched or disposed of, in accordance with point 2.U.K.
CHAPTER IIU.K. SPECIAL FEEDING RULES
Section 1 U.K. General requirements
Category 2 and 3 materials as referred to in Article 18(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be fed to the animals referred to in paragraph (1)(a), (d), (f), (g) and (h) of that Article subject to compliance with at least the following conditions, in addition to any conditions laid down by the competent authority in accordance with Article 18(1) of that Regulation:
The animal by-products shall be transported to the users or to collection centres in accordance with Sections 1 and 3 of Chapter I of Annex VIII.
Collection centres shall be registered by the competent authority, provided that:
they comply with the requirements for plants carrying out the intermediate operations set out in Chapter II of Annex IX; and
they have adequate facilities for destroying unused material, or send it to an approved processing plant or to an approved incineration or co-incineration plant in accordance with this Regulation.
Member States may authorise the use of a processing plant for Category 2 material as a collection centre.
Operators of collection centres supplying material, other than animal by-products originating from aquatic animals and from aquatic invertebrates, to final users must ensure that it undergoes one of the following treatments:
denaturing with a solution of a colouring agent; the solution must be of such a strength that the colouring on the stained material is clearly visible and does not disappear when the coloured materials are subject to freezing or chilling, and the whole surface of all pieces of material must have been covered with such solution either by immersing the material in, or spraying or otherwise applying the solution;
sterilisation by boiling or steaming under pressure until every piece of material is cooked throughout; or
any other handling or treatment authorised by the competent authority responsible for the operator.
Section 2 U.K. Feeding of certain species in feeding stations
1.The competent authority may authorise the use of Category 1 material referred to in Article 18(2)(b) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 for the feeding of the following endangered and protected species in feeding stations under the following conditions:U.K.
The material must be fed to:
one of the following species of necrophagous birds in the following Member States:
| Member State | Animal species |
|---|---|
| Bulgaria | bearded vulture (Gypaetus barbatus) black vulture (Aegypius monachus) Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus) golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) imperial eagle (Aquila heliaca) white-tailed eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) black kite (Milvus migrans) red kite (Milvus milvus) |
| Greece | bearded vulture (Gypaetus barbatus) black vulture (Aegypius monachus) Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus) golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) imperial eagle (Aquila heliaca) white-tailed eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) black kite (Milvus migrans) |
| Spain | bearded vulture (Gypaetus barbatus) black vulture (Aegypius monachus) Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus) golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) Spanish imperial eagle (Aquila adalberti) black kite (Milvus migrans) red kite (Milvus milvus) |
| France | bearded vulture (Gypaetus barbatus) black vulture (Aegypius monachus) Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus) golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) white-tailed eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) black kite (Milvus migrans) red kite (Milvus milvus) |
| Italy | bearded vulture (Gypaetus barbatus) black vulture (Aegypius monachus) Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus) golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) black kite (Milvus migrans) red kite (Milvus milvus) |
| Cyprus | black vulture (Aegypius monachus) griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus) |
| Portugal | black vulture (Aegypius monachus) Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus) golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) |
| Slovakia | golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) imperial eagle (Aquila heliaca) white-tailed eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) black kite (Milvus migrans) red kite (Milvus milvus) |
one of the species of the order Carnivora which are listed in Annex II to Directive 92/43/EEC, in special areas of conservation which have been set up under that Directive; or
one of the species of the orders Falconiformes or Strigiformes, which are listed in Annex I to Directive 2009/147/EC, in special protection areas which have been set up under that Directive;
The competent authority has granted an authorisation to the operator responsible for the feeding station.
The competent authority shall grant such authorisations provided that:
the feeding is not used as an alternative way of disposal of specified risk materials or the disposal of fallen ruminant stock containing such material posing a TSE risk;
an appropriate surveillance system for TSEs as laid down in Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 is in place involving regular laboratory testing of samples for TSE;
The competent authority must ensure coordination with any other competent authorities responsible for the supervision of the requirements laid down in the authorisation;
The competent authority must be satisfied, on the basis of an assessment of the specific situation of the species concerned and their habitat, that the conservation status of the species will be improved;
The authorisation granted by the competent authority must:
refer to and name the species actually concerned;
describe in detail the location of the feeding station in the geographical area where feeding shall take place; and
be immediately suspended in the case of:
a suspected or confirmed link to the spread of TSE until the risk can be excluded, or
non-compliance with any of the rules provided for in this Regulation.
The operator responsible for the feeding shall:
dedicate an area to the feeding that is enclosed and to which access is limited to animals of the species to be conserved, if appropriate by fences or by other means which correspond to the natural feeding patterns of those species;
ensure that eligible bodies of bovine animals and at least 4 % of eligible bodies of ovine and caprine animals intended to be used for feeding are tested prior to that use with a negative result, in the TSE monitoring programme carried out in accordance with Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 and, if applicable, in accordance with a Decision adopted in accordance with the second subparagraph of Article 6(1b) of that Regulation; and
keep records at least of the number, nature, estimated weight and origin of the carcases of the animals used for feeding, the date of the feeding, the location where feeding took place and if applicable, the results of the TSE tests.
2.When a Member State applies to the Commission to be included into the list set out under point 1(a), it shall submit:U.K.
a detailed justification for the extension of the list to include certain species of necrophagous birds in that Member State, including an explanation of the reasons why it is necessary to feed such birds with Category 1 material instead of with Category 2 or Category 3 material;
an explanation of the measures which will be taken in order to ensure compliance with point 1.
Section 3 U.K. Feeding of wild animals outside feeding stations
The competent authority may authorise the use of Category 1 material comprising of entire bodies or parts of dead animals containing specified risk materials outside feeding stations, if appropriate without prior collection of the dead animals, for feeding to wild animals referred to in point 1(a) of Section 2 under the following conditions:
The competent authority must be satisfied, on the basis of an assessment of the specific situation of the species concerned and their habitat, that the conservation status of the species will be improved;
The competent authority must identify in the authorisation, holdings or herds within a geographically defined feeding zone under the following conditions:
The feeding zone must not extend to areas where intensive farming of animals takes place;
Farmed animals in holdings or herds in the feeding zone must be under the regular surveillance of an official veterinarian regarding the prevalence of TSE and of diseases transmissible to humans or animals;
Feeding must be immediately suspended in the case of:
a suspected or confirmed link to the spread of TSE in a holding or herd, until the risk can be excluded;
a suspected or confirmed outbreak of a serious disease transmissible to humans or animals in a holding or herd, until the risk can be excluded; or
non-compliance with any of the rules provided for in this Regulation;
The competent authority must specify in the authorisation:
appropriate measures to prevent the transmission of TSE and of transmissible diseases from the dead animals to humans or other animals, such as measures targeted at the feeding patterns of the species to be conserved, seasonal feeding restrictions, movement restrictions for farmed animals and other measures intended to control possible risks of transmission of a disease communicable to humans or animals, such as measures relating to species present in the feeding zone for the feeding of which the animal by-products are not used;
the responsibilities of persons or entities in the feeding zone who are assisting with the feeding or responsible for farmed animals, in relation to the measures referred to under point (i);
the conditions for the imposition of penalties as referred to in Article 53 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 which are applicable to infringements of measures referred to under point (i) by the persons or entities referred to under point (ii) of this point (d);
Where the feeding is carried out without the prior collection of the dead animals, an estimate of the likely mortality rate of farmed animals in the feeding zone and of the likely feeding requirements of the wild animals must be carried out, as a basis for the assessment of the potential risks of disease transmission.
Section 4 U.K. Feeding of zoo animals with Category 1 material
The competent authority may authorise the use of Category 1 material comprising of entire bodies or parts of dead animals containing specified risk materials and the use of material derived from zoo animals, for the feeding of zoo animals under the following conditions:
The competent authority must have granted an authorisation to the operator responsible for the feeding. The competent authority shall grant such authorisations provided that:
the feeding is not used as an alternative way of disposal of specified risk materials or disposal of fallen ruminant stock containing such material posing a TSE risk;
when Category 1 material comprising of entire bodies or parts of dead animals containing specified risk material, which originates from bovine animals is used, an appropriate surveillance system for TSEs as laid down in Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 is in place involving regular laboratory testing of samples for TSEs;
The authorisation granted by the competent authority must be immediately suspended in the case of:
a suspected or confirmed link to the spread of TSEs until the risk can be excluded; or
non-compliance with any of the rules provided for in this Regulation;
The operator responsible for the feeding shall:
store the material to be used for the feeding and carry out the feeding in an enclosed and fenced area to ensure that no carnivorous animal other than the zoo animals for which the authorisation has been granted have access to the material for the feeding;
ensure that ruminant animals intended to be used for feeding are included in the TSE monitoring programme carried out in accordance with Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 and, if applicable, in accordance with a Decision adopted in accordance with the second subparagraph of Article 6(1b) of that Regulation;
keep records at least of the number, nature, estimated weight and origin of the bodies of the animals used for feeding, the results of the TSE tests and the date of the feeding.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. SPECIAL RULES ON COLLECTION AND DISPOSAL
Section 1 U.K. Special disposal rules for animal by-products
1.If the competent authority authorises the disposal of animal by-products on site in accordance with Article 19(1)(a), (b), (c) and (e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, such disposal may take place:U.K.
by burning or burial on the premises on which the animal by-products originate;
in an authorised landfill; or
by burning or burial at a site which minimises the risk to animal and public health and the environment, provided that the site is located within a range of distance sufficient to enable the competent authority to manage the prevention of the risk to animal and public health and the environment.
2.The burning of animal by-products on the sites referred to in Article 19(1)(b), (c) and (e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 must be carried out in such a way to ensure that they are burnt:U.K.
on a properly constructed pyre and the animal by-products reduced to ash;
without endangering human health;
without using processes or methods which could harm the environment, in particular when they could result in risks to water, air, soil and plants and animals or through noise or odours;
under conditions which ensure that any resulting ash is disposed of by burial in an authorised landfill.
3.The burial of animal by-products on the sites referred to in Article 19(1)(a), (b), (c) and (e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 must be carried out to ensure that they are buried:U.K.
in such a way that carnivorous or omnivorous animals cannot gain access to them;
in an authorised landfill or in another site without endangering human health and using processes or methods which do not harm the environment, in particular when they could result in risks to water, air, soil and plants and animals, or through noise or odours.
4.In the case of disposal in accordance with Article 19(1)(a), (b), (c) and (e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the movement of the animal by-products from the place of origin to the place of disposal must be carried out under the following conditions:U.K.
the animal by-products are transported in secure, leak-proof containers or vehicles;
the loading and unloading of the animal by-products is supervised by the competent authority, if appropriate;
the vehicle wheels are disinfected upon leaving the site of origin;
containers and vehicles used for transporting animal by-products are thoroughly cleansed and disinfected after unloading of the animal by-products; and
adequate escorts for the vehicles, leak testing and double covering are provided, if appropriate.
Section 2 U.K. Burning and burial of animal by-products in remote areas
The maximum percentage as referred to in Article 19(2) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 shall not exceed the following:
10 % of the bovine population of the Member State concerned;
25 % of the ovine and caprine population of the Member State concerned;
10 % of the porcine population of the Member State concerned; and
a percentage of the population of other species which is determined by the competent authority, on the basis of an assessment of the possible risks for public and animal health which arise from the disposal of animals of those species by burning or burial on site.
Section 3 U.K. Burning and burial of bees and apiculture by-products
In the case of bees and apiculture by-products, the competent authority may authorise the disposal by burning or burial on site, as referred to in Article 19(1)(f) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, provided that all necessary measures are taken to ensure that the burning or burial does not endanger animal or human health or the environment.
CHAPTER IVU.K. DISPOSAL BY OTHER MEANS
By way of derogation from Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, Member States may authorise the collection, transport and disposal of the Category 3 materials referred to in Article 10(f) of that Regulation by means other than burning or burial on site provided that:
the materials do not exceed a volume of 20 kg per week from the establishment or plant where the materials are collected, regardless of the species of origin of the materials;
the materials are collected, transported and disposed of by means which prevent the transmission of unacceptable risks to public and animal health;
the competent authority carries out regular checks, including checks on the records kept by operators, in the establishments or plants where the materials are collected, to ensure compliance with the provisions of this Section.
Member States may decide to increase the volume referred to in point (a) to a maximum of 50 kg per week, provided that they present a detailed justification to the Commission and to the other Member States in the framework of the Standing Committee on the Food Chain and Animal Health referred to in Article 52(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, which specifies the nature of the activities for which the volume is to be increased, the species of origin of the animal by-products concerned, and an explanation of the reasons why it is necessary to increase the volume, in view of the adequate system for the handling and disposal of animal by-products and derived products on their territory, as referred to in Article 4(4) of that Regulation.
ANNEX VIIU.K. STANDARD FORMAT FOR APPLICATIONS FOR ALTERNATIVE METHODS
CHAPTER IU.K. Language regime
1.Applications for authorisation of an alternative method of use or disposal of animal by-products or derived products as referred to in Article 20 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 (applications) shall be submitted in one of the official languages of the European Union as referred to in Article 1 of Regulation No 1 of 1958.U.K.
2.Interested parties that submit such applications in a language other than English shall validate the official translation of their application, which EFSA shall provide, prior to the assessment.U.K.
The period referred to in Article 20(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 shall only start once the interested party has validated the official translation of the application.
CHAPTER IIU.K. Content of applications
1.Applications shall contain all necessary information concerning the following points, in order to allow EFSA to assess the safety of their proposed alternative method:U.K.
the categories of animal by-products which are intended to be submitted to the alternative method, by reference to the categories referred to in Articles 8,9, and 10 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
the identification and characterisation of risk materials according to the following principles:
Significant risk materials must be identified separately. For each material, the likelihood of human and animal exposure under normal and emergency/abnormal operating conditions must be assessed. In the case of significant exposure, the potential risk must be assessed;
the agent risk reduction according to the following principles:
The risk reduction for human and animal health which can be achieved by the process must be estimated on the basis of direct measurements.
Where no direct measurement is available, modelling or extrapolation from other processes may also be used. In order to demonstrate effective risk reduction, the identified hazard (such as Salmonella) must be quantified both in the input (raw) material and in the resulting output material. For the purpose of this Chapter, output material comprises any end-products resulting from and by-products derived from the process.
Estimates must be accompanied by evidence. This includes – for measurements – information on the methodology used (sensitivity and reliability of the methods used), nature of samples which have been analysed and evidence that samples are representative (relevant real samples, number of tests performed).
If surrogates for prion measurement are used, an explanation should be given of their relevance. An evaluation of the validity with the uncertainties involved must be provided;
the risk containment according to the following principles:
The likely effectiveness of the technical measures used to ensure that the risks are contained must be analysed.
That analysis must reflect normal and abnormal/emergency operating conditions including a breakdown of the process.
Monitoring and surveillance procedures to demonstrate containment must be specified.
If full containment is not achievable, an assessment shall be required of any potential risk;
the identification of interdependent processes according to the following principles:
Possible indirect impacts which may influence the risk reduction capacity of a particular process must be evaluated.
Indirect impacts may arise from transport, storage and safe disposal of end-products resulting from and by-products derived from a process;
the intended end use of the end products and by-products according to the following principles:
The intended end use of end products and by-products of a process must be specified.
The likely risks involved must be calculated from the risk reduction estimated in accordance with point (c), which may arise to human and animal health.
2.Applications shall be submitted with documentary evidence, in particular a flow diagram showing the functioning of the process, the evidence indicated under point 1(c), as well as other evidence aiming to substantiate the explanation given under the framework set out under point 1.U.K.
3.Applications shall include a contact address for the interested party, which shall include the name and full address, telephone and/or fax numbers and/or the electronic mail address of a particular contact person that is responsible as or on behalf of the interested party.U.K.
ANNEX VIIIU.K. COLLECTION, TRANSPORT AND TRACEABILITY
CHAPTER IU.K. COLLECTION AND TRANSPORT
Section 1 U.K. Vehicles and containers
1.As from the starting point in the manufacturing chain referred to in Article 4(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, animal by-products and derived products must be collected and transported in sealed new packaging or covered leak-proof containers or vehicles.U.K.
2.Vehicles and reusable containers, and all reusable items of equipment or appliances that come into contact with animal by-products or derived products, other than derived products which are placed on the market in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 767/2009 and which are stored and transported in accordance with Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 183/2005, must be maintained in a clean condition.U.K.
In particular, unless they are dedicated to the carriage of particular animal by-products or derived products in a way which avoids cross-contamination, they must be:
clean and dry before use; and
cleaned, washed and/or disinfected after each use to the extent necessary to avoid cross-contamination.
3.Reusable containers must be dedicated to the carriage of a particular animal by-product or derived product to the extent necessary to avoid cross-contamination.U.K.
However, reusable containers may be used, provided the competent authority has authorised such use:
for the carriage of different animal by-products or derived products provided that they are cleaned and disinfected between the different uses in a manner which prevents cross-contamination;
for the carriage of animal by-products or derived products referred to in Article 10(f) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, following their use for the carriage of products intended for human consumption, under conditions which prevent cross-contamination.
4.Packaging material must be disposed of, by incineration or by other means in accordance with Union legislation.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Temperature conditions
1.The transport of animal by-products destined for the production of feed material or raw petfood must take place at an appropriate temperature, in the case of animal by-products from meat and meat products which have been destined for purposes other than human consumption, at a maximum of 7 °C, unless they are used for feeding purposes in accordance with Chapter I of Annex II, in order to avoid any risk to animal or public health.U.K.
2.Unprocessed Category 3 material destined for the production of feed material or petfood must be stored and transported chilled, frozen or ensiled, unless:U.K.
it is processed within 24 hours after collection or after the end of storage in chilled or frozen form, if the subsequent transport takes place in means of transport in which the storage temperature is maintained;
in the case of milk, milk-based products or milk-derived products which have not been subject to any of the treatments referred to in Part I of Section 4 of Chapter II of Annex X, it is transported chilled and in insulated containers, unless risks can be mitigated by other measures, due to the characteristics of the material.
3.The design of vehicles used for refrigerated transport must ensure the maintenance of an appropriate temperature throughout transport, and allow that temperature to be monitored.U.K.
Section 3 U.K. Derogation for collection and transport of Category 3 material comprising of milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products
Section 1 shall not apply to the collection and transportation of Category 3 material comprising of milk, milk-based products and milk derived products by operators of milk-processing establishments which have been approved in accordance with Article 4 of Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, where they are receiving products which they have previously delivered and which are returned to them, in particular from their customers.
Section 4 U.K. Derogation for collection and transport of manure
By way of derogation from Section 1, the competent authority may accept the collection and transport of manure transported between two points located on the same farm or between farmers and users in the same Member State under other conditions which provide for the prevention of unacceptable risks to public and animal health.
CHAPTER IIU.K. IDENTIFICATION
1.All necessary measures must be taken to ensure that:U.K.
consignments of animal by-products and derived products are identifiable and kept separate and identifiable during collection where the animal by-products originate and during transportation;
a marking substance for the identification of animal by-products or derived products of a specific category is only used for the category for which its use is required under this Regulation, or is established or laid down pursuant to point 4;
consignments of animal by-products and derived products are dispatched from one Member State to another Member State in packaging, containers or vehicles which are prominently and, at least for the period of transport, indelibly colour-coded for displaying information as provided for in this Regulation on the surface or part of the surface of a packaging, container or vehicle, or on a label or symbol applied to them as follows:
in the case of Category 1 materials, using the colour black;
in the case of Category 2 materials (other than manure and digestive tract content), using the colour yellow;
in the case of Category 3 materials, using the colour green with a high content of blue to ensure that it is clearly distinguishable from the other colours;
in the case of imported consignments, the colour referred to for the respective material under points (i), (ii) and (iii), as from the time when the consignment has passed the border inspection post of first entry into the Union.
2.During transport and storage, a label attached to the packaging, container or vehicle must:U.K.
clearly indicate the category of the animal by-products or of the derived products; and
bear the following words visibly and legibly displayed on the packaging, a container or vehicle, as applicable:
in the case of Category 3 material, ‘not for human consumption’;
in the case of Category 2 material (other than manure and digestive tract content) and derived products from Category 2 material, ‘not for animal consumption’; however, when Category 2 material is intended for the feeding of animals referred to in Article 18(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 under the conditions provided for or laid down in accordance with that Article, the label shall instead indicate ‘for feeding to …’ completed with the name of the specific species of those animals for the feeding of which the material is intended;
in the case of Category 1 material and derived products from Category 1 material where they are destined for
disposal, ‘for disposal only’;
the manufacture of petfood, ‘for manufacture of pet food only’;
the manufacture of a derived product referred to in Article 36 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, ‘for manufacture of derived products only. Not for human or animal consumption or for application to land’;
in the case of milk, milk-based products, milk-derived products, colostrum and colostrum products, ‘not for human consumption’;
in the case of gelatine produced from Category 3 material, ‘gelatine suitable for animal consumption’;
in the case of collagen produced from Category 3 material, ‘collagen suitable for animal consumption’;
in the case of raw petfood, ‘as pet food only’;
in the case of fish and derived products from fish intended for feed for fish, and treated and packaged before distribution, the name and address of the feed manufacturing establishment of origin, marked clearly and legibly, and
in the case of fishmeal from wild fish, bearing the words ‘contains fishmeal from wild fish only – may be used for the feeding of farmed fish of all species’;
in the case of fishmeal from farmed fish, bearing the words ‘contains fishmeal from farmed fish of the […] species only – may only be used for the feeding of farmed fish of other fish species’;
in the case of fishmeal from wild fish and from farmed fish, bearing the words ‘contains fishmeal from wild fish and farmed fish of the […] species – may only be used for the feeding of farmed fish of other fish species’;
in the case of blood products from equidae for purposes other than in feed, ‘blood and blood products from equidae. Not for human or animal consumption’;
in the case of horns, hooves and other materials for the production of organic fertilisers and soil improvers referred to in Section 12 of Chapter II of Annex XIV, ‘not for human or animal consumption’;
in the case of organic fertilisers and soil improvers, ‘organic fertilisers or soil improvers/no grazing of farmed animals or use of crops as herbage during at least 21 days following application’;
in the case of material used for feeding in accordance with Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex VI, the name and the address of the collection centre, and the indication ‘not for human consumption’;
in the case of manure and digestive tract content, ‘manure’;
in the case of intermediate products, on the outer packaging, bearing the words ‘for medicinal products/veterinary medicinal products/medical devices/active implantable medical devices/in vitro diagnostic medical devices/laboratory reagents only’;
in the case of research and diagnostic samples, the words ‘for research and diagnostic purposes’, instead of the label text laid down in point (a);
in the case of trade samples, the words ‘trade sample not for human consumption’, instead of the label text laid down in point (a);
in the case of display items, the words ‘display item not for human consumption’, instead of the label text laid down in point (a).
However, the label referred to in point (b)(xi) shall not be required for the following organic fertilisers and soil improvers:
in ready-to-sell packages of not more than 50 kg in weight for use by the final consumer; or
in big bags of not more than 1 000 kg in weight, provided that:
they are authorised by the competent authority of the Member State where the organic fertiliser or soil improver is to be applied to land,
it is indicated on those bags that they are not destined for application to land to which farmed animals have access.
3.Member States may establish systems or lay down rules for the colour-coding of packaging, containers or vehicles used for the transport of animal by-products and derived products originating in and remaining on their territory, provided that those systems or rules do not confuse the colour-coding system provided for in point 1(c).U.K.
4.Member States may establish systems or lay down rules for the marking of animal by-products originating in and remaining on their territory provided that those systems or rules do not conflict with the marking requirements set out for derived products in Chapter V of this Annex.U.K.
5.By way of derogation from points 3 and 4, Member States may use the systems or rules referred to in those points for animal by-products originating in but not intended to remain on their territory if the Member State or third country of destination has communicated its agreement.U.K.
6.However:U.K.
points 1 and 2 of this Chapter shall not apply to the identification of Category 3 material comprising of milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products, by operators of milk-processing establishments which have been approved in accordance with Article 4 of Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, where they are receiving products which they have previously delivered and which are returned to them, in particular from their customers;
the competent authority may accept the identification of manure which is transported between two points located on the same farm or between farms and users located in the same Member State by other means, by way of derogation from points 1 and 2;
compound feeds as defined in Article 3(2)(h) of Regulation (EC) No 767/2009 which have been manufactured from animal by-products or from derived products and which are packaged and placed on the market as feed in accordance with Article 4 of Regulation (EC) No 767/2009 do not have to be identified in accordance with point 1 and they do not have to be labelled in accordance with point 2.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. COMMERCIAL DOCUMENTS AND HEALTH CERTIFICATES
1.During transportation, a commercial document in accordance with the model set out in this Chapter, or, when required by this Regulation, a health certificate must accompany animal by-products and derived products.U.K.
However, such document or certificate shall not be necessary, provided that:
derived products from Category 3 material and organic fertilisers and soil improvers are supplied within the same Member State by retailers to final users other than business operators;
milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products which are Category 3 materials are collected and returned to operators of milk-processing establishments, which have been approved in accordance with Article 4 of Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, if those operators are receiving products, in particular from their customers, which they have previously delivered;
compound feeds as defined in Article 3(2)(h) of Regulation (EC) No 767/2009 which have been manufactured from animal by-products or from derived products, are placed on the market packaged and labelled in accordance with Article 4 of Regulation (EC) No 767/2009.
2.The commercial document must be produced at least in triplicate (one original and two copies). The original must accompany the consignment to its final destination. The receiver must retain it. The producer must retain one of the copies and the carrier the other.U.K.
Member States may require that proof of the arrival of the consignments is provided by the TRACES system or by a fourth copy of the commercial document which is sent back by the receiver to the producer.
3.Health certificates must be issued and signed by the competent authority.U.K.
4.A commercial document in accordance with the model set out under point 6 shall accompany animal by-products and derived products as from the starting point in the manufacturing chain referred to in Article 4(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, during transportation within the Union.U.K.
However, in addition to the authorisation to transmit information by way of an alternative system as referred to in the second subparagraph of Article 21(3) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the competent authority may authorise that animal by-products and derived products which are transported on its territory are accompanied by:
a different commercial document, in paper or in electronic form, provided that such commercial document contains the information referred to in point (f) of the Notes under point 6 of this Chapter;
a commercial document in which the quantity of the material is expressed in weight or volume of the material or in the number of packages.
5.Records and related commercial documents or health certificates shall be kept for a period of at least two years for presentation to the competent authority.U.K.
6.Model commercial documentU.K.
Notes U.K.
(a)Commercial documents shall be produced, according to the layout of the model appearing in this Chapter.U.K.
It shall contain, in the numbered order that appears in the model, the attestations that are required for the transportation of animal by-products and derived products.
(b)It shall be drawn up in one of the official languages of the Member State of origin and of the Member State of destination, as appropriate.U.K.
However, it may also be drawn up in other official Union languages, if accompanied by an official translation or if previously agreed by the competent authority of the Member State of destination.
(c)The original of each commercial document shall consist of a single sheet of paper, both sides, or, where more text is required it shall be in such a form that all sheets of paper needed are demonstrably part of an integrated whole and indivisible.U.K.
(d)If for reasons of identification of the items of the consignment, additional sheets of paper are attached to the commercial document, these sheets of paper shall also be considered as forming part of the original document by the application of the signature of the person responsible for the consignment, on each of the pages.U.K.
(e)When the commercial document, including additional sheets of paper referred to in point (d), comprises more than one page, each page shall be numbered – (page number) of (total number of pages) – at the bottom of the page and shall bear the code number of the document that has been designated by the responsible person at the top of the page.U.K.
(f)The original of the commercial document must be completed and signed by the responsible person.U.K.
The commercial document must specify:
the date on which the material was taken from the premises;
the description of the material, including
the identification of the material according to one of the categories referred to in Articles 8, 9 and 10 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009,
the animal species and the specific reference to the applicable point in Article 10 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 for Category 3 material and products derived therefrom which are destined for feeding and,
if applicable, the ear-tag number of the animal;
the quantity of the material, in volume, weight or number of packages;
the place of origin of the material, from where the material is dispatched;
the name and the address of the carrier of the material;
the name and the address of the receiver and, if applicable, its approval or registration number, which has been issued under Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 or Regulations (EC) No 852/2004, (EC) No 853/2004 or (EC) No 183/2005, as applicable;
if appropriate, the approval or registration number of the establishment or plant of origin, which has been issued under Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 or Regulations (EC) No 852/2004, (EC) No 853/2004 or (EC) No 183/2005, as applicable, and the nature and the methods of the treatment.
(g)The colour of the signature of the responsible person shall be different to that of the printing.U.K.
(h)The document reference number and the local reference number shall only be issued once for the same consignment.U.K.
Commercial document U.K.
For the transport of animal by-products and derived products not intended for human consumption in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 within the European Union
CHAPTER IVU.K. RECORDS
Section 1 U.K. General provisions
1.The records as referred to in Article 22(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 for animal by-products and derived products, other than compound feeds as defined in Article 3(2)(h) of Regulation (EC) No 767/2009, which have been manufactured from animal by-products or from derived products and which are placed on the market in accordance with Article 4 of Regulation (EC) No 767/2009, shall contain:U.K.
a description of:
the animal species for Category 3 material and derived products therefrom, destined for use as feed material and, if applicable, in the case of whole carcases and heads, the ear-tag number;
the quantity of the material;
in the case of records kept by any person consigning animal by-products or derived products, the following information:
the date on which the material was taken from the premises;
the name and the address of the transporter and of the receiver and, if applicable, their approval or registration number;
in the case of records kept by any person transporting animal by-products or derived products, the following information:
the date on which the material was taken from the premises;
the place of origin of the material, from where the material is dispatched;
the name and the address of the receiver and, if applicable, its approval or registration number;
in the case of records kept by any person receiving animal by-products or derived products, the following information:
the date of reception of the material;
the place of origin of the material, from where the material is dispatched;
the name and address of the transporter.
2.By way of derogation from point 1 of this Section, operators do not have to keep the information referred to in point 1(a) and points (b)(i), (c)(i) and (iii) and d(ii) and (iii) separately, if they keep a copy of the commercial document laid down in Chapter III for each consignment and make such information available in conjunction with the other information required under point 1 of this Section.U.K.
3.Operators of incineration plants and co-incineration plants shall keep records of the quantities and category of the animal by-products and derived products incinerated or co-incinerated, as applicable, and the date at which those operations were carried out.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Additional requirements in case of use for special feeding purposes
In addition to the records required in accordance with Section 1, operators shall keep the following records in relation to relevant material if animal by-products are used for special feeding purposes in accordance with Chapter II of Annex VI:
in the case of final users, the quantity used, the animals that it is intended to be fed to and the date of use;
in the case of collection centres:
the quantity handled or treated in accordance with point 4 of Section 1 of Chapter I of Annex VI;
the name and address of each final user using the material;
the premises to which the material is taken for use;
the quantity dispatched; and
the date on which the material was dispatched.
Section 3 U.K. Requirements in case of certain fur animals
The operator of the farm referred to in Chapter I of Annex II shall keep records at least of:
the number of furs and carcases of animals fed with materials originating of their own species; and
each consignment in order to ensure the traceability of the material.
Section 4 U.K. Requirements for the application of certain organic fertilisers and soil improvers to land
The person responsible for land to which organic fertilisers and soil improvers, other than the materials referred to in the second paragraph of Chapter II of Annex II are applied and to which farmed animals have access or from which herbage is cut for feeding to farmed animals, shall keep records of the following for a period of at least two years:
the quantities of organic fertilisers and soil improvers applied;
the date on which the organic fertilisers and soil improvers were applied to land and the places of such application;
the dates, following the application of the organic fertiliser or soil improver, on which livestock has been allowed to graze on the land or on which the land has been cut for herbage to be used for feeding.
Section 5 U.K. Requirements for animal by-products derived from aquatic animals and feeding of fish
Processing plants producing fishmeal or other feed originating from aquatic animals shall keep records of the following:
the quantities produced each day;
the species of origin, including an indication of whether the aquatic animals were caught in the wild or produced in aquaculture;
in the case of fishmeal from farmed fish which is intended for feeding to farmed fish of another species, the scientific name of the species of origin.
Section 6 U.K. Requirements for the burning and burial of animal by-products
In the case of burning or burial of animal by-products as provided for in Article 19(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the person responsible for such burning or burial shall keep records of the following:
the quantities, categories and species of animal by-products burned or buried;
the date and place of burning and burial.
Section 7 U.K. Requirements for photogelatine
Operators of approved photographic factories referred to in Section 11 of Chapter II of Annex XIV shall keep records detailing the purchases and uses of photogelatine, as well as the disposal of residues and surplus material.
CHAPTER VU.K. MARKING OF CERTAIN DERIVED PRODUCTS
1.In processing plants for the processing of Category 1 or Category 2 material, derived products shall be permanently marked with glyceroltriheptanoate (GTH) in such a way that:U.K.
GTH is added to derived products that have undergone a preceding sanitising thermal treatment at a core temperature of at least 80 °C and remain subsequently protected from re-contamination;
all derived products contain homogenously throughout the substance a minimum concentration of at least 250 mg GTH per kg fat.
2.The operators of processing plants referred to in point 1 shall have in place a system of monitoring and recording of parameters suitable to demonstrate to the competent authority that the required homogeneous minimum concentration of GTH is achieved.U.K.
That monitoring and recording system shall include the determination of the content of intact GTH as triglyceride in a cleaned petroleum-ether 40-70 extract of GTH from samples taken at regular intervals.
3.The marking with GTH shall not be required for:U.K.
liquid derived products destined for biogas or composting plants;
derived products used for feeding to fur animals in accordance with Chapter I of Annex II;
biodiesel produced in accordance with point D of Section 2 of Chapter IV of Annex IV;
derived products obtained in accordance with Article 12(a)(ii) and (b)(ii) and Article 13(a)(ii) and (b)(ii) and Article 16(e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, where such products are:
moved by a closed conveyer system, which may not be by-passed, and provided such a system has been authorised by the competent authority, from the processing plant for:
immediate direct incineration or co-incineration,
immediate use in accordance with a method approved for animal by-products of Category 1 and Category 2 in accordance with Chapter IV of Annex IV; or
intended for research and other specific purposes as referred to in Article 17 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 which have been authorised by the competent authority.
ANNEX IXU.K. REQUIREMENTS APPLICABLE TO CERTAIN APPROVED AND REGISTERED ESTABLISHMENTS AND PLANTS
CHAPTER IU.K. MANUFACTURING OF PETFOOD
Establishments or plants manufacturing petfood as referred to in Article 24(1)(e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 shall have adequate facilities for:
storing and treating incoming material in complete safety; and
disposing of unused animal by-products remaining after the production of the products in accordance with this Regulation, or such material must be sent to an incineration plant, a co-incineration plant, a processing plant or, in the case of Category 3 material, to a biogas or composting plant in accordance with Articles 12, 13 and 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with this Regulation.
CHAPTER IIU.K. HANDLING OF ANIMAL BY-PRODUCTS AFTER THEIR COLLECTION
The requirements of this Chapter shall apply to the storage of animal by-products, as referred to in Article 24(1)(i) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and to the following operations involving the handling of animal by-products after their collection, as referred to in Article 24(1)(h) of that Regulation:
sorting;
cutting;
chilling;
freezing;
salting or other preservation processes;
removal of hides and skins;
removal of specified risk material;
operations involving the handling of animal by-products which are carried out in compliance with obligations under Union veterinary legislation, such as post-mortem examination or the taking of samples;
hygienisation/pasteurisation of animal by-products destined for transformation into biogas or composting, prior to such transformation or composting in another establishment or plant in accordance with Annex V hereto;
sieving.
Section 1 U.K. General requirements
1.Premises and facilities where intermediate operations are carried out shall meet at least the following requirements:U.K.
They must be adequately separated from thoroughfares through which contamination may be spread and from other premises such as slaughterhouses. The layout of plants shall ensure the total separation of Category 1 and Category 2 material from Category 3 material respectively, from reception until dispatch, unless in a completely separate building.
The plant must have a covered space to receive and dispatch animal by-products, unless the animal by-products are being discharged through installations which prevent the spreading of risks to public and animal health, such as through closed tubes for liquid animal by-products.
The plant must be constructed in such a way that it is easy to clean and disinfect. Floors must be laid down in such a way as to facilitate the draining of liquids.
The plant must have adequate facilities including lavatories, changing rooms, washbasins for staff and, if appropriate, office space which can be made available to the staff performing official controls.
The plant must have appropriate arrangements for protection against pests, such as insects, rodents and birds.
Where it is necessary for the purpose of achieving the objectives of this Regulation, plants must have suitable temperature-controlled storage facilities of sufficient capacity for maintaining animal by-products at appropriate temperatures and designed to allow the monitoring and recording of those temperatures.
2.The plant shall be equipped with adequate facilities for cleaning and disinfecting the containers or receptacles in which animal by-products are received and for the vehicles, other than ships, in which they are transported. Adequate facilities shall be available for the disinfecting of vehicle wheels.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Hygiene requirements
1.The sorting of animal by-products shall be carried out in such a way as to avoid any risk of the propagation of animal diseases.U.K.
2.At all times during storage, animal by-products shall be handled and stored separately from other goods and in such a way as to prevent any propagation of pathogens.U.K.
3.Animal by-products shall be stored properly, including under appropriate temperature conditions, until re-dispatched.U.K.
Section 3 U.K. Processing standards for hygienisation/pasteurisation
Hygienisation/pasteurisation as referred to in point (i) of the initial paragraph of this Chapter shall be carried out in accordance with the processing standards referred to in point 1 of Section 1 of Chapter I of Annex V or in accordance with alternative transformation parameters which have been authorised in accordance with point 1 of Section 2 of Chapter III of the same Annex.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. REQUIREMENTS FOR STORAGE OF DERIVED PRODUCTS
Section 1 U.K. General requirements
Premises and facilities storing derived products shall meet at least the following requirements:
Premises and facilities storing derived products from Category 3 material must not be at the same site as premises storing derived products from Category 1 or Category 2 material, unless cross-contamination is prevented due to the layout and management of the premises, such as by means of storage in completely separate buildings.
The plant must:
have a covered space to receive and dispatch the derived products, unless the derived products are:
being discharged through installations which prevent the spreading of risks to public and animal health, such as through closed tubes for liquid products; or
received in packaging, such as in big bags, or in covered leak-proof containers or means of transport;
be constructed in such a way that it is easy to clean and disinfect. Floors must be laid down in such a way as to facilitate the draining of liquids;
have adequate facilities including lavatories, changing rooms and washbasins for staff;
have appropriate arrangements for protection against pests, such as insects, rodents and birds.
The plant must have adequate facilities for cleaning and disinfecting the containers or receptacles in which the derived products are received and the vehicles, other than ships, in which they are transported.
Derived products must be stored properly until redispatched.
Section 2 U.K. Specific requirements for storage of certain milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products
1.The storage of the products referred to in Part II of Section 4 of Chapter II of Annex X shall take place at an appropriate temperature to avoid any risk to public or animal health in a dedicated approved or registered storage establishment or plant or in a dedicated, separate storage area within an approved or registered storage establishment or plant.U.K.
2.Samples of the final products taken during storage or at the time of withdrawal from storage, shall at least comply with the microbiological standards set out in Chapter I of Annex X.U.K.
CHAPTER IVU.K. REGISTERED OPERATORS
1.Operators of registered plants or establishments or other registered operators shall handle animal by-products and derived products under the following conditions:U.K.
premises must be constructed in a way permitting their effective cleaning and disinfection, where appropriate;
premises must have appropriate arrangements for protection against pests, such as insects, rodents and birds;
installations and equipment must be kept in hygienic condition, where necessary;
animal by-products and derived products must be stored under conditions preventing contamination.
2.Operators shall keep records in a form which is accessible to the competent authority.U.K.
3.Registered operators transporting animal by-products or derived products, other than between premises of the same operator, shall in particular:U.K.
have information at their disposal with regard to the identification of their vehicles, which allows the verification of the use of the vehicles for the transport of animal by-products or derived products;
clean and disinfect their vehicles, as appropriate;
take all other necessary measures to prevent contamination and the spreading of diseases communicable to humans or animals.
ANNEX XU.K. FEED MATERIALS
CHAPTER IU.K. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PROCESSING AND PLACING ON THE MARKET
Microbiological standards for derived products
The following microbiological standards shall apply to derived products:
Samples of the final products taken during or on withdrawal from storage at the processing plant must comply with the following standards:
Salmonella: absence in 25 g: n = 5, c = 0, m = 0, M = 0
Enterobacteriaceae: n = 5, c = 2, m = 10, M = 300 in 1 g
where:
=
number of samples to be tested;
=
threshold value for the number of bacteria; the result is considered satisfactory if the number of bacteria in all samples does not exceed m;
=
maximum value for the number of bacteria; the result is considered unsatisfactory if the number of bacteria in one or more samples is M or more; and
=
number of samples the bacterial count of which may be between m and M, the sample still being considered acceptable if the bacterial count of the other samples is m or less.
However, the microbiological standards set out in this Chapter shall not apply to rendered fats and fish oil from the processing of animal by-products, when the processed animal protein, which is obtained during the same processing, is subject to sampling to ensure compliance with those standards.
CHAPTER IIU.K. SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR PROCESSED ANIMAL PROTEIN AND OTHER DERIVED PRODUCTS
Section 1 U.K. Specific requirements for processed animal protein
A.Raw materialsU.K.
Only animal by-products which are Category 3 material or products which are derived from such animal by-products, other than the Category 3 materials referred to in Article 10(n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, may be used for the production of processed animal protein.
B.Processing standardsU.K.
1.Processed animal protein of mammalian origin must have been submitted to processing method 1 (pressure sterilisation) as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV.U.K.
However,
porcine blood or fractions of porcine blood for the production of bloodmeal may have been submitted instead to any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7 as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV, provided that in the case of processing method 7, a heat treatment throughout its substance at a temperature of 80 °C has been applied;
processed animal protein of mammalian origin
may have been submitted to any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7, as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV, provided that it is subsequently disposed of or used as a fuel for combustion;
where it is exclusively destined for use in petfood, it may have been submitted to any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7, as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV, provided that it is:
transported in dedicated containers that are not used for the transport of animal by-products or feedingstuffs for farmed animals, and
consigned directly from a processing plant for Category 3 material to the petfood plant or to an approved storage plant, from where it is directly consigned to a petfood plant.
2.Non-mammalian processed animal protein, with the exception of fishmeal, must have been submitted to any of processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7, as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV.U.K.
3.Fishmeal must have been submitted to:U.K.
any of the processing methods set out in Chapter III of Annex IV; or
another method which ensures that the product complies with the microbiological standards for derived products set in Chapter I of this Annex.
C.StorageU.K.
1.Processed animal protein must be packed and stored in new or sterilised bags or stored in properly constructed bulk bins or in storage sheds.U.K.
Sufficient measures must be taken to minimise condensation inside bins, conveyors or elevators.
2.Products in conveyors, elevators and bins must be protected from casual contamination.U.K.
3.Equipment for handling processed animal protein must be maintained in a clean and dry condition and must have adequate inspection points so that equipment can be examined for cleanliness.U.K.
All storage facilities must be emptied and cleaned regularly, to the extent necessary to prevent contamination.
4.Processed animal protein must be kept dry.U.K.
Leakages and condensation in the storage area must be prevented.
Section 2 U.K. Specific requirements for blood products
A.Raw materialU.K.
Only blood referred to in Article 10(a) and Article 10(b)(i) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be used for the production of blood products.
B.Processing standardsU.K.
Blood products must have been submitted to:
any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7, as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV; or
another method which ensures that the blood product complies with the microbiological standards for derived products set out in Chapter I of this Annex.
Section 3 U.K. Specific requirements for rendered fats, fish oil and fat derivatives from Category 3 material
A.Raw materialsU.K.
1.Rendered fatsU.K.
Only Category 3 material, other than Category 3 materials referred to in Article 10(i), (j), (n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, may be used for the production of rendered fat.
2.Fish oilU.K.
Only Category 3 material referred to in Article 10(i) and (j) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and Category 3 material of aquatic animal origin referred to in Article 10(e) and (f) of that Regulation may be used for the production of fish oil.
B.Processing standardsU.K.
Unless the fish oil or rendered fats have been produced in accordance with Sections VIII or XII of Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, respectively, rendered fats must be produced using any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7, and fish oils may be produced:
using processing methods 1 to 7, as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV; or
in accordance with another method which ensures that the product complies with the microbiological standards for derived products set out in Chapter I of this Annex.
Rendered fats derived from ruminant animals must be purified in such a way that the maximum level of remaining total insoluble impurities does not exceed 0,15 % in weight.
Fat derivatives from Category 3 rendered fats or fish oil shall be produced in accordance with one of the processing methods referred to in Chapter III of Annex IV.
C.Hygiene requirementsU.K.
Where rendered fat or fish oil is packaged, it must be packaged in new containers or in containers that have been cleaned and disinfected if necessary for the prevention of contamination and all precautions must be taken to prevent its recontamination.
Where bulk transport of those products is intended, the pipe, pumps and bulk tanks and any other bulk container or bulk road tanker used in the transportation of the products from the manufacturing plant either directly on to the ship or into shore tanks or directly to plants must be clean before use.
Section 4 U.K. Specific requirements for milk, colostrum and certain other products derived from milk or colostrum
Part I U.K. General requirements
A.Raw materialU.K.
Only milk referred to in Article 10(e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, other than centrifuge or separator sludge, and milk referred to in Article 10(f) and (h) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be used for the production of milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products.
Colostrum may only be used provided that it originates from live animals that did not show any signs of disease communicable through the colostrum to humans or animals.
B.Processing standardsU.K.
1.Milk must be subjected to one of the following treatments:U.K.
sterilisation at an F0 (54) value of three or more;
UHT(55) combined with one of the following:
a subsequent physical treatment, by:
a drying process, combined in the case of milk intended for feeding with additional heating to 72 °C or more; or
lowering the pH below 6 for at least 1 hour;
the condition that the milk, milk-based product or milk-derived product has been produced at least 21 days before shipping and that during that period no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been detected in the Member State of origin;
HTST(56) applied twice;
HTST in combination with one of the following:
a subsequent physical treatment, by:
a drying process, combined in the case of milk intended for feeding with additional heating to 72 °C or more; or
lowering the pH below 6,0 for at least 1 hour;
the condition that the milk, milk-based product or milk-derived product has been produced at least 21 days before shipping and that during that period no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been detected in the Member State of origin.
2.Milk-based products and milk-derived products must either be subjected to at least one of the treatments provided for in point 1 or be produced from milk treated in accordance with point 1.U.K.
3.Whey to be fed to animals of species susceptible to foot-and-mouth disease and produced from milk treated in accordance with point 1 must:U.K.
either be collected at least 16 hours following milk clotting and its pH must be recorded as below 6,0 before transport to animal holdings; or
have been produced at least 21 days before shipping and during that period no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been detected in the Member State of origin.
4.In addition to the requirements set out in points 1, 2 and 3, milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products must meet the following requirements:U.K.
after completion of the processing, every precaution must be taken to prevent contamination of the products;
the final product must be labelled so as to indicate that it contains Category 3 material and is not intended for human consumption, and it must be:
packed in new containers; or
transported in bulk in containers or other means of transport that before use were thoroughly cleansed and disinfected.
5.Raw milk must be produced under conditions offering adequate guarantees as regards animal health.U.K.
6.Colostrum and colostrum products must:U.K.
be obtained from bovine animals kept on a holding on which all bovine herds are recognised as officially tuberculosis-free, officially brucellosis-free and officially enzootic-bovine-leukosis-free as defined in Article 2(2)(d), (f) and (j) of Directive 64/432/EEC;
have been produced at least 21 days before shipping and during that period no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been detected in the Member State of origin;
have undergone a single HTST treatment(56);
comply with the requirements set out in point 4 of this Part.
Part II U.K. Derogation for the placing on the market of milk processed in accordance with national standards
1.The requirements laid down in points 2 and 3 of this Part shall apply to the processing, use and storage of milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products which are Category 3 material, as referred to in Article 10(e) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, other than centrifuge or separator sludge, and milk referred to in Article 10 (f) and (h) of that Regulation, that have not been processed in accordance with Part I of this Section.U.K.
2.The competent authority shall authorise milk processing establishments approved or registered in accordance with Article 4 of Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 to supply milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products for the purposes referred to in point 3 of this Part provided the establishment concerned ensures the traceability of the products.U.K.
3.Milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products may be supplied and used as feed material:U.K.
in the Member State concerned and in cross-border areas where the Member States concerned have a mutual agreement to that effect, in the case of derived products, including white water, which have been in contact with raw milk and/or milk pasteurised in accordance with the requirements for heat treatment set out in point II.1(a) or (b) of Chapter II of Section IX of Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, if those derived products have been subject to one of the following treatments:
UHT;
sterilisation whereby either an Fc value equal or greater than 3 is achieved, or which was carried out at a temperature of at least 115 °C for 15 minutes or an equivalent combination of temperature and time;
pasteurisation or sterilisation, other than that referred to in point (ii), followed by:
in the case of dried milk or dried milk-based products or milk-derived products, a drying process;
in the case of an acidified milk product, a process by which the pH is reduced and kept for at least one hour at a level below 6;
in the Member State concerned,
in the case of derived products, including white water, which have been in contact with milk that has only been pasteurised in accordance with the requirements for heat treatment set out in point II.1 (a) of Chapter II of Section IX of Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, and whey produced from non heat-treated milk-based products, which has been collected at least 16 hours after milk clotting and where the pH must be recorded as < 6,0 before supplying the whey for feeding, provided that they are sent to a limited number of authorised animal holdings, fixed on the basis of the risk assessment for the best and worst case scenarios carried out by the Member State concerned in preparation of the contingency plans for epizootic diseases, in particular foot-and-mouth disease;
in the case of raw products, including white water that has been in contact with raw milk and other products for which the treatments referred to in point (a) and point (b)(i) cannot be ensured, provided that they are sent to a limited number of authorised animal holdings, fixed on the basis of a risk assessment for the best and worst case scenarios carried out by the Member State concerned in preparation of the contingency plans for epizootic diseases, in particular foot-and-mouth disease, and provided that the animals present in the authorised animal holdings can only be moved
either directly to a slaughterhouse located in the same Member State, or
to another holding in the same Member State, for which the competent authority guarantees that animals susceptible to foot-and-mouth disease may leave the holding only either directly to a slaughterhouse located in the same Member State, or if the animals have been dispatched to a holding not feeding the products referred to in this point (ii), after a 21-day standstill period has elapsed from the introduction of the animals.
4.The competent authority may authorise the supply of colostrum which does not comply with the conditions set out in point B.6 of Part I from one farmer to another farmer within the same Member State for feeding purposes, under conditions which prevent the transmission of health risks.U.K.
Part III U.K. Special requirements for centrifuge or separator sludge
Category 3 material comprising of centrifuge or separator sludge must have been subjected to a heat treatment of at least 70 °C for 60 minutes or of at least 80 °C for 30 minutes, before it may be placed on the market for feeding to farmed animals.
Section 5 U.K. Specific requirements for gelatine and hydrolysed protein
A.Raw materialsU.K.
Only animal by-products which are Category 3 material or products which are derived from such animal by-products, other than materials referred to in Article 10(m), (n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be used for the production of gelatine and hydrolysed protein.
B.Processing standards for gelatineU.K.
1.Unless the gelatine has been produced in accordance with Section XIV of Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, it must be produced by a process that ensures that Category 3 material is subjected to a treatment with acid or alkali, followed by one or more rinses.U.K.
The pH must be adjusted subsequently. Gelatine must be extracted by heating one or several times in succession, followed by purification by means of filtration and sterilisation.
2.After having been subjected to the processes referred to in point 1, gelatine may undergo a drying process and, where appropriate, a process of pulverisation or lamination.U.K.
3.The use of preservatives, other than sulphur dioxide and hydrogen peroxide, shall be prohibited.U.K.
C.Other requirements for gelatineU.K.
Gelatine must be wrapped, packaged, stored and transported under satisfactory hygiene conditions.
In particular:
a room or a dedicated place must be provided for storing materials for wrapping and packaging;
wrapping and packaging must take place in a room or in a place intended for that purpose.
D.Processing standards for hydrolysed proteinU.K.
Hydrolysed protein must be produced using a production process involving appropriate measures to minimise contamination. Hydrolysed protein derived from ruminants shall have a molecular weight below 10 000 Dalton.
In addition to the requirements of the first paragraph, hydrolysed proteins entirely or partly derived from ruminants’ hides and skins shall be produced in a processing plant dedicated only to hydrolysed protein production, using a process involving the preparation of raw Category 3 material by brining, liming and intensive washing followed by exposure of the material to:
a pH of more than 11 for more than three hours at a temperature of more than 80 °C and subsequently by heat treatment at more than 140 °C for 30 minutes at more than 3,6 bar; or
a pH of 1 to 2, followed by a pH of more than 11, followed by heat treatment at 140 °C for 30 minutes at 3 bar.
Section 6 U.K. Specific requirements for dicalcium phosphate
A.Raw materialsU.K.
Only animal by-products which are Category 3 material or products which are derived from such animal by-products, other than materials referred to in Article 10(m), (n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be used for the production of dicalcium phosphate.
B.Processing standardsU.K.
1.Dicalcium phosphate must be produced by a process that comprises the three following stages:U.K.
firstly, ensures that all bone that is Category 3 material is finely crushed and degreased with hot water and treated with dilute hydrochloric acid (at a minimum concentration of 4 % and a pH of less than 1,5) over a period of at least two days;
secondly, following the part of the process referred to in point (a), applies a treatment of the obtained phosphoric liquor with lime, resulting in a precipitate of dicalcium phosphate at pH 4 to 7;
finally, air-dries the precipitate of dicalcium phosphate with inlet temperature of 65 °C to 325 °C and end temperature between 30 °C and 65 °C.
2.Where dicalcium phosphate is derived from defatted bones, it shall be derived from bones referred to in Article 10(a) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.U.K.
Section 7 U.K. Specific requirements for tricalcium phosphate
A.Raw materialsU.K.
Only animal by-products which are Category 3 material or products which are derived from such animal by-products, other than materials referred to in Article 10(m), (n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be used for the production of tricalcium phosphate.
B.Processing standardsU.K.
Tricalcium phosphate must be produced by a process that ensures:
that all bone that is Category 3 material is finely crushed and degreased in counterflow with hot water (bone chips must be less than 14 mm);
continuous cooking with steam at 145 °C during 30 minutes at 4 bars;
separation of the protein broth from the hydroxyapatite (tricalcium phosphate) by centrifugation;
granulation of the tricalcium phosphate after drying in a fluidised bed with air at 200 °C.
Section 8 U.K. Specific requirements for collagen
A.Raw materialsU.K.
Only animal by-products which are Category 3 material or products which are derived from such animal by-products, other than materials referred to in Article 10(m), (n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be used for the production of collagen.
B.Processing standardsU.K.
1.Unless the collagen has been produced in accordance with the requirements for collagen set out in Section XV of Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004, it must be produced by a process ensuring that unprocessed Category 3 material is subjected to a treatment involving washing, pH adjustment using acid or alkali followed by one or more rinses, filtration and extrusion.U.K.
After that treatment collagen may undergo a drying process.
2.The use of preservatives, other than those permitted under Union legislation shall be prohibited.U.K.
C.Other requirementsU.K.
Collagen must be wrapped, packaged, stored and transported under satisfactory hygiene conditions. In particular:
a room or a dedicated place must be provided for storing materials for wrapping and packaging;
wrapping and packaging must take place in a room or in a place intended for that purpose.
Section 9 U.K. Specific requirements for egg products
A.Raw materialsU.K.
Only animal by-products referred to in Article 10(e) and (f) and Article 10(k)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be used for the production of egg products.
B.Processing standardsU.K.
Egg products must have been:
submitted to any of the processing methods 1 to 5 or processing method 7 set out in Chapter III of Annex IV;
submitted to another method and parameters which ensure that the products comply with the microbiological standards for derived products set out in Chapter I; or
treated in accordance with the requirements for eggs and egg products set out in Chapters I, II and III of Section X of Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004.
Section 10 U.K. Specific requirements for certain Category 3 material
Category 3 material comprising products of animal origin, or foodstuffs containing products of animal origin, which are no longer intended for human consumption for commercial reasons or due to problems of manufacturing or packaging defects or other defects from which no risk to public or animal health arise, referred to in Article 10(f) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 may be placed on the market for feeding to farmed animals, provided that:
the material is not composed of and has not been in contact with material of animal origin which has not undergone processing:
in accordance with this Regulation;
as defined in Article 2(1)(m) of Regulation (EC) No 852/2004;
all necessary precautions have been taken to prevent the contamination of the material.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. REQUIREMENTS FOR CERTAIN FISH FEED AND FISHING BAITS
1.Animal by-products from fish or aquatic invertebrates and derived products therefrom that are intended as feed for farmed fish or for other aquaculture species shall:U.K.
be handled and processed separately from material not authorised for that purpose;
originate
from wild fish or other aquatic animals, except sea mammals, landed for commercial purposes, or from animal by-products from wild fish originating in plants manufacturing fish products for human consumption; or
from farmed fish, provided it is fed to farmed fish of another species;
be processed in a processing plant in accordance with a method which ensures a microbiologically safe product, including with regard to fish pathogens.
2.The competent authority may lay down conditions, aimed at preventing unacceptable risks for the transmission of diseases communicable to humans or animals, for the use of aquatic animals and of aquatic and terrestrial invertebrates:U.K.
as feed for farmed fish or for aquatic invertebrates, when the animal by-products have not been processed in accordance with point 1(c);
as fishing bait, including bait for aquatic invertebrates.
ANNEX XIU.K. ORGANIC FERTILISERS AND SOIL IMPROVERS
CHAPTER IU.K. REQUIREMENTS FOR UNPROCESSED MANURE, PROCESSED MANURE AND DERIVED PRODUCTS FROM PROCESSED MANURE
Section 1 U.K. Unprocessed manure
1.Trade in unprocessed manure of species other than poultry or equidae between Member States shall be subject to the following conditions, in addition to the consent of the Member State of destination referred to in Article 48(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009:U.K.
Trade in unprocessed manure of species other than poultry or equidae shall be prohibited, except for manure:
from an area which is not subject to restrictions by virtue of a serious transmissible disease; and
intended for application, under the supervision of the competent authorities, to land forming part of a single holding located on both sides of the border of two Member States.
However, the competent authority of the Member State of destination may, having regard to the origin of the manure, its destination and health considerations, grant specific authorisation for the introduction on to its territory of:
manure intended for:
processing in a plant for the manufacture of derived products which are destined for uses outside the feed chain, or
transformation into biogas or composting in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with Annex V to this Regulation with a view to the manufacture of the products referred to in Section 2 of this Chapter.
In those cases, the competent authority shall take account of the origin of the manure when authorising the introduction to such plants; or
manure intended for applying to land on a holding, provided that the competent authority of the Member State of origin has communicated its agreement to such trade.
in the cases referred to in point (b), a health attestation in accordance with the model set out in point 3 shall be added to the commercial document which accompanies the consignment of manure.
2.Trade in unprocessed poultry manure between Member States shall be subject to the following conditions, in addition to the consent of the Member State of destination referred to in Article 48(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009:U.K.
the manure must originate in an area which is not subject to restrictions by virtue of Newcastle disease or avian influenza;
in addition, unprocessed manure from poultry flocks vaccinated against Newcastle disease must not be dispatched to a region which has obtained Newcastle disease non-vaccinating status pursuant to Article 15(2) of Directive 2009/158/EC; and
a health attestation in accordance with the model set out in point 3 shall be added to the commercial document which accompanies the consignment of manure.
3.Model health attestation to be added to the commercial document:U.K.
4.Unprocessed manure of equidae may be traded between Member States, provided that the Member State of destination has given its consent to the trade as referred to in Article 48(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, and provided it does not originate from a holding subject to animal health restrictions pertaining to glanders, vesicular stomatitis, anthrax or rabies in accordance with Article 4(5) of Directive 2009/156/EC.U.K.
5.In accordance with Article 48(1)(c)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the competent authority of the Member State of destination may require operators dispatching unprocessed manure from another Member State:U.K.
to transmit further information in relation to an intended dispatch, such as precise geographical indications regarding the place where the manure is to be unloaded; and
to store the manure before application to land.
6.The competent authority may authorise the dispatch of manure transported between two points located on the same farm subject to conditions for the control of possible health risks, such as obligations for the operators concerned to keep appropriate records.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Guano from bats, processed manure and derived products from processed manure
The placing on the market of processed manure, derived products from processed manure and guano from bats shall be subject to the following conditions, in addition to the consent of the Member State of destination referred to in Article 48(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009:
They must come from a plant for derived products for uses outside the feed chain or from a biogas or a composting plant or from a plant for the manufacturing of organic fertilisers or soil improvers.
They shall have been subjected to a heat treatment process of at least 70 °C for at least 60 minutes and they shall have been subjected to reduction in spore-forming bacteria and toxin formation, where they are identified as a relevant hazard.
However, the competent authority may authorise the use of other standardised process parameters than those referred to in point (b), provided an applicant demonstrates that such parameters ensure minimising of biological risks.
That demonstration shall include a validation, which shall be carried out as follows:
Identification and analysis of possible hazards including the impact of input material, based on a full definition of the processing conditions, and a risk assessment, which evaluates how the specific processing conditions are achieved in practice under normal and atypical situations.
Validation of the intended process
by measuring the reduction of viability/infectivity of endogenous indicator organisms during the process, where the indicator is:
consistently present in the raw material in high numbers,
not less heat resistant to the lethal aspects of the treatment process, but also not significantly more resistant than the pathogens for which it is being used to monitor,
relatively easy to quantify and relatively easy to identify and confirm; or
by measuring the reduction of viability/infectivity, during exposure, of a well-characterised test organism or virus introduced in a suitable test body into the starting material.
The validation referred to in point (ii) must demonstrate that the process achieves the following overall risk reduction:
for thermal and chemical processes by reduction of Enterococcus faecalis by at least 5 log10 and by reduction of infectivity titre of thermoresistant viruses such as parvovirus, where they are identified as a relevant hazard, by at least 3 log10,
for chemical processes also by reduction of resistant parasites such as eggs of Ascaris sp. by at least 99,9 % (3 log10) of viable stages.
Designing a complete control programme including procedures for monitoring the process.
Measures ensuring continuous monitoring and supervision of the relevant process parameters fixed in the control programme when operating the plant.
Details on the relevant process parameters used in a plant as well as other critical control points shall be recorded and maintained so that the owner, operator or their representative and the competent authority can monitor the operation of the plant. Information relating to a process authorised under this point must be made available to the Commission on request;
Representative samples of the manure taken during or immediately after processing at the plant in order to monitor the process must comply with the following standards:
Escherichia coli: n = 5, c = 5, m = 0, M = 1 000 in 1 g;
or
Enterococcaceae: n = 5, c = 5, m = 0, M = 1 000 in 1 g;
and
Representative samples of the manure taken during or on withdrawal from storage at the plant of production or the biogas or composting plant must comply with the following standards:
Salmonella: absence in 25 g: n = 5; c = 0; m = 0; M = 0
where:
=
number of samples to be tested;
=
threshold value for the number of bacteria; the result is considered satisfactory if the number of bacteria in all samples does not exceed m;
=
maximum value for the number of bacteria; the result is considered unsatisfactory if the number of bacteria in one or more samples is M or more; and
=
number of samples the bacterial count of which may be between m and M, the sample still being considered acceptable if the bacterial count of the other samples is m or less.
Processed manure or processed manure products not complying with the standards in this point shall be regarded as unprocessed;
They must be stored in such a way that once processed contamination or secondary infection and dampness is minimised. They must therefore be stored in:
well-sealed and insulated silos or properly constructed storage sheds; or
properly sealed packs, such as plastic bags or ‘big bags’.
CHAPTER IIU.K. REQUIREMENTS FOR CERTAIN ORGANIC FERTILISERS AND SOIL IMPROVERS
Section 1 U.K. Conditions for the production
1.Organic fertilisers and soil improvers, other than manure, digestive tract content, compost, milk, milk-based products, milk-derived products, colostrum, colostrum products and digestion residues from the transformation of animal by-products or derived products into biogas, shall be produced by:U.K.
applying processing method 1 (pressure sterilisation), when Category 2 material is used as starting material;
using processed animal protein which has been produced from Category 3 material in accordance with Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex X, or materials which have been subject to another treatment, where such materials may be used for organic fertilisers and soil improvers in accordance with this Regulation; or
by applying any of the processing methods 1 to 7, as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV, when Category 3 material is used as starting material which is not used for the production of processed animal protein.
2.Organic fertilisers and soil improvers which consist of or which have been produced from meat-and-bone meal derived from Category 2 material or from processed animal protein, shall be mixed, in a registered establishment or plant, with a sufficient minimum proportion of a component which is authorised by the competent authority of the Member State where the product is to be applied to land, in order to exclude the subsequent use of the mixture for feeding purposes.U.K.
3.The competent authority shall authorise the component referred to in point 2 according to the following:U.K.
the component shall consist of lime, manure, urine, compost or digestion residues from the transformation of animal by-products into biogas or other substances, such as mineral fertilisers, which are not used in animal feed and which exclude the subsequent use of the mixture for feeding purposes according to good agricultural practice;
the component shall be determined based on an assessment of the climatic and soil conditions for the use of the mixture as a fertiliser, on indications that the component renders the mixture unpalatable to animals or it is otherwise effective in preventing misuse of the mixture for feeding purposes and in accordance with the requirements laid down in Union legislation or, where applicable, national legislation, for the protection of the environment regarding the protection of soil and groundwater.
The competent authority shall make the list of the authorised components available to the Commission and to other Member States upon request.
4.However, the requirements referred to in point 2 shall not apply:U.K.
to organic fertilisers and soil improvers which are in ready-to-sell packages of not more than 50 kg in weight for use by the final consumer; or
to organic fertilisers and soil improvers in big bags of not more than 1 000 kg in weight, on the packages of which it is indicated that the organic fertilisers are not destined to land to which farmed animals have access, provided that the competent authority of the Member State where the organic fertiliser or soil improver is to be applied to land, has authorised the use of such big bags on the basis of an assessment of the likelihood of a potential diversion of the materials to farms keeping animals or to land to which farmed animals have access.
5.Producers of organic fertilisers and soil improvers must ensure that decontamination of pathogens is carried out prior to their placing on the market, in accordance with:U.K.
Chapter I of Annex X, in the case of processed animal protein or derived products from Category 2 or Category 3 material,
Section 3 of Chapter III of Annex V in the case of compost and digestion residues from the transformation of animal by-products or derived products into biogas.
Section 2 U.K. Storage and transport
After processing or transformation, organic fertilisers and soil improvers shall be properly stored and transported:
in bulk, under appropriate conditions that prevent contamination;
packaged or in big bags, in the case of organic fertilisers or soil improvers destined for sale to final users; or
in the case of storage on farm, in an adequate storage space to which no farmed animals have access.
ANNEX XIIU.K. INTERMEDIATE PRODUCTS
In accordance with Article 34(2) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the following conditions shall apply to the importation and transit through the Union of intermediate products:
The import and transit of intermediate products shall be authorised, provided that:
they are derived from the following materials:
Category 3 material, other than materials referred to in Article 10(c), (n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
products generated by the animals referred to in Article 10(i), (l) and (m) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; or
mixtures of the materials referred to in points (i) and (ii);
in the case of intermediate products destined for the production of medical devices, in vitro diagnostic medical devices and laboratory reagents, they are derived from:
materials which fulfil the criteria referred to in point (a), except that they may have originated from animals which have been submitted to illegal treatment as defined in Article 1(2)(d) of Directive 96/22/EC or Article 2(b) of Directive 96/23/EC;
Category 2 material referred to in Article 9(f) and (h) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; or
mixtures of the materials referred to in points (i) and (ii);
in the case of intermediate products destined for the production of active implantable medical devices, medicinal products and veterinary medicinal products, they are derived from the materials referred to in point (b), where the competent authority considers the use of such materials justified for the protection of public or animal health;
they come from a third country listed as a member of the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) in the OIE bulletin;
they come from an establishment or plant registered or approved by the competent authority of a third country referred to in point (d), in accordance with the conditions set out in point 2;
each consignment is accompanied by a declaration of the importer in accordance with the model declaration set out in Chapter 20 of Annex XV, which must be at least in one of the official languages of the Member State in which the inspection at the border inspection post must be carried out and of the Member State of destination; these Member States may allow the use of other languages and request official translations for declarations in such other languages;
in the case of materials referred to in point (b), the importer demonstrates to the competent authority that the materials:
do not carry any risk of transmission of a disease communicable to humans or animals; or
are transported under conditions which prevent the transmission of any diseases communicable to humans or animals.
An establishment or plant may be registered or approved by the competent authority of a third country, as referred to in point 1(e), provided that:
the operator or owner of the plant or his representative:
demonstrates that the plant has adequate facilities for the transformation of the materials referred to in point 1(a), (b) or (c), as applicable, to ensure the completion of the necessary design, transformation and manufacturing stages;
establishes and implements methods of monitoring and checking the critical control points on the basis of the process used;
keeps a record of the information obtained pursuant to point (ii) for a period of at least two years for submission to the competent authority;
informs the competent authority if any available information reveals the existence of a serious animal health or public health risk;
the competent authority of the third country carries out, at regular intervals, inspections of the establishment or plant and supervises the plant in accordance with the following conditions:
the frequency of inspections and supervision shall depend on the size of the plant, the type of products manufactured, risk assessment and guarantees offered, based on a system of checks which has been set up in accordance with the hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) principles;
if the inspection carried out by the competent authority reveals that the provisions of this Regulation are not being complied with, the competent authority shall take appropriate action;
the competent authority shall draw up a list of establishments or plants approved or registered in accordance with this Annex and shall assign an official number to each plant, which identifies the establishment or plant with respect to the nature of its activities; that list and subsequent amendments to it shall be submitted to the Member State where the inspection at the border inspection post must be carried out and to the Member State of destination.
The intermediate products imported into the Union shall be checked at the border inspection post in accordance with Article 4 of Directive 97/78/EC and transported directly from the border inspection post either to:
a registered establishment or plant for the production of the derived products referred to in Article 33 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, where the intermediate products must be further mixed, used for coating, assembled, packaged or labelled before they are placed on the market or put into services in accordance with the Union legislation applicable to the derived product;
an establishment or plant which has been approved for the storage of animal by-products in accordance with Article 24(1)(i) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, from where they must only be dispatched to an establishment or plant referred to in (a) of this point for the uses referred to in (a).
Intermediate products in transit through the Union shall be transported in accordance with Article 11 of Directive 97/78/EC.
The official veterinarian at the border inspection post concerned shall inform the authority in charge of the establishment or plant at the place of destination of the consignment by means of the TRACES system.
The operator or owner of the establishment or plant of destination or his representative shall keep records in accordance with Article 22 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and shall provide the competent authority on request with the necessary details of purchases, sales, uses, stocks and disposals of surplus of the intermediate products for the purposes of checking compliance with this Regulation.
The competent authority shall ensure, in accordance with Directive 97/78/EC, that the consignments of intermediate products are sent from the Member State where the inspection at the border inspection post must be carried out to the plant of destination, as referred to in point 3 or, in the case of transit, to the border inspection post of exit.
The competent authority shall carry out documentary checks at regular intervals for the purpose of reconciliation of the quantities of intermediate products imported on the one hand, and stocked, used, dispatched or disposed of on the other, in order to check compliance with this Regulation.
For consignments of intermediate products in transit, the competent authorities responsible for the border inspection posts of entry and of exit respectively shall cooperate as necessary to ensure that effective checks are carried out and to ensure the traceability of such consignments.
ANNEX XIIIU.K. PETFOOD AND CERTAIN OTHER DERIVED PRODUCTS
CHAPTER IU.K. General requirements
Petfood plants and establishments or plants producing derived products referred to in this Annex shall have adequate facilities for:
storing and treating incoming material under conditions which prevent the introduction of risks to public and animal health;
disposing of unused animal by-products and derived products remaining after production, unless the unused material is sent for processing or disposal to another establishment or plant, in accordance with this Regulation.
CHAPTER IIU.K. Specific requirements for petfood, including dogchews
1.Raw petfoodU.K.
Operators may only manufacture raw petfood from Category 3 material referred to in Article 10(a) and Article 10(b)(i) and (ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
Raw petfood must be packed in new packaging preventing any leakage.
Effective steps must be taken to ensure that the product is not exposed to contamination throughout the production chain and up to the point of sale.
2.Raw material for processed petfood and for dogchewsU.K.
Operators may manufacture processed petfood and dogchews only from:
Category 3 material, other than material referred to in Article 10(n), (o) and (p) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; and
in the case of imported petfood or petfood produced from imported materials, from Category 1 material comprising of animal by-products derived from animals which have been submitted to illegal treatment as defined in Article 1(2)(d) of Directive 96/22/EC or Article 2(b) of Directive 96/23/EC.
3.Processed petfoodU.K.
Canned petfood must be subjected to heat treatment to a minimum Fc value of 3.
Processed petfood other than canned petfood must:
be subjected to a heat treatment of at least 90 °C throughout the substance of the final product;
be subjected to a heat treatment to at least 90 °C of the ingredients of animal origin; or
be produced as regards feed material of animal origin exclusively using:
animal by-products or derived products from meat or meat products which have been subject to a heat treatment of at least 90 °C throughout their substance;
the following derived products which have been produced in accordance with the requirements of this Regulation: milk and milk-based products, gelatine, hydrolysed protein, egg products, collagen, blood products referred to in Section 2 of Chapter II of Annex X, processed animal protein including fishmeal, rendered fat, fish oils, dicalcium phosphate, tricalcium phosphate or flavouring innards;
if authorised by the competent authority, be subject to a treatment such as drying or fermentation, which ensures that the petfood poses no unacceptable risks to public and animal health;
in the case of animal by-products referred to in Article 10(l) and (m) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and in the case of animal by-products generated by aquatic animals, aquatic and terrestrial invertebrates, and if authorised by the competent authority, be subject to a treatment which ensures that the petfood poses no unacceptable risks to public and animal health.
After production, every precaution must be taken to ensure that such processed petfood is not exposed to contamination.
The processed petfood must be packaged in new packaging.
4.Dogchews must be subjected to a treatment that is sufficient to destroy pathogenic organisms, including salmonella.U.K.
After that treatment, every precaution must be taken to ensure that such dogchews are not exposed to contamination.
The dogchews must be packed in new packaging.
5.Random samples must be taken from dogchews and from processed petfood, other than from canned petfood and other than from such processed petfood which has been treated in accordance in point 3(b)(v), during production and/or during storage (before dispatch) to verify compliance with the following standards:U.K.
Salmonella: absence in 25 g, n = 5, c = 0, m = 0, M = 0.
Enterobacteriaceae: n = 5, c = 2, m = 10, M = 300 in 1 g
Where:
=
number of samples to be tested;
=
threshold value for the number of bacteria; the result shall be considered satisfactory if the number of bacteria in all samples does not exceed m;
=
maximum value for the number of bacteria; the result shall be considered unsatisfactory if the number of bacteria in one or more samples is M or more; and
=
number of samples the bacterial count of which may be between m and M, the sample shall still be considered acceptable if the bacterial count of the other samples is m or less.
6.Random samples must be taken from raw petfood during production and/or during storage (before dispatch) to verify compliance with the following standards:U.K.
Salmonella: absence in 25 g, n = 5, c = 0, m = 0, M = 0.
Enterobacteriaceae: n = 5, c = 2, m = 10, M = 5 000 in 1 g
Where:
=
number of samples to be tested;
=
threshold value for the number of bacteria; the result shall be considered satisfactory if the number of bacteria in all samples does not exceed m;
=
maximum value for the number of bacteria; the result shall be considered unsatisfactory if the number of bacteria in one or more samples is M or more; and
=
number of samples the bacterial count of which may be between m and M, the sample shall still be considered acceptable if the bacterial count of the other samples is m or less.
7.End point for processed petfood and dogchewsU.K.
The following may be placed on the market without restrictions in accordance with this Regulation:
processed petfood
which has been manufactured and packaged in the Union in accordance with point 3 and which has been tested in accordance with point 5; or
which has been subject to veterinary checks in accordance with Directive 97/78/EC at a border inspection post.
dogchews
which have been manufactured and packaged in the Union in accordance with point 4 and which has been tested in accordance with point 5; or
which have been subject to veterinary checks in accordance with Directive 97/78/EC at a border inspection post.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. Specific requirements for flavouring innards for the manufacture of petfood
1.Operators may only use animal by-products which may be used as raw material for processed petfood and dogchews in accordance with point 2 of Chapter II for the production of liquid or dehydrated derived products used to enhance the palatability values of petfood.U.K.
2.Flavouring innards must have been submitted to a treatment method and parameters, which ensure that the product complies with the microbiological standards set out in point 5 of Chapter II of this Annex. After treatment, every precaution must be taken to ensure that the product is not exposed to contamination.U.K.
3.The end product must be:U.K.
packed in new or sterilised packaging; or
transported in bulk in containers or other means of transport that were thoroughly cleaned and disinfected.
CHAPTER IVU.K. Specific requirements for blood and blood products from equidae
The placing on the market of blood and blood products from equidae for purposes other than in feed shall be subject to the following conditions:
Blood may be placed on the market for such purposes provided that it has been collected:
from equidae which:
at inspection on the date of blood collection do not show clinical signs of any of the compulsorily notifiable diseases listed in Annex I to Directive 2009/156/EC and of equine influenza, equine piroplasmosis, equine rhinopneumonitis and equine viral arteritis listed in point 4 of Article 1.2.3. of the Terrestrial Animal Health Code of the OIE, 2010 edition;
have been kept for a period of at least 30 days prior to the date of and during blood collection on holdings under veterinary supervision which were not subject to a prohibition order pursuant to Article 4(5) of Directive 2009/156/EC or restrictions pursuant to Article 5 of that Directive;
for the periods laid down in Article 4(5) of Directive 2009/156/EC had no contact with equidae from holdings which were subject to a prohibition order for animal health reasons pursuant to that Article and for a period of at least 40 days prior to the date of and during blood collection had no contact with equidae from a Member State or third country not considered free of African horse sickness in accordance with points (a) and (b) of the first subparagraph of Article 5(2) of that Directive;
under veterinary supervision either:
in slaughterhouses registered or approved in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 853/2004; or
in facilities approved, furnished with a veterinary approval number and supervised by the competent authority for the purpose of collecting blood from equidae for the production of blood products for purposes other than feeding.
Blood products may be placed on the market for such purposes provided that:
all precautions have been taken to avoid contamination of the blood products with pathogenic agents during production, handling and packaging;
the blood products have been produced from blood which:
either fulfils the conditions set out in point 1(a); or
has been subjected to at least one of the following treatments, followed by an effectiveness check, for the inactivation of possible causative pathogens for African horse sickness, equine encephalomyelitis of all types including Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis, equine infectious anaemia, vesicular stomatitis and glanders (Burkholderia mallei):
heat treatment at a temperature of 65 °C for at least three hours,
irradiation at 25 kGy by gamma rays,
change in pH to pH 5 for two hours,
heat treatment of at least 80 °C throughout their substance.
Blood and blood products from equidae must be packed in sealed impermeable containers which, in the case of blood from equidae, bear the approval number of the slaughterhouse or facilities of collection referred to in point 1(b).
CHAPTER VU.K. Specific requirements for hides and skins of ungulates and products derived therefrom
A.Establishments and plantsU.K.
The competent authority may authorise plants handling hides and skins, including limed hides, to supply trimmings and splittings of these hides and skins for the production of gelatine for animal consumption, organic fertilisers or soil improvers, provided that:
the plant has storage rooms with hard floors and smooth walls that are easy to clean and disinfect and, where appropriate, provided with refrigeration facilities;
the storage rooms are kept in a satisfactory state of cleanliness and repair, so that they do not constitute a source of contamination for the raw materials;
if raw material not in conformity with this Chapter is stored and/or processed in these premises, it must be segregated from raw material in conformity with this Chapter throughout the period of receipt, storage, processing and dispatch;
in the case of trimmings and splittings derived from limed hides, the trimmings and splittings are submitted to a treatment which ensures that no risks to public and animal health remain before being used for the production of:
gelatine for animal consumption; or
organic fertilisers or soil improvers.
B.Placing on the market of animal by-products and of derived productsU.K.
1.Untreated hides and skins may be placed on the market subject to the health conditions applicable to fresh meat pursuant to Directive 2002/99/EC.U.K.
2.Treated hides and skins may be placed on the market, provided that:U.K.
they have not been in contact with other animal products or live animals presenting a risk of spreading a serious transmissible disease;
the commercial document laid down in Chapter III of Annex VIII contains a statement indicating that all precautions have been taken to avoid contamination with pathogenic agents.
C.End point for hides and skinsU.K.
1.Hides and skins of ungulates which pursuant to the decision of an operator are destined for purposes other than human consumption, and which comply with the requirements of Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 for raw materials for gelatine or collagen intended for use in food may be placed on the market without restrictions in accordance with this Regulation.U.K.
2.The following treated hides and skins may be placed on the market without restrictions in accordance with this Regulation:U.K.
hides and skins having undergone the complete process of tanning;
‘wet blue’;
‘pickled pelts’;
limed hides (treated with lime and in brine at a pH of 12 to 13 for at least eight hours).
3.By way of derogation from point C.2, the competent authority may require that consignments of treated hides and skins referred to in point 2(c) and (d) are accompanied by a commercial document in accordance with the model set out under point 6 of Chapter III of Annex VIII, when they are supplied to establishments or plants producing petfood, organic fertilisers or soil improvers or transforming those materials into biogas.U.K.
CHAPTER VIU.K. Specific requirements for game trophies and other preparations from animals
A.The provisions of this Chapter are without prejudice to the measures for the protection of wild fauna, adopted pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 338/97.U.K.
B.Safe sourcingU.K.
Game trophies and other preparations from animals, where for the preparation the animal by-products have been submitted to a treatment or are presented in a state which does not pose any health risks, may be placed on the market, provided they originate from:
species other than ungulates, birds and animals of the biological class Insecta or Arachnida; and
animals originating in an area not subject to restrictions as a result of the presence of serious transmissible diseases to which animals of the species concerned are susceptible.
C.Safe treatmentU.K.
1.Game trophies or other preparations from animals, where for the preparation the animal by-products have been submitted to a treatment or are presented in a state which does not pose any health risks, may be placed on the market, provided they:U.K.
originate from ungulates or birds which have undergone a complete taxidermy treatment ensuring their preservation at ambient temperatures;
are mounted ungulates or birds or mounted parts of such animals;
have been subject to an anatomical preparation such as by plastination; or
are animals of the biological class Insecta or Arachnida which have been subject to a treatment such as drying to prevent any transmission of diseases communicable to humans or animals.
2.Game trophies or other preparations, other than those referred to under points B and C.1, which come from animals originating in an area subject to restrictions as a result of the presence of serious transmissible diseases to which animals of the species concerned are susceptible, may be placed on the market, provided that:U.K.
in the case of game trophies or other preparations solely of bone, horns, hooves, claws, antlers or teeth,
they have been immersed in boiling water for an appropriate time so as to ensure that any matter other than bone, horns, hooves, claws, antlers or teeth is removed;
they have been disinfected with a product authorised by the competent authority, in particular with hydrogen peroxide where parts consisting of bone are concerned;
they have been packaged, immediately after treatment, without being in contact with other products of animal origin likely to contaminate them, in individual, transparent and closed packages so as to avoid any subsequent contamination; and
they are accompanied by a health certificate certifying that the conditions set out in (i), (ii) and (iii) have been met;
in case of game trophies or other preparations consisting solely of hides or skin,
they have been:
dried,
dry- or wet-salted for a period of at least 14 days before the date of dispatch, or
subject to a preservation process other than tanning;
they have been packaged, immediately after treatment, without being in contact with other products of animal origin likely to contaminate them, in individual, transparent and closed packages so as to avoid any subsequent contamination; and
they are accompanied by a commercial document or a health certificate certifying that the conditions set out in (i) and (ii) have been met.
CHAPTER VIIU.K. Specific requirements for wool, hair, pig bristles, feathers, parts of feathers and down
A.Raw materialU.K.
1.Untreated wool, untreated hair, untreated pig bristles and untreated feathers, parts of feathers and down must be Category 3 materials referred to in Article 10(b) (iii), (iv) and (v) and Article 10(h) and (n) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.U.K.
They must be securely enclosed in packaging and dry.
However, in the case of untreated feathers, parts of feathers and down sent directly from the slaughterhouse to the processing plant, the competent authority may allow a derogation from the requirement to dry materials transported on its territory, provided that:
all necessary measures are taken to avoid any possible spread of disease;
the transport takes place in waterproof containers and/or vehicles which must be cleaned and disinfected immediately after each use.
2.Movements of pig bristles from regions in which African swine fever is endemic shall be prohibited except for pig bristles that have:U.K.
been boiled, dyed or bleached; or
undergone some other form of treatment which is certain to kill pathogenic agents, provided that evidence to this effect is submitted in the form of a certificate from the veterinarian responsible for the place of origin. Factory washing may not be regarded as a form of treatment for the purposes of this provision.
3.The provisions of point 1 shall not apply to decorative feathers or feathers:U.K.
carried by travellers for their private use; or
in the form of consignments sent to private individuals for non-industrial purposes.
B.End point for wool and hairU.K.
Factory-washed wool and hair, and wool and hair which has been treated by another method which ensures that no unacceptable risks remain, may be placed on the market without restrictions in accordance with this Regulation.
Member States may authorise the placing on the market of untreated wool and hair from farms or from establishments or plants which have been registered in accordance with Article 23 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 or approved in accordance with Article 24(1)(i) of the same Regulation on their territory without restrictions in accordance with this Regulation, if they are satisfied that no unacceptable risks to public and animal health arise from the wool and from the hair.
C.End point for feathers and downU.K.
Feathers, parts of feathers and down which have been factory-washed and treated with hot steam at 100 °C for at least 30 minutes may be placed on the market without restrictions in accordance with this Regulation.
CHAPTER VIIIU.K. Specific requirements for furs
End point
Furs which have been dried at an ambient temperature of 18 °C for two days at a humidity of 55 % may be placed on the market without restrictions in accordance with this Regulation.
CHAPTER IXU.K. Specific requirements for apiculture by-products
Apiculture by-products intended exclusively for use in apiculture must:
not come from an area which is subject of a prohibition order associated with an occurrence of:
American foulbrood (Paenibacillus larvae larvae), except where the competent authority has assessed the risk to be negligible, issued a specific authorisation for use only in that Member State, and taken all other necessary measures to ensure no spread of that disease;
acariosis (Acarapis woodi (Rennie)), except where the area of destination has obtained additional guarantees in accordance with Article 14(2) of Directive 92/65/EEC;
small hive beetle (Aethina tumida); or
Tropilaelaps mite (Tropilaelaps spp.); and
meet the requirements provided for in Article 8(a) of Directive 92/65/EEC.
CHAPTER XU.K. Specific requirements for rendered fats from Category 1 or Category 2 materials for oleochemical purposes
1.Rendered fats derived from Category 1 material or from Category 2 material which are destined for oleochemical purposes must be produced using any of the processing methods 1 to 5 as set out in Chapter III of Annex IV.U.K.
2.Rendered fats derived from ruminant animals must be purified in such a way that the maximum level of remaining total insoluble impurities does not exceed 0,15 % in weight.U.K.
CHAPTER XIU.K. Specific requirements for fat derivatives
1.The following processes may be used to produce fat derivatives from rendered fats derived from Category 1 and Category 2 material:U.K.
transesterification or hydrolysis at least 200 °C, under corresponding appropriate pressure, for 20 minutes (glycerol, fatty acids and esters);
saponification with NaOH 12M (glycerol and soap):
in a batch process at 95 °C for three hours; or
in a continuous process at 140 °C 2 bars (2 000 hPa) for eight minutes; or
hydrogenation at 160 °C at 12 bars (12 000 hPa) for 20 minutes.
2.Fat derivatives produced in accordance with this Chapter may only be placed on the market:U.K.
for uses other than in feed, cosmetics and medicinal products;
in addition, in the case of fat derivatives from Category 1 material, for uses other than in organic fertilisers and soil improvers.
CHAPTER XIIU.K. Specific requirements for horns and horn products, excluding horn meal, and hooves and hoof products, excluding hoof meal, intended for the production of organic fertilisers or soil improvers
The placing on the market of horns and horn products, excluding horn meal, and hooves and hoof products, excluding hoof meal, intended for the production of organic fertilisers or soil improvers shall be subject to the following conditions:
they must originate from animals that:
either have been slaughtered in a slaughterhouse, after undergoing an ante-mortem inspection, and were found fit, as a result of such inspection, for slaughter for human consumption in accordance with Union legislation; or
did not show clinical signs of any disease communicable through that product to humans or animals;
they must have undergone a heat treatment for one hour at a core temperature of at least 80 °C;
the horns must be removed without opening the cranial cavity;
at any stage of processing, storage or transport, every precaution shall be taken to avoid cross-contamination;
they shall be packed either in new packaging or containers; or transported in vehicles or bulk containers which have been disinfected prior to loading using a product approved by the competent authority;
the packaging or containers must:
indicate the type of product (such as horns, horn products, hooves or hoof products);
be marked with the name and address of the approved or registered establishment or plant of destination.
ANNEX XIVU.K. IMPORTATION, EXPORT AND TRANSIT
CHAPTER IU.K. SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR THE IMPORTATION INTO AND TRANSIT THROUGH THE UNION OF CATEGORY 3 MATERIAL AND DERIVED PRODUCTS FOR USES IN THE FEED CHAIN OTHER THAN FOR PETFOOD OR FOR FEED TO FUR ANIMALS
Section 1 U.K.
As referred to in Article 41(1)(a) and Article 41(3) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the following requirements shall apply to imported consignments of Category 3 material and derived products therefrom for uses in the feed chain other than for petfood or for feed to fur animals and consignments of such materials and products in transit:
they must consist of or have been produced from, as applicable, Category 3 material referred to in the column ‘raw materials’ of Table 1;
they must comply with the import and transit conditions set out in the column ‘import and transit conditions’ of Table 1;
they must come from a third country or part of a third country listed in the column ‘third countries’ list’ of Table 1; and
they shall be accompanied during transportation to the point of entry into the Union where the veterinary checks take place by the health certificate referred to in the column ‘certificates/model documents’ of Table 1; or
they shall be presented at the point of entry into the Union where the veterinary checks take place accompanied by a document corresponding to the model referred to in the column ‘certificates/model documents’ of Table 1.
Table 1
Section 2 U.K. Imports of processed animal protein
The following requirements shall apply to the importation of processed animal protein:
Before consignments are released for free circulation within the Union, the competent authority must sample processed animal protein from imported consignments at the border inspection post to ensure compliance with the general requirements of Chapter I of Annex X.
The competent authority must:
sample each consignment of products carried in bulk;
carry out random sampling of consignments of products packaged in the manufacturing plant of origin.
By way of derogation from point 1, when six consecutive tests on bulk consignments originating in a given third country prove negative, the competent authority of the border inspection post may carry out random sampling of subsequent bulk consignments from that third country.
If one of those random samples proves positive, the competent authority carrying out the sampling must inform the competent authority of the third country of origin so that it can take appropriate measures to remedy the situation.
The competent authority of the third country of origin must bring these measures to the attention of the competent authority carrying out the sampling.
In the event of a further positive result from the same source, the competent authority of the border inspection post must sample each consignment from the same source until six consecutive tests again prove negative.
Competent authorities must keep a record for at least three years of the results of sampling carried out on all consignments that have undergone sampling.
Where a consignment imported into the Union proves to be positive for salmonella or where it does not meet the microbiological standards for enterobacteriaceae set out in Chapter I of Annex X, it must either:
be dealt with in accordance with the procedure laid down by Article 17(2)(a) of Directive 97/78/EC; or
reprocessed in a processing plant or decontaminated by a treatment authorised by the competent authority. The consignment must not be released until it has been treated, tested for salmonella or enterobacteriaceae, as necessary, by the competent authority in accordance with Chapter I of Annex X, and a negative result obtained.
Section 3 U.K. Imports of rendered fats
The following requirements shall apply to the importation of rendered fats:
Rendered fat shall:
be entirely or partly derived from porcine raw material and come from a third country or a part of the territory of a third country free from foot-and-mouth disease for the previous 24 months and free from classical swine fever and African swine fever for the previous 12 months;
be entirely or partly derived from poultry raw material and come from a third country or a part of the territory of a third country free from Newcastle disease and avian influenza for the previous six months;
be entirely or partly derived from ruminant raw material and come from a third country or a part of the territory of a third country free from foot-and-mouth disease for the previous 24 months and free from rinderpest for the previous 12 months; or
where there has been an outbreak of one of the diseases referred to in points (a), (b) and (c) during the relevant period referred to in those points, have been subjected to one of the following heat treatments:
at least 70 °C for at least 30 minutes; or
at least 90 °C for at least 15 minutes.
Details of the critical control points shall be recorded by operators and maintained so that the owner, operator or their representative and, as necessary, the competent authority can monitor the operation of the plant; and the recorded information shall include the particle size, critical temperature and, as appropriate, the absolute time, pressure profile, raw material feed rate and fat recycling rate.
Section 4 U.K. Imports of milk, milk-based products, milk-derived products, colostrum and colostrum products
A.The following requirements shall apply to the importation of milk, milk-based products, milk-derived products, colostrum and colostrum products:U.K.
Milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products shall:
have undergone at least one of the treatments provided for in points 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 and point (a) of point B.1.4 of Part I of Section 4 of Chapter II of Annex X;
comply with points B.2 and B.4, and, in the case of whey, point B.3 of Part I of Section 4 of Chapter II of Annex X.
By way of derogation from point B.1.4 of Part I of Section 4 of Chapter II of Annex X, milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products may be imported from third countries so authorised in column ‘A’ of Annex I to Regulation (EU) No 605/2010, provided that the milk, milk-based products or milk-derived products have undergone a single HTST treatment and:
have not been shipped before a period of at least 21 days has elapsed after production and during that period no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been detected in the exporting third country; or
have been presented at a border inspection post of entry into the Union at least 21 days after production and during that period no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been detected in the exporting third country.
B.The following requirements shall apply to the importation of colostrum and colostrum products:U.K.
The materials shall have undergone a single HTST treatment and:
have not been shipped before a period of at least 21 days has elapsed after production and during that period no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been detected in the exporting third country; or
have been presented at a border inspection post of entry into the Union at least 21 days after production and during that period no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been detected in the exporting third country.
The materials shall have been obtained from bovine animals subject to regular veterinary inspections to ensure that they come from holdings on which all bovine herds are:
either recognised as officially tuberculosis-free and officially brucellosis-free as defined in Article 2(2)(d) and (f) of Directive 64/432/EEC or not restricted under the national legislation of the third country of origin of the colostrum regarding eradication of tuberculosis and brucellosis; and
either recognised as official enzootic-bovine-leukosis-free as defined in Article 2(2)(j) of Directive 64/432/EEC or included in an official system for the control of enzootic bovine leukosis and there has been no evidence as a result of clinical and laboratory testing of this disease in the herd during the past two years.
After completion of the processing, every precaution shall have been taken to prevent contamination of the colostrum or colostrum products.
The final product must bear a label so as to indicate that it contains Category 3 material and is not intended for human consumption, and it must have been:
packed in new containers; or
transported in bulk in containers or other means of transport that before use were thoroughly cleaned and disinfected.
CHAPTER IIU.K. SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR THE IMPORTATION INTO AND TRANSIT THROUGH THE UNION OF ANIMAL BY-PRODUCTS AND DERIVED PRODUCTS FOR USES OUTSIDE THE FEED CHAIN FOR FARMED ANIMALS OTHER THAN FUR ANIMALS
Section 1 U.K. Specific requirements
As referred to in Article 41(1)(a) and (2)(c) and Article 41(3) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the following specific requirements shall apply to imported consignments of animal by-products and derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals and consignments of such products in transit:
they must consist of or have been produced from animal by-products referred to in the column ‘raw materials’ of Table 2;
they must comply with the import and transit conditions set out in the column ‘import and transit conditions’ of Table 2;
they must come from a third country or part of a third country listed in the column ‘third countries’ list’ of Table 2; and
they shall be accompanied during transportation to the point of entry into the Union where the veterinary checks take place by the health certificate or other document, as applicable, referred to in the column ‘certificates/ model documents’ of Table 2; or
they shall be presented at the point of entry into the Union where the veterinary checks take place accompanied by a document corresponding to the model referred to in the column ‘certificates/ model documents’ of Table 2.
Table 2
Section 2 U.K. Imports of blood and blood products, excluding from equidae, for the manufacture of derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals
The following requirements shall apply to the import of blood and blood products, excluding those from equidae, for the manufacture of derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals:
The blood products must originate from a plant for the production of derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals which meets the specific conditions laid down in this Regulation or from the establishment of collection.
The blood from which blood products for the manufacture of derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals are produced must have been collected:
in slaughterhouses approved in accordance with Union legislation;
in slaughterhouses approved and supervised by the competent authority of the third country; or
from live animals in facilities approved and supervised by the competent authority of the third country.
In the case of blood products for the manufacture of derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals which have been derived from animals belonging to the taxa Artiodactyla, Perissodactyla and Proboscidea, including their crossbreeds, they must comply with the conditions of either point (a) or (b):
the products must have undergone one of the following treatments guaranteeing the absence of pathogens of the diseases referred to in point (b):
heat treatment at a temperature of 65 °C for at least three hours, followed by an effectiveness check;
irradiation at 25 kGy by gamma rays, followed by an effectiveness check;
heat treatment of at least 80 °C throughout their substance, followed by an effectiveness check;
in the case of animals other than Suidae and Tayassuidae only: change in pH to pH 5 for two hours, followed by an effectiveness check;
in the case of blood products not treated in accordance with point (a) the products must originate from a third country or region:
where no case of rinderpest, peste des petits ruminants and Rift Valley fever has been recorded for a period of at least 12 months and in which vaccination has not been carried out against those diseases for a period of at least 12 months;
where no case of foot-and-mouth disease has been recorded for a period of at least 12 months, and,
in which vaccination has not been carried out against this disease for a period of at least 12 months, or
in which vaccination programmes against foot-and-mouth disease are being officially carried out and controlled in domestic ruminant animals for a period of at least 12 months; in this case, following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, the products must be transported directly to the registered establishment or plant of destination and all precautions, including safe disposal of waste, unused or surplus material, must be taken to avoid risks of spreading diseases to animals or humans.
In addition to point (b)(i) and (ii) of point 3.1, in the case of animals other than Suidae and Tayassuidae, one of the following conditions must be complied with:
in the third country or region of origin no case of vesicular stomatitis and bluetongue (including the presence of seropositive animals) has been recorded for a period of at least 12 months and vaccination has not been carried out against those diseases for a period of at least 12 months in the susceptible species;
following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, the products must be transported directly to the plant of destination and all precautions, including safe disposal of waste, unused or surplus material, must be taken to avoid risks of spreading diseases to animals or humans.
In addition to point (b)(i) and (ii) of point 3.1, in the case of Suidae and Tayassuidae, in the third country or region of origin no case of swine vesicular disease, classical swine fever and African swine fever has been recorded for a period of at least 12 months, vaccination has not been carried out against those diseases for a period of at least 12 months and one of the following conditions are complied with:
in the country or region of origin no case of vesicular stomatitis (including the presence of seropositive animals) has been recorded for a period of 12 months and vaccination has not been carried out against this disease for a period of at least 12 months in the susceptible species;
following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, the products must be transported directly to the registered establishment or plant of destination and all precautions, including safe disposal of waste, unused or surplus material, must be taken to avoid risks of spreading diseases to animals or humans.
In the case of blood products for the manufacture of derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals which have been derived from poultry and other avian species, they must comply with the following conditions of either point (a) or (b):
the products must have undergone one of the following treatments guaranteeing the absence of pathogens of the diseases referred to in point (b):
heat treatment at a temperature of 65 °C for at least three hours, followed by an effectiveness check;
irradiation at 25 kGy by gamma rays, followed by an effectiveness check;
heat treatment of at least 70 °C throughout their substance, followed by an effectiveness check;
in case of blood products not treated in accordance with point (a) the products must originate from a third country or region:
which has been free from Newcastle disease and highly pathogenic avian influenza as listed in the Terrestrial Animal Health Code of the OIE, 2010 edition;
which during the last 12 months has not carried out vaccination against avian influenza;
where the poultry or other avian species from which the products derive have not been vaccinated against Newcastle disease with vaccines prepared from a Newcastle disease master strain showing a higher pathogenicity than lentogenic virus strains.
Section 3 U.K. Imports of blood and blood products from equidae
The following requirements shall apply to the import of blood and blood products from equidae:
The blood must comply with the conditions set out in point 1(a) of Chapter IV of Annex XIII and must be collected under veterinary supervision either in:
slaughterhouses
approved in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 853/2004; or
approved and supervised by the competent authority of the third country; or
facilities approved and furnished with a veterinary approval number and supervised by the competent authority of the third country for the purpose of collecting blood from equidae for the production of blood products for purposes other than feeding.
The blood products must comply with the conditions set out in point 2 of Chapter IV of Annex XIII.
In addition, the blood products referred to in point 2(b)(i) of Chapter IV of Annex XIII must be produced from blood collected from equidae which have been kept for a period of at least three months, or since birth if less than three months old, prior to the date of collection on holdings under veterinary supervision in the third country of collection which during that period and the period of blood collection has been free of:
African horse sickness in accordance with points (a) and (b) of the first subparagraph of Article 5(2) of Directive 2009/156/EC;
Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis for a period of at least two years;
glanders:
for a period of three years; or
for a period of six months where the animals have shown no clinical signs of glanders (Burkholderia mallei) during the post-mortem inspection in the slaughterhouse referred to in point 1(a), including a careful examination of mucous membranes from the trachea, larynx, nasal cavities and sinuses and their ramifications, after splitting the head in the median plane and excising the nasal septum;
in the case of blood products other than serum, vesicular stomatitis for a period of at least six months.
Blood products must come from an establishment or plant which has been approved or registered by the competent authority of the third country.
Blood and blood products shall be packed and labelled in accordance with point 3 of Chapter IV of Annex XIII.
Section 4 U.K. Imports of hides and skins of ungulates
The following requirements shall apply to the import of hides and skins of ungulates:
Fresh or chilled hides and skins may be imported if:
they come from a third country referred to in the applicable column of row 4 of Table 2 set out in Section 1 which, as appropriate to the species concerned:
for a period of at least 12 months before dispatch, has been free from all of the following diseases:
classical swine fever,
African swine fever, and
Rinderpest; and
has been free from foot-and-mouth disease for a period of at least 12 months before the date of dispatch and where, for a period of at least 12 months before the date of dispatch, no vaccination has been carried out against that disease;
they have been obtained from:
animals that have remained in the territory of the third country of origin for a period of at least three months before being slaughtered or since birth in the case of animals less that three months old;
in the case of hides and skins from bi-ungulates, animals that come from holdings in which there has been no outbreak of foot-and mouth disease in the previous 30 days, and around which within a radius of 10 km there has been no case of foot-and-mouth disease for 30 days;
in the case of hides and skins from swine, animals that come from holdings in which there has been no outbreak of swine vesicular disease in the previous 30 days, or of classical or African swine fever in the previous 40 days, and around which within a radius of 10 km there has been no case of these diseases for 30 days; or
animals that have passed the ante-mortem health inspection at the slaughterhouse during the 24 hours before slaughter and have shown no evidence of foot-and-mouth disease, rinderpest, classical swine fever, African swine fever or swine vesicular disease; and
they have undergone all precautions to avoid recontamination with pathogenic agents.
Treated hides and skins referred to in point C.2 of Chapter V of Annex XIII may be imported without any restrictions.
Other treated hides and skins may be imported if:
they come either from:
a third country or, in the case of regionalisation in accordance with Union legislation, from a part of a third country, appearing on the list set out in point (a) of the column ‘third countries’ list’ of row 5 of Table 2 set out in Section 1 from which imports of fresh meat of the corresponding species are authorised and they have been treated as referred to in point 28(a), (b) and (c) of Annex I;
a third country appearing on the list set out in point (a) of the applicable column of row 5 of Table 2 set out in Section 1 and they have been treated as referred to in point 28(c) or (d) of Annex I; or
equidae or ruminant animals from a third country appearing on the list set out in point (b) of the column ‘third countries’ list’ of row 5 of Table 2 of Section 1, and have been treated as referred to in point 28(a), (b) and (c) of Annex I and after treatment have been kept separate for a period of at least 21 days; and
in the case of salted hides and skins transported by ship, they have been treated as referred to in point 28(b) or (c) of Annex I and have been kept separated after treatment during transportation for a period of at least 14 days in the case of the treatment referred to in point 28(b) or seven days in the case of the treatment referred to in point 28(c) before importation and the health certificate accompanying the consignment attests such treatment and the duration of the transportation.
Fresh, chilled or treated hides and skins of ungulates must be imported in containers, road vehicles, railway wagons or bales sealed under the responsibility of the competent authority of the third country of dispatch.
Section 5 U.K. Imports of game trophies and other preparations from animals
The following requirements shall apply to the import of game trophies and other preparations from animals:
Game trophies or other preparations from animals which fulfil the conditions referred to in points B and C.1 of Chapter VI of Annex XIII may be imported without restrictions.
Treated game trophies or other preparations from birds and ungulates, being solely comprised of bones, horns, hooves, claws, antlers, teeth, hides or skins, from third countries may be imported if they comply with the requirements of point C.1(a) and point C.2(a), (i) to (iii) and (b)(i) and (ii) of Chapter VI of Annex XIII.
However, in the case of dry-salted or wet-salted skins transported by ship, the skins need not be salted 14 days before dispatch, provided that they are salted for 14 days before importation.
Game trophies or other preparations from birds and ungulates consisting of entire anatomical parts, not having been treated in any way may be imported if:
they come from animals originating in an area not subject to restrictions as a result of the presence of serious transmissible diseases to which animals of the species concerned are susceptible;
they were packaged without being in contact with other products of animal origin likely to contaminate them, in individual, transparent and closed packages so as to avoid any subsequent contamination.
Section 6 U.K. Imports of treated feathers, parts of feathers and down
Treated feathers and parts of feathers and down may be imported:
if they are treated decorative feathers, treated feathers carried by travellers for their private use or consignments of treated feathers or down sent to private individuals for non-industrial purposes; or
if they are accompanied by a commercial document stating that the feathers and parts of feathers or down have been treated with a steam current or by another method that ensures that no unacceptable risks remain and are securely enclosed in packaging and dry; and
unless the commercial document states that they have been factory-washed and treated with hot steam at 100 °C for at least 30 minutes, they are sent to a registered establishment or plant for such treatment.
Section 7 U.K. Imports of bones and bone products (excluding bone meal), horns and horn products (excluding horn meal) and hooves and hoof products (excluding hoof meal) intended for use other than as feed material, organic fertilisers or soil improvers
1.Bones and bone products (excluding bone meal), horns and horn products (excluding horn meal) and hooves and hoof products (excluding hoof meal) may be imported to produce derived products for uses outside the feed chain if:U.K.
the products are dried before export to the Union and not chilled or frozen;
the products are conveyed only by land and sea from their third country of origin direct to a border inspection post of entry into the Union and are not transhipped at any port or place outside the Union;
following the document checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, the products are conveyed directly to the registered establishment or plant of destination.
2.Each consignment must be accompanied by a commercial document stamped by the competent authority supervising the establishment of origin, including the following information:U.K.
the third country of origin;
the name of the establishment or plant of production;
the nature of the product (dried bone/dried bone product/dried horns/dried horn products/dried hooves/dried hoof products), and
confirmation of the fact that the product was:
derived from healthy animals slaughtered in a slaughterhouse;
dried for a period of 42 days at an average temperature of at least 20 °C;
heated for one hour to at least 80 °C to the core before drying;
ashed for one hour to at least 800 °C to the core before drying;
underwent an acidification process such that the pH was maintained at less than 6 to the core for at least one hour before drying, and
is not intended at any stage to be diverted for any use in food, feed material, organic fertilisers or soil improvers.
3.On dispatch to the Union, the material must be enclosed in sealed containers or vehicles or carried in bulk in a ship.U.K.
If transported in containers, the containers, and in all cases all the accompanying documents, must bear the name and the address of the registered establishment or plant of destination.
4.Following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, the material must be transported directly to the registered establishment or plant of destination.U.K.
Section 8 U.K. Imports of animal by-products for the manufacture of feed for fur animals, petfood, other than raw petfood, and derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals
Animal by-products intended for the manufacture of feed for fur animals, petfood, other than raw petfood, and for derived products for uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals may be imported provided that:
the animal by-products have been deep-frozen at the plant of origin or have been preserved in accordance with Union legislation in such a way to prevent spoiling between dispatch and delivery to the establishment or plant of destination;
the animal by-products have undergone all precautions to avoid contamination with pathogenic agents;
the animal by-products were packed in new packaging preventing any leakage or in packaging which has been cleaned and disinfected before use;
following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, the animal by-products are transported directly either to:
a petfood plant or to a registered establishment or plant of destination, which has provided a guarantee that the animal by-products shall be used only for the purpose of producing the products for which it has been registered or approved, as applicable, as specified by the competent authority if necessary, and shall not leave the establishment or plant untreated other than for direct disposal;
an establishment or plant which has been approved in accordance with Article 24(1)(h) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
a registered user or collection centre, which has provided a guarantee that the animal by-products shall be used only for permitted purposes, as specified by the competent authority if necessary; or
an establishment or plant which has been approved in accordance with Article 24(1)(a) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; and
in the case of raw material for petfood production referred to in Article 35(a)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the raw material shall:
be marked in the third country before entry into the Union by a cross of liquefied charcoal or activated carbon, on each outer side of each frozen block, or, when the raw material is transported in pallets which are not divided into separate consignments during transport to the petfood plant of destination, on each outer side of each pallet, in such a way that the marking covers at least 70 % of the diagonal length of the side of the frozen block and is at least 10 cm in width;
in the case of material which is not frozen, be marked in the third country before entry into the Union by spraying it with liquefied charcoal or by applying charcoal powder in such a way that the charcoal is clearly visible on the material;
be transported directly to:
the petfood plant of destination in accordance with point 4(a); or
an establishment or plant of destination which has been approved in accordance with Article 24(1)(h) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, in accordance with point 4(b) of this Section and from there directly to the petfood plant referred to under (i), provided that the plant of destination:
only handles material covered by this point 5.1, or
only handles material destined for a petfood plant as referred to under (i); and
be manipulated to remove the marking provided for in points (a) and (b) only in the petfood plant of destination and only immediately prior to use of the material for the manufacture of petfood, in accordance with the conditions applicable to petfood produced from Category 3 material set out in Chapter II of Annex XIII;
in the case of consignments made up of raw material, which has been treated as referred to in point 5.1 above and other non-treated raw material, all the raw materials in the consignment have been marked as laid down in point 5.1(a) and (b) above;
the marking referred to in point 5.1(a) and (b) and point 5.2 remains visible from the dispatch and until the delivery to the petfood plant of destination;
In the petfood plant of destination, raw material for petfood production referred to in Article 35(a)(ii) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 shall be stored before production, used and disposed of under conditions authorised by the competent authority, which allow official controls on the amounts of material received, used for production and disposed of, if applicable.
The competent authority may authorise the operator of the petfood plant to store such materials together with Category 3 material.
Section 9 U.K. Imports of rendered fats for certain purposes outside the feed chain for farmed animals
Rendered fats which are not destined to the production of feed for farmed animals, the manufacture of cosmetics, medicinal products or medical devices, may be imported, provided:
they are derived from:
in the case of materials destined to the production of biodiesel, animal by-products referred to in Articles 8, 9 and 10 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
in the case of materials destined to the production of organic fertilisers and soil improvers, Category 2 materials referred to in points (c), (d) and (f)(i) of Article 9 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, or Category 3 materials, other than materials referred to in points (c) and (p) of Article 10 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
in the case of other materials, Category 1 materials referred to in points (b), (c) and (d) of Article 8 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, Category 2 materials referred to in points (c), (d) and (f)(i) of Article 9 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 or Category 3 materials, other than materials referred to in points (c) and (p) of Article 10 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
they have been processed by processing method 1 (pressure sterilisation) or in accordance with one of the other processing methods referred to in Chapter III of Annex IV;
in the case of fat from ruminant origin, insoluble impurities in excess of 0,15 % by weight have been removed;
they have been marked before shipment to the Union so that the minimum concentration of GTH referred to in point 1(b) of Chapter V of Annex VIII is achieved;
following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, the rendered fats are transported directly to the registered establishment or plant of destination, under conditions which prevent contamination; and
they bear labels, on the packaging or container indicating ‘NOT FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL CONSUMPTION’.
Section 10 U.K. Imports of fat derivatives
1.Fat derivatives may be imported if the health certificate accompanying the consignment certifies:U.K.
whether the fat derivatives derive from Category 1, 2 or 3 materials;
in the case of fat derivatives produced from Category 2 material, that the products:
have been produced using a method that at least meets the standards of one of the processes referred to in point 1 of Chapter XI of Annex XIII; and
shall only be used in organic fertiliser or soil improvers or other uses outside the feed chain for farmed animals, other than in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and medical devices;
in the case of fat derivatives produced from Category 1 material, that the products must not be used in organic fertilisers and soil improvers, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and medical devices; however, they may be used for other purposes outside the feed chain for farmed animals.
2.The health certificate referred to in point 1 must be presented to the competent authority at the border inspection post at the first point of entry of the goods into the Union, and thereafter a copy must accompany the consignment until its arrival at the plant of destination.U.K.
3.Following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, the fat derivatives shall be transported directly to the registered establishment or plant of destination.U.K.
Section 11 U.K. Imports of photogelatine
1.Gelatine which has been produced from material containing bovine vertebral column comprising of Category 1 material in accordance with Article 8(b) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and which is intended for the photographic industry (photogelatine) may be imported, provided the photogelatine:U.K.
originates from one of the plants of origin indicated in Table 3;
has been produced in accordance with point 6;
is imported through one of the border inspection posts of first entry into the Union indicated in Table 3; and
is destined for production in an approved photographic factory indicated in Table 3.
Table 3
Imports of photogelatine
| Third country of origin | Plants of origin | Member State of destination | Border inspection post of first entry into the Union | Approved photographic factories |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | Nitta Gelatin Inc., 2-22 Futamata Yao-City, Osaka 581-0024 Japan Jellie Co. Ltd. 7-1, Wakabayashi 2-Chome, Wakabayashi-ku, Sendai-City; Miyagi, 982 Japan NIPPI Inc. Gelatine Division 1 Yumizawa-Cho Fujinomiya City Shizuoka 418-0073 Japan | The Netherlands | Rotterdam | FujifilmEurope, Oudenstaart 1, 5047 TK Tilburg, The Netherlands |
| Nitta Gelatin Inc., 2-22 Futamata Yao-City, Osaka 581-0024 Japan | United Kingdom | Liverpool Felixstowe Heathrow | Kodak Ltd. Headstone Drive, Harrow, Middlesex, HA4 4TY, United Kingdom | |
| Czech Republic | Hamburg | FOMA Bohemia, spol. SRO Jana Krušinky 1604 501 04 Hradec Králove, Czech Republic | ||
| United States | Eastman Gelatine Corporation, 227 Washington Street, Peabody, MA, 01960 USA Gelita North America, 2445 Port Neal Industrial Road Sergeant Bluff, Iowa, 51054 USA | United Kingdom | Liverpool Felixstowe Heathrow | Kodak Ltd. Headstone Drive, Harrow, Middlesex, HA4 4TY, United Kingdom |
| Czech Republic | Hamburg | FOMA Bohemia spol. SRO Jana Krušinky 1604 501 04 Hradec Králove, Czech Republic |
2.Once the photogelatine has entered the Member State of destination, it shall not be traded between Member States but shall only be used in the approved photographic factory in the same Member State of destination and solely for photographic production purposes.U.K.
3.Following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, the photogelatine shall be transported directly to the approved photographic factory of destination.U.K.
4.The transport referred to in point 3 shall be carried out in vehicles or containers in which the photogelatine is physically separated from any products intended for food or feed.U.K.
5.In the approved photographic factory of destination, the operator shall ensure that any surpluses or residues of and other waste derived from the photogelatine are:U.K.
transported in sealed leak-proof containers labelled ‘for disposal only’ in vehicles under satisfactory hygiene conditions;
disposed of in accordance with Article 12(a)(i) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 or exported to the third country of origin in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1013/2006.
6.Photogelatine shall be produced according to the following requirements:U.K.
Photogelatine shall only be produced in plants which do not produce gelatine for food or feed intended for dispatch to the European Union, and which are approved by the competent authority of the third country concerned.
Photogelatine shall be produced by a process that ensures that raw material is treated by processing method 1 (pressure sterilisation) as referred to in Chapter III of Annex IV or subjected to a treatment with acid or alkali for a period of at least two days, washing with water, and:
following an acid treatment, treating with alkaline solution for a period of at least 20 days; or
following an acid treatment, treating with an acid solution for a period of 10 to 12 hours.
The pH must then be adjusted and the material purified by means of filtration and sterilisation at 138°C to 140°C for 4 seconds.
After having been subjected to the process referred to in point (b), the photogelatine may undergo a drying process and, where appropriate, a process of pulverisation or lamination.
The photogelatine shall be wrapped, packaged in new packages, stored and transported in sealed leak-proof, labelled containers in a vehicle under satisfactory hygiene conditions.
If leakage is observed, the vehicle and containers shall be thoroughly cleaned and inspected before reuse.
Wrapping and packages containing the photogelatine must carry the words ‘photogelatine for the photographic industry only’.
Section 12 U.K. Imports of horns and horn products, excluding horn meal, and hooves and hoof products, excluding hoof meal, intended for the production of organic fertilisers or soil improvers
Horns and horn products, excluding horn meal, and hooves and hoof products, excluding hoof meal, intended for the production of organic fertilizers or soil improvers, may be imported, provided that:
they have been produced in accordance with Chapter XII of Annex XIII; and
they are conveyed following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, directly to an approved or registered establishment or plant.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. SPECIAL RULES FOR CERTAIN SAMPLES
Section 1 U.K. Research and diagnostic samples
Unless they are kept for reference purposes or redispatched to the third country of origin, research and diagnostic samples and any products derived from the use of those samples shall be disposed of:
as waste by incineration;
by pressure sterilisation and subsequent disposal or use in accordance with Articles 12 to 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; or
in accordance with point 4(b) of Section 1 of Chapter I of Annex VI in case:
of quantities not exceeding 2 000 ml; and
provided the samples or derived products have been produced in and dispatched from third countries or parts of third countries, from which Member States authorise imports of fresh meat of domestic bovine animals, which are listed in Part I of Annex II to Regulation (EU) No 206/2010.
Section 2 U.K. Trade samples
1.The competent authority may authorise the import and transit of trade samples, provided that:U.K.
they originate from:
third countries referred to in the column ‘third countries’ list’ of row 14 of Table 2 of Section 1 of Chapter II of this Annex;
in the case of trade samples which consist of milk, milk-based products or milk-derived products, authorised third countries listed in Annex I to Regulation (EU) No 605/2010;
they are accompanied by a health certificate as referred to in Chapter 8 of Annex XV; and
following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, and in accordance with the conditions laid down in Article 8(4) of that Directive, they are transported directly to the approved or registered establishment or plant indicated in the authorisation of competent authority.
2.Unless the trade samples are kept for reference purposes, they shall be:U.K.
disposed of or used in accordance with Articles 12, 13 and 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; or
redispatched to the third country of origin.
3.If trade samples are used for testing of machinery, the testing shall be carried out:U.K.
with dedicated equipment; or
with equipment which is cleaned and disinfected before it is used for purposes other than the testing.
During transport to the approved or registered establishment or plant, the trade samples must be packaged in leak-proof containers.
Section 3 U.K. Display items
1.Import and transit of display items shall take place in accordance with the following conditions:U.K.
they originate from third countries referred to in the column ‘third countries’ list’ of row 14 of Table 2 of Section 1 of Chapter II;
their introduction has been authorised in advance by the competent authority of the Member State where the display item is intended to be used;
following the veterinary checks provided for in Directive 97/78/EC, display items must be sent directly to the authorised user.
2.Each consignment must be packed in packaging preventing any leakage and must be accompanied by a commercial document which specifies:U.K.
the description of the material and the animal species of origin;
the category of the material;
the quantity of the material;
the place of dispatch of the material;
the name and the address of the consignor;
the name and the address of the consignee; and
details allowing the identification of the authorisation of the competent authority of destination.
3.After the exhibition or after the artistic activity has been concluded, display items shall be:U.K.
redispatched to the third country of origin;
dispatched to another Member State or third country, if such dispatch has been authorised by the competent authority of the Member State or third country of destination in advance; or
disposed of in accordance with Articles 12, 13 and 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
CHAPTER IVU.K. SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR CERTAIN MOVEMENTS OF ANIMAL BY-PRODUCTS
Section 1 U.K. Imports of certain Category 1 materials
Materials referred to in Article 26 shall be imported under the following conditions:
The materials shall be imported with a label attached to the packaging, container or vehicle which indicates ‘Prohibited in food, feed, fertilisers, cosmetics, medicinal products and medical devices’.
The materials shall be directly delivered to an approved or registered establishment or plant for the manufacture of derived products, other than the products referred to in point 1.
Unused or surplus materials shall be used or disposed of in accordance with Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
Section 2 U.K. Imports of certain materials for purposes other than feeding to farmed land animals
1.The competent authority may authorise the import of the following materials for purposes other than feeding to farmed land animals, except for feeding to fur animals, provided there is no unacceptable risk for the transmission of diseases communicable to humans or animals:U.K.
animal by-products from aquatic animals and derived products from aquatic animals;
aquatic invertebrates and derived products from aquatic invertebrates;
terrestrial invertebrates, including any of their transformation forms, such as larvae, and derived products therefrom;
products generated by the animals referred to in points (a), (b) and (c), such as fish eggs;
Category 3 material comprising of animals and parts thereof of the zoological orders of Rodentia and Lagomorpha.
2.Imports of consignments of the materials referred to in point 1 shall take place in accordance with sanitary certification requirements in accordance with national rules.U.K.
ANNEX XVU.K. MODEL HEALTH CERTIFICATES
The model health certificates in this Annex shall apply to the importation from third countries and to the transit through the European Union of the animal by-products and the derived products referred to in the respective model health certificates.
Notes U.K.
(a)Veterinary certificates shall be produced by the exporting third country, based on the models set out in this Annex, according to the layout of the model that corresponds to the animal by-products or derived products concerned. They shall contain, in the numbered order that appears in the model, the attestations that are required for any third country and, as the case may be, those supplementary guarantees that are required for the exporting third country or part thereof.U.K.
(b)Where the model certificate states that certain statements shall be kept as appropriate, statements which are not relevant may be crossed out and initialled and stamped by the certifying officer, or completely deleted from the certificate.U.K.
(c)The original of each certificate shall consist of a single sheet of paper, both sides, or, where more text is required; it shall be in such a form that all sheets of paper needed are part of an integrated whole and indivisible.U.K.
(d)It shall be drawn up in at least one of the official languages of the EU Member State in which the inspection at the border post shall be carried out and of the EU Member State of destination. However, these Member States may allow other languages, accompanied, if necessary, by an official translation.U.K.
(e)If for reasons of identification of the items of the consignment, additional sheets of paper are attached to the certificate, these sheets of paper shall also be considered as forming part of the original of the certificate by the application of the signature and stamp of the certifying official veterinarian, in each of the sheets of paper.U.K.
(f)When the certificate, including additional schedules referred to in e), comprises more than one page, each page shall be numbered – (page number) of (total number of pages) – at the bottom of the page and shall bear the code number of the certificate that has been designated by the competent authority at the top of the page.U.K.
(g)The original of the certificate must be completed and signed by an official veterinarian. In doing so, the competent authorities of the exporting country shall ensure that the principles of certification equivalent to those laid down in Directive 96/93/EC are followed.U.K.
(h)The colour of the signature shall be different to that of the printing. The same rule applies to stamps other than those embossed or watermark.U.K.
(i)The original of the certificate must accompany the consignment at the EU border inspection post.U.K.
(j)If health certificates are used for consignments in transit, box No I.5 (‘Consignee’) of the relevant health certificate shall be completed with the name and address of the border inspection post through which the consignment is intended to leave the European Union.U.K.
CHAPTER 1U.K. Health certificate
For processed animal protein not intended for human consumption, including mixtures and products other than petfood containing such protein, for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 2(A)U.K. Health certificate
For milk, milk-based products and milk-derived products not intended for human consumption for dispatch to or transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 2(B)U.K. Health certificate
For colostrum and colostrum products from bovine animals not intended for human consumption for dispatch to or transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 3(A)U.K. Health certificate
For canned petfood intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 3(B)U.K. Health certificate
For processed petfood other than canned petfood, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 3(C)U.K. Health certificate
For dogchews intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 3(D)U.K. Health certificate
For raw petfood for direct sale or animal by-products to be fed to fur animals, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 3(E)U.K. Health certificate
For flavouring innards for use in the manufacture of petfood, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 3(F)U.K. Health certificate
For animal by-products (3) for the manufacture of petfood, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 4(A)U.K. Health certificate
For the import of blood and blood products from equidae to be used outside the feed chain, for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 4(B)U.K. Health certificate
For blood products not intended for human consumption that could be used as feed material, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 4(C)U.K. Health certificate
For untreated blood products, excluding of equidae, for the manufacture of derived products for purposes outside the feed chain for farmed animals, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 4(D)U.K. Health certificate
For treated blood products, excluding of equidae, for the manufacture of derived products for purposes outside the feed chain for farmed animals, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 5(A)U.K. Health certificate
For fresh or chilled hides and skins of ungulates, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 5(B)U.K. Health certificate
For treated hides and skins of ungulates, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 5(C)U.K. Official declaration
For treated hides and skins of ruminants and of equidae that are intended for dispatch to or for transit through (1) the European Union and have been kept separate for 21 days or will undergo transport for 21 uninterrupted days before importation
CHAPTER 6(A)U.K. Health certificate
For treated game trophies and other preparations of birds and ungulates, being solely bones, horns, hooves, claws, antlers, teeth, hides or skins, for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 6(B)U.K. Health certificate
For game trophies or other preparations of birds and ungulates consisting of entire parts not having been treated, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 7(A)U.K. Health certificate
For pig bristles from third countries or regions thereof that are free from African swine fever, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 7(B)U.K. Health certificate
For pig bristles from third countries or regions thereof that are not free from African swine fever, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 8U.K. Health certificate
For animal by-products to be used for purposes outside the feed chain or for trade samples (2), intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 9U.K. Health certificate
For fish oil not intended for human consumption to be used as feed material or for purposes outside the feed chain, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 10(A)U.K. Health certificate
For rendered fats not intended for human consumption to be used as feed material, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 10(B)U.K. Health certificate
For rendered fats not intended for human consumption to be used for certain purposes outside the feed chain, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 11U.K. Health certificate
For gelatine and collagen not intended for human consumption to be used as feed material or for purposes outside the feed chain, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 12U.K. Health certificate
For hydrolysed protein, dicalcium phosphate and tricalcium phosphate not intended for human consumption to be used as feed material or for uses outside the feed chain, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 13U.K. Health certificate
For apiculture by-products intended exclusively for use in apiculture, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 14(A)U.K. Health certificate
For fat derivatives not intended for human consumption to be used outside the feed chain, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 14(B)U.K. Health certificate
For fat derivatives not intended for human consumption to be used as feed or outside the feed chain, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 15U.K. Health certificate
For egg products not intended for human consumption that could be used as feed material, intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 16U.K. Model declaration
CHAPTER 17U.K. Health certificate
For processed manure, derived products from processed manure and guano from bats intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 18U.K. Health certificate
For horns and horn products, excluding horn meal, and hooves and hoof products, excluding hoof meal, intended for the production of organic fertilisers or soil improvers intended for dispatch to or for transit through (2) the European Union
CHAPTER 19U.K. Health certificate
For gelatine not intended for human consumption to be used by the photographic industry, intended for dispatch to the European Union
CHAPTER 20U.K. Model declaration
Declaration for the import from third countries and for the transit through the European Union of intermediate products to be used for the manufacture of medicinal products, veterinary medicinal products, medical devices, in vitro diagnostics and laboratory reagents
ANNEX XVIU.K. OFFICIAL CONTROLS
CHAPTER IU.K. OFFICIAL CONTROLS IN PROCESSING PLANTS
Section 1 U.K. Supervision of the production
1.The competent authority shall supervise processing plants to ensure compliance with the requirements of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with this Regulation.U.K.
It shall, in particular:
check:
the general conditions of hygiene of the premises, equipment and staff;
the efficacy of the own checks carried out by the operator of the processing plant, in accordance with Article 28 of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; such checks must include an examination of the results of those checks and if necessary, the taking of samples;
the effective implementation of the permanent written procedure based on the HACCP principles in accordance with Article 29(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009; such checks must include an examination of the results of this implementation and if necessary, the taking of samples;
the standards of the products after processing; the analyses and tests must be carried out in accordance with scientifically recognised methods, in particular, those laid down in Union legislation or, where no such methods are laid down in Union legislation, in accordance with recognised international standards or, in their absence, national standards; and
the storage conditions;
take any samples required for laboratory tests; and
make any other checks it considers necessary to ensure compliance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with this Regulation.
2.To allow it to carry out its responsibilities under point 1, the competent authority must have free access at all times to all parts of the processing plant and to records, commercial documents and health certificates.U.K.
Section 2 U.K. Validation procedures
1.Prior to issuing an approval for a processing plant, as provided for in Article 44(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the competent authority must check that a validation of the processing plant has been carried out by the operator in accordance with the following procedures and indicators:U.K.
a description of the process by a process flow diagram;
an identification of critical control points (CCPs) including the material process rate for continuous systems;
the compliance with the specific process requirements laid down by this Regulation; and
the achievement of the following requirements:
particle size for batch-pressure and continuous processes, defined by the mincer hole or the anvil gap size;
temperature, pressure, processing time and, in the case of continuous processing systems, the material processing rate, as specified in points 2 and 3.
2.In the case of a batch pressure system:U.K.
the temperature must be monitored with a permanent thermocouple and it must be plotted against real time;
the pressure stage must be monitored with a permanent pressure gauge; pressure must be plotted against real time;
the processing time must be shown by time/temperature and time/pressure diagrams.
At least once a year the thermocouple and the pressure gauge must be calibrated.
3.In the case of a continuous pressure system:U.K.
the temperature and the pressure must be monitored with thermocouples, or an infrared temperature gun, and pressure gauges must be used at defined positions throughout the process system in such a way that temperature and pressure comply with the required conditions inside the whole continuous system or in a section of it; the temperature and pressure must be plotted against real time;
measurement of the minimum transit time inside the whole relevant part of the continuous system where the temperature and pressure comply with the required conditions, must be provided to the competent authorities, using insoluble markers, such as manganese dioxide, or a method which offers equivalent guarantees.
Accurate measurement and control of the material process rate is essential and must be measured during the validation test in relation to a CCP that can be continuously monitored such as:
feed screw revolutions per minute (rev./min.);
the electric power (amps at given voltage);
the evaporation/condensation rate; or
the number of pump strokes per unit time.
All measuring and monitoring equipment must be calibrated at least once a year.
4.The competent authority must repeat the checks on the validation procedures when it considers it necessary, and in any case each time any significant alterations are made to the process, such as modifications of the machinery or changes of raw materials.U.K.
CHAPTER IIU.K. LISTS OF REGISTERED AND APPROVED ESTABLISHMENTS, PLANTS AND OPERATORS
1.Access to lists of registered and approved establishments, plants and operatorsU.K.
In order to assist Member States in making up-to-date lists of registered and approved establishments, plants and operators available to other Member States and to the public, the Commission shall provide a website which shall contain links to the national websites provided by each Member State, as referred to in point 2(a).
2.Format for national websitesU.K.
Each Member State shall provide the Commission with a linking address to a single national website containing the master list of all registered and approved establishments, plants and operators on its territory (‘master list’).
Each master list shall consist of one sheet and shall be completed in one or more official languages of the Union.
3.The layout, including the relevant information and codes, of master lists shall follow the technical specifications which are published by the Commission on its website.U.K.
CHAPTER IIIU.K. SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR OFFICIAL CONTROLS
Section 1 U.K. Official controls regarding marking of derived products
The competent authority shall carry out a performance check of the monitoring and recording system referred to in point 2 of Chapter V of Annex VIII to this Regulation to ascertain compliance with this Regulation and may, where necessary, request the testing of additional samples in accordance with the method referred to in the second paragraph of the same point.
Section 2 U.K. Official controls in low-capacity incineration plants
The competent authority shall inspect a low-capacity incineration plant for incineration of specified risk materials before approval, and at least once a year to monitor compliance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with this Regulation.
Section 3 U.K. Official controls in remote areas
In the case of disposal of animal by-products in remote areas in accordance with Article 19(1)(b) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, the competent authority shall monitor regularly the areas categorised as remote areas to ensure that those areas and the disposal operations are properly controlled.
Section 4 U.K. Official controls in registered farms for the feeding of fur animals
1.The competent authority shall take the necessary measures to control:U.K.
the appropriate composition, processing and use of the feed containing meat-and-bone meal or other products which have been processed in accordance with the processing methods set out in Chapter III of Annex IV and which are derived from the bodies or parts of bodies of animals of the same species;
that the animals are fed with the feed referred to in point (a), including:
strict supervision of the health status of those animals; and
appropriate TSE surveillance involving regular sampling and laboratory examination for TSEs.
2.The samples referred to in point 1(b)(ii) shall include samples taken from animals showing neurological symptoms and from older breeding animals.U.K.
Section 5 U.K. Official controls regarding collection centres
1.The competent authority shall:U.K.
include collection centres into the list drawn up in accordance with Article 47(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009;
assign an official number to each collection centre; and
update the list of collection centres and make it available together with the list drawn up in accordance with Article 47(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009.
2.The competent authority shall carry out official controls at collection centres in order to verify compliance with this Regulation.U.K.
Section 6 U.K. Official controls regarding the feeding of necrophagous birds with Category 1 material
The competent authority shall supervise the health status of the farmed animals in the region where the feeding of necrophagous birds with Category 1 material takes place, and shall carry out an appropriate TSE surveillance involving regular sampling and laboratory examination for TSEs.
Those samples shall include samples taken from animals showing neurological symptoms and from older breeding animals.
Section 7 U.K. Official controls regarding the application of certain organic fertilisers and soil improvers
The competent authority shall carry out controls along the entire chain of production and use of organic fertilisers and soil improvers subject to the restrictions referred to in Chapter II of Annex II.
Those controls shall include checks on the mixing with a component referred to in point 2 of Section 1 of Chapter II of Annex XI, and checks on the stocks of such products kept on farm and the records kept in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and with this Regulation.
Section 8 U.K. Official controls regarding approved photographic factories
The competent authority shall carry out documentary checks in approved photographic factories referred to in Table 3 of point 1 of Section 11 of Chapter II of Annex XIV on the channelling chain from the border inspection posts of first entry to the approved photographic factories for the purpose of reconciliation of the quantities of products imported, used and disposed of.
Section 9 U.K. Official controls regarding certain imported rendered fats
The competent authority shall carry out documentary checks in registered establishments or plants receiving rendered fats which have been imported in accordance with Section 9 of Chapter II of Annex XIV on the channelling chain from the border inspection posts of first entry to the registered establishment or plant for the purpose of reconciliation of the quantities of products imported, used and disposed of.
Section 10 U.K. Standard format for applications for certain authorisations in intra-Union trade
Operators shall submit applications for the authorisation of the dispatch of animal by-products referred to in Article 48(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 in accordance with the following format:
CEN TC/102 – Sterilisers for medical purposes – EN 285:2006 + A2:2009 – Sterilization - Steam Sterilisers - Large Sterilisers, reference published in OJ C 293, 2.12.2009, p. 39.
F0 is the calculated killing effect on bacterial spores. An F0 value of 3, 00 means that the coldest point in the product has been heated sufficiently to achieve the same killing effect as 121 °C (250 °F) in three minutes with instantaneous heating and chilling.
UHT = Ultra High Temperature treatment at 132 °C for at least one second.
HTST = High Temperature Short Time pasteurisation at 72 °C for at least 15 seconds or equivalent pasteurisation effect achieving a negative reaction to a phosphatase test.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
The Schedules you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources