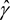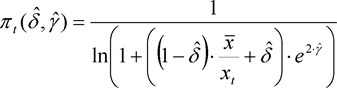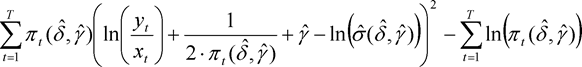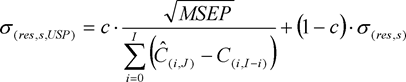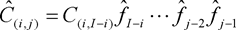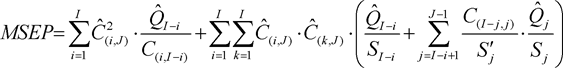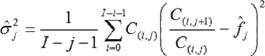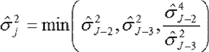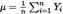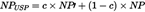- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/35Show full title
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/35 of 10 October 2014 supplementing Directive 2009/138/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the taking-up and pursuit of the business of Insurance and Reinsurance (Solvency II) (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Regulations originating from the EU
- 2015 No. 35
- Annexes only
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 30/07/202048.27 MB
- Revised 01/01/202048.00 MB
- Revised 08/07/201944.91 MB
- Revised 01/01/201946.16 MB
- Revised 15/09/201740.90 MB
- Revised 09/04/201746.19 MB
- Revised 02/04/201646.19 MB
- Revised 17/01/201539.54 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Status:
This is the original version as it was originally adopted in the EU.
This legislation may since have been updated - see the latest available (revised) version
ANNEX I LINES OF BUSINESS
A. Non-life insurance obligations
(1) Medical expense insurance
Medical expense insurance obligations where the underlying business is not pursued on a similar technical basis to that of life insurance, other than obligations included in the line of business 3.
(2) Income protection insurance
Income protection insurance obligations where the underlying business is not pursued on a similar technical basis to that of life insurance, other than obligations included in the line of business 3.
(3) Workers' compensation insurance
Health insurance obligations which relate to accidents at work, industrial injury and occupational diseases and where the underlying business is not pursued on a similar technical basis to that of life insurance.
(4) Motor vehicle liability insurance
Insurance obligations which cover all liabilities arising out of the use of motor vehicles operating on land (including carrier's liability).
(5) Other motor insurance
Insurance obligations which cover all damage to or loss of land vehicles (including railway rolling stock).
(6) Marine, aviation and transport insurance
Insurance obligations which cover all damage or loss to sea, lake, river and canal vessels, aircraft, and damage to or loss of goods in transit or baggage irrespective of the form of transport. Insurance obligations which cover liabilities arising out of the use of aircraft, ships, vessels or boats on the sea, lakes, rivers or canals (including carrier's liability).
(7) Fire and other damage to property insurance
Insurance obligations which cover all damage to or loss of property other than those included in the lines of business 5 and 6 due to fire, explosion, natural forces including storm, hail or frost, nuclear energy, land subsidence and any event such as theft.
(8) General liability insurance
Insurance obligations which cover all liabilities other than those in the lines of business 4 and 6.
(9) Credit and suretyship insurance
Insurance obligations which cover insolvency, export credit, instalment credit, mortgages, agricultural credit and direct and indirect suretyship.
(10) Legal expenses insurance
Insurance obligations which cover legal expenses and cost of litigation.
(11) Assistance
Insurance obligations which cover assistance for persons who get into difficulties while travelling, while away from home or while away from their habitual residence.
(12) Miscellaneous financial loss
Insurance obligations which cover employment risk, insufficiency of income, bad weather, loss of benefit, continuing general expenses, unforeseen trading expenses, loss of market value, loss of rent or revenue, indirect trading losses other than those mentioned above, other financial loss (non-trading) as well as any other risk of non-life insurance not covered by the lines of business 1 to 11.
B. Proportional non-life reinsurance obligations
The lines of business 13 to 24 shall include proportional reinsurance obligations which relate to the obligations included in lines of business 1 to 12 respectively.
C. Non-proportional non-life reinsurance obligations
(25) Non-proportional health reinsurance
Non-proportional reinsurance obligations relating to insurance obligations included in lines of business 1 to 3.
(26) Non-proportional casualty reinsurance
Non-proportional reinsurance obligations relating to insurance obligations included in lines of business 4 and 8.
(27) Non-proportional marine, aviation and transport reinsurance
Non-proportional reinsurance obligations relating to insurance obligations included in line of business 6.
(28) Non-proportional property reinsurance
Non-proportional reinsurance obligations relating to insurance obligations included in lines of business 5, 7 and 9 to 12.
D. Life insurance obligations
(29) Health insurance
Health insurance obligations where the underlying business is pursued on a similar technical basis to that of life insurance, other than those included in line of business 33.
(30) Insurance with profit participation
Insurance obligations with profit participation other than obligations included in line of business 33 and 34.
(31) Index-linked and unit-linked insurance
Insurance obligations with index-linked and unit-linked benefits other than those included in lines of business 33 and 34.
(32) Other life insurance
Other life insurance obligations other than obligations included in lines of business 29 to 31, 33 and 34.
(33) Annuities stemming from non-life insurance contracts and relating to health insurance obligations
(34) Annuities stemming from non-life insurance contracts and relating to insurance obligations other than health insurance obligations
E. Life reinsurance obligations
(35) Health reinsurance
Reinsurance obligations which relate to the obligations included in lines of business 29 and 33.
(36) Life reinsurance
Reinsurance obligations which relate to the obligations included in lines of business 30 to 32 and 34.
ANNEX II SEGMENTATION OF NON-LIFE INSURANCE AND REINSURANCE OBLIGATIONS AND STANDARD DEVIATIONS FOR THE NON-LIFE PREMIUM AND RESERVE RISK SUB-MODULE
| Segment | Lines of business, as set out in Annex I, that the segment consists of | Standard deviation for gross premium risk of the segment | Standard deviation for reserve risk of the segment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Motor vehicle liability insurance and proportional reinsurance | 4 and 16 | 10 % | 9 % |
| 2 | Other motor insurance and proportional reinsurance | 5 and 17 | 8 % | 8 % |
| 3 | Marine, aviation and transport insurance and proportional reinsurance | 6 and 18 | 15 % | 11 % |
| 4 | Fire and other damage to property insurance and proportional reinsurance | 7 and 19 | 8 % | 10 % |
| 5 | General liability insurance and proportional reinsurance | 8 and 20 | 14 % | 11 % |
| 6 | Credit and suretyship insurance and proportional reinsurance | 9 and 21 | 12 % | 19 % |
| 7 | Legal expenses insurance and proportional reinsurance | 10 and 22 | 7 % | 12 % |
| 8 | Assistance and its proportional reinsurance | 11 and 23 | 9 % | 20 % |
| 9 | Miscellaneous financial loss insurance and proportional reinsurance | 12 and 24 | 13 % | 20 % |
| 10 | Non-proportional casualty reinsurance | 26 | 17 % | 20 % |
| 11 | Non-proportional marine, aviation and transport reinsurance | 27 | 17 % | 20 % |
| 12 | Non-proportional property reinsurance | 28 | 17 % | 20 % |
ANNEX III FACTOR FOR GEOGRAPHICAL DIVERSIFICATION OF PREMIUM AND RESERVE RISK
1.For all segments set out in Annexes II and XIV, the factor for geographical diversification of a particular segment s referred to in Articles 116 and 147 shall be equal to the following:
where:
each of the sums cover all the geographical regions set out in paragraph 8;
V(prem,r,s) denotes the volume measure for premium risk of the segment s and the region r;
V(res,r,s) denotes volume measure for reserve risk of the segment s and the region r.
2.For all segments set out in Annexes II and XIV and all geographical regions set out in paragraph 8, the volume measure for premium risk of a particular segment s and a particular region r shall be calculated in the same way as the volume measure for non-life or NSLT health premium risk of the segment s as referred to in Articles 116 and 147, but taking into account only insurance and reinsurance obligations where the underlying risk is situated in the region r.
3.For all segments set out in Annexes II and XIV and all geographical regions set out in paragraph 8, the volume measure for reserve risk of a particular segment s and a particular region r shall be calculated in the same way as the volume measure for non-life or NSLT health reserve risk of the segment s as referred to in Articles 116 and 147, but taking into account only insurance and reinsurance obligations where the underlying risk is situated in the region r.
4.For the purpose of the calculations set out in paragraphs 2 and 3, the criteria set out in Article 13(13) of Directive 2009/138/EC in the case of non-life insurance and the criteria set out in Article 13(14) of Directive 2009/138/EC in the case of life insurance shall be applied as if references in those criteria to Member States extended to regions also.
5.Notwithstanding paragraph 1, the factor for geographical diversification shall be equal to 1 for segments 6, 10, 11 and 12 set out in Annex II and for segment 4 set out in Annex XIV.
6.Notwithstanding paragraph 1, the factor for geographical diversification for a segment set out in Annex II shall be equal to 1 if insurance and reinsurance undertakings use an undertaking-specific parameter for the standard deviation for non-life premium risk or non-life reserve risk of the segment to calculate the non-life premium and reserve risk sub-module.
7.Notwithstanding paragraph 1, the factor for geographical diversification for a segment set out in Annex XIV shall be equal to 1 if insurance and reinsurance undertakings use an undertaking-specific parameter for the standard deviation for NSLT health premium risk or NSLT health reserve risk of the segment to calculate the NSLT health premium and reserve risk sub-module.
8.Regions for the calculation of the factor for geographical diversification
ANNEX III Table 1: rows 1 - 19
ANNEX IV CORRELATION MATRIX FOR NON-LIFE PREMIUM AND RESERVE RISK
The correlation parameter CorrS(s,t) referred to in Article 117(1) shall be equal to the item set out in row s and in column t of the following correlation matrix. The headings of the rows and columns denote the numbers of the segments set out Annex II:
| t s | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 2 | 0,5 | 1 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 3 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 1 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,25 |
| 4 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| 5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 6 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 7 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 1 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 8 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 |
| 9 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 1 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,25 |
| 10 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 11 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 1 | 0,25 |
| 12 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1 |
ANNEX V
PARAMETERS FOR THE WINDSTORM RISK SUB-MODULE
Regions and windstorm risk factors
ANNEX V Table 1: rows 1 - 21
WINDSTORM RISK CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR REGIONS
ANNEX V Table 2: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX VI
PARAMETERS FOR THE EARTHQUAKE RISK SUB-MODULE
Regions and earthquake risk factors
ANNEX VI Table 1: rows 1 - 21
EARTHQUAKE RISK CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR REGIONS
ANNEX VI Table 2: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX VII
PARAMETERS FOR THE FLOOD RISK SUB-MODULE
Regions and flood risk factors
ANNEX VII Table 1: rows 1 - 15
FLOOD RISK CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR REGIONS
| AT | BE | CH | CZ | FR | DE | HU | IT | BG | PL | RO | SI | SK | UK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,50 | 0,00 |
| BE | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| CH | 0,25 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| CZ | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 0,00 |
| FR | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| DE | 0,75 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 |
| HU | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 |
| IT | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| BG | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| PL | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 |
| RO | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 |
| SI | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 |
| SK | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,00 |
| UK | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 |
ANNEX VIII
PARAMETETERS FOR THE HAIL RISK SUB-MODULE
Regions and hail risk factors
| a except Guadeloupe, Martinique, the Collectivity of Saint Martin and Réunion | ||
| Abbreviation of region r | Region r | Hail risk factor Q(hail,r) |
|---|---|---|
| AT | Republic of Austria | 0,08 % |
| BE | Kingdom of Belgium | 0,03 % |
| CH | Swiss Confederation; Principality of Lichtenstein | 0,06 % |
| FR | French Republica; Principality of Monaco; Principality of Andorra | 0,01 % |
| DE | Federal Republic of Germany | 0,02 % |
| IT | Italian Republic; Republic of San Marino; Vatican City State | 0,05 % |
| LU | Grand Duchy of Luxemburg | 0,03 % |
| NL | Kingdom of the Netherlands | 0,02 % |
| ES | Kingdom of Spain | 0,01 % |
HAIL RISK CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR REGIONS
| AT | BE | FR | DE | IT | LU | NL | CH | ES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| BE | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| FR | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| DE | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| IT | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| LU | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| NL | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| CH | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 |
| ES | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 |
ANNEX IX THE GEOGRAPHICAL DIVISION OF REGIONS SET OUT IN ANNEX V INTO RISK ZONES
The risk zones of regions set out in annex V as referred to in VIII-XIII shall be equal to the postal code areas or administrative units in the following tables.
Mappings of risk zones for regions with only one risk zone
The regions LU, MT, Guadeloupe, Martinique, St Martin and Reunion shall consist of only one zone.
Mappings of risk zones for the regions with only one risk zone which are part of another region
The regions Principality of Andorra, Principality of Lichtenstein, Principality of Monaco, Republic of San Marino and Vatican City State shall consist of only one zone each. The zones shall be mapped to the following regions:
| Principality of Andorra | zone 9 of the region FR |
| Principality of Lichtenstein | zone 19 of the region CH |
| Principality of Monaco | zone 06 of the region FR |
| Republic of San Marino | zone 47 of the region IT |
| Vatican City State | zone 00 of the region IT |
Mappings of risk zones for regions where the zonation is based on postal codes
For the purpose of this Annex, the following shall apply:
The mapping of risk zones for the regions AT, CZ, CH, DE, HE, IT, NL, NO, PL, ES, SK and SE shall be based on the first 2 digits of the postal code;
The mapping of risk zones for the regions BE and CY shall be based on the first digit of the postal code;
The mapping of risk zones for IE shall be based on the first 2 letters of the postal code;
The mapping of risk zones for UK shall be based on the first 2 letters of the postal code where the risk is located, with the exception of postal codes which have a digit in the second position. The risks in those postal codes postal codes which have a digit in the second position shall be mapped to zones identified by a 1-letter code.
ANNEX IX Table 2: rows 1 - 100
ANNEX IX Table 2: rows 101 - 125
Mapping of risk zones for regions where the zonation is based on administrative units — part 1
ANNEX IX Table 3: rows 1 - 42
Mappings of risk zones for regions where the zonation is based on administrative units — part 2
ANNEX IX Table 4: rows 1 - 27
Mapping of risk zones for the Republic of France
The mapping of risk zones for the region FR shall be based on the first 2 digits of the postal code.
ANNEX IX Table 5: rows 1 - 25
Mapping of risk zones for the Republic of Slovenia
The mappings for the region SI shall be based on the 4 digits of the postal code.
ANNEX IX Table 6: rows 1 - 48
Mapping of risk zones for the Kingdom of Denmark
The mapping of risk zones for the region DK shall be based on the first 2 digits of the postal code.
| Risk Zone | Region | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | |
| 2 | 69 | 74 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | |||
| 3 | 80 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | |
| 4 | 62 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 72 | ||||
| 5 | 60 | 61 | 63 | 64 | 70 | 71 | 73 | |||
| 6 | 50 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | |
| 7 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | ||||
| 8 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | ||||||
| 9 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | |||
| 10 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | |
| 11 | 37 | |||||||||
ANNEX X RISK WEIGHTS FOR CATASTROPHE RISK ZONES
Risk weights for windstorm risk
ANNEX X Table 1: rows 1 - 100
ANNEX X Table 1: rows 101 - 125
Risk weights for earthquake risk
ANNEX X Table 2: rows 1 - 96
Risk weights for flood risk
ANNEX X Table 3: rows 1 - 100
ANNEX X Table 3: rows 101 - 125
Risk weights for hail risk
ANNEX X Table 4: rows 1 - 96
Risk weights for subsidence risk
ANNEX X Table 5: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XI LIABILITY RISK GROUPS, RISK FACTORS AND CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR THE LIABILITY RISK SUB-MODULE
| i | Liability risk group i | Risk factor f(liability,i) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Professional malpractice liability insurance and proportional reinsurance obligations other than professional malpractice liability insurance and reinsurance for self-employed craftspersons or artisans | 100 % |
| 2 | Employers liability insurance and proportional reinsurance obligations | 160 % |
| 3 | Directors and officers liability insurance and proportional reinsurance obligations | 160 % |
| 4 | Liability insurance and reinsurance obligations included in lines of business 8 and 20 as set out in Annex I, other than obligations included in liability risk groups 1 to 3 and other than personal liability insurance and proportional reinsurance and other than professional malpractice liability insurance and reinsurance for self-employed craftspersons or artisans | 100 % |
| 5 | Non-proportional reinsurance of obligations relating to insurance obligations included in line of business 8 as set out in Annex I | 210 % |
For the purpose of the above table, the following definitions shall apply:
Professional malpractice liability insurance obligations mean liability insurance obligations included in line of business 8 as set out in Annex I which cover liabilities arising out of professional practice in relation to clients and patients;
Employers liability insurance obligations mean liability insurance obligations included in line of business 8 as set out in Annex I which cover liabilities of employers arising out of death, illness, accident, disability or infirmity of an employee in the course of the employment;
Directors and officers insurance obligations mean liability insurance obligations included in line of business 8 as set out in Annex I which cover liabilities of directors and officers of a company, arising out of the management of that company, or losses of the company itself to the extent it indemnifies its directors and officers in relation to such liabilities.
Personal liability insurance obligations mean liability insurance obligations included in line of business 8 as set out in Annex I which cover liabilities of natural persons in their capacity of private householders.
LIABILITY RISK CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS
| j i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,5 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0,25 | 0,5 |
| 3 | 0,5 | 0 | 1 | 0,25 | 0,5 |
| 4 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1 | 0,5 |
| 5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 1 |
ANNEX XII GROUPS OF OBLIGATIONS AND RISK FACTORS FOR THE SUB-MODULE FOR OTHER NON-LIFE CATASTROPHE RISK
| i | Group of insurance and reinsurance obligations i | Risk factor ci |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Insurance and reinsurance obligations included in lines of business 6 and 18 as set out in Annex I other than marine insurance and reinsurance and aviation insurance and reinsurance | 100 % |
| 2 | Reinsurance obligations included in line of business 27 as set out in Annex I other than marine reinsurance and aviation reinsurance | 250 % |
| 3 | Insurance and reinsurance obligations included in lines of business 12 and 24 as set out in Annex I, other than extended warranty insurance and reinsurance obligations provided that the portfolio of these obligations is highly diversified and these obligation do not cover the costs of product recalls | 40 % |
| 4 | Reinsurance obligations included in line of business 26 as set out in Annex I other than general liability reinsurance | 250 % |
| 5 | Non-proportional reinsurance obligations relating to insurance obligations included in lines of business 9 and 21 as set out in Annex I | 250 % |
For the purpose of group 3, ‘extended warranty insurance obligation’ means insurance obligations which cover the cost of repair or replacement in the event of a breakdown of a consumer good used by the individuals in a private capacity and which may also provide additional cover against eventualities such as accidental damage, loss or theft and assistance in setting up, maintaining and operating the good.
ANNEX XIII LIST OF REGIONS FOR WHICH NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK IS NOT CALCULATED BASED ON PREMIUMS
Member States of the European Union
Principality of Andorra
Republic of Iceland
Principality of Lichtenstein
Principality of Monaco
Kingdom of Norway
Republic of San Marino
Swiss Confederation
Vatican City State
ANNEX XIV SEGMENTATION OF NSLT HEALTH INSURANCE AND REINSURANCE OBLIGATIONS AND STANDARD DEVIATIONS FOR THE NSLT HEALTH PREMIUM AND RESERVE RISK SUB-MODULE
| Segment | Lines of business, as set out in Annex I that the segment consists of | Standard deviation for gross premium risk of the segment | Standard deviation for reserve risk of the segment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Medical expense insurance and proportional reinsurance | 1 and 13 | 5 % | 5 % |
| 2 | Income protection insurance and proportional reinsurance | 2 and 14 | 8.5 % | 14 % |
| 3 | Workers' compensation insurance and proportional reinsurance | 3 and 15 | 8 % | 11 % |
| 4 | Non-proportional health reinsurance | 25 | 17 % | 20 % |
ANNEX XV CORRELATION MATRIX FOR NSLT HEALTH PREMIUM AND RESERVE RISK
The correlation parameter CorrHS(s,t) referred to in Article 148(1) shall be equal to the item set out in row s and in column t of the following correlation matrix. The headings of the rows and columns denote the numbers of the segments set out Annex XIV:
| t s | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| 2 | 0,5 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| 3 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 1 | 0,5 |
| 4 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 1 |
ANNEX XVI HEALTH CATASTROPHE RISK SUB-MODULE OF THE SOLVENCY CAPITAL REQUIREMENT STANDARD FORMULA
GEOGRAPHICAL SEGMENTATION AND RISK FACTORS FOR THE MASS ACCIDENT RISK SUB-MODULE
ANNEX XVI Table 1: rows 1 - 32
DEFINITION OF EVENTS AND RISK FACTORS FOR THE MASS ACCIDENT RISK SUB-MODULE AND ACCIDENT CONCENTRATION RISK SUB-MODULE
| Event type e | xe — Ratio of persons which will be affected by event type e as the result of the accident |
|---|---|
| Death caused by an accident | 10 % |
| Permanent disability caused by an accident | 1,5 % |
| Disability that lasts 10 years caused by an accident | 5 % |
| Disability that lasts 12 months caused by an accident | 13,5 % |
| Medical treatment caused by an accident | 30 % |
DEFINITION OF HEALTHCARE UTILISATION AND RISK FACTORS FOR THE PANDEMIC RISK SUB-MODULE
| Healthcare utilisation type h | Hh — Ratio of persons with clinical symptoms which will utilise healthcare of type h |
|---|---|
| Hospitalisation | 1 % |
| Consultation with a medical practitioner | 20 % |
| No formal medical care sought | 79 % |
ANNEX XVII METHOD-SPECIFIC DATA REQUIREMENTS AND METHOD SPECIFICATIONS FOR UNDERTAKING-SPECIFIC PARAMETERS OF THE STANDARD FORMULA
A. Definitions and notations
(1)For the purpose of this Annex, the following definitions shall apply:
‘accident year’ means, with respect to a payment for an insurance or reinsurance claim, the year in which the insured event that gave rise to that claim took place;
‘development year’ means, with respect to a payment for an insurance or reinsurance claim, the difference between the year of that payment and the accident year of that payment.
‘reporting year’ means, with respect to a payment for an insurance or reinsurance claim, the year in which the insured event that gave rise to that claim was notified to the insurance or reinsurance undertaking;
‘financial year’ means, with respect to a payment for an insurance or reinsurance claim, the year in which this payment took place.
(2)For the purpose of this annex, ‘segment s’ denotes the segment for which the undertaking-specific parameter is determined, being one of the segments set out in Annex II or one of the segments set out in Annex XIV.
B. Premium risk method
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific standard deviation of segment s shall consist of the following:
the payments made and the best estimates of the provision for claims outstanding in segment s after the first development year of the accident year of those claims (aggregated losses);
the premiums earned in segment s;
Those aggregated losses and earned premiums shall be available separately for each accident year of the insurance and reinsurance claims in segment s.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the premium risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months;
data are available for at least five consecutive accident years;
where the premium risk method is applied to replace the standard parameters referred to in Article 218(1)(a)(i) and (c)(i), the aggregated losses and earned premiums are not adjusted for recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles or reinsurance premiums;
where the premium risk method is applied to replace the standard parameters referred to in Article 218(1)(a)(ii) and (c)(ii):
the aggregated losses are adjusted for amounts recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles which are consistent with the reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles that are in place to provide cover for the following twelve months;
the earned premiums are adjusted for reinsurance premiums which are consistent with the reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles that are in place to provide cover for the following twelve months;
the aggregated losses are adjusted for catastrophe claims to the extent that the risk of those claims is reflected in the non-life or health catastrophe risk sub-modules;
the aggregated losses include the expenses incurred in servicing the insurance and reinsurance obligations;
the data fit the following assumptions:
expected aggregated losses in a particular segment and accident year are linear proportional in premiums earned in a particular accident year;
the variance of aggregated losses in a particular segment and accident year is quadratic in premiums earned in a particular accident year;
aggregated losses follow a lognormal distribution;
maximum likelihood estimation is appropriate.
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4-6, the following notation shall apply:
accident years are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 1 for the first accident year for which data are available;
T denotes the latest accident year for which data are available;
for all accident years, the aggregated losses in segment s in a particular accident year t are denoted by yt ;
for all accident years, the premiums earned in segment s in a particular accident year t are denoted by xt .
(4)The undertaking-specific standard deviation of segment s shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
σ(prem,s) denotes the standard parameter that should be replaced by the undertaking-specific parameter.
(5)The standard deviation function shall be equal to the following function of two variables:
where:
(6)The mixing parameter and the logarithmic variation coefficient shall be the values  and
and  respectively for which the following amount becomes minimal:
respectively for which the following amount becomes minimal:
where:
For the determination of the minimal amount, no values for the mixing parameter less than zero or exceeding 1 shall be considered.
C. Reserve risk method 1
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific standard deviation for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s shall consist of the following:
the sum of the best estimate provision at the end of the financial year for claims that were outstanding in segment s at the beginning of the financial year and the payments made during the financial year for claims that were outstanding in segment s at the beginning of the financial year;
the best estimate of the provision for claims outstanding in segment s at the beginning of the financial year.
The amounts referred to in points (a) and (b) shall be available separately for different financial years.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the reserve risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months
data are available for at least five consecutive financial years;
the data are adjusted for amounts recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles which are consistent with the reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles that are in place to provide cover for the following twelve months;
the data include the expenses incurred in servicing the insurance and reinsurance obligations.
the data fit the following assumptions:
the amount referred to paragraph 1(a) in that particular segment and financial year is linear proportional in the best estimate of the provision for claims outstanding in that particular segment and financial year;
the variance of the amount referred to paragraph 1(a) in a particular segment and financial year is quadratic in the provision for claims outstanding in a particular segment and financial year;
the amount referred to paragraph 1(a) follows a lognormal distribution;
maximum likelihood estimation is appropriate.
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4-6, the following notation shall apply:
the financial years are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 1 for the first financial year for which data are available;
T denotes the latest financial year for which data are available;
for all financial years, the amount referred to paragraph 1(a) in segment s in a particular financial year t is denoted by yt ;
for all financial years, the best estimate of the provision for claims outstanding in segment s in a particular financial year t are denoted by xt .
(4)The undertaking-specific standard deviation for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
σ(prem,s) denotes the standard parameter that should be replaced by the undertaking-specific parameter.
(5)The standard deviation function shall be equal to the following function of two variables:
where:
(6)The mixing parameter and the logarithmic variation coefficient shall be the values 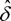 and
and  respectively for which the following amount becomes minimal:
respectively for which the following amount becomes minimal:
where:
For the determination of the minimal amount, no values for the mixing parameter less than zero or exceeding 1 shall be considered.
D. Reserve risk method 2
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific standard deviation for deviation for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s shall consist of cumulative payment amounts for insurance or reinsurance claims in segment s (cumulative claims amounts), separately for each accident year and development year of the payments.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the reserve risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months;
data are available for at least five consecutive accident years;
in the first accident year, data are available for at least five consecutive development years;
in the first accident year the cumulative payment amount of the last development year for which data are available includes all the payments of the accident year except an immaterial amount;
the number of consecutive accident years for which data are available is not less than the number of consecutive development years in the first accident year for which data are available;
the cumulative claims amounts are adjusted for amounts recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles which are consistent with the reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles that are in place to provide cover for the following twelve months;
the cumulative claims amounts shall include the expenses incurred in servicing the insurance or reinsurance obligations;
the data are consistent with the following assumptions about the stochastic nature of cumulative claims amounts:
cumulative claims amounts for different accident years are mutually stochastically independent;
for all accident years the implied incremental claim amounts are stochastically independent;
for all accident years the expected value of the cumulative claims amount for a development year is proportional to the cumulative claims amount for the preceding development year;
for all accident years the variance of the cumulative claims amount for a development year is proportional to the cumulative claims amount for the preceding development year.
For the purposes of point (d), a payment amount shall be considered to be material where ignoring it in the calculation of the undertaking-specific parameter could influence the decision-making or the judgement of the users of that information, including the supervisory authorities
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4 and 5, the following notation shall apply:
the accident years are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 0 for the first accident year for which data are available;
I denotes the latest accident year for which data are available;
J denotes the latest development year in the first accident year for which data are available;
C(i,j) denotes the cumulative claims for accident year i and development year j.
(4)The undertaking-specific standard deviation for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
MSEP denotes the mean squared error of prediction as specified in paragraph 5;
for all accident years and development years, 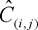
where for all development years 
σ(res,s) denotes the standard parameter for non-life reserve risk or NSLT health reserve risk of segment s.
(5)The mean squared error of prediction shall be equal to the following:
where:
E. Revision risk method
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific increase in the amount of annuity benefits shall consist of annual amounts of annuity benefits of annuity insurance obligations where the benefits payable could increase as a result of changes in the legal environment or in the state of health of the person insured (annuity benefits), separately for consecutive financial years and each beneficiary.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the revision risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months;
data are available for at least five consecutive financial years;
the annuity benefits are gross, without deduction of the amounts recoverable from reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles;
the annuity benefits shall include the expenses incurred in servicing the annuity obligations;
the data are consistent with the following assumptions about the stochastic nature of increases in the amount of annuity benefits:
the annual number of annuity increases follows a negative binomial distribution, including in the tail of the distribution;
the amount of an annuity increase follows a lognormal distribution, including in the tail of the distribution;
the annual number of annuity increases and the amounts of the annuity increase are mutually stochastically independent.
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4-8, the following notation shall apply:
the financial years are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 1 for the first financial year for which data are available;
T denotes the latest financial year for which data are available;
A(i,t) denotes the annuity benefits of beneficiary i in financial year t;
(4)The undertaking-specific increase in the amount of annuity benefits shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
VaR 0,995(R) denotes the 99,5 % quantile of the distribution of annuity increases set out in paragraph 6;
S is equal to 3 % where the calculation is done for the purpose of the revision risk sub-module set out in Article 141 and equal to 4 % where the calculation is done for the purpose of the health revision risk sub-module set out in Article 158.
(5)The expected value of annuity increases shall be equal to the following:
where:
(6)The annuity increases shall be equal to the following:
where:
N denotes the annual number of annuity increases and follows a negative binominal distribution with an expected value that is equal to the estimated number of changes in annuity benefits set out in point (b) of paragraph 5 and with a standard deviation that is equal to the estimated standard deviation of the number of changes in annuity benefits set out in paragraph 7;
Xk denotes the amount of an annuity increase and follows a lognormal distribution with an expected value that is equal to the estimated average change in annuity benefits set out in point (a) of paragraph 5 and with a standard deviation that is equal to the estimated standard deviation of changes in annuity benefits set out in paragraph 8;
the annual number of annuity increases and the amounts of the annuity increase are mutually stochastically independent.
(7)The estimated standard deviation of the number of changes in annuity benefits shall be equal to the following:
where:
(8)The estimated standard deviation of changes in annuity benefits shall be equal to the following:
where:
F. Non-proportional reinsurance method
Input data and method-specific data requirements
(1)The data for estimating the undertaking-specific adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance shall consist of the ultimate claim amounts of insurance and reinsurance claims that were reported to the insurance or reinsurance undertaking in segment s during the last financial years, separately for each insurance and reinsurance claim.
(2)The following method-specific data requirements shall apply:
the data are representative for the premium risk that the insurance or reinsurance undertaking is exposed to during the following twelve months;
the data do not indicate a higher premium risk than reflected in the standard deviation for premium risk used to calculate the Solvency Capital Requirement;
the ultimate claim amounts are estimated in the year the insurance and reinsurance claims were reported;
data are available for at least five reporting years;
where the recognisable excess of loss reinsurance contract applies to gross claims, the ultimate claim amounts are gross;
where the recognisable excess of loss reinsurance contract applies to claims after deduction of the recoverables from certain other reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles, the amounts receivable from those certain other reinsurance contracts and special purpose vehicles are deducted from the ultimate claim amounts;
the ultimate claim amounts shall not include expenses incurred in servicing the insurance and reinsurance obligations;
the data are consistent with the assumption that ultimate claim amounts follow a lognormal distribution, including in the tail of the distribution.
Method specification
(3)For the purpose of paragraphs 4-7, the following notation shall apply:
insurance and reinsurance claims for which data are available are denoted by consecutive numbers starting with 1;
n denotes the number of insurance and reinsurance claim for which data are available;
Yi denotes the ultimate claim amount of insurance or reinsurance claim i;
μ and ω denote the first and second moment, respectively, of the claim amount distribution, being equal to the following amounts:
b 1 denotes the amount of the retention of the recognisable excess of loss reinsurance contract referred to in Article 218(2);
where the recognisable excess of loss reinsurance contract referred to in Article 196(1) provides compensation only up to a specified limit, b 2 denotes the amount of that limit.
(4)The undertaking-specific specific adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance shall be equal to the following:
where:
c denotes the credibility factor set out in section G;
NP′ denotes the estimated adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance set out in paragraph 5;
NP denotes the adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance set out in Article 117(2).
(5)The estimated adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance shall be equal to the following:
where the parameters μ 2, ω 1 and ω 2 are set out in paragraph 6.
(6)The parameters, μ 2, ω 1 and ω 2 shall be equal to the following:
where:
(7)Notwithstanding paragraph 5, where non-proportional reinsurance covers homogeneous risk-groups within a segment, the estimated adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance shall be equal to the following:
where:
V(prem,h) denotes the volume measure for premium risk of the homogeneous risk group h determined in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 116;
NP′(h) denotes the estimated adjustment factor for non-proportional reinsurance of homogeneous risk group h determined in accordance with paragraph 5.
G. Credibility factor
(1)The credibility factor for segments 1, 5 and 6 set out in Annex II shall be equal to the following:
| Time lengths in years | Credibility factor c |
|---|---|
| 5 | 34 % |
| 6 | 43 % |
| 7 | 51 % |
| 8 | 59 % |
| 9 | 67 % |
| 10 | 74 % |
| 11 | 81 % |
| 12 | 87 % |
| 13 | 92 % |
| 14 | 96 % |
| 15 and larger | 100 % |
(2)The credibility factor for segments 2 to 4 and 7 to 12 set out in Annex II, for the segments set out Annex XIV and for the revision risk method shall be equal to the following:
| Time lengths in years | Credibility factor c |
|---|---|
| 5 | 34 % |
| 6 | 51 % |
| 7 | 67 % |
| 8 | 81 % |
| 9 | 92 % |
| 10 and larger | 100 % |
(3)The time length shall be equal to the following:
for the premium risk method, the number of accident years for which data are available;
for reserve risk method 1, the number of financial years for which data are available;
for reserve risk method 2, the number of accident years for which data are available;
for the revision risk method, the number of financial years for which data are available;
for the non-proportional reinsurance method, the number of reporting years for which data are available.
ANNEX XVIII INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES FOR PARTIAL INTERNAL MODELS
A. General provisions
(1)For the purposes of this Annex, the following definitions shall apply:
‘unit of the partial internal model’ is a component of the partial internal model that is separately calculated and not aggregated within the partial internal model;
(2)Where insurance and reinsurance undertakings apply integration techniques 1 to 5, their Solvency Capital Requirement shall be the sum of the following items:
the Basic Solvency Capital Requirements as laid down in sections C to F;
the capital requirement for operational risk as laid down in Article 107 of Directive 2009/138/EC, where that capital requirement is not within the scope of the partial internal model, and calculated with the partial internal model, where that capital requirement is within the scope of the partial internal model;
the adjustment for the loss-absorbing capacity of technical provisions and deferred taxes, as laid down in paragraph 3, where that adjustment is not within the scope of the partial internal model, and calculated with the partial internal model where that adjustment is within the scope of the partial internal model.
(3)Where the adjustment for the loss-absorbing capacity of technical provisions and deferred taxes is not within the scope of the partial internal model, it shall be calculated as laid down in Articles 205 to 207, but with the following changes:
the Basic Solvency Capital Requirement referred to in Articles 206(1) and (2) and 207(1) is calculated in accordance with sections B to F;
points (a) to (d) of Article 206(2) apply only to calculations with the standard formula;
for the purposes of Article 206(2) the capital requirements used in the calculation of the Basic Solvency Capital Requirement that are calculated with the partial internal take into account the risk-mitigating effect provided by future discretionary benefits of insurance contracts;
the capital requirement for operational risk referred to in Article 207(1)(c) is calculated in accordance with paragraph 2(b).
B. Integration technique 1
The Basic Solvency Capital Requirement shall be equal to the sum of the capital requirements for the units of the partial internal model, the capital requirement derived by applying the standard formula for the Basic Solvency Capital Requirement only to the risks that are out of the scope of the partial internal model and the capital requirement for intangible asset risk as set out in Article 203.
C. Integration technique 2
(1)The Basic Solvency Capital Requirement shall be equal to the following:
where:
the sum covers all possible combinations (i,j) of the aggregation list set out in paragraph 2;
Corr(i,j) denotes the correlation parameter, for items i and j of the aggregation list;
SCRi and SCRj denote the capital requirements for the items i and j of the aggregation list respectively;
SCRint denotes the capital requirement for intangible asset risk as set out in Article 203.
(2)The items on the aggregation list shall meet the following requirements:
they shall cover each of the units of the partial internal model;
none of the following sub-modules of the standard formula shall be within the scope of the partial internal model:
the sub-modules of the non-life underwriting risk module set out in Article 114(1);
the sub-modules of the life underwriting risk module set out in Article 105(3) of Directive 2009/138/EC;
the sub-modules of the health underwriting risk module set out in Article 151(1);
the sub-modules of the market risk module set out in Article 105(5) of Directive 2009/138/EC;
the counterparty default risk module of the standard formula shall not be within the scope of the partial internal model.
However, where none of the sub-modules of a module of the standard formula are within the scope of the partial internal module, the aggregation list shall include that module instead of its sub-modules.
(3)The correlation parameters referred to in point (b) of paragraph 1 shall comply with the following requirements:
for all items i and j from the aggregation list the correlation parameter Corr(i,j) shall not be less than – 1 and shall not exceed 1;
for all items i and j from the aggregation list the correlation parameters Corr(i,j) and Corr(j,i) shall be equal;
for all items i from the aggregation list the correlation parameter Corr(i,i) shall be equal to 1;
for any assignment of real numbers to the items of the aggregation list the following shall hold:
where:
the sum covers all possible combinations (i,j) of the aggregation list;
xi and xj are the numbers assigned to the items i and j, respectively, of the aggregation list;
where the items i and j from the aggregation list are modules of the standard formula, the correlation parameter Corr(i,j) shall be equal to the correlation parameter of the standard formula that is used to aggregate those two modules;
where the items i and j from the aggregation list are sub-modules of the same module of the standard formula, then the correlation parameter Corr(i,j) shall be equal to the correlation parameter of the standard formula that is used to aggregate those two sub-modules;
for all items i and j from the aggregation list the correlation parameter Corr(i,j) shall not be less than Corrmin (i,j) and shall not exceed Corrmax (i,j) , where Corrmin (i,j) and Corrmax (i,j) are appropriate lower and upper bounds selected by the undertaking.
Insurance and reinsurance undertakings shall choose the correlation parameters referred to in point (b) of paragraph 1 in such a way that no other set of correlation parameters that meets the requirements set out in points (a) to (g) results in a higher Solvency Capital Requirement, calculated in accordance with paragraph 1.
D. Integration technique 3
(1)The Basic Solvency Capital Requirement shall be equal to the following:
where:
SS denotes the capital requirement derived by applying the standard formula for the Basic Solvency Capital Requirement only to the risks not covered by the partial internal model;
ω 1 denotes the first implied correlation parameter as set out in paragraph 2;
Pc denotes the capital requirement reflecting the risks that are both within the scope of the standard formula and the partial internal model, calculated with the partial internal model;
ω 2 denotes the second implied correlation parameter as set out in paragraph 3;
Ps is the capital requirement reflecting the risks within the scope of the partial internal model but not within the scope of the standard formula, calculated with the partial internal model;
P denotes the capital requirement reflecting the risks that are within the scope of the partial internal model, calculated with the partial internal model.
SCRint denotes the capital requirement for intangible asset risk as set out in Article 203.
(2)The first implied correlation parameter shall be equal to the following:
where:
S denotes the capital requirement calculated in the same way as the Basic Solvency Capital Requirement by means of the standard formula, but where capital requirements for modules or sub-modules are replaced by capital requirements for those modules or sub-modules that are calculated with the partial internal model where possible;
SC denotes the capital requirement derived by applying the standard formula for the Basic Solvency Capital Requirement only to the risks that are within the scope of the standard formula and the partial internal model, but where the capital requirements for the modules and sub-modules are replaced by capital requirements for those modules or sub-modules that are calculated with the partial internal model;
SS is defined as in paragraph 1(a);
d 1 is equal to 1 where SS or SC are zero and equal to zero where SS and SC are different from zero.
(3)The second implied correlation parameter shall be equal to the following:
where ω 1 is as defined in paragraph 2 and ω 3 is the third implied correlation parameter as set out in paragraph 4.
(4)The third implied correlation parameter shall be equal to the following:
where:
P, Ps and Pc are as defined in paragraph 1;
d 2 is equal to 1 where Ps or Pc are zero and equal to zero where Ps and Pc are different from zero.
E. Integration technique 4
(1)The Basic Solvency Capital Requirement shall be equal to the following:
where:
P denotes the capital requirement reflecting the risks that are within the scope of the partial internal model, calculated with the partial internal model;
SS denotes the capital requirement derived by applying the standard formula for the Basic Solvency Capital Requirement only to the risks not covered by the partial internal model;
k denotes the number of modules of the standard formula that are within the scope of the partial internal model;
n denotes the number of modules of the standard formula;
l denotes the number of modules of the standard formula for each of which the capital requirement can be calculated with the partial internal model;
Corr(i,j) denotes the correlation parameter of the standard formula for the aggregation of modules i and j;
Pi denotes the capital requirement for the module i of the standard formula, calculated with the partial internal model;
Si and Sj denote the capital requirement for modules i and j of the standard formula respectively which are calculated in the following way:
the module is calculated with the standard formula provided that the module does not consists of sub-modules;
the module is calculated in accordance with paragraph 2 provided that the module consist of sub-modules.
SCRint denotes the capital requirement for intangible asset risk as set out in Article 203.
(2)For all modules of the standard formula referred to in paragraph 1(h)(ii), the capital requirement of a particular module shall be calculated with the formula set out in paragraph 1, applying the following denominations:
P denotes the capital requirement reflecting the risks of the sub-modules of that particular module which are within the scope of the partial internal model, calculated with the partial internal model;
SS denotes the capital requirement derived by applying that particular module only to the risks not covered by the partial internal model;
k denotes the number of sub-modules of that particular module that are within the scope of the partial internal model;
n denotes the number of sub-modules of that particular module;
l denotes the number of sub-modules of that particular module for each of which the capital requirement can be calculated with the partial internal model;
Corr(i,j) denotes the correlation parameter of the standard formula for the aggregation of sub-modules i and j of that particular module;
Pi denotes the capital requirement for the sub-module i of that particular module, calculated with the partial internal model;
Si and Sj denote the capital requirement for sub-modules i and j of that particular module respectively which are calculated in the following way:
the sub-module is calculated with the standard formula provided that the sub-module does not consists of other sub-modules;
the sub-module is calculated in accordance with paragraph 3 provided that the sub-module consist of other sub-modules.
SCRint shall be set to zero.
(3)For all sub-modules of the standard formula referred to in paragraph 2(h)(ii), the capital requirement of a particular sub-module shall be calculated with the formula set out in paragraph 1, applying the following denominations:
P denotes the capital requirement reflecting the risks of the sub-modules of that particular sub-module which are within the scope of the partial internal model, calculated with the partial internal model;
SS denotes the capital requirement derived by applying that particular sub-module only to the risks not covered by the partial internal model;
k denotes the number of sub-modules of that particular sub-module that are within the scope of the partial internal model;
n denotes the number of sub-modules of that particular sub-module;
l denotes the number of sub-modules of that particular sub-module for each of which the a capital requirement can be calculated with the partial internal model;
Corr(i,j) denotes the correlation parameter of the standard formula for the aggregation of sub-modules i and j of that particular sub-module;
Pi denotes the capital requirement for the sub-module i of that particular sub-module, calculated with the partial internal model;
Si and Sj denote the capital requirement for sub-modules i and j of that particular sub-module respectively which are calculated in the following way:
the sub-module is calculated with the standard formula provided that the sub-module does not consists of other sub-modules;
the sub-module is calculated in accordance with this paragraph provided that the sub-module consist of other sub-modules.
SCRint shall be set to zero.
F. Integration technique 5
(1)The Basic Solvency Capital Requirement shall be equal to the following:
where:
P, SS , k, n, Corr(i,j) and SCRint are defined as in paragraph 1 of section E;
Si and Sj denote the capital requirement for modules i and j respectively of the standard formula which are calculated in the following way:
the module is calculated with the standard formula provided that the module does not consists of sub-modules;
the module is calculated in accordance with paragraph 2 provided that the module consist of sub-modules.
(2)For all modules of the standard formula referred to in paragraph 1(b)(ii), the capital requirement of a particular module shall be calculated with the formula set out in paragraph 1, applying the following denominations:
P, SS , k, n, Corr(i,j) and SCRint are defined as in paragraph 2 of section E;
Si and Sj denote the capital requirement for sub-modules i and j of that particular module respectively which are calculated in the following way:
the sub-module is calculated with the standard formula provided that the sub-module does not consists of other sub-modules;
the sub-module is calculated in accordance with paragraph 3 provided that the sub-module consist of other sub-modules.
(3)For all modules of the standard formula referred to in paragraph 2(b)(ii), the capital requirement of a particular module shall be calculated with the formula set out in paragraph 1, applying the following denominations:
P, SS , k, n, Corr(i,j) and SCRint are defined as in paragraph 3 of section E;
Si and Sj denote the capital requirement for sub-modules i and j of that particular module respectively which are calculated in the following way:
the sub-module is calculated with the standard formula provided that the sub-module does not consists of other sub-modules;
the sub-module is calculated in accordance with this paragraph provided that the sub-module consist of other sub-modules.
ANNEX XIX MCR RISK FACTORS FOR NON-LIFE AND HEALTH INSURANCE OR REINSURANCE OBLIGATIONS
ANNEX XIX Table 1: rows 1 - 17
ANNEX XX STRUCTURE OF THE SOLVENCY AND FINANCIAL CONDITION REPORT AND REGULAR SUPERVISORY REPORT
Summary
A. Business and Performance
A.1Business
A.2Underwriting Performance
A.3Investment Performance
A.4Performance of other activities
A.5Any other information
B. System of Governance
B.1General information on the system of governance
B.2Fit and proper requirements
B.3Risk management system including the own risk and solvency assessment
B.4Internal control system
B.5Internal audit function
B.6Actuarial function
B.7Outsourcing
B.8Any other information
C. Risk Profile
C.1Underwriting risk
C.2Market risk
C.3Credit risk
C.4Liquidity risk
C.5Operational risk
C.6Other material risks
C.7Any other information
D. Valuation for Solvency Purposes
D.1Assets
D.2Technical provisions
D.3Other liabilities
D.4Alternative methods for valuation
D.5Any other information
E. Capital Management
E.1Own funds
E.2Solvency Capital Requirement and Minimum Capital Requirement
E.3Use of the duration-based equity risk sub-module in the calculation of the Solvency Capital Requirement
E.4Differences between the standard formula and any internal model used
E.5Non-compliance with the Minimum Capital Requirement and non-compliance with the Solvency Capital Requirement
E.6Any other information
ANNEX XXI AGGREGATE STATISTICAL DATA
A. Data on supervised undertakings and groups
Data with regard to insurance and reinsurance undertakings supervised under Directive 2009/138/EC
(1)The number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings, the number of branches as referred to in Article 13(11) of Directive 2009/138/EC and the number of branches as referred to in Article 162(3) of Directive 2009/138/EC established in the Member State of the supervisory authority;
(2)The number of branches of insurance and reinsurance undertakings established in the Member State of the supervisory authority carrying out relevant business in one or more other Member States;
(3)The number of insurance undertakings established in the Member State of the supervisory authority pursuing business in other Member States under the freedom to provide services;
(4)The number of insurance undertakings established in other Member States which have notified their intention to pursue business in the Member State of the supervisory authority under the freedom to provide services and those which actually pursue business;
(5)The number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings falling outside the scope of Directive 2009/138/EC;
(6)The number of special purpose vehicles authorised in accordance with Article 211 of Directive 2009/138/EC;
(7)The number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings subject to reorganisation measures or winding-up proceedings;
(8)The number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings and the number of their portfolios where the matching adjustment referred to in Article 77b of Directive 2009/138/EC is applied.
(9)The number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings applying the volatility adjustment referred to in Article 77d of Directive 2009/138/EC.
(10)The number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings applying the transitional risk-free interest rate term structure referred to in Article 308c Directive 2009/138/EC.
(11)The number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings applying the transitional deduction to technical provisions referred to in Article 308d Directive 2009/138/EC.
(12)The total amount of assets of the insurance and reinsurance undertakings valued in accordance with Article 75 of Directive 2009/138/EC, by material asset classes;
(13)The total amount of liabilities of the insurance and reinsurance undertakings valued in accordance with Articles 75 to 86 of Directive 2009/138/EC, divided by technical provisions and other liabilities, with separate indication of the subordinated liabilities which are not included in the own funds;
(14)The total amount of basic own funds, with separate indication of the subordinated liabilities which are included in own funds, and the total amount of ancillary own funds;
(15)The total eligible amount of own funds to cover the Solvency Capital Requirement, classified by tiers;
(16)The total eligible amount of basic own funds to cover the Minimum Capital Requirement, classified by tiers;
(17)The total amount of the Minimum Capital Requirement;
(18)The total amount of the Solvency Capital Requirement;
(19)Where the Solvency Capital Requirement is calculated using the standard formula the total amount of the Solvency Capital Requirement by risk module and sub-module — at the level of aggregation available — expressed as percentage of the total amount of the Solvency Capital Requirement;
(20)Where the Solvency Capital Requirement for credit risk is calculated using the standard formula the total amount of the Solvency Capital Requirement for spread risk and market risk concentration sub-modules and for counterparty default risk module for which a reassessment of the credit quality steps of the larger or more complex exposures has been conducted in accordance with paragraph 5 of Article 4 — at the level of aggregation available — expressed as percentage of the total amount of the respective sub-modules or module;
(21)Where the Solvency Capital Requirement is calculated using an approved partial internal model the total amount of the Solvency Capital Requirement by risk module and sub-module — at the level of aggregation available — expressed as percentage of the total amount of the Solvency Capital Requirement; data on internal models which scope includes credit risk in both market risk and counterparty default risk shall be separately disclosed;
(22)The number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings using an approved full internal model and the number of insurance and reinsurance undertakings using an approved partial internal model for the calculation of the Solvency Capital Requirement; data on internal models which scope includes credit risk in both market risk and counterparty default risk shall be separately disclosed;
(23)The number of capital add-ons, the average capital add-on per undertaking and the distribution of capital add-ons measured as a percentage of the Solvency Capital Requirement, with regard to all insurance and reinsurance undertakings supervised under Directive 2009/138/EC.
The information set out in paragraphs 1 to 5, 7 to 17 shall be provided separately for:
all insurance and reinsurance undertakings;
life insurance undertakings;
non-life insurance undertakings;
insurance undertakings which simultaneously pursue both life and non-life insurance activities;
reinsurance undertakings.
Data with regard to insurance groups supervised under Directive 2009/138/EC
(24)The number of insurance groups of which the supervisory authority is the group supervisor including, the number of insurance and reinsurance subsidiary undertakings at national level, in other Member States and third countries, further split by equivalent and non-equivalent third countries in accordance with Article 260 of Directive 2009/138/EC;
(25)The number of insurance groups of which the supervisory authority is the group supervisor, where the ultimate parent insurance or reinsurance undertaking or insurance holding company or mixed financial holding company which has its head office in the Union is a subsidiary undertaking of a company which has its head office outside of the Union;
(26)The number of ultimate parent insurance or reinsurance undertakings or insurance holding companies or mixed financial holding companies subject to group supervision at national level by the supervisory authority in accordance with Article 216 of Directive 2009/138/EC, including for each such undertaking and holding company the number of its insurance and reinsurance subsidiary undertakings at national level, in other Member States and third countries, further split by equivalent and non-equivalent third countries in accordance with Article 260 of Directive 2009/138/EC;
(27)The number of ultimate parent insurance or reinsurance undertakings or insurance holding companies or mixed financial holding companies subject to group supervision at national level by the supervisory authority in accordance with Article 216 of Directive 2009/138/EC, where another related ultimate parent undertaking at national level is present as referred to in Article 217 of Directive 2009/138/EC;
(28)The number of cross-border insurance groups where the supervisory authority is the group supervisor;
(29)The number of insurance groups that have been allowed to use method 2 or a combination of methods 1 and 2 in accordance with Article 220(2) of Directive 2009/138/EC for the calculation of the solvency at the level of the group;
(30)The total amount of the group eligible own funds for the insurance groups of which the supervisory authority is the group supervisor, separately for group eligible own funds calculated in accordance with method 1 as referred to in Article 230(1) of Directive 2009/138/EC and for group eligible own funds calculated in accordance with method 2 as referred to in Article 233 of Directive 2009/138/EC;
(31)The total amount of the group Solvency Capital Requirement for the insurance groups of which the supervisory authority is the group supervisor separately for the group Solvency Capital Requirement calculated in accordance with method 1 as referred to in Article 230(1) of Directive 2009/138/EC and for the group Solvency Capital Requirement calculated in accordance with method 2 as referred to in Article 233 of Directive 2009/138/EC;
(32)The number of insurance groups of which the supervisory authority is the group supervisor using an approved full internal model for the calculation of the group Solvency Capital Requirements, and the number of insurance groups of which the supervisory authority is the group supervisor using an approved partial internal model for the calculation of the group Solvency Capital Requirement. The information shall be disclosed separately for approvals in accordance with Article 230 and Article 231 of Directive 2009/138/EC.
The information set out in paragraphs 1 to 27 shall be provided in relation to the end of the last calendar year. In relation to paragraphs 8 to 17, 25 and 26 the information shall relate to the financial year ends of insurance and reinsurance undertakings and insurance groups which ended in the last calendar year.
B. Data on the supervisory authority
(1)The structure of the supervisory authority including the number of staff at the end of the last calendar year;
(2)The number of on-site inspections undertaken both at solo and group level, and the total number of man-days spent on them, also specifying the number of regular inspections and ad-hoc inspections, inspections mandated to third parties and on-site inspections under group supervision which were undertaken jointly with other members of the group's College of supervisors; data on inspections conducted in order to review and evaluate the reliance of undertakings on external ratings shall be separately disclosed;
(3)The number of formal reviews both at solo and group level, of ongoing compliance of full or partial internal models with the requirements in relation to the number of internal models in use; data on reviews conducted in order to review and evaluate the reliance of undertakings on external ratings shall be separately disclosed;
(4)The number of partial and of full internal models submitted for approval and how many of those application were successful, divided into solo undertakings and groups; data on internal models which scope includes credit risk in both market risk and counterparty default risk shall be separately disclosed;
(5)The number of corrective measures taken, as defined by Articles 110, 117, 119, 137, 138 and 139 of Directive 2009/138/EC, by type of measure; the number of corrective measures as defined by Article 119 triggered by a deviation of the risk profile of the insurance or reinsurance undertakings with respect to their credit risk;
(6)The number of authorisations withdrawn;
(7)The number of authorisations granted to insurance or reinsurance undertakings;
(8)The criteria used for the application of capital add-ons and the criteria for their calculation and removal;
(9)The number of applications submitted to the supervisory authorities to use the matching adjustment referred to in Article 77b Directive 2009/138/EC and how many were successful.
(10)Where Member States have chosen to require prior approval for use of the volatility adjustment referred to in Article 77d of Directive 2009/138/EC, the number of applications submitted to the supervisory authorities to use this adjustment and how many were successful.
(11)The number of extensions granted in accordance with Article 138(4) of Directive 2009/138/EC, and their average duration;
(12)The number of authorisations granted in accordance with Article 304 of Directive 2009/138/EC;
(13)The number of applications submitted to the supervisory authority to use the transitional risk-free interest rate term structure referred to in Article 308c Directive 2009/138/EC, how many were successful and the number of decisions to revoke the approval of this transitional measure pursuant to article 308e of Directive 2009/138/EC.
(14)The number of applications submitted to the supervisory authority to use the transitional deduction to technical provisions referred to in Article 308d Directive 2009/138/EC and how many were successful.
(15)The number of meetings of Colleges of supervisors which the supervisory authority attended as a member and those chaired as group supervisor;
(16)The number of applications submitted to the supervisory authority for the approval of ancillary own funds, how many of those applications were successful and the main feature of the items approved;
(17)The number of applications submitted to the supervisory authority for approval of the assessment and classification of own-fund items, which are not covered by the list of the Articles 69, 72, 74, 76 and 78, how many of those applications were successful, the main features of the items and the method used to assess and classify them;
(18)The number and scope of peer review analyses organised and conducted by EIOPA in accordance with Article 30 of the Regulation (EU) No 1094/2010, in which the supervisory authority participated.
The information set out in paragraphs 2 to 15 shall be provided in relation to the last calendar year.
ANNEX XXII CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR WINDSTORM RISK
The correlation parameter Corr(windstorm,r,i,j) referred to in Article 121(5) for region r shall be equal to the item set out in row i and in column j of the following correlation matrices. The headings of the rows and columns denote the region specific risk zones according to the numbers of the segments set out in Annex IX.
Correlation coefficients for regions with only one risk zone
The correlation coefficients for the regions Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, Guadeloupe, Martinique, St Martin and Réunion shall be equal to 1.
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Republic of Austria
ANNEX XXII Table 1: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 2: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 3: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXII Table 4: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 5: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 6: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXII Table 7: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 8: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 9: rows 1 - 28
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Kingdom of Belgium
| j i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
| 2 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
| 3 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 |
| 4 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 |
| 5 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 |
| 6 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 |
| 7 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
| 8 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
| 9 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Czech Republic
ANNEX XXII Table 11: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXII Table 12: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 13: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 14: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXII Table 15: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 16: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 17: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXII Table 18: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 19: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Kingdom of Denmark
| j i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 |
| 2 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,25 |
| 3 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,50 |
| 4 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,50 |
| 5 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,50 |
| 6 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 |
| 7 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 |
| 8 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,75 |
| 9 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 |
| 10 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 |
| 11 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the French Republic
ANNEX XXII Table 21: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 22: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 23: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 24: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 25: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 26: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 27: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 28: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 29: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 30: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 31: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 32: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 33: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 34: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 35: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 36: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Federal Republic of Germany
ANNEX XXII Table 37: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 38: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 39: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 40: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 41: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 42: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 43: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 44: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 45: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 46: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 47: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 48: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 49: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 50: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 51: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 52: rows 1 - 27
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Republic of Ireland
ANNEX XXII Table 53: rows 1 - 27
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Kingdom of the Netherlands
ANNEX XXII Table 54: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 55: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 56: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 57: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXII Table 58: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 59: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 60: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 61: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXII Table 62: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 63: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 64: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 65: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXII Table 66: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 67: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 68: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXII Table 69: rows 1 - 20
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Kingdom of Norway
ANNEX XXII Table 70: rows 1 - 20
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Republic of Poland
ANNEX XXII Table 71: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 72: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 73: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 74: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 75: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 76: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 77: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 78: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 79: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 80: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 81: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 82: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXII Table 83: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXII Table 84: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 85: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 86: rows 1 - 24
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Kingdom of Spain
ANNEX XXII Table 87: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 88: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 89: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 90: rows 1 - 26
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Kingdom of Sweden
ANNEX XXII Table 91: rows 1 - 22
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the Swiss Confederation
ANNEX XXII Table 92: rows 1 - 27
Correlation coefficients for windstorm risk in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
ANNEX XXII Table 93: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 94: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 95: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 96: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 97: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXII Table 98: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 99: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 100: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 101: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 102: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXII Table 103: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 104: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 105: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 106: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 107: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXII Table 108: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 109: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 110: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 111: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 112: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXII Table 113: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 114: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 115: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 116: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXII Table 117: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR EARTHQUAKE RISK
The correlation parameter Corr(earthquake,r,i,j) referred to in Article 122(2) for region r shall be equal to the item set out in row i and in column j of the following correlation matrices. The headings of the rows and columns denote the region specific risk zones according to the numbers of the segments set out in Annex IX.
Correlation coefficients for regions with only one risk zone
The correlation coefficients for the regions Republic of Malta, Guadeloupe, Martinique and St Martin shall be equal to 1.
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Republic of Austria
ANNEX XXIII Table 1: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIII Table 2: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIII Table 3: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 4: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIII Table 5: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIII Table 6: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 7: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIII Table 8: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIII Table 9: rows 1 - 26
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Kingdom of Belgium
| j i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
| 2 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
| 3 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,75 |
| 4 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,75 |
| 5 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 |
| 6 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 |
| 7 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 |
| 8 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
| 9 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Republic of Bulgaria
ANNEX XXIII Table 11: rows 1 - 29
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Czech Republic
ANNEX XXIII Table 12: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 13: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 14: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXIII Table 15: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 16: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 17: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXIII Table 18: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 19: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 20: rows 1 - 20
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Republic of Croatia
ANNEX XXIII Table 21: rows 1 - 22
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Republic of Cyprus
| j i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,75 |
| 2 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 3 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 0,25 |
| 4 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,50 |
| 5 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,75 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 |
| 6 | 0,75 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the French Republic
ANNEX XXIII Table 23: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 24: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 25: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 26: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 27: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 28: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 29: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 30: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 31: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 32: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 33: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 34: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 35: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 36: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 37: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIII Table 38: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Federal Republic of Germany
ANNEX XXIII Table 39: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIII Table 40: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 41: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 42: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 43: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIII Table 44: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 45: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 46: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 47: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIII Table 48: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 49: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 50: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 51: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIII Table 52: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 53: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 54: rows 1 - 25
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Guadalupe
| j i | 1 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Hellenic Republic
ANNEX XXIII Table 56: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 57: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 58: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXIII Table 59: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 60: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 61: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXIII Table 62: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 63: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 64: rows 1 - 23
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Republic of Hungary
ANNEX XXIII Table 65: rows 1 - 25
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Italian Republic
ANNEX XXIII Table 66: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 67: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 68: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 69: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 70: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 71: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 72: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 73: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 74: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 75: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 76: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 77: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 78: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 79: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 80: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIII Table 81: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Portuguese Republic
ANNEX XXIII Table 82: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 83: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 84: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 85: rows 1 - 17
ANNEX XXIII Table 86: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 87: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 88: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 89: rows 1 - 17
ANNEX XXIII Table 90: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 91: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 92: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 93: rows 1 - 17
ANNEX XXIII Table 94: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 95: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 96: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 97: rows 1 - 17
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Republic of Romania
ANNEX XXIII Table 98: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 99: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIII Table 100: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIII Table 101: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Slovak Republic
ANNEX XXIII Table 102: rows 1 - 25
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Republic of Slovenia
| j i | 01 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,00 |
| 03 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 |
| 04 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 05 | 0,25 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 06 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 |
| 07 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 08 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 |
| 09 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 |
| 10 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,00 |
| 12 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,00 |
| 13 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for earthquake risk in the Swiss Confederation
ANNEX XXIII Table 104: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR FLOOD RISK
The correlation parameter Corr(flood,r,i,j) referred to in Article 123(5) for region r shall be equal to the item set out in row i and in column j of the following correlation matrices. The headings of the rows and columns denote the region specific risk zones according to the numbers of the segments set out in Annex IX.
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Republic of Austria
ANNEX XXIV Table 1: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 2: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXIV Table 3: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXIV Table 4: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 5: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXIV Table 6: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXIV Table 7: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 8: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXIV Table 9: rows 1 - 28
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Kingdom of Belgium
| j i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 2 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 |
| 3 | 0,00 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 4 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 |
| 5 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 |
| 6 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 7 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
| 8 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,50 |
| 9 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Republic of Bulgaria
ANNEX XXIV Table 11: rows 1 - 29
ANNEX XXIV Table 12: rows 1 - 29
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Czech Republic
ANNEX XXIV Table 13: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXIV Table 14: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 15: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 16: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXIV Table 17: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 18: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 19: rows 1 - 20
ANNEX XXIV Table 20: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 21: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the French Republic
ANNEX XXIV Table 22: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 23: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 24: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 25: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 26: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 27: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 28: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 29: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 30: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 31: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 32: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 33: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 34: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 35: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 36: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 37: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Federal Republic of Germany
ANNEX XXIV Table 38: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 39: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 40: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 41: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 42: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 43: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 44: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 45: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 46: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 47: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 48: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 49: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 50: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 51: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXIV Table 52: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 53: rows 1 - 26
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Republic of Hungary
ANNEX XXIV Table 54: rows 1 - 25
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Italian Republic
ANNEX XXIV Table 55: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV Table 56: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 57: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 58: rows 1 - 17
ANNEX XXIV Table 59: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV Table 60: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 61: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 62: rows 1 - 17
ANNEX XXIV Table 63: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV Table 64: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 65: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 66: rows 1 - 17
ANNEX XXIV Table 67: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV Table 68: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 69: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 70: rows 1 - 17
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Republic of Poland
ANNEX XXIV Table 71: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV Table 72: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 73: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 74: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 75: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV Table 76: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 77: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 78: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 79: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV Table 80: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 81: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 82: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 83: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXIV Table 84: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 85: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 86: rows 1 - 26
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Republic of Romania
ANNEX XXIV Table 87: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 88: rows 1 - 22
ANNEX XXIV Table 89: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXIV Table 90: rows 1 - 22
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Slovak Republic
ANNEX XXIV Table 91: rows 1 - 25
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Swiss Confederation
ANNEX XXIV Table 92: rows 1 - 27
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the Republic of Slovenia
| j i | 01 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,25 |
| 03 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 |
| 04 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 |
| 05 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 |
| 06 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 |
| 07 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 |
| 08 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 |
| 09 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,50 |
| 10 | 0,75 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 1,00 | 0,50 | 0,25 |
| 12 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 1,00 | 0,50 |
| 13 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for flood risk in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
ANNEX XXIV Table 94: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 95: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 96: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 97: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 98: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 99: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 100: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 101: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 102: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 103: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 104: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 105: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 106: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 107: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 108: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 109: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 110: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 111: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 112: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 113: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 114: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 115: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 116: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXIV Table 117: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXIV Table 118: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR HAIL RISK
The correlation parameter Corr(hail,r,i,j) referred to in Article 124(5) for region r shall be equal to the item set out in row i and in column j of the following correlation matrices. The headings of the rows and columns denote the region specific risk zones according to the numbers of the segments set out in Annex IX.
Correlation coefficients for regions with only one risk zone
The correlation coefficients for the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg shall be equal to 1.
Correlation coefficients for hail risk in the Republic of Austria
ANNEX XXV Table 1: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 2: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 3: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXV Table 4: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 5: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 6: rows 1 - 28
ANNEX XXV Table 7: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 8: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 9: rows 1 - 28
Correlation coefficients for hail risk in the Kingdom of Belgium
| j i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 2 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 3 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 4 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 5 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 6 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 |
| 7 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| 8 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,00 | 1,00 | 0,00 |
| 9 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 1,00 |
Correlation coefficients for hail risk in the French Republic
ANNEX XXV Table 11: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 12: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 13: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 14: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXV Table 15: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 16: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 17: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 18: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXV Table 19: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 20: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 21: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 22: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXV Table 23: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 24: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 25: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 26: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for hail risk in the Federal Republic of Germany
ANNEX XXV Table 27: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXV Table 28: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 29: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 30: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 31: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXV Table 32: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 33: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 34: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 35: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXV Table 36: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 37: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 38: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 39: rows 1 - 24
ANNEX XXV Table 40: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 41: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 42: rows 1 - 25
Correlation coefficients for hail risk in the Italian Republic
ANNEX XXV Table 43: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 44: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 45: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 46: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXV Table 47: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 48: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 49: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 50: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXV Table 51: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 52: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 53: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 54: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXV Table 55: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 56: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 57: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 58: rows 1 - 21
Correlation coefficients for hail risk in the Kingdom of the Netherlands
ANNEX XXV Table 59: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 60: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 61: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 62: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 63: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 64: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 65: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 66: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 67: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 68: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 69: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 70: rows 1 - 25
ANNEX XXV Table 71: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 72: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 73: rows 1 - 23
ANNEX XXV Table 74: rows 1 - 25
Correlation coefficients for hail risk in the Kingdom of Spain
ANNEX XXV Table 75: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 76: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 77: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXV Table 78: rows 1 - 26
Correlation coefficients for hail risk in the Swiss Confederation
ANNEX XXV Table 79: rows 1 - 27
ANNEX XXVI CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS FOR SUBSIDENCE RISK
The correlation parameter Corr(subsidence,i,j) referred to in Article 125(1) for region r shall be equal to the item set out in row i and in column j of the following correlation matrices. The headings of the rows and columns denote the region specific risk zones according to the numbers of the segments set out in Annex IX.
Correlation coefficients for subsidence risk in the French Republic
ANNEX XXVI Table 1: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 2: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 3: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 4: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXVI Table 5: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 6: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 7: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 8: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXVI Table 9: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 10: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 11: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 12: rows 1 - 21
ANNEX XXVI Table 13: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 14: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 15: rows 1 - 26
ANNEX XXVI Table 16: rows 1 - 21
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThe Annexes only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation without Annexes
The Whole Regulation without Annexes you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
The Schedules you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources