- Latest available (Revised)
- Point in Time (01/09/2020)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Regulation (EU) 2018/858 of the European Parliament and of the CouncilShow full title
Regulation (EU) 2018/858 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 on the approval and market surveillance of motor vehicles and their trailers, and of systems, components and separate technical units intended for such vehicles, amending Regulations (EC) No 715/2007 and (EC) No 595/2009 and repealing Directive 2007/46/EC (Text with EEA relevance)
You are here:
- Regulations originating from the EU
- 2018 No. 858
- Annexes only
- Show Geographical Extent(e.g. England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland)
- Show Timeline of Changes
More Resources
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Changes over time for: Regulation (EU) 2018/858 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Annexes only)
Version Superseded: 31/12/2020
Alternative versions:
Status:
Point in time view as at 01/09/2020.
Changes to legislation:
Regulation (EU) 2018/858 of the European Parliament and of the Council is up to date with all changes known to be in force on or before 05 November 2024. There are changes that may be brought into force at a future date. Changes that have been made appear in the content and are referenced with annotations.![]()
Changes to Legislation
Changes and effects yet to be applied by the editorial team are only applicable when viewing the latest version or prospective version of legislation. They are therefore not accessible when viewing legislation as at a specific point in time. To view the ‘Changes to Legislation’ information for this provision return to the latest version view using the options provided in the ‘What Version’ box above.
LIST OF ANNEXESU.K.
| Annex I | General definitions, criteria for vehicle categorisation, types of vehicle and types of bodywork |
| Appendix 1: | Procedure for checking whether a vehicle can be categorised as off-road vehicle |
| Appendix 2: | Digits used to supplement the codes to be used for various kinds of bodywork |
| Annex II | Requirements for the purpose of EU type-approval of vehicles, systems, components or separate technical units |
| Part I | Regulatory acts for EU type-approval of vehicles produced in unlimited series |
| Appendix 1: | Regulatory acts for EU type-approval of vehicles produced in small series pursuant to Article 41 |
| Appendix 2: | Requirements for EU individual vehicle approval pursuant to Article 44 |
| Part II | List of UN Regulations recognised as an alternative to the Directives or Regulations referred to in Part I |
| Part III | List of regulatory acts setting out the requirements for the purpose of EU type-approval of special purpose vehicles |
| Appendix 1: | Motor-caravans, ambulances and hearses |
| Appendix 2: | Armoured vehicles |
| Appendix 3: | Wheelchair accessible vehicles |
| Appendix 4: | Other special purpose vehicles (including special group, multi-equipment carrier and trailer caravans) |
| Appendix 5: | Mobile cranes |
| Appendix 6: | Exceptional load transport vehicles |
| Annex III | Procedures to be followed with respect to EU type-approval |
| Appendix 1: | Standards with which the technical services referred to in Article 68 have to comply |
| Appendix 2: | Procedure for the assessment of the technical services |
| Annex IV | Conformity of production procedures |
| Annex V | Small series and end-of-series limits |
| Annex VI | List of parts or equipment that may pose a serious risk to the correct functioning of systems that are essential for the safety of the vehicle or its environmental performance, their performance requirements of such parts and equipment, the appropriate test procedures and marking and packaging provisions |
| Annex VII | Regulatory acts for which a manufacturer may be designated as a technical service |
| Appendix: | Designation of an in-house technical service of a manufacturer as technical service and subcontracting |
| Annex VIII | Conditions for the use of virtual testing methods by a manufacturer or a technical service |
| Appendix 1: | General conditions for the use of virtual testing methods |
| Appendix 2: | Specific conditions for the use of virtual testing methods |
| Appendix 3: | Validation process |
| Annex IX | Procedures to be followed during multi-stage type-approval |
| Appendix: | Model of the manufacturer's additional plate |
| Annex X | Access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information |
| Appendix 1: | Manufacturer's certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information |
| Appendix 2: | Vehicle OBD information |
| Annex XI | Correlation table |
ANNEX IU.K. GENERAL DEFINITIONS, CRITERIA FOR VEHICLE CATEGORISATION, TYPES OF VEHICLE AND TYPES OF BODYWORK
INTRODUCTORY PART Definitions and general provisions U.K.
1.DefinitionsU.K.
1.1.‘Seating position’ means any location capable of accommodating one person seated who is at least as large as:U.K.
the manikin of the 50th percentile adult male in the case of the driver;
the manikin of the 5th percentile adult female in all other cases.
1.2.‘Seat’ means a complete structure with trim, integral or not with the vehicle body structure, which is intended to seat one person.U.K.
It includes both an individual seat and a bench seat, as well as folding seats and removable seats.
1.3.‘Goods’ means primarily any movable things.U.K.
It includes products in bulk, manufactured goods, liquids, living animals, crops, indivisible loads.
1.4.‘Maximum mass’ means the ‘technically permissible maximum laden mass’.U.K.
2.General provisionsU.K.
2.1.Number of seating positionsU.K.
2.1.1.The requirements regarding the number of seating positions apply to seats that are designed for use when the vehicle is travelling on the road.U.K.
2.1.2.They do not apply to seats that are designed for use when the vehicle is stationary and which are clearly identified to users either by means of a pictogram or a sign with an appropriate text.U.K.
2.1.3.The following requirements apply for the counting of the seating positions:U.K.
each individual seat shall be counted as one seating position;
in the case of a bench seat, any space having a width of at least 400 mm measured at the seat cushion level shall be counted as one seating position.
This condition shall not prevent the manufacturer from using the general provisions referred to in point 1.1;
however, a space as referred to in point (b) shall not be counted as one seating position where:
the bench seat includes features that prevent the bottom of the manikin from sitting in a natural way - for example: the presence of a fixed console box, an unpadded area or an interior trim interrupting the nominal seating surface;
the design of the floor pan located immediately in front of a presumed seating position (for example the presence of a tunnel) prevents the feet of the manikin from being positioned in a natural way.
2.1.4.With respect to vehicles covered by UN Regulations No 66 and No 107, the dimension referred to in point 2.1.3(b) shall be aligned with the minimum space required for one person in relation to the various classes of vehicles.U.K.
2.1.5.When seat anchors for a removable seat are present in a vehicle, the removable seat shall be counted in the determination of the number of the seating positions.U.K.
2.1.6.An area intended for an occupied wheelchair shall be regarded as one seating position.U.K.
2.1.6.1.This provision shall be without prejudice to the requirements of paragraphs 3.6.1 and 3.7 of Annex 8 to UN Regulation No 107.U.K.
2.2.Maximum massU.K.
2.2.1.In the case of a tractor unit for semi-trailer, the maximum mass to be considered for classifying the vehicle shall include the maximum mass of the semi-trailer borne by the fifth wheel coupling.U.K.
2.2.2.In the case of a motor vehicle that can tow a centre-axle trailer or a rigid drawbar trailer, the maximum mass to be considered for classifying the motor vehicle shall include the maximum mass transferred to the towing vehicle by the coupling.U.K.
2.2.3.In the case of a semi-trailer, a centre-axle trailer and a rigid drawbar trailer, the maximum mass to be considered for classifying the vehicle shall correspond to the maximum mass transmitted to the ground by the wheels of an axle or group of axles when coupled to the towing vehicle.U.K.
2.2.4.In the case of a converter dolly, the maximum mass to be considered for classifying the vehicle shall include the maximum mass of the semi-trailer borne by the fifth wheel coupling.U.K.
2.3.Special equipmentU.K.
2.3.1.Vehicles fitted primarily with fixed equipment such as machinery or apparatus shall be regarded as N or O category.U.K.
2.4.UnitsU.K.
2.4.1.Unless otherwise stated any unit of measurement and associated symbol shall conform to Council Directive 80/181/EEC(1).U.K.
3.Categorisation into vehicle categoriesU.K.
3.1.The manufacturer is responsible for the categorisation of a type of vehicle into a specific category.U.K.
For such purposes, all the relevant criteria described in this Annex shall be met.
3.2.The approval authority may request from the manufacturer appropriate additional information with the aim of demonstrating that a type of vehicle needs to be categorised as special purpose vehicle in the special group (‘SG Code’).U.K.
PART AU.K. Criteria for vehicle categorisation
1.Vehicle categoriesU.K.
For the purposes of EU type-approval and national type-approval, as well as for EU individual vehicle approval and national individual vehicle approval, vehicles shall be categorised in accordance with the classification referred to in Article 4.
Approval can only be granted for the categories referred to in Article 4(1).
2.Vehicle subcategoriesU.K.
2.1.Off-road vehiclesU.K.
‘Off-road vehicle (ORV)’ means a vehicle that belongs to category M or N, having specific technical features which permit its use off the normal roads.
For those categories of vehicles, the letter ‘G’ shall be added as suffix to the letter and numeral identifying the vehicle category.
The criteria for the subcategorisation of vehicles as ORV are specified in point 4 of this Part.
2.2.Special purpose vehicles (SPV)U.K.
2.2.1.For incomplete vehicles that are intended to fall into the SPV subcategory, the letter ‘S’ shall be added as suffix to the letter and numeral identifying the vehicle category.U.K.
The various types of special purpose vehicles are defined and listed in point 5.
2.3.Off road special purpose vehicleU.K.
2.3.1.‘Off road special purpose vehicle (ORV-SPV)’ means a vehicle that belongs either to category M or N having the specific technical features referred to in points 2.1 and 2.2.U.K.
For those categories of vehicles, the letter ‘G’ shall be added as suffix to the letter and numeral identifying the vehicle category.
Moreover, for incomplete vehicles that are intended to fall into the SPV subcategory, the letter ‘S’ shall be added as second suffix.
3.Criteria for the categorisation of vehicles in category NU.K.
3.1.The categorisation of a type of vehicle in category N shall be based on the technical features of the vehicle as referred to in points 3.2 to 3.6.U.K.
3.2.As a matter of principle, the compartment(s) where all the seating positions are located, shall be completely separated from the loading area.U.K.
3.3.By way of derogation from the requirements of point 3.2, persons and goods may be transported in the same compartment under the condition that the loading area is provided with securing devices designed to protect persons transported against the displacement of the load during driving, including severe braking and cornering.U.K.
3.4.Securing devices - lashing devices - intended for securing the load as required in point 3.3 as well as partitioning systems, intended for vehicles up to 7,5 tonnes shall be designed in accordance with the provisions of sections 3 and 4 of international standard ISO 27956:2009 ‘Road vehicles – Securing of cargo in delivery vans – Requirements and test methods’.U.K.
3.4.1.The requirements referred to in point 3.4 may be verified by a statement of compliance provided by the manufacturer.U.K.
3.4.2.As an alternative to the requirements of point 3.4, the manufacturer may demonstrate to the satisfaction of the approval authority that the securing devices fitted show an equivalent level of protection as provided in the referred standard.U.K.
3.5.The number of seating positions excluding the driver's seating position shall not exceed:U.K.
6 in the case of N1 vehicles;
8 in the case of N2 or N3 vehicles.
3.6.Vehicles shall show a goods-carrying capacity equal or higher than the person-carrying capacity expressed in kg.U.K.
3.6.1.For such purposes, the following equations shall be satisfied in all configurations, in particular when all seating positions are occupied:U.K.
when N = 0:
P – M ≥ 100 kg
when 0 < N ≤ 2:
P – (M + N × 68) ≥ 150 kg;
when N > 2:
P – (M + N × 68) ≥ N × 68;
where the letters have the following meaning:
‘P’ is the technically permissible maximum laden mass;
‘M’ is the mass in running order;
‘N’ is the number of seating positions excluding the driver's seating position.
3.6.2.The mass of equipment that is fitted to the vehicle in order to accommodate goods (e.g. tank, bodywork, etc.), to handle goods (e.g. crane, lift, etc.) and to secure goods (e.g. cargo securing devices) shall be included in M.U.K.
3.6.3.The mass of equipment that is not used for the purposes referred to in point 3.6.2 (such as a compressor, a winch, an electric power generator, broadcasting equipment, etc.) shall not be included in M for the purposes of the application of the formulae referred to in point 3.6.1.U.K.
3.7.The requirements referred to in points 3.2 to 3.6 shall be met for all variants and versions within the type of vehicle.U.K.
3.8.Criteria for the categorisation of vehicles as N1.U.K.
3.8.1.A vehicle shall be categorised as N1 when all the applicable criteria are met.U.K.
When one or more of the criteria are not met, the vehicle shall be categorised as M1.
3.8.2.In addition to the general criteria referred to in points 3.2 to 3.6, the criteria specified in this point shall be met for the categorisation of vehicles for which the compartment where the driver is located and the load are within a single unit (i.e. bodywork ‘BB’).U.K.
3.8.2.1.The fact that a wall or a partition, complete or partial, is fitted between a seat row and the cargo area shall not rule out the obligation to meet the required criteria.U.K.
3.8.2.2.The criteria shall be as follows:U.K.
the loading of the goods shall be possible by a rear door, a tailgate or a side-door designed and constructed for that purposes;
in the case of a rear door or a tailgate, the loading aperture shall meet the following requirements:
in the case the vehicle is fitted with only one row of seats or with only the driver seat, the minimum height of the loading aperture shall be at least 600 mm;
in the case the vehicle is fitted with two or more rows of seats, the minimum height of the loading aperture shall be at least 800 mm and the aperture shall show a surface of at least 12 800 cm2;
The cargo area shall meet the following requirements:
‘cargo area’ means the part of the vehicle located behind the row(s) of seats or behind the driver seat when the vehicle is fitted with only one driver seat;
the loading surface of the cargo area shall be generally flat;
where the vehicle is fitted with only one row of seats or with one seat, the minimum length of the cargo area shall be at least 40 % of the wheelbase;
where the vehicle is fitted with two or more rows of seats, the minimum length of the cargo area shall be at least 30 % of the wheelbase.
Where the seats of the last row of seats can be easily removed from the vehicle without the use of special tools, the requirements regarding the length of the cargo area shall be met with all the seats installed in the vehicle;
the requirements regarding the length of the cargo area shall be met when the seats of the first row or of the last row, as the case may be, are upright in their normal position for use by the vehicle occupants.
3.8.2.3.Specific conditions for measurementU.K.
3.8.2.3.1.DefinitionsU.K.
‘Height of the loading aperture’, means the vertical distance between two horizontal planes tangent respectively to the highest point of the lower part of the doorway and the lowest point of the upper part of the doorway;
‘Surface of the loading aperture’ means the greatest surface of the orthogonal projection on a vertical plane, perpendicular to the centreline of the vehicle, of the maximum aperture permitted when the rear door(s) or tailgate is (are) wide open;
‘Wheelbase’, for the purposes of application of the formulae in points 3.8.2.2 and 3.8.3.1, means the distance between:
the centreline of the front axle and the centreline of the second axle in the case of a two axle vehicle; or
the centreline of the front axle and the centreline of a virtual axle equally distant from the second and third axle in the case of a three axle vehicle.
3.8.2.3.2.Seat adjustmentsU.K.
The seats shall be adjusted at their rear outermost positions;
The seat back, if adjustable, shall be adjusted as to accommodate the three-dimensional H-point machine at a torso angle of 25 degrees;
The seat back, if not adjustable, shall be in the position designed by the vehicle manufacturer;
When the seat is adjustable in height, it shall be adjusted to its lowest position.
3.8.2.3.3.Vehicle conditionsU.K.
The vehicle shall be in loaded conditions corresponding to its maximum mass;
The vehicle shall be with its wheels straight ahead.
3.8.2.3.4.The requirements of point 3.8.2.3.2 shall not apply when the vehicle is fitted with a wall or a partition.U.K.
3.8.2.3.5.Measurement of the length of the cargo areaU.K.
When the vehicle is not fitted with a partition or a wall, the length shall be measured from a vertical plane tangent to the rear outermost point of the top of the seat back to the rear internal pane or door or tailgate, in closed position;
When the vehicle is fitted with a partition or a wall, the length shall be measured from a vertical plane tangent to the rear outermost point of the partition or the wall to the rear internal pane or door or tailgate, as the case may be, in closed position;
The requirements concerning the length shall be fulfilled at least along a horizontal line situated in the longitudinal vertical plane passing through the centreline of the vehicle, at the level of the load floor.
3.8.3.In addition to the general criteria referred to in points 3.2 to 3.6, the criteria specified in this point shall be met for the categorisation of vehicles for which the compartment where the driver is located and the load are not within a single unit (i.e. bodywork ‘BE’).U.K.
3.8.3.1.Where the vehicle is fitted with an enclosure type body, the following shall apply:U.K.
the loading of the goods shall be possible by a rear door, a tailgate or a panel or other means;
the minimum height of the loading aperture shall be at least 800 mm and the aperture shall show a surface of at least 12 800 cm2;
The minimum length of the cargo area shall be at least 40 % of the wheelbase.
3.8.3.2.Where the vehicle is fitted with an open type cargo area, only the provisions referred to in points 3.8.3.1(a) and (c) shall apply.U.K.
3.8.3.3.For the application of the provisions referred to in point 3.8.3, the definitions in point 3.8.2.3.1 shall apply.U.K.
3.8.3.4.However, the requirements concerning the length of the cargo area shall be fulfilled along a horizontal line situated in the longitudinal plane passing through the centreline of the vehicle at the level of the load floor.U.K.
4.Criteria for the sub-categorisation of vehicles as off-road vehiclesU.K.
4.1.M1 or N1 vehicles shall be subcategorised as off-road vehicles if they satisfy at the same time the following conditions:U.K.
at least one front and at least one rear axle designed to be driven simultaneously irrespective of whether one powered axle can be disengaged;
at least one differential locking mechanism or a mechanism having similar effect is fitted;
they are able to climb at least a 25 % gradient as a solo vehicle;
they satisfy five out of the following six requirements:
the approach angle shall be at least 25 degrees;
the departure angle shall be at least 20 degrees;
the ramp angle shall be at least 20 degrees;
the ground clearance under the front axle shall be at least 180 mm;
the ground clearance under the rear axle shall be at least 180 mm;
the ground clearance between the axles shall be at least 200 mm.
4.2.M2, N2 or M3 vehicles the maximum mass of which does not exceed 12 tonnes shall be subcategorised as off-road vehicles if they satisfy either the condition set out in point (a) or the conditions set out in both points (b) and (c):U.K.
all their axles are driven simultaneously, irrespective of whether one or more powered axles can be disengaged;
at least one front and at least one rear axle are designed to be driven simultaneously irrespective of whether one powered axle can be disengaged;
at least one differential locking mechanism or a mechanism having the same effect is fitted;
they are able to climb a 25 % gradient as a solo vehicle;
they satisfy at least five out of the following six requirements if their maximum mass does not exceed 7,5 tonnes and at least four if their maximum mass exceeds 7,5 tonnes:
the approach angle shall be at least 25 degrees;
the departure angle shall be at least 25 degrees;
the ramp angle shall be at least 25 degrees;
the ground clearance under the front axle shall be at least 250 mm;
the ground clearance between axles shall be at least 300 mm;
the ground clearance under the rear axle shall be at least 250 mm.
4.3.M3 or N3 vehicles whose maximum mass exceeds 12 tonnes shall be subcategorised as off-road vehicles if they satisfy either the condition set out in point (a) or the conditions set out in both points (b) and (c):U.K.
all their axles are driven simultaneously, irrespective of whether one or more powered axles can be disengaged;
at least half of the axles (or two axles out of the three in the case of a three axle vehicle and three axles in the case of a five axle vehicle) is designed to be driven simultaneously, irrespective of whether one powered axle can be disengaged;
there is at least one differential locking mechanism or a mechanism having similar effect;
they are able to climb a 25 % gradient as solo vehicle;
they satisfy at least four out of the following six requirements:
the approach angle shall be at least 25 degrees;
the departure angle shall be at least 25 degrees;
the ramp angle shall be at least 25 degrees;
the ground clearance under the front axle shall be at least 250 mm;
the ground clearance between axles shall be at least 300 mm;
the ground clearance under the rear axle shall be at least 250 mm.
4.4.The procedure for checking compliance with the geometrical provisions referred to in this Part shall be set out in Appendix 1.U.K.
4.5.The requirements in points 4.1(a), 4.2(a), 4.2(b), 4.3(a), 4.3(b) on simultaneous driven axles are considered to have been fulfilled if one of the following conditions is fulfilled:U.K.
the transmission of the tractive power to all axles is performed by mechanical means only which provides traction in heavy off-road; or
each of the wheels of the axle in question is driven by an individual hydraulic or electric motor.
If the axles according to the requirements in points 4.1(a), 4.2(a), 4.2(b), 4.3(a), 4.3(b) on simultaneous driven axles are not powered by mechanical means only, the propulsion of the individual wheels shall be designed for heavy off-road operation. In such case it shall be ensured that at least 75 % of total tractive power can be transmitted to the wheel in question when the tractive conditions under the other wheels do not allow to transmit the tractive power properly via these wheels.
The auxiliary drive system according to point 4.5(b) shall not allow to disengage the tractive power automatically until the vehicle reaches 75 % of the maximum vehicle design speed or reaches 65 km/h.
5.Special purpose vehiclesU.K.
| Name | Code | Definition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.1. | Motor caravan | SA | A vehicle of category M with living accommodation space which contains the following equipment as a minimum: (a) seats and table; (b) sleeping accommodation which may be converted from the seats; (c) cooking facilities; (d) storage facilities. This equipment shall be rigidly fixed to the living compartment. However, the table may be designed to be easily removable. |
| 5.2. | Armoured vehicle | SB | A vehicle intended for the protection of conveyed persons or goods with anti-bullet armour plating. |
| 5.3. | Ambulance | SC | A vehicle of category M intended for the transport of sick or injured persons and having special equipment for such purpose. |
| 5.4. | Hearse | SD | A vehicle of category M intended for the transport of deceased persons and having special equipment for such purpose. |
| 5.5. | Wheelchair accessible vehicle | SH | A vehicle of category M1 constructed or converted specifically so that they accommodate one or more persons seated in their wheelchairs when travelling on the road. |
| 5.6. | Trailer caravan | SE | A vehicle of category O as defined in term 3.2.1.3 of international standard ISO 3833:1977. |
| 5.7. | Mobile crane | SF | A vehicle of category N3, not fitted for the carriage of goods, provided with a crane whose lifting moment is equal to or higher than 400 kNm. |
| 5.8. | Special group | SG | A special purpose vehicle that does not enter in any of the definitions mentioned in this Part. |
| 5.9. | Converter dolly | SJ | A vehicle of category O equipped with a fifth-wheel coupling to support a semi-trailer with a view to converting the latter into a trailer. |
| 5.10. | Exceptional load transport trailer | SK | A vehicle of category O4 intended for the transport of indivisible loads that is subject to speed and traffic restrictions because of its dimensions. Under this term are also included hydraulic modular trailers irrespective of the number of modules. |
| 5.11. | Exceptional load transport motor vehicle | SL | A road tractor or tractor unit for semi-trailer of category N3 meeting all the following conditions: (a) having more than two axles and at least half of the axles (two axles out of three in the case of a three axle vehicle and three axles out of five in the case of a five axle vehicle) designed to be driven simultaneously, irrespective of whether one powered axle can be disengaged; (b) that is designed for towing and pushing exceptional load transport trailer of category O4; (c) that has a minimum engine power of 350 kW; and (d) that can be equipped with an additional front coupling device for heavy towable masses. |
| 5.12. | Multi-equipment carrier | SM | An off-road vehicle of category N (as defined in point 2.3) designed and constructed for pulling, pushing, carrying and actuating certain inter-changeable equipment: (a) with not less than two mounting areas for this equipment; (b) with standardised, mechanical, hydraulic and/or electrical interfaces (e.g. Power take off) for powering and actuating the inter-changeable equipment; and (c) that fulfils the definition of international standard ISO 3833-1977, paragraph 3.1.4 (special vehicle). If the vehicle is equipped with an auxiliary load platform, its maximum length shall not exceed: (a) 1,4 times of the front or rear track width of the vehicle, whichever is the larger in the case of two axle vehicles; or (b) 2,0 times of the front or rear track width of the vehicle, whichever is the larger in the case of vehicles having more than two axles. |
6.RemarksU.K.
6.1.Type-approval shall not be granted:U.K.
to converter dolly as defined in point 5.9 of this Part;
to rigid drawbar trailers as defined in point 5.4 of Part C;
to trailers in which persons may be carried when travelling on the road.
6.2.Point 6.1 is without prejudice to Article 42 on national small series type-approval.U.K.
PART BU.K. Criteria for types of vehicle, variants and versions
1.Category M1 U.K.
1.1.Type of vehicleU.K.
1.1.1.A ‘type of vehicle’ shall consist of vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the manufacturer's company name.
A change in the legal form of ownership of the company does not require that a new approval has to be granted;
the design and assembly of the essential parts of the body structure in the case of a self-supporting body.
The same shall apply to vehicles the bodywork of which is bolted on or welded to a separate frame;
1.1.2.By way of derogation from the requirements of point 1.1.1(b), when the manufacturer uses the floor portion of the body structure as well as the essential constituent elements forming the front part of the body structure located directly in front of the windscreen bay, in the construction of different kinds of bodywork (for example a saloon and a coupe), those vehicles may be considered as belonging to the same type. Evidence thereof shall be provided by the manufacturer.U.K.
1.1.3.A type shall consist of at least one variant and one version.U.K.
1.2.VariantU.K.
1.2.1.A ‘variant’ within a type of vehicle shall group the vehicles that have the following construction features in common:U.K.
the number of lateral doors or the type of bodywork as defined in point 2 of Part C when the manufacturer uses the criterion of point 1.1.2;
the power plant with regard to the following construction features:
the type of energy supply (internal combustion engine, electric motor or other);
the working principle (positive ignition, compression ignition or other);
the number and arrangement of cylinders in the case of internal combustion engine (L4, V6 or other);
the number of axles;
the number, and interconnection of powered axles;
the number of steered axles;
the stage of completion (e.g. complete/incomplete);
in the case of multi-stage built vehicles, the manufacturer and the type of the previous stage vehicle.
1.3.VersionU.K.
1.3.1.A ‘version’ within a variant shall group the vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the technically permissible maximum laden mass;
the engine capacity in the case of internal combustion engine;
the maximum engine power output or the maximum continuous rated power (electric motor);
the nature of the fuel (petrol, gas oil, LPG, bi-fuel or other);
the maximum number of seating positions;
drive-by sound level;
exhaust emission level (for example Euro 5, Euro 6 or other);
combined or weighted, combined CO2 emissions;
electric energy consumption (weighted, combined);
combined or weighted, combined fuel consumption;
As an alternative to the criteria in points (h), (i) and (j), the vehicles grouped into a version shall have in common all tests performed for the calculation of their CO2 emissions, electric energy consumption and fuel consumption in accordance with sub-Annex 6 to Annex XXI to Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1151(2).
2.Categories M2 and M3 U.K.
2.1.Type of vehicleU.K.
2.1.1.A ‘type of vehicle’ shall consist of vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the manufacturer's company name.
A change in the legal form of ownership of the company does not require that a new approval has to be granted;
the category;
the following aspects of construction and design:
the design and construction of the essential constituent elements forming the chassis;
the design and construction of the essential constituent elements forming the body structure in the case of a self-supporting body;
the number of decks (single or double);
the number of sections (rigid/articulated);
the number of axles;
the mode of energy supply (on-board or off-board);
2.1.2.A type of vehicle shall consist of at least one variant and one version.U.K.
2.2.VariantU.K.
2.2.1.A ‘variant’ within a type of vehicle shall group the vehicles that have all of the following construction features in common:U.K.
the type of bodywork as defined in point 3 of Part C;
the class or combination of classes of vehicles as defined in paragraph 2.1.1 of UN Regulation No 107 (only in the case of complete and completed vehicles);
the stage of completion (e.g. complete/incomplete/completed);
the power plant with regard to the following construction features:
the type of energy supply (internal combustion engine, electric motor or other);
the working principle (positive ignition, compression ignition or other);
the number and arrangement of cylinders in the case of internal combustion engine (L6, V8 or other);
in the case of multi-stage built vehicles, the manufacturer and the type of the previous stage vehicle.
2.3.VersionU.K.
2.3.1.A ‘version’ within a variant shall group the vehicles that have all the following features in common:U.K.
the technically permissible maximum laden mass;
the ability of the vehicle to tow a trailer or not;
the engine capacity in the case of internal combustion engine;
the maximum engine power output or the maximum continuous rated power (electric motor);
the nature of the fuel (petrol, gas oil, LPG, bi-fuel or other);
drive-by sound level;
exhaust emission level (for example Euro IV, Euro V or other).
3.Category N1 U.K.
3.1.Type of vehicleU.K.
3.1.1.A ‘type of vehicle’ shall consist of vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the manufacturer's company name.
A change in the legal form of ownership of the company does not require that a new approval has to be granted;
the design and assembly of the essential parts of the body structure in the case of a self-supporting body;
the design and the construction of the essential constituent elements forming the chassis in the case of a non-self-supporting body.
3.1.2.By way of derogation from the requirements of point 3.1.1(b), when the manufacturer uses the floor portion of the body structure as well the essential constituent elements forming the front part of the body structure located directly in front of the windscreen bay, in the construction of different kinds of bodywork (for example a van and a chassis-cab, different wheelbases and different roof heights), those vehicles may be considered as belonging to the same type. Evidence thereof shall be provided by the manufacturer.U.K.
3.1.3.A type of vehicle shall consist of at least one variant and one version.U.K.
3.2.VariantU.K.
3.2.1.A ‘variant’ within a type of vehicle shall group the vehicles that have the following construction features in common:U.K.
the number of lateral doors or the type of bodywork as defined in point 4 of Part C (for complete and completed vehicles) when the manufacturer uses the criterion of point 3.1.2;
the stage of completion (e.g. complete/incomplete/completed);
the power plant with regard to the following construction features:
the type of energy supply (internal combustion engine, electric motor or other);
the working principle (positive ignition, compression ignition or other);
the number and arrangement of cylinders in the case of internal combustion engine (L6, V8 or other);
the number of axles;
the number and interconnection of powered axles;
the number of steered axles.
in the case of multi-stage built vehicles, the manufacturer and the type of the previous stage vehicle.
3.3.VersionU.K.
3.3.1.A ‘version’ within a variant shall group the vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the technically permissible maximum laden mass;
the engine capacity in the case of internal combustion engine;
the maximum engine power output or maximum continuous rated power (electric motor);
the nature of the fuel (petrol, gas oil, LPG, bi-fuel or other);
the maximum number of seating positions;
drive-by sound level;
exhaust emission level (for example Euro 5, Euro 6 or other);
combined or weighted, combined CO2 emissions;
electric energy consumption (weighted, combined);
combined or weighted, combined fuel consumption;
the existence of a unique set of innovative technologies, as specified in Article 12 of Regulation (EU) No 510/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council(3).
As an alternative to the criteria in points (h), (i) and (j), the vehicles grouped into a version shall have in common all tests performed for the calculation of their CO2 emissions, electric energy consumption and fuel consumption in accordance with sub-Annex 6 to Annex XXI of Regulation (EU) 2017/1151.
4.Categories N2 and N3 U.K.
4.1.Type of vehicleU.K.
4.1.1.A ‘type of vehicle’ shall consist of vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the manufacturer's company name.
A change in the legal form of ownership of the company does not require that a new approval has to be granted;
the category;
the design and construction of the chassis that are common to a single line of product;
the number of axles;
4.1.2.A type of vehicle shall consist of at least one variant and one version.U.K.
4.2.VariantU.K.
4.2.1.A ‘variant’ within a type of vehicle shall group the vehicles that have the following construction features in common:U.K.
the body structural concept or type of bodywork as defined in point 4 of Part C and in Appendix 2 (only for complete and completed vehicles);
the stage of completion (e.g. complete/incomplete/completed);
the power plant with regard to the following construction features:
the type of energy supply (internal combustion engine, electric motor or other);
the working principle (positive ignition, compression ignition or other);
the number and arrangement of cylinders in the case of internal combustion engine (L6, V8 or other);
the number and interconnection of powered axles;
the number of steered axles;
in the case of multi-stage built vehicles, the manufacturer and the type of the previous stage vehicle.
4.3.VersionU.K.
4.3.1.A ‘version’ within a variant shall group the vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the technically permissible maximum laden mass;
the ability or not to tow a trailer as follows:
an unbraked trailer;
a trailer with an inertia (or overrun) braking system as defined in paragraph 2.12 of UN Regulation No 13;
a trailer with a continuous or semi-continuous braking system as defined in paragraphs 2.9 and 2.10 of UN Regulation No 13;
a trailer of category O4 that results in a maximum mass of the combination not exceeding 44 tonnes;
a trailer of category O4 that results in a maximum mass of the combination exceeding 44 tonnes;
the engine capacity;
the maximum engine power output;
the nature of the fuel (petrol, gas oil, LPG, bi-fuel or other);
drive-by sound level;
exhaust emission level (for example Euro IV, Euro V or other).
5.Categories O1 and O2 U.K.
5.1.Type of vehicleU.K.
5.1.1.A ‘type of vehicle’ shall consist of vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the manufacturer's company name.
A change in the legal form of ownership of the company does not require that a new approval has to be granted;
the category;
the concept as defined in point 5 of Part C;
the following aspects of construction and design:
the design and construction of the essential constituent elements forming the chassis;
the design and construction of the essential constituent elements forming the body structure in the case of a self-supporting body;
the number of axles.
5.1.2.A type of vehicle shall consist of at least one variant and one version.U.K.
5.2.VariantU.K.
5.2.1.A ‘variant’ within a type of vehicle shall group the vehicles that have the following construction features in common:U.K.
the kind of bodywork as referred to in Appendix 2 (for complete and completed vehicles);
the stage of completion (e.g. complete/incomplete/completed);
the type of braking system (e.g. unbraked/inertia/power);
in the case of multi-stage built vehicles, the manufacturer and the type of the previous stage vehicle.
5.3.VersionU.K.
5.3.1.A ‘version’ within a variant shall group the vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the technically permissible maximum laden mass;
the concept of the suspension (air, steel or rubber suspension, torsion bar or other);
the concept of the drawbar (triangle, tube or other).
6.Categories O3 and O4 U.K.
6.1.Type of vehicleU.K.
6.1.1.A ‘type of vehicle’ shall consist of vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the manufacturer's company name.
A change in the legal form of ownership of the company does not require that a new approval has to be granted;
the category;
the concept of the trailer with relation to the definitions in point 5 of Part C;
the following aspects of construction and design:
the design and construction of the essential constituent elements forming the chassis;
the design and construction of the essential constituent elements forming the body structure in the case of trailers with a self-supporting body;
the number of axles.
6.1.2.A type of vehicle shall consist of at least one variant and one version.U.K.
6.2.VariantsU.K.
6.2.1.A ‘variant’ within a type of vehicle shall group the vehicles that have the following construction and design features in common:U.K.
the kind of bodywork as referred to in Appendix 2 (for complete and completed vehicles);
the stage of completion (e.g. complete/incomplete/completed);
the concept of the suspensions (steel, air or hydraulic suspension);
the following technical features:
the capability or not for the chassis to be extendible;
the deck height (normal, low loader, semi-low loader etc.);
in the case of multi-stage built vehicles, the manufacturer and the type of the previous stage vehicle.
6.3.VersionsU.K.
6.3.1.A ‘version’ within a variant shall group the vehicles that have the following features in common:U.K.
the technically permissible maximum laden mass;
the subdivisions or combination of subdivisions referred to in points 3.2 and 3.3 of Annex I to Directive 96/53/EC into which the axle spacing between two consecutive axles forming a group belongs;
the definition of the axles in the following respects:
lift axles (number and position);
loadable axles (number and position);
steered axle (number and position).
7.Common requirements for all vehicle categoriesU.K.
7.1.When a vehicle falls into several categories because of its maximum mass or the number of seating positions or both, the manufacturer may select to use the criteria of one or the other vehicle category for the definition of the variants and the versions.U.K.
7.1.1.Examples:U.K.
a vehicle ‘A’ may be type-approved as N1 (3,5 tonnes) and N2 (4,2 tonnes) in relation to its maximum mass. In such a case, the parameters mentioned in category N1 may be used also for the vehicle that falls into category N2 (or vice-versa);
a vehicle ‘B’ may be type-approved as M1 and M2 in relation to the number of seating positions (7 + 1 or 10 + 1), the parameters mentioned in category M1 may be used also for the vehicle that falls into category M2 (or vice-versa).
7.2.A vehicle of category N may be type-approved against the provisions required for category M1 or M2, as the case may be, when it is intended to be converted into a vehicle of that category during the next step of a multi-stage type-approval procedure.U.K.
7.2.1.This option shall only be permitted for incomplete vehicles.U.K.
Such vehicles shall be identified by a specific variant code given by the manufacturer of the base vehicle.
7.3.Type-, variant- and version designationsU.K.
7.3.1.The manufacturer shall allocate an alphanumeric code to each type of vehicle, variant and version, made up of Roman letters and/or Arabic numerals.U.K.
The use of brackets and hyphens is permitted provided they do not replace a letter or a numeral.
7.3.2.The whole code shall be designated: Type-Variant-Version or ‘TVV’.U.K.
7.3.3.The TVV shall clearly and unequivocally identify a unique combination of technical features in relation to the criteria defined in this Part.U.K.
7.3.4.The same manufacturer may use the same code in order to define a type of vehicle when the latter falls in two or more categories.U.K.
7.3.5.The same manufacturer shall not use the same code in order to define a type of vehicle for more than one type-approval within the same vehicle category.U.K.
7.4.Number of characters for the TVVU.K.
7.4.1.The number of characters shall not exceed:U.K.
15 for the code of the type of vehicle;
25 for the code of one variant;
35 for the code of one version.
7.4.2.The complete alphanumeric ‘TVV’ shall not contain more than 75 characters.U.K.
7.4.3.When the TVV is used as a whole, a space shall be left between the type, the variant and the version.U.K.
Example of such TVV: 159AF[…space]0054[…space]977K(BE).
PART CU.K. Definitions of types of bodywork
1.GeneralU.K.
1.1.The type of bodywork as well as the code for bodywork shall be indicated by means of codes.U.K.
The list of codes shall apply primarily to complete and completed vehicles.
1.2.As regards vehicles of categories M, the type of bodywork shall consist of two letters as specified in points 2 and 3.U.K.
1.3.As regards vehicles of categories N and O, the type of bodywork shall consist of two letters as referred to in points 4 and 5.U.K.
1.4.Where necessary (especially for the types of bodywork referred to respectively in points 4.1 and 4.6 and in points 5.1 to 5.4), they shall be supplemented by two digits.U.K.
1.4.1.The list of digits shall be laid down in Appendix 2.U.K.
1.5.For special purpose vehicles, the type of bodywork to be used shall be linked to the category of the vehicle.U.K.
2.Vehicles belonging to category M1 U.K.
| Ref. | Code | Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1. | AA | Saloon | A vehicle defined in term 3.1.1.1 of international standard ISO 3833:1977, fitted with at least four side windows. |
| 2.2. | AB | Hatchback | A saloon as defined in 2.1 with a hatch at the rear end of the vehicle. |
| 2.3. | AC | Station wagon | A vehicle defined in term 3.1.1.4 of international standard ISO 3833:1977. |
| 2.4. | AD | Coupé | A vehicle defined in term 3.1.1.5 of international standard ISO 3833:1977. |
| 2.5. | AE | Convertible | A vehicle defined in terms No 3.1.1.6 of international standard ISO 3833:1977. However, a convertible may have no door. |
| 2.6. | AF | Multi-purpose vehicle | A vehicle other than AG and those mentioned in AA to AE intended for carrying persons and their luggage or occasionally goods, in a single compartment. |
| 2.7. | AG | Truck station wagon | A vehicle defined in term No 3.1.1.4.1 of international standard ISO 3833:1977. However, the luggage compartment must be completely separated from the passenger compartment. In addition, the reference point of the driver's seating position needs not to be at least at 750 mm above the surface supporting the vehicle. |
3.Vehicles belonging to category M2 or M3 U.K.
| Ref. | Code | Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1. | CA | Single-deck vehicle | A vehicle where the spaces provided for persons are arranged in a single level or in a way that they do not constitute two superimposed levels; |
| 3.2. | CB | Double-deck vehicle | A vehicle defined in paragraph 2.1.6 of UN Regulation No 107; |
| 3.3. | CC | Single-deck articulated vehicle | A vehicle defined in paragraph 2.1.3 of UN Regulation No 107 with a single deck; |
| 3.4. | CD | Double-deck articulated vehicle | A vehicle defined in paragraph 2.1.3.1 of UN Regulation No 107; |
| 3.5. | CE | Low-floor single-deck vehicle | A vehicle defined in paragraph 2.1.4 of UN Regulation No 107 with a single deck; |
| 3.6. | CF | Low-floor double-deck vehicle | A vehicle defined in paragraph 2.1.4 of UN Regulation No 107 with a double deck; |
| 3.7. | CG | Articulated low-floor single-deck vehicle | A vehicle that combines the technical features of points 3.3 and 3.5 of this table; |
| 3.8. | CH | Articulated low-floor double-deck vehicle | A vehicle that combines the technical features of points 3.4 and 3.6 of this table; |
| 3.9. | CI | Open top single deck vehicle | A vehicle with partial roof or without roof; |
| 3.10. | CJ | Open top double deck vehicle | A vehicle without roof over all or part of its upper deck; |
| 3.11. | CX | Bus chassis | An incomplete vehicle with just chassis rails or tube assembly, power train, axles, that is intended to be completed with bodywork, customised to the needs of the transport operator. |
4.Motor vehicles of category N1, N2 or N3 U.K.
| Ref. | Code | Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.1. | BA | Lorry | A vehicle that is designed and constructed exclusively or principally for conveying goods. It may also tow a trailer. |
| 4.2. | BB | Van | A lorry with the compartment where the driver is located and cargo area within a single unit. |
| 4.3. | BC | Tractor unit for semi-trailer | A towing vehicle that is designed and constructed exclusively or principally to tow semi-trailers. |
| 4.4. | BD | Road tractor | A towing vehicle that is designed and constructed exclusively to tow trailers other than semi-trailers. |
| 4.5. | BE | Pick-up truck | A vehicle of a maximum mass not exceeding 3 500 kg in which the seating positions and the cargo area are not located in a single compartment. |
| 4.6. | BX | Chassis-cab or chassis-cowl | An incomplete vehicle with just a cabin (complete or partial), chassis rails, power train, axles, which is intended to be completed with bodywork, customised to the needs of the transport operator. |
5.Vehicles of category OU.K.
| Ref. | Code | Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.1. | DA | Semi-trailer | A trailer that is designed and constructed to be coupled to a tractor unit or to a converter dolly and to impose a substantial vertical load on the towing vehicle or on the converter dolly. The coupling to be used for a vehicle combination shall consist of a king pin and a fifth wheel. |
| 5.2. | DB | Drawbar trailer | A trailer having at least two axles, of which at least one is a steered axle: (a) equipped with a towing device which can move vertically (in relation to the trailer); and (b) that transmits less than 100 daN as a static vertical load to the towing vehicle. |
| 5.3. | DC | Centre-axle trailer | A trailer where the axle(s) is (are) positioned close to the centre of gravity of the vehicle (when uniformly loaded) so that only a small static vertical load, not exceeding 10 % of that corresponding to the maximum mass of the trailer or a load of 1 000 daN (whichever is the lesser) is transmitted to the towing vehicle. |
| 5.4. | DE | Rigid drawbar trailer | A trailer with one axle or one group of axles fitted with a drawbar which transmits a static load not exceeding 4 000 daN to the towing vehicle due to its construction and that does not meet the definition of a centre-axle trailer. The coupling to be used for a vehicle combination shall not consist of a king pin and a fifth wheel. |
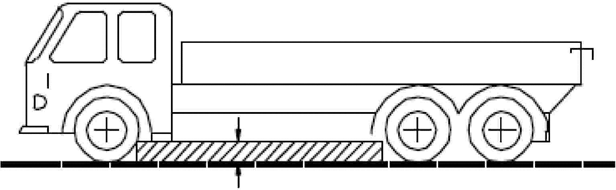
Appendix 1Procedure for checking whether a vehicle can be categorised as off-road vehicle
1.GeneralU.K.
1.1.For the purposes of classification of a vehicle as off-road vehicle, the procedure described in this Appendix shall apply.U.K.
2.Test conditions for geometric measurementsU.K.
2.1.Vehicles belonging to category M1 or N1 shall be in unloaded conditions with a manikin of the 50th percentile male installed on the driver's seat and fitted with coolant fluid, lubricants, fuel, tools, spare-wheel (if fitted as OEM equipment).U.K.
The manikin may be replaced by a similar device having the same mass.
2.2.Vehicles other than those referred to in point 2.1 shall be loaded to their technically permissible maximum laden mass.U.K.
The distribution of the mass on the axles shall be the one that represents the worst case with respect to compliance with the respective criteria.
2.3.A vehicle representative of the type shall be submitted to the technical service in the conditions specified in point 2.1 or 2.2. The vehicle shall be in a stationary position with its wheels set straight ahead.U.K.
The ground on which measurements are made shall be as flat and horizontal (maximum of inclination 0,5 %) as possible.
3.Measurement of approach, departure and ramp anglesU.K.
3.1.The approach angle shall be measured in accordance with paragraph 6.10 of international standard ISO 612:1978.U.K.
3.2.The departure angle shall be measured in accordance with paragraph 6.11 of international standard ISO 612:1978.U.K.
3.3.The ramp angle shall be measured in accordance with paragraph 6.9 of international standard ISO 612:1978.U.K.
3.4.When measuring the departure angle rear underrun protection devices which are adjustable in height may be set in the upper position.U.K.
3.5.The prescription in point 3.4 shall not be construed as an obligation for the base vehicle to be fitted with a rear underrun protection as original equipment. However, the base vehicle manufacturer shall inform the next stage manufacturer that the vehicle has to comply with the requirements on departure angle when fitted with a rear underrun protection.U.K.
4.Measurement of ground clearanceU.K.
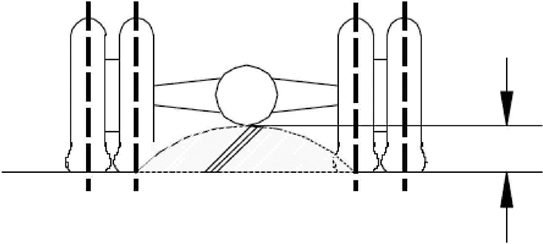
4.1.Ground clearance between the axlesU.K.
4.1.1.‘Ground clearance between the axles’ means the shortest distance between the ground plane and the lowest fixed point of the vehicle.U.K.
For the application of the definition, the distance between the last axle of a front group of axle and the first axle of a rear group of axle shall be considered.
4.1.2.No rigid part of the vehicle may project into the shaded area shown on the figure.U.K.
4.2.Ground clearance beneath one axleU.K.
4.2.1.‘Ground clearance beneath one axle’ means the distance beneath the highest point of the arc of a circle passing through the centre of the tyre footprint of the wheels on one axle (the inner wheels in the case of twin tyres) and touching the lowest fixed point of the vehicle between the wheels.U.K.
4.2.2.Where appropriate, the measurement of ground clearance shall be conducted on each of the several axles of a group of axles.U.K.
5.GradeabilityU.K.
5.1.‘Gradeability’ means the ability of a vehicle to negotiate a gradient.U.K.
5.2.To the effect of checking the gradeability of an incomplete and a complete vehicle of category M2, M3, N2 and N3, a test shall be performed.U.K.
5.3.The test shall be conducted by the technical service on a vehicle representative of the type to be tested.U.K.
5.4.At the request of the manufacturer and under the conditions specified in Annex VIII, the gradeability of a type of vehicle may be demonstrated by virtual testing.U.K.
6.Test conditions and pass-fail criterionU.K.
6.1.The conditions set out in Annex II to Commission Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012(4) shall apply.U.K.
6.2.The vehicle shall climb the gradient at a steady speed without any wheel slipping, longitudinally or laterally.U.K.
Appendix 2Digits used to supplement the codes to be used for various kinds of bodywork
Flat bed;
Drop-side;
Box body;
Conditioned body with insulated walls and equipment to maintain the interior temperature;
Conditioned body with insulated walls but without equipment to maintain the interior temperature;
Curtain-sided;
Swap body (interchangeable superstructure);
Container carrier;
Vehicles fitted with hook lift;
Tipper;
Tank;
Tank intended for transport of dangerous goods;
Livestock carrier;
Vehicle transporter;
Concrete mixer;
Concrete pump vehicle;
Timber;
Refuse collection vehicle;
Street sweeper, cleansing and drain clearing;
Compressor;
Boat carrier;
Glider carrier;
Vehicles for retail or display purposes;
Recovery vehicle;
Ladder vehicle;
Crane lorry (other than a mobile crane as defined in point 5.7 of Part A);
Aerial work platform vehicle;
Digger derrick vehicle;
Low floor trailer;
Glazing transporter;
Fire engine;
Bodywork that is not included in this list.
ANNEX IIU.K. REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PURPOSE OF EU TYPE-APPROVAL OF VEHICLES, SYSTEMS, COMPONENTS OR SEPARATE TECHNICAL UNITS
PART IU.K.Regulatory acts for EU type-approval of vehicles produced in unlimited series
| a Regulation (EU) No 540/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 April 2014 on the sound level of motor vehicles and of replacement silencing systems, and amending Directive 2007/46/EC and repealing Directive 70/157/EEC (OJ L 158, 27.5.2014, p. 131). | |||||||||||||
| b Commission Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 of 8 November 2010 concerning type-approval requirements for the space for mounting and the fixing of rear registration plates on motor vehicles and their trailers and implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning type-approval requirements for the general safety of motor vehicles, their trailers and systems, components and separate technical units intended therefor (OJ L 291, 9.11.2010, p. 22). | |||||||||||||
| c Commission Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 of 15 February 2012 concerning type-approval requirements for motor vehicles with regard to vehicle access and manoeuvrability and implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning type-approval requirements for the general safety of motor vehicles, their trailers and systems, components and separate technical units intended therefor (OJ L 43, 16.2.2012, p. 6). | |||||||||||||
| d Commission Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 of 8 November 2010 concerning type-approval requirements for motor vehicle towing devices and implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning type-approval requirements for the general safety of motor vehicles, their trailers and systems, components and separate technical units intended therefor (OJ L 291, 9.11.2010, p. 36). | |||||||||||||
| e Commission Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 of 27 July 2010 concerning type-approval requirements for windscreen defrosting and demisting systems of certain motor vehicles and implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning type-approval requirements for the general safety of motor vehicles, their trailers and systems, components and separate technical units intended therefor (OJ L 196, 28.7.2010, p. 5). | |||||||||||||
| f Commission Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 of 9 November 2010 concerning type-approval requirements for windscreen wiper and washer systems of certain motor vehicles and implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning type-approval requirements for the general safety of motor vehicles, their trailers and systems, components and separate technical units intended therefor (OJ L 292, 10.11.2010, p. 2). | |||||||||||||
| g Commission Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010 of 9 November 2010 concerning type-approval requirements for wheel guards of certain motor vehicles and implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning type-approval requirements for the general safety of motor vehicles, their trailers and systems, components and separate technical units intended therefor (OJ L 292, 10.11.2010, p. 21). | |||||||||||||
| h Commission Regulation (EU) No 109/2011 of 27 January 2011 implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards type-approval requirements for certain categories of motor vehicles and their trailers as regards spray suppression systems (OJ L 34, 9.2.2011, p. 2). | |||||||||||||
| i Commission Regulation (EU) No 458/2011 of 12 May 2011 concerning type-approval requirements for motor vehicles and their trailers with regard to the installation of their tyres and implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning type-approval requirements for the general safety of motor vehicles, their trailers and systems, components and separate technical units intended therefor (OJ L 124, 13.5.2011, p. 11). | |||||||||||||
| j Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 January 2009 on the type-approval of motor vehicles with regard to the protection of pedestrians and other vulnerable road users, amending Directive 2007/46/EC and repealing Directives 2003/102/EC and 2005/66/EC (OJ L 35, 4.2.2009, p. 1). | |||||||||||||
| l Directive 2005/64/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 October 2005 on the type-approval of motor vehicles with regard to their reusability, recyclability and recoverability and amending Council Directive 70/156/EEC (OJ L 310, 25.11.2005, p. 10). | |||||||||||||
| k Directive 2006/40/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 May 2006 relating to emissions from air conditioning systems in motor vehicles and amending Council Directive 70/156/EEC (OJ L 161, 14.6.2006, p. 12). | |||||||||||||
| m Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 January 2009 on type-approval of hydrogen-powered motor vehicles, and amending Directive 2007/46/EC (OJ L 35, 4.2.2009, p. 32). | |||||||||||||
| n Commission Regulation (EU) No 65/2012 of 24 January 2012 implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards gear shift indicators and amending Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 28, 31.1.2012, p. 24). | |||||||||||||
| o Commission Regulation (EU) No 347/2012 of 16 April 2012 implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council with respect to type-approval requirements for certain categories of motor vehicles with regard to advanced emergency braking systems (OJ L 109, 21.4.2012, p. 1). | |||||||||||||
| p Commission Regulation (EU) No 351/2012 of 23 April 2012 implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards type-approval requirements for the installation of lane departure warning systems in motor vehicles (OJ L 110, 24.4.2012, p. 18). | |||||||||||||
| q Regulation (EU) 2015/758 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2015 concerning type-approval requirements for the deployment of the eCall in-vehicle system based on the 112 service and amending Directive 2007/46/EC (OJ L 123, 19.5.2015, p. 77). | |||||||||||||
| Item | Subject | Regulatory act reference | Applicability | STU or component | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | N1 | N2 | N3 | O1 | O2 | O3 | O4 | ||||
| 1A | Sound level | Regulation (EU) No 540/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Councila | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 2A | Emissions (Euro 5 and Euro 6) light duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 | X (1) | X (1) | X (1) | X (1) | X | ||||||
| 3A | Prevention of fire risks (liquid fuel tanks) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 34 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 3B | Rear underrun protective devices (RUPDs) and their installation; rear underrun protection (RUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 58 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 4A | Space for mounting and fixing rear registration plates | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010b | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 5A | Steering equipment | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 79 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 6A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (steps, running boards and handholds) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 130/2012c | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| 6B | Door latches and door retention components | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 11 | X | X | |||||||||
| 7A | Audible warning devices and signals | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 28 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 8A | Devices for indirect vision and their installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 46 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 9A | Braking of vehicles and trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13 | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | ||
| 9B | Braking of passenger cars | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13-H | X (4) | X (4) | |||||||||
| 10A | Electromagnetic compatibility | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 10 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 12A | Interior fittings | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 21 | X | ||||||||||
| 13A | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 18 | X (4A) | X (4A) | X (4A) | X (4A) | X | ||||||
| 13B | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 116 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 14A | Protection of the driver against the steering mechanism in the event of impact | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 12 | X | X | |||||||||
| 15A | Seats, their anchorages and any head restraints | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 17 | X | X (4B) | X (4B) | X | X | X | |||||
| 15B | Seats of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 80 | X | X | |||||||||
| 16A | External projections | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 26 | X | X | |||||||||
| 17A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (reverse gear) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 17B | Speedometer equipment including its installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 39 | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 18A | Manufacturer's statutory plate and VIN | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 19A | Safety-belt anchorages, Isofix anchorages systems and Isofix top tether anchorages | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 14 | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 21A | Retro-reflecting devices for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 3 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 22A | Front and rear position lamps, stop-lamps and end-outline marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 22B | Daytime running lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 87 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 22C | Side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 91 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 23A | Direction indicators for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 6 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 24A | Illumination of rear-registration plates of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 4 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 25A | Power-driven vehicle's sealed-beam headlamps (SB) emitting an European asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 31 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25B | Filament lamps for use in approved lamp units of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 37 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 25C | Motor vehicle headlamps equipped with gas-discharge light sources | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 98 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25D | Gas-discharge light sources for use in approved gas-discharge lamp units of power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 99 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25E | Motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or LED modules | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 112 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25F | Adaptive front-lighting systems (AFS) for motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 123 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 26A | Power-driven vehicle front fog lamps | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 19 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010d | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 28A | Rear fog lamps for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 38 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 29A | Reversing lights for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 23 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 30A | Parking lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 77 | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 31A | Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and Isofix child restraint systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 16 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 32A | Forward field of vision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 125 | X | ||||||||||
| 33A | Location and identification of hand controls, tell-tales and indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 121 | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 34A | Windscreen defrosting and demisting systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 672/2010e | X | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | |||||
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010f | X | (6) | (6) | (6) | (6) | (6) | X | ||||
| 36A | Heating systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 122 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 37A | Wheel guards | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010g | X | ||||||||||
| 38A | Head restraints (headrests), whether or not incorporated in vehicle seats | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 25 | X | ||||||||||
| 41A | Emissions (Euro VI) heavy duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 | X (9) | X (9) | X | X (9) | X (9) | X | X | ||||
| 42A | Lateral protection of goods vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 73 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| 43A | Spray suppression systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 109/2011h | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| 44A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | X | ||||||||||
| 45A | Safety glazing materials and their installation on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 43 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 46A | Installation of tyres | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 458/2011i | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 46B | Pneumatic tyres for motor vehicles and their trailers (Class C1) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 30 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| 46C | Pneumatic tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers (Classes C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 54 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| 46D | Tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surfaces and rolling resistance (Classes C1, C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 117 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 46E | Temporary-use spare unit, run-flat tyres/system and tyre pressure monitoring system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 64 | X (9A) | X (9A) | X | ||||||||
| 47A | Speed limitation of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 89 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| 48A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| 49A | Commercial vehicles with regard to their external projections forward of the cab's rear panel | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 61 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X | X | X | X | X |
| 50B | Close-coupling device (CCD); fitting of an approved type of CCD | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 102 | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X | ||||||
| 51A | Burning behaviour of materials used in the interior construction of certain categories of motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 118 | X | ||||||||||
| 52A | M2 and M3 vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 107 | X | X | |||||||||
| 52B | Strength of the superstructure of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 66 | X | X | |||||||||
| 53A | Protection of occupants in the event of a frontal collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 94 | X (11) | ||||||||||
| 54A | Protection of occupants in the event of lateral collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 95 | X (12) | X (12) | |||||||||
| 56A | Vehicles for the carriage of dangerous goods | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 105 | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | ||||
| 57A | Front underrun protective devices (FUPDs) and their installation; front underrun protection (FUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 93 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 58 | Pedestrian protection | Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Councilj | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 59 | Recyclability | Directive 2005/64/EC of the European Parliament and of the Councill | X | X | |||||||||
| 61 | Air-conditioning systems | Directive 2006/40/EC of the European Parliament and of the Councilk | X | X (14) | |||||||||
| 62 | Hydrogen system | Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 of the European parliament and the Councilm | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 63 | General Safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | |
| 64 | Gear shift indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 65/2012n | X | ||||||||||
| 65 | Advanced emergency braking system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 347/2012o | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| 66 | Lane departure warning system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Commission Regulation (EU) No 351/2012p | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| 67 | Specific components for liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 67 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 68 | Vehicle alarm systems (VAS) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 97 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 69 | Electric safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 100 | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 70 | Specific components for CNG and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 110 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 71 | Cab strength | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 29 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 72 | eCall system | Regulation (EU) 2015/758 of the European Parliament and of the Councilq | X | X | |||||||||
Explanatory notesU.K.
Relevant regulatory act.
(1)For vehicles with a reference mass not exceeding 2 610 kg. At the manufacturer's request, Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 may apply to vehicles with a reference mass not exceeding 2 840 kg.U.K.
(2)In case of vehicles equipped with a LPG or CNG installation, a vehicle type-approval in accordance with UN Regulation No 67 or UN Regulation No 110 is required.U.K.
(3)The fitting of an electronic stability control (‘ESC’) system is required in accordance with Article 12 and Article 13 of Regulation (EC) No 661/2009.U.K.
(4)The fitting of an ESC system is required in accordance with Article 12 and Article 13 of Regulation (EC) No 661/2009.U.K.
(4A)If fitted, the protective device shall fulfil the requirements of UN Regulation No 18.U.K.
(4B)This Regulation applies to seats not falling within the scope of UN Regulation No 80.U.K.
(5)Vehicles of this category shall be fitted with a suitable windscreen defrosting and demisting device.U.K.
(6)Vehicles of this category shall be fitted with a suitable windscreen washing and wiping devices.U.K.
(9)For vehicles with a reference mass exceeding 2 610 kg which are not type-approved (at the manufacturer's request and provided their reference mass does not exceed 2 840 kg) under Regulation (EC) No 715/2007.U.K.
(9A)Applies only where such vehicles are fitted with equipment covered by UN Regulation No 64. Tyre pressure monitoring system for M1 vehicles applies on a compulsory basis in accordance with Article 9(2) of Regulation (EC) No 661/2009.U.K.
(10)Applies only to vehicles equipped with coupling(s).U.K.
(11)Applies to vehicles with a technically permissible maximum laden mass not exceeding 2,5 tonnes.U.K.
(12)Only applicable to vehicles where the ‘Seating Reference Point (“R” point)’ of the lowest seat is not more than 700 mm above the ground level.U.K.
(13)Applies only when the manufacturer applies for type-approval of vehicles intended for the transport of dangerous goods.U.K.
(14)Applies only for vehicles of category N1, class I as described in Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 715/2007.U.K.
(15)Compliance with Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 is mandatory, however, type-approval under this item number is not foreseen as it represents the collection of individual items 3A, 3B, 4A, 5A, 6A, 6B, 7A, 8A, 9A, 9B, 10A, 12A, 13A, 13B, 14A, 15A, 15B, 16A, 17A, 17B, 18A, 19A, 20A, 21A, 22A, 22B, 22C, 23A, 24A, 25A, 25B, 25C, 25D, 25E, 25F, 26A, 27A, 28A, 29A, 30A, 31A, 32A, 33A, 34A, 35A, 36A, 37A, 38A, 42A, 43A, 44A, 45A, 46A, 46B, 46C, 46D, 46E, 47A, 48A, 49A, 50A, 50B, 51A, 52A, 52B, 53A, 54A, 56A, 57A and 64 to 71. The series of amendments of the UN Regulations which apply on a compulsory basis are listed in Annex IV to Regulation (EC) No 661/2009. The series of amendments adopted subsequently are accepted as an alternative.U.K.
Appendix 1Regulatory acts for EU type-approval of vehicles produced in small series pursuant to Article 41
Table 1
M1 vehicles
Explanatory notesU.K.
XU.K.
Full application of the regulatory act as follows:
a type-approval certificate shall be issued;
tests and checks shall be conducted by the technical service or the manufacturer under the conditions laid down in Articles 67 to 81;
a test report shall be drafted in accordance with Annex III;
Conformity of Production (COP) shall be ensured.
AU.K.
Application of the regulatory act as follows:
all requirements of the regulatory act shall be fulfilled unless otherwise stated;
no type-approval certificate shall be required;
tests and checks shall be conducted by the technical service or the manufacturer under the conditions laid down in Articles 67 to 81;
a test report shall be drafted in accordance with Annex III;
COP shall be ensured.
BU.K.
Application of the regulatory act as follows:
Same as for letter ‘A’ with the exception that the tests and checks may be performed by the manufacturer himself, subject to the agreement of the approval authority.
CU.K.
Application of the regulatory act as follows:
only the technical requirements from the regulatory shall be fulfilled, irrespective of any transitional provision;
no type-approval certificate shall be required;
tests and checks shall be conducted by the technical service or by the manufacturer (see decisions for letter ‘B’);
a test report shall be drafted in accordance with Annex III;
COP shall be ensured.
DU.K.
Same as for decisions in letters ‘B’ and ‘C’, with the exception that a statement of compliance submitted by the manufacturer is sufficient. No test report shall be required.
The approval authority or technical service may require additional information of further evidence, if need be.
N/AU.K.
The regulatory act shall not apply. Compliance with one or more specific aspects included in the regulatory act may however be imposed.
The series of amendments of the UN Regulations to be used are listed in Annex IV to Regulation (EC) No 661/2009. The series of amendments adopted subsequently are accepted as an alternative.
Table 2
N1 vehicles a
Appendix 2Requirements for EU individual vehicle approval pursuant to Article 44
1.APPLICATIONU.K.
For the purpose of application of this Appendix, a vehicle is deemed to be new where:
it has never been registered previously; or
it has been registered for less than six months at the time of the application for individual vehicle approval.
A vehicle shall be considered registered where it has obtained a permanent, temporary or short-term administrative authorisation for entry into service in road traffic, involving its identification and the issuing of a registration number(6).
2.ADMINISTRATIVE PROVISIONSU.K.
2.1.Categorisation of the vehicleU.K.
Vehicles shall be categorised in accordance with the criteria set out in Annex I as follows:
the actual number of seating positions shall be taken into consideration; and
the technically maximum permissible laden mass shall be the maximum mass stated by the manufacturer in the country of origin and available in his official documentation.
Where it is not possible to easily determine the vehicle category because of the design of the bodywork, the conditions set out in Annex I shall apply.
2.2.Application for individual vehicle approvalU.K.
The applicant shall submit an application to the approval authority accompanied by all relevant documentation necessary for the operation of the approval procedure.
Where the submitted documentation is incomplete, falsified or forged the application for approval shall be rejected.
Only one application for a particular vehicle may be submitted in only one Member State. The approval authority may require from the applicant a written commitment that only one application will be submitted in the Member State of the approval authority.
By a particular vehicle, it shall be understood a physical vehicle the VIN of which is clearly identified.
However, any applicant may apply for EU individual vehicle approval in another Member State in respect of another particular vehicle with technical characteristics identical or similar to the one that has been granted an EU individual vehicle approval.
The model of the application form and the layout of the file shall be laid down by the approval authority.
The particulars of the vehicle requested may only consist in an appropriate selection of the information included in Annex I.
The technical requirements to be complied with are those laid down in point 4.
The technical requirements shall be those applicable to vehicles belonging to a type of vehicle currently in production, in relation to the date of the submission of the application.
With respect to the tests required under the regulatory acts listed in this Annex, the applicant shall supply a statement of compliance with recognised international standards or regulations. The statement in question may only be issued by the vehicle manufacturer.
‘Statement of compliance’ shall mean a statement issued by the office or department within the manufacturer's organisation that is duly authorised by the management to fully engage the legal responsibility of the manufacturer with respect to the design and the construction of a vehicle.
The regulatory acts for which such a statement has to be supplied shall be those referred to in point 4.
Where a statement of compliance gives rise to uncertainty, the applicant may be required to obtain from the manufacturer a piece of evidence, including a test report, in order to corroborate the manufacturer's statement.
2.3.Technical services entrusted with individual vehicle approvalsU.K.
The technical services entrusted with individual vehicle approvals shall be of category A as referred to in Article 68(1).
By way of derogation from the requirement to demonstrate their compliance with the standards listed in Appendix 1 to Annex III, technical services shall comply with the following standards:
EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 when they perform tests themselves;
EN ISO/IEC 17020:2012 when they check compliance of the vehicle with the requirements included in this Appendix.
Where specific tests requiring specific skills have to be conducted at the request of the applicant, they shall be conducted by one of the technical services notified to the Commission at the choice of the applicant.
2.4.Test reportsU.K.
Test reports shall be drafted in accordance with paragraph 5.10.2 of standard EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005.
Test reports shall be drafted in one of the languages of the Union determined by the approval authority.
Where in application of point 2.3(c) a test report has been issued in a Member State other than the one entrusted with the individual vehicle approval, the approval authority may require that the applicant submits a true translation of the test report.
Test reports shall include a description of the vehicle tested, including its identification. The parts that play a significant role with regard to the results of the tests shall be described and their identification number reported.
At the request of an applicant, a test report delivered for a system related to a particular vehicle may be presented repeatedly either by the same or another applicant for the purposes of individual approval of another vehicle.
In such a case, the approval authority shall ensure that the technical characteristics of the vehicle are properly inspected against the test report.
Inspection of the vehicle and the documentation accompanying the test report shall demonstrate that the vehicle for which an individual approval is sought has the same characteristics as the vehicle described in the report.
Only authenticated copies of a test report may be submitted.
Test reports referred to in point (d) do not include the reports drawn up in order to grant the individual vehicle approval.
2.5.In the individual vehicle approval procedure each particular vehicle shall be inspected physically by the technical service.U.K.
No exemption to this principle shall be permitted.
2.6.Where the approval authority is satisfied that the vehicle meets the technical requirements specified in this Appendix and conforms to the description included in the application, it shall grant approval in accordance with Article 44.U.K.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.7.The certificate of approval shall be drafted in accordance with Article 44.U.K.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.8.The approval authority shall keep record of all approvals granted under Article 44.U.K.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.REVIEW OF THE TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
The list of the technical requirements included in point 4 shall be regularly reviewed in order to take account of the results of the harmonisation work in progress at the World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations (WP.29) in Geneva and legislative developments in the third countries.
4.TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTSU.K.
Part I: Vehicles belonging to category M1 U.K.
| a Council Directive 70/157/EEC of 6 February 1970 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to the permissible sound level and the exhaust system of motor vehicles (OJ L 42, 23.2.1970, p. 16). | ||
| Item | Regulatory act reference | Alternative requirements |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Council Directive 70/157/EECa (Permissible sound level) | Drive-by test(a) A test shall be conducted in accordance with the ‘Method A’ referred to in Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 51. Limits are those specified in point 2.1 of Annex I to Directive 70/157/EEC. 1 decibel in addition to the permitted limits shall be allowed. (b) The test track shall comply with Annex 8 to UN Regulation No 51. A test track having different specifications may be used under the condition that correlation tests have been conducted by the technical service. A correction factor shall be applied if necessary. (c) Exhaust systems containing fibrous materials need not be conditioned as prescribed in Annex 5 to UN Regulation No 51. Stationary testA test shall be conducted in accordance with paragraph 3.2 of Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 51. |
| 2A | Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 (Emissions (Euro 5 and Euro 6) light duty vehicles/access to information) | Tailpipe emissions(a) A type I test shall be conducted in accordance with Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 using the deterioration factors set out in point 1.4 of Annex VII to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. The limits to be applied shall be those specified in Table I and Table II in Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 715/2007. (b) The vehicle shall not be required to exhibit 3 000 km as mentioned in paragraph 3.1.1 of Annex 4 to UN Regulation No 83. (c) The fuel to be used for the test shall be the reference fuel as prescribed in Annex IX to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. (d) The dynamometer shall be set up in accordance with the technical requirements set out in paragraph 3.2 of Annex 4 to UN Regulation No 83. (e) The test referred to in point (a) shall not be conducted where it can be shown that the vehicle complies with the California Code Regulations referred to in point 2.1.1 of Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. Evaporative emissionsFor petrol-fuelled engines, the presence of an evaporate emissions control system shall be required (e.g. a charcoal canister). Crankcase emissionsThe presence of a device for recycling crankcase gases shall be required. OBD(a) The vehicle shall be fitted with an OBD system. (b) OBD-interface must be able to communicate with common diagnostic tools used for periodic technical inspections. Smoke opacity(a) Vehicles equipped with a diesel-fuelled engine shall be tested in accordance with the tests methods referred to in Appendix 2 to Annex IV to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. (b) The corrected value of the absorption coefficient shall be affixed conspicuously and in a readily accessible place. CO2 emissions and fuel consumption(a) A test shall be conducted in accordance with Annex XII to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. (b) The vehicle shall not be required to exhibit 3 000 km as requested in paragraph 3.1.1 of Annex 4 to UN Regulation No 83. (c) Where the vehicle complies with the California Code Regulations referred to in point 2.1.1 of Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 and therefore no test of tailpipe emissions is required to be performed, Member States shall calculate CO2 emissions and fuel consumption with the formula laid down in the explanatory notes (b) and (c). Access to informationThe provisions regarding access to information shall not apply. Power measurement(a) The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer stating the maximum engine power output in kW as well as the corresponding engine speed in revolutions per minute. (b) An engine power output curve providing the same information may alternatively be provided by the applicant. |
| 3A | UN Regulation No 34 (Fuel tanks — Rear protective devices) | Fuel tanks(a) Fuel tanks shall comply with paragraph 5 of UN Regulation No 34 with the exception of paragraphs 5.1, 5.2 and 5.12. In particular, they shall comply with paragraphs 5.9 and 5.9.1 but no dripping test shall be conducted. (b) LPG or CNG tanks shall be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 67, series of amendments 01, or UN Regulation No 110 (a), respectively. Specific provisions for fuel tanks made of a plastic materialThe applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the fuel tank on the particular vehicle, the VIN of which has to be specified, complies either with at least one of the following:
Rear protective deviceThe rear part of the vehicle shall be constructed in accordance with paragraphs 8 and 9 of UN Regulation No 34. |
| 3B | UN Regulation No 58 (Rear underrun protection) | The rear part of the vehicle shall be constructed in accordance with paragraph 2 UN Regulation No 58. It is sufficient that the requirements set out in paragraph 2.3 are fulfilled. |
| 4A | Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 (Rear registration plate space) | Space, inclination, angles for visibility and position of the registration plate shall comply with Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010. |
| 5A | UN Regulation No 79 (Steering equipment) | Mechanical systems(a) The steering mechanism shall be built as to self-centre. In order to check compliance with this provision, a test shall be conducted in accordance with paragraphs 6.1.2 and 6.2.1 of UN Regulation No 79. (b) The failure of the power steering equipment shall not lead to a complete loss of control of the vehicle. Complex electronic vehicle control system (‘Drive-by wire’ devices)Complex electronic control system shall be permitted only if they comply with Annex 6 to UN Regulation No 79. |
| 6A | UN Regulation No 11 (Door latches and hinges) | Compliance with paragraph 6.1.5.4 of UN Regulation No 11. |
| 7A | UN Regulation No 28 (Audible warning) | ComponentsThe audible warning devices are not required to be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 28. However, they shall emit a continuous sound as required in paragraph 6.1.1 of UN Regulation No 28. Installation on vehicle(a) A test shall be conducted in accordance with paragraph 6.2 of UN Regulation No 28. (b) The maximum sound pressure level shall be in accordance with paragraph 6.2.7. |
| 8A | UN Regulation No 46 (Indirect vision devices) | Components(a) The vehicle shall be fitted with the rear-view mirrors prescribed in paragraph 15.2 of UN Regulation No 46. (b) They are not required to be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 46. (c) The radii of curvature of the mirrors shall not cause significant image distortions. At the discretion of the technical service, the radii of curvature shall be checked in accordance with the method described in Annex 7 to UN Regulation No 46. The radii of curvature shall not be less than those required by paragraph 6.1.2.2.4 of UN Regulation No 46. Installation on vehicleMeasurement shall be conducted in order to ensure that the fields of vision comply with paragraph 15.2.4. of UN Regulation No 46. |
| 9B | UN Regulation No 13-H (Braking) | General provisions(a) The braking system shall be built in accordance with paragraph 5 of UN Regulation No 13-H. (b) Vehicles shall be fitted with an electronic antilock braking system acting on all wheels. (c) The performances of the braking system shall comply with Annex III to UN Regulation No 13-H. (d) For those purposes, road tests shall be conducted on a track the surface of which possesses high adhesion. The test on the parking brake shall be conducted on a 18 % gradient (up and down). Only those tests mentioned under the headings ‘Service brake’ and ‘Parking brake’ below shall be conducted. In each case, the vehicle shall be in fully laden conditions. (e) The road test referred to in point (d) shall not be conducted where the applicant can submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the vehicle complies either with UN Regulation No 13-H, including supplement 5, or with FMVSS No 135. Service brake(a) A ‘Type 0’ test as prescribed in paragraphs 1.4.2 and 1.4.3 of Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 13-H shall be conducted. (b) In addition, a ‘Type I’ test as prescribed in paragraph 1.5 of Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 13-H shall be conducted. Parking brakeA test shall be conducted in accordance with paragraph 2.3 of Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 13-H. |
| 10A | UN Regulation No 10 (Radio interference (electromagnetic compatibility)) | Components(a) Electrical/electronic sub-assemblies are not required to be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 10. (b) However, electric/electronic devices retrofitted shall comply with UN Regulation No 10. Emitted electromagnetic radiationsThe applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the vehicle complies with UN Regulation No 10 or with the following alternative standards:
Immunity testsImmunity test shall be waived. |
| 12A | UN Regulation No 21 (Interior fittings) | Interior arrangement(a) With respect to the requirements on energy absorption, the vehicle shall be deemed to comply with UN Regulation No 21 if the vehicle is fitted with at least two front airbags, one inserted into the steering wheel and the other into the dashboard. (b) Where the vehicle is fitted with only one front air bag inserted in the steering wheel, the dashboard shall be made up of energy absorbing materials. (c) The technical service shall check that there are no sharp edges in the zones defined in paragraphs 5.1 to 5.7 of UN Regulation No 21. Electrical controls(a) Power-operated windows, roof-panel systems and partitioning systems shall be tested in accordance with paragraph 5.8 of UN Regulation No 21. The sensitivity of auto-reverse systems referred to in paragraph 5.8.3 may diverge from the requirements set out in paragraph 5.8.3.1.1 of UN Regulation No 21. (b) Electric windows which cannot be closed when the ignition is off shall be exempt from the requirements concerning auto-reverse systems. |
| 13A | UN Regulation No 18 (Anti-theft and immobiliser) | (a) In order to prevent unauthorised use, the vehicle shall be fitted with:
(b) If, in accordance with point (a), an immobiliser has to be retrofitted, it shall be of an approved type in accordance with UN Regulations No 18, No 97, or No 116. |
| 14A | UN Regulation No 12 (Protective steering) | (a) The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, the VIN of which has to be specified, complies with at least one of the following:
(b) A test in accordance with Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 12 may be conducted on a production vehicle at the request of the applicant. The test shall be conducted by a technical service that has been designated for carrying out this test. A detailed report shall be issued by that technical service to the applicant. |
| 15A | UN Regulation No 17 (Seat strength — head restraints) | Seats, seat anchorages and adjustment systemsThe applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, the VIN of which has to be specified, complies with at least one of the following:
Head restraints(a) Where the statement is based on FMVSS No 207, the head restraints shall fulfil, in addition, the requirements of paragraph 5 and Annex 4 to UN Regulation No 17. (b) Only the tests described in paragraphs 5.12, 6.5, 6.6 and 6.7 of UN Regulation No 17 shall be conducted. (c) In the other event, the applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, the VIN of which has to be specified, complies with FMVSS No 202a (Head restraints). |
| 16A | UN Regulation No 17 (Exterior projections) | (a) The external surface of the bodywork shall comply with the general requirements included in paragraph 5 of UN Regulation No 17. (b) At the discretion of the technical service the provisions referred to in paragraphs 6.1, 6.5, 6.6, 6.7, 6.8 and 6.11 of UN Regulation No 17 shall be checked. |
| 17A, 17B | UN Regulation No 39 (Speedometer — reverse gear) | Speedometer equipment(a) The dial shall comply with paragraphs 5.1 to 5.1.4 of UN Regulation No 39. (b) Where the technical service wants to verify that the speedometer is calibrated with sufficient accuracy, it may require the tests prescribed in paragraph 5.2 of UN Regulation No 39 to be conducted. Reverse gearThe gear mechanism shall include a reverse gear. |
| 18A | Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 (Statutory plates) | VIN(a) The vehicle shall be fitted with a VIN comprising a minimum of 8 and a maximum of 17 characters. VIN comprising 17 characters shall fulfil the requirements set out in international standards ISO 3779:1983 and 3780:1983. (b) VIN shall be located in a clearly visible and accessible position in such a way as it cannot be obliterated or deteriorate. (c) Where no VIN is stamped in the chassis or in the body, a Member State may require the applicant that the VIN is retrofitted in application of its national law. In such a case, the competent authority of that Member State shall supervise the operation. Statutory plateThe vehicle shall be fitted with an identification plate affixed by the vehicle manufacturer. No additional plate shall be requested after the approval by the approval authority has been granted. |
| 19A | UN Regulation No 14 (Seat belt anchorages) | The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, the VIN of which has to be specified, complies with at least one of the following:
|
| 20A | UN Regulation No 48 (Installation of lighting and light signalling devices) | (a) The lighting installation shall meet the requirements of UN Regulation No 48, series of amendments 03, with the exception of the requirements of Annexes 5 and 6 to that Regulation. (b) No exemption shall be permitted in respect of the number, the essential design characteristics, the electrical connections, and the colour of light emitted or retro-reflected of the lights and signalling devices referred to in items 21 to 26 and in items 28 to 30. (c) Lights and signalling devices that, for the purpose of fulfilling the requirements of point (a) must be retrofitted shall bear an ‘EU’ type-approval mark. (d) Lamps fitted with gas-discharged light source are only permitted in conjunction with the installation of headlamp cleaning device and an automatic headlamp-levelling device where appropriate. (e) Headlamp dipped-beams shall be adapted to the direction of traffic legally in force in the country where the vehicle is granted approval. |
| 21A | UN Regulation No 3 (Retro reflectors) | Where necessary, two additional retro reflectors bearing an ‘EU’ approval mark shall be added at the rear, the position of which shall comply with UN Regulation No 48. |
| 22A | UN Regulations No 7, No 87 and No 91 (End-outline, front position (side), rear-position (side), stop, side marker, daytime running lamps) | The requirements set out in the UN Regulations No 7, No 87 and No 91 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 23A | UN Regulation No 6 (Direction indicators) | The requirements set out in UN Regulation No 6 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 24A | UN Regulation No 4 (Rear registration plate lamps) | The requirements set out in UN Regulation No 4 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 25C, 25E, 25F | UN Regulations No 98, No 112 and No 123 (Headlamps (including bulbs)) | (a) The illumination produced by the passing beam of the headlamps fitted to the vehicle shall be checked under paragraph 6 of UN Regulation No 112 concerning headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam. The tolerances included in Annex 5 to that Regulation may be referred to for that purpose. (b) The same requirement shall be fulfilled for the passing beam of headlamps covered by UN Regulation No 98 or No 123. |
| 26A | UN Regulation No 19 (Front fog lamps) | The requirements set out in UN Regulation No 19 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights if fitted shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 27A | Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 (Towing hooks) | The requirements set out in Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 shall not apply. |
| 28A | UN Regulation No 38 (Rear fog lamps) | The requirements set out in UN Regulation No 38 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 29A | UN Regulation No 23 (Reversing lamps) | The requirements set out in UN Regulation No 23 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights if fitted shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 30A | UN Regulation No 77 (Parking lamps) | The requirements set out in UN Regulation No 77 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights if fitted shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 31A | UN Regulation No 16 (Seat belts and restraint systems) | Components(a) Seat belts shall not be required to be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 16. (b) However, each seat belt shall bear an identification label. (c) The indications on the label shall be consistent with the decision concerning seat belt anchorages (Re: entry 19). Installation requirements(a) The vehicle shall be fitted with seat belts in accordance with the requirements set out in Annex XVI to UN Regulation No 16. (b) Where a number of seat belts have to be retrofitted in accordance with point (a), they shall be of an approved type in accordance with UN Regulation No 16. |
| 32A | UN Regulation No 125 (Forward vision) | (a) No obstruction in the 180° forward field of vision of the driver as defined in paragraph 5.1.3 of UN Regulation No 125 shall be permitted. (b) By derogation from point (a), the ‘A pillars’ and the equipment listed in paragraph 5.1.3 of UN Regulation No 125 shall not be considered as obstruction. (c) The number of ‘A pillars’ shall not exceed 2. |
| 33A | UN Regulation No 121 (Identification of controls, tell-tales and indicators) | (a) The symbols including the colour of their corresponding tell-tales the presence of which is mandatory by virtue of UN Regulation No 121 shall comply with that UN Regulation. (b) Where this is not the case, the technical service shall verify that the symbols, tell-tales and indicators fitted to the vehicle provide the driver with comprehensible information about the operation of the controls in question. |
| 34A | Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 (Defrost/Demist) | The vehicle shall be equipped with adequate windscreen defrosting and windscreen demisting devices. A windscreen defrosting device which complies as a minimum with point 1.1.1 of Annex II to Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 shall be deemed ‘adequate’. A windscreen demisting device which complies as a minimum with point 1.2.1 of Annex II to Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 shall be deemed ‘adequate’. |
| 35A | Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 (Wash/Wipe) | The vehicle shall be equipped with adequate windscreen washing and windscreen wiping devices. A windscreen washing and wiping device that complies as a minimum with the conditions set out in point 1.1.5 of Annex III to Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 shall be deemed ‘adequate’. |
| 36A | UN Regulation No 122 (Heating systems) | (a) The passenger compartment shall be fitted with a heating system. (b) Combustion heaters and their installation shall comply with Annex 7 to UN Regulation No 122. In addition, LPG combustion heaters and LPG heating systems shall fulfil the requirements set out in Annex 8 to UN Regulation No 122. (c) Additional heating systems which are retrofitted shall comply with the requirements set out in that UN Regulation No 122. |
| 37A | Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010 (Wheel guards) | (a) The vehicle shall be designed as to protect other road users against thrown-up stones, mud, ice, snow and water and to reduce the dangers due to contact with the moving wheels. (b) The technical service may check that the technical requirements set out in Annex II to Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010 are complied with. (c) Section 3 of Annex I to that Regulation shall not apply. |
| 38A | UN Regulation No 25 (Head restraints) | The requirements of UN Regulation No 25 shall not apply. |
| 44A | Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 (Masses and dimensions) | (a) The requirements of point 1 of Part A of Annex I to Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 shall be fulfilled. (b) For the purposes of point (a), the masses to be considered are the following:
(c) No exemption shall be permitted in respect of the maximum permissible dimensions. |
| 45A | UN Regulation No 43 (Safety glazing) | Components(a) The glazing shall be made either of tempered or laminated safety glass. (b) Fitting of plastic glazing shall be permitted only on locations situated behind the ‘B’ pillar. (c) Glazing shall not be required to be approved under UN Regulation No 43. Installation(a) The installation requirements set out in Annex 21 to UN Regulation No 43 shall apply. (b) No tinted films that would reduce the regular light transmission under the required minimum shall be permitted on the windscreen and on the glazing located in front of the ‘B’ pillar. |
| 46 | Directive 92/23/EEC (Tyres) | ComponentsTyres shall bear an ‘EC’ type-approval mark including the symbol ‘s’ (for sound). Installation(a) The dimensions, load-capacity index and speed category of the tyres shall fulfil the requirements of Annex IV to Directive 92/23/EEC. (b) The speed category symbol of the tyre shall be compatible with the maximum design speed of the vehicle. This requirement shall apply notwithstanding the presence of a speed limiter. (c) The maximum speed of the vehicle shall be stated by the vehicle manufacturer. However, the technical service may assess the maximum design speed of the vehicle by using the engine maximum power output, the maximum number of revolutions per minute and the data concerning the kinematic chain. |
| 50A | UN Regulation No 55 (Couplings) | Separate technical units(a) OEM couplings intended for towing a trailer whose maximum mass does not exceed 1 500 kg shall not be required to be type-approved under UN Regulation No 55. A coupling is deemed OEM equipment where it is described in the owner's manual or an equivalent supporting document provided to the buyer by the vehicle manufacturer. Where such coupling is approved with the vehicle, an appropriate text shall be included in the approval certificate stating that the owner is responsible for ensuring compatibility with the coupling device fitted to the trailer. (b) Couplings other than those referred to in point (a), as well as couplings that are retrofitted, shall be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 55. Installation on the vehicleThe technical service shall check that the installation of the coupling devices comply with paragraph 6 of UN Regulation No 55. |
| 53A | UN Regulation No 94 (Frontal impact) (e) | (a) The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, of which the VIN has to be specified, complies with at least one of the following:
(b) A test in accordance with paragraph 5 of UN Regulation No 94 may be conducted on a production vehicle at the request of the applicant. The test shall be conducted by a technical service that has been designated for carrying out this test. A detailed report shall be issued by that technical service to the applicant. |
| 54A | UN Regulation No 95 (Side impact) | (a) The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, of which the VIN has to be specified complies with at least one of the following:
(b) A test in accordance with section 5 of UN Regulation No 95 may be conducted on a production vehicle at the request of the applicant. The test shall be conducted by a technical service that has been designated for carrying out this test. A detailed report shall be issued by that technical service to the applicant. |
| 58 | Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 (Pedestrian protection) | Brake assistVehicles shall be fitted with an electronic antilock braking system acting on all wheels. Pedestrian protectionThe requirements of Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 shall apply. Frontal protection systemsFrontal protection systems installed on the vehicle shall be type-approved in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 and their installation shall comply with the requirements set out in point 6 of Annex I to that Regulation. |
| 59 | Directive 2005/64/EC (Recyclability) | The requirements of that Directive shall not apply. |
| 61 | Directive 2006/40/EC (Air-conditioning system) | The requirements of that Directive shall apply. |
| 72 | Regulation (EU) 2015/758 (eCall system) | The requirements of that Regulation shall not apply. |
Part II: Vehicles belonging to category N1 U.K.
| a Commission Regulation (EU) No 582/2011 of 25 May 2011 implementing and amending Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council with respect to emissions from heavy duty vehicles (Euro VI) and amending Annexes I and III to Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 167, 25.6.2011, p. 1). | ||
| Item | Regulatory act reference | Alternative requirements |
|---|---|---|
| 2A | Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 (Emissions (Euro 5 and Euro 6) light duty vehicles / access to information) | Tailpipe emissions(a) A type 1 test shall be conducted in accordance with Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 using the deterioration factors set out in point 1.4 of Annex VII to that Regulation. The emission limits to be applied shall be those specified in Table 1 and Table 2 of Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 715/2007. (b) The vehicle shall not be required to exhibit 3 000 km as mentioned in paragraph 3.1.1 of Annex 4 to UN Regulation No 83. (c) The fuel to be used for the test shall be the reference fuel as prescribed in Annex IX to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. (d) The dynamometer shall be set up in accordance with the technical requirements of paragraph 3.2 of Annex 4 to UN Regulation No 83. (e) The test referred to in point (a) shall not be conducted where it can be shown that the vehicle complies with the California Code Regulations referred to in point 2 of Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. Evaporative emissionsFor petrol-fuelled engines, the presence of an evaporate emissions control system (e.g. a charcoal canister) shall be required. Crankcase emissionsThe presence of a device for recycling crankcase gases shall be required. OBDThe vehicle shall be fitted with an OBD system. OBD-interface must be able to communicate with common diagnostic tools used for periodic technical inspections. Smoke opacity(a) Vehicles equipped with a diesel-fuelled engine shall be tested in accordance with the tests methods referred to in Appendix 2 to Annex IV to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. (b) The corrected value of the absorption coefficient shall be affixed, conspicuously and in a readily accessible place. CO2 emissions and fuel consumption(a) A test shall be conducted in accordance with Annex XII to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008. (b) The vehicle shall not be required to exhibit 3 000 km as requested in paragraph 3.1.1 of Annex 4 to UN Regulation No 83. (c) Where the vehicle complies with the California Code Regulations referred to in point 2.1.1 of Annex I to Commission Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 and therefore no test of tailpipe emissions is required to be performed, Member States shall calculate CO2 emissions and fuel consumption with the formula laid down in the explanatory notes (b) and (c). Access to informationThe provisions regarding access to information shall not apply. Power measurement(a) The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer stating the maximum engine power output in kW as well as the corresponding regime in revolutions per minute. (b) An engine power output curve providing the same information may alternatively be provided by the applicant. |
| 3A | UN Regulation No 34 (Fuel tanks — Rear protective devices) | Fuel tanks(a) Fuel tanks shall comply with paragraph 5 of UN Regulation No 34 with the exception of paragraphs 5.1, 5.2 and 5.12. In particular, they shall comply with paragraph 5.9 and 5.9.1 but no dripping test shall be conducted. (b) LPG or CNG tanks shall be type-approved in accordance with, respectively UN Regulations No 67, series of amendments 01, or UN Regulation No 110 (a). Specific provisions for fuel tanks made of a plastic materialThe applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the fuel tank on the particular vehicle, of which the VIN has to be specified, complies either with at least one of the following:
Rear protective device(a) The rear part of the vehicle shall be constructed in accordance with paragraphs 8 and 9 of UN Regulation No 34. |
| 4A | Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 (Rear registration plate space) | Space, inclination, angles for visibility and position of the registration plate shall comply with Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010. |
| 5A | UN Regulation No 79 (Steering effort) | Mechanical systems(a) The steering mechanism shall be built as to self-centre. In order to check compliance with this provision, a test shall be conducted in accordance with paragraphs 6.1.2 and 6.2.1 of UN Regulation No 79. (b) The failure of the power steering equipment shall not lead to a complete loss of control of the vehicle. Complex electronic vehicle control system (‘Drive-by wire’ devices)Complex electronic control system shall be permitted only if they comply with Annex 6 to UN Regulation No 79. |
| 6A | UN Regulation No 11 (Door latches and hinges) | Compliance with paragraph 6.1.5.4 of UN Regulation No 11 |
| 7A | UN Regulation No 28 (Audible warning) | ComponentsThe audible warning devices are not required to be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 28. However, they shall emit a continuous sound as required in paragraph 6.1.1 of UN Regulation No 28. Installation on vehicle(a) A test shall be conducted in accordance with paragraph 6.2 of UN Regulation No 28. (b) The maximum sound pressure level shall be in accordance with paragraph 6.2.7. |
| 8A | UN Regulation No 46 (Indirect vision devices) | Components(a) The vehicle shall be fitted with the rear-view mirrors prescribed in paragraph 15.2 of UN Regulation No 46. (b) They are not required to be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 46. (c) The radii of curvature of the mirrors shall not cause significant image distortions. At the discretion of the technical service, the radii of curvature shall be checked in accordance with the method described in Appendix 1 to Annex 7 to UN Regulation No 46. The radii of curvature shall not be less than those required by paragraph 6.1.2.2.4 of UN Regulation No 46. Installation on vehicleMeasurement shall be conducted in order to ensure that the fields of vision comply with paragraph 15.2.4 of UN Regulation No 46. |
| 9B | UN Regulation No 13-H (Braking) | General provisions(a) The braking system shall be built in accordance with paragraph 5 of UN Regulation No 13-H. (b) Vehicles shall be fitted with an electronic antilock braking system acting on all wheels. (c) The performances of the braking system shall comply with Annex III to UN Regulation No 13-H. (d) For these purposes, road tests shall be conducted on a track the surface of which possesses high adhesion. The test on the parking brake shall be conducted on a 18 % gradient (up and down). Only those tests mentioned under the headings ‘Service brake’ and ‘Parking brake’ below shall be conducted. In each case, the vehicle shall be in fully laden conditions. (e) The road test referred to in point (c) shall not be conducted where the applicant can submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the vehicle complies either with UN Regulation No 13-H including supplement 5 or with FMVSS No 135. Service brake(a) A ‘Type 0’ test as prescribed in paragraphs 1.4.2 and 1.4.3 of Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 13-H shall be conducted. (b) In addition, a ‘Type I’ test as prescribed in paragraph 1.5 of Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 13-H shall be conducted. Parking brakeA test shall be conducted in accordance with paragraph 2.3 of Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 13-H. |
| 10A | UN Regulation No 10 (Radio interference (electromagnetic compatibility)) | Components(a) Electrical/electronic sub-assemblies are not required to be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 10. (b) However, electric/electronic devices retrofitted shall comply with UN Regulation No 10. Emitted electromagnetic radiationsThe applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the vehicle complies with UN Regulation No 10 or with the following alternative standards:
Immunity testsImmunity test shall be waived. |
| 13B | UN Regulation No 116 (Anti-theft and immobiliser) | (a) In order to prevent unauthorised use, the vehicle shall be fitted with a locking device as defined in paragraph 5.1.2 of UN Regulation No 116. (b) If an immobiliser is fitted, it shall comply with the technical requirements of paragraph 8.1.1 of UN Regulation No 116. |
| 14A | UN Regulation No 12 (Protective steering) | (a) The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, the VIN of which has to be specified, complies with at least one of the following:
(b) A test in accordance with Annex 3 to UN Regulation No 12 may be conducted on a production vehicle at the request of the applicant. The test shall be conducted by a technical service that has been designated for carrying out this test. A detailed report shall be issued by that technical service to the applicant. |
| 15A | UN Regulation No 17 (Seats strength — head restraints) | Seats, seat anchorages and adjustment systemsSeats and their adjustable systems shall comply with paragraph 5.3 of UN Regulation No 17. Head restraints(a) Head restraints shall fulfil the requirements of section 5 of UN Regulation No 17 and Annex 4 to UN Regulation No 17. (b) Only the tests described in paragraphs 5.12, 6.5, 6.6 and 6.7 of UN Regulation No 17 shall be conducted. |
| 17A | UN Regulation No 39 (Speedometer — reverse gear) | Speedometer equipment(a) The dial shall comply with paragraphs 5.1 to 5.1.4 of UN Regulation No 39. (b) When the technical service has reasonable grounds to believe that the speedometer is not calibrated with a sufficient accuracy, it may require that the tests prescribed in paragraph 5.2 of UN Regulation No 39 be conducted. Reverse gearThe gear mechanism shall include a reverse gear. |
| 18A | Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 (Statutory plates) | VIN(a) The vehicle shall be fitted with a VIN comprising a minimum of 8 and a maximum of 17 characters. VIN comprising 17 characters shall fulfil the requirements set out in international standards ISO 3779:1983 and 3780:1983. (b) The VIN shall be located in a clearly visible and accessible position in such a way as it cannot be obliterated or deteriorate. (c) Where no VIN is stamped in the chassis or in the body, a Member State may require that it is retrofitted in application of its national law. In such a case, the competent authority of that Member State shall supervise the operation. Statutory plateThe vehicle shall be fitted with an identification plate affixed by the vehicle manufacturer. No additional plate shall be requested after the approval has been granted. |
| 19A | UN Regulation No 14 (Seat belt anchorages) | The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, of which the VIN has to be specified, complies with at least one of the following:
|
| 20A | UN Regulation No 48 (Installation of lighting and light signalling devices) | (a) The lighting installation shall meet the essential requirements of UN Regulation No 48 series of amendments 03 with the exception of those of Annexes 5 and 6 to UN Regulation No 48. (b) No exemption shall be permitted in respect of the number, the essential design characteristics, the electrical connections, and the colour of light emitted or retro-reflected of the lights and signalling devices referred to in items 21 to 26 and in items 28 to 30. (c) Lights and signalling devices that, for the purpose of fulfilling with the requirements of point (a) must be retrofitted shall bear an ‘EU’ type-approval mark. (d) Lamps fitted with gas-discharged light source are only permitted in conjunction with the installation of headlamp cleaning device and an automatic headlamp-levelling device where appropriate. (e) Headlamp dipped-beams shall be adapted to the direction of traffic legally in force in the country where the vehicle is granted approval. |
| 21A | UN Regulation No 3 (Retro reflectors) | Where necessary, two additional retro reflectors bearing an ‘EC’ approval mark shall be added at the rear, the position of which shall comply with UN Regulation No 48. |
| 22A | UN Regulations No 7, No 87 and No 91 (End-outline, front position (side), rear-position (side), stop, side marker, daytime running lamps) | The requirements set out in UN Regulations No 7, No 87 and No 91 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 23A | UN Regulation No 6 (Direction indicators) | The requirements set out in UN Regulation No 6 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 24A | UN Regulation No 4 (Rear registration plate lamps) | The requirements set out in UN Regulation No 4 shall not apply. However, the correct functioning of the lights shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 25C, 25E, 25F | UN Regulations No 98, No 112 and No 123 (Headlamps (including bulbs)) | (a) The illumination produced by the passing beam of the headlamps fitted to the vehicle shall be checked under the provisions of paragraph 6 of UN Regulation No 112 concerning headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam. The tolerances included in Annex 5 to that Regulation may be referred to for that purpose. (b) The same requirement shall apply to the passing beam of headlamps covered by UN Regulation No 98 or No 123. |
| 26A | UN Regulation No 19 (Front fog lamps) | The provisions of UN Regulation No 19 shall be waived. However, the correct functioning of the lights if fitted shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 27A | Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 (Towing hooks) | The requirements of Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 shall be waived. |
| 28A | UN Regulation No 38 (Rear fog lamps) | The provisions of UN Regulation No 38 shall be waived. However, the correct functioning of the lights shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 29A | UN Regulation No 23 (Reversing lamps) | The provisions of UN Regulation No 23 shall be waived. However, the correct functioning of the lights if fitted shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 30A | UN Regulation No 77 (Parking lamps) | The provisions of UN Regulation No 77 shall be waived. However, the correct functioning of the lights if fitted shall be checked by the technical service. |
| 31A | UN Regulation No 16 (Seat belts and restraint systems) | Components(a) Seat belts shall not be required to be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 16. (b) However, each seat belt shall bear an identification label. (c) The indications on the label shall be consistent with the decision concerning seat belt anchorages (Re: entry 19). Installation requirements(a) The vehicle shall be fitted with seat belts in accordance with the requirements set out in Annex XVI to UN Regulation No 16. (b) Where a number of seat belts have to be retrofitted in accordance with point (a), they shall be of an approved type in accordance with UN Regulation No 16. |
| 33A | UN Regulation No 121 (Identification of controls, tell-tales and indicators) | (a) The symbols including the colour of their corresponding tell-tales the presence of which is mandatory by virtue of UN Regulation No 121 shall comply with that UN Regulation. (b) Where this is not the case, the technical service shall verify that the symbols, tell-tales and indicators fitted to the vehicle provide the driver with comprehensible information about the operation of the controls in question. |
| 34A | Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 (Defrost/Demist) | The vehicle shall be equipped with adequate windscreen defrosting and windscreen demisting devices. |
| 35A | Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 (Wash/Wipe) | The vehicle shall be equipped with adequate windscreen washing and windscreen wiping devices. |
| 36A | UN Regulation No 122 (Heating systems) | (a) The passenger compartment shall be fitted with a heating system. (b) Combustion heaters and their installation shall comply with Annex 7 to UN Regulation No 122. In addition, LPG combustion heaters and LPG heating systems shall fulfil the requirements set out in Annex 8 to UN Regulation No 122. (c) Additional heating systems that are retrofitted shall comply with the requirements set out in UN Regulation No 122. |
| 41A | Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 (Emissions (Euro VI) heavy-duty vehicles – OBD) | Tailpipe emissions(a) A test shall be conducted in accordance with Annex III to Commission Regulation (EU) No 582/2011a using the deterioration factors set out in point 3.6.1 of Annex VI to Regulation (EU) No 582/2011. (b) The limits to be applied shall be those set out in the table of Annex I to Regulation (EC) No 595/2009. (c) The fuel to be used for the test shall be the reference fuel as prescribed in Annex IX to Regulation (EU) No 582/2011. CO2 emissionsThe CO2 emissions and fuel consumption shall be determined in accordance with Annex VIII to Regulation (EU) No 582/2011. OBD(a) The vehicle shall be fitted with an OBD system. (b) The OBD-interface must be able to communicate with an external OBD scan-tool as described in Annex X to Regulation (EU) No 582/2011. Requirements to ensure the correct operation of NOx control measuresThe vehicle shall be fitted with a system ensuring the correct operation of NOx control measures in accordance with Annex XIII to Regulation (EU) No 582/2011. Power measurement(a) The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer stating the maximum engine power output in Kw as well as the corresponding regime. (b) An engine power output curve providing the same information may alternatively be provided by the applicant. |
| 45A | UN Regulation No 43 | Components(a) The glazing shall be made either of tempered or laminated safety glass. (b) Fitting of plastic glazing shall be permitted only on locations situated behind the ‘B’ pillar. (c) Glazing shall not be required to be approved under UN Regulation No 43. Installation(a) The installation requirements set out in Annex 21 to UN Regulation No 43 shall apply. (b) No tinted films that reduce the regular light transmission under the required minimum shall be permitted on the windscreen and on the glazing located in front of the ‘B’ pillar. |
| 46A | Commission Regulation (EU) 458/2011 (Installation of tyres) | Installation(a) The dimensions, load-capacity index and speed category of the tyres shall fulfil the requirements of Commission Regulation (EU) 458/2011. (b) The speed category symbol of the tyre shall be compatible with the maximum design speed of the vehicle. (c) This requirement shall apply notwithstanding the presence of a speed limiter. (d) The maximum speed of the vehicle shall be stated by the vehicle manufacturer. However, the technical service may assess the maximum design speed of the vehicle by using the engine maximum power output, the maximum number of revolutions per minute and the data concerning the kinematic chain. |
| 46B | UN Regulation No 30 (C1 tyres) | Components Tyres shall bear a type-approval mark. |
| 46D | UN Regulation No 117 (Tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surface and rolling resistance) | Components Tyres shall bear a type-approval mark. |
| 46E | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 64 (Temporary use spare unit, run-flat tyres, tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surface and rolling resistance) | Components Tyres shall bear type-approval mark. The fitting of TPMS shall not be required. |
| 48A | Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 (Masses and dimensions) | (a) The requirements of Annex I, Part A to Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 shall be fulfilled. However, the requirements set out in point 5 of Part A of Annex I do not need to be fulfilled. (b) For the purposes of point (a) the masses to be considered are the following:
(c) Technical changes made by the applicant in order to decrease the maximum technically permissible laden mass of the vehicle to 3,5 tonnes or less, so that the vehicle may be granted individual vehicle approval shall not be permitted. (d) No exemption shall be permitted in respect of the maximum permissible dimensions. |
| 49A | UN Regulation No 61 (External projections of cabs) | (a) The general requirements set out in section 5 of UN Regulation No 17 shall be fulfilled. (b) At the discretion of the technical service, the requirements set out in paragraphs 6.1, 6.5, 6.6, 6.7, 6.8 and 6.11 of UN Regulation No 17 shall be fulfilled. |
| 50A | UN Regulation No 55 (Couplings) | Separate technical units(a) OEM couplings intended for towing a trailer of which the maximum mass does not exceed 1 500 kg shall not be required to be type-approved under UN Regulation No 55. (b) A coupling is deemed OEM equipment where it is described in the owner's manual or in an equivalent supporting document provided to the buyer by the vehicle manufacturer. (c) Where such coupling is approved with the vehicle, an appropriate text shall be included in the approval certificate stating that the owner is responsible for ensuring compatibility with the coupling device fitted to the trailer. (d) Couplings other than those referred to in point (a), as well as couplings that are retrofitted, shall be type-approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 55. Installation on the vehicleThe technical service shall check that the installation of the coupling devices comply with paragraph 6 to UN Regulation No 55. |
| 54 | UN Regulation No 95 (Side impact) | (a) The applicant shall submit a statement from the manufacturer establishing that the particular vehicle, of which the VIN has to be specified, complies with at least one of the following:
(b) A test in accordance with section 5 of UN Regulation No 95 may be conducted on a production vehicle at the request of the applicant. (c) The test shall be conducted by a technical service that been designated for carrying out this test. A detailed report shall be issued by that technical service to the applicant. |
| 56A | UN Regulation No 105 (Vehicles intended for the transport of dangerous goods) | Vehicles intended for the transport of dangerous goods shall comply with UN Regulation No 105. |
| 58 | Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 (Pedestrian protection) | Brake assistVehicles shall be fitted with an electronic antilock braking system acting on all wheels. Pedestrian protectionUntil 24 February 2018, the requirements of Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 shall not apply to vehicles of which the maximum mass does not exceed 2 500 kg and until 24 August 2019 to vehicles of which the maximum mass exceeds 2 500 kg. Frontal protection systemsHowever, frontal protection systems installed on the vehicle shall be type-approved in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 and their installation shall comply with the requirements set out in point 6 of Annex I to that Regulation. |
| 59 | Directive 2005/64/EC (Recyclability) | The requirements of that Directive shall not apply. |
| 61 | Directive 2006/40/EC (Air-conditioning system) | The requirements of that Directive shall apply. |
| 72 | Regulation (EU) 2015/758 (eCall system) | The requirements of that Regulation shall not apply. |
Explanatory notes to Appendix 2U.K.
1.Abbreviations used in this Appendix:U.K.
:
original equipment provided by the manufacturer
:
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard of the U.S. Department of Transportation
:
Japan Safety Regulations for Road Vehicles
:
Society of Automotive Engineers
:
Comité international spécial des perturbations radioélectriques.
2.Remarks:U.K.
the complete LPG or CNG installation shall be checked against the UN Regulations No 67, No 110 or No 115, as appropriate;
the formula to be used for the assessment of CO2 emissions shall be as follows:
Petrol engine and manual gearbox:
CO2 = 0,047 m + 0,561 p + 56,621
Petrol engine and automatic gearbox
CO2 = 0,102 m + 0,328 p + 9,481
Petrol engine and hybrid electric:
CO2 = 0,116 m – 57,147
Diesel engine and manual gearbox:
CO2 = 0,108 m – 11,371
Diesel engine and automatic gearbox:
CO2 = 0,116 m – 6,432
Where: CO2 is the combined mass of CO2 emissions in g/km, ‘m’ is the mass of the vehicle in running order in kg and ‘p’ the maximum engine power output in kW.
Combined mass of CO2 shall be calculated with one decimal place, then rounded to the nearest whole number as follows:
if the figure following the decimal point is below 5, the total is rounded down;
if the figure following the decimal point is equal to 5 or above 5, the total is rounded up;
the formula to be used for the assessment of fuel consumption shall be as follows:
CFC = CO2 × k – 1
Where: CFC is the combined fuel consumption in l/100 km, CO2 is the combined mass of CO2 emissions in g/km after it has been rounded in accordance with the rule referred to in Remark (2 b), ‘k’ a coefficient equal to:
23,81 in the case of a petrol engine;
26,49 in the case of a diesel engine.
Combined fuel consumption shall be calculated with two decimal places, then rounded as follows:
if the figure following the first decimal is below 5, the total is rounded down;
if the figure following the first decimal is equal to 5 or above 5, the total is rounded up.
PART IIU.K.List of UN Regulations recognised as an alternative to the Directives or Regulations referred to in Part I
Where reference is made to a separate Directive or Regulation in the table of Part I, an approval granted under the following UN Regulations which the Union has accepted as a Contracting Party to the ‘Revised 1958 Agreement’ by virtue of Decision 97/836/EC, or subsequent Council Decisions as referred to in Article 3(3) of that Decision, shall be considered as equivalent to an EU type-approval granted under the relevant separate Directive or Regulation.
Any further amendment to the UN Regulations listed in the following table(5) shall also be deemed to be equivalent to an EU type-approval, subject to the Decision referred to in Article 4(2) of Decision 97/836/EC.
| a The numbering of the entries in this table refers to the numbering used in the table of Part I. | |||
| Subject | UN Regulation number | Series of amendments | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1Aa | Permissible sound level (not covering AVAS and replacement silencers) | 51 | 03 |
| AVAS | 138 | 00 | |
| Replacement silencing systems | 59 | 02 | |
| 9B | Braking of passenger cars (ESC part) | 140 | 00 |
| 58 | Pedestrian protection (not covering brake assist) | 127 (pedestrian protection) | 00 |
| Pedestrian protection (brake assist part) | 13-H (brake assist) or 139 (brake assist) | 00 (Supplement 9 and above) 00 | |
| 65 | Advanced emergency braking system | 131 | 01 |
| 66 | Lane departure warning system | 130 | 00 |
| Where the separate Directive or Regulation contains installation requirements, these apply also to components and separate technical units approved in accordance with UN Regulations. | |||
PART IIIU.K.List of regulatory acts setting out the requirements for the purpose of EU type-approval of special purpose vehicles
Appendix 1Motor-caravans, ambulances and hearses
| a Technically permissible maximum laden mass. | ||||||
| Item | Subject | Regulatory act reference | M1 ≤ 2 500 kga | M1 > 2 500 kga | M2 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | Sound level | Regulation (EU) No 540/2014 | H | G+H | G+H | G+H |
| 2 | Emissions (Euro 5 and Euro 6) light duty vehicles / access to information | Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 | Q (1) | G+Q (1) | G+Q (1) | |
| 3A | Prevention of fire risks (liquid fuel tanks) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 34 | F (2) | F (2) | F (2) | F (2) |
| 3B | Rear underrun protective devices (RUPDs) and their installation; rear underrun protection (RUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 58 | X | X | X | X |
| 4A | Space for mounting and fixing rear registration plates | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 | X | X | X | X |
| 5A | Steering equipment | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 79 | X | G | G | G |
| 6A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | X | ||
| 6B | Door latches and door retention components | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 11 | B | G+B | ||
| 7A | Audible warning devices and signals | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 28 | X | X | X | X |
| 8A | Devices for indirect vision and their installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 46 | X | G | G | G |
| 9A | Braking of vehicles and trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13 | G (3) | G (3) | ||
| 9B | Braking of passenger cars | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13-H | X (4) | G+A1 | ||
| 10A | Electromagnetic compatibility | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 10 | X | X | X | X |
| 12A | Interior fittings | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 21 | C | G+C | ||
| 13A | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 18 | G (4A) | G (4A) | ||
| 13B | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 116 | X | G | ||
| 14A | Protection of the driver against the steering mechanism in the event of impact | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 12 | X | G | ||
| 15A | Seats, their anchorages and any head restraints | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 17 | D | G+D | G+D (4B) | G+D (4B) |
| 15B | Seats of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 80 | X | X | ||
| 16A | External projections | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 26 | X for the cab; A+Z for the remaining part | G for the cab; A+Z for the remaining part | ||
| 17A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | X | X | X |
| 17B | Speedometer equipment including its installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 39 | X | X | X | X |
| 18A | Manufacturer's statutory plate and VIN | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 | X | X | X | X |
| 19A | Safety-belt anchorages, Isofix anchorages systems and Isofix top tether anchorages | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 14 | D | G+L | G+L | G+L |
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 | A+N | A+G+N for the cab; A+N for the remaining part | A+G+N for the cab; A+N for the remaining part | A+G+N for the cab; A+N for the remaining part |
| 21A | Retro-reflecting devices for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 3 | X | X | X | X |
| 22A | Front and rear position lamps, stop-lamps and end-outline marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 7 | X | X | X | X |
| 22B | Daytime running lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 87 | X | X | X | X |
| 22C | Side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 91 | X | X | X | X |
| 23A | Direction indicators for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 6 | X | X | X | X |
| 24A | Illumination of rear-registration plates of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 4 | X | X | X | X |
| 25A | Power-driven vehicle's sealed-beam headlamps (SB) emitting an European asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 31 | X | X | X | X |
| 25B | Filament lamps for use in approved lamp units of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 37 | X | X | X | X |
| 25C | Motor vehicle headlamps equipped with gas-discharge light sources | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 98 | X | X | X | X |
| 25D | Gas-discharge light sources for use in approved gas-discharge lamp units of power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 99 | X | X | X | X |
| 25E | Motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or LED modules | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 112 | X | X | X | X |
| 25F | Adaptive front-lighting systems (AFS) for motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 123 | X | X | X | X |
| 26A | Power-driven vehicle front fog lamps | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 19 | X | X | X | X |
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 | E | E | E | E |
| 28A | Rear fog lamps for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 38 | X | X | X | X |
| 29A | Reversing lights for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 23 | X | X | X | X |
| 30A | Parking lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 77 | X | X | X | X |
| 31A | Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and Isofix child restraint systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 16 | D | G+M | G+M | G+M |
| 32A | Forward field of vision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 125 | X | G | ||
| 33A | Location and identification of hand controls, tell-tales and indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 121 | X | X | X | X |
| 34A | Windscreen defrosting and demisting systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 | X | G (5) | (5) | (5) |
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 | X | G (6) | (6) | (6) |
| 36A | Heating systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 122 | X | X | X | X |
| 37A | Wheel guards | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010 | X | G | ||
| 38A | Head restraints (headrests), whether or not incorporated in vehicle seats | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 25 | D | G+D | ||
| 44A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | X | X | ||
| 45A | Safety glazing materials and their installation on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 43 | J | G+J | G+J | G+J |
| 46A | Installation of tyres | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 458/2011 | X | G | G | G |
| 46B | Pneumatic tyres for motor vehicles and their trailers (Class C1) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 30 | X | G | ||
| 46C | Pneumatic tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers (Classes C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 54 | — | G | G | G |
| 46D | Tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surfaces and rolling resistance (Classes C1, C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 117 | X | G | G | G |
| 46E | Temporary-use spare unit, run-flat tyres/system and tyre pressure monitoring system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 64 | X | G | ||
| 47A | Speed limitation of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 89 | X | X | ||
| 48A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | X | X | ||
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 | X (10) | G (10) | G (10) | G (10) |
| 51A | Burning behaviour of materials used in the interior construction of certain categories of motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 118 | G for the cab; X for the remaining part | |||
| 52A | M2 and M3 vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 107 | A | A | ||
| 52B | Strength of the superstructure of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 66 | A | A | ||
| 53A | Protection of occupants in the event of a frontal collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 94 | N/A | N/A | ||
| 54A | Protection of occupants in the event of lateral collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 95 | N/A | N/A | ||
| 58 | Pedestrian protection | Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 | X | N/A However, any frontal protection systems supplied with the vehicle shall comply and shall be marked | ||
| 59 | Recyclability | Directive 2005/64/EC | N/A | N/A | ||
| 61 | Air-conditioning system | Directive 2006/40/EC | X | G (14) | ||
| 62 | Hydrogen system | Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 | Q | G+Q | G+Q | G+Q |
| 63 | General safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) |
| 64 | Gear shift indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 65/2012 | X | G | ||
| 65 | Advanced emergency braking system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 347/2012 | N/A (16) | N/A (16) | ||
| 66 | Lane departure warning system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 351/2012 | N/A (17) | N/A (17) | ||
| 67 | Specific components for liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 67 | X | X | X | X |
| 68 | Vehicle alarm systems (VAS) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 97 | X | G | ||
| 69 | Electrical safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 100 | X | X | X | X |
| 70 | Specific components for CNG and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 110 | X | X | X | X |
| 72 | eCall system | Regulation (EU) 2015/758 | G | G | N/A | N/A |
Additional requirements for ambulancesU.K.
The patient compartment of ambulances shall comply with the requirements of EN 1789:2007 +A1: 2010 +A2:2014 on Medical vehicles and their equipment – Road ambulances with the exception of section 6.5, list of equipment. Proof of compliance shall be provided with a test report of a technical service. If a wheelchair space is foreseen, the requirements of Appendix 3 relating to the wheelchair tie-down and occupant restraint systems shall apply.
Appendix 2Armoured vehicles
| Item | Subject | Regulatory act reference | M1 | M2 | M3 | N1 | N2 | N3 | O1 | O2 | O3 | O4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | Sound level | Regulation (EU) No 540/2014 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 2 | Emissions (Euro 5 and Euro 6) light duty vehicles / access to information | Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 | A (1) | A (1) | A (1) | A (1) | ||||||
| 3A | Prevention of fire risks (liquid fuel tanks) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 34 | X (2) | X (2) | X (2) | X (2) | X (2) | X (2) | X | X | X | X |
| 3B | Rear underrun protective devices (RUPDs) and their installation; rear underrun protection (RUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 58 | X | X | X | X | A | A | X | X | X | X |
| 4A | Space for mounting and fixing rear registration plates | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 5A | Steering equipment | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 79 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 6A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (steps, running boards and handholds) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 6B | Door latches and door retention components | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 11 | X | X | ||||||||
| 7A | Audible warning devices and signals | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 28 | A+K | A+K | A+K | A+K | A+K | A+K | ||||
| 8A | Devices for indirect vision and their installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 46 | A | A | A | A | A | A | ||||
| 9A | Braking of vehicles and trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13 | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | |
| 9B | Braking of passenger cars | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13-H | X (4) | X (4) | ||||||||
| 10A | Electromagnetic compatibility | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 10 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 12A | Interior fittings | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 21 | A | |||||||||
| 13A | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 18 | X (4A) | X (4A) | X (4A) | X (4A) | ||||||
| 13B | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 116 | X | X | ||||||||
| 14A | Protection of the driver against the steering mechanism in the event of impact | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 12 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
| 15A | Seats, their anchorages and any head restraints | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 17 | X | D (4B) | D (4B) | D | D | D | ||||
| 15B | Seats of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 80 | D | D | ||||||||
| 16A | External projections | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 26 | A | |||||||||
| 17A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (reverse gear) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 17B | Speedometer equipment including its installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 39 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 18A | Manufacturer's statutory plate and VIN | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 19A | Safety-belt anchorages, Isofix anchorages systems and Isofix top tether anchorages | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 14 | A | A | A | A | A | A | ||||
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N |
| 21A | Retro-reflecting devices for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 3 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 22A | Front and rear position lamps, stop-lamps and end-outline marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 22B | Daytime running lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 87 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 22C | Side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 91 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 23A | Direction indicators for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 6 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 24A | Illumination of rear-registration plates of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 4 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 25A | Power-driven vehicle's sealed-beam headlamps (SB) emitting an European asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 31 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25B | Filament lamps for use in approved lamp units of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 37 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 25C | Motor vehicle headlamps equipped with gas-discharge light sources | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 98 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25D | Gas-discharge light sources for use in approved gas-discharge lamp units of power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 99 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25E | Motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or LED modules | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 112 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25F | Adaptive front-lighting systems (AFS) for motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 123 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 26A | Power-driven vehicle front fog lamps | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 19 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 | A | A | A | A | A | A | ||||
| 28A | Rear fog lamps for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 38 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 29A | Reversing lights for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 23 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 30A | Parking lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 77 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 31A | Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and Isofix child restraint systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 16 | A | A | A | A | A | A | ||||
| 32A | Forward field of vision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 125 | S | |||||||||
| 33A | Location and identification of hand controls, tell-tales and indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 121 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 34A | Windscreen defrosting and demisting systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 | A | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | ||||
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 | A | (6) | (6) | (6) | (6) | (6) | ||||
| 36A | Heating systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 122 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 37A | Wheel guards | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010 | X | |||||||||
| 38A | Head restraints (headrests), whether or not incorporated in vehicle seats | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 25 | X | |||||||||
| 41A | Emissions (Euro VI) heavy duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 | X (9) | X (9) | X | X (9) | X (9) | X | ||||
| 42A | Lateral protection of goods vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 73 | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| 43A | Spray suppression systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 109/2011 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| 44A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | X | |||||||||
| 45A | Safety glazing materials and their installation on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 43 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 46A | Installation of tyres | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 458/2011 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| 46B | Pneumatic tyres for motor vehicles and their trailers (Class C1) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 30 | A | A | A | A | ||||||
| 46C | Pneumatic tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers (Classes C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 54 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |||
| 46D | Tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surfaces and rolling resistance (Classes C1, C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 117 | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A |
| 46E | Temporary-use spare unit, run-flat tyres/system and tyre pressure monitoring system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 64 | A (9A) | A (9A) | ||||||||
| 47A | Speed limitation of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 89 | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| 48A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 49A | Commercial vehicles with regard to their external projections forward of the cab's rear panel | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 61 | A | A | A | |||||||
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X | X | X | X |
| 50B | Close-coupling device (CCD); fitting of an approved type of CCD | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 102 | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | ||||||
| 51A | Burning behaviour of materials used in the interior construction of certain categories of motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 118 | X | |||||||||
| 52A | M2 and M3 vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 107 | A | A | ||||||||
| 52B | Strength of the superstructure of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 66 | A | A | ||||||||
| 53A | Protection of occupants in the event of a frontal collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 94 | N/A | |||||||||
| 54A | Protection of occupants in the event of lateral collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 95 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
| 56A | Vehicles for the carriage of dangerous goods | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 105 | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | |||
| 57A | Front underrun protective devices (FUPDs) and their installation; front underrun protection (FUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 93 | X | X | ||||||||
| 58 | Pedestrian protection | Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
| 59 | Recyclability | Directive 2005/64/EC | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
| 61 | Air-conditioning system | Directive 2006/40/EC | X | X (14) | ||||||||
| 62 | Hydrogen system | Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 | A | A | A | A | A | A | ||||
| 63 | General Safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) |
| 64 | Gear shift indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 65/2012 | X | |||||||||
| 65 | Advanced emergency braking system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 347/2012 | (16) | (16) | (16) | (16) | ||||||
| 66 | Lane departure warning system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 351/2012 | (17) | (17) | (17) | (17) | ||||||
| 67 | Specific components for liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 67 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 68 | Vehicle alarm systems (VAS) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 97 | X | X | ||||||||
| 69 | Electrical safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 100 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 70 | Specific components for CNG and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 110 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 72 | eCall system | Regulation (EU) 2015/758 | G | N/A | N/A | G | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Appendix 3Wheelchair accessible vehicles
| Item | Subject | Regulatory act | M1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | Sound level | Regulation (EU) No 540/2014 | G+W9 |
| 2 | Emissions (Euro 5 and Euro 6) light duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 | G+W1 |
| 3A | Prevention of fire risks (liquid fuel tanks) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 34 | X+W2 |
| 3B | Rear underrun protective devices (RUPDs) and their installation; rear underrun protection (RUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 58 | X |
| 4A | Space for mounting and fixing rear registration plates | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 | X |
| 5A | Steering equipment | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 79 | G |
| 6A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (steps, running boards and handholds) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X |
| 6B | Door latches and door retention components | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 11 | X |
| 7A | Audible warning devices and signals | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 28 | X |
| 8A | Devices for indirect vision and their installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 46 | X |
| 9B | Braking of passenger cars | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13-H | G+A1 |
| 10A | Electromagnetic compatibility | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 10 | X |
| 12A | Interior fittings | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 21 | G+C |
| 13B | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 116 | X |
| 14A | Protection of the driver against the steering mechanism in the event of impact | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 12 | G |
| 15A | Seats, their anchorages and any head restraints | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 17 | G+W3 |
| 16A | External projections | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 26 | G+W4 |
| 17A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (reverse gear) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X |
| 17B | Speedometer equipment including its installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 39 | X |
| 18A | Manufacturer's statutory plate and VIN | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 | X |
| 19A | Safety-belt anchorages, Isofix anchorages systems and Isofix top tether anchorages | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 14 | X+W5 |
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 | X |
| 21A | Retro-reflecting devices for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 3 | X |
| 22A | Front and rear position lamps, stop-lamps and end-outline marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 7 | X |
| 22B | Daytime running lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 87 | X |
| 22C | Side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 91 | X |
| 23A | Direction indicators for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 6 | X |
| 24A | Illumination of rear-registration plates of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 4 | X |
| 25A | Power-driven vehicle's sealed-beam headlamps (SB) emitting an European asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 31 | X |
| 25B | Filament lamps for use in approved lamp units of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 37 | X |
| 25C | Motor vehicle headlamps equipped with gas-discharge light sources | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 98 | X |
| 25D | Gas-discharge light sources for use in approved gas-discharge lamp units of power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 99 | X |
| 25E | Motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or LED modules | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 112 | X |
| 25F | Adaptive front-lighting systems (AFS) for motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 123 | X |
| 26A | Power-driven vehicle front fog lamps | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 19 | X |
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 | E |
| 28A | Rear fog lamps for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 38 | X |
| 29A | Reversing lights for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 23 | X |
| 30A | Parking lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 77 | X |
| 31A | Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and Isofix child restraint systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 16 | X+W6 |
| 32A | Forward field of vision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 125 | G |
| 33A | Location and identification of hand controls, tell-tales and indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 121 | X |
| 34A | Windscreen defrosting and demisting systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 | G (5) |
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 | G (6) |
| 36A | Heating systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 122 | X |
| 37A | Wheel guards | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010 | G |
| 38A | Head restraints (headrests), whether or not incorporated in vehicle seats | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 25 | X |
| 41A | Emissions (Euro VI) heavy duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 | X+W1 (9) |
| 44A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | X+W8 |
| 45A | Safety glazing materials and their installation on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 43 | G |
| 46A | Installation of tyres | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 458/2011 | X |
| 46B | Pneumatic tyres for motor vehicles and their trailers (Class C1) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 30 | X |
| 46D | Tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surfaces and rolling resistance (Classes C1, C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 117 | X |
| 46E | Temporary-use spare unit, run-flat tyres/system and tyre pressure monitoring system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 64 | G (9A) |
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 | X (10) |
| 53A | Protection of occupants in the event of a frontal collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 94 | N/A |
| 54A | Protection of occupants in the event of lateral collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 95 | N/A |
| 58 | Pedestrian protection | Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 | G |
| 59 | Recyclability | Directive 2005/64/EC | N/A |
| 61 | Air-conditioning systems | Directive 2006/40/EC | G |
| 62 | Hydrogen system | Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 | X |
| 63 | General Safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 | X (15) |
| 64 | Gear shift indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 65/2012 | G |
| 67 | Specific components for liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 67 | X |
| 68 | Vehicle alarm systems (VAS) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 97 | X |
| 69 | Electric safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 100 | X |
| 70 | Specific components for CNG and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 110 | X |
| 72 | eCall system | Regulation (EU) 2015/758 | G |
Additional requirements for testing the wheelchair tie-down and occupant restraint systemU.K.
The following point 2 and either point 3 or 4 shall apply.
1.DefinitionsU.K.
1.1.Surrogate wheelchair (SWC) means a rigid, re-usable test wheelchair, as defined in section 3 of international standard ISO 10542-1:2012.U.K.
1.2.Point P means a representation of the position of the wheelchair occupant's hip when seated in the SWC, as defined in section 3 of international standard ISO 10542-1:2012.U.K.
2.General requirementsU.K.
2.1.Each wheelchair location shall be provided with anchorages to which a wheelchair tie-down and occupant restraint system (WTORS) shall be fitted.U.K.
2.2.The wheelchair occupant's lower belt anchorages shall be located in accordance with UN Regulation No 14.07, paragraph 5.4.2.2, relative to Point P on the SWC, when placed in the travelling position designated by the manufacturer. The upper actual anchorage(s) shall be located at least 1 100 mm above the horizontal plane passing through the points of contact between the rear tyres of the SWC and the vehicle floor. That condition shall still be satisfied after the test carried out in accordance with point 3 of this Appendix.U.K.
2.3.An assessment shall be made of the WTORS occupant belt to ensure compliance with the UN Regulation No 16.06, paragraphs 8.2.2 to 8.2.2.4 and 8.3.1 to 8.3.4.U.K.
2.4.The minimum number of ISOFIX child seat anchorages need not to be provided. In the case of a multi-stage type-approval where an ISOFIX anchorage system has been affected by the conversion, either the system shall be re-tested or the anchorages shall be rendered unusable. In the latter case the ISOFIX labels shall be removed and appropriate information shall be given to the vehicle purchaser.U.K.
3.Static in-vehicle testingU.K.
3.1.Wheelchair occupant restraint anchoragesU.K.
3.1.1.The wheelchair occupant restraint anchorages shall resist the static forces prescribed for occupant restraint anchorages in UN Regulation No 14.07, simultaneously with the static forces applied to the wheelchair tie-down anchorages as specified in point 3.2 of this Appendix.U.K.
3.2.Wheelchair tie-down anchoragesU.K.
The wheelchair tie-down anchorages shall resist the following forces, for at least 0,2 seconds, applied via the SWC (or a suitable surrogate wheelchair having a wheelbase, seat height and tie-down attachment points in accordance with the specification for the SWC), at a height of 300 +/– 100 mm from the surface on which the SWC rests:
In the case of a forward-facing wheelchair, a simultaneous force, coincident with the force applied to the occupant restraint anchorages, of 24,5 kN, and
a second test applying a static force of 8,2 kN directed towards the rear of the vehicle.
In the case of a rearward-facing wheelchair, a simultaneous force, coincident with the force applied to the occupant restraint anchorages, of 8,2 kN, and
a second test applying a static force of 24,5 kN directed towards the front of the vehicle.
3.3.Components of the systemU.K.
3.3.1.All components of the WTORS shall meet the relevant requirements of international standard ISO 10542-1:2012. However, the dynamic test specified in Annex A and paragraphs 5.2.2 and 5.2.3 of international standard ISO 10542-1:2012 shall be carried out on the complete WTORS using the vehicle anchorage geometry instead of the test geometry specified in Annex A of international standard ISO 10542-1:2012. This may be carried out within the vehicle structure or on a surrogate structure representative of the vehicle's WTORS anchorage geometry. The location of each anchorage shall lie within the tolerance provided for in paragraph 7.7.1 of UN Regulation No 16.06.U.K.
3.3.2.Where the occupant restraint part of the WTORS is approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 16.06, it shall be subject to the dynamic test of the complete WTORS specified in paragraph 3.3.1 of this Appendix but the requirements of paragraphs 5.1, 5.3 and 5.4 of international standard ISO10542-1:2012 shall be considered to have been met.U.K.
4.Dynamic in-vehicle testingU.K.
4.1.The full assembly of the WTORS system shall be tested by an in-vehicle dynamic test in accordance with paragraphs 5.2.2 and 5.2.3 and Annex A of international standard ISO 10542-1:2012, testing all components/anchorages simultaneously, using a vehicle body-in-white or representative structure.U.K.
4.2.The component parts of the WTORS shall meet the relevant requirements of international standard ISO 10542-1:2012, paragraphs 5.1, 5.3 and 5.4. These requirements shall be deemed to have been met in respect of the occupant restraint if it is approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 16.06.U.K.
Appendix 4
Other special purpose vehicles(including special group, multi-equipment carrier and trailer caravans)U.K.
The exemptions provided for in this Appendix are only permitted if the manufacturer demonstrates to the satisfaction of the approval authority that the vehicle, due to the special function, cannot meet all the requirements set out in Part I of this Annex.
| Item | Subject | Reference to regulatory act | M2 | M3 | N1 | N2 | N3 | O1 | O2 | O3 | O4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | Sound level | Regulation (EU) No 540/2014 | H | H | H | H | H | ||||
| 2 | Emissions (Euro 5 and Euro 6) light duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 | Q (1) | Q+V1 (1) | Q+V1 (1) | ||||||
| 3A | Prevention of fire risks (liquid fuel tanks) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 34 | F | F | F | F | F | X | X | X | X |
| 3B | Rear underrun protective devices (RUPDs) and their installation; rear underrun protection (RUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 58 | X | X | A | A | A | X | X | X | X |
| 4A | Space for mounting and fixing rear registration plates | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 | A+R | A+R | A+R | A+R | A+R | A+R | A+R | A+R | A+R |
| 5A | Steering equipment | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 79 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 6A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (steps, running boards and handholds) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | X | B | B | B | ||||
| 6B | Door latches and door retention components | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 11 | B | ||||||||
| 7A | Audible warning devices and signals | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 28 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 8A | Devices for indirect vision and their installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 46 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 9A | Braking of vehicles and trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13 | X (3) | X (3) | X (3) | X+U1 (3) | X+U1 (3) | X | X | X (3) | X (3) |
| 9B | Braking of passenger cars | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13-H | X (4) | ||||||||
| 10A | Electromagnetic compatibility | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 10 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 13A | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 18 | X (4A) | X (4A) | X (4A) | X (4A) | |||||
| 13B | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 116 | X | ||||||||
| 14A | Protection of the driver against the steering mechanism in the event of impact | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 12 | X | ||||||||
| 15A | Seats, their anchorages and any head restraints | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 17 | D (4B) | D (4B) | D | D | D | ||||
| 15B | Seats of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 80 | D | D | |||||||
| 17A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (reverse gear) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 17B | Speedometer equipment including its installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 39 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 18A | Manufacturer's statutory plate and VIN | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 19A | Safety-belt anchorages, Isofix anchorages systems and Isofix top tether anchorages | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 14 | D | D | D | D | D | ||||
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N | A+N |
| 21A | Retro-reflecting devices for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 3 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 22A | Front and rear position lamps, stop-lamps and end-outline marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 22B | Daytime running lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 87 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 22C | Side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 91 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 23A | Direction indicators for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 6 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 24A | Illumination of rear-registration plates of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 4 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 25A | Power-driven vehicle's sealed-beam headlamps (SB) emitting an European asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 31 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25B | Filament lamps for use in approved lamp units of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 37 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 25C | Motor vehicle headlamps equipped with gas-discharge light sources | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 98 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25D | Gas-discharge light sources for use in approved gas-discharge lamp units of power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 99 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25E | Motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or LED modules | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 112 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 25F | Adaptive front-lighting systems (AFS) for motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 123 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 26A | Power-driven vehicle front fog lamps | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 19 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 | A | A | A | A | A | ||||
| 28A | Rear fog lamps for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 38 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 29A | Reversing lights for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 23 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 30A | Parking lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 77 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 31A | Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and Isofix child restraint systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 16 | D | D | D | D | D | ||||
| 33A | Location and identification of hand controls, tell-tales and indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 121 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 34A | Windscreen defrosting and demisting systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | ||||
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 | (6) | (6) | (6) | (6) | (6) | ||||
| 36A | Heating systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 122 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 38A | Head restraints (headrests), whether or not incorporated in vehicle seats | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 25 | X | ||||||||
| 41A | Emissions (Euro VI) heavy duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 | H (9) | H | H (9) | H (9) | H | ||||
| 42A | Lateral protection of goods vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 73 | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 43A | Spray suppression systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 109/2011 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| 45A | Safety glazing materials and their installation on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 43 | J | J | J | J | J | J | J | J | J |
| 46A | Installation of tyres | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 458/2011 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 46B | Pneumatic tyres for motor vehicles and their trailers (Class C1) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 30 | X | X | X | ||||||
| 46C | Pneumatic tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers (Classes C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 54 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| 46D | Tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surfaces and rolling resistance (Classes C1, C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 117 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 46E | Temporary-use spare unit, run-flat tyres/system and tyre pressure monitoring system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 64 | X (9A) | ||||||||
| 47A | Speed limitation of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 89 | X | X | X | X | |||||
| 48A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 49A | Commercial vehicles with regard to their external projections forward of the cab's rear panel | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 61 | X | X | X | ||||||
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X | X | X | X |
| 50B | Close-coupling device (CCD); fitting of an approved type of CCD | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 102 | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | X (10) | |||||
| 51A | Burning behaviour of materials used in the interior construction of certain categories of motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 118 | X | ||||||||
| 52A | M2 and M3 vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 107 | X | X | |||||||
| 52B | Strength of the superstructure of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 66 | X | X | |||||||
| 54A | Protection of occupants in the event of lateral collision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 95 | A | ||||||||
| 56A | Vehicles for the carriage of dangerous goods | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 105 | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | X (13) | ||
| 57A | Front underrun protective devices (FUPDs) and their installation; front underrun protection (FUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 93 | X | X | |||||||
| 58 | Pedestrian protection | Regulation (EC) No 78/2009 | N/A (2) | ||||||||
| 59 | Recyclability | Directive 2005/64/EC | N/A | ||||||||
| 61 | Air-conditioning systems | Directive 2006/40/EC | X (14) | ||||||||
| 62 | Hydrogen system | Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 63 | General Safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) | X (15) |
| 65 | Advanced emergency braking system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 347/2012 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 66 | Lane departure warning system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 351/2012 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 67 | Specific components for liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 67 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 68 | Vehicle alarm systems (VAS) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 97 | X | ||||||||
| 69 | Electric safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 100 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 70 | Specific components for CNG and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 110 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 72 | eCall system | Regulation (EU) 2015/758 | N/A | N/A | G | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Appendix 5Mobile cranes
| Item | Subject | Reference to regulatory act | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | Sound level | Regulation (EU) No 540/2014 | T+Z1 |
| 3A | Prevention of fire risks (liquid fuel tanks) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 34 | X |
| 3B | Rear underrun protective devices (RUPDs) and their installation; rear underrun protection (RUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 58 | A |
| 4A | Space for mounting and fixing rear registration plates | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 | X |
| 5A | Steering equipment | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 79 | X Crab steering allowed |
| 6A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (steps, running boards and handholds) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | A |
| 7A | Audible warning devices and signals | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 28 | X |
| 8A | Devices for indirect vision and their installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 46 | X |
| 9A | Braking of vehicles and trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13 | U (3) |
| 10A | Electromagnetic compatibility | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 10 | X |
| 13A | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 18 | X (4A) |
| 15A | Seats, their anchorages and any head restraints | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 17 | X |
| 17A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (reverse gear) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X |
| 17B | Speedometer equipment including its installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 39 | X |
| 18A | Manufacturer's statutory plate and VIN | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 | X |
| 19A | Safety-belt anchorages, Isofix anchorages systems and Isofix top tether anchorages | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 14 | X |
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 | A+Y |
| 21A | Retro-reflecting devices for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 3 | X |
| 22A | Front and rear position lamps, stop-lamps and end-outline marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 7 | X |
| 22B | Daytime running lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 87 | X |
| 22C | Side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 91 | X |
| 23A | Direction indicators for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 6 | X |
| 24A | Illumination of rear-registration plates of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 4 | X |
| 25A | Power-driven vehicle's sealed-beam headlamps (SB) emitting an European asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 31 | X |
| 25B | Filament lamps for use in approved lamp units of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 37 | X |
| 25C | Motor vehicle headlamps equipped with gas-discharge light sources | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 98 | X |
| 25D | Gas-discharge light sources for use in approved gas-discharge lamp units of power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 99 | X |
| 25E | Motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or LED modules | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 112 | X |
| 25F | Adaptive front-lighting systems (AFS) for motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 123 | X |
| 26A | Power-driven vehicle front fog lamps | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 19 | X |
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 | A |
| 28A | Rear fog lamps for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 38 | X |
| 29A | Reversing lights for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 23 | X |
| 30A | Parking lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 77 | X |
| 31A | Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and Isofix child restraint systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 16 | X |
| 33A | Location and identification of hand controls, tell-tales and indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 121 | X |
| 34A | Windscreen defrosting and demisting systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 | (5) |
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 | (6) |
| 36A | Heating systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 122 | X |
| 41A | Emissions (Euro VI) heavy duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 | V |
| 42A | Lateral protection of goods vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 73 | A |
| 43A | Spray suppression systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 109/2011 | Z1 |
| 45A | Safety glazing materials and their installation on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 43 | J |
| 46A | Installation of tyres | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 458/2011 | X |
| 46C | Pneumatic tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers (Classes C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 54 | X |
| 46D | Tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surfaces and rolling resistance (Classes C1, C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 117 | X |
| 47A | Speed limitation of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 89 | X |
| 48A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | A |
| 49A | Commercial vehicles with regard to their external projections forward of the cab's rear panel | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 61 | A |
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 | X (10) |
| 50B | Close-coupling device (CCD); fitting of an approved type of CCD | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 102 | X (10) |
| 57A | Front underrun protective devices (FUPDs) and their installation; front underrun protection (FUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 93 | X |
| 62 | Hydrogen system | Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 | X |
| 63 | General Safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 | X (15) |
| 65 | Advanced emergency braking system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 347/2012 | N/A (16) |
| 66 | Lane departure warning system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 351/2012 | N/A (17) |
| 67 | Specific components for liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 67 | X |
| 69 | Electric safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 100 | X |
| 70 | Specific components for CNG and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 110 | X |
Appendix 6Exceptional load transport vehicles
| Item | Subject | Reference to regulatory act | N3 | O4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Permissible sound level | Directive 70/157/EEC | T | |
| 3A | Prevention of fire risks (liquid fuel tanks) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 34 | X | X |
| 3B | Rear underrun protective devices (RUPDs) and their installation; rear underrun protection (RUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 58 | A | A |
| 4A | Space for mounting and fixing rear registration plates | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 | X | A+R |
| 5A | Steering equipment | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 79 | X Crab steering allowed | X |
| 6A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (steps, running boards and handholds) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | |
| 7A | Audible warning devices and signals | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 28 | X | |
| 8A | Devices for indirect vision and their installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 46 | X | |
| 9A | Braking of vehicles and trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 13 | U (3) | X (3) |
| 10A | Electromagnetic compatibility | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 10 | X | X |
| 13A | Protection of motor vehicles against unauthorised use | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 18 | X (4A) | |
| 15A | Seats, their anchorages and any head restraints | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 17 | X | |
| 17A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (reverse gear) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 | X | |
| 17B | Speedometer equipment including its installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 39 | X | |
| 18A | Manufacturer's statutory plate and VIN | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 | X | X |
| 19A | Safety-belt anchorages, Isofix anchorages systems and Isofix top tether anchorages | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 14 | X | |
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 | X | A+N |
| 21A | Retro-reflecting devices for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 3 | X | X |
| 22A | Front and rear position lamps, stop-lamps and end-outline marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 7 | X | X |
| 22B | Daytime running lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 87 | X | |
| 22C | Side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 91 | X | X |
| 23A | Direction indicators for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 6 | X | X |
| 24A | Illumination of rear-registration plates of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 4 | X | X |
| 25A | Power-driven vehicle's sealed-beam headlamps (SB) emitting an European asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 31 | X | |
| 25B | Filament lamps for use in approved lamp units of power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 37 | X | X |
| 25C | Motor vehicle headlamps equipped with gas-discharge light sources | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 98 | X | |
| 25D | Gas-discharge light sources for use in approved gas-discharge lamp units of power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 99 | X | |
| 25E | Motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps and/or LED modules | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 112 | X | |
| 25F | Adaptive front-lighting systems (AFS) for motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 123 | X | |
| 26A | Power-driven vehicle front fog lamps | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 19 | X | |
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 | A | |
| 28A | Rear fog lamps for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 38 | X | X |
| 29A | Reversing lights for power-driven vehicles and their trailers | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 23 | X | X |
| 30A | Parking lamps for power-driven vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 77 | X | |
| 31A | Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and Isofix child restraint systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 16 | X | |
| 33A | Location and identification of hand controls, tell-tales and indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 121 | X | |
| 34A | Windscreen defrosting and demisting systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 | (5) | |
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 | (6) | |
| 36A | Heating systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 122 | X | |
| 41A | Emissions (Euro VI) heavy duty vehicles/access to information | Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 | X (9) | |
| 42A | Lateral protection of goods vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 73 | X | A |
| 43A | Spray suppression systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 109/2011 | X | A |
| 45 | Safety glazing | Directive 92/22/EEC | X | |
| 45A | Safety glazing materials and their installation on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 43 | X | |
| 46A | Installation of tyres | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 458/2011 | X | I |
| 46C | Pneumatic tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers (Classes C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 54 | X | I |
| 46D | Tyre rolling sound emissions, adhesion on wet surfaces and rolling resistance (Classes C1, C2 and C3) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 117 | X | I |
| 47A | Speed limitation of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 89 | X | |
| 48A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 | A | A |
| 49A | Commercial vehicles with regard to their external projections forward of the cab's rear panel | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 61 | A | |
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 | X (10) | X |
| 50B | Close-coupling device (CCD); fitting of an approved type of CCD | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 102 | X (10) | X (10) |
| 56A | Vehicles for the carriage of dangerous goods | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 105 | X (13) | X (13) |
| 57A | Front underrun protective devices (FUPDs) and their installation; front underrun protection (FUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 93 | A | |
| 62 | Hydrogen system | Regulation (EC) No 79/2009 | X | |
| 63 | General Safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 | X (15) | X (15) |
| 65 | Advanced emergency braking system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 347/2012 | N/A (16) | |
| 66 | Lane departure warning system | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 351/2012 | N/A (17) | |
| 67 | Specific components for liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 67 | X | |
| 69 | Electric safety | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 100 | X | |
| 70 | Specific components for CNG and their installation on motor vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 110 | X |
Explanatory Notes on the applicability of the requirements in this PartU.K.
The requirements set out in the relevant regulatory act are applicable. The series of amendments of the UN Regulations that apply on a compulsory basis are listed in Annex IV to Regulation (EC) No 661/2009. The series of amendments adopted subsequently are accepted as an alternative. Member States may grant extensions to existing type-approvals granted in accordance with the Directives repealed by Regulation (EC) 661/2009 under the conditions laid down in Article 13(14) of that Regulation.
This regulatory act is not applicable to this vehicle (no requirements).
(1)For vehicles with a reference mass not exceeding 2 610 kg. At the manufacturer's request, Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 may apply to vehicles with a reference mass not exceeding 2 840 kg.U.K.
With regard to access to information, for other parts (e.g. living compartment) than the base vehicle, it is sufficient that the manufacturer provides access to vehicle repair and maintenance information in a readily accessible and prompt manner.
(2)In case of vehicles equipped with a LPG or CNG installation, a vehicle type-approval in accordance with UN Regulation No 67 or UN Regulation No 110 is required.U.K.
(3)The fitting of an ESC system is required by Article 12 and Article 13 of Regulation (EC) No 661/2009. However, in accordance with UN Regulation No 13, the fitting of an ESC system is not required for special purpose vehicles of categories M2, M3, N2 and N3 and for vehicles for exceptional load transport and trailers with areas for standing passengers. N1 vehicles may be approved in accordance with UN Regulations No 13 or No 13-H.U.K.
(4)The fitting of an ESC system is required by Article 12 and Article 13 of Regulation (EC) No 661/2009. Therefore, the requirements set out in Part A of Annex 9 to UN Regulation No 13-H shall be fulfilled. N1 vehicles may be approved in accordance with UN Regulation No 13 or UN Regulation No 13-H.U.K.
(4A)If fitted, the protective device shall fulfil the requirements set out in UN Regulation No 18.U.K.
(4B)This Regulation applies to seats not falling within the scope of UN Regulation No 80. For other options, see Article 2 of Regulation (EC) No 595/2009.U.K.
(5)Vehicles of categories other than M1 do not need to fully comply with Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 but shall be fitted with a windscreen defrosting and demisting device.U.K.
(6)Vehicles of categories other than M1 do not need to fully comply with Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 but shall be fitted with a windscreen washing and wiping devices.U.K.
(8)For vehicles with a reference mass exceeding 2 610 kg and that did not benefit from the possibility offered in note (1).U.K.
(9)For vehicles with a reference mass exceeding 2 610 kg that are not type-approved (at the manufacturer's request and provided their reference mass does not exceed 2 840 kg) under Regulation (EC) No 715/2007. For other parts than the base vehicle, it is sufficient that the manufacturer provides access to vehicle repair and maintenance information in a readily accessible and prompt manner.U.K.
(9A)Applies only where such vehicles are fitted with equipment covered by UN Regulation No 64. Tyre pressure monitoring system for M1 vehicles applies on a compulsory basis in accordance with Article 9(2) of Regulation (EC) No 661/2009.U.K.
(10)Applies only to vehicles equipped with coupling(s).U.K.
(11)Applies to vehicles with a technically permissible maximum laden mass not exceeding 2,5 tonnes.U.K.
(12)Only applicable to vehicles where the ‘Seating Reference Point (“R” point)’ of the lowest seat is not more than 700 mm above the ground level.U.K.
(13)Applies only where the manufacturer applies for type-approval of vehicles intended for the transport of dangerous goods.U.K.
(14)Applies only for vehicles of category N1, class I (reference mass ≤ 1 305 kg).U.K.
(15)At the request of the manufacturer, a type-approval may be granted under this item, as an alternative to obtaining type-approvals under each individual item covered by Regulation (EC) No 661/2009.U.K.
(16)The fitting of an advanced emergency braking system is not required for special purpose vehicles in accordance with Article 1 of Regulation (EU) No 347/2012.U.K.
(17)The fitting of a lane departure warning system is not required for special purpose vehicles in accordance with Article 1 of Regulation (EU) No 351/2012.U.K.
The approval authority may only grant exemption(s) if the manufacturer demonstrates that the vehicle cannot meet the requirements due to its special purpose. The exemptions granted are to be described on the vehicle type-approval certificate and the certificate of conformity.
The fitting of ESC is not mandatory. In the case of multi-stage type-approvals, where the modifications made at a particular stage are likely to affect the function of the base vehicle's ESC system, the manufacturer may either disable the system or demonstrate that the vehicle has not been rendered unsafe or unstable. This may be demonstrated, e.g., by performing rapid double lane-change manoeuvres in each direction at 80 km/h with sufficient severity to cause intervention by the ESC system. These interventions are to be well-controlled and should improve the stability of the vehicle. The technical service has the right to request further testing if deemed necessary.
Application limited to doors giving access to the seats designated for normal use where the vehicle is used on a public road and where the distance between the R point of the seat and the average plane of the door surface, measured perpendicular to the longitudinal medium plane of the vehicle, does not exceed 500 mm.
Application limited to that part of the vehicle in front of the rearmost seat designated for normal use where the vehicle is used on a public road and also limited to the head impact zone as defined in the relevant regulatory act.
Application limited to seats designated for normal use where the vehicle is used on a public road. Seats that are not designated for use where the vehicle is used on the public road are to be clearly identified to users either by means of a pictogram or a sign with an appropriate text. The luggage retention requirements of UN Regulation No 17 do not apply.
Front only.
Modification to the routing and length of the refuelling duct and re-positioning of the tank inboard is permissible.
In case of multi-stage type-approval, requirements according to the category of the base/incomplete vehicle (e.g. the chassis of which was used to build the special purpose vehicle) may also be used.
Modification of exhaust system length after the last silencer not exceeding 2 m is permissible without any further test.
Tyres are to be type-approved in accordance with the requirements set out in UN Regulation No 54 even if the design speed of the vehicle is less than 80 km/h. The load capacity may be adjusted in relation to the maximum design speed of the trailer in agreement with the tyre manufacturer.
For all window glazing other than driver's cab glazing (windshield and side glasses), the material may be either of safety glass or rigid plastic glazing.
Additional panic alarm devices are permitted.
Application limited to seats designated for normal use where the vehicle is used on a public road. At least anchorages for lap belts are required in the rear seating positions. Seats that are not designated for use where the vehicle is used on a public road are to be clearly identified to users either by means of a pictogram or a sign with an appropriate text. ISOFIX is not required on ambulances and hearses.
Application limited to seats designated for normal use where the vehicle is used on a public road. At least lap belts are required in all rear seating positions. Seats that are not designated for use when the vehicle is used on a public road are to be clearly identified to users either by means of a pictogram or a sign with an appropriate text. ISOFIX is not required on ambulances and hearses.
Provided that all mandatory lighting devices are installed and that the geometric visibility is not affected.
Modification of exhaust system length after the last silencer not exceeding 2 m is permissible without any further test. An EU type-approval granted to the most representative base vehicle remains valid irrespective of change in the reference weight.
Provided that the registration plates of all Member States can be mounted and remain visible.
The light transmission factor is at least 60 % and the ‘A’ pillar obstruction angle is not more than 10 degrees.
Test to be performed only with the complete/completed vehicle. The vehicle can be tested in accordance with Directive 70/157/EEC. Concerning point 5.2.2.1 of Annex I to Directive 70/157/EEC, the following limit values are applicable:
81 dB(A) for vehicles with an engine power of less than 75 kW;
83 dB(A) for vehicles with an engine power of not less than 75 kW but less than 150 kW;
84 dB(A) for vehicles with an engine power of not less than 150 kW.
Test to be performed only with the complete/completed vehicle. Vehicles up to 4 axles are to comply with all the requirements laid down in the relevant regulatory acts. Derogations are admitted for vehicles having more than 4 axles, provided that:
they are justified by the particular construction; and
all the braking performances, related to parking, service and secondary braking laid down in the relevant regulatory act are fulfilled.
ABS is not mandatory for vehicles with hydrostatic drive.
Alternatively, Directive 97/68/EC may also apply.
Alternatively, Directive 97/68/EC may also apply to vehicles with hydrostatic drive.
Modification of exhaust system length is permitted without any further test, provided that the back pressure is similar. If a new test is required, an extra 2dB(A) above the applicable limit is allowed.
Modification in the exhaust system is permitted without any further test of tailpipe emissions and CO2/fuel consumption provided that the emission control devices, including particulate filters (if any), are not affected. If the evaporative control devices are kept as fitted by the manufacturer of the base vehicle, no new evaporative test is required on the modified vehicle.
An EU type-approval granted to the most representative base vehicle remains valid irrespective of change in the reference mass.
Modification of the routing, length of the refuelling duct, fuel hoses and fuel vapour pipes is permitted without further test. Re-location of the original fuel tank is permitted provided all requirements are met. However, further testing in accordance with Annex 5 to UN Regulation No 34 are not required.
The longitudinal plane of the intended wheelchair-travelling position should be parallel to the longitudinal plane of the vehicle.
Appropriate information is to be made available to the vehicle owner that, in order to withstand the forces transmitted by the tie-down mechanism during the various driving conditions, a wheelchair with a structure meeting the relevant part of ISO 7176-19:2008 is recommended.
The seats of the vehicle may be adapted without further testing, provided it can be demonstrated to the technical service that their anchorages, mechanisms and head restraints provide the same level of performance.
The luggage retention requirements set out in UN Regulation No 17 do not apply.
Compliance with the relevant regulatory act(s) is required for the boarding aids when in the resting position.
Each wheelchair location is to be provided with anchorages to which a wheelchair tie-down and occupant restraint system (WTORS) is to be fitted, and that complies with the additional provisions for testing the wheelchair tie-down and occupant restraint system set out in Appendix 3.
Each wheelchair location is to be provided with an occupant restraint belt that complies with the additional provisions for testing the wheelchair tie-down and occupant restraint system of set out in Appendix 3.
When, due to the conversion, anchorage points for the safety belts need to be moved outside the tolerance provided for in paragraph 7.7.1 of UN Regulation No 16.06, the technical service is to check whether the alteration constitutes a worst case or not. If that is the case, the test provided for in paragraph 7.7.1. of UN Regulation No 16.06 is to be performed. Extension to the EU type-approval does not need to be issued. The test may be performed using components that have not undergone the conditioning test prescribed by UN Regulation No 16.06.
For the purposes of calculations, the mass of the wheel-chair including the user is assumed to be 160 kg. The mass is to be concentrated at the P point of the surrogate wheelchair in its travelling position declared by the manufacturer.
Any limitation in the passenger capacity resulting from the use of wheelchair(s) is to be recorded in the owner's handbook, on side 2 of the EU type-approval certificate and in the certificate of conformity.
Modification of the exhaust system length is permitted without the need for retesting, provided that the exhaust back pressure remains similar.
Provided that all mandatory lighting devices are installed.
The requirements on the protrusion of open windows do not apply to the living compartment.
Mobile cranes with more than six axles are considered to be off-road vehicles (N3G) when at least three axles are driven and provided they meet the provisions of point 4.3(b)(ii) and (iii), as well as point 4.3(c) of Part A of Annex I.
ANNEX IIIU.K. PROCEDURES TO BE FOLLOWED WITH RESPECT TO EU TYPE-APPROVAL
1.Objectives and scopeU.K.
1.1.This Annex establishes the procedures for the proper conduct of the vehicle type-approval in accordance with Articles 26, 27 and 28.U.K.
1.2.It also includes:U.K.
the list of international standards which are of relevance for the designation of the technical services in accordance with Articles 68 and 70;
the description of the procedure to be followed for the assessment of the skills of technical services in accordance with Article 73;
the general requirements for the drafting of test reports by technical services.
2.Type-approval procedureU.K.
When receiving an application for vehicle type-approval, the approval authority shall:
verify that all EU type-approval certificates issued pursuant to the regulatory acts as listed in Annex II which are applicable for vehicle type-approval cover the type of vehicle and correspond to the prescribed requirements;
make sure that the vehicle specifications and data are included in the data in the information packages and in the EU type-approval certificates issued in accordance with the relevant regulatory acts;
when an item number is not included in the information package as provided for in any of the regulatory acts, confirm that the relevant part or characteristic conforms to the particulars in the information folder;
on a selected sample of vehicles from the type to be approved carry out or arrange to be carried out inspections of vehicle parts and systems to verify that the vehicle or vehicles are built in accordance with the relevant data contained in the authenticated information package in respect of the relevant EU type-approval certificates;
carry out or arrange to be carried out relevant installation checks in respect of separate technical units, where applicable;
carry out or arrange to be carried out necessary checks in respect of the presence of the devices provided for in explanatory notes 1 and 2 of Part I of Annex II, where applicable;
carry out or arrange to be carried out necessary checks in order to ensure that the requirements set out in explanatory note 5 of Part I of Annex II are fulfilled.
3.Combination of technical specificationsU.K.
The number of vehicles to be submitted shall be sufficient to permit the proper check of the various combinations to be type-approved according to the following criteria:
| Technical specifications | Vehicle category | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | N1 | N2 | N3 | O1 | O2 | O3 | O4 | |
| Engine | X | X | X | X | X | X | — | — | — | — |
| Gear box | X | X | X | X | X | X | — | — | — | — |
| Number of axles | — | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Powered axles (number, position and interconnection) | X | X | X | X | X | X | — | — | — | — |
| Steered axles (number and position) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Body styles | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Number of doors | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Hand of drive | X | X | X | X | X | X | — | — | — | — |
| Number of seats | X | X | X | X | X | X | — | — | — | — |
| Level of equipment | X | X | X | X | X | X | — | — | — | — |
4.Specific provisionsU.K.
Where no approval certificates as provided for in the relevant regulatory acts are available, the approval authority shall:
arrange for the necessary tests and checks as required by each of the relevant regulatory acts;
verify that the vehicle conforms to the particulars in the information folder and that it meets the technical requirements of each of the relevant regulatory acts;
carry out or arrange to be carried out relevant installation checks in respect of separate technical units, where applicable;
carry out or arrange to be carried out necessary checks in respect of the presence of the devices provided for in explanatory notes 1 and 2 of Part I of Annex II where applicable;
carry out or arrange to be carried out necessary checks in order to ensure that the requirements set out in explanatory note 5 of Part I of Annex II are fulfilled.
Appendix 1Standards with which the technical services referred to in Article 68 have to comply
1.Activities related to testing for type-approval to be carried out in accordance with the regulatory acts listed in Annex II:U.K.
1.1.Category A (tests performed in own facilities):U.K.
Standard EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 on the general requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories.
A technical service designated for category A activities may also carry out the tests provided for in the regulatory acts for which it has been designated, in the facilities of a manufacturer or of a third party. In either case, the personnel responsible for using professional judgement for determination of conformity with the regulatory acts for which the technical service has been designated shall comply with the Standard EN ISO/IEC 17020:2012.
1.2.Category B (supervision of tests, which includes test preparation, where such tests are performed at the manufacturer's facilities or at the facilities of a third party):U.K.
Standard EN ISO/IEC 17020:2012 on the general criteria for the operation of various types of bodies performing inspection.
Before performing or supervising any test in the manufacturer's facilities or in the facilities of a third party, the technical service shall verify that the tests facilities and measurement devices comply with the appropriate requirements of Standard EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005.
2.Activities related to conformity of productionU.K.
2.1.Category C (procedure for the initial assessment and surveillance audits of the manufacturer's quality management system):U.K.
Standard EN ISO/IEC 17021:2011 on the requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of management systems.
2.2.Category D (inspection or testing of production samples or supervision thereof):U.K.
Standard EN ISO/IEC 17020:2012 on the general criteria for the operation of various types of bodies performing inspection.
Appendix 2Procedure for the assessment of the technical services
1.Objective and scopeU.K.
1.1.This Appendix establishes the conditions in accordance with which the assessment procedure of the technical services shall be conducted by the authority, competent under Article 73 (‘competent authority’).U.K.
1.2.Those requirements shall apply to all technical services, irrespective of their legal status (independent organisation, manufacturer or approval authority acting as technical service).U.K.
2.AssessmentsU.K.
The carrying out of an assessment shall be governed by the following:
principle of independence, which is the basis for the impartiality and objectivity of the conclusions; and
an evidence-based approach, which guarantees reliable and reproducible conclusions.
Auditors shall show trust and integrity. They shall respect confidentiality and discretion.
They shall report truthfully and accurately about findings and conclusions.
3.Skills requirements for auditorsU.K.
3.1.The assessments may only be conducted by auditors having the technical and administrative knowledge necessary for such purposes.U.K.
3.2.The auditors shall have been trained specifically for assessment activities. In addition, they shall have the specific knowledge of the technical area in which the technical service will exercise its activities.U.K.
3.3.Without prejudice to points 3.1 and 3.2, the assessment referred to in Article 73 shall be conducted by auditors independent of the activities for which the assessment is conducted.U.K.
4.Application for designationU.K.
4.1.A duly authorised representative of the applicant technical service shall submit a formal application to the competent authority that includes the following information:U.K.
general features of the technical service, including corporate entity, name, addresses, legal status and technical resources;
a detailed description, including curriculum vitae, of the personnel in charge of testing and of the managerial staff, setting out their educational qualifications and professional skills;
technical services which use virtual testing methods shall provide evidence of their ability to work in a Computer-Aided-x environment;
general information concerning the technical service, including its activities, its relationship in a larger corporate entity, if any, and addresses of all its physical location(s) to be covered by the scope of designation;
an agreement to fulfil the requirements for designation and the other obligations of the technical service as provided for in the relevant regulatory acts for which it is designated;
a description of the conformity assessment services that the technical service undertakes in the framework of the relevant regulatory acts and a list of the regulatory acts for which the technical service applies for designation, including limits of capability, where applicable;
a copy of the quality assurance manual of the technical service.
4.2.The competent authority shall review the adequacy of the information provided by the technical service.U.K.
4.3.The technical service shall notify to the competent authority any modifications to the information provided in accordance with point 4.1.U.K.
5.Resource reviewU.K.
The competent authority shall review its ability to carry out the assessment of the technical service, in terms of its own policy, its competence and the availability of suitable auditors and experts.
6.Subcontracting the assessmentU.K.
6.1.The competent authority may subcontract parts of the assessment to another competent authority or ask for support from technical experts provided by other competent authorities. The subcontractors and experts have to be accepted by the applicant technical service.U.K.
6.2.The competent authority shall take into account accreditation certificates with adequate scope in order to complete its global assessment of the technical service.U.K.
7.Preparation for assessmentU.K.
7.1.The competent authority shall formally appoint a joint assessment team. The competent authority shall ensure that the expertise brought to each joint assessment team is appropriate. In particular, the joint assessment team as a whole shall have both:U.K.
appropriate knowledge of the specific scope for which designation is sought; and
sufficient understanding to reliably assess the competence of the technical service to operate within its scope of designation.
7.2.The competent authority shall clearly define the assignment given to the joint assessment team. The task of the joint assessment team is to review the documents collected from the applicant technical service and to conduct the on-site assessment.U.K.
7.3.The competent authority shall agree, together with the technical service and the assigned assessment team, to the date and timetable for the assessment. However, it remains the responsibility of the competent authority to pursue a date that is in accordance with the surveillance and reassessment plan.U.K.
7.4.The competent authority shall ensure that the joint assessment team is provided with the appropriate criteria documents, previous assessment records, and the relevant documents and records of the technical service.U.K.
8.On-site assessmentU.K.
The joint assessment team shall conduct the assessment of the technical service at the premises of the technical service from which one or more key activities are performed and, where relevant, shall perform eyewitness assessment at other selected locations where the technical service operates.
9.Analysis of findings and assessment reportU.K.
9.1.The joint assessment team shall analyse all relevant information and evidence gathered during the document and record review and the on-site assessment. That analysis shall be sufficient to allow the team to determine the extent of competence and conformity of the technical service with the requirements for designation.U.K.
9.2.The competent authority's reporting procedures shall ensure that the following requirements are fulfilled.U.K.
9.2.1.A meeting shall take place between the joint assessment team and the technical service prior to leaving the site. At that meeting, the joint assessment team shall provide a written and/or oral report on its findings obtained from the analysis. An opportunity shall be provided for the technical service to ask questions about the findings, including non-compliance, if any, and its basis.U.K.
9.2.2.A written report on the outcome of the assessment shall be promptly brought to the attention of the technical service. That assessment report shall contain comments on competence and compliance, and shall identify non-compliance, if any, to be resolved in order to conform to all of the requirements for designation.U.K.
9.2.3.The technical service shall be invited to respond to the assessment report and to describe the specific actions taken or planned to be taken, within a specific period of time, to resolve any identified non-compliance.U.K.
9.3.The competent authority shall ensure that the responses of the technical service are sufficient and effective to resolve non-compliance. If the technical service responses are found to be insufficient, further information shall be requested. Additionally, evidence of effective implementation of actions taken may be requested, or a follow-up assessment may be carried out, to verify effective implementation of corrective actions.U.K.
9.4.The assessment report shall include at least the following:U.K.
unique identification of the technical service;
date(s) of the on-site assessment;
name(s) of the auditors(s) and/or expert(s) involved in the assessment;
unique identification of all premises assessed;
proposed scope of designation that was assessed;
a statement on the adequacy of the internal organisation and procedures adopted by the technical service supporting its competence, as determined through its fulfilment of the requirements for designation;
information on resolving all non-compliance;
a recommendation of whether the applicant should be designated or confirmed as technical service and, if so, the scope of designation.
10.Granting, confirming or extending a designationU.K.
10.1.The competent authority shall, without undue delay, make the decision on whether to grant, confirm or extend a designation on the basis of the assessment report(s) and any other relevant information.U.K.
10.2.The competent authority shall provide a certificate to the technical service. That certificate shall identify the following:U.K.
the identity and logo of the competent- authority;
the unique identity of the designated technical service;
the effective date of designation and the expiry date;
a brief indication of or a reference to the scope of designation (relevant regulatory acts or part of them);
a statement of conformity and a reference to this Regulation.
11.Reassessment and surveillanceU.K.
11.1.Reassessment is similar to an initial assessment except that experience gained during previous assessments shall be taken into account. Surveillance on-site assessments are less comprehensive than reassessments.U.K.
11.2.The competent authority shall design its plan for reassessment and surveillance of each designated technical service so that representative samples of the scope of designation are assessed on a regular basis.U.K.
The interval between on-site assessments, whether reassessment or surveillance, depends on the proven stability that the technical service has reached.
11.3.Where, during surveillance or reassessments, non-compliance is identified, the competent authority shall define strict time limits for corrective actions to be taken.U.K.
11.4.Where the corrective or improvement actions have not been taken within the agreed time limit or are not deemed to be sufficient, the competent authority shall adopt appropriate measures, such as conducting a further assessment, or suspending or withdrawing the designation for one or more of the activities for which the technical service has been designated.U.K.
11.5.Where the competent authority decides to suspend or withdraw the designation of a technical service, it shall inform the technical service of its decision by registered mail. In any case, the competent authority shall adopt all the necessary measures to ensure the continuity of the activities already undertaken by the technical service.U.K.
12.Records on designated technical servicesU.K.
12.1.The competent authority shall maintain records on technical services to demonstrate that the requirements for designation, including competence, have been effectively fulfilled.U.K.
12.2.The competent authority shall keep the records on technical services secure to ensure confidentiality.U.K.
12.3.Records on technical services shall include at least the following:U.K.
relevant correspondence;
assessment records and reports;
copies of designation certificates.
ANNEX IVU.K. CONFORMITY OF PRODUCTION PROCEDURES
1.ObjectivesU.K.
1.1.The conformity of production procedure aims to ensure that each vehicle, system, component and technical separate unit, part or equipment produced is in conformity with the approved type.U.K.
1.2.The conformity of production procedure shall always include the assessment of quality-assurance management systems, referred to in point 2 as the ‘initial assessment’, and the verification of the type-approval subject and product-related controls, referred to in point 3 as ‘product conformity arrangements’.U.K.
2.Initial assessmentU.K.
2.1.Before granting type-approval, the approval authority shall verify that the manufacturer has established satisfactory arrangements and procedures for ensuring that vehicles, systems, components, separate technical units or parts and equipment are produced in conformity with the approved type.U.K.
2.2.Guidance for conducting those assessments may be found in standard EN ISO 19011:2011 — Guidelines for auditing management systems.U.K.
2.3.Compliance with the requirements of point 2.1 shall be verified to the satisfaction of the approval authority, as follows:U.K.
The approval authority shall be satisfied with the initial assessment and the product conformity arrangements referred to in point 3, taking into account one of the arrangements referred to in points 2.3.1 to 2.3.3, or a combination of those arrangements in full or in part as appropriate.
2.3.1.The initial assessment and verification of product conformity arrangements shall be carried out by the approval authority or a body designated for that purpose by the approval authority.U.K.
2.3.1.1.When considering the extent of the initial assessment to be carried out, the approval authority may take into account the following information:U.K.
whether the manufacturer has a certification similar to the one referred to in point 2.3.3, but which has not been qualified or recognised under that point;
in the case of a type-approval of a system, component or separate technical unit, quality system assessments that have been performed by vehicle manufacturer(s) in the premises of the manufacturer of the system, component or separate technical unit, in accordance with one or more of the industry sector specifications satisfying the requirements in the standard EN ISO 9001:2015 or ISO/TS16949:2009;
whether in one of the Member States one or more of the manufacturer's type-approvals recently have been withdrawn, due to unsatisfactory control of conformity of production. In that case, the initial assessment by the approval authority shall not be limited to accepting the manufacturer's quality system certification, but shall include a verification whether all necessary improvements for ensuring effective control have been implemented, so that vehicles, components, systems or separate technical units are produced in conformity with the approved type.
2.3.2.The initial assessment and verification of product conformity arrangements may be carried out by the approval authority of another Member State or by the body designated for that purpose by the approval authority.U.K.
2.3.2.1.The approval authority of that other Member State shall in that case prepare a statement of compliance, which outlines the areas and production facilities that that approval authority has covered as relevant to the product(s) to be type-approved and to the regulatory acts in accordance with which these products are to be type-approved.U.K.
2.3.2.2.Upon receiving a request for a statement of compliance from the approval authority of a Member State granting type-approval, the approval authority of another Member State shall immediately send that statement of compliance or inform that approval authority that is unable to provide such a statement.U.K.
2.3.2.3.The statement of compliance shall include at least the following:U.K.
2.3.3.An approval authority may also accept the manufacturer's certification to standards EN ISO 9001:2015 or ISO/TS16949:2009 (the scope of that certification shall in that case cover the product(s) to be approved), or an equivalent certification standard as satisfying the initial assessment requirements of point 2.3., provided that conformity of production is indeed covered by the quality management system and that the manufacturer's type-approval has not been withdrawn as referred to in point 2.3.1.1.(c). The manufacturer shall provide details of the certification and inform the approval authority of any revisions to its validity or scope.U.K.
2.4.For the purpose of vehicle type-approval, the initial assessments carried out for the granting of type-approvals for systems, components and separate technical units of the vehicle need not be repeated, but shall be completed by an assessment of the locations and activities relating to the assembly of the whole vehicle that have not been covered by the initial assessments.U.K.
3.Product conformity arrangementsU.K.
3.1.Every vehicle, system, component or separate technical unit, part or item of equipment approved pursuant to a UN Regulation annexed to the Revised 1958 Agreement and to this Regulation shall be so manufactured as to conform to the type approved by meeting the requirements of this Annex, the said UN Regulation and this Regulation.U.K.
3.2.Before granting a type-approval pursuant to this Regulation and to a UN Regulation annexed to the Revised 1958 Agreement, the approval authority shall verify the existence of adequate product conformity arrangements and documented control plans, to be agreed with the manufacturer for each approval, to carry out at specified intervals the tests or associated checks that are necessary to verify continued conformity with the approved type, including, where applicable, tests specified in this Regulation and the said UN Regulation.U.K.
3.3.The holder of the type-approval shall, in particular:U.K.
ensure the existence and application of procedures for effective control of the conformity of vehicles, systems, components, separate technical units, parts or equipment to the approved type;
have access to the testing or other appropriate equipment necessary for checking the conformity to each approved type;
ensure that the data resulting from tests or checks are recorded and that annexed documents remain available for a period of up to 10 years to be determined in agreement with the approval authority;
analyse the results of each type of test or check, in order to verify and ensure the stability of the product characteristics, making allowance for variation of an industrial production;
ensure that for each type of product, at least the checks prescribed in this Regulation and the tests prescribed in the relevant regulatory acts listed in Annex II are carried out;
ensure that any set of samples or test pieces that gives evidence of non-conformity in the type of test in question, gives rise to a further sampling and testing. All the necessary steps shall be taken to restore the production process to ensure conformity with the approved type.
3.4.In the case of step-by-step, mixed or multi-stage type-approvals, the approval authority that is granting a whole-vehicle type-approval may request from any approval authority that has granted type-approval of any relevant system, component or separate technical unit specific details regarding compliance with the conformity of production requirements set out in this Annex.U.K.
3.5.The approval authority that is granting a whole-vehicle type-approval and is not satisfied with the reported information referred to in point 3.4., and that has communicated this in writing to the relevant manufacturer and to the approval authority granting the type-approval for the system, component or separate technical unit, shall request the performance of additional conformity of production audits or checks, which shall be performed at the site of the manufacturer(s) of those systems, components or separate technical units. The results of this additional conformity of production audits or checks shall immediately be made available to that approval authority.U.K.
3.6.Where points 3.4. and 3.5. apply and the approval authority granting the whole-vehicle type-approval has not been satisfied with the additional audit or check results, the manufacturer shall ensure that conformity of production is restored as soon as possible to the satisfaction of that approval authority and of the approval authority granting type-approval of the system, component or separate technical unit.U.K.
4.Continued verification arrangementsU.K.
4.1.The approval authority that has granted type-approval may at any time verify the conformity control methods applied in each production facility by means of periodic audits. The manufacturer shall for that purpose allow access to that authority to the manufacturing, inspection, testing, storage and distribution sites and shall provide all necessary information with regard to the quality management system documentation and records.U.K.
4.1.1.The normal arrangements for such periodic audits shall be to monitor the continued effectiveness of the procedures laid down in points 2 and 3 (initial assessment and product conformity arrangements).U.K.
4.1.1.1.Surveillance activities carried out by the technical services (qualified or recognised as required in point 2.3.3) shall be accepted as satisfying the requirement of point 4.1.1 with regard to the procedures established at initial assessment.U.K.
4.1.1.2.The normal frequency of verifications by the approval authority (other than those referred to in point 4.1.1.1) shall be such as to ensure that the relevant controls applied in accordance with points 2 and 3 are reviewed at intervals based on a risk assessment methodology that complies with the international standard ISO 31000:2018 – Risk Management – Principles and Guidelines, and such verification shall in any case be conducted at least once every three years. This methodology shall in particular take into account any non-conformity raised by other Member States in the context of Article 54(1).U.K.
4.2.At every review, records of tests or checks and records of production, in particular records of those tests or checks documented as required in point 2.2, shall be made available to the inspector.U.K.
4.3.The inspector may select samples at random manner to be tested in the manufacturer's laboratory or in the facilities of the technical service. In such a case only physical test shall be carried out. The minimum number of samples may be determined on the basis of the results of the manufacturer's own verification.U.K.
4.4.The inspector who is of the opinion that the level of control is unsatisfactory, or who deems it necessary to verify the validity of the tests carried out in accordance with point 4.2, shall select samples to be sent to a technical service to perform physical tests in accordance with the requirements on conformity of production, set out in the regulatory acts listed in Annex II.U.K.
4.5.Where unsatisfactory results are found during an inspection or a monitoring review, the approval authority shall take all necessary steps to ensure that the manufacturer restores the conformity of production as rapidly as possible.U.K.
4.6.In cases where compliance with UN Regulations is required by this Regulation, the manufacturer may choose to apply this Annex as an equivalent alternative to the conformity of production requirements in the respective UN Regulations. However, if points 4.4. or 4.5. apply, all separate conformity of production requirements in the UN Regulations have to be complied with to the satisfaction of the approval authority until it decides that conformity of production has been restored.U.K.
ANNEX VU.K. SMALL SERIES AND END-OF-SERIES LIMITS
A.SMALL SERIES QUANTITIVE ANNUAL LIMITSU.K.
1.The number of units of one type of vehicle to be registered, made available on the market or entered into service annually in the Union shall not exceed, pursuant to Article 41, the quantitive annual limits shown in the following table for the vehicle category in question:U.K.
| Category | Units |
|---|---|
| M1 | 1 500 |
| M2, M3 | 0 |
| N1 | 1 500 |
| N2, N3 | 0 until the date of application of the delegated acts referred to in Article 41(5). 1 500 after that date |
| O1, O2 | 0 |
| O3, O4 | 0 |
2.The number of units of one type of vehicle to be registered, made available on the market or entered into service annually in a Member State, shall be determined by that Member State but shall not exceed, pursuant to Article 42, the quantitative annual limits shown in the following table for the vehicle category in question:U.K.
| Category | Units |
|---|---|
| M1 | 250 |
| M2, M3 | 250 |
| N1 | 250 |
| N2, N3 | 250 |
| O1, O2 | 500 |
| O3, O4 | 250 |
B.END-OF-SERIES LIMITSU.K.
The maximum number of complete and completed vehicles entered into service in each Member State under the procedure ‘End-of-Series’ shall be restricted in one of the following ways to be chosen by the Member State:
The maximum number of vehicles of one or more types may, in the case of category M1, not exceed 10 % and in the case of all other categories not exceed 30 % of the vehicles of all types concerned entered into service in that Member State during the previous year. Should 10 %, respectively 30 %, be less than 100 vehicles, then the Member State may allow the entry into service of a maximum of 100 vehicles.
Vehicles of any one type shall be restricted to those for which a valid certificate of conformity was issued on or after the date of manufacture of the vehicle and which remained valid for at least three months after its date of issue but subsequently lost its validity due to the entry into force of a regulatory act.
ANNEX VIU.K. LIST OF PARTS OR EQUIPMENT THAT MAY POSE A SERIOUS RISK TO THE CORRECT FUNCTIONING OF SYSTEMS THAT ARE ESSENTIAL FOR THE SAFETY OF THE VEHICLE OR ITS ENVIRONMENTAL PERFORMANCE, THE PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS OF SUCH PARTS AND EQUIPMENT, THE APPROPRIATE TEST PROCEDURES, AND MARKING AND PACKAGING PROVISIONS
I.Parts or equipment having a significant impact on vehicle safetyU.K.
| Item No | Item description | Performance requirement | Test procedure | Marking requirement | Packaging requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | […] | ||||
| 2 | |||||
| 3 |
II.Parts or equipment having a significant impact on the environmental performance of the vehicleU.K.
| Item No | Item description | Performance requirement | Test procedure | Marking requirement | Packaging requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | […] | ||||
| 2 | |||||
| 3 |
ANNEX VIIU.K. REGULATORY ACTS FOR WHICH A MANUFACTURER MAY BE DESIGNATED AS A TECHNICAL SERVICE
1.Objectives and scopeU.K.
1.1.This Annex lays down the list of the regulatory acts for which an in-house technical service of a manufacturer may be designated as a technical service in accordance with Article 72(1).U.K.
1.2.It also includes appropriate provisions concerning the designation of an in-house technical service of a manufacturer as technical service, to be applied in the framework of the type-approval of vehicles, components and separate technical units concerned by Part I of Annex II.U.K.
1.3.This Annex however does not apply to manufacturers who apply for the EU type-approval of vehicles produced in small series, as referred to in Article 41.U.K.
2.Designation of an in-house technical service of a manufacturer as a technical serviceU.K.
2.1.An in-house technical service of a manufacturer designated as a technical service is a manufacturer which has been designated by the type-approval authority as a testing laboratory to carry out on its behalf the approval tests.U.K.
The expression ‘to carry out tests’ is not restricted to the measurement of performances, but also covers the registration of test results and the submission to the type-approval authority of a report, including the relevant conclusions.
It also covers the checking of compliance with those provisions that do not necessarily require measurement. This is the case for the assessment whether the design complies with the legislative requirements.
3.List of regulatory acts and restrictionsU.K.
| Subject | Regulatory act reference | |
|---|---|---|
| 4A | Space for mounting and fixing rear registration plates | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1003/2010 |
| 7A | Audible warning devices and signals | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 28 |
| 10A | Electromagnetic compatibility | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 10 |
| 18A | Manufacturer's statutory plate and VIN | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 19/2011 |
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 |
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 |
| 33A | Location and identification of hand controls, tell-tales and indicators | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 121 |
| 34A | Windscreen defrosting and demisting systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 672/2010 |
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 |
| 36A | Heating systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 122 Except the provisions in Annex 8 relating to LPG combustion heaters and LPG heating systems |
| 37A | Wheel guards | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010 |
| 44A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 |
| 45A | Safety glazing materials and their installation on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 43 Restricted to the provisions included in Annex 21 |
| 46A | Installation of tyres | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 458/2011 |
| 48A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 |
| 49A | Commercial vehicles with regard to their external projections forward of the cab's rear panel | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 61 |
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 Restricted to the provisions included in Annex 5 (up to and including paragraph 8) and Annex 7 |
| 61 | Air-conditioning system | Directive 2006/40/EC |
AppendixDesignation of an in-house technical service of a manufacturer as technical service and subcontracting
1.GeneralU.K.
1.1.The designation and notification of an in-house technical service of a manufacturer as a technical service shall be made in accordance with Articles 68 to 81 and any subcontracting shall be done in accordance with this Appendix.U.K.
2.SubcontractingU.K.
2.1.In accordance with Article 71(1), a technical service may nominate a subcontractor for performing tests on his behalf.U.K.
2.2.For the purposes of this Appendix ‘Subcontractor’ means either a subsidiary of the technical service that has been entrusted by that technical service with testing activities inside its own organisation or a third party under contract with that technical service to perform test activities.U.K.
2.3.The use of the services of a subcontractor does not release the technical service from its obligation to comply with Articles 69, 70, 80 and 81, and in particular with those concerning the skills of the technical services and compliance with Standard EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005.U.K.
2.4.Point 2 of Annex VII shall apply to the subcontractor.U.K.
3.Test reportU.K.
Test reports shall be drafted in accordance with the implementing acts referred to in Article 30(3).
ANNEX VIIIU.K. CONDITIONS FOR THE USE OF VIRTUAL TESTING METHODS BY A MANUFACTURER OR A TECHNICAL SERVICE
1.Objectives and scopeU.K.
This Annex lays down provisions concerning virtual testing in accordance with Article 30(7).
2.List of regulatory actsU.K.
| Subject | Regulatory act reference | |
|---|---|---|
| 3B | Rear underrun protective devices (RUPDs) and their installation; rear underrun protection (RUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 58 |
| 6A | Vehicle access and manoeuvrability (steps, running boards and handholds) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 130/2012 |
| 6B | Door latches and door retention components | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 11 |
| 8A | Devices for indirect vision and their installation | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 46 |
| 12A | Interior fittings | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 21 |
| 16A | External projections | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 26 |
| 20A | Installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 48 |
| 27A | Towing device | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1005/2010 |
| 32A | Forward field of vision | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 125 |
| 35A | Windscreen wiper and washer systems | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1008/2010 |
| 37A | Wheel guards | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1009/2010 |
| 42A | Lateral protection of goods vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 73 |
| 48A | Masses and dimensions | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 |
| 49A | Commercial vehicles with regard to their external projections forward of the cab's rear panel | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 61 |
| 50A | Mechanical coupling components of combinations of vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 55 |
| 50B | Close-coupling device (CCD); fitting of an approved type of CCD | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 102 |
| 52A | M2 and M3 vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 107 |
| 52B | Strength of the superstructure of large passenger vehicles | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 66 |
| 57A | Front underrun protective devices (FUPDs) and their installation; front underrun protection (FUP) | Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 UN Regulation No 93 |
Appendix 1General conditions for the use of virtual testing methods
1.Virtual test patternU.K.
The following scheme shall be used as basis structure for describing and conducting virtual testing:
purpose;
structure model;
boundary conditions;
load assumptions;
calculation;
assessment;
documentation.
2.Fundamentals of computer simulation and calculationU.K.
2.1.Mathematical modelU.K.
The mathematical model shall be supplied by the manufacturer. It shall reflect the complexity of the structure of the vehicle, system, component or separate technical unit to be tested in relation to the requirements of the relevant regulatory act and its boundary conditions.
The same provisions shall apply for testing components or separate technical units independently from the vehicle.
2.2.Validation process of the mathematical modelU.K.
The mathematical model shall be validated against the actual test conditions.
To that effect a physical test shall be conducted to compare the results obtained when using the mathematical model with the results of a physical test. Comparability of the test results shall be proven. The manufacturer or the technical service shall draft a validation report and submit it to the approval authority.
Any change to the mathematical model or to the software that is likely to invalidate the validation report shall be brought to the attention of the approval authority, which may require that a new validation process is conducted.
The flow chart of the validation process is shown in Appendix 3.
2.3.DocumentationU.K.
The manufacturer shall make available to the technical service and document the data and auxiliary tools used for simulation and calculation.
3.Tools and supportU.K.
The manufacturer shall supply the technical service at its request with the necessary tools to conduct the virtual testing, including appropriate software, or provide that technical service access to these tools.
The manufacturer shall also provide appropriate support to the technical service.
The access and support provided by the manufacturer to a technical service does not exempt the technical service from its obligations regarding the skills of its personnel, the payment of licence rights and confidentiality.
Appendix 2Specific conditions for the use of virtual testing methods
1.List of regulatory actsU.K.
Appendix 3Validation process
ANNEX IXU.K. PROCEDURES TO BE FOLLOWED DURING MULTI-STAGE TYPE-APPROVAL
1.Obligations of manufacturersU.K.
1.1.The satisfactory operation of the multi-stage type-approval requires joint action by all the manufacturers concerned. To that end approval authorities must ensure, before granting first and subsequent stage type-approvals, that suitable arrangements exist between the relevant manufacturers for the supply and interchange of documents and information, so that the completed type of vehicle meets the technical requirements of all the relevant regulatory acts listed in Annex II. Such information must include details of relevant system, component and separate technical unit type-approvals and of vehicle parts that form part of the incomplete vehicle but have not yet been type-approved.U.K.
1.2.Each manufacturer involved in a multi-stage type-approval shall be responsible for the approval and conformity of production of all systems, components or separate technical units manufactured or added by that manufacturer to the previously built stage. The manufacturer of the subsequent stage shall not be responsible for objects that have been approved in an earlier stage, except where that manufacturer modifies relevant parts to such an extent that the previously granted type-approval becomes invalid.U.K.
2.Obligations of approval authoritiesU.K.
2.1.The approval authority shall:U.K.
verify that all EU type-approval certificates issued pursuant to the regulatory acts that are applicable for vehicle type-approval cover the type of vehicle at its state of completion and correspond to the prescribed requirements;
ensure that all the relevant data, taking account of the state of completion of the vehicle, is included in the information folder;
by reference to the documentation ensure that the vehicle specification(s) and data contained in the information folder are included in the data in the information packages and in the EU type-approval certificates issued in accordance with the relevant regulatory acts; and in the case of a completed vehicle, where an item number of the information folder is not included in the information package of any of the regulatory acts, confirm that the relevant part or characteristic conforms to the particulars in the information folder;
on a selected sample of vehicles from the type to be approved carry out or arrange to be carried out inspections of vehicle parts and systems to verify that the vehicle(s) is/are built in accordance with the relevant data contained in the authenticated information package in accordance with all relevant regulatory acts; and
where required carry out, or arrange to be carried out, relevant installation checks for separate technical units.
2.2.The number of vehicles to be inspected for the purposes of point 2.1 (d) shall be sufficient to permit the proper control of the various combinations to be EU type-approved according to the state of completion of the vehicle and the following criteria:U.K.
engine;
gearbox;
powered axles (number, position, interconnection);
steered axles (number and position);
body styles;
number of doors;
hand of drive;
number of seats;
level of equipment.
3.Applicable requirementsU.K.
3.1.Multi-stage type-approvals shall be granted on the basis of the state of completion of the type of vehicle and shall incorporate all type-approvals granted at earlier stages.U.K.
3.2.For the whole-vehicle type-approval, this Regulation (in particular the requirements of Annex I and the particular regulatory acts listed in Annex II) shall apply in the same manner as if the approval would have been granted (or extended) to the manufacturer of the base vehicle.U.K.
3.2.1.Where a type of system, component or separate technical unit has not been modified, the system, component or separate technical unit type-approval granted in the previous stage shall remain valid until the expiration date for the first registration, as specified in the particular regulatory act.U.K.
3.2.2.Where a type of system has been modified at the subsequent stage of completion of the vehicle, to the extent that the system has to be retested for type-approval purposes, that retesting shall be limited to only those parts of the system that have been modified or affected by the changes.U.K.
3.2.3.Where a type of vehicle or a type of system has been modified by another manufacturer at the subsequent stage of completion of the vehicle, to the extent that, apart from the manufacturers name, the vehicle or system may still be considered as the same type, the requirement applying to existing types may still be applied as long as the date for first registration in the relevant regulatory act has not been reached.U.K.
3.2.4.The change of category of a vehicle shall lead to the application of the relevant requirements to the new category of vehicle. The EU type-approval certificates from the previous category shall be accepted provided that the vehicle complies with the same requirements as, or more stringent than, those applying to the new category.U.K.
3.3.Subject to the agreement of the approval authority, a whole-vehicle type-approval granted to the manufacturer of the subsequent stage of completion of the vehicle does not need to be extended or revised where an extension given at the previous stage vehicle does not affect the subsequent stage or the technical data of the vehicle. However, the type-approval number including the extension of the previous stage(s) vehicle shall be copied in the certificate of conformity of the subsequent stage vehicle.U.K.
3.4.Where the cargo area of a complete or completed vehicle of category N or O is modified by another manufacturer for the addition of removable fittings to store and secure the cargo (for example, load space lining, storage racks and roof racks), such items can be treated as part of the pay-mass and a type-approval is not needed, provided both of the following conditions are met:U.K.
the modifications do not affect the vehicle's type-approval in any way, other than an increase of the actual mass of the vehicle;
the added fittings can be removed without using special tools.
4.Identification of the vehicleU.K.
4.1.The VIN, prescribed by Regulation (EU) No 19/2011, shall be retained during all the subsequent stages of the type-approval to ensure the traceability of the process.U.K.
4.2.At the second and subsequent stages, in addition to the statutory plate prescribed by Regulation (EU) No 19/2011, each manufacturer shall affix to the vehicle an additional plate the model of which is shown in the Appendix to this Annex. This plate shall be firmly attached, in a conspicuous and readily accessible position on a part not subject to replacement in use. It shall clearly and indelibly show the following information in the order listed:U.K.
the name of the manufacturer;
sections 1, 3 and 4 of the EU type-approval number;
the stage of approval;
the VIN of the base vehicle;
the technically permissible maximum laden mass of the vehicle where the value has changed during the current stage of approval;
the technically permissible maximum laden mass of the combination (where the value has changed during the current stage of approval and where the vehicle is permitted to tow a trailer). ‘0’ shall be used if the vehicle is not permitted to tow a trailer;
the technically permissible maximum mass on each axle, listed in order from front to rear where the value has changed during the current stage of approval;
in the case of a semi-trailer or centre axle trailer, the technically permissible maximum mass at the coupling point where the value has changed during the current stage of approval.
Unless otherwise provided for in point 4.1 and this point the additional plate shall comply with the requirements set out in Annex I and Annex II to Regulation (EU) No 19/2011.
AppendixModel of the manufacturer's additional plate
The example below is given as a guide only.
MANUFACTURER'S NAME (stage 3)U.K.
e2*201X/XX*2609
Stage 3
WD9VD58D98D234560
1 500 kg
2 500 kg
1 – 700 kg
2 – 810 kg
ANNEX XU.K. ACCESS TO VEHICLE OBD INFORMATION AND VEHICLE REPAIR AND MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
1.IntroductionU.K.
This Annex lays down technical requirements for the access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information.
2.Access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance informationU.K.
2.1.A manufacturer shall put in place the necessary arrangements and procedures, in accordance with Article 61, to ensure that vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information is accessible through websites using a standardised format in a readily accessible and prompt manner, and in a manner which is non-discriminatory compared to the provisions given or access granted to authorised dealers and repairers.U.K.
2.2.An approval authority shall only grant type-approval after receiving from the manufacturer a certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information.U.K.
2.3.The certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information shall serve as the proof of compliance with Article 64.U.K.
2.4.The certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information shall be drawn up in accordance with the model set out in Appendix 1.U.K.
2.5.The vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information shall include the following:U.K.
an unequivocal identification of the vehicle, system, component or separate technical unit for which the manufacturer is responsible;
service handbooks, including service and maintenance records;
technical manuals;
component and diagnosis information (such as minimum and maximum theoretical values for measurements);
wiring diagrams;
diagnostic trouble codes, including manufacturer specific codes;
the software calibration identification number applicable to a type of vehicle;
information provided concerning, and delivered by means of, proprietary tools and equipment;
data record information and two-directional monitoring and test data;
standard work units or time periods for repair and maintenance tasks if they are made available to authorised dealers and repairers of the manufacturer either directly or through a third party;
in case of multi-stage type-approval, the information required under point 3, and all other information necessary to comply with the requirements set out in Article 61.
2.6.The manufacturer shall make available to interested parties the following information:U.K.
relevant information to enable the development of replacement components that are critical to the correct functioning of the OBD system;
information to enable the development of generic diagnostic tools.
2.7.For the purposes of point 2.6.1., the development of replacement components shall not be restricted by any of the following:U.K.
the unavailability of pertinent information;
the technical requirements relating to malfunction indication strategies if the OBD thresholds are exceeded or if the OBD system is unable to fulfil the basic OBD monitoring requirements of this Regulation;
specific modifications to the handling of OBD information to deal independently with vehicle operation on petrol or on gas;
the type-approval of gas-fuelled vehicles that contain a limited number of minor deficiencies.
2.8.For the purposes of point 2.6.2, where manufacturers use diagnostic and test tools in accordance with ISO 22900 – Modular vehicle communication interface (MVCI) – and ISO 22901 – Open diagnostic data exchange (ODX) in their franchised networks –, the ODX files shall be accessible to independent operators via the website of the manufacturer.U.K.
2.9.For the purpose of vehicle OBD, diagnostics, repair and maintenance, the direct vehicle data stream shall be made available through the serial data port on the standardised data link connector specified in paragraph 6.5.1.4 of Appendix 1 of Annex 11 to UN Regulation No 83 and paragraph 4.7.3 of Annex 9B to UN Regulation No 49.U.K.
When the vehicle is in motion, the data shall only be made available for read-only functions.
3.Multi-stage type-approvalU.K.
3.1.In the case of a multi-stage type-approval, the final manufacturer shall be responsible for providing access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information regarding its own manufacturing stage(s) and the link to the previous stage(s).U.K.
3.2.In addition, the final manufacturer shall on its website provide independent operators with the following information:U.K.
the website address of the manufacturer(s) responsible for the previous stage(s);
the name and address of all the manufacturers responsible for the previous stage(s);
the type-approval number(s) of the previous stage(s);
the engine number.
3.3.Each manufacturer responsible for a particular stage or stages of type-approval shall be responsible for providing through his website access to vehicle OBD and vehicle repair and maintenance information regarding the stage(s) of type-approval for which he is responsible and the link to the previous stage(s).U.K.
3.4.The manufacturer responsible for a particular stage or stages of type-approval shall provide the following information to the manufacturer responsible for the next stage:U.K.
the certificate of conformity relating to the stage(s) for which he is responsible;
the certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information, including its annexes;
the type-approval number corresponding to the stage(s) for which he is responsible;
the documents referred to in points 3.4.1, 3.4.2 and 3.4.3 as provided by the manufacturer(s) involved in the previous stage(s).
3.5.Each manufacturer shall authorise the manufacturer responsible for the next stage to pass the documents to the manufacturers responsible for any subsequent stages and the final stage.U.K.
3.6.In addition, on a contractual basis, the manufacturer responsible for a particular stage or stages of type-approval shall:U.K.
provide the manufacturer responsible for the next stage with access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information and interface information corresponding to the particular stage(s) for which he is responsible;
provide, at the request of a manufacturer responsible for a subsequent stage of type-approval, with access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information and interface information corresponding to the particular stage(s) for which he is responsible.
3.7.A manufacturer, including a final manufacturer, may only charge fees in accordance with Article 63 concerning the particular stage(s) for which he is responsible.U.K.
A manufacturer, including a final manufacturer, shall not charge fees for providing information relating to the website address or contact details of any other manufacturer.
4.Customer adaptationsU.K.
4.1.By derogation from point 2, if the number of systems, components or separate technical units subject to a specific customer adaptation is lower than 250 units produced worldwide, repair and maintenance information for the customer adaptation shall be provided in a readily accessible and prompt manner, and in a manner which is non-discriminatory compared to the provisions given or access granted to authorised dealers and repairers.U.K.
For the servicing and reprogramming of the electronic control units relating to the customer adaptation, the manufacturer shall make the respective proprietary specialist diagnostic tool or test equipment available to independent operators as provided to authorised repairers.
The customer adaptations shall be listed on the manufacturer's repair and maintenance information website and mentioned in the certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information at the time of type-approval.
4.2.Manufacturers shall make the proprietary specialist diagnostic tool or test equipment to service the customer-adapted systems, components or technical units available to independent operators via sale and rent.U.K.
4.3.The manufacturer shall mention in the certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information, at the time of type-approval, the customer adaptations for which the obligation under point 2 to provide access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information in a standardised format is derogated from and any electronic control unit related to them.U.K.
Those customer adaptations and any electronic control unit related to them shall also be listed on the manufacturer's repair and maintenance information website.
5.Small volume manufacturersU.K.
5.1.By derogation from point 2, manufacturers whose worldwide annual production of a type of vehicle, system, component or separate technical unit subject to this Regulation is for vehicles of category M1 and N1 less than 1 000 vehicles or for vehicles of category M2, M3, N2, N3 and O less than 250 units, shall provide access to vehicle repair and maintenance information in a readily accessible and prompt manner, and in a manner that is non-discriminatory compared to the provisions given or access granted to authorised dealers and repairers.U.K.
5.2.The vehicle, system, component and separate technical unit subject to point 5.1 shall be listed on the manufacturer's repair and maintenance information website.U.K.
5.3.The approval authority shall inform the Commission of each type-approval granted to small volume manufacturers.U.K.
6.RequirementsU.K.
6.1.Vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information available through websites shall follow the relevant common standard referred to in Article 61.U.K.
Those requiring the right to duplicate or republish the information shall negotiate directly with the manufacturer concerned. Information for training material shall also be available, but may be presented through other media than websites.
Information on all parts of the vehicle, with which the vehicle, as identified by the VIN and any additional criteria such as wheelbase, engine output, trim level or options, is equipped by the vehicle manufacturer and that can be replaced by spare parts offered by the vehicle manufacturer to its authorised repairers or dealers or third parties by means of reference to original equipment (OE) parts number, shall be made available, in the form of machine readable and electronically processable datasets, in a database that is easily accessible to independent operators.
This database shall comprise the VIN, OE parts numbers, OE naming of the parts, validity attributes (valid-from and valid-to dates), fitting attributes and, where applicable, structuring characteristics.
The information on the database shall be updated regularly. If this information is available to authorised dealers, the updates shall include in particular all modifications to individual vehicles after their production.
6.2.Access to vehicle security features used by authorised dealers and repairers shall be made available to independent operators under protection of security technology in accordance with the following requirements:U.K.
data shall be exchanged ensuring confidentiality, integrity and protection against replay;
the standard https//ssl-tls (RFC4346) shall be used;
security certificates in accordance with international standard ISO 20828 shall be used for mutual authentication of independent operators and manufacturers;
the independent operator's private key shall be protected by secure hardware.
6.3.The Forum on Access to Vehicle Information referred to in Article 66 shall specify the parameters for fulfilling the requirements referred to in point 6.2 in accordance with the state of the art. The independent operator shall be approved and authorised for this purpose on the basis of documents demonstrating that he pursues a legitimate business activity and has not been convicted of any relevant criminal activity.U.K.
6.4.Reprogramming of control units shall be conducted in accordance with either international standard ISO 22900-2 or SAE J2534 or TMC RP1210B using non-proprietary hardware.U.K.
For the validation of the compatibility of the manufacturer-specific application and the vehicle communication interfaces (VCI) complying to international standard ISO 22900-2 or SAE J2534 or TMC RP1210B, the manufacturer shall offer either a validation of independently developed VCIs or the information, and loan of any special hardware, required for a VCI manufacturer to conduct such validation himself.
The conditions of Article 63(1) shall apply to fees for such validation or information and hardware.
6.5.The requirements of point 6.4. shall not apply in the case of reprogramming of speed limitation devices and recording equipment.U.K.
6.6.All emission-related DTCs shall be consistent with Annex XI to Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 and Annex X to Regulation (EU) No 582/2011.U.K.
6.7.For access to any vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information other than that relating to secure areas of the vehicle, registration requirements for use of the manufacturer's website by an independent operator shall require only such information as is necessary to confirm how payment for the information is to be made. For information concerning access to secure areas of the vehicle, the independent operator shall present a certificate in accordance with international standard ISO 20828 to identify himself and the organisation to which he belongs and the manufacturer shall respond with his own certificate in accordance with international standard ISO 20828 to confirm to the independent operator that he is accessing a legitimate site of the intended manufacturer. Both parties shall keep a log of any such transactions indicating the vehicles and changes made to them under this provision.U.K.
6.8.Manufacturers shall indicate in their repair information websites the type-approval number by model.U.K.
6.9.If the vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information that is available on a manufacturer's website does not contain specific relevant information to permit the proper design and manufacture of alternative fuels retrofit systems, any interested alternative fuels retrofit system manufacturer shall be able to obtain the information required by contacting the manufacturer directly with such a request. Contact details for that purpose shall be clearly indicated on the manufacturer's website and the information shall be provided within 30 days. It shall only be necessary to provide such information for alternative fuels retrofit systems that are subject to UN Regulation No 115 or for alternative fuels retrofit components that form part of systems subject to UN Regulation No 115. In addition, it shall only be necessary to provide such information in response to a request that clearly specifies the exact specification of the vehicle model for which the information is required and that specifically confirms that the information is required for the development of alternative fuels retrofit systems or components subject to UN Regulation No 115.U.K.
7.Requirements for type-approvalU.K.
7.1.In order to receive a type-approval, the manufacturer shall submit the filled in certificate, the template of which is provided in Appendix 1.U.K.
7.2.Where the vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information is not available, or does not conform to the requirements of this Annex, the manufacturer shall provide that information within six months of the date of the type-approval.U.K.
7.3.The obligation to provide information within the period referred to in point 7.2. shall apply only if, following the type-approval, the vehicle is placed on the market.U.K.
Where the vehicle is placed on the market more than six months after the type-approval has been granted the information shall be provided on the date on which the vehicle is placed on the market.
7.4.On the basis of a completed certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information, the approval authority may presume that the manufacturer has put in place satisfactory arrangements and procedures with regard to access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information, provided that no complaint has been made and that the manufacturer provides that certificate within the period referred to in point 7.2.U.K.
Appendix 1Manufacturer's certificate on access to vehicle OBD information and vehicle repair and maintenance information
ANNEX A WEBSITE ADDRESSES REFERRED TO IN THIS CERTIFICATE:
ANNEX B CONTACT DETAILS OF THE MANUFACTURER'S REPRESENTATIVE REFERRED TO IN THIS CERTIFICATE:
ANNEX C TYPES OF VEHICLE, SYSTEM, COMPONENT OR SEPARATE TECHNICAL UNIT:
Appendix 2Vehicle OBD information
1.The vehicle manufacturer shall provide the information required in this Appendix for the purposes of enabling the manufacture of OBD-compatible replacement or service parts and diagnostic tools and test equipment.U.K.
2.Upon request, the following information shall be made available, on a non-discriminatory basis, to any interested manufacturer of components, diagnostic tools or test equipment:U.K.
a description of the type and number of the preconditioning cycles used for the original type-approval of the vehicle;
a description of the type of the OBD demonstration cycle used for the original type-approval of the vehicle for the component monitored by the OBD system;
a comprehensive document describing all sensed components with the strategy for fault detection and MI activation (fixed number of driving cycles or statistical method), including a list of relevant secondary sensed parameters for each component monitored by the OBD system and a list of all OBD output codes and format used (with an explanation of each code and format) associated with individual emission-related power-train components and individual non-emission related components, where monitoring of the component is used to determine MI activation. In particular, in the case of types of vehicles that use a communication link in accordance with ISO 15765-4 ‘Road vehicles — Diagnostics on controller area network (CAN) — Part 4: Requirements for emissions-related systems’, a comprehensive explanation for the data given in service $ 05 Test ID $ 21 to FF and the data given in service $ 06, and a comprehensive explanation for the data given in service $ 06 Test ID $ 00 to FF, for each OBD monitor ID supported, shall be provided.
In case other communication protocols standards are used, equivalent comprehensive explanation shall be provided.
This information may be provided in the form of a table, with the following column and row headings:
Component Fault code; Monitoring strategy; Fault detection criteria; MI activation criteria; Secondary parameters; Preconditioning Demonstration test.
Catalyst P0420 Oxygen sensor; 1 and 2 signals; Difference between sensor 1 and sensor 2 signals; 3rd cycle Engine speed; engine load; A/F mode; catalyst temperature; Two Type 1 cycles; Type 1.
3.Information required for the manufacturing of diagnostic toolsU.K.
In order to facilitate the provision of generic diagnostic tools for multi-make repairers, vehicle manufacturers shall make available the information referred to in points 3.1, 3.2 and 3.3 through their repair information websites. That information shall include all diagnostic tool functions and all the links to repair information and troubleshooting instructions. The access to the information may be subject to the payment of a reasonable fee.
3.1.Communication protocol informationU.K.
The following information shall be required indexed against vehicle make, model and variant, or another workable definition such as the VIN or the vehicle and systems identification:
any additional protocol information system necessary to enable complete diagnostics in addition to the standards prescribed in paragraph 4.7.3 of Annex 9B to UN Regulation No 49 and in paragraph 6.5.1.4 of Annex 11 to UN Regulation No 83, including any additional hardware or software protocol information, parameter identification, transfer functions, ‘keep alive’ requirements, or error conditions;
details of how to obtain and interpret all the fault codes that do not comply with the standards prescribed in paragraph 4.7.3 of Annex 9B to UN Regulation No 49 and in paragraph 6.5.1.4 of Annex 11 to UN Regulation No 83;
a list of all available live data parameters, including scaling and access information;
a list of all available functional tests, including device activation or control and the means to implement them;
details of how to obtain all component and status information, time stamps, pending DTC and freeze frames;
resetting adaptive learning parameters, variant coding and replacement component setup, and customer preferences;
Electronic control unit (ECU) identification and variant coding;
details of how to reset service lights;
location of diagnostic connector and connector details;
engine code identification.
3.2.Test and diagnosis of OBD monitored componentsU.K.
The following information shall be required:
a description of tests to confirm the functionality, at the component or in the harness;
information concerning the test procedure, including test parameters and component information;
connection details, including minimum and maximum input and output and driving and loading values;
values to be expected under certain driving conditions, including idling;
electrical values for the component in its static and dynamic states;
failure mode values for each of the scenarios;
failure mode diagnostic sequences, including fault trees and guided diagnostics elimination.
3.3.Data required to perform the repairU.K.
The following information shall be required:
ECU and component initialisation (in the event of replacements being fitted);
initialisation of new or replacement ECU's where relevant using pass-through (re-) programming techniques.
ANNEX XIU.K. CORRELATION TABLE
1.Regulation (EC) No 715/2007U.K.
| Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 | This Regulation |
|---|---|
| Article 1(2) | Article 86(1), point (2) |
| Article 3, points (14) and (15) | Article 3, points (48) and (45) |
| Article 6 | Article 61 |
| Article 7 | Article 63 |
| Article 8 | — |
| Article 9 | — |
| Article 13(2), point (e) | Article 86(1), point (5) |
2.Regulation (EC) No 595/2009U.K.
| Regulation (EC) No 595/2009 | This Regulation |
|---|---|
| Article 1, second paragraph | Article 87(1), point 2 |
| Article 3, points (11) and (13) | Article 3, points (48) and (45) |
| Article 6 | Article 61 |
| Article 11(2), point (e) | Article 84(3), point (a) |
3.Directive 2007/46/ECU.K.
| Directive 2007/46/EC | This Regulation |
|---|---|
| Article 1 | Article 1(1) |
| — | Article 1(2) |
| Article 2 | Article 2 |
| Article 3, point (1) | — |
| Article 3, point (2) | — |
| Article 3, point (3) | Article 3, point (1) |
| Article 3, point (4) | Article 3, point (3) |
| Article 3, point (5) | Article 3, point (2) |
| Article 3, point (6) | Article 3, point (6) |
| Article 3, point (7) | Article 3, point (8) |
| Article 3, point (8) | Article 3, point (9) |
| Article 3, point (9) | Article 3, point (10) |
| Article 3, point (10) | Article 3, point (11) |
| Article 3, point (11) | Article 3, point (16) |
| Article 3, point (12) | Article 3, point (17) |
| Article 3, point (13) | Article 3, point (15) |
| Article 3, point (14) | — |
| Article 3, point (15) | — |
| Article 3, point (16) | — |
| Article 3, point (17) | Article 3, point (32) |
| Article 3, point (18) | Article 3, point (24) |
| Article 3, point (19) | Article 3, point (25) |
| Article 3, point (20) | Article 3, point (26) |
| Article 3, point (21) | Article 3, point (27) |
| Article 3, point (22) | Article 3, point (28) |
| Article 3, point (23) | Article 3, point (18) |
| Article 3, point (24) | Article 3, point (19) |
| Article 3, point (25) | Article 3, point (20) |
| Article 3, point (26) | — |
| Article 3, point (27) | Article 3, point (40) |
| Article 3, point (28) | Article 3, point (41) |
| Article 3, point (29) | Article 3, point (36) |
| Article 3, point (30) | — |
| Article 3, point (31) | Article 3, point (38) |
| Article 3, point (32) | Article 3, point (54) |
| Article 3, point (33) | Article 3, point (4) |
| Article 3, point (34) | — |
| Article 3, point (35) | — |
| Article 3, point (36) | Article 3, point (5) |
| Article 3, points (37) to (40) | — |
| — | Article 3, point (7) |
| — | Article 3, points (12), (13) and (14)) |
| — | Article 3, points (21), (22) and (23) |
| — | Article 3, points (29), (30), (31), (33), (34) and (35) |
| — | Article 3, point (37) |
| — | Article 3, point (39) |
| — | Article 3, points (42) to (53) |
| — | Article 3, points (55) to (58) |
| — | Article 5(2) and (3) |
| — | Article 6(1), third subparagraph, (2) and (3) |
| — | Article 7(2), (3) and (4) |
| Article 4(1) | — |
| Article 4(2) | Article 7(1) |
| Article 4(3), first subparagraph | Article 6(4) |
| Article 4(3), second subparagraph | Article 6(5), first subparagraph |
| Article 4(4) | Article 6(1), first and second subparagraphs |
| — | Article 6(5), second subparagraph and (6) to (10) |
| — | Article 8 |
| — | Article 9 |
| — | Article 10 |
| — | Article 11 |
| — | Article 12 |
| Article 5(1) | Article 13(1) and (2), first subparagraph |
| Article 5(2), first subparagraph | Article 13(2), second subparagraph |
| Article 5(2), second subparagraph | Article 13(3) |
| Article 5(3) | Article 13(4), first sentence |
| — | Article 13(4), second sentence and (5) to (10) |
| — | Article 14 |
| — | Article 15 |
| — | Article 16 |
| — | Article 17 |
| — | Article 18 |
| — | Article 19 |
| — | Article 20 |
| — | Article 21 |
| Article 6(1) | Article 22(1) |
| — | Article 22(2) and (4) |
| Article 6(2) | Article 25(1) |
| Article 6(3) | — |
| Article 6(4) | Article 25(2) |
| Article 6(5) | Article 22(5) and (6), and Article 25(3) |
| Article 6(6) and Article 7(1) | Article 23 |
| Article 6(7) and Article 7(3) | Article 25(4) |
| Article 6(8) and Article 7(4) | Article 30(4) |
| Article 7(2) | Article 24 |
| Article 8(1) and (2) | Article 26(1) and (3) |
| — | Article 26(2) and (4) |
| Article 8(3) | Article 26(5) |
| Article 8(4) | Article 28(2) |
| Article 8(5) to (8) | Article 27(1) and (2) |
| — | Article 27(3) |
| Article 9(1) | Article 5(1) |
| Article 9(2) | Article 22(3) |
| — | Article 28(1) and (3) |
| Article 9(3) | Article 28(4) |
| Article 9(4) | Article 28(5) |
| Article 9(5) | — |
| Article 9(6) and (7) | Article 28(6) and (7) |
| Article 10(1) and (2) | Article 29(1) |
| Article 10(3) | Article 29(2) |
| Article 10(4) | Article 29(3) |
| Article 11 | Article 30(1), (2) and (5) to (8) |
| Article 12(1) | Article 31(1) |
| — | Article 31(2) |
| Article 12(2), first subparagraph | Article 31(3) |
| Article 12(2), second subparagraph | Article 31(4) |
| — | Article 31(5), (6) and (8) |
| Article 12(3) | Article 31(7) |
| — | Article 32 |
| Article 13(1) | Article 33(1) |
| Article 13(2) | Article 33(2) |
| Article 13(3) | Article 33(3) and (4) |
| — | Article 33(5) |
| Article 14(1) and Article 15(1) | Article 34(1) |
| Article 14(2) and Article 15(2) | Article 34(2) |
| Article 14(3) and Article 15(3) | Article 34(3) |
| Article 14(4) | Article 34(4) |
| Article 16(1) and (2) | Article 27(1) |
| Article 16(3) | Article 27(2) |
| Article 17(1) to (4) | Article 35(2) to (5) |
| Article 18(1) and (3) | Article 36(1) and (4) |
| — | Article 36(2) |
| Article 18(2) | Article 36(5) |
| — | Article 36(6) and (7) |
| Article 18(4) | Article 36(8) and (9) |
| Article 18(5) and (6) | Article 36(4) |
| Article 18(7) | Article 37(2) |
| Article 18(8) | Article 36(3) |
| — | Article 37(1) and (3) to (9) |
| — | Article 38(1) |
| Article 19(1) and (2) | Article 38(2) |
| Article 19(3) | Article 38(3) |
| Article 20(1) | Article 39(1) |
| Article 20 (2), introductory wording | Article 39(4) |
| Article 20 (2), points (a), (b) and (c) | Article 39(2) |
| Article 20(3) | Article 39(5) |
| Article 20(4), first subparagraph | Article 39(3) |
| Article 20(4), second subparagraph | Article 39(6) |
| Article 20(4), third subparagraph | Article 39(7) |
| Article 20 (5) | — |
| Article 21 | Article 40 |
| Article 22 | Article 41 |
| Article 23(1) | Article 42(1) |
| Article 23(2) and (3) | Article 42(2) |
| Article 23(4) | Article 42(3) |
| Article 23(5) | Article 42(4) |
| — | Article 42(5) |
| Article 23(6), first subparagraph | Article 43(1) and (2) |
| Article 23(6), second subparagraph | Article 43(3) |
| Article 23(6), third subparagraph | Article 43(4) |
| Article 23(7) | Article 43(5) |
| — | Article 44 |
| Article 24 | Articles 45 and 46 |
| Article 25 | Article 47 |
| Article 26(1) | Article 48(1) |
| Article 26(2) | — |
| Article 26(3) | Article 48(2) |
| Article 27 | Article 49 |
| Article 28 | Article 50 |
| — | Article 51 |
| Article 29(1), first subparagraph | Article 52(1) and (3) |
| — | Article 52(2) |
| — | Article 52(4) |
| Article 29(1), second subparagraph | Article 53(1) and (2) |
| — | Article 53(3) and (4) |
| Article 29(2) | Article 53(5), first subparagraph |
| — | Article 53(5), second subparagraph, (6) and (8) |
| Article 29(3) | Article 53(7) |
| Article 29(4) | — |
| Article 30(1) | Article 53(1) |
| Article 30(2), first subparagraph | Article 53(2) |
| Article 30(2), second subparagraph | — |
| Article 30(3) | Article 54(1) |
| Article 30(4) | Article 54(2), (3) and (4), first subparagraph |
| Article 30(5) | Article 54(4), second subparagraph |
| Article 30(6) | Article 54(5) |
| Article 31(1) to (4) | Article 55 |
| Article 31(5), first subparagraph | Article 56(1) |
| Article 31(5), second and third subparagraphs | Article 56(2) |
| Article 31(6) and (7) | — |
| Article 31(8) | Article 56(3) |
| Article 31(9) | Article 56(4) |
| — | Article 56(5) |
| Article 31(10) | Article 56(6) |
| Article 31(11) | — |
| Article 31(12), first subparagraph | Article 56(7) |
| Article 31(12), second subparagraph | — |
| Article 31(13) | — |
| Article 32 | Article 53 |
| Article 33 | — |
| Article 34(1) | Article 57(1) |
| Article 34(2) | Article 57(2) |
| Article 34(3) and (4) | — |
| Article 35 | Article 58 |
| Article 36 | — |
| Article 37 | Article 59 |
| Article 38 | Article 60 |
| — | Article 62 |
| — | Article 64 |
| — | Article 65 |
| — | Article 66 |
| — | Article 67 |
| Article 39 | Article 82 |
| Article 40 | Article 83 |
| Article 41(1) and (3) | Article 68(1) |
| Article 41(2) | Article 80(1) |
| Article 41(4) | Article 70 |
| Article 41(5) | Article 68(2) |
| — | Article 69(3) and (4) |
| Article 41(6) | Article 72(1) |
| Article 41(7) | Article 72(2) and (3) |
| Article 41(8) | Article 68(5) |
| — | Article 69 |
| — | Article 71 |
| Article 42 | Article 73 |
| Article 43(1) and (3) | Article 74(1) |
| Article 43(2) | Article 74(2) |
| Article 43(4) | Article 75 |
| Article 43(5) | Article 74(3) |
| — | Article 76 |
| — | Article 77 |
| — | Article 78 |
| — | Article 79 |
| — | Article 80(2) and (3) |
| — | Article 81 |
| Article 44 | Article 89 |
| Article 45 | Article 91 |
| Article 46 | Article 84 |
| — | Article 85 |
| Article 47 | Article 90 |
| Article 48 | — |
| Article 49 | Article 88 |
| — | Article 86 |
| — | Article 87 |
| Article 50 | Article 91 |
| Article 51 | — |
| Annexes I and III | Article 24(4) |
| Annex II, part A, points 1 to 1.3.4. | Article 4 |
| Annex II, part A, points 2 to 6.2, part B, part C, Appendices 1 and 2 | Annex I |
| Annex IV | Annex II, parts I and II |
| Annex V, Appendices 1 and 2 | Annex III |
| Annex V, Appendix 3 | Article 30(3) |
| Annexes VI, VII and VIII | Article 28(3) |
| Annex IX | Article 36(3) |
| Annex X | Annex IV |
| Annex XI | Annex IV, part III |
| Annex XII | Annex V |
| Annex XIII | Annex VI |
| Annex XIV | — |
| Annex XV | Annex VII |
| Annex XVI | Annex VIII |
| Annex XVII | Annex IX |
| — | Annex X |
| Annex XIX | — |
| Annex XX | — |
| Annex XXI | Annex XI |
Council Directive 80/181/EEC of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to units of measurement and on the repeal of Directive 71/354/EEC (OJ L 39, 15.2.1980, p. 40).
Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1151 of 1 June 2017 supplementing Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council on type-approval of motor vehicles with respect to emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro 5 and Euro 6) and on access to vehicle repair and maintenance information, amending Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 and Commission Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 and repealing Commission Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 (OJ L 175, 7.7.2017, p. 1).
Regulation (EU) No 510/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 May 2011 setting emission performance standards for new light commercial vehicles as part of the Union's integrated approach to reduce CO2 emissions from light-duty vehicles (OJ L 145, 31.5.2011, p. 1).
Commission Regulation (EU) No 1230/2012 of 12 December 2012 implementing Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to type-approval requirements for masses and dimensions of motor vehicles and their trailers and amending Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 353, 21.12.2012, p. 31).
For subsequent amendments, see UNECE TRANS/WP.29/343.
In the absence of a registration document, the competent authority may refer to available documented evidence of date of manufacture or documented evidence of first purchase.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Regulation
PrintThe Annexes only
You have chosen to open the Whole Regulation
The Whole Regulation you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
You have chosen to open Schedules only
The Schedules you have selected contains over 200 provisions and might take some time to download. You may also experience some issues with your browser, such as an alert box that a script is taking a long time to run.
Would you like to continue?
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
Point in Time: This becomes available after navigating to view revised legislation as it stood at a certain point in time via Advanced Features > Show Timeline of Changes or via a point in time advanced search.
See additional information alongside the content
Geographical Extent: Indicates the geographical area that this provision applies to. For further information see ‘Frequently Asked Questions’.
Show Timeline of Changes: See how this legislation has or could change over time. Turning this feature on will show extra navigation options to go to these specific points in time. Return to the latest available version by using the controls above in the What Version box.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Timeline of Changes
This timeline shows the different versions taken from EUR-Lex before exit day and during the implementation period as well as any subsequent versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation.
The dates for the EU versions are taken from the document dates on EUR-Lex and may not always coincide with when the changes came into force for the document.
For any versions created after the implementation period as a result of changes made by UK legislation the date will coincide with the earliest date on which the change (e.g an insertion, a repeal or a substitution) that was applied came into force. For further information see our guide to revised legislation on Understanding Legislation.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources