- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As made)
The Antarctic (Amendment) Regulations 2003
You are here:
- UK Statutory Instruments
- 2003 No. 323
- Whole Instrument
- Previous
- Next
More Resources
Status:
This is the original version (as it was originally made). This item of legislation is currently only available in its original format.
Statutory Instruments
2003 No. 323
ANTARCTICA
The Antarctic (Amendment) Regulations 2003
Made
17th February 2003
Laid before Parliament
18th February 2003
Coming into force
11th March 2003
The Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs, in exercise of his powers under sections 9(1), 25(1) and (3) and 32 of the Antarctic Act 1994(1), and of all other powers enabling him in that behalf, hereby makes the following Regulations:
Citation and commencement
1. These Regulations may be cited as the Antarctic (Amendment) Regulations 2003 and shall come into force on 11th March 2003. The Antarctic Regulations 1995(2) (“the principal Regulations”), as amended(3), and these Regulations may be cited together as the Antarctic Regulations 1995 to 2003.
Amendment of Schedule 1 to the principal Regulations
2. Schedule 1 to the principal Regulations shall be amended as follows:
(a)There shall be added to Schedule 1 the areas listed and described in the Schedule to these Regulations.
(b)There shall be deleted from Schedule 1 the area listed and described as “Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 157 “Cape Royds Historic Site No. 15””.
Valerie Amos
For the Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs
17th February 2003
Regulation 2
SCHEDULERESTRICTED AREAS
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 106, Cape Hallett, Northern Victoria Land, Ross Sea, Lat. 72°19−S; Long. 170°16−E
Cape Hallett is located at the southern end of Moubray Bay, Northern Victoria Land, in the western Ross Sea. The protected area occupies ice-free ground of a cuspate spit of low elevation known as Seabee Hook and includes the adjacent western slopes of the north end of the Hallett Peninsula. The Area includes Seabee Hook and the adjacent western slopes up to the crest of the ridge of the north end of the Hallett Peninsula, east of Willett Cove to the margin of the permanent ice sheet. The sea-level boundary is predominantly defined by the coastline of Seabee Hook, and extends south along the east shore of Willett Cove to the southernmost boundary at 72°19−S (approximately 800 metres south of the Moubray Bay coast). The east boundary of the Area follows the edge of the permanent ice sheet near the ridge of Hallett Peninsula.
Map: Cape Hallett, ASPA No. 106, Northern Victoria Land, Ross Sea
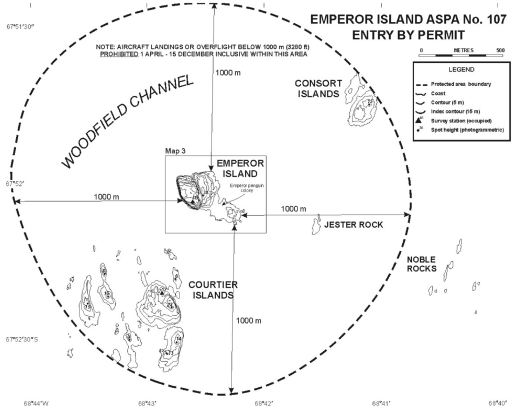
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 107 Emperor Island, Dion Islands, Marguerite Bay, Antarctic Peninsula Lat. 67°52−S; Long. 68°42−W
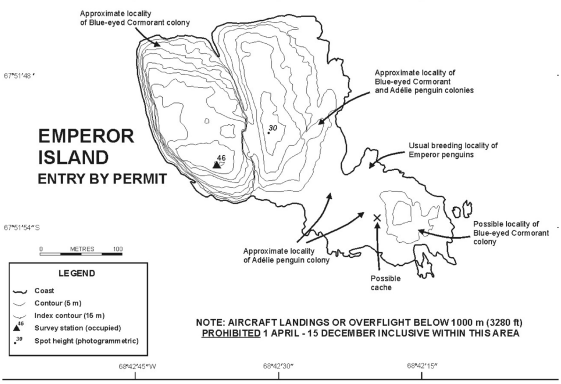
The Dion Islands, situated 13.5 kilometres south of the south-western extremity of Adelaide Island in north-western Marguerite Bay (Map 1), is a small archipelago comprising the following islands, rocks and reefs: Envoy Rock, Regent Reef, Consort Islands (approximately 3 hectares), Emperor Island (approximately 5 hectares), Jester Rock, Noble Rocks, Courtier Islands (approximately 8 hectares), Embassy Islands and Consul Reef. The islands are generally small, rocky and precipitous, especially Emperor Island, which at a maximum elevation of 46 metres is also the highest.
Map 1: Emperor Island, ASPA No. 107, Dion Islands
Map 2: Emperor Island, ASPA No. 107, Dion Islands, topographic map
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 108 Green Island, Berthelot Islands, Antarctic Peninsula Lat. 65°19−S; Long. 64°09−W
Green Island is a small island situated 150 metres north of the largest of the Berthelot Islands group, Grandidier Channel, approximately 3 kilometres off the Graham Coast of the Antarctic Peninsula (Map 1). Green Island is 520 metres from north to south and 500 metres from east to west, rising to a rounded peak at a height of 83 metres. The island rises steeply on all sides, with high precipitous cliffs on the south and east side.
Map 1: Green Island, ASPA No. 108, Berthelot Islands, location map
Map 2: Green Island, ASPA No. 108, Berthelot Islands, topographic map
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 117 Avian Island, Marguerite Bay, Antarctic PeninsulaLat. 67°46−S; Long. 68°54−W
Avian Island is situated in the north-west of Marguerite Bay, 400 metres south of the south-western extremity of Adelaide Island. The island is 1.45 kilometres long by 0.8 kilometres at its widest, and is of roughly triangular shape. It is rocky with a low relief of generally less than 10 metres in the north, rising to about 30 metres at the centre, and 40 metres in the south where several rock and ice slopes of up to 30 metres drop steeply to the sea. The coastline is irregular and rocky with numerous offshore islets, although there are several accessible beaches on the northern and eastern coasts. The designated Area comprises the whole of Avian Island and the littoral zone, offshore islets and rocks, and a buffer zone of the surrounding marine environment (including sea ice when present) within 100 metres of the shoreline of the main island (Map 2).
Map 1: Avian Island, ASPA No. 117, Marguerite Bay, Antarctic Peninsula, location map
Map 2: Avian Island, ASPA No. 117, Marguerite Bay, Antarctic Peninsula, topographic map
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 121 Cape Royds, Ross Island Lat. 77°33−S; Long. 166°10−E
Cape Royds is situated on the west side of Ross Island, McMurdo Sound, at the western extremity of a coastal strip of ice-free land approximately 8 kilometres wide, on the west slope of Mount Erebus. The Area comprises both a terrestrial and marine component.
The marine component of the Area extends for approximately 5 kilometres from Derrick Point in the south to Rocky Point in the north, including Horseshoe Bay. The marine boundary is defined as extending NE along the Arrival Bay coastline from the most easterly corner of the terrestrial boundary at Arrival Bay to Derrick Point. From Derrick Point the marine boundary extends offshore 500 metres in a SE direction and thence extends parallel to the coast 500 metres offshore from the mean high water mark, around Cape Royds and north for 5.3 kilometres to a point 500 metres due north of Rocky Point then due south to Rocky Point.
Map A: Cape Royds, Ross Island ASPA No. 121, regional topographic map
Map B: Cape Royds, Ross Island ASPA No. 121, (formerly SSSI No. 1) terrestrial area topographic map
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 123 Barwick and Balham Valleys, South Victoria Land Lat. 160°34−E; Long. 77°19−S
Barwick Valley is situated about 65 kilometres inland from the Ross Sea coast of South Victoria Land. The Area includes Barwick and Balham Valleys and their respective catchments and is bordered on the south, west and north by the McKelvey Valley, the Willet Range and the divide between the Victoria and Barwick Valleys, respectively.
Map: Barwick and Balham Valleys, ASPA No. 123 (formerly SSSI No. 3), South Victoria Land
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 124 Cape Crozier, Ross Island Lat. 77°26−S; Long. 169°12−E
Cape Crozier is at the eastern extremity of Ross Island, where an ice-free area comprises the lower eastern slopes of Mount Terror. The designated area is situated in the vicinity of Post Office Hill (407 metres), extending to encompass the adjacent Ross Ice Shelf where large cracks in the shelf are covered by fast-ice which is occupied annually by breeding Emperor penguins.
Map A: Cape Crozier, ASPA No. 124 (formerly SSSI No. 4), Ross Island, regional topographic map
Map B: Cape Crozier, ASPA No. 124 (formerly SSSI No. 4), Ross Island, site topographic map
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 126 Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island, South Shetland Islands Lat. 62°35−S; Long. 61°13−W
Byers Peninsula is situated at the west end of Livingston Island, the second-largest of the South Shetland Islands (Map 1). The peninsula has a central west-east extent of about 9 kilometres and a NW-SE extent of 18.2 kilometres, and is the largest ice-free area in the South Shetland Islands. The peninsula is generally of low, gently rolling relief, although there are a number of prominent hills ranging in altitude between 80–265 metres. The interior is dominated by a series of extensive platforms at altitudes of up to 105 metres, interrupted by isolated volcanic plugs such as Chester Cone (188 metres) and Cerro Negro (143 metres).
Map 1: Byers Peninsula, ASPA No. 126, Livingstone Island, South Shetland Islands, location mapInset: location of Byers Peninsula on the Antarctic Peninsula
Map 2: Byers Peninsula, ASPA No. 126, topographic map
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 137 Northwest White Island, McMurdo Sound Lat. 78°00−S; Long. 167°20−E.
White Island, part of the McMurdo volcanic complex, is situated approximately 20 kilometres SE of the edge of the McMurdo Ice Shelf and 25 kilometres SE of Hut Point, the location of McMurdo Station (United States) and Scott Base (New Zealand) on Ross Island. The roughly triangular island is approximately 30 kilometres long and 15 kilometres wide at its maximum, and rises to a maximum elevation of 762 metres in several locations. The island is predominantly ice-covered with most of the rock outcrops being in the north, and is completely surrounded by the permanent shelf ice, between 10 metres and 100 metres in thickness, of the McMurdo Ice Shelf and Ross Ice Shelf.
Map: Northwest White Island, ASPA No. 137, McMurdo Sound
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 147 Ablation Valley and Ganymede Heights, Alexander Island Lat. 70°48−S; Long. 68°30−W
Ablation Valley-Ganymede Heights is situated on the east side of Alexander Island, the largest island off the western coast of Palmer Land, Antarctic Peninsula (Map 1). The Area has a central west–east extent of about 10 kilometres and a north–south extent of about 18 kilometres, flanked to the west by the upper part of Jupiter Glacier, to the east by the permanent ice shelf in George VI Sound, to the north by Grotto Glacier and to the south by the lower reaches of Jupiter Glacier. Ablation Valley-Ganymede Heights contains the largest contiguous ice-free area in the Antarctic Peninsula sector of Antarctica.
Map 1: Ablation Valley and Ganymede Heights, ASPA No. 147, location mapInset: Location of Ablation Valley on the Antarctic Peninsula
Map 2: Ablation Valley and Ganymede Heights, ASPA No. 147, location map
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 148Mount Flora, Hope Bay, Antarctic PeninsulaLat. 63°25−S; Long. 57°01−W
Mount Flora is situated on the southeastern flank of Hope Bay, at the northern end of Trinity Peninsula, Antarctic Peninsula. The summit of Mount Flora (520 metres) is approximately 1 kilometre from the southern shore of Hope Bay. Four glaciers surround Mount Flora. The Flora Glacier extends from the cirque below the summit of Mount Flora in a northeasterly direction for one kilometre before it flows into a larger glacier that flanks the eastern and southern slopes of Mount Flora, extending northeast from The Pyramid (565 metres). The western slopes of Mount Flora are bounded by the Kenney Glacier, which joins Depot Glacier before flowing into the head of Hope Bay.
Map 1: Mount Flora, ASPA No. 148, Hope Bay, location mapInset: Location of Mount Flora on the Antarctic Peninsula
Map 2: Mount Flora, ASPA No. 148, Hope Bay, topographic map
Antarctic Specially Protected Area No. 157 Backdoor Bay, Cape Royds, Ross Island Lat. 77°33−S; Long. 166°10−E
Cape Royds is an ice-free area at the western extremity of Ross Island, approximately 40 kilometres to the south of Cape Bird and 35 kilometres to the north of Hut Point Peninsula on Ross Island. It contains the hut built in February 1908 by the British Antarctic Expedition of 1907–1909 led by Sir Ernest Shackleton.
Map: Backdoor Bay, ASPA No. 157 (formerly SPA No. 27), which borders Cape Royds, ASPA 121 (formerly SSSI 1), Cape Royds, Ross Island
Explanatory Note
(This note is not part of the Regulations)
The Regulations amend Schedule 1 to the Antarctic Regulations 1995 by adding further restricted areas, and by modifying the designation and boundary of one restricted area, to give effect to Measure 1(2002) of the Twenty-fifth Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (Warsaw, 2002).
Advice on where to obtain copies of the Measure referred to above may be obtained from Polar Regions Unit, Overseas Territories Department, Foreign and Commonwealth Office, London SW1A 2AH, Telephone 0207 7008 3986.
Options/Help
Print Options
Official printed copies
PrintThe Whole Instrument
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As Enacted or Made): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was enacted or made. No changes have been applied to the text.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as enacted version that was used for the print copy
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as made version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources