- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As adopted by EU)
Decision No 661/2010/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council (repealed)Show full title
Decision No 661/2010/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 7 July 2010 on Union guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network (recast) (Text with EEA relevance) (repealed)
You are here:
- Decisions originating from the EU
- 2010 No. 661
- Annexes only
More Resources
Revised version PDFs
- Revised 21/12/20130.44 MB
- Revised 01/07/201382.92 MB
When the UK left the EU, legislation.gov.uk published EU legislation that had been published by the EU up to IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.). On legislation.gov.uk, these items of legislation are kept up-to-date with any amendments made by the UK since then.
This item of legislation originated from the EU
Legislation.gov.uk publishes the UK version. EUR-Lex publishes the EU version. The EU Exit Web Archive holds a snapshot of EUR-Lex’s version from IP completion day (31 December 2020 11.00 p.m.).
Status:
This is the original version as it was originally adopted in the EU.
This legislation may since have been updated - see the latest available (revised) version
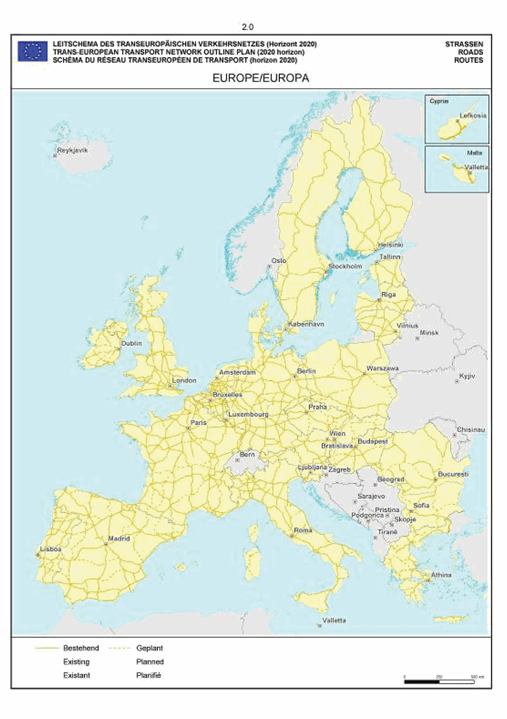
ANNEX I NETWORK SCHEMES ILLUSTRATED BY MAPS (1)
Section 2: Road network
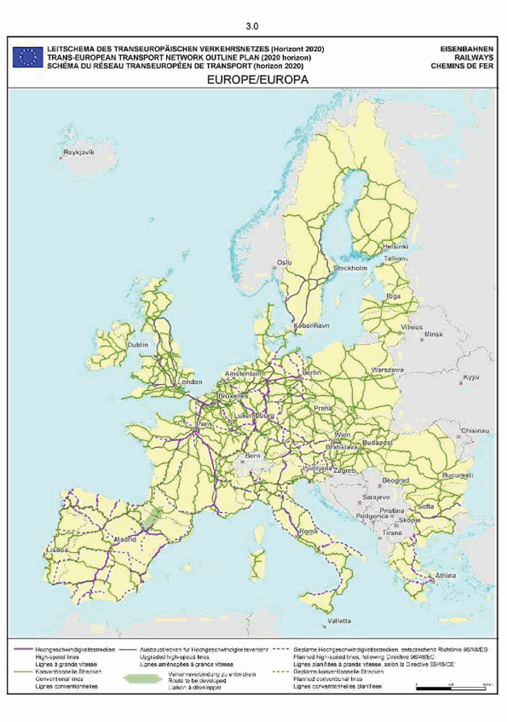
Europe
Belgium
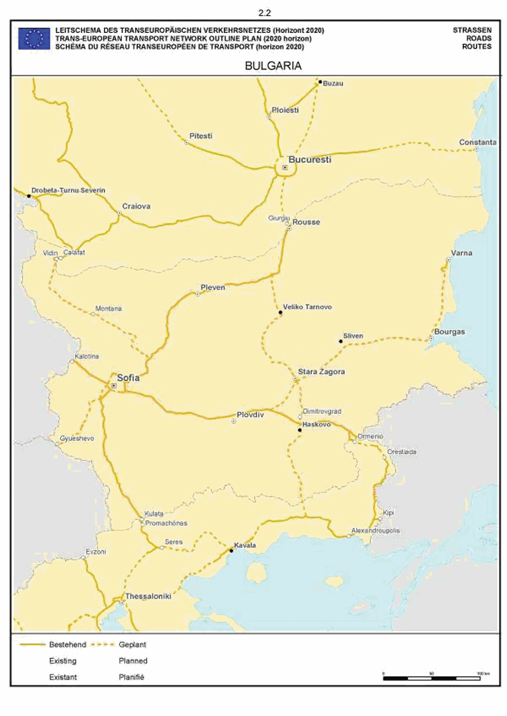
Bulgaria
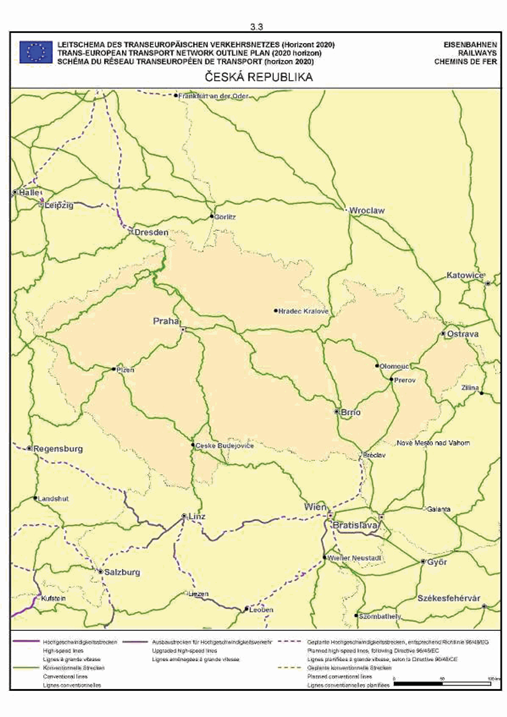
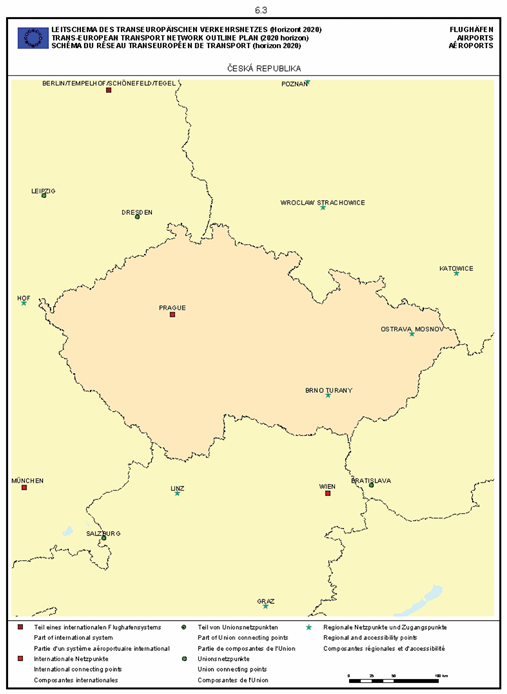
Czech Republic
Denmark
Germany
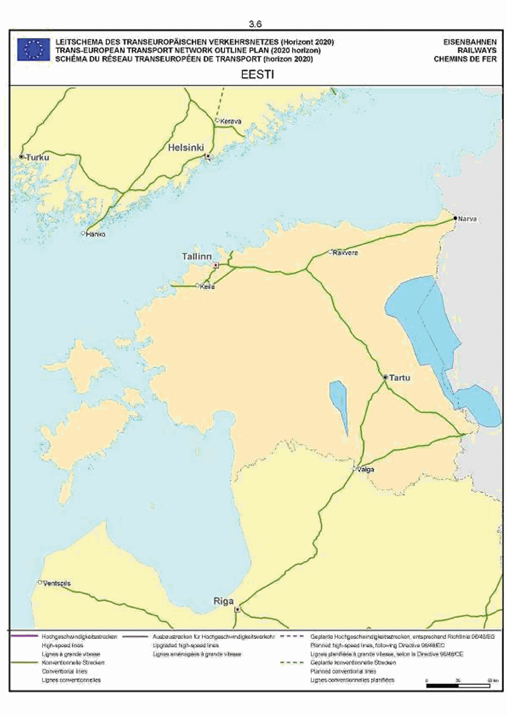
Estonia
Ireland
Greece
Spain
France
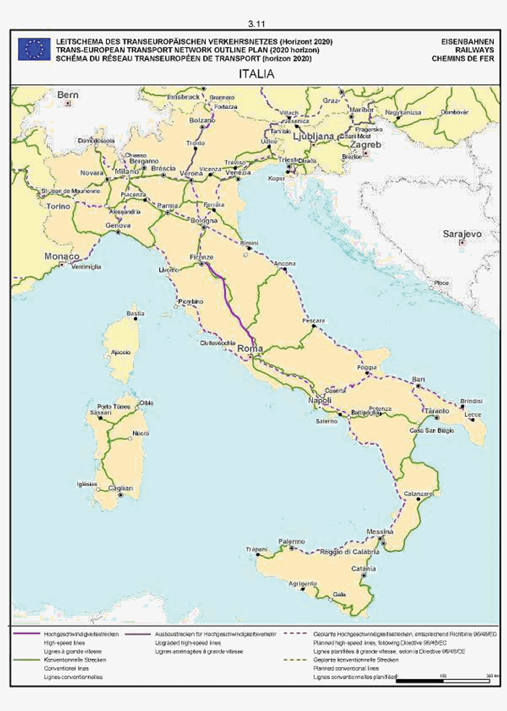
Italy
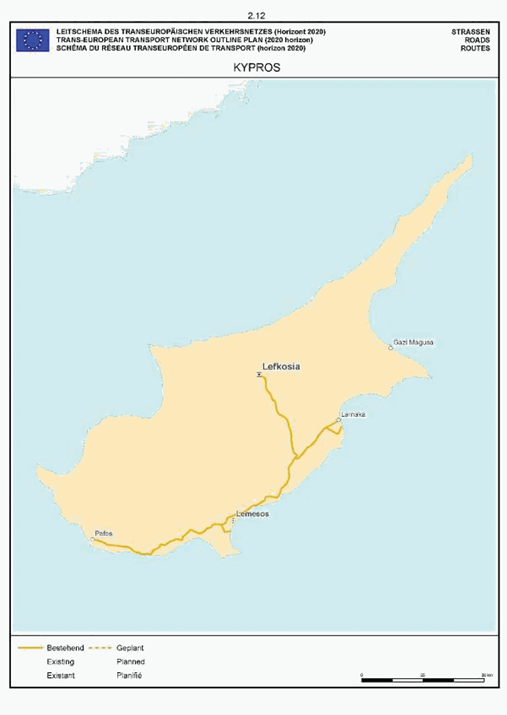
Cyprus
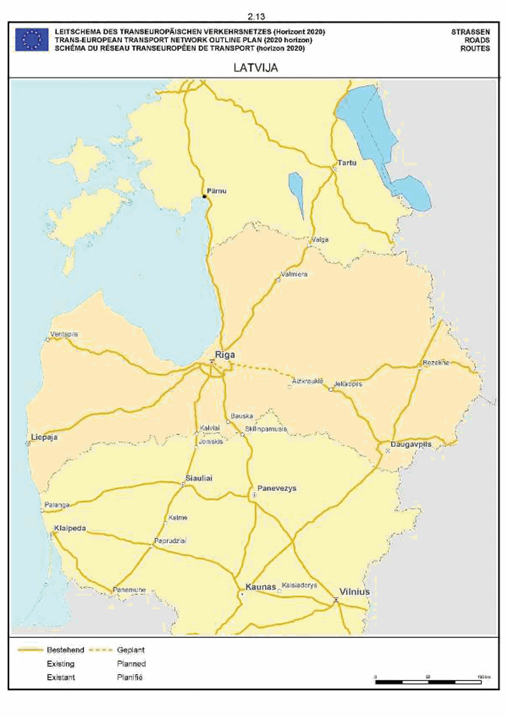
Latvia
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Hungary
Malta
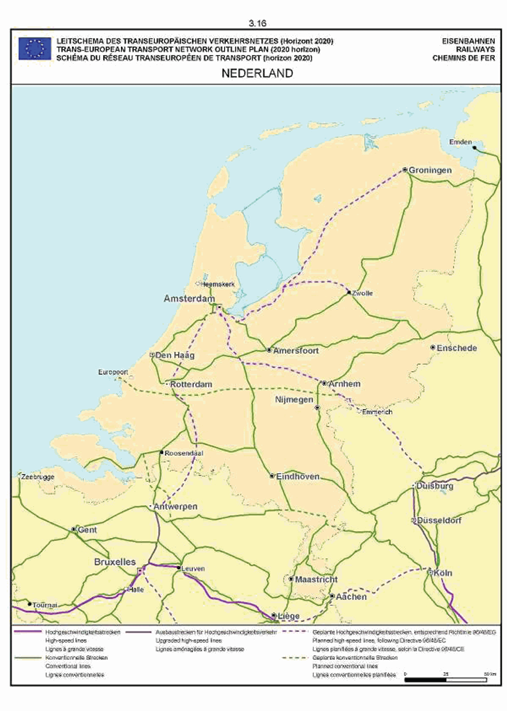
Netherlands
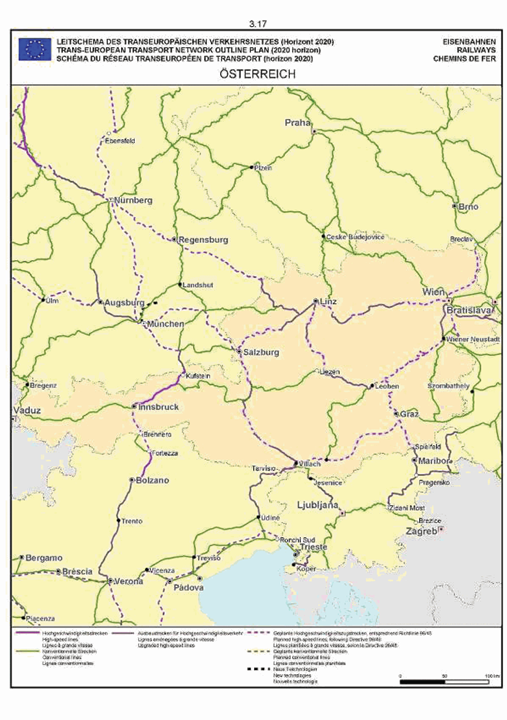
Austria
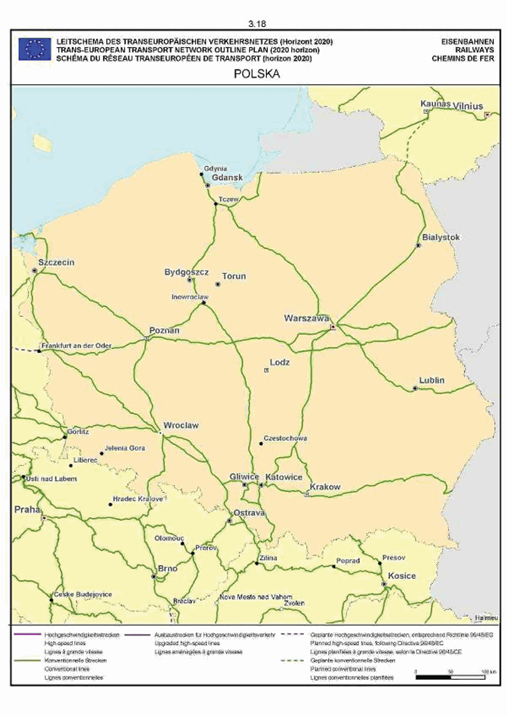
Poland
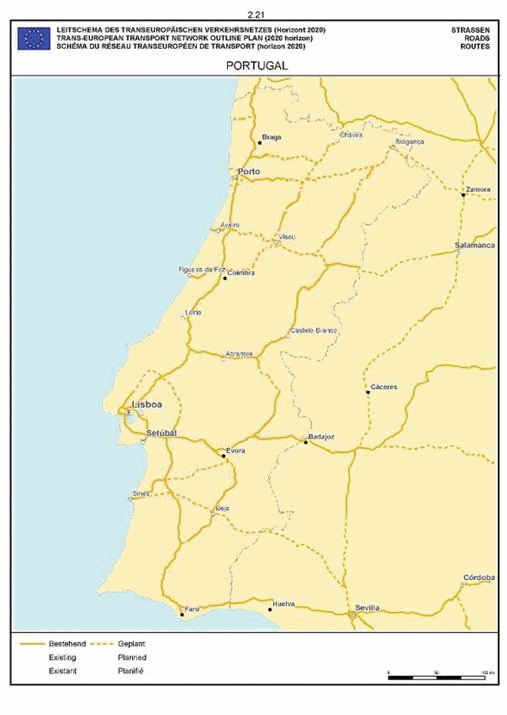
Portugal
Romania
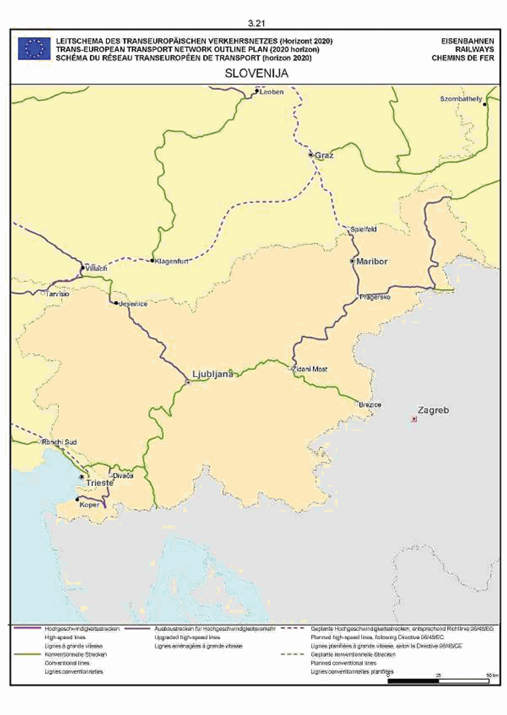
Slovenia
Slovakia
Finland
Sweden
United Kingdom
Section 3: Rail network
Europe
Belgium
Bulgaria
Czech Republic
Denmark
Germany
Estonia
Ireland
Greece
Spain
France
Italy
Latvia
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Hungary
Netherlands
Austria
Poland
Portugal
Romania
Slovenia
Slovakia
Finland
Sweden
United Kingdom
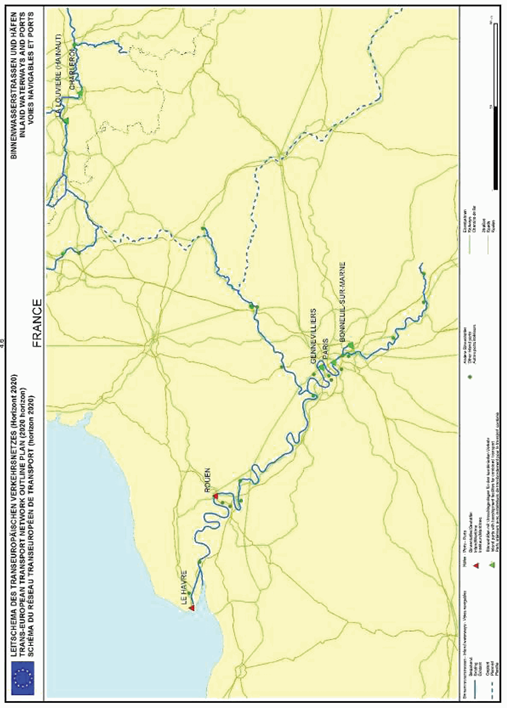
Section 4: Inland waterways network and inland ports
Europe
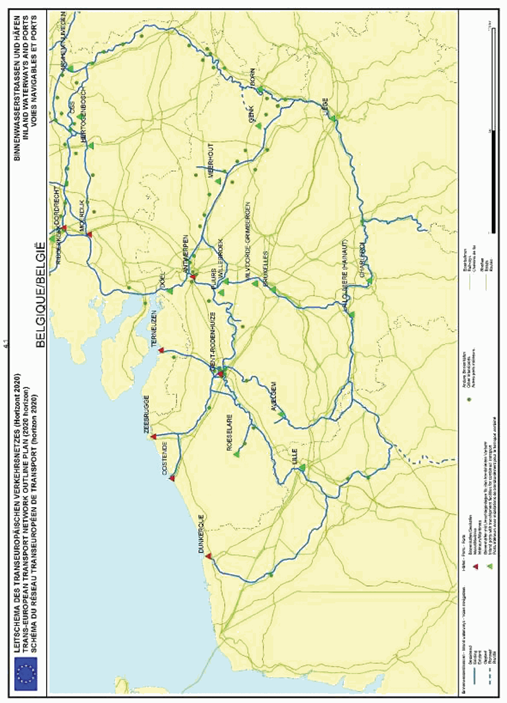
Belgium
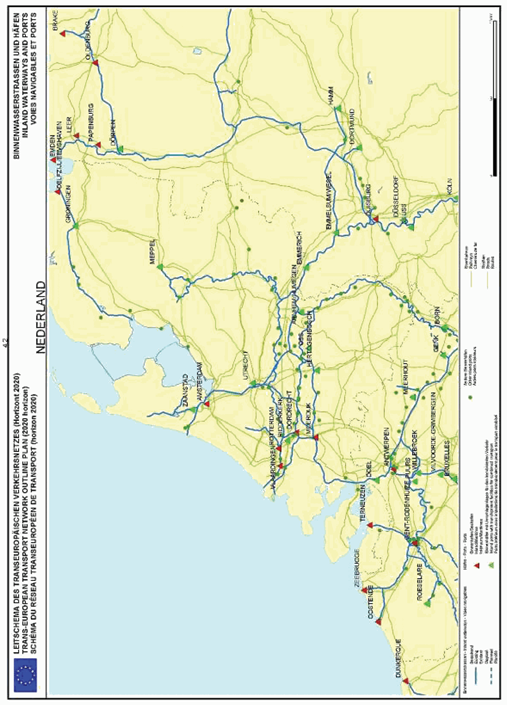
Netherlands
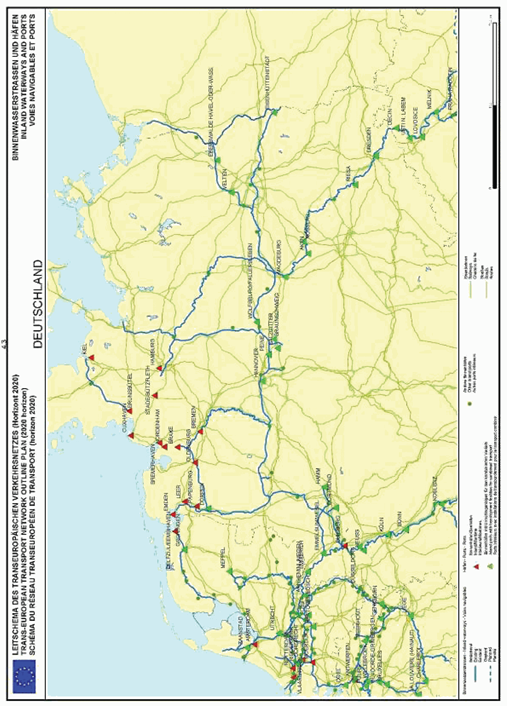
Germany
Germany / Austria
France / Italy
France
Bulgaria
Czech Republic
Lithuania
Hungary
Poland
Romania
Slovakia
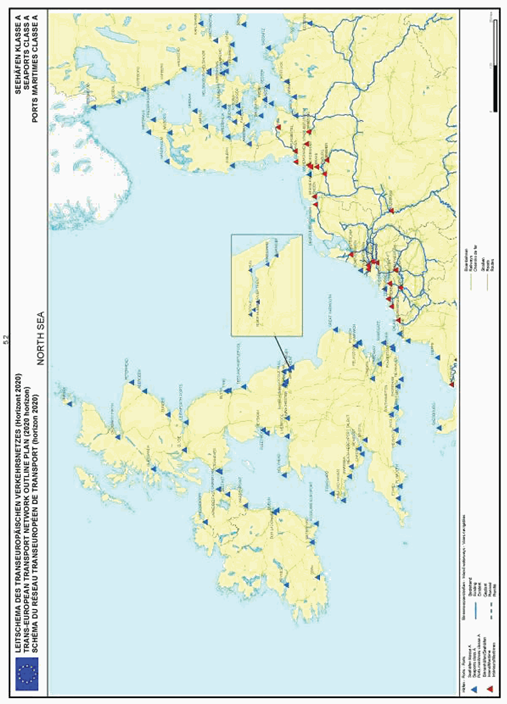
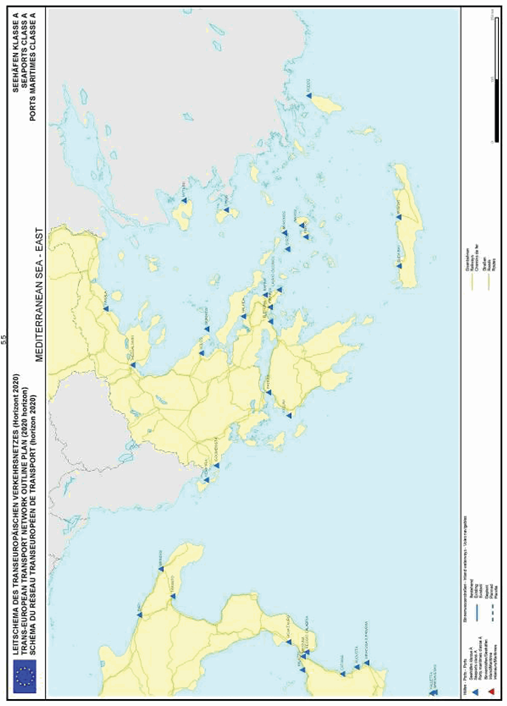
Section 5: Seaports - category A
Europe
Baltic Sea
North Sea
Atlantic Ocean
Mediterranean Sea - western part
Mediterranean Sea - eastern part
Bulgaria / Romania
Cyprus
Malta
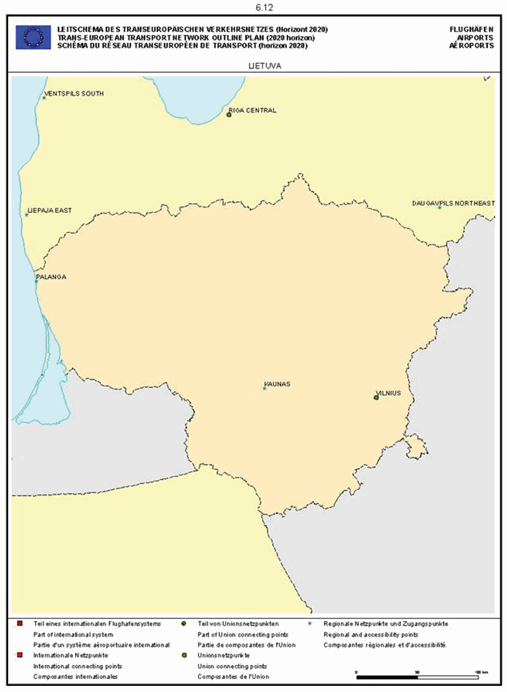
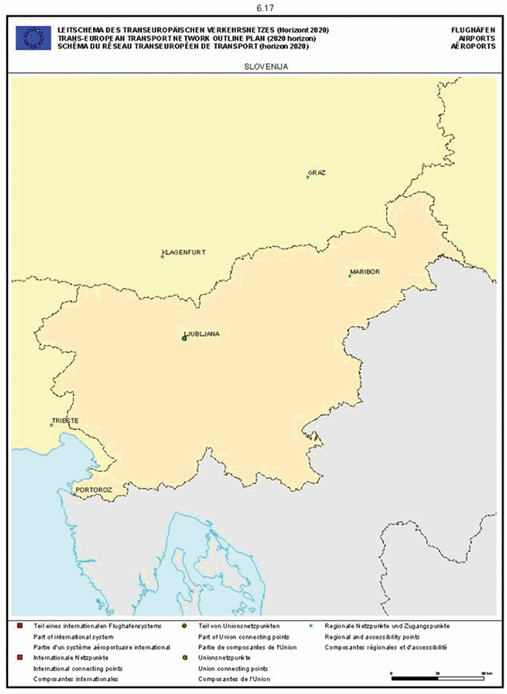
Section 6: Airports
Europe
Belgium Denmark / Germany / Luxembourg/ Netherlands / Austria
Bulgaria
Czech Republic
Estonia
Ireland / United Kingdom
Greece
Spain / Portugal
France
Italy
Cyprus
Latvia
Lithuania
Hungary
Malta
Poland
Romania
Slovenia
Slovakia
Finland / Sweden
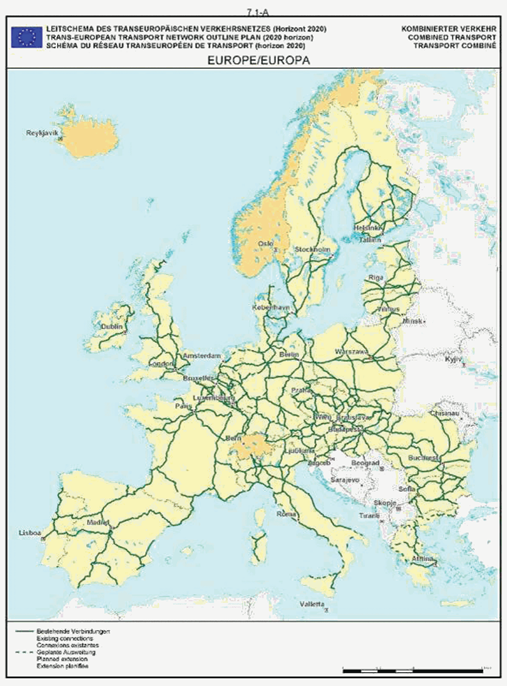
Section 7: Combined transport network
7.1
Rail
Rail, large-scale
NB: The term ‘planned’ in keys to the maps covers all stages of an infrastructure project of common interest from preliminary studies until construction.
SECTION 2 ROAD NETWORK
SECTION 3 RAIL NETWORK
SECTION 4 INLAND WATERWAYS NETWORK AND INLAND PORTS
SECTION 5 SEAPORTS - CATEGORY A
SECTION 6 AIRPORTS
SECTION 7 COMBINED TRANSPORT NETWORK
ANNEX II CRITERIA AND SPECIFICATIONS FOR PROJECTS OF COMMON INTEREST (2)
:
Road network
:
Rail network
:
Inland waterways network and inland ports
:
Seaports
:
Airports
:
Combined transport network
:
Shipping information and management network
:
Air traffic management network
:
Positioning and navigation network
SECTION 2 ROAD NETWORK
In addition to projects relating to the links in Annex I, projects of common interest will be deemed to include any infrastructure project relating to such links which deals with:
Development of the network, and in particular:
widening of motorways or upgrading of roads,
construction or improvement of bypasses or ring roads,
increasing the interoperability of national networks.
Development of traffic management and user information systems, and in particular:
establishment of telematic infrastructures for collecting traffic data,
developing traffic information centres and traffic control centres, as well as exchanges of data between traffic information centres in different countries,
establishing road information services, in particular the RDS-TMC system(3),
technical interoperability of telematic infrastructures.
SECTION 3 RAIL NETWORK
In addition to projects relating to the links in Annex I, projects of common interest will be deemed to include any infrastructure project relating to such links which deals with:
interoperability between trans-European railway systems,
interconnection with networks of other modes of transport.
SECTION 4 INLAND WATERWAYS NETWORK AND INLAND PORTS
A. Inland ports
Projects of common interest must relate solely to infrastructure open to any user on a non-discriminatory basis.
In addition to projects relating to the connections and inland ports mentioned in Annex I, projects of common interest will be deemed to include any infrastructure project corresponding to one or more of the following categories:
access to the port from waterways;
port infrastructure inside the port area;
other transport infrastructures inside the port area;
other transport infrastructures linking the port to other elements of the trans-European transport network.
Any project which concerns the following work will be deemed to be of common interest: construction and maintenance of all elements of the transport system generally open to all transport users within the port and of links with the national or international transport network. In particular, this includes the development and maintenance of land for commercial and other port-related purposes, the construction and maintenance of road and rail connections, the construction and maintenance, including dredging, of access routes and of other areas of water in the port, and the construction and maintenance of navigation aids and traffic management, communication and information systems in the port and on the access routes.
B. Traffic management
Projects of common interest will be deemed to include in particular:
a signalling and guidance system for vessels, in particular those carrying dangerous or polluting goods,
communications systems for emergencies and inland waterway safety.
SECTION 5 SEAPORTS
1. Common conditions for projects of common interest relating to seaports in the network
Projects of common interest must relate solely to infrastructure open to any user on a non-discriminatory basis.
Any project which concerns the following work will be deemed to be of common interest: construction and maintenance of all elements of the transport system generally open to all transport users within the port and of links with the national or international transport network. In particular, this includes the development and maintenance of land for commercial and other port-related purposes, the construction and maintenance of road and rail connections, the construction and maintenance, including dredging, of access routes and of other areas of water in the port, and the construction and maintenance of navigation aids and traffic management, communication and information systems in the port and on the access routes.
2. Specifications for projects of common interest relating to the seaport network
Any project which meets the following specifications will be deemed to be of common interest:
| Project specifications | Port category |
|---|---|
| I. Promotion of Short Sea Shipping | |
| Infrastructure necessary for the development of short-distance sea and sea-river shipping | Projects relating to ports in category A |
| II. Access to ports | |
| Access to ports from sea or inland waterway | Projects relating to ports in categories A and B |
| Permanent accessibility of ports in the Baltic Sea situated at approximately latitude 60° north and beyond, including capital costs for ice-breaking works during winter | Projects relating to ports in categories A, B and C |
| Creation or improvement of hinterland access linking the port to other elements of the trans-European transport network through rail, road and inland-waterway connections | Projects relating to ports in category A |
| Development of existing hinterland access linking the port to other elements of the trans-European transport network through rail, road and inland-waterway connections | Projects relating to ports in categories A and B |
| III. Port infrastructure within the port area | |
| Development of port infrastructure in order to increase intermodal efficiency | Projects relating to ports in categories A and B |
| Upgrading of the port infrastructure, in particular in ports on islands and in peripheral and outermost regions | Projects relating to ports in category C |
| Development and installation of management and information systems such as EDI (electronic data interchange) or other systems of intelligent management of goods and passenger traffic using integrated technologies | Projects relating to ports in categories A, B and C |
| Development of port installations to receive waste | Projects relating to ports in categories A, B and C |
SECTION 6 AIRPORTS
I. Eligibility criteria for airports of common interest
Airports of common interest must meet the criteria of one of the following connecting points:
International connecting points will include:
all airports or airport systems(4) with an annual traffic volume of no less than:
5 000 000 passenger movements minus 10 %,
or
100 000 commercial aircraft movements,
or
150 000 tonnes freight throughput,
or
1 000 000 extra-Union passenger movements;
or
any new airport constructed to replace an existing international connecting point which cannot be developed further on its site.
Union connecting points will include:
all airports or airport systems with an annual traffic volume of:
between 1 000 000 minus 10 % and 4 499 999 passenger movements,
or
between 50 000 and 149 999 tonnes freight throughput,
or
between 500 000 and 899 999 passenger movements, of which at least 30 % are non-national,
or
between 300 000 and 899 999 passenger movements and located off the European mainland at a distance of over 500 km from the nearest international connecting point;
or
any new airport constructed to replace an existing Union connecting point which cannot be developed further on its site.
Regional connecting points and accessibility points will include all airports
with an annual traffic volume of between 500 000 and 899 999 passenger movements, of which less than 30 % are non-national,
or
with an annual traffic volume of between 250 000 minus 10 % and 499 999 passenger movements,
or
with an annual traffic volume of between 10 000 and 49 999 tonnes freight throughput,
or
located on an island of a Member State,
or
located in a landlocked area of the Union with commercial services operated by aircraft with a maximum take-off weight in excess of 10 tonnes.
An airport is located in a landlocked area if it is situated outside a radius of over 100 km from the nearest international or Union connecting point. This distance may, by way of exception, be reduced to 75 km in order to take account of difficult access due to the geographical situation or the poor quality of the inland transport infrastructure.
II. Specifications for projects of common interest related to the airport network
All project will qualify as a project of common interest if it meets the following specifications:
| a This table does not exclude the measures concerned from being extended to other connecting points in certain, duly justified, special cases. | |
| Project specifications | Type of connecting point principally concerneda |
|---|---|
| I. Optimisation of existing airport capacity | |
| Measure 1: Optimisation of the existing capacity in terms of aircraft, passenger or freight movements, including the airport's air navigation equipment | International connecting point Union connecting point Regional connecting point and accessibility point |
| Measure 2: Improvement of airport security and safety | International connecting point Union connecting point Regional connecting point and accessibility point |
| Measure 3: Adaptation of existing infrastructures made necessary by completion of the internal market and in particular by the measures governing the free movement of persons within the Union | International connecting point Union connecting point Regional connecting point and accessibility point |
| II. Development of new airport capacities | |
| Measure 4: Development of the infrastructure and equipment which determine airport capacity in terms of aircraft, passenger or freight movements, including the airport's air navigation equipment | International connecting point Union connecting point |
| Measure 5: Construction of new airport to replace an existing airport or airport system which cannot be developed further on its site | International connecting point Union connecting point |
| III. Improvement of protection against nuisances generated by airport activities | |
| Measure 6: Improvement of environmental compatibility in terms of noise and the treatment of airport effluent | International connecting point Union connecting point |
| IV. Improvement or development of airport access | |
| Measure 7: Improvement or development of interfaces between the airport and access infrastructures | International connecting point Union connecting point |
| Measure 8: Improvement and development of interconnections with other transport networks, and more specifically the rail network | International connecting point Union connecting point |
SECTION 7 COMBINED TRANSPORT NETWORK
In addition to the projects relating to links specified in Annex I, projects of common interest will be deemed to include any project concerning:
construction or upgrading of railway or inland waterway infrastructures in order to make the transport of intermodal loading units technically possible and economically viable,
construction or development of centres for transfers between inland types of transport, including the setting up within the terminal of transhipment equipment with the corresponding infrastructure,
adaptation of port areas, making it possible to develop or improve combined transport between sea transport and rail, inland waterway or road transport,
railway transport equipment specially adapted to combined transport where so required by the nature of the infrastructure, particularly as regards the cost of the possible adaptation of such infrastructure and subject to the use of such equipment being associated with the infrastructure in question and the operators concerned being able to avail themselves of it on a non-discriminatory basis.
SECTION 8 SHIPPING INFORMATION AND MANAGEMENT NETWORK
Projects of common interest will be deemed to include any project:
relating to the objectives of Union shipping safety policy,
or
designed to implement international conventions and resolutions of the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) in the area of shipping safety and concerning:
implementation of the Union system of notification of vessels bound for or coming from Union ports or transiting off Union coasts, with the aid of an electronic system of data exchanges also including transmission of data between vessels and land installations via transponders, particular attention will be given to EDI (electronic data interchange) electronic systems of data exchange including compatible interfaces,
the development and improvement of the LORAN-C land-based radio-navigation channels,
the development or improvement of coastal and port shipping management and information systems (VTS) and their interconnection, with a view to safer and more effective surveillance and management of shipping, in particular in converging, busy, or environmentally sensitive areas,
the development of tools to improve understanding of traffic: databases on traffic flows and shipping accidents, development of the European Permanent Traffic Observatory (EPTO) tool for analysing traffic flows,
the development of infrastructure and equipment in order to further the implementation of the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS),
the improvement of telematic data exchange systems in the context of port state control of vessels.
SECTION 9 AIR TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT NETWORK
Projects of common interest are deemed to include any project leading to an increase in the capacity of the system and optimising its use which forms part of a pattern of harmonisation and integration of the facilities and procedures of the various national connecting points and complies with the relevant international standards defined by the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) and by the competent European bodies, all of the foregoing taking account in particular of the European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation (Eurocontrol).
Such projects relate to:
studies on better utilisation of airspace by the various users and the establishment of a consistent and efficient system of routes,
air traffic planning and management which helps supply keep pace with demand and makes optimal use of available control capacities,
the studies and work necessary for the harmonisation of facilities and procedures so as to integrate the various service providers taking particular account of the guidelines adopted by the European Civil Aviation Conference (ECAC),
the improvement of system productivity, in particular by means of automated control assistance and potential conflict detection and resolution systems,
contributions to the installation of means of communication, navigation and surveillance necessary for air traffic control, including the promotion of new technologies, in particular satellites and digital data networks, where that leads to compliance with European common specifications.
SECTION 10 POSITIONING AND NAVIGATION NETWORK
Projects of common interest are deemed to include any project relating to the establishment of any component of the future European Radio Navigation Plan or of a global satellite positioning and navigation system forming part of the following structure:
control centre comprising a processing and control system,
network of earth navigation stations,
space segment composed of satellites enabling navigation signals to be transmitted,
network of surveillance stations.
ANNEX III PRIORITY PROJECTS ON WHICH WORK IS DUE TO START BEFORE 2010
1.Railway axis Berlin-Verona/Milan-Bologna-Naples-Messina-Palermo
Halle/Leipzig-Nuremberg (2015)
Nuremberg-Munich (2006)
Munich-Kufstein (2015)
Kufstein-Innsbruck (2009)
Brenner Tunnel (2015), cross-border section
Verona-Naples (2007)
Milan-Bologna (2006)
Rail/road bridge over the Strait of Messina-Palermo (2015)
2.High-speed railway axis Paris-Brussels-Cologne-Amsterdam-London
Channel tunnel-London (2007)
Brussels-Liège-Cologne (2007)
Brussels-Rotterdam-Amsterdam (2007)(5)
3.High-speed railway axis of south-west Europe
Lisbon/Porto-Madrid (2011)(6)
Madrid-Barcelona (2005)
Barcelona-Figueras-Perpignan (2008)
Perpignan-Montpellier (2015)
Montpellier-Nîmes (2010)
Madrid-Vitoria-Irún/Hendaye (2010)
Irún/Hendaye-Dax, cross-border section (2010)
Dax-Bordeaux (2020)
Bordeaux-Tours (2015)
4.High-speed railway axis east
Paris-Baudrecourt (2007)
Metz-Luxembourg (2007)
Saarbrücken-Mannheim (2007)
5.Betuwe line (2007)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.Lyon-Trieste-Divača/Koper-Divača-Ljubljana-Budapest-Ukrainian border rail link(7)
Lyon-St Jean de Maurienne (2015)
Mont-Cenis tunnel (2015-2017), cross-border section
Bussoleno-Turin (2011)
Turin-Venice (2010)
Venice-Ronchi Sud-Trieste-Divača (2015)
Koper-Divača-Ljubljana (2015)
Ljubljana-Budapest (2015)
7.Motorway axis Igoumenitsa/Patra-Athens-Sofia-Budapest
Via Egnatia (2006)
Pathe (2008)
Sofia-Kulata-Greek/Bulgarian border motorway (2010), with Promahon-Kulata as cross-border section
Nadlac-Sibiu motorway (branch towards Bucharest and Constanța) (2007)
8.Multimodal axis Portugal/Spain-rest of Europe(8)
Railway La Coruña-Lisbon-Sines (2010)
Railway Lisbon-Valladolid (2010)
Railway Lisbon-Faro (2004)
Lisbon-Valladolid motorway (2010)
La Coruña-Lisbon motorway (2003)
Seville-Lisbon motorway (completed 2001)
New Lisbon airport (2015)
9.Railway axis Cork-Dublin-Belfast-Stranraer(9) (2001)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10.Malpensa (completed 2001)(10)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11.Öresund fixed link (completed 2000)(11)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12.Nordic triangle railway/road axis
Road and railway projects in Sweden (2010)(12)
Helsinki-Turku motorway (2010)
Railway Kerava-Lahti (2006)
Helsinki-Vaalimaa motorway (2015)
Railway Helsinki-Vainikkala (Russian border) (2014)
13.UK/Ireland/Benelux road axis (2010)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14.West coast main line (2007)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15.Galileo (2008)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16.Freight railway axis Sines/Algeciras-Madrid-Paris
New high-capacity rail axis across the Pyrenees
Railway Sines-Badajoz (2010)
Railway line Algeciras-Bobadilla (2010)
17.Railway axis Paris-Strasbourg-Stuttgart-Vienna-Bratislava
Baudrecourt-Strasbourg-Stuttgart (2015) with the Kehl bridge as cross-border section
Stuttgart-Ulm (2012)
Munich-Salzburg (2015), cross-border section
Salzburg-Vienna (2012)
Vienna-Bratislava (2010), cross-border section
18.Rhine/Meuse-Main-Danube inland waterway axis(13)
Rhine-Meuse (2019) with the lock of Lanaye as cross-border section
Vilshofen-Straubing (2013)
Vienna-Bratislava (2015), cross-border section
Sap-Mohács (2014)
Bottlenecks in Romania and Bulgaria (2011)
19.High-speed rail interoperability on the Iberian peninsula
Madrid-Andalusia (2010)
North-east (2010)
Madrid-Levante and Mediterranean (2010)
North/North-west corridor, including Vigo-Porto (2010)
Extremadura (2010)
20.Fehmarn Belt railway axis
Fehmarn Belt fixed rail/road link (2014)
Railway for access in Denmark from Öresund (2015)
Railway for access in Germany from Hamburg (2015)
Railway Hannover-Hamburg/Bremen (2015)
21.Motorways of the Sea (MoS)
Projects of common interest identified in accordance with Article 13 and concerning the following motorways of the sea:
motorway of the Baltic Sea (linking the Baltic Sea Member States with Member States in central and western Europe, including the route through the North Sea/Baltic Sea Canal (Kiel Canal) (2010)),
motorway of the sea of western Europe (leading from Portugal and Spain via the Atlantic Arc to the North Sea and the Irish Sea) (2010),
motorway of the sea of south-east Europe (connecting the Adriatic Sea to the Ionian Sea and the Eastern Mediterranean to include Cyprus) (2010),
motorway of the sea of south-west Europe (western Mediterranean), connecting Spain, France, Italy and including Malta, and linking with the motorway of the sea of south-east Europe (2010)(14).
22.Athens-Sofia-Budapest-Vienna-Prague-Nuremberg/Dresden rail link(15)
Railway Greek/Bulgarian border-Kulata-Sofia-Vidin/Calafat (2015)
Railway Curtici-Brașov (towards Bucharest and Constanța) (2010)
Railway Budapest-Vienna (2010), cross-border section
Railway Břeclav-Prague-Nuremberg (2010), with Nuremberg-Prague as cross-border section
Railway axis Prague-Linz (2016)
23.Railway axis Gdańsk-Warsaw-Brno/Bratislava-Vienna(16)
Railway Gdańsk-Warsaw-Katowice (2015)
Railway Katowice-Břeclav (2010)
Railway Katowice-Žilina-Nové Mesto n. V. (2010)
24.Lyon/Genova-Basel-Duisburg-Rotterdam/Antwerp rail link
Lyon-Mulhouse-Mülheim(17), with Mulhouse-Mülheim as cross-border section (2018)
Genova-Milan/Novara-Swiss border (2013)
Basel-Karlsruhe (2015)
Frankfurt-Mannheim (2012)
Duisburg-Emmerich (2009)(18)
‘Iron Rhine’ Rheidt-Antwerp, cross-border section (2010)
25.Motorway axis Gdańsk-Brno/Bratislava-Vienna(19)
Gdańsk-Katowice motorway (2010)
Katowice-Brno/Žilina motorway (2010), cross-border section
Brno-Vienna motorway (2009), cross-border section
26.Railway/road axis Ireland/United Kingdom/continental Europe
Road/railway axis linking Dublin with the North (Belfast-Larne) and South (Cork) (2010)(20)
Road/railway axis Hull-Liverpool (2015)
Railway Felixstowe-Nuneaton (2011)
Railway Crewe-Holyhead (2008)
27.‘Rail Baltica’ axis Warsaw-Kaunas-Riga-Tallinn-Helsinki
Warsaw-Kaunas (2010)
Kaunas-Riga (2014)
Riga-Tallinn (2016)
28.‘Eurocaprail’ on the Brussels-Luxembourg-Strasbourg railway axis
Brussels-Luxembourg-Strasbourg (2012)
29.Railway axis of the Ionian/Adriatic intermodal corridor
Kozani-Kalambaka-Igoumenitsa (2012)
Ioannina-Antirrio-Rio-Kalamata (2014)
30.Inland waterway Seine-Scheldt
Navigability improvements Deulemont-Gent (2012-2014-2016)
Compiègne-Cambrai (2012-2014-2016)
The date, agreed in advance, for completing the work is shown in brackets. The dates for completing the work for projects 1 to 20 and 30 and the details of the sections are as indicated in the High-Level Group's report where these have actually been identified.
ANNEX IV
Repealed Decision with list of its successive amendments
| Decision No 1692/96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council | |
| Decision No 1346/2001/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council | |
| 2003 Act of Accession, Annex II, point 8.F | |
| Decision No 884/2004/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council | |
| Council Regulation (EC) No 1791/2006 | Point 6(D) of the Annex only |
ANNEX V
Correlation table
| Decision No 1692/96/EC | This Decision |
|---|---|
| Article 1(1) | Article 1(1) |
| Article 1(2), first sentence | Article 1(2), first sentence |
| Article 1(2), second sentence | Article 7(1) |
| Article 1(2), third sentence | Article 1(2), second sentence |
| Article 1(3) | Article 1(3) |
| Articles 2 to 6 | Articles 2 to 6 |
| Article 7(1), introductory wording | Article 7(2), introductory wording |
| Article 7(1), first indent | Article 7(2)(a) |
| Article 7(1), second indent | Article 7(2)(b) |
| Article 7(1), third indent | Article 7(2)(c) |
| Article 7(1), fourth indent | Article 7(2)(d) |
| Article 7(2), introductory wording | Article 7(3), introductory wording |
| Article 7(2), first indent | Article 7(3)(a) |
| Article 7(2), second indent | Article 7(3)(b) |
| Article 7(3) | Article 7(4) |
| Article 8(1), first subparagraph | Article 8(1), first subparagraph |
| Article 8(1), second subparagraph, first sentence | Article 8(1), second subparagraph |
| Article 8(1), second subparagraph, second sentence | Article 8(1), third subparagraph |
| Article 8(2) | Article 8(2) |
| Article 9(1), introductory wording | Article 9(1), introductory wording |
| Article 9(1), first indent | Article 9(1)(a) |
| Article 9(1), second indent | Article 9(1)(b) |
| Article 9(1), third indent | Article 9(1)(c) |
| Article 9(1), fourth indent | Article 9(1)(d) |
| Article 9(2) and (3) | Article 9(2) and (3) |
| Article 10(1) | Article 10(1) |
| Article 10(2), first subparagraph | Article 10(2), first subparagraph |
| Article 10(2), second subparagraph, first sentence | Article 10(2), second subparagraph |
| Article 10(2), second subparagraph, second sentence | Article 10(2), third subparagraph |
| Article 10(3) to (6) | Article 10(3) to (6) |
| Article 11(1), (2) and (3) | Article 11(1), (2) and (3) |
| Article 11(3a) | Article 11(4), first subparagraph |
| Article 11(3b) | Article 11(4), second subparagraph |
| Article 11(4) | Article 11(5) |
| Article 12 | Article 12 |
| Article 12a(1) to (4) | Article 13(1) to (4) |
| Article 12a(5), introductory wording | Article 13(5), introductory wording |
| Article 12a(5), first indent | Article 13(5)(a) |
| Article 12a(5), second indent | Article 13(5)(b) |
| Article 12a(5), third indent | Article 13(5)(c) |
| Article 12a(6), first and second sentences | Article 13(7), first subparagraph |
| Article 12a(6), third sentence | Article 13(7), second subparagraph |
| Article 12a(7) | Article 13(6) |
| Article 13 | Article 14 |
| Article 14, introductory sentence | Article 15, introductory sentence |
| Article 14, first indent | Article 15(a) |
| Article 14, second indent | Article 15(b) |
| Article 14, third indent | Article 15(c) |
| Article 15, introductory and final sentences | Article 16, introductory sentence |
| Article 15, first indent | Article 16(a) |
| Article 15, second indent | Article 16(b) |
| Article 15, third indent | Article 16(c) |
| Article 15, fourth indent | Article 16(d) |
| Article 16 | Article 17 |
| Article 17 | Article 18 |
| Article 17a(1), first sentence | Article 19(1) |
| Article 17a(1), second, third and fourth sentences | Article 19(4) |
| Article 17a(2) and (3) | Article 19(2) and 3) |
| Article 17a(4) | Article 19(6) |
| Article 17a(5) | Article 19(5) |
| Article 17a(6) | Article 19(7) |
| Article 18(1) | Article 20 |
| Article 18(2), first sentence | Article 21(1) |
| Article 18(2), second sentence | Article 21(2) |
| Article 18(3), first sentence | Article 22, first paragraph |
| Article 18(3), second sentence | Article 22, second paragraph |
| Article 18(3), third and fourth sentences | Article 22, third paragraph |
| Article 19 | Article 23 |
| Article 19a(1) | Article 24 |
| Article 19a(2), introductory wording | Article 25(1), introductory wording |
| Article 19a(2)(a) and (b) | Article 25(1)(a) and (b) |
| — | Article 25(2), introductory wording |
| Article 19a(2)(c) and (d) | Article 25(2)(a) and (b) |
| Article 19a(3) | Article 25(3) |
| Article 19a(4) | Article 26(1) |
| Article 19a(5), first sentence | Article 26(2), first subparagraph |
| Article 19a(5), second sentence | Article 26(2), second subparagraph |
| Article 19a(6) | Article 27(1) |
| Article 19a(7) | Article 27(2) |
| Article 19a(8) | Article 27(3) |
| Article 19a(9) | Article 27(4) |
| Article 19b, first sentence | Article 28, first paragraph |
| Article 19b, second sentence | Article 28, second paragraph |
| Article 22 | Article 29, first paragraph |
| — | Article 29, second paragraph |
| Article 23 | Article 30 |
| Article 24 | Article 31 |
| Annex I | Annex I |
| Annex II | Annex II |
| Annex III | Annex III |
| — | Annex IV |
| — | Annex V |
The maps relate to the corresponding sections mentioned in the enacting terms and/or Annex II.
These criteria and specifications refer to the corresponding sections referred to in the enacting terms and/or Annex I.
A radio-based digital road traffic message system in which the general message stream can be tuned to the individual needs of the road user.
Airport systems (OJ L 240, 24.8.1992, p. 14).
Including the two high-speed train stations in Rotterdam and Amsterdam which were not included in the project endorsed by the Essen European Council in 1994.
Including links Lisbon-Porto (2013), Lisbon-Madrid (2010) and Aveiro-Salamanca (2015).
Parts of this route correspond to pan-European corridor V.
Including upgrade of ports and airports (2015) as in accordance with the contents endorsed by the Essen/Dublin European Council.
A further increase in capacity on this line was decided in 2003 and added as a separate project.
Project completed.
Project completed.
A few short sections of road and railway line will be completed between 2010 and 2015.
Part of this route corresponds to the definition of pan-European Corridor VII.
Including to the Black Sea.
This major route largely corresponds to the definition of pan-European corridor IV.
This major route largely corresponds to the definition of pan-European corridor VI.
Including the TGV Rhin-Rhône, minus the western branch.
Project No 5 (Betuwe line) links Rotterdam and Emmerich.
This major route largely corresponds to the definition of pan-European corridor VI.
Including Essen project No 13: road axis Ireland/United Kingdom/Benelux.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Decision
PrintThe Annexes only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As adopted by EU): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was first adopted in the EU. No changes have been applied to the text.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the EU Official Journal
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as adopted version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources