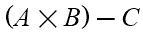Statutory Instruments
1998 No. 1833
TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF EMPLOYMENT
The Working Time Regulations 1998
Laid before Parliament
30th July 1998
Coming into force
1st October 1998
The Secretary of State, being a Minister designated for the purposes of section 2(2) of the European Communities Act 1972 in relation to measures relating to the organization of working time and measures relating to the employment of children and young persons, in exercise of the powers conferred on him by that provision hereby makes the following Regulations—
PART IE+W+S GENERAL
Citation, commencement and extentE+W+S
1.—(1) These Regulations may be cited as the Working Time Regulations 1998 and shall come into force on 1st October 1998.
(2) These Regulations extend to Great Britain only.
InterpretationE+W+S
2.—(1) In these Regulations—
“the 1996 Act" means the Employment Rights Act 1996 ;
“adult worker" means a worker who has attained the age of 18;
“the armed forces" means any of the naval, military and air forces of the Crown;
“calendar year" means the period of twelve months beginning with 1st January in any year;
“the civil protection services" includes the police, fire brigades and ambulance services, the security and intelligence services, customs and immigration officers, the prison service, the coastguard, and lifeboat crew and other voluntary rescue services;
“collective agreement" means a collective agreement within the meaning of section 178 of the Trade Union and Labour Relations (Consolidation) Act 1992 , the trade union parties to which are independent trade unions within the meaning of section 5 of that Act;
“day" means a period of 24 hours beginning at midnight;
“employer", in relation to a worker, means the person by whom the worker is (or, where the employment has ceased, was) employed;
“employment", in relation to a worker, means employment under his contract, and “employed" shall be construed accordingly;
[“fishing vessel” has the same meaning as in section 313 of the Merchant Shipping Act 1995;]
[“mobile worker” means any worker employed as a member of travelling or flying personnel by an undertaking which operates transport services for passengers or goods by road or air;]
“night time", in relation to a worker, means a period—
(a)
the duration of which is not less than seven hours, and
(b)
which includes the period between midnight and 5 a.m.,
which is determined for the purposes of these Regulations by a relevant agreement, or, in default of such a determination, the period between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m.;
“night work" means work during night time;
“night worker" means a worker—
(a)
who, as a normal course, works at least three hours of his daily working time during night time, or
(b)
who is likely, during night time, to work at least such proportion of his annual working time as may be specified for the purposes of these Regulations in a collective agreement or a workforce agreement;
and, for the purpose of paragraph (a) of this definition, a person works hours as a normal course (without prejudice to the generality of that expression) if he works such hours on the majority of days on which he works;
[“offshore work” means work performed mainly on or from offshore installations (including drilling rigs), directly or indirectly in connection with the exploration, extraction or exploitation of mineral resources, including hydrocarbons, and diving in connection with such activities, whether performed from an offshore installation or a vessel[, including any such work performed in the territorial waters of the United Kingdom adjacent to Great Britain or in any area (except one or part of one in which the law of Northern Ireland applies) designated under section 1(7) of the Continental Shelf Act 1964];]
“relevant agreement", in relation to a worker, means a workforce agreement which applies to him, any provision of a collective agreement which forms part of a contract between him and his employer, or any other agreement in writing which is legally enforceable as between the worker and his employer;
“relevant training" means work experience provided pursuant to a training course or programme, training for employment, or both, other than work experience or training—
(a)
the immediate provider of which is an educational institution or a person whose main business is the provision of training, and
(b)
which is provided on a course run by that institution or person;
“rest period", in relation to a worker, means a period which is not working time, other than a rest break or leave to which the worker is entitled under these Regulations;
[“the restricted period”, in relation to a worker, means the period between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m. or, where the worker’s contract provides for him to work after 10 p.m., the period between 11 p.m. and 7 a.m.]
[“ship” has the same meaning as in section 313 of the Merchant Shipping Act 1995;]
“worker" means an individual who has entered into or works under (or, where the employment has ceased, worked under)—
(a)
a contract of employment; or
(b)
any other contract, whether express or implied and (if it is express) whether oral or in writing, whereby the individual undertakes to do or perform personally any work or services for another party to the contract whose status is not by virtue of the contract that of a client or customer of any profession or business undertaking carried on by the individual;
and any reference to a worker’s contract shall be construed accordingly;
“worker employed in agriculture" has the same meaning as in the Agricultural Wages Act 1948 or the Agricultural Wages (Scotland) Act 1949 , and a reference to a worker partly employed in agriculture is to a worker employed in agriculture whose employer also employs him for non-agricultural purposes;
“workforce agreement" means an agreement between an employer and workers employed by him or their representatives in respect of which the conditions set out in Schedule 1 to these Regulations are satisfied;
“working time", in relation to a worker, means—
(a)
any period during which he is working, at his employer’s disposal and carrying out his activity or duties,
(b)
any period during which he is receiving relevant training, and
(c)
any additional period which is to be treated as working time for the purpose of these Regulations under a relevant agreement;
and “work" shall be construed accordingly;
“Working Time Directive" means Council Directive 93/104/EC of 23rd November 1993 concerning certain aspects of the organization of working time ;
“young worker" means a worker who has attained the age of 15 but not the age of 18 and who, as respects England and Wales, is over compulsory school age (construed in accordance with section 8 of the Education Act 1996) and, as respects Scotland, is over school age (construed in accordance with section 31 of the Education (Scotland) Act 1980) , and
“Young Workers Directive" means Council Directive 94/33/EC of 22nd June 1994 on the protection of young people at work .
(2) In the absence of a definition in these Regulations, words and expressions used in particular provisions which are also used in corresponding provisions of the Working Time Directive or the Young Workers Directive have the same meaning as they have in those corresponding provisions.
(3) In these Regulations—
(a)a reference to a numbered regulation is to the regulation in these Regulations bearing that number;
(b)a reference in a regulation to a numbered paragraph is to the paragraph in that regulation bearing that number; and
(c)a reference in a paragraph to a lettered sub-paragraph is to the sub-paragraph in that paragraph bearing that letter.
Textual Amendments
Marginal Citations
PART IIE+W+S RIGHTS AND OBLIGATIONS CONCERNING WORKING TIME
GeneralE+W+S
3.— [(1)] The provisions of this Part have effect subject to the exceptions provided for in Part III of these Regulations.
[(2) Where, in this Part, separate provision is made as respects the same matter in relation to workers generally and to young workers, the provision relating to workers generally applies only to adult workers and those young workers to whom, by virtue of any exception in Part 3, the provision relating to young workers does not apply.]
Maximum weekly working timeE+W+S
4.—(1) [Unless his employer has first obtained the worker’s agreement in writing to perform such work], a worker’s working time, including overtime, in any reference period which is applicable in his case shall not exceed an average of 48 hours for each seven days.
(2) An employer shall take all reasonable steps, in keeping with the need to protect the health and safety of workers, to ensure that the limit specified in paragraph (1) is complied with in the case of each worker employed by him in relation to whom it applies [and shall keep up-to-date records of all workers who carry out work to which it does not apply by reason of the fact that the employer has obtained the worker’s agreement as mentioned in paragraph (1)].
(3) Subject to paragraphs (4) and (5) and any agreement under regulation 23(b), the reference periods which apply in the case of a worker are—
(a)where a relevant agreement provides for the application of this regulation in relation to successive periods of 17 weeks, each such period, or
(b)in any other case, any period of 17 weeks in the course of his employment.
(4) Where a worker has worked for his employer for less than 17 weeks, the reference period applicable in his case is the period that has elapsed since he started work for his employer.
(5) Paragraphs (3) and (4) shall apply to a worker who is excluded from the scope of certain provisions of these Regulations by regulation 21 as if for each reference to 17 weeks there were substituted a reference to 26 weeks.
(6) For the purposes of this regulation, a worker’s average working time for each seven days during a reference period shall be determined according to the formula—
where—A is the aggregate number of hours comprised in the worker’s working time during the course of the reference period;
B is the aggregate number of hours comprised in his working time during the course of the period beginning immediately after the end of the reference period and ending when the number of days in that subsequent period on which he has worked equals the number of excluded days during the reference period; and
C> is the number of weeks in the reference period.
(7) In paragraph (6), “excluded days" means days comprised in—
(a)any period of annual leave taken by the worker in exercise of his entitlement under regulation 13;
(b)any period of sick leave taken by the worker;
(c)any period of maternity [paternity, adoption or parental] leave taken by the worker; and
(d)any period in respect of which the limit specified in paragraph (1) did not apply in relation to the worker [by reason of the fact that the employer has obtained the worker’s agreement as mentioned in paragraph (1)].
Agreement to exclude the maximumE+W+S
5.—(1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(2) An agreement for the purposes of [regulation 4]—
(a)may either relate to a specified period or apply indefinitely; and
(b)subject to any provision in the agreement for a different period of notice, shall be terminable by the worker by giving not less than seven days’ notice to his employer in writing.
(3) Where an agreement for the purposes of [regulation 4] makes provision for the termination of the agreement after a period of notice, the notice period provided for shall not exceed three months.
(4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
[Maximum working time for young workersE+W+S
5A.—(1) A young worker’s working time shall not exceed—
(a)eight hours a day, or
(b)40 hours a week.
(2) If, on any day, or, as the case may be, during any week, a young worker is employed by more than one employer, his working time shall be determined for the purpose of paragraph (1) by aggregating the number of hours worked by him for each employer.
(3) For the purposes of paragraphs (1) and (2), a week starts at midnight between Sunday and Monday.
(4) An employer shall take all reasonable steps, in keeping with the need to protect the health and safety of workers, to ensure that the limits specified in paragraph (1) are complied with in the case of each worker employed by him in relation to whom they apply.]
Length of night workE+W+S
6.—(1) A night worker’s normal hours of work in any reference period which is applicable in his case shall not exceed an average of eight hours for each 24 hours.
(2) An employer shall take all reasonable steps, in keeping with the need to protect the health and safety or workers, to ensure that the limit specified in paragraph (1) is complied with in the case of each night worker employed by him.
(3) The reference periods which apply in the case of a night worker are—
(a)where a relevant agreement provides for the application of this regulation in relation to successive periods of 17 weeks, each such period, or
(b)in any other case, any period of 17 weeks in the course of his employment.
(4) Where a worker has worked for his employer for less than 17 weeks, the reference period applicable in his case is the period that has elapsed since he started work for his employer.
(5) For the purposes of this regulation, a night worker’s average normal hours of work for each 24 hours during a reference period shall be determined according to the formula—
where—A is the number of hours during the reference period which are normal working hours for that worker;
B is the number of days during the reference period, and
C is the total number of hours during the reference period comprised in rest periods spent by the worker in pursuance of his entitlement under regulation 11, divided by 24.
(6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(7) An employer shall ensure that no night worker employed by him whose work involves special hazards or heavy physical or mental strain works for more than eight hours in any 24-hour period during which the night worker performs night work.
(8) For the purposes of paragraph (7), the work of a night worker shall be regarded as involving special hazards or heavy physical or mental strain if—
(a)it is identified as such in—
(i)a collective agreement, or
(ii)a workforce agreement,
which takes account of the specific effects and hazards of night work, or
(b)it is recognised in a risk assessment made by the employer under [regulation 3 of the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999] as involving a significant risk to the health or safety of workers employed by him.
[Night work by young workersE+W+S
6A. An employer shall ensure that no young worker employed by him works during the restricted period.]
Health assessment and transfer of night workers to day workE+W+S
7.—(1) An employer—
(a)shall not assign an adult worker to work which is to be undertaken during periods such that the worker will become a night worker unless—
(i)the employer has ensured that the worker will have the opportunity of a free health assessment before he takes up the assignment; or
(ii)the worker had a health assessment before being assigned to work to be undertaken during such periods on an earlier occasion, and the employer has no reason to believe that that assessment is no longer valid, and
(b)shall ensure that each night worker employed by him has the opportunity of a free health assessment at regular intervals of whatever duration may be appropriate in his case.
(2) Subject to paragraph (4), an employer—
(a)shall not assign a young worker to work during [the restricted period] unless—
(i)the employer has ensured that the young worker will have the opportunity of a free assessment of his health and capacities before he takes up the assignment; or
(ii)the young worker had an assessment of his health and capacities before being assigned to work during the restricted period on an earlier occasion, and the employer has no reason to believe that that assessment is no longer valid; and
(b)shall ensure that each young worker employed by him and assigned to work during the restricted period has the opportunity of a free assessment of his health and capacities at regular intervals of whatever duration may be appropriate in his case.
(3) For the purposes of paragraphs (1) and (2), an assessment is free if it is at no cost to the worker to whom it relates.
(4) The requirements in paragraph (2) do not apply in a case where the work a young worker is assigned to do is of an exceptional nature.
(5) No person shall disclose an assessment made for the purposes of this regulation to any person other than the worker to whom it relates, unless—
(a)the worker has given his consent in writing to the disclosure, or
(b)the disclosure is confined to a statement that the assessment shows the worker to be fit—
(i)in a case where paragraph (1)(a)(i) or (2)(a)(i) applies, to take up an assignment, or
(ii)in a case where paragraph (1)(b) or (2)(b) applies, to continue to undertake an assignment.
(6) Where—
(a)a registered medical practitioner has advised an employer that a worker employed by the employer is suffering from health problems which the practitioner considers to be connected with the fact that the worker performs night work, and
(b)it is possible for the employer to transfer the worker to work—
(i)to which the worker is suited, and
(ii)which is to be undertaken during periods such that the worker will cease to be a night worker,
the employer shall transfer the worker accordingly.
Pattern of workE+W+S
8. Where the pattern according to which an employer organizes work is such as to put the health and safety of a worker employed by him at risk, in particular because the work is monotonous or the work-rate is predetermined, the employer shall ensure that the worker is given adequate rest breaks.
RecordsE+W+S
9. An employer shall—
(a)keep records which are adequate to show whether the limits specified in regulations 4(1) [, 5A(1)] and 6(1) and (7) and the requirements in regulations [6A and] 7(1) and (2) are being complied with in the case of each worker employed by him in relation to whom they apply; and
(b)retain such records for two years from the date on which they were made.
Daily restE+W+S
10.—(1) [A worker] is entitled to a rest period of not less than eleven consecutive hours in each 24-hour period during which he works for his employer.
(2) Subject to paragraph (3), a young worker is entitled to a rest period of not less than twelve consecutive hours in each 24-hour period during which he works for his employer.
(3) The minimum rest period provided for in paragraph (2) may be interrupted in the case of activities involving periods of work that are split up over the day or of short duration.
Weekly rest periodE+W+S
11.—(1) Subject to paragraph (2), [a worker] is entitled to an uninterrupted rest period of not less than 24 hours in each seven-day period during which he works for his employer.
(2) If his employer so determines, [a worker] shall be entitled to either—
(a)two uninterrupted rest periods each of not less than 24 hours in each 14-day period during which he works for his employer; or
(b)one uninterrupted rest period of not less than 48 hours in each such 14-day period,
in place of the entitlement provided for in paragraph (1).
(3) Subject to paragraph (8), a young worker is entitled to a rest period of not less than 48 hours in each seven-day period during which he works for his employer.
(4) For the purpose of paragraphs (1) to (3), a seven-day period or (as the case may be) 14-day period shall be taken to begin—
(a)at such times on such days as may be provided for for the purposes of this regulation in a relevant agreement; or
(b)where there are no provisions of a relevant agreement which apply, at the start of each week or (as the case may be) every other week.
(5) In a case where, in accordance with paragraph (4), 14-day periods are to be taken to begin at the start of every other week, the first such period applicable in the case of a particular worker shall be taken to begin—
(a)if the worker’s employment began on or before the date on which these Regulations come into force, on 5th October 1998; or
(b)if the worker’s employment begins after the date on which these Regulations come into force, at the start of the week in which that employment begins.
(6) For the purposes of paragraphs (4) and (5), a week starts at midnight between Sunday and Monday.
(7) The minimum rest period to which [a worker] is entitled under paragraph (1) or (2) shall not include any part of a rest period to which the worker is entitled under regulation 10(1), except where this is justified by objective or technical reasons or reasons concerning the organization of work.
(8) The minimum rest period to which a young worker is entitled under paragraph (3)—
(a)may be interrupted in the case of activities involving periods of work that are split up over the day or are of short duration; and
(b)may be reduced where this is justified by technical or organization reasons, but not to less than 36 consecutive hours.
Rest breaksE+W+S
12.—(1) Where [a worker's] daily working time is more than six hours, he is entitled to a rest break.
(2) The details of the rest break to which [a worker] is entitled under paragraph (1), including its duration and the terms on which it is granted, shall be in accordance with any provisions for the purposes of this regulation which are contained in a collective agreement or a workforce agreement.
(3) Subject to the provisions of any applicable collective agreement or workforce agreement, the rest break provided for in paragraph (1) is an uninterrupted period of not less than 20 minutes, and the worker is entitled to spend it away from his workstation if he has one.
(4) Where a young worker’s daily working time is more than four and a half hours, he is entitled to a rest break of at least 30 minutes, which shall be consecutive if possible, and he is entitled to spend it away from his workstation if he has one.
(5) If, on any day, a young worker is employed by more than one employer, his daily working time shall be determined for the purpose of paragraph (4) by aggregating the number of hours worked by him for each employer.
Entitlement to annual leaveE+W+S
13.—[(1) Subject to paragraph (5), a worker is entitled to four weeks' annual leave in each leave year.]
(2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(3) A worker’s leave year, for the purposes of this regulation, begins—
(a)on such date during the calendar year as may be provided for in a relevant agreement; or
(b)where there are no provisions of a relevant agreement which apply—
(i)if the worker’s employment began on or before 1st October 1998, on that date and each subsequent anniversary of that date; or
(ii)if the worker’s employment begins after 1st October 1998, on the date on which that employment begins and each subsequent anniversary of that date.
(4) Paragraph (3) does not apply to a worker to whom Schedule 2 applies (workers employed in agriculture) except where, in the case of a worker partly employed in agriculture, a relevant agreement so provides.
(5) Where the date on which a worker’s employment begins is later than the date on which (by virtue of a relevant agreement) his first leave year begins, the leave to which he is entitled in that leave year is a proportion of the period applicable under [paragraph (1)] equal to the proportion of that leave year remaining on the date on which his employment begins.
(6) Where by virtue of paragraph ... (5) the period of leave to which a worker is entitled is or includes a proportion of a week, the proportion shall be determined in days and any fraction of a day shall be treated as a whole day.
(7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(9) Leave to which a worker is entitled under this regulation may be taken in instalments, but—
(a)it may only be taken in the leave year in respect of which it is due, and
(b)it may not be replaced by a payment in lieu except where the worker’s employment is terminated.
Compensation related to entitlement to leaveE+W+S
14.—(1) This regulation applies where—
(a)a worker’s employment is terminated during the course of his leave year, and
(b)on the date on which the termination takes effect (“the termination date"), the proportion he has taken of the leave to which he is entitled in the leave year under [regulation 13] differs from the proportion of the leave year which has expired.
(2) Where the proportion of leave taken by the worker is less than the proportion of the leave year which has expired, his employer shall make him a payment in lieu of leave in accordance with paragraph (3).
(3) The payment due under paragraph (2) shall be—
(a)such sum as may be provided for for the purposes of this regulation in a relevant agreement, or
(b)where there are no provisions of a relevant agreement which apply, a sum equal to the amount that would be due to the worker under regulation 16 in respect of a period of leave determined according to the formula—
where—A is the period of leave to which the worker is entitled under [regulation 13];
B is the proportion of the worker’s leave year which expired before the termination date, and
C is the period of leave taken by the worker between the start of the leave year and the termination date.
(4) A relevant agreement may provide that, where the proportion of leave taken by the worker exceeds the proportion of the leave year which has expired, he shall compensate his employer, whether by a payment, by undertaking additional work or otherwise.
Dates on which leave is takenE+W+S
15.—(1) A worker may take leave to which he is entitled under [regulation 13] on such days as he may elect by giving notice to his employer in accordance with paragraph (3), subject to any requirement imposed on him by his employer under paragraph (2).
(2) A worker’s employer may require the worker—
(a)to take leave to which the worker is entitled under [regulation 13]; or
(b)not to take such leave,
on particular days, by giving notice to the worker in accordance with paragraph (3).
(3) A notice under paragraph (1) or (2)—
(a)may relate to all or part of the leave to which a worker is entitled in a leave year;
(b)shall specify the days on which leave is or (as the case may be) is not to be taken and, where the leave on a particular day is to be in respect of only part of the day, its duration; and
(c)shall be given to the employer or, as the case may be, the worker before the relevant date.
(4) The relevant date, for the purposes of paragraph (3), is the date—
(a)in the case of a notice under paragraph (1) or (2)(a), twice as many days in advance of the earliest day specified in the notice as the number of days or part-days to which the notice relates, and
(b)in the case of a notice under paragraph (2)(b), as many days in advance of the earliest day so specified as the number of days or part-days to which the notice relates.
(5) Any right or obligation under paragraphs (1) to (4) may be varied or excluded by a relevant agreement.
(6) This regulation does not apply to a worker to whom Schedule 2 applies (workers employed in agriculture) except where, in the case of a worker partly employed in agriculture, a relevant agreement so provides.
[Leave during the first year of employmentE+W+S
15A.—(1) During the first year of his employment, the amount of leave a worker may take at any time in exercise of his entitlement under regulation 13 is limited to the amount which is deemed to have accrued in his case at that time under paragraph (2), as modified under paragraph (3) in a case where that paragraph applies, less the amount of leave (if any) that he has already taken during that year.
(2) For the purposes of paragraph (1), leave is deemed to accrue over the course of the worker’s first year of employment, at the rate of one-twelfth of the amount specified in regulation 13(1) on the first day of each month of that year.
(3) Where the amount of leave that has accrued in a particular case includes a fraction of a day other than a half-day, the fraction shall be treated as a half-day if it is less than a half-day and as a whole day if it is more than a half-day.
(4) This regulation does not apply to a worker whose employment began on or before 25th October 2001.]
Payment in respect of periods of leaveE+W+S
16.—(1) A worker is entitled to be paid in respect of any period of annual leave to which he is entitled under regulation 13, at the rate of a week’s pay in respect of each week of leave.
(2) Sections 221 to 224 of the 1996 Act shall apply for the purpose of determining the amount of a week’s pay for the purposes of this regulation, subject to the modifications set out in paragraph (3).
(3) The provisions referred to in paragraph (2) shall apply—
(a)as if references to the employee were references to the worker;
(b)as if references to the employee’s contract of employment were references to the worker’s contract;
(c)as if the calculation date were the first day of the period of leave in question; and
(d)as if the references to sections 227 and 228 did not apply.
(4) A right to payment under paragraph (1) does not affect any right of a worker to remuneration under his contract (“contractual remuneration").
(5) Any contractual remuneration paid to a worker in respect of a period of leave goes towards discharging any liability of the employer to make payments under this regulation in respect of that period; and, conversely, any payment of remuneration under this regulation in respect of a period goes towards discharging any liability of the employer to pay contractual remuneration in respect of that period.
Entitlements under other provisionsE+W+S
17. Where during any period a worker is entitled to a rest period, rest break or annual leave both under a provision of these Regulations and under a separate provision (including a provision of his contract), he may not exercise the two rights separately, but may, in taking a rest period, break or leave during that period, take advantage of whichever right is, in any particular respect, the more favourable.
PART IIIE+W+S EXCEPTIONS
[ Excluded sectorsE+W+S
18.—(1) These Regulations do not apply—
(a)to workers to whom the European Agreement on the organisation of working time of seafarers dated 30th September 1998 and put into effect by Council Directive 1999/63/EC of 21st June 1999 applies;
[(b)to workers to whom the Fishing Vessels (Working Time: Sea-fishermen) Regulations 2004 apply];
[(c)to workers to whom the Merchant Shipping (Working Time: Inland Waterways) Regulations 2003 apply].
(2) Regulations 4(1) and (2), 6(1), (2) and (7), 7(1) and (6), 8, 10(1), 11(1) and (2), 12(1), 13 and 16 do not apply—
(a)where characteristics peculiar to certain specific services such as the armed forces or the police, or to certain specific activities in the civil protection services, inevitably conflict with the provisions of these Regulations;
(b)to workers to whom the European Agreement on the organisation of working time of mobile staff in civil aviation concluded on 22nd March 2000 and implemented by Council Directive 2000/79/EC of 27th November 2000 applies; or
(c)to the activities of workers who are doctors in training.
(3) Paragraph (2)(c) has effect only until 31st July 2004.
(4) Regulations 4(1) and (2), 6(1), (2) and (7), 8, 10(1), 11(1) and (2) and 12(1) do not apply to workers to whom Directive 2002/15/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the organisation of the working time of persons performing mobile road transport activities, dated 11th March 2002 applies.]
Domestic serviceE+W+S
19. Regulations 4(1) and (2) [, 5A(1) and (4),] 6(1), (2) and (7), [6A,] 7(1), (2) and (6) and 8 do not apply in relation to a worker employed as a domestic servant in a private household.
Unmeasured working timeE+W+S
20.— [(1)] Regulations 4(1) and (2), 6(1), (2) and (7), 10(1), 11(1) and (2) and 12(1) do not apply in relation to a worker where, on account of the specific characteristics of the activity in which he is engaged, the duration of his working time is not measured or predetermined or can be determined by the worker himself, as may be the case for—
(a)managing executives or other persons with autonomous decision-taking powers;
(b)family workers; or
(c)workers officiating at religious ceremonies in churches and religious communities.
(2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Other special casesE+W+S
21. Subject to regulation 24, regulations 6(1), (2) and (7), 10(1), 11(1) and (2) and 12(1) do not apply in relation to a worker—
(a)where the worker’s activities are such that his place of work and place of residence are distant from one another [, including cases where the worker is employed in offshore work,] or his different places of work are distant from one another;
(b)where the worker is engaged in security and surveillance activities requiring a permanent presence in order to protect property and persons, as may be the case for security guards and caretakers or security firms;
(c)where the worker’s activities involve the need for continuity of service or production, as may be the case in relation to—
(i)services relating to the reception, treatment or care provided by hospitals or similar establishments [(including the activities of doctors in training)], residential institutions and prisons;
(ii)work at docks or airports;
(iii)press, radio, television, cinematographic production, postal and telecommunications services and civil protection services;
(iv)gas, water and electricity production, transmission and distribution, household refuse collection and incineration;
(v)industries in which work cannot be interrupted on technical grounds;
(vi)research and development activities;
(vii)agriculture;
[(viii)the carriage of passengers on regular urban transport services;]
(d)where there is a foreseeable surge of activity, as may be the case in relation to—
(i)agriculture;
(ii)tourism; and
(iii)postal services;
(e)where the worker’s activities are affected by—
(i)an occurrence due to unusual and unforeseeable circumstances, beyond the control of the worker’s employer;
(ii)exceptional events, the consequences of which could not have been avoided despite the exercise of all due care by the employer; or
(iii)an accident or the imminent risk of an accident;
[(f)where the worker works in railway transport and—
(i)his activities are intermittent;
(ii)he spends his working time on board trains; or
(iii)his activities are linked to transport timetables and to ensuring the continuity and regularity of traffic.]
Shift workersE+W+S
22.—(1) Subject to regulation 24—
(a)regulation 10(1) does not apply in relation to a shift worker when he changes shift and cannot take a daily rest period between the end of one shift and the start of the next one;
(b)paragraphs (1) and (2) of regulation 11 do not apply in relation to a shift worker when he changes shift and cannot take a weekly rest period between the end of one shift and the start of the next one; and
(c)neither regulation 10(1) nor paragraphs (1) and (2) of regulation 11 apply to workers engaged in activities involving periods of work split up over the day, as may be the case for cleaning staff.
(2) For the purposes of this regulation—
“shift worker" means any worker whose work schedule is part of shift work; and
“shift work" means any method of organizing work in shifts whereby workers succeed each other at the same workstations according to a certain pattern, including a rotating pattern, and which may be continuous or discontinuous, entailing the need for workers to work at different times over a given period of days or weeks.
Collective and workforce agreementsE+W+S
23. A collective agreement or a workforce agreement may—
(a)modify or exclude the application of regulations 6(1) to (3) and (7), 10(1), 11(1) and (2) and 12(1), and
(b)for objective or technical reasons or reasons concerning the organization of work, modify the application of regulation 4(3) and (4) by the substitution, for each reference to 17 weeks, of a different period, being a period not exceeding 52 weeks,
in relation to particular workers or groups of workers.
Compensatory restE+W+S
24. Where the application of any provision of these Regulations is excluded by regulation 21 or 22, or is modified or excluded by means of a collective agreement or a workforce agreement under regulation 23(a), and a worker is accordingly required by his employer to work during a period which would otherwise be a rest period or rest break—
(a)his employer shall wherever possible allow him to take an equivalent period of compensatory rest, and
(b)in exceptional cases in which it is not possible, for objective reasons, to grant such a period of rest, his employer shall afford him such protection as may be appropriate in order to safeguard the worker’s health and safety.
[Mobile workersE+W+S
24A.—(1) Regulations 6(1), (2) and (7), 10(1), 11(1) and (2) and 12(1) do not apply to a mobile worker in relation to whom the application of those regulations is not excluded by any provision of regulation 18.
(2) A mobile worker, to whom paragraph (1) applies, is entitled to adequate rest, except where the worker’s activities are affected by any of the matters referred to in regulation 21(e).
(3) For the purposes of this regulation, “adequate rest” means that a worker has regular rest periods, the duration of which are expressed in units of time and which are sufficiently long and continuous to ensure that, as a result of fatigue or other irregular working patterns, he does not cause injury to himself, to fellow workers or to others and that he does not damage his health, either in the short term or in the longer term.]
Workers in the armed forcesE+W+S
25.—(1) Regulation 9 does not apply in relation to a worker serving as a member of the armed forces.
(2) Regulations [5A, 6A,] 10(2) and 11(3) do not apply in relation to a young worker serving as a member of the armed forces.
(3) In a case where a young worker is accordingly required to work during [the restricted period, or is not permitted the minimum rest period provided for in regulation 10(2) or 11(3),] he shall be allowed an appropriate period of compensatory rest.
[Doctors in trainingE+W+S
25A.—(1) Paragraph (1) of regulation 4 is modified in its application to workers who are doctors in training as follows—
(a)for the reference to 48 hours there is substituted a reference to 58 hours with effect from 1st August 2004 until 31st July 2007;
(b)for the reference to 48 hours there is substituted a reference to 56 hours with effect from 1st August 2007 until 31st July 2009.
(2) In the case of workers who are doctors in training, paragraphs (3)–(5) of regulation 4 shall not apply and paragraphs (3) and (4) of this regulation shall apply in their place.
(3) Subject to paragraph (4), the reference period which applies in the case of a worker who is a doctor in training is, with effect from 1st August 2004—
(a)where a relevant agreement provides for the application of this regulation in relation to successive periods of 26 weeks, each such period; and
(b)in any other case, any period of 26 weeks in the course of his employment.
(4) Where a doctor in training has worked for his employer for less than 26 weeks, the reference period applicable in his case is the period that has elapsed since he started work for his employer.]
[Workers employed in offshore workE+W+S
25B.—(1) In the case of workers employed in offshore work, paragraphs (3)–(5) of regulation 4 shall not apply and paragraphs (2) and (3) of this regulation shall apply in their place.
(2) Subject to paragraph (3), the reference period which applies in the case of workers employed in offshore work is—
(a)where a relevant agreement provides for the application of this regulation in relation to successive periods of 52 weeks, each such period; and
(b)in any other case, any period of 52 weeks in the course of his employment.
(3) Where a worker employed in offshore work has worked for his employer for less than 52 weeks, the reference period applicable in his case is the period that has elapsed since he started work for his employer.]
Young workers employed on shipsE+W+S
26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Young workers:force majeureE+W+S
27.—(1) Regulations [5A, 6A,] 10(2) and 12(4) do not apply in relation to a young worker where his employer requires him to undertake work which no adult worker is available to perform and which—
(a)is occasioned by either—
(i)an occurrence due to unusual and unforseeable circumstances, beyond the employer’s control, or
(ii)exceptional events, the consequences of which could not have been avoided despite the exercise of all due care by the employer;
(b)is of a temporary nature; and
(c)must be performed immediately.
(2) Where the application of regulation [5A, 6A,] 10(2) or 12(4) is excluded by paragraph (1), and a young worker is accordingly required to work during a period which would otherwise be a rest period or rest break, his employer shall allow him to take an equivalent period of compensatory rest within the following three weeks.
[Other exceptions relating to young workersE+W+S
27A.—(1) Regulation 5A does not apply in relation to a young worker where—
(a)the young worker’s employer requires him to undertake work which is necessary either to maintain continuity of service or production or to respond to a surge in demand for a service or product;
(b)no adult worker is available to perform the work, and
(c)performing the work would not adversely affect the young worker’s education or training.
(2) Regulation 6A does not apply in relation to a young worker employed—
(a)in a hospital or similar establishment, or
(b)in connection with cultural, artistic, sporting or advertising activities,
in the circumstances referred to in paragraph (1).
(3) Regulation 6A does not apply, except in so far as it prohibits work between midnight and 4 a.m., in relation to a young worker employed in—
(a)agriculture;
(b)retail trading;
(c)postal or newspaper deliveries;
(d)a catering business;
(e)a hotel, public house, restaurant, bar or similar establishment, or
(f)a bakery,
in the circumstances referred to in paragraph (1).
(4) Where the application of regulation 6A is excluded by paragraph (2) or (3), and a young worker is accordingly required to work during a period which would otherwise be a rest period or rest break—
(a)he shall be supervised by an adult worker where such supervision is necessary for the young worker’s protection, and
(b)he shall be allowed an equivalent period of compensatory rest.]
PART IVE+W+S MISCELLANEOUS
[EnforcementE+W+S
28.—(1) In this regulation, regulations 29–29E and Schedule 3—
“the 1974 Act” means the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974;
“the Civil Aviation Authority” means the authority referred to in section 2(1) of the Civil Aviation Act 1982;
“code of practice” includes a standard, a specification and any other documentary form of practical guidance;
“the Commission” means the Health and Safety Commission referred to in section 10(2) of the 1974 Act;
“enforcement authority” means the Executive, a local authority, the Civil Aviation Authority [, VOSA or the Office of Rail Regulation];
“the Executive” means the Health and Safety Executive referred to in section 10(5) of the 1974 Act;
“local authority” means—
(a)
in relation to England, a county council so far as they are the council for an area for which there are no district councils, a district council, a London borough council, the Common Council of the City of London, the Sub-Treasurer of the Inner Temple or the Under-Treasurer of the Middle Temple;
(b)
in relation to Wales, a county council or a county borough council;
(c)
in relation to Scotland, a council constituted under section 2 of the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994;
“premises” includes any place and, in particular, includes—
(a)
any vehicle, vessel, aircraft or hovercraft;
(b)
any installation on land (including the foreshore and other land intermittently covered by water), any offshore installation, and any other installation (whether floating, or resting on the seabed or the subsoil thereof, or resting on other land covered with water or the subsoil thereof) and
(c)
any tent or movable structure;
“relevant civil aviation worker” means a mobile worker who works mainly on board civil aircraft, excluding any worker to whom regulation 18(2)(b) applies;
“the relevant requirements” means the following provisions—
(a)
regulations 4(2), 5A(4), 6(2) and (7), 6A, 7(1), (2) and (6), 8, 9 and 27A(4)(a);
(b)
regulation 24, in so far as it applies where regulation 6(1), (2) or (7) is modified or excluded, and
(c)
regulation 24A(2), in so far as it applies where regulations 6(1), (2) or (7) is excluded;
“relevant road transport worker” means a mobile worker to whom one or more of the following applies—
(b)
the European Agreement concerning the Work of Crews of Vehicles engaged in International Road Transport (AETR) of 1st July 1970, and
(c)
the United Kingdom domestic driver’s hours code, which is set out in Part VI of the Transport Act 1968;
“the relevant statutory provisions” means—
(a)
the provisions of the 1974 Act and of any regulations made under powers contained in that Act; and
(b)
while and to the extent that they remain in force, the provisions of the Acts mentioned in Schedule 1 to the 1974 Act and which are specified in the third column of that Schedule and the regulations, orders or other instruments of a legislative character made or having effect under a provision so specified; and
“VOSA” means the Vehicle and Operator Services Agency.
(2) It shall be the duty of the Executive to make adequate arrangements for the enforcement of the relevant requirements except to the extent that—
(a)a local authority is made responsible for their enforcement by paragraph (3);
(b)the Civil Aviation Authority is made responsible for their enforcement by paragraph (5);...
(c)VOSA is made responsible for their enforcement by paragraph (6);
[(d)the Office of Rail Regulation is made responsible for their enforcement by paragraph (3A).]
(3) Where the relevant requirements apply in relation to workers employed in premises in respect of which a local authority is responsible, under the Health and Safety (Enforcing Authority) Regulations 1998, for enforcing any of the relevant statutory provisions, it shall be the duty of that authority to enforce those requirements.
[(3A) Where the relevant requirements apply in relation to workers employed in the carrying out of any of the activities specified in regulation 3(2) of the Health and Safety (Enforcing Authority for Railways and Other Guided Transport Systems) Regulations 2006 it shall be the duty of the Office of Rail Regulation to enforce those requirements.]
(4) The duty imposed on local authorities by paragraph (3) shall be performed in accordance with such guidance as may be given to them by the Commission.
(5) It shall be the duty of the Civil Aviation Authority to enforce the relevant requirements in relation to relevant civil aviation workers.
(6) It shall be the duty of VOSA to enforce the relevant requirements in relation to relevant road transport workers.
(7) The provisions of Schedule 3 shall apply in relation to the enforcement of the relevant requirements.
(8) Any function of the Commission under the 1974 Act which is exercisable in relation to the enforcement by the Executive of the relevant statutory provisions shall be exercisable in relation to the enforcement by the Executive of the relevant requirements.]
[ OffencesE+W+S
29.—(1) An employer who fails to comply with any of the relevant requirements shall be guilty of an offence.
(2) The provisions of paragraph (3) shall apply where an inspector is exercising or has exercised any power conferred by Schedule 3.
(3) It is an offence for a person—
(a)to contravene any requirement imposed by the inspector under paragraph 2 of Schedule 3;
(b)to prevent or attempt to prevent any other person from appearing before the inspector or from answering any question to which the inspector may by virtue of paragraph 2(2)(e) of Schedule 3 require an answer;
(c)to contravene any requirement or prohibition imposed by an improvement notice or a prohibition notice (including any such notice as is modified on appeal);
(d)intentionally to obstruct the inspector in the exercise or performance of his powers or duties;
(e)to use or disclose any information in contravention of paragraph 8 of Schedule 3;
(f)to make a statement which he knows to be false or recklessly to make a statement which is false, where the statement is made in purported compliance with a requirement to furnish any information imposed by or under these Regulations.
(4) An employer guilty of an offence under paragraph (1) shall be liable—
(a)on summary conviction, to a fine not exceeding the statutory maximum;
(b)on conviction on indictment, to a fine.
(5) A person guilty of an offence under paragraph (3) shall be liable to the penalty prescribed in relation to that provision by paragraphs (6), (7) or (8) as the case may be.
(6) A person guilty of an offence under sub-paragraph (3)(a), (b) or (d) shall be liable on summary conviction to a fine not exceeding level 5 on the standard scale.
(7) A person guilty of an offence under sub-paragraph (3)(c) shall be liable—
(a)on summary conviction, to imprisonment for a term not exceeding three months, or a fine not exceeding the statutory maximum;
(b)on conviction on indictment, to imprisonment for a term not exceeding two years, or a fine, or both.
(8) A person guilty of an offence under any of the sub-paragraphs of paragraph (3) not falling within paragraphs (6) or (7) above, shall be liable—
(a)on summary conviction, to a fine not exceeding the statutory maximum;
(b)on conviction on indictment—
(i)if the offence is under sub-paragraph (3)(e), to imprisonment for a term not exceeding two years or a fine or both;
(ii)if the offence is not one to which the preceding sub-paragraph applies, to a fine.
(9) The provisions set out in regulations 29A–29E below shall apply in relation to the offences provided for in paragraphs (1) and (3).]
[Offences due to fault of other personE+W+S
29A. Where the commission by any person of an offence is due to the act or default of some other person, that other person shall be guilty of the offence, and a person may be charged with and convicted of the offence by virtue of this paragraph whether or not proceedings are taken against the first-mentioned person.]
[Offences by bodies corporateE+W+S
29B.—(1) Where an offence committed by a body corporate is proved to have been committed with the consent or connivance of, or to have been attributable to any neglect on the part of, any director, manager, secretary or other similar officer of the body corporate or a person who was purporting to act in any such capacity, he as well as the body corporate shall be guilty of that offence and shall be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly.
(2) Where the affairs of a body corporate are managed by its members, the preceding paragraph shall apply in relation to the acts and defaults of a member in connection with his functions of management as if he were a director of the body corporate.]
[Restriction on institution of proceedings in England and WalesE+W+S
29C. Proceedings for an offence shall not, in England and Wales, be instituted except by an inspector or by or with the consent of the Director of Public Prosecutions.]
[Prosecutions by inspectorsE+W+S
29D.—(1) An inspector, if authorised in that behalf by an enforcement authority, may, although not of counsel or a solicitor, prosecute before a magistrate’s court proceedings for an offence under these Regulations.
(2) This regulation shall not apply to Scotland.]
[Power of court to order cause of offence to be remediedE+W+S
29E.—(1) Where a person is convicted of an offence in respect of any matters which appear to the court to be matters which it is in his power to remedy, the court may, in addition to or instead of imposing any punishment, order him, within such time as may be fixed by the order, to take such steps as may be specified in the order for remedying the said matters.
(2) The time fixed by an order under paragraph (1) may be extended or further extended by order of the court on an application made before the end of that time as originally fixed or as extended under this paragraph, as the case may be.
(3) Where a person is ordered under paragraph (1) to remedy any matters, that person shall not be liable under these Regulations in respect of those matters in so far as they continue during the time fixed by the order or any further time allowed under paragraph (2).]
RemediesE+W+S
30.—(1) A worker may present a complaint to an employment tribunal that his employer—
(a)has refused to permit him to exercise any right he has under—
(i)regulation 10(1) or (2), 11(1), (2) or (3), 12(1) or (4) or [13];
(ii)regulation 24, in so far as it applies where regulation 10(1), 11(1) or (2) or 12(1) is modified or excluded; ...
[(iii)regulation 24A, in so far as it applies where regulation 10(1), 11(1) or (2) or 12(1) is excluded; or
(iv)regulation 25(3), 27A(4)(b) or 27(2); or]
(b)has failed to pay him the whole or any part of any amount due to him under regulation 14(2) or 16(1).
(2) An employment tribunal shall not consider a complaint under this regulation unless it is presented—
(a)before the end of the period of three months (or, in a case to which regulation 38(2) applies, six months) beginning with the date on which it is alleged that the exercise of the right should have been permitted (or in the case of a rest period or leave extending over more than one day, the date on which it should have been permitted to begin) or, as the case may be, the payment should have been made;
(b)within such further period as the tribunal considers reasonable in a case where it is satisfied that it was not reasonably practicable for the complaint to be presented before the end of that period of three or, as the case may be, six months.
[(2A) Where the period within which a complaint must be presented in accordance with paragraph (2) is extended by regulation 15 of the Employment Act 2002 (Dispute Resolution) Regulations 2004, the period within which the complaint must be presented shall be the extended period rather than the period in paragraph (2).]
(3) Where an employment tribunal finds a complaint under paragraph (1)(a) well-founded, the tribunal—
(a)shall make a declaration to that effect, and
(b)may make an award of compensation to be paid by the employer to the worker.
(4) The amount of the compensation shall be such as the tribunal considers just and equitable in all the circumstances having regard to—
(a)the employer’s default in refusing to permit the worker to exercise his right, and
(b)any loss sustained by the worker which is attributable to the matters complained of.
(5) Where on a complaint under paragraph (1)(b) an employment tribunal finds that an employer has failed to pay a worker in accordance with regulation 14(2) or 16(1), it shall order the employer to pay to the worker the amount which it finds to be due to him.
Textual Amendments
Modifications etc. (not altering text)
Right not to suffer detrimentE+W+S
31.—(1) After section 45 of the 1996 Act there shall be inserted—
“45A. Working time cases.
(1) A worker has the right not to be subjected to any detriment by any act, or any deliberate failure to act, by his employer done on the ground that the worker—
(a)refused (or proposed to refuse) to comply with a requirement which the employer imposed (or proposed to impose) in contravention of the Working Time Regulations 1998,
(b)refused (or proposed to refuse) to forgo a right conferred on him by those Regulations,
(c)failed to sign a workforce agreement for the purposes of those Regulations, or to enter into, or agree to vary or extend, any other agreement with his employer which is provided for in those Regulations,
(d)being—
(i)a representative of members of the workforce for the purposes of Schedule 1 to those Regulations, or
(ii)a candidate in an election in which any person elected will, on being elected, be such a representative,
performed (or proposed to perform) any functions or activities as such a representative or candidate,
(e)brought proceedings against the employer to enforce a right conferred on him by those Regulations, or
(f)alleged that the employer had infringed such a right.
(2) It is immaterial for the purposes of subsection (1)(e) or (f)—
(a)whether or not the worker has the right, or
(b)whether or not the right has been infringed,
but, for those provisions to apply, the claim to the right and that it has been infringed must be made in good faith.
(3) It is sufficient for subsection (1)(f) to apply that the worker, without specifying the right, made it reasonably clear to the employer what the right claimed to have been infringed was.
(4) This section does not apply where a worker is an employee and the detriment in question amounts to dismissal within the meaning of Part X, unless the dismissal is in circumstances in which, by virtue of section 197, Part X does not apply.”
(2) After section 48(1) of the 1996 Act there shall be inserted the following subsection—
“(1ZA) A worker may present a complaint to an employment tribunal that he has been subjected to a detriment in contravention of section 45A.”
(3) In section 49 of the 1996 Act (remedies)—
(a)in subsection (2), for “subsection (6)" there shall be substituted “ subsections (5A) and (6) ”, and
(b)after subsection (5), there shall be inserted—
“(5A) Where—
(a)the complaint is made under section 48 (1ZA),
(b)the detriment to which the worker is subjected is the termination of his worker’s contract, and
(c)that contract is not a contract of employment,
any compensation must not exceed the compensation that would be payable under Chapter II of Part X if the worker had been an employee and had been dismissed for the reason specified in section 101A.”
(4) In section 192(2) of the 1996 Act (provisions applicable in relation to service in the armed forces), after paragraph (a) there shall be inserted—
“(aa)in Part V, section 45A, and sections 48 and 49 so far as relating to that section,”.
(5) In sections 194(2)(c), 195(2)(c) and 202(2)(b) of the 1996 Act, for “sections 44 and 47"there shall be substituted “ sections 44, 45A and 47 ”.
(6) In section 200(1) of the 1996 Act (which lists provisions of the Act which do not apply to employment in police service), after “45," there shall be inserted “ 45A, ”.
(7) In section 205 of the 1996 Act (remedy for infringement of certain rights), after subsection (1) there shall be inserted the following subsection—
“(1ZA) In relation to the right conferred by section 45A, the reference in subsection (1) to an employee has effect as a reference to a worker.”
Unfair dismissalE+W+S
32.—(1) After section 101 of the 1996 Act there shall be inserted the following section—
“101A. Working time cases.
An employee who is dismissed shall be regarded for the purposes of this Part as unfairly dismissed if the reason (or, if more than one, the principal reason) for the dismissal is that the employee—
(a)refused (or proposed to refuse) to comply with a requirement which the employer imposed (or proposed to impose) in contravention of the Working Time Regulations 1998,
(b)refused (or proposed to refuse) to forgo a right conferred on him by those Regulations,
(c)failed to sign a workforce agreement for the purposes of those Regulations, or to enter into, or agree to vary or extend, any other agreement with his employer which is provided for in those Regulations, or
(d)being—
(i)a representative of members of the workforce for the purposes of Schedule 1 to those Regulations, or
(ii)a candidate in an election in which any person elected will, on being elected, be such a representative,
performed (or proposed to perform) any functions or activities as such a representative or candidate.”
(2) In section 104 of the 1996 Act (right of employees not to be unfairly dismissed for asserting particular rights) in subsection (4)—
(a)at the end of paragraph (b), the word “and" shall be omitted, and
(b)after paragraph (c), there shall be inserted the words—
“and
(d)the rights conferred by the Working Time Regulations 1998.”
(3) In section 105 of the 1996 Act (redundancy as unfair dismissal), after subsection (4) there shall be inserted the following subsection—
“(4A) This subsection applies if the reason (or, if more than one, the principal reason) for which the employee was selected for dismissal was one of those specified in section 101A.”
(4) In sections 108(3) and 109(2) of the 1996 Act, after paragraph (d) there shall be inserted—
“(dd)section 101A applies,”.
(5) In sections 117(4)(b), 118(3), 120(1), 122(3), 128(1)(b) and 129(1) of the 1996 Act, after “100(1)(a) and (b)," there shall be inserted “ 101A(d), ”.
(6) In section 202(2) (cases where disclosure of information is restricted on ground of national security)—
(a)in paragraph (g)(i), after “100" there shall be inserted “ , 101A(d) ”, and
(b)in paragraph (g)(ii), after “of that section," there shall be inserted “ or by reason of the application of subsection (4A) in so far as it applies where the reason (or, if more than one, the principal reason) for which an employee was selected for dismissal was that specified in section 101A(d) ”.
(7) In section 209(2) of the 1996 Act (which lists provisions excluded from the scope of the power to amend the Act by order), after “101," in paragraph (e) there shall be inserted “ 101A, ”.
(8) In sections 237(1A) and 238(2A) of the Trade Union and Labour Relations (Consolidation) Act 1992 (cases where employee can complain of unfair dismissal notwithstanding industrial action at time of dismissal), after “100" there shall be inserted “ , 101A(d) ”.
(9) In section 10(5)(a) of the Employment Tribunals Act 1996 (cases where Minister’s certificate is not conclusive evidence that action was taken to safeguard national security), after “100" there shall be inserted “ , 101A(d) ”.
ConciliationE+W+S
33. In section 18(1) of the Employment Tribunals Act 1996 (cases where conciliation provisions apply)—
(a)at the end of paragraph (e), the word “or" shall be omitted, and
(b)after paragraph (f), there shall be inserted the words—
“or
(ff)under regulation 30 of the Working Time Regulations 1998,”.
AppealsE+W+S
34. In section 21 of the Employment Tribunals Act 1996 (jurisdiction of the Employment Appeal Tribunal)—
(a)at the end of subsection (1) (which confers jurisdiction by reference to Acts under or by virtue of which decisions are made) there shall be inserted—
“or under the Working Time Regulations 1998.”;
(b)in subsection (2), after “the Acts listed" there shall be inserted—
“or the Regulations referred to”.
Restrictions on contracting outE+W+S
35.—(1) Any provision in an agreement (whether a contract of employment or not) is void in so far as it purports—
(a)to exclude or limit the operation of any provision of these Regulations, save in so far as these Regulations provide for an agreement to have that effect, or
(b)to preclude a person from bringing proceedings under these Regulations before an employment tribunal.
(2) Paragraph (1) does not apply to—
(a)any agreement to refrain from instituting or continuing proceedings where a conciliation officer has taken action under section 18 of the Employment Tribunals Act 1996 (conciliation); or
(b)any agreement to refrain from instituting or continuing proceedings within section 18(1)(ff) of the Employment Tribunals Act 1996 (proceedings under these Regulations where conciliation is available), if the conditions regulating compromise agreements under these Regulations are satisfied in relation to the agreement.
(3) For the purposes of paragraph (2)(b) the conditions regulating compromise agreements under these Regulations are that—
(a)the agreement must be in writing,
(b)the agreement must relate to the particular complaint,
(c)the worker must have received advice from a relevant independent adviser as to the terms and effect of the proposed agreement and, in particular, its effect on his ability to pursue his rights before an employment tribunal,
(d)there must be in force, when the adviser gives the advice, a contract of insurance, or an indemnity provided for members of a profession or professional body, covering the risk of a claim by the worker in respect of loss arising in consequence of the advice,
(e)the agreement must identify the adviser, and
(f)the agreement must state that the conditions regulating compromise agreements under these Regulations are satisfied.
(4) A person is a relevant independent adviser for the purposes of paragraph (3)(c)—
(a)if he is a qualified lawyer,
(b)if he is an officer, official, employee or member of an independent trade union who has been certified in writing by the trade union as competent to give advice and as authorised to do so on behalf of the trade union, or
(c)if he works at an advice centre (whether as an employee or as a volunteer) and has been certified in writing by the centre as competent to give advice and as authorised to do so on behalf of the centre.
(5) But a person is not a relevant independent adviser for the purposes of paragraph (3)(c) in relation to the worker—
(a)if he is, is employed by or is acting in the matter for the employer or an associated employer,
(b)in the case of a person within paragraph (4)(b) or (c), if the trade union or advice centre is the employer or an associated employer, or
(c)in the case of a person within paragraph (4)(c), if the worker makes a payment for the advice received from him.
(6) In paragraph (4)(a), “qualified lawyer" means—
(a)as respects England and Wales, a barrister (whether in practice as such or employed to give legal advice), a solicitor who holds a practising certificate, or a person other than a barrister or solicitor who is an authorised advocate or authorised litigator (within the meaning of the Courts and Legal Services Act 1990) ; and
(b)as respects Scotland, an advocate (whether in practice as such or employed to give legal advice), or a solicitor who holds a practising certificate.
[(6A) A person shall be treated as being a qualified lawyer within paragraph (6)(a) if he is a Fellow of the Institute of Legal Executives employed by a solicitors' practice.]
(7) For the purposes of paragraph (5) any two employers shall be treated as associated if—
(a)one is a company of which the other (directly or indirectly) has control; or
(b)both are companies of which a third person (directly or indirectly) has control;
and “associated employer" shall be construed accordingly.
Textual Amendments
Marginal Citations
[35A.—(1) The Secretary of State shall, after consulting persons appearing to him to represent the two sides of industry, arrange for the publication, in such form and manner as he considers appropriate, of information and advice concerning the operation of these Regulations.E+W+S
(2)The information and advice shall be such as appear to him best calculated to enable employers and workers affected by these Regulations to understand their respective rights and obligations under them.]
PART VE+W+S SPECIAL CLASSES OF PERSON
Agency workers not otherwise “workers"E+W+S
36.—(1) This regulation applies in any case where an individual (“the agency worker")—
(a)is supplied by a person (“the agent") to do work for another (“the principal") under a contract or other arrangements made between the agent and the principal; but
(b)is not, as respects that work, a worker, because of the absence of a worker’s contract between the individual and the agent or the principal; and
(c)is not a party to a contract under which he undertakes to do the work for another party to the contract whose status is, by virtue of the contract, that of a client or customer of any profession or business undertaking carried on by the individual.
(2) In a case where this regulation applies, the other provisions of these Regulations shall have effect as if there were a worker’s contract for the doing of the work by the agency worker made between the agency worker and—
(a)whichever of the agent and the principal is responsible for paying the agency worker in respect of the work; or
(b)if neither the agent nor the principal is so responsible, whichever of them pays the agency worker in respect of the work,
and as if that person were the agency worker’s employer.
Crown employmentE+W+S
37.—(1) Subject to paragraph (4) and regulation 38, these Regulations have effect in relation to Crown employment and persons in Crown employment as they have effect in relation to other employment and other workers.
(2) In paragraph (1) “Crown employment" means employment under or for the purposes of a government department or any officer or body exercising on behalf of the Crown functions conferred by a statutory provision.
(3) For the purposes of the application of the provisions of these Regulations in relation to Crown employment in accordance with paragraph (1)—
(a)references to a worker shall be construed as references to a person in Crown employment; and
(b)references to a worker’s contract shall be construed as references to the terms of employment of a person in Crown employment.
(4) No act or omission by the Crown which is an offence under regulation 29 shall make the Crown criminally liable, but the High Court or, in Scotland, the Court of Session may, on the application of a person appearing to the Court to have an interest, declare any such act or omission unlawful.
Armed forcesE+W+S
38.—(1) Regulation 37 applies—
(a)subject to paragraph (2), to service as a member of the armed forces, and
(b)to employment by an association established for the purposes of Part XI of the Reserve Forces Act 1996 .
(2) No complaint concerning the service of any person as a member of the armed forces may be presented to an employment tribunal under regulation 30 unless—
(a)that person has made a complaint in respect of the same matter to an officer under the service redress procedures, and
(b)that complaint has not been withdrawn.
(3) For the purposes of paragraph (2)(b), a person shall be treated as having withdrawn his complaint if, having made a complaint to an officer under the service redress procedures, he fails to submit the complaint to the Defence Council under those procedures.
(4) Where a complaint of the kind referred to in paragraph (2) is presented to an employment tribunal, the service redress procedures may continue after the complaint is presented.
(5) In this regulation, “the service redress procedures" means the procedures, excluding those which relate to the making of a report on a complaint to Her Majesty, referred to in section 180 of the Army Act 1955 , section 180 of the Air Force Act 1955 and section 130 of the Naval Discipline Act 1957 .
House of Lords staffE+W+S
39.—(1) These Regulations have effect in relation to employment as a relevant member of the House of Lords staff as they have effect in relation to other employment.
(2) Nothing in any rule of law or the law or practice of Parliament prevents a relevant member of the House of Lords staff from presenting a complaint to an employment tribunal under regulation 30.
(3) In this regulation “relevant member of the House of Lords staff" means any person who is employed under a worker’s contract with the Corporate Officer of the House of Lords.
House of Commons staffE+W+S
40.—(1) These Regulations have effect in relation to employment as a relevant member of the House of Commons staff as they have effect in relation to other employment.
(2) For the purposes of the application of the provisions of these Regulations in relation to a relevant member of the House of Commons staff—
(a)references to a worker shall be construed as references to a relevant member of the House of Commons staff; and
(b)references to a worker’s contract shall be construed as references to the terms of employment of a relevant member of the House of Commons staff.
(3) Nothing in any rule of law or the law or practice of Parliament prevents a relevant member of the House of Commons staff from presenting a complaint to an employment tribunal under regulation 30.
(4) In this regulation “relevant member of the House of Commons staff" means any person—
(a)who was appointed by the House of Commons Commission; or
(b)who is a member of the Speaker’s personal staff.
Police serviceE+W+S
41.—(1) [Subject to paragraph (1A),] for the purposes of these Regulations, the holding, otherwise than under a contract of employment, of the office of constable or an appointment as a police cadet shall be treated as employment, under a worker’s contract, by the relevant officer.
[(1A) For the purposes of these Regulations, any constable who has been seconded to the Serious Organised Crime Agency to serve as a member of its staff shall be treated as employed by the Serious Organised Crime Agency.]
(2) Any matter relating to the employment of a worker which may be provided for for the purposes of these Regulations in a workforce agreement may be provided for for the same purposes in relation to the service of a person holding the office of constable or an appointment as a police cadet by an agreement between the relevant officer and a joint branch board.
(3) In this regulation—
“a joint branch board" means a joint branch board constituted in accordance with regulation 7(3) of the Police Federation Regulations 1969 or regulation 7(3) of the Police Federation (Scotland) Regulations 1985 , and
“the relevant officer" means—
(a)
in relation to a member of a police force or a special constable or police cadet appointed for a police area, the chief officer of police (or, in Scotland, the chief constable);
(c)
in relation to any other person holding the office of constable or an appointment as a police cadet, the person who has the direction and control of the body of constables or cadets in question.
[(4) For the purposes of these Regulations the relevant officer, as defined by paragraph (3), shall be treated as a corporation sole.
(5) Where, in a case in which the relevant officer, as so defined, is guilty of an offence under these Regulations, it is proved—
(a)that the office-holder personally consented to the commission of the offence;
(b)that he personally connived in its commission; or
(c)that the commission of the offence was attributable to personal neglect on his part,
the office-holder (as well as the corporation sole) shall be guilty of an offence and shall be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly.
(6) In paragraph (5) above “the office-holder”, in relation to the relevant officer, means an individual who, at the time of the consent, connivance or neglect—
(a)held the office or other position mentioned in paragraph (3) above as the office or position of that officer; or
(b)was for the time being responsible for exercising and performing the powers and duties of that office or position.
(7) In the application of this regulation to Scotland—
(a)paragraph (4) shall have effect as if for the words “corporation sole” there were substituted “distinct juristic person (that is to say, as a juristic person distinct from the individual who for the time being is the office-holder)”;
(b)paragraph (5) shall have effect as if for the words “corporation sole” there were substituted “juristic person”; and
(c)paragraph (6) shall have effect as if for the words “paragraph (5)” there were substituted “paragraphs (4) and (5).”]
Textual Amendments
Marginal Citations
Non-employed traineesE+W+S
42. For the purposes of these Regulations, a person receiving relevant training, otherwise than under a contract of employment, shall be regarded as a worker, and the person whose undertaking is providing the training shall be regarded as his employer.
Agricultural workersE+W+S
43. The provisions of Schedule 2 have effect in relation to workers employed in agriculture.
Ian McCartney
Minister of State,
Department of Trade and Industry
Regulation 2
SCHEDULE 1E+W+S WORKFORCE AGREEMENTS
1. An agreement is a workforce agreement for the purposes of these Regulations if the following conditions are satisfied—E+W+S
(a)the agreement is in writing;
(b)it has effect for a specified period not exceeding five years;
(c)it applies either—
(i)to all of the relevant members of the workforce, or
(ii)to all of the relevant members of the workforce who belong to a particular group;
(d)the agreement is signed—
(i)in the case of an agreement of the kind referred to in sub-paragraph (c)(i), by the representatives of the workforce, and in the case of an agreement of the kind referred to in sub-paragraph (c)(ii) by the representatives of the group to which the agreement applies (excluding, in either case, any representative not a relevant member of the workforce on the date on which the agreement was first made available for signature), or
(ii)if the employer employed 20 or fewer workers on the date referred to in sub-paragraph (d)(i), either by the appropriate representatives in accordance with that sub-paragraph or by the majority of the workers employed by him;
(e)before the agreement was made available for signature, the employer provided all the workers to whom it was intended to apply on the date on which it came into effect with copies of the text of the agreement and such guidance as those workers might reasonably require in order to understand it fully.
2. For the purposes of this Schedule—E+W+S
“a particular group" is a group of the relevant members of a workforce who undertake a particular function, work at a particular workplace or belong to a particular department or unit within their employer’s business;
“relevant members of the workforce" are all of the workers employed by a particular employer, excluding any worker whose terms and conditions of employment are provided for, wholly or in part, in a collective agreement;
“representatives of the workforce" are workers duly elected to represent the relevant members of the workforce, “representatives of the group" are workers duly elected to represent the members of a particular group, and representatives are “duly elected" if the election at which they were elected satisfied the requirements of paragraph 3 of this Schedule.
3. The requirements concerning elections referred to in paragraph 2 are that—E+W+S
(a)the number of representatives to be elected is determined by the employer;
(b)the candidates for election as representatives of the workforce are relevant members of the workforce, and the candidates for election as representatives of a group are members of the group;
(c)no worker who is eligible to be a candidate is unreasonably excluded from standing for election;
(d)all the relevant members of the workforce are entitled to vote for representatives of the workforce, and all the members of a particular group are entitled to vote for representatives of the group;
(e)the workers entitled to vote may vote for as many candidates as there are representatives to be elected;
(f)the election is conducted so as to secure that—
(i)so far as is reasonably practicable, those voting do so in secret, and
(ii)the votes given at the election are fairly and accurately counted.
Regulations 13(4), 15(6) and 43
SCHEDULE 2E+W+S WORKERS EMPLOYED IN AGRICULTURE
1. Except where, in the case of a worker partly employed in agriculture, different provision is made by a relevant agreement—E+W+S
(a)for the purposes of regulation 13, the leave year of a worker employed in agriculture begins on 6th April each year or such other date as may be specified in an agricultural wages order which applies to him; and
(b)the dates on which leave is taken by a worker employed in agriculture shall be determined in accordance with an agricultural wages order which applies to him.
2. Where, in the case referred to in paragraph 1 above, a relevant agreement makes provision different from sub-paragraph (a) or (b) of that paragraph—E+W+S
(a)neither section 11 of the Agricultural Wages Act 1948 nor section 11 of the Agricultural Wages (Scotland) Act 1949 shall apply to that provision; and
(b)an employer giving effect to that provision shall not thereby be taken to have failed to comply with the requirements of an agricultural wages order.
3. In this Schedule, “an agricultural wages order" means an order under section 3 of the Agricultural Wages Act 1948 or section 3 of the Agricultural Wages (Scotland) Act 1949.E+W+S
Regulation 28(7)
[SCHEDULE 3E+W+SENFORCEMENT
Appointment of inspectorsE+W+S
1.—(1) Each enforcement authority may appoint as inspectors (under whatever title it may from time to time determine) such persons having suitable qualifications as it thinks necessary for carrying into effect these Regulations within its field of responsibility, and may terminate any appointment made under this paragraph.
(2) Every appointment of a person as an inspector under this paragraph shall be made by an instrument in writing specifying which of the powers conferred on inspectors by these Regulations are to be exercisable by the person appointed; and an inspector shall in right of his appointment under this paragraph—
(a)be entitled to exercise only such of those powers as are so specified; and
(b)be entitled to exercise the powers so specified only within the field of responsibility of the authority which appointed him.
(3) So much of an inspector’s instrument of appointment as specifies the powers which he is entitled to exercise may be varied by the enforcement authority which appointed him.
(4) An inspector shall, if so required when exercising or seeking to exercise any power conferred on him by these Regulations, produce his instrument of appointment or a duly authenticated copy thereof.
Powers of inspectorsE+W+S
2.—(1) Subject to the provisions of paragraph 1 and this sub-paragraph, an inspector may, for the purpose of carrying into effect these Regulations within the field of responsibility of the enforcement authority which appointed him, exercise the powers set out in sub-paragraph (2) below.
(2) The powers of an inspector referred to in the preceding sub-paragraph are the following, namely—
(a)at any reasonable time (or, in a situation which in his opinion is or may be dangerous, at any time) to enter any premises which he has reason to believe it is necessary for him to enter for the purpose mentioned in sub-paragraph (1) above;
(b)to take with him a constable if he has reasonable cause to apprehend any serious obstruction in the execution of his duty;
(c)without prejudice to the preceding sub-paragraph, on entering any premises by virtue of paragraph (a) above to take with him—
(i)any other person duly authorised by the inspector’s enforcement authority; and
(ii)any equipment or materials required for any purpose for which the power of entry is being exercised;
(d)to make such examination and investigation as may in any circumstances be necessary for the purpose mentioned in sub-paragraph (1) above;
(e)to require any person whom he has reasonable cause to believe to be able to give any information relevant to any examination or investigation under paragraph (d) above to answer (in the absence of persons other than a person nominated by him to be present and any persons whom the inspector may allow to be present) such questions as the inspector thinks fit to ask and to sign a declaration of the truth of his answers;
(f)to require the production of, inspect, and take copies of or of any entry in—
(i)any records which by virtue of these Regulations are required to be kept, and
(ii)any other books, records or documents which it is necessary for him to see for the purposes of any examination or investigation under paragraph (d) above;
(g)to require any person to afford him such facilities and assistance with respect to any matters or things within that person’s control or in relation to which that person has responsibilities as are necessary to enable the inspector to exercise any of the powers conferred on him by this paragraph;
(h)any other power which is necessary for the purpose mentioned in sub-paragraph (1) above.
(3) No answer given by a person in pursuance of a requirement imposed under sub-paragraph (2)(e) above shall be admissible in evidence against that person or the husband or wife of that person in any proceedings.
(4) Nothing in this paragraph shall be taken to compel the production by any person of a document of which he would on grounds of legal professional privilege be entitled to withhold production on an order for discovery in an action in the High Court or, as the case may be, on an order for the production of documents in an action in the Court of Session.
Improvement noticesE+W+S
3. If an inspector is of the opinion that a person—
(a)is contravening one or more of these Regulations; or
(b)has contravened one or more of these Regulations in circumstances that make it likely that the contravention will continue or be repeated,
he may serve on him a notice (in this Schedule referred to as “an improvement notice”) stating that he is of that opinion, specifying the provision or provisions as to which he is of that opinion, giving particulars of the reasons why he is of that opinion, and requiring that person to remedy the contravention or, as the case may be, the matters occasioning it within such period (ending not earlier than the period within which an appeal against the notice can be brought under paragraph 6) as may be specified in the notice.
Prohibition noticesE+W+S
4.—(1) This paragraph applies to any activities which are being or are likely to be carried on by or under the control of any person, being activities to or in relation to which any of these Regulations apply or will, if the activities are so carried on, apply.
(2) If as regards any activities to which this paragraph applies an inspector is of the opinion that, as carried on or likely to be carried on by or under the control of the person in question, the activities involve or, as the case may be, will involve a risk of serious personal injury, the inspector may serve on that person a notice (in this Schedule referred to as “a prohibition notice”).
(3) A prohibition notice shall—
(a)state that the inspector is of the said opinion;
(b)specify the matters which in his opinion give or, as the case may be, will give rise to the said risk;
(c)where in his opinion any of those matters involves or, as the case may be, will involve a contravention of any of these Regulations, state that he is of that opinion, specify the regulation or regulations as to which he is of that opinion, and give particulars of the reasons why he is of that opinion; and
(d)direct that the activities to which the notice relates shall not be carried on by or under the control of the person on whom the notice is served unless the matters specified in the notice in pursuance of paragraph (b) above and any associated contraventions of provisions so specified in pursuance of paragraph (c) above have been remedied.
(4) A direction contained in a prohibition notice in pursuance of sub-paragraph (3)(d) above shall take effect—
(a)at the end of the period specified in the notice; or
(b)if the notice so declares, immediately.
Provisions supplementary to paragraphs 3 and 4E+W+S
5.—(1) In this paragraph “a notice” means an improvement notice or a prohibition notice.
(2) A notice may (but need not) include directions as to the measures to be taken to remedy any contravention or matter to which the notice relates; and any such directions—
(a)may be framed to any extent by reference to any approved code of practice; and
(b)may be framed so as to afford the person on whom the notice is served a choice between different ways of remedying the contravention or matter.
(3) Where an improvement notice or a prohibition notice which is not to take immediate effect has been served—
(a)the notice may be withdrawn by an inspector at any time before the end of the period specified therein in pursuance of paragraph 3 or paragraph 4(4) as the case may be; and
(b)the period so specified may be extended or further extended by an inspector at any time when an appeal against the notice is not pending.
Appeal against improvement or prohibition noticeE+W+S
6.—(1) In this paragraph “a notice” means an improvement or a prohibition notice.
(2) A person on whom a notice is served may within 21 days from the date of its service appeal to an employment tribunal; and on such an appeal the tribunal may either cancel or affirm the notice and, if it affirms it, may do so either in its original form or with such modifications as the tribunal may in the circumstances think fit.
(3) Where an appeal under this paragraph is brought against a notice within the period allowed under the preceding sub-paragraph, then—
(a)in the case of an improvement notice, the bringing of the appeal shall have the effect of suspending the operation of the notice until the appeal is finally disposed of or, if the appeal is withdrawn, until the withdrawal of the appeal;
(b)in the case of a prohibition notice, the bringing of the appeal shall have the like effect if, but only if, on the application of the appellant the tribunal so directs (and then only from the giving of the direction).
(4) One or more assessors may be appointed for the purposes of any proceedings brought before an employment tribunal under this paragraph.
Power of enforcement authority to indemnify inspectorsE+W+S
7. Where an action has been brought against an inspector in respect of an act done in the execution or purported execution of these Regulations and the circumstances are such that he is not legally entitled to require the enforcement authority to indemnify him, that authority may, nevertheless, indemnify him against the whole or part of any damages and costs or expenses which he may have been ordered to pay or may have incurred, if the authority is satisfied that the inspector honestly believed that the act complained of was within his powers and that his duty as an inspector required or entitled him to do it.
Restrictions on disclosure of informationE+W+S
8.—(1) In this and the two following sub-paragraphs—
(a)“relevant information” means information obtained by an inspector in pursuance of a requirement imposed under paragraph 2(2)(e) or (f); and
(b)“the recipient”, in relation to any relevant information, means the person by whom that information was so obtained or to whom that information was so furnished, as the case may be.
(2) Subject to the following sub-paragraph, no relevant information shall be disclosed without the consent of the person by whom it was furnished.
(3) The preceding sub-paragraph shall not apply to—
(a)disclosure of information to the Commission, a government department or any enforcement authority;
(b)without prejudice to paragraph (a) above, disclosure by the recipient of information to any person for the purpose of any function conferred on the recipient by or under any of the relevant statutory provisions or under these Regulations;
(c)without prejudice to paragraph (a) above, disclosure by the recipient of information to—
(i)an officer of a local authority who is authorised by that authority to receive it; or
(ii)a constable authorised by a chief officer of police to receive it; or
(d)disclosure by the recipient of information in a form calculated to prevent it from being identified as relating to a particular person or case.
(4) In the preceding sub-paragraph any reference to the Commission, a government department or an enforcement authority includes respectively a reference to an officer of that body or authority (including in the case of an enforcement authority, any inspector appointed by it), and also, in the case of a reference to the Commission, includes a reference to—
(a)a person performing any functions of the Commission or the Executive on its behalf by virtue of section 13(1)(a) of the 1974 Act;
(b)an officer of a body which is so performing any such functions; and
(c)an adviser appointed in pursuance of section 13(1)(d) of the 1974 Act.
(5) A person to whom information is disclosed in pursuance of sub-paragraph (3) above shall not use the information for a purpose other than—
(a)in a case falling within sub-paragraph (3)(a), a purpose of the Commission, of the government department, or of the enforcement authority in question in connection with these Regulations or with the relevant statutory provisions, as the case may be;
(b)in the case of information given to an officer of a body which is a local authority, the purposes of the body in connection with the relevant statutory provisions or any enactment whatsoever relating to working time, public health, public safety or the protection of the environment;
(c)in the case of information given to a constable, the purposes of the police in connection with these Regulations, the relevant statutory provisions or any enactment whatsoever relating to working time, public health, public safety or the safety of the State.
(6) A person shall not disclose any information obtained by him as a result of the exercise of any power conferred by paragraph 2 of this Schedule (including in particular any information with respect to any trade secret obtained by him in any premises entered by him by virtue of any such power) except—
(a)for the purposes of his functions;
(b)for the purposes of any legal proceedings; or
(c)with the relevant consent.
In this sub-paragraph “the relevant consent” means the consent of the person who furnished it, and, in any other case, the consent of a person having responsibilities in relation to the premises where the information was obtained.
(7) Notwithstanding anything in the preceding sub-paragraph an inspector shall, in circumstances in which it is necessary to do so for the purpose of assisting in keeping persons (or the representatives of persons) employed at any premises adequately informed about matters affecting their health, safety and welfare or working time, give to such persons or their representatives the following descriptions of information, that is to say—
(a)factual information obtained by him as mentioned in that sub-paragraph which relates to those premises or anything which was or is therein or was or is being done therein; and
(b)information with respect to any action which he has taken or proposes to take in or in connection with those premises in the performance of his functions;
and, where an inspector does as aforesaid, he shall give the like information to the employer of the first-mentioned persons.
(8) Notwithstanding anything in sub-paragraph (6) above, a person who has obtained such information as is referred to in that sub-paragraph may furnish to a person who appears to him to be likely to be a party to any civil proceedings arising out of any accident, occurrence, situation or other matter, a written statement of the relevant facts observed by him in the course of exercising any of the powers referred to in that sub-paragraph.]
(This note is not part of the Regulations)
These Regulations implement Council Directive 93/104/EC concerning certain aspects of the organization of working time (O.J. No. L307, 13.12.93, p.18) and provisions concerning working time in Council Directive 94/33/EC on the protection of young people at work (O.J. No. L216, 20.8.94, p.12). The provisions in the latter Directive which are implemented relate only to adolescents (those aged between 15 and 18 who are over compulsory school age); provisions in that Directive relating to children were implemented by the Children (Protection at Work) Regulations 1998 (S.I.1998/276). Provisions implementing that Directive in relation to adolescents employed on ships are to be included in separate regulations to be made shortly after the date on which these Regulations are made, and adolescents employed on ships are accordingly excluded from the scope of these Regulations (regulation 26).
Regulations 4 to 9 in these Regulations impose obligations on employers, enforceable by the Health and Safety Executive and local authorities; failure to comply is an offence. The obligations concern the maximum average weekly working time of workers (subject to provision for individual workers to agree that the maximum should not apply to them), the average normal hours of night workers, the provision of health assessments for night workers, and rest breaks to be given to workers engaged in certain kinds of work; employers are also required to keep records of workers’ hours of work.
Regulations 10 to 17 confer rights on workers, enforceable by proceedings before employment tribunals. The rights are to a rest period in every 24 hours during which a worker works for his employer and longer rest periods each week or fortnight, to a rest break in the course of a working day, and to a period of paid annual leave.
Regulations 18 to 27 provide for particular regulations not to apply, either in relation to workers engaged in certain kinds of work or where particular circumstances arise. There is also provision for groups of workers and their employers to agree to modify or exclude the application of particular regulations.
The remaining regulations make provision in relation to enforcement and remedies, and in respect of agency workers, Crown servants, Parliamentary staff, the police, trainees and agricultural workers. The Employment Rights Act 1996 is amended to include a right for workers not to be subjected to any detriment for refusing to comply with a requirement contrary to these Regulations or to forgo a right conferred by them, and to provide that the dismissal of an employee on account of any such refusal is unfair dismissal for the purposes of the Act.